Brazil is the largest country in South America and the fifth largest nation in the world.
Brazil is the largest country in South America and the fifth largest nation in the world. It forms an enormous triangle on the eastern side of the continent with a 4,500-mile (7,400-kilometer) coastline along the Atlantic Ocean. It has borders with every South American country except Chile and Ecuador .
The Brazilian landscape is very varied. It is most well known for its dense forests, including the Amazon, the world's largest jungle, in the north. But there are also dry grasslands (called pampas), rugged hills, pine forests, sprawling wetlands, immense plateaus, and a long coastal plain.
Northern Brazil is dominated by the Amazon River and the jungles that surround it. The Amazon is not one river but a network of many hundreds of waterways. Its total length stretches 4,250 miles (6,840 kilometers). Thousands of species live in the river, including the infamous piranha and the boto, or pink river dolphin.
Map created by National Geographic Maps

PEOPLE & CULTURE
Most Brazilians are descended from three ethnic groups: Amerindians, European settlers (mainly from Portugal), and Africans. Starting in the 19th century, waves of immigrants from Europe, the Middle East, and even Japan added to this mix. This diversity of cultures has created a rich religious, musical, and culinary culture.
Brazilians are soccer crazy, and their country has produced some of the best players. The most famous of all is Edson Arantes do Nascimento, better known as Pelé. Brazil has won the World Cup soccer finals five times, more than any other nation.
Brazil has the greatest variety of animals of any country in the world. It is home to 600 mammal species, 1,500 fish species, 1,600 bird species, and an amazing 100,000 different types of insects . Brazil's jungles are home to most of its animal life, but many unique species also live in the pampas and semidesert regions.
In the central-western part of Brazil sits a flat, swampy area called the Pantanal. This patchwork of flooded lagoons and small islands is the world's largest wetland. Here live giant anacondas , huge guinea pig relatives called capybaras, and fierce South American alligators called caimans .
For thousands of years, people have been exploiting the jungles of Brazil. But since Europeans arrived about five centuries ago, forest destruction has been rampant. Most of Brazil's Atlantic rain forest is now gone, and huge tracts of the Amazon are disappearing every year. The government has established many national parks and refuges, but they only cover about 7 percent of the country.
GOVERNMENT & ECONOMY
Brazil is a federal republic with a president, a National Congress, and a judiciary. From 1888 until recently, the country struggled with democracy. But in 1985, the military government was peacefully removed, and by 1995, Brazil's politics and economy had become fairly stable.
Brazil has many different soils and climates, so it can produce a great variety of crops. Its agricultural exports include sugarcane, latex, coffee, cocoa beans, cotton, soybeans, rice, and tropical fruits.
Brazil is also South America's most industrial nation, producing chemicals, steel, aircraft, and cars.
Until recently, scientists thought Brazil was first settled by Asians about 10,000 years ago. But new evidence shows there were people living there at least 32,000 years ago. Some experts think they may have arrived from islands in the Pacific Ocean.
Brazil was added to the map of the world during the great European explorations in the late 15th century led by Portugal and Spain. When Europeans first reached the coast of Brazil, the country was home to about 30 million indigenous people, or Amerindians. Today, only about 300,000 remain, living primarily in Brazil's remotest places.
Portugal established its first colony in Brazil in 1530. Colonists created sugarcane plantations along the coast and sent diamonds and gold back to Europe. Soon, people from West Africa were brought to Brazil to work as slaves. The discovery of large inland gold reserves brought thousands of people from the coasts and as far away as Europe to the interior of the country.
In 1789, Brazilians tried to kick out their Portuguese rulers. The rebellion was soon put down, but it started a movement toward independence. By 1822, Brazil was a sovereign nation. Kings of Portuguese blood ruled until 1888, when military leaders and landowners expelled the king, and Brazil became a federal republic.
More to explore
U.s. states and territories facts and photos, destination world.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
- News for Kids
- Dominican Republic
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Switzerland
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
- 7 Continents
- Australia/Oceania
- North America
- South America
- Chinese New Year
- Elections 2024
- Olympics 2024
- European Union
- Trivia & Quizzes
- Solar System Quiz
- Travel Reviews
- Travel Health
- Travel Links
Competition 2024
- Winners 2023
- Winners 2022
- Winners 2021
- Winners 2020
- Winners 2019
- Request A Correction
Brazil Facts
Interesting facts for kids.
Here are some interesting Brazil Facts which were chosen and researched by kids especially for kids.

- Population : 219 million people live in Brazil (2023)
- Capital : Brasilia, with 5 million inhabitants is the country's fourth largest city. The largest city in Brazil is Sao Paulo with about 23 million inhabitants.
- Name : Republica Federativa do Brasil, Federative Republic of Brazil
- Government : Democracy, Republic
- Language : Portuguese
- Literacy : More than 91% of the people can read and write.
- Religion : mainly Christians (Roman Catholics 65%, Protestants 22%)
- Currency : 1 real=100 centavos
- National symbols : Jaguar (national animal), macaw (national bird) and cattleya orchid (national flower), national colours: green, yellow and blue, the constellation of the Southern Cross
- National anthem : " Hino Nacional Brasileiro "

- History : The country was inhabited mainly by semi-nomadic tribes before the arrival of the colonialists. The land was claimed by Portuguese and Portuguese settlers founded the colony in 1532. By the 17th century sugar cane was the main export product and the slave trade brought many African slaves to the country. The Brazilian gold rush attracted many fortune seekers to the country. In 1822, Brazil declared independence from Portugal, although independence was officially recognised by the Portuguese only three years later! Brazil was ruled by various Brazilian emperors until in 1889 it was finally declared a republic. Brazil's president is Luiz Inácio LULA da Silva since January 2023.
- National Holiday : 7 September (Independence Day)
Brazil Facts | Geography Where is Brazil?
Bra zil is located on the South American continent. Brazil also belongs to the Latin American countries. The country borders the Atlantic Ocean.
The largest Latin American country shares borders with all other South American countries except for Chile and Ecuador. The longest border is shared with Bolivia and is 3,400 km/ 2,113 miles long.
Below see a map of Brazil with the neighbouring countries and you will find Brazil's capital city: Brasilia.
Regarding the size of Brazil, all the countries of the European Union could fit twice into the country! Brazil is slightly smaller than the USA.
A flight to Sao Paolo takes roughly 11.5 hours from London/UK and 9.5 hours from New York/USA.
Brazil for Kids | More Facts about Brazil
- The country has almost 7,500 km/ 4,660 miles of coastline and is known for its many great beaches.
- The northern and western parts of Brazil are largely dominated by the Amazon Basin. In the South, you will find the Brazilian Highlands.
- The Amazon, the Paraná, the Madeira River, the Rio de la Plata and the Rio Negro are among the biggest rivers in Brazil.
- The climate in Brazil is mostly tropical with a temperate climate in the Southern parts of the country.
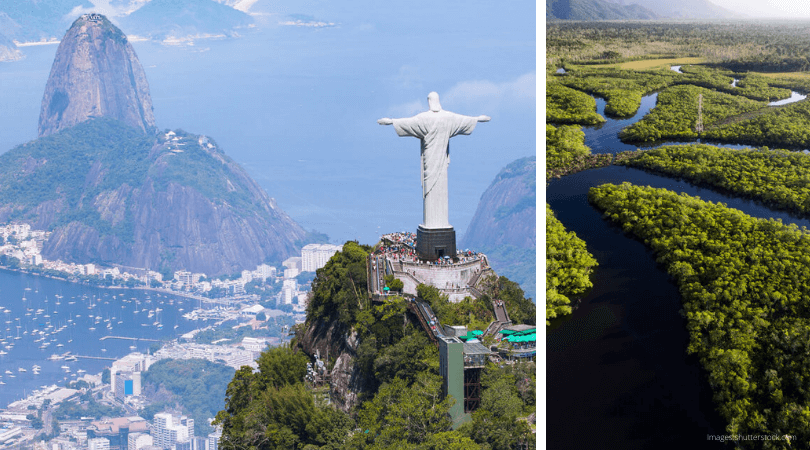
- The most famous landmark of Brazil is located in Rio de Janeiro. The Christ the Redeemer statue overlooks the city and Sugarloaf mountain.

Brazil Geo Superlatives
- Brazil is South America's biggest and the world's fifth largest country. The country covers three time zones!
- Brazil is also the largest country in the Southern hemisphere as it is bigger than Australia.
- The Amazon river is the world's second longest river. It is about 6,400 km/ 4,000 miles long. The river flows through Peru, Colombia and enters the Atlantic Ocean in Brazil.
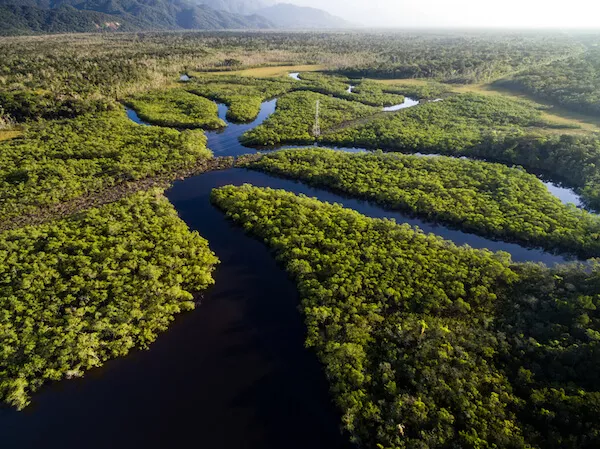

- The Amazon rain forest is the largest rainforest in the world. About 60% of the world's rainforests are located in Brazil.
- Brazil is one of the 17 megadiverse countries in the world due to the many species of plants and animals.
- The highest lying area of Brazil is in the North and is called the Guiana highlands.
- Brazil's highest mountain is the 'Pico de Neblina' and is 2,994 m/ 9,822 ft. high.
- Brazil is the only country on the planet where the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn run through the country.
- The Pantanal is the world's largest tropical wetland and covers most of the country's western parts.
- Brazil shares the Iguazu Falls, the largest waterfall system in the world with Argentina. There are over 270 waterfalls in this waterfall system.
Brazil Attractions for Kids
- Rio de Janeiro: Copacabana and Ipanema are great for beach holidays

- Capivara National Park is known for ancient rock paintings

- Recife, the country's fourth largest city is also nicknamed 'Venice of Brazil' because of its over 50 bridges and many waterways.

- Pantanal National park is also called the 'Brazilian Garden of Eden'

- Florianópolis is located on Santa Catarina Island which stretches over 54 km/ 33 miles. The island has some of the most amazing beaches in the country.

Brazil Facts | People in Brazil
Brazil is the country with the fifth largest population in the world, after China, India, the USA and Indonesia.
Most Brazilians (87%) live in urban centres, mainly along the Atlantic coast and in the major cities.

The biggest cities in Brazil are Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and Brasilia. The Brazilian cities are known for the extensive favelas . These are the neighbourhoods or shanty towns, where mainly poor people live.
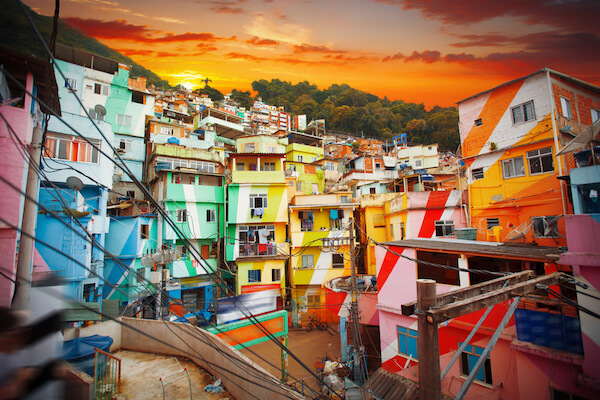

The northern parts of the country are the least populated area in Brazil.
Among the Brazilian people are more than 800,000 indigenous people, some of them Amerindians.

Brazil Facts | Language in Brazil
Brazil is the only Portuguese-speaking country in South America. The Brazilian Portuguese is slightly different to the Portuguese spoken in Portugal. The pronunciation sounds different and some of the words are used only in Brazil.
Brazil Facts | Carnival in Brazil
Brazil is known for its cheerful and vibrant atmosphere during Carnival time starting on the Friday before Ash Wednesday. Carneval do Brasil is celebrated in many cities such as in Sao Paolo, Salvador or Rio de Janeiro.

The Brazilian carnival starts on the Friday before Ash Wednesday, or the beginning of the Christian period of fasting called Lent. This usually is in February.
In Brazil, carnival is celebrated with the parades of the various samba schools. The communities are usually widely involved as drumming, dancing and marching are practised all year round for this special annual event.
Brazil Facts | Brazil Economy
Brazil is the eighth largest economy in the world. The country belongs to the BRICS which includes the countries Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
The main agricultural products of Brazil include coffee, soybeans, wheat, corn and sugar cane. Brazil is the world's largest exporter of coffee, soybean and beef.

About one third of the country is agricultural land, however, only about 10% of all Brazilians work in the agricultural sector. The unemployment rate in Brazil stands at 12% and about 4% live in extremely poor conditions.
The largest trading partners of Brazil are China, the USA and Argentina.
Sports in Brazil
The people in Brazil love being outdoors, the main sports are soccer, volleyball and water sports.

The South American country hosted the soccer world cup in 2014. Brazil won the world cup five times in 1958, 1962, 1970, 1994 and 2002 and the country has participated in all the tournament since it began.
Brazil also hosted the last Summer Olympic Games in August 2016. The XXXVI (16th) Olympiad in Rio was the first Olympic Games on the South American continent! Over ten thousand athletes from 206 countries took part in these summer sports games. Read more about the Rio Olympics here.
Brazil Facts | Animals in Brazil

Brazil's national animal is the Jaguar.

Brazil is home to many other fascinating mammals too, such as armadillos, tapirs and pumas.
The Amazon is home to many fish species, also the piranha. The national bird is the macaw. The colourful toucans with their big horned beaks also can be seen in Brazil.
Brazil Facts | Food in Brazil
Brazilians love their fresh fruits and vegetables such as okra, coconuts corn and beans. Many traditional dishes contain beans, rice or manioc flour. The most favourite dish in Brazil is probably the feijoada , a bean stew made with pork and rice.
Typical Brazilian food and drinks :
- Pão de Queijo : delicious cheese bread
- Guarana : drink made with small red berries
- Feijoada : a bean stew made with pork and rice.
- Coxinha de Galena : Brazilian breaded and deep fried snack filled with shredded chicken. Usually served with a chili dip, see below:

Resources for Brazil Facts
- Central Intelligence Agency. "Brazil" CIA World Factbook . Updated 28 March 2023. Last Accessed 31 March 2023.
- The Olympic Committee. "Rio 2016." Olympic.org . Last Accessed 31 March 2023.
- Presidency of the Republic of Brazil. "Brazil in Numbers: Fact Sheet - Brazil". gov.br. Updated 1 October 2018. Last Accessed 31 March 2023.
Popular Pages
Images on Brazil facts page: shutterstock.com and own images
Return from Brazil Facts to Kids World Travel Guide Homepage
Competition 2024 is open!

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.

Events & Celebrations
Organisations, games & quizzes, travel tips, competition, recent articles.
Facts about Liberia for Kids | Africa Facts for Kids | Geography
Apr 25, 24 09:36 AM
UAE Facts for Kids | United Arab Emirates Facts | Geography | Travel
Apr 19, 24 04:33 AM
Argentina Facts for Kids | Geography | Attractions | People | Animals
Apr 12, 24 05:32 AM
More about South America

More about Countries in South America

Temperature in Celsius
Temperature in fahrenheit.

Popular Countries worldwide

Winning Essays 2020

Spread the Word

Like us on Facebook
Kids World Travel Guide
Brilliantly
Content & links.
Verified by Sur.ly
©Kids-World-Travel-Guide.com 2010-2024 | Created by Regina Gräff and KidsWorldTravels
All rights reserved | Privacy Policy | Disclaimer


- DIGITAL MAGAZINE
MOST POPULAR
Brazil primary resource
Discover 30 cool things about brazil; from its native animals to some of its impressive sports history.
This primary resource explores the different wildlife, habitats and landmarks of Brazil. Discover 30 cool things about Brazil; from its native animals to some of its impressive sports history. How many native languages are spoken in Brazil? What is the capital of Brazil shaped like? What is distinctive about Brazil’s toco toucan?
Pupils will learn about some of the unique features of Brazil, including its wildlife, produce and sporting achievements in our National Geographic Kids’ Geography primary resource sheet.
The teaching resource can be used in study group tasks, as a printed handout for each pupil, or for display on the interactive whiteboard using the images and information included in the resource for class discussion.
Activity: Ask children to cut out the facts from their handout and, in small groups, group together all the facts about: i) wildlife, ii) sports, iii) food, iv) natural landscapes, v) culture fact, etc. Pupils could each be assigned one of the numbers between 1 – 30, and further research its corresponding fact. They could research individually, or as a group.
N.B. The following information for mapping the resource documents to the school curriculum is specifically tailored to the English National Curriculum and Scottish Curriculum for Excellence . We are currently working to bring specifically tailored curriculum resource links for our other territories; including South Africa , Australia and New Zealand . If you have any queries about our upcoming curriculum resource links, please email: [email protected]
This Geography primary resource assists with teaching the following Key Stage 1 Geography objectives from the National Curriculum :
Pupils should be taught to:
- name and locate the world’s seven continents and five oceans
- use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to: key physical features, including: beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation, season and weather
National Curriculum Key Stage 2 Geography objectives:
Pupils should extend their knowledge and understanding beyond the local area to include the United Kingdom and Europe, North and South America. This will include the location and characteristics of a range of the world’s most significant human and physical features. They should develop their use of geographical knowledge, understanding and skills to enhance their locational and place knowledge.
Pupils should be taught to:
- locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities/em>
- understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country, and a region within North or South America
This Geography primary resource assists with teaching the following Social Studies First level objective from the Scottish Curriculum for Excellence :
- By exploring a natural environment different from my own, I can discover how the physical features influence the variety of living things.
Scottish Curriculum for Excellence Second level Social Studies objective :
- I can explain how the physical environment influences the ways in which people use land by comparing my local area with a contrasting area.
Download primary resource
Leave a comment.
Your comment will be checked and approved shortly.
WELL DONE, YOUR COMMENT HAS BEEN ADDED!
Customize your avatar.

Autumn Animals!

Canada facts

NASA’s Curiosity Rover spots a ‘mouse’ on Mars!

30 freaky facts about the weather!

Sign up to our newsletter
Get uplifting news, exclusive offers, inspiring stories and activities to help you and your family explore and learn delivered straight to your inbox.
You will receive our UK newsletter. Change region
WHERE DO YOU LIVE?
COUNTRY * Australia Ireland New Zealand United Kingdom Other
By entering your email address you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy and will receive emails from us about news, offers, activities and partner offers.
You're all signed up! Back to subscription site
Type whatever you want to search
More Results

You’re leaving natgeokids.com to visit another website!
Ask a parent or guardian to check it out first and remember to stay safe online.

You're leaving our kids' pages to visit a page for grown-ups!
Be sure to check if your parent or guardian is okay with this first.

Exploring Brazil – KS2
Exploring Brazil is a Geography unit designed for students in KS2 (Y4-6).
The planning overview, topic title page and vocabulary page can be downloaded for free here . Lessons include:
L1 – Identifying the countries and capitals of South America
L2 – Writing a Brazil fact file
L3 – Using 4 and 6-figure grid references to locate Brazilian cities
L4 – Identifying the human and physical features of Brazil
L5 – Exploring Brazil’s ecosystems
L6 – Investigating Brazil’s weather and climate
Each lesson includes a presentation and differentiated activities/worksheets.
If you like this resource, please review it. We will happily send you a free resource of your choice in return for useful feedback. Contact us at [email protected] .
£ 4.00
- Reviews (6)
6 reviews for Exploring Brazil – KS2
J Wengrowe – September 4, 2020
Great resources, thank you.
Towsif Rehman – February 13, 2021
Excellent resource!
Olivia Houghton – October 27, 2022
Fantastic resource for my year 5 class. Thank you!
Sara Farnaby – January 4, 2023
So pleased I stumbled upon this while planning for my South America topic (Year 6). It has saved me hours and the quality of the resources is superb I usually faff on and tinker with things I buy/download but this is good to go. Great value and I’m already looking at my next topic. Thank you!
Anonymous – February 22, 2023
Really great resources. Particularly the lesson on the 4 and 6 grid references where the PowerPoint made it really clear. Easiest way I’ve ever taught that skill!
Francesca – August 23, 2023
A brilliant set of resources which really helped me to plan and create an interesting and useful set of lessons. I am looking forward to teaching this and I’m sure the children will benefit from great lessons.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
- Español NEW
Brazil facts for kids
Brazil (officially called Federative Republic of Brazil ) is a country in South America . It is the world 's fifth largest country. The country has about 209 million people. The capital of Brazil is Brasília .
Biodiversity and environment
Government and politics, architecture, popular dishes, visual arts, interesting facts about brazil, images for kids.
The first people to come to Brazil came around 9,000 B.C. That group of people is often called the South American Indians. They probably came from North America . Some of them were hunters and gatherers, but others were farmers.
Pedro Álvares Cabral was the first European to see Brazil. He saw it in 1500. He was from Portugal and the Portuguese government claimed Brazil. Soon, explorers explored the whole coastline of Brazil and colonies were set up. In the late 1500s and early 1600s the Dutch and the French would sometimes try to take land in Brazil. Brazilians started moving inland farther than the Treaty of Tordesillas said they could. This caused some fights with the Spaniards and native people in the area.
In 1822, Brazil claimed to be its own country and not a part of Portugal anymore. Soon there was civil war . But the emperor Pedro II improved the economy, and in 1888, he freed the slaves . In 1889, there was a military coup and Pedro II had to leave the country.
In 1889, Brazil became a republic . It was not very democratic, because the only people who could vote were people who owned land. There were some uprisings in the 1920s because some people thought the government was unfairly helping coffee growers. Brazil joined the Allies during World War II .
During the 1960s, the leader Castelo Branco made the government like a dictatorship . Since then, the country has become more democratic, but some people feel that there are still big problems in health and education.
In September 2016, then- president Dilma Rousseff was removed from office because of impeachment .
Most people in Brazil speak Portuguese . Brazil is the only country in Latin America that speaks Portuguese .
Some people in Brazil speak German dialects. That came from German immigrants. 0.8% of Brazilians speak German as their first language .
Other people in Brazil speak indigenous Brazilian languages, Italian , Japanese , French , or Spanish . Guaraní and Aymará are the first languages of a small number of Brazilians.
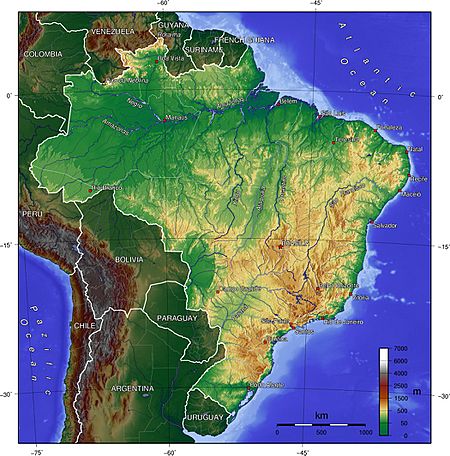
Brazil occupies a large area along the eastern coast of South America and includes much of the continent's interior, sharing land borders with Uruguay to the south; Argentina and Paraguay to the southwest; Bolivia and Peru to the west; Colombia to the northwest; and Venezuela , Guyana , Suriname and France (French overseas region of French Guiana ) to the north. It shares a border with every South American country except Ecuador and Chile . It also encompasses a number of oceanic archipelagos , such as Fernando de Noronha, Rocas Atoll, Saint Peter and Paul Rocks, and Trindade and Martim Vaz . Its size, relief, climate, and natural resources make Brazil geographically diverse. Including its Atlantic islands, Brazil lies between latitudes 6°N and 34°S, and longitudes 28° and 74°W.
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world, and third largest in the Americas, with a total area of 8,515,767.049 km 2 (3,287,956 sq mi), including 55,455 km 2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. It spans four time zones ; from UTC−5 comprising the state of Acre and the westernmost portion of Amazonas , to UTC−4 in the western states, to UTC−3 in the eastern states (the national time) and UTC−2 in the Atlantic islands.
Brazil is the only country in the world that has the equator and the Tropic of Capricorn running through it. It is also the only country to have contiguous territory both inside and outside the tropics. Brazilian topography is also diverse and includes hills, mountains, plains, highlands, and scrublands. Much of the terrain lies between 200 metres (660 ft) and 800 metres (2,600 ft) in elevation. The main upland area occupies most of the southern half of the country. The northwestern parts of the plateau consist of broad, rolling terrain broken by low, rounded hills.
The southeastern section is more rugged, with a complex mass of ridges and mountain ranges reaching elevations of up to 1,200 metres (3,900 ft). These ranges include the Mantiqueira and Espinhaço mountains and the Serra do Mar . In the north, the Guiana Highlands form a major drainage divide, separating rivers that flow south into the Amazon Basin from rivers that empty into the Orinoco River system, in Venezuela, to the north. The highest point in Brazil is the Pico da Neblina at 2,994 metres (9,823 ft), and the lowest is the Atlantic Ocean.
Brazil has a dense and complex system of rivers, one of the world's most extensive, with eight major drainage basins, all of which drain into the Atlantic. Major rivers include the Amazon (the world's second-longest river and the largest in terms of volume of water), the Paraná and its major tributary the Iguaçu (which includes the Iguazu Falls ), the Negro , São Francisco , Xingu, Madeira and Tapajós rivers.
- Geography of Brazil

Trindade and Martin Vaz is a volcanic archipelago off the coast of the Brazil.

Serra dos Órgãos, part of the Serra do Mar .

Chapada Diamantina, in the Chapada Diamantina National Park, Bahia .

Iguazu Falls , Paraná , is the largest waterfalls system in the world.

Pico da Neblina , Amazonas , the highest mountain in Brazil.

Cavern in Bonito, Mato Grosso do Sul .
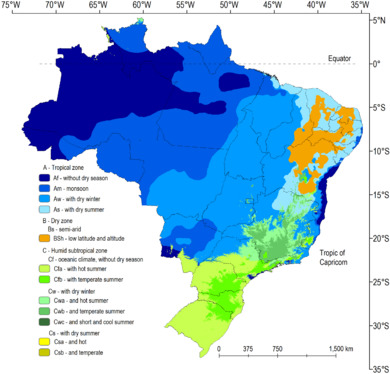
The climate of Brazil comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large area and varied topography, but most of the country is tropical. According to the Köppen system , Brazil hosts six major climatic subtypes: desert , equatorial , tropical , semiarid, oceanic and subtropical . The different climatic conditions produce environments ranging from equatorial rainforests in the north and semiarid deserts in the northeast, to temperate coniferous forests in the south and tropical savannas in central Brazil. Many regions have starkly different microclimates.
An equatorial climate characterizes much of northern Brazil. There is no real dry season , but there are some variations in the period of the year when most rain falls. Temperatures average 25 °C (77 °F), with more significant temperature variation between night and day than between seasons.
Over central Brazil rainfall is more seasonal, characteristic of a savanna climate. This region is as extensive as the Amazon basin but has a very different climate as it lies farther south at a higher altitude. In the interior northeast, seasonal rainfall is even more extreme. The semiarid climatic region generally receives less than 800 millimetres (31.5 in) of rain, most of which generally falls in a period of three to five months of the year and occasionally less than this, creating long periods of drought. Brazil's 1877–78 Grande Seca (Great Drought), the worst in Brazil's history, caused approximately half a million deaths. A similarly devastating drought occurred in 1915.
South of Bahia, near the coasts, and more southerly most of the state of São Paulo, the distribution of rainfall changes, with rain falling throughout the year. The south enjoys subtropical conditions, with cool winters and average annual temperatures not exceeding 18 °C (64.4 °F); winter frosts and snowfall are not rare in the highest areas.
Brazil's large territory comprises different ecosystems, such as the Amazon rainforest , recognized as having the greatest biological diversity in the world, with the Atlantic Forest and the Cerrado , sustaining the greatest biodiversity. In the south, the Araucaria pine forest grows under temperate conditions. The rich wildlife of Brazil reflects the variety of natural habitats. Scientists estimate that the total number of plant and animal species in Brazil could approach four million, mostly invertebrates.

Larger mammals include carnivores pumas , jaguars , ocelots , rare bush dogs , and foxes , and herbivores peccaries , tapirs , anteaters , sloths , opossums , and armadillos . Deer are plentiful in the south, and many species of New World monkeys are found in the northern rain forests . Concern for the environment has grown in response to global interest in environmental issues. Brazil's Amazon Basin is home to an extremely diverse array of fish species, including the red-bellied piranha. Despite its reputation as a ferocious freshwater fish, the red-bellied piranha is actually a generally timid scavenger. Biodiversity can contribute to agriculture , livestock, forestry and fisheries extraction. However, almost all economically exploited species of plants, such as soybeans and coffee, or animals, such as chickens, are imported from other countries, and the economic use of native species still crawls. In the Brazilian GDP, the forest sector represents just over 1% and fishing 0.4%.
The natural heritage of Brazil is severely threatened by cattle ranching and agriculture, logging, mining, resettlement, oil and gas extraction, over-fishing, wildlife trade, dams and infrastructure, water pollution, climate change, fire, and invasive species. In many areas of the country, the natural environment is threatened by development. Construction of highways has opened up previously remote areas for agriculture and settlement; dams have flooded valleys and inundated wildlife habitats; and mines have scarred and polluted the landscape. At least 70 dams are said to be planned for the Amazon region, including the controversial Belo Monte hydroelectric dam.
- Biodiversity of Brazil

Blue poison dart frog, found in the forests of the far northern Brazil.

Toco toucan , a Brazilian symbol, a country with one of the largest variety of birds in the world.

Female pantanal jaguar in Piquirí River, Pantanal .

Golden lion tamarin , an endemic animal of Brazil, in the Poço das Antas Biological Reserve.

Lear's macaw, endemic to Raso da Catarina, Bahia .

The form of government is a democratic federative republic , with a presidential system . The president is both head of state and head of government of the Union and is elected for a four-year term, with the possibility of re-election for a second successive term. The President appoints the Ministers of State , who assist in government.
Legislative houses in each political entity are the main source of law in Brazil. The National Congress is the Federation's bicameral legislature, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies and the Federal Senate . Judiciary authorities exercise jurisdictional duties almost exclusively. In 2021, the Economist Intelligence Unit's Democracy Index categorized Brazil as a "flawed democracy", ranking 46th in the report, and Freedom House classified it as a free country at Freedom in the World report.
The political-administrative organization of the Federative Republic of Brazil comprises the Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities. The Union, the states, the Federal District, and the municipalities, are the "spheres of government". The federation is set on five fundamental principles: sovereignty, citizenship, dignity of human beings, the social values of labor and freedom of enterprise, and political pluralism.
The classic tripartite branches of government (executive, legislative and judicial under a checks and balances system) are formally established by the Constitution. The executive and legislative are organized independently in all three spheres of government , while the judiciary is organized only at the federal and state and Federal District spheres. All members of the executive and legislative branches are directly elected.
For most of its democratic history, Brazil has had a multi-party system , with proportional representation . Voting is compulsory for the literate between 18 and 70 years old and optional for illiterates and those between 16 and 18 or beyond 70. The country has more than 40 active political parties. Fifteen political parties are represented in Congress. It is common for politicians to switch parties, and thus the proportion of congressional seats held by particular parties changes regularly.

Brazil is the largest national economy in Latin America , the world's ninth largest economy and the eighth largest in purchasing power parity (PPP) according to 2018 estimates. Brazil has a mixed economy with abundant natural resources.
The country has been expanding its presence in international financial and commodities markets , and is one of a group of four emerging economies called the BRIC countries. Brazil has been the world's largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years. The country is a major exporter of soy, iron ore, pulp (cellulose), maize, beef, chicken meat, soybean meal, sugar, coffee, tobacco, cotton, orange juice, footwear, airplanes, cars, vehicle parts, gold, ethanol, semi-finished iron, among other products.

Tourism in Brazil is a growing sector and key to the economy of several regions of the country. In the list of world tourist destinations, in 2018, Brazil was the 48th most visited country, with 6.6 million tourists (and revenues of 5.9 billion dollars).
Natural areas are its most popular tourism product, a combination of ecotourism with leisure and recreation, mainly sun and beach, and adventure travel, as well as cultural tourism. Among the most popular destinations are the Amazon Rainforest , beaches and dunes in the Northeast Region, the Pantanal in the Center-West Region, beaches at Rio de Janeiro and Santa Catarina , cultural tourism in Minas Gerais and business trips to São Paulo .

The core culture of Brazil is derived from Portuguese culture, because of its strong colonial ties with the Portuguese Empire. Among other influences, the Portuguese introduced the Portuguese language , Roman Catholicism and colonial architectural styles. The culture was also strongly influenced by African, indigenous and non-Portuguese European cultures and traditions.
Some aspects of Brazilian culture were influenced by the contributions of Italian, German and other European as well as Japanese, Jewish and Arab immigrants who arrived in large numbers in the South and Southeast of Brazil during the 19th and 20th centuries. The indigenous Amerindians influenced Brazil's language and cuisine ; and the Africans influenced language, cuisine, music, dance and religion.
Brazilian art has developed since the 16th century into different styles that range from Baroque (the dominant style in Brazil until the early 19th century) to Romanticism, Modernism , Expressionism , Cubism , Surrealism and Abstractionism . Brazilian cinema dates back to the birth of the medium in the late 19th century and has gained a new level of international acclaim since the 1960s.

The architecture of Brazil is influenced by Europe, especially Portugal. It has a history that goes back 500 years to the time when Pedro Álvares Cabral landed in Brazil in 1500. Portuguese colonial architecture was the first wave of architecture to go to Brazil. It is the basis for all Brazilian architecture of later centuries. In the 19th century during the time of the Empire of Brazil , the country followed European trends and adopted Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture . Then in the 20th century especially in Brasilia, Brazil experimented with Modernist architecture.
The colonial architecture of Brazil dates to the early 16th century when Brazil was first explored, conquered and settled by the Portuguese. The Portuguese built architecture familiar to them in Europe in their aim to colonize Brazil. They built Portuguese colonial architecture which included churches, civic architecture including houses and forts in Brazilian cities and the countryside.
During 19th century, Brazilian architecture saw the introduction of more European styles to Brazil such as Neoclassical and Gothic Revival architecture. This was usually mixed with Brazilian influences from their own heritage which produced a unique form of Brazilian architecture.
In the 1950s, the modernist architecture was introduced when Brasilia was built as new federal capital in the interior of Brazil to help develop the interior. The architect Oscar Niemeyer idealized and built government buildings, churches and civic buildings in the modernist style.

The music of Brazil was formed mainly from the fusion of European, Native Indigenous, and African elements. Until the nineteenth century, Portugal was the gateway to most of the influences that built Brazilian music, although many of these elements were not of Portuguese origin, but generally European. The first was José Maurício Nunes Garcia , author of sacred pieces with influence of Viennese classicism. The major contribution of the African element was the rhythmic diversity and some dances and instruments that had a bigger role in the development of popular music and folk, flourishing especially in the twentieth century.
Popular music since the late eighteenth century began to show signs of forming a characteristically Brazilian sound, with samba considered the most typical and on the UNESCO cultural heritage list. Maracatu and Afoxê are two music traditions that have been popularized by their appearance in the annual Brazilian Carnivals. Capoeira is usually played with its own music referred to as capoeira music, which is usually considered to be a call-and-response type of folk music. Forró is a type of folk music prominent during the Festa Junina in northeastern Brazil. Jack A. Draper III, a professor of Portuguese at the University of Missouri , argues that Forró was used as a way to subdue feelings of nostalgia for a rural lifestyle.
Choro is a very popular music instrumental style. Its origins are in 19th-century Rio de Janeiro. In spite of the name, the style often has a fast and happy rhythm, characterized by virtuosity, improvisation, subtle modulations and full of syncopation and counterpoint . Bossa nova is also a well-known style of Brazilian music developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s. The phrase "bossa nova" means literally "new trend". A lyrical fusion of samba and jazz , bossa nova acquired a large following starting in the 1960s.

Brazilian literature dates back to the 16th century, to the writings of the first Portuguese explorers in Brazil, such as Pêro Vaz de Caminha , filled with descriptions of fauna , flora and commentary about the indigenous population that fascinated European readers.
Brazil produced significant works in Romanticism – novelists like Joaquim Manuel de Macedo and José de Alencar wrote novels about love and pain. Alencar, in his long career, also treated indigenous people as heroes in the Indigenist novels O Guaraní , Iracema and Ubirajara . Machado de Assis , one of his contemporaries, wrote in virtually all genres and continues to gain international prestige from critics worldwide.
Brazilian Modernism, evidenced by the Modern Art Week in 1922, was concerned with a nationalist avant-garde literature, while Post-Modernism brought a generation of distinct poets like João Cabral de Melo Neto , Carlos Drummond de Andrade, Vinicius de Moraes , Cora Coralina , Graciliano Ramos , Cecília Meireles , and internationally known writers dealing with universal and regional subjects like Jorge Amado , João Guimarães Rosa , Clarice Lispector and Manuel Bandeira .
Brazil's most significant literary award is the Camões Prize, which it shares with the rest of the Portuguese-speaking world. As of 2016, Brazil has eleven recipients of the prize. Brazil also holds its own literary academy, the Brazilian Academy of Letters, a non-profit cultural organization pointed in perpetuating the care of the national language and literature.

Brazilian cuisine varies greatly by region, reflecting the country's varying mix of indigenous and immigrant populations. This has created a national cuisine marked by the preservation of regional differences. Examples are Feijoada , considered the country's national dish; and regional foods such as beiju, feijão tropeiro, vatapá , moqueca , polenta (from Italian cuisine) and acarajé (from African cuisine).
The national beverage is coffee and cachaça is Brazil's native liquor . Cachaça is distilled from sugar cane and is the main ingredient in the national cocktail, Caipirinha .
The basis of Brazilian daily cuisine is the starch (most often a cereal ), legume, protein and vegetable combination. There is also a differentiation between vegetables of the verduras group, or greens, and the legumes group (no relation to the botanic concept), or non-green vegetables.
A typical meal consists mostly of rice and beans with beef , salad , french fries and a fried egg . Often, it is mixed with cassava flour ( farofa ). Fried potatoes, fried cassava, fried banana, fried meat and fried cheese are very often eaten in lunch and served in most typical restaurants. Popular snacks are pastel (a fried pastry); coxinha (a variation of chicken croquete); pão de queijo (cheese bread and cassava flour / tapioca ); pamonha (corn and milk paste); esfirra (a variation of Lebanese pastry); kibbeh (from Arabic cuisine); empanada (pastry) and empada, little salt pies filled with shrimps or heart of palm.
Brazil has a variety of desserts such as brigadeiros (chocolate fudge balls), bolo de rolo (roll cake with goiabada ), cocada (a coconut sweet), beijinhos (coconut truffles and clove) and Romeu e Julieta (cheese with goiabada). Peanuts are used to make paçoca , rapadura and pé-de-moleque . Local common fruits like açaí , cupuaçu , mango , papaya , cocoa , cashew , guava , orange , lime , passionfruit , pineapple , and hog plum are turned in juices and used to make chocolates , ice pops and ice cream .
Brazilian cuisine is recognized around the world for its variety and quality. The city of São Paulo was chosen as the 7th main gastronomic destination in the world, for its recognized restaurants and bars . This Brazilian city comes after Rome , London , Paris , Dubai , Barcelona and Madrid . The city of São Paulo alone has more than 9,000 restaurants and bars.
- Churrasco is the main dish of southern Brazil . Over time, other regions of Brazil adopted churrasco and created other ways of making it. The restaurant specializing in churrasco is a churrascaria .
- Virado , typical dish from the state of São Paulo, where it is also known as Virado à Paulista, which consists of a pork chop, fried plantain, cassava flour beans, rice, cabbage and fried egg.
- Tutu de feijão , typical dish from the state of Minas Gerais, made with boiled beans, sautéed and thickened with cassava or corn flour. It is usually sautéed with pieces of fried bacon, onion and garlic, and mixed with cassava flour or corn flour depending on the type of bean.
- Arroz carreteiro is a typical dish from the southern region of Brazil, made from rice to which is added finely chopped and sautéed beef, shredded or minced dried meat or sun-dried meat, sometimes paio, bacon and chorizo. in pieces, sautéed in a lot of fat, with garlic, onion, tomato and parsley, always with a lot of seasoning.
- Galinhada is a typical dish from the states of São Paulo, Minas Gerais and Goiás, which consists of cooked rice and cooked chicken pieces. The seasoning is composed of saffron (which gives the rice the typical yellowish color), vinaigrette (optional and to accompany), and bean tutu. The typical Goiás chicken dish contains guariroba (a type of bitter palm) and pequi.
- Barreado is a typical dish of Parana State, Brazil. It is a slow-cooked meat stew prepared in a clay pot whose lid is sealed with a sort of clay made from wheat or cassava flour, hence the name (which means, literally, "muddied"). Traditionally, Barreado was made of buffalo meat, but nowadays it is usually made of beef, bacon, tomatoes, onion, cumin and other spices, placed in successive layers in a large clay urn, covered and then "barreada" (sealed) with a paste of ash and farinha (manioc flour), and then slowly cooked in a wood-fired oven for 12 to 18 hours. Nowadays pressure cookers and gas or electric ovens are more commonly used.
- Cachorro quente is the Brazilian version of hot dogs . It is another dish that has been modified in Brazil, practically becoming a complete lunch. There, the most common version is the "X-Tudo" (in literal translation, cheese-everything), or "Podrão", where, in addition to conventional bread and sausages with ketchup, mustard and mayonnaise, it is filled with a series of additional ingredients ranging from straw fries, grated Parmesan cheese, corn kernels, peas and olives to quail eggs.
- Misto-quente is grilled ham and cheese sandwich.
- Angu is a popular side dish (or a substitution for rice replacing the "starch element" and it is commonly used in Southern and Southeastern Brazil ). It is similar to the Italian polenta.
- Arroz com pequi is a traditional dish from the Brazilian Cerrado , and the symbol of Center-Western Brazil's cuisine. It is basically made with rice seasoned on pequi , also known as a souari nut, and often chicken.
- Cuscuz branco is a dessert consisting of milled tapioca cooked with coconut milk and sugar and is the couscous equivalent of rice pudding.

The Brazilian film industry began in the late 19th century, during the early days of the Belle Époque . While there were national film productions during the early 20th century, American films such as Rio the Magnificent were made in Rio de Janeiro to promote tourism in the city. The films Limite (1931) and Ganga Bruta (1933), the latter being produced by Adhemar Gonzaga through the prolific studio Cinédia, were poorly received at release and failed at the box office, but are acclaimed nowadays and placed among the finest Brazilian films of all time. The 1941 unfinished film It's All True was divided in four segments, two of which were filmed in Brazil and directed by Orson Welles ; it was originally produced as part of the United States' Good Neighbor Policy during Getúlio Vargas' Estado Novo government.
During the 1960s, the Cinema Novo movement rose to prominence with directors such as Glauber Rocha , Nelson Pereira dos Santos , Paulo Cesar Saraceni and Arnaldo Jabor. Rocha's films Deus e o Diabo na Terra do Sol (1964) and Terra em Transe (1967) are considered to be some of the greatest and most influential in Brazilian film history.
During the 1990s, Brazil saw a surge of critical and commercial success with films such as O Quatrilho ( Fábio Barreto , 1995), O Que É Isso, Companheiro? (Bruno Barreto, 1997) and Central do Brasil ( Walter Salles , 1998), all of which were nominated for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film, the latter receiving a Best Actress nomination for Fernanda Montenegro . The 2002 crime film City of God , directed by Fernando Meirelles , was critically acclaimed, scoring 90% on Rotten Tomatoes , being placed in Roger Ebert 's Best Films of the Decade list and receiving four Academy Award nominations in 2004, including Best Director . Notable film festivals in Brazil include the São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro International Film Festivals and the Gramado Festival.

Brazilian painting emerged in the late 16th century, influenced by Baroque , Rococo , Neoclassicism , Romanticism , Realism , Modernism , Expressionism , Surrealism , Cubism and Abstracionism making it a major art style called Brazilian academic art.
The French Artistic Mission arrived in Brazil in 1816 proposing the creation of an art academy modeled after the respected Académie des Beaux-Arts, with graduation courses both for artists and craftsmen for activities such as modeling, decorating, carpentry and others and bringing artists like Jean-Baptiste Debret.
Upon the creation of the Imperial Academy of Fine Arts, new artistic movements spread across the country during the 19th century and later the event called Modern Art Week definitely broke with academic tradition in 1922 and started a nationalist trend which was influenced by modernist arts.
Among the best-known Brazilian painters are Ricardo do Pilar and Manuel da Costa Ataíde (baroque and rococo), Victor Meirelles, Pedro Américo and Almeida Júnior (romanticism and realism), Anita Malfatti , Ismael Nery, Lasar Segall , Emiliano di Cavalcanti, Vicente do Rego Monteiro, and Tarsila do Amaral (expressionism, surrealism and cubism), Aldo Bonadei, José Pancetti and Cândido Portinari (modernism).

The most popular sport in Brazil is football .
Volleyball , basketball , auto racing , and martial arts also attract large audiences. The Brazil men's national volleyball team, for example, currently holds the titles of the World League , World Grand Champions Cup, World Championship and the World Cup. In auto racing, three Brazilian drivers have won the Formula One world championship eight times. The country has also produced significant achievements in other sports such as sailing , swimming , tennis , surfing , skateboarding , MMA , gymnastics , boxing , judo , athletics and table tennis .
Some sport variations have their origins in Brazil: beach football, futsal (indoor football) and footvolley emerged in Brazil as variations of football. In martial arts, Brazilians developed Capoeira , Vale tudo, and Brazilian jiu-jitsu .
Brazil has hosted several high-profile international sporting events, like the 1950 FIFA World Cup and recently has hosted the 2014 FIFA World Cup , 2019 Copa América and 2021 Copa América . The São Paulo circuit, Autódromo José Carlos Pace , hosts the annual Grand Prix of Brazil . São Paulo organized the IV Pan American Games in 1963, and Rio de Janeiro hosted the XV Pan American Games in 2007. On 2 October 2009, Rio de Janeiro was selected to host the 2016 Olympic Games and 2016 Paralympic Games, making it the first South American city to host the games and second in Latin America, after Mexico City . Furthermore, the country hosted the FIBA Basketball World Cups in 1954 and 1963. At the 1963 event, the Brazil national basketball team won one of its two world championship titles.
- Brazil is the largest country in South America.
- It is the only Portuguese-speaking nation in the Americas.
- Brazil was named after brazilwood . Brazilwood is a tree that once grew very well along the Brazilian coast.
- The Brazilian men's national team is ranked among the best in the world according to the FIFA World Rankings , and has won the World Cup tournament a record five times.
- Brazil has the largest Japanese community outside Japan .

Rock art at Serra da Capivara National Park, one of the largest and oldest concentrations of prehistoric sites in the Americas .

Depiction of Pedro Álvares Cabral landing in Porto Seguro in 1500, ushering in more than 300 years of Portuguese rule of Colonial Brazil .

Painting showing the arrest of Tiradentes; he was sentenced to death for his involvement in the best known movement for independence in Colonial Brazil. Painting of 1914.

The Acclamation of King João VI of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves in Rio de Janeiro , 6 February 1818

Declaration of the Brazilian independence by Prince Pedro (later Emperor Pedro I ) on 7 September 1822.

Pedro II , Emperor of Brazil between 1831 and 1889.

Soldiers of the FEB , the only Latin American military force in World War II , in Massarosa, Italy, 1944.

Ulysses Guimarães holding the Constitution of 1988 in his hands

Coin of 1 real commemorating 25 years of Real Plan, which brought stability to the Brazilian economy after years of hyperinflation.

Historical building of the Federal University of Paraná, one of the oldest universities in Brazil, located in Curitiba .

Former President Dilma Rousseff at Jornal Nacional news program. Rede Globo is the world's second-largest commercial television network.
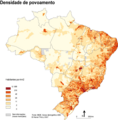
Population density of Brazilian municipalities

Museum of the Portuguese Language in São Paulo

In the region of Pomerode, Santa Catarina , Hunsrückisch and East Pomeranian are two of the minor languages (see Brazilian German).

Parade of Portela samba school at the Rio Carnival , the largest carnival in the world

The Cathedral of Brasilia, designed by Brazilian architect Oscar Niemeyer for the federal capital , an example of Modern architecture
- This page was last modified on 20 February 2024, at 12:05. Suggest an edit .
Find out why teachers and school leaders love PlanBee
- 📚 Cross-Curricular Topics
- ✂️ Design & Technology
- ♻️ Education for Social Responsibility
- 🌍 Geography
- ⛪️ Religious Education
- 🎉 Special Days
- 🦸♀️ Special People
- 🏫 Whole School CURRICULUM PACKS
- Vision and Principles
- Our Curriculum Offer
- Whole School Curriculum Packs
- Become a Whole School Member
- FREE Schemes of Work
- Sample Packs
- Learn at Home
- Objective Checker
- How does it work?
- Special Offers
- BECOME A MEMBER 🧡
Exploring Brazil
What's Your Email?
In this Exploring Brazil KS2 Geography planning pack for Year 5 and Year 6, your class will find out about all the different aspects of this amazing country.
#TheCompleteSeries7lessons
They will begin by using their map skills to locate Brazil, and then go on to explore the physical geography of the country, including an in-depth look at the Amazon rainforest. Children will find out how urbanisation is affecting Brazil, and explore why Rio de Janeiro is often called a 'city of two halves'. They will explore the tourist attractions the city has to offer, and finally immerse themselves in the culture of Brazil.
This Exploring Brazil lesson plan pack contains easy-to-follow lesson plans, slides for the teaching input of each lesson, differentiated activity ideas and a range of printable teaching resources - everything you need to explore the country of Brazil with your class!
#Lesson1WhereisBrazil
Where is Brazil? Which continent is it in? Which countries surround it? In the first lesson of this Exploring Brazil scheme of work, your KS2 class will use maps to answer these questions and find out some detailed information about the location of Brazil and its regions.
In their independent activities, children locate and label their own map of Brazil. Alternatively, children read and give six-figure grid references using a map of Brazil.
There 'Where is Brazil?' lesson comes fully planned and ready to teach. There's a detailed lesson plan with three-way differentiation plus an alternative activity, a slideshow for the teaching input and a range of printable teaching resources.
What's included:
- Lesson plan
- Activity ideas
- Differentiated worksheets
- Challenge Cards
- Six-Figure Grid Reference Help Sheet
- Grid Reference Map of Brazil

#Lesson2PhysicalGeographyofBrazil
In this lesson, your class will explore the physical geography of Brazil. After defining exactly what 'physical geography' means, your KS2 children will then explore three different natural landscapes of Brazil in more detail: the Amazon Basin, the Pantanal, and the Brazilian Highlands.
In their independent activities, your Year 5 or Year 6 children will look more closely at the landscape, climate, wildlife and population of each of these areas. Alternatively, children are challenged to research five given natural attractions in Brazil, and share what they have found as a class.
This Physical Geography of Brazil lesson comes with a detailed lesson plan, a slideshow for the teaching input, differentiated activity ideas and a range of printable teaching resources.
- Amazon Basin Information Sheet
- Pantanal Information Sheet
- Brazilian Highlands Information Sheet
- Question Cards
- Natural Wonders Challenge Sheet
#Lesson3TheAmazonRainforest
The Amazon Rainforest KS2 lesson planning pack – full of fascinating information and things to explore around this incredible ecosystem.
The included slideshow presentations goes through some information about the Amazon rainforest, including layers of vegetation, biodiversity, native tribes and more. During their independent learning activities, your Year 5 or Year 6 children will explore a major threat to the Amazon rainforest - deforestation - and discuss the reasons for, and effects of, this. Alternatively, children are challenged to create a group presentation explaining the importance of the rainforest.
This Amazon Rainforest KS2 pack comes with a lesson plan, a slideshow for the teaching input, differentiated activity ideas and a range of printable resources – everything you need to deliver an amazing Amazon Geography lesson!
- Deforestation Information Sheet
- Reasons or Effects Cards
- Viewpoints Sheet
- Debate Talk Show Sheet & Name Tags
#Lesson4Urbanisation
In this Urbanisation lesson for KS2, children first find out what is meant by the term ‘urbanisation’, and look at reasons for why this is happening in Brazil. They then identify push and pull factors for moving from a rural area to an urban area.
In their independent activities, children look at the situation of a fictional family who is trying to decide whether or not to move from their village to a city. They discuss the push and pull factors, and are encouraged to give their own opinions as to what the family should do.
This lesson is fully prepared and ready to deliver to your class. There's a lesson plan, slideshow, differentiated activities and printable teaching resources.
- Push and Pull Factor Cards
- Reasons to Stay Sheet
- Reasons to Move Sheet
#Lesson5RiodeJaneiro
In this Rio de Janeiro KS2 lesson, your Year 5 or Year 6 will explore one of the effects of urbanisation on the city of Rio de Janeiro: overcrowding. They will look at two very different neighbourhoods in Brazil; a wealthy area and a deprived area.
The included slideshow presentation goes through some key information about Rio de Janeiro so that children can compare two opposing areas of the city.
This interesting and thought-provoking lesson is fully prepared and ready for you to teach to your class. All you need to do is download, teach and enjoy!
- Life in Barra Di Tijuca Sheet
- Life in Rocinha Sheet
- Diary Challenge Cards
- Brasilia Information Sheet
- Residents of Brasilia Comments Sheet
- Brasilia Photo Cards
- Urban Planners Sheet
#Lesson6TouristAttractions
Pack up your classroom and head off to Brazil in this fun Geography lesson for Year 5 or Year 6 children!
In this lesson, your class will begin to think about Brazil as a tourist destination, and are encouraged to discuss what would attract tourists to a particular place. During their independent activities, children can explore the attractions of Rio de Janeiro, and write postcards, letters, or reviews about visiting them. Alternatively, they are challenged to plan a schedule for a school trip to the city.
This fully-prepared lesson comes with a detailed lesson plan, a slideshow for the teaching input, differentiated activity ideas and a range of printable teaching resources.
- Tourist Attraction Cards
- Review Cards
- School Trip Schedule Sheet
#Lesson7BrazilianCulture
In this Brazilian Culture KS2 Geography lesson, your Year 5 or Year 6 children will discuss the definition of culture, and talk about what the culture of Brazil might be like, based on what they already know.
During their independent learning activities, they are then given Information Packs about a particular aspect of Brazilian culture, and after reading and discussing them, either take part in a class quiz, or devise their own quiz in pairs.
This lesson comes with a comprehensive lesson plan, an engaging slideshow for the teaching input, differentiated activity ideas and a range of handy printable teaching resources.
- Brazilian Culture Packs
- Brazilian Culture Quiz Q&A Sheet
- Culture Experts Labels
- Culture Quiz Challenge Cards
- Culture Quiz Template
Free Overview (Medium-Term Plan)
Download a free overview to support your teaching of this scheme of work.
Free Assessment Grid
Download a free, editable assessment grid to support your teaching of this scheme of work.
Curriculum Objectives covered
- KS2 - locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities
- KS2 - describe and understand key aspects of physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle
- KS2 - describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water
Customer Reviews
Thank you, Halys!
Really useful resource for me as a student teacher. Saved lots of planning time. Clear lesson objectives and quality worksheets.
Thank you, Carly! We are so pleased to hear that our resources have saved you time :-)
Great resource
Fab resource!
Added to your cart:
Let customers speak for us.
I needed for my brownies local history badge
Thanks, Rosemary! We're so pleased that this FreeBee was helpful for you :-)
Everyday Materials
Thanks, Claire!
Thanks, a great range of resources
You're welcome, Ian!
This was a great unit. Had some time in our day to schedule in an art activity and this fit the bill brilliantly
Thanks, Dawn! We're so pleased that you enjoyed these art lessons :-)
This chart breaks the classifications down to simple concepts that my students can understand.
Thanks, Dian - we're happy to hear that this was useful for your students :-)
You'll need JavaScript enabled to experience the full functionality of this site. Please enable JavaScript by following the instructions at enable-javascript.com .
Sorry, the browser you're currently using is not supported by this site. Please upgrade your browser by following the instructions at browser-update.org .
- Go to cgpbooks.co.uk
- Your Lessons

Country Profile — Brazil (Years 5-6)
Write a review

Choose your format:
Save to Your Lessons
Save to Homework
Share resource
Your download limit has been reached!
Check out our FAQs for more info.
Teach children all about Brazil with this country profile. The first page includes key facts about Brazil's capital city, language, population and currency, as well as a map to show the location of Brazil within South America. The second page gives more information about the history of Brazil, its climate and biodiversity and growing tourism industry.
- Key Stage: Key Stage 2
- Subject: Geography
- Topic: South America
- Topic Group: Locations
- Year(s): Years 5-6
- Media Type: PDF
- Resource Type: Handout
- Last Updated: 17/01/2023
- Resource Code: G2WAT408
Related Topics:
Other Teachers Downloaded...

Brazil Fact File (Years 5-6)
- South America
- Key Stage 2 Geography

Rainforest Layers and Wildlife (Years 5-6)

South America — Where Is It? (Years 3-4)

The Tropical Rainforest Biome (Years 5-6)

Biomes of South America (Years 5-6)

Fact File: Amazon River (Years 3-4)
No reviews (yet!)
Related Resources

City Profile — São Paulo (Years 5-6)

Country Profile — Suriname (Years 5-6)

Country Profile — Chile (Years 5-6)

Country Profile: Cuba (Years 5-6)
- North America

City Profile — Rio de Janeiro (Years 5-6)

City Profile — Caracas (Years 5-6)

Country Profile — Ecuador (Years 5-6)

Countries of South America 1 (Years 5-6)

Countries of South America 2 (Years 5-6)

Deforestation Photo Discussion (Years 5-6)

Country Profile — Mexico (Years 5-6)
Cookies are disabled on your browser. This means some features of the site won't be fully available to you.
CGP uses cookies to give you a smooth shopping experience and to help us understand how well our site is working. To agree to us using all cookies, click 'Accept', or to reject optional cookies click 'Customise'.
Accept cookies Customise cookies
- Create new account
- Reset your password
Register and get FREE resources and activities
Ready to unlock all our resources?

Where is Brazil?
Brazil is in South America, which is in the western hemisphere. In fact, Brazil is the largest country in South America , and the fifth-largest in the world!
There are 13 countries in South America, and only two of them don’t share part of their border with Brazil: Chile and Ecuador. Brazil has the fifth highest population in the world , and the capital is Brasilia.
Top 10 facts
- Brazil is the largest country in South America , and the fifth highest population compared to all other countries in the world (the highest is China ).
- The official language of Brazil is Portuguese.
- The capital of Brazil is Brasilia, but the largest city is Sao Paulo.
- The Brazilian population was 209 million in 2017.
- The currency in Brazil is the ‘real’. One ‘real’ is divided up into 100 ‘centavos’ (like our pence).
- Brazil has 26 states and one federal district – the federal district is Brasilia.
- A famous holiday in Brazil is Carnival , which is a week of parades and celebrations that takes place 46 days before Easter every year.
- The first European settlers in Brazil were from Portugal.
- Brazil’s Independence Day is celebrated on 7 September.
- The 2016 Olympic Games were held in Rio de Janeiro.

Boost Your Child's Maths & English Skills!
- Start your child on a tailored learning programme
- Weekly resources sent direct to your inbox
- Keep your child's learning on track
Did you know?
People in Brazil speak Portuguese. It is the only country in South America that speaks Portuguese. ‘Brazil’ is spelled differently in Portuguese – ‘Brasil’.
The capital of Brazil is Brasilia. That’s easy to remember!
The enormous statue of Christ the Redeemer in Rio de Janeiro is considered to be one of the seven wonders of the modern world.
There are over 200 million people in Brazil – that’s more than three times as many people as live in the United Kingdom!
In Brazil, people pay for things in ‘real’ (pronounced ray-al). One real is divided up into 100 centavos, and is worth about the same as 30p in the UK. You can see a picture of reals and centavos below.
The main religion in Brazil is Christianity .
Brazil has a very long coastal border with the Atlantic Ocean – it is 7,491km (4,655 miles) long. That’s as long as it would take to travel from Plymouth to Aberdeen about seven times!
Brazil shares a border with all but two (Chile and Ecuador) of the other 12 countries in South America.
The Amazon River runs across northern Brazil. It is the second longest river in the world and carries the largest amount of water of any river in the world.
Brazil is home to a part of the Amazon rainforest. This is a tropical rainforest that is home to many rare and interesting species of plants and animals, but many of them are becoming rarer and are considered ‘endangered’. Learn more about conservation and endangered species
Brazil’s major exports include coffee, bananas, sugar, tobacco, soya, orange juice, beef and chicken.
Look through the pictures in the gallery and see if you can spot the following:
- The Brazilian flag
- Map of Brazil
- Brazilian currency: real and centavos
- Dancers in the Carnival
- Christ the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro
- The rainforest is home to amazing birds and animals
- Iguazu Falls in Brazil
- Brazil is famous for its beautiful beaches
- Beach-goers in Rio

The largest country in South America, Brazil is made up of varied landscapes: mountains , grasslands , deserts , rainforest and a very long coastline . The climate in Brazil is mostly tropical and subtropical, but temperatures vary because it has lots of different kinds of terrain.
Brazil is rich in minerals (gold, diamonds, uranium and oil) and one of the largest producers of coffee in the world.
Brazil is made up of 26 states, and one federal district. Each state has its own capital. The federal district is Brasilia, the capital of Brazil.
A popular dish in Brazil is feijoada , which is a stew with beans and pork. Brazil has a good climate for growing many different kinds of foods, especially fruit.
You can find lots of different foods in Brazil because many immigrants from other countries have settled there over the years – from Europe (Portugal, Italy and Poland), Asia (Japan), Africa (because of the slave trade until the late 1800s) and the Middle East. There are also many descendants from the native tribes who lived there before settlers came.
People from Portugal were the main settlers in Brazil, which is why Portuguese is still spoken there now. The first explorer to claim land there was Pedro Álvares Cabral in 1500. (To put that into context in UK history, Henry VIII was crowned king in 1509.) Brazilian Independence Day is celebrated on 7 September; on 7 September 1822, Brazil declared independence from Portugal.
The national flag in Brazil has a green background with a dark blue sphere and yellow diamond in the centre. Each part of the flag has a special meaning:
- Green represents the lush vegetation that can be found in Brazil.
- Yellow represents wealth and riches.
- The dark blue sphere represents the colour of the sky in the tropics.
- Inside the sphere are 27 stars of different sizes, which represent the 26 states and one federal district that make up Brazil.
- In the middle of the sphere is a banner with the words ‘ ordem e progresso ’ on it – this means ‘order and progress’.
Brazil also has a national coat of arms, which was made in 1889 – just after Brazil became a republic on 15 November 1889. On it are this date, the coffee plant and tobacco plant (two main crops at the time), the Southern Cross, and stars representing the 26 states and one federal district.
The Southern Cross is a constellation that you can only see when you’re in the Southern Hemisphere of the globe. Brazil is just one of the countries that has the Southern Cross on its flag – both Australia and New Zealand have it on their flags too.
One of Brazil’s most famous events is Carnival, which is held 40 days before Easter. It lasts for about a week, and each part of the country has different events. There are parades, lots of music, lavish costumes, dancing and singing. People from all over the world visit Brazil during Carnival to experience the events and excitement.
The 2016 Olympic Games in Rio (5-21 August) was the first Games to take place in South America. Over 17 days 10,500 athletes from 205 countries competed in 306 medal events!
Names to know
Dilma Rousseff (1947-present) – Dilma Rousseff was the first woman to be elected as president in Brazil.
Pedro Álvares Cabral (1467/68-1520) – In 1500, Cabral, from Portugal, was the first explorer to claim land where Brazil is now located.
João Faras – Faras was an astronomer who travelled with Pedro Álvares Cabral when he discovered Brazil in 1500. He is thought to be the first European to record the Southern Cross constellation correctly.
Marshal Deodoro da Fonseca (1827-1892) – Fonseca took over the government of Brazil on 15 November 1889 and reorganised it as a constitutional republic. Before this, Brazil had been an empire ruled by an emperor.
Edson Arantes do Nascimento (1940-present) – Better known by his nickname, Pelé, he is a famous footballer from Brazil who scored the most League goals (541).
Oscar Niemeyer (1907-present) – Neimeyer is a famous architect, and most known for the buildings he designed in Brasilia.
Related Videos
Just for fun...
- Take an interactive look at Brazilian objects and customs
- Hear simple phrases in Portuguese , Brazil's official language
- Try some Brazilian-themed crafts
- Make your own Brazilian chocolate truffles, brigadeiro , or other Brazilian food
Children's books about Brazil

Find out more
The Kiddle guide to Brazil is packed with information
Introducing Brazil
A children's guide to Brazil
Find out about the legacy of the Rio 2016 Olympic Games
See a BBC Newsround report about a child's life in Rio
Find out about some popular Brazilian foods
Watch a video about the Bolsa family who live in a favela , a shantytown in Brazil
Find out about the Brazilian martial art of capoeira
Information about the world-famous statue of Christ the Redeemer in Rio
Explore Brazil with a variety of engaging, story-led resources produced for KS1 and KS2 teachers by Action Aid
Discover Brazil's famous Carnival celebrations
See for yourself
Top sights in Brazil include:
- Christ the Redeemer Statue, Rio de Janeiro
- Brasilia, famous for its architecture
- The Amazon River and rainforest
- The Iguassu Waterfalls
- Fernando de Noronha, an archipelago off the coast of Brazil
- The Pantanal (the largest wetland in the world)
- Sao Paulo, Brazil’s largest city

Give your child a headstart
- FREE articles & expert information
- FREE resources & activities
- FREE homework help
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Exploring Brazil's ecosystems - KS2
Subject: Geography
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
10 April 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This lesson is part of Exploring Brazil , a Geography unit designed for students in KS2 (Y4-6), but can also be taught as a stand alone lesson.
The presentation introduces students to Brazil’s six main biomes including the tropical rainforest, caatinga (desert), Pantanal wetlands, cerrado (savannah) and Atlantic Forest. Students then read an information text to find out more.
In the activity, students write an information text about Brazil’s ecosystems. This can either be done as a short activity or as an extended write in Literacy. (N.B. The activity sheets need to be enlarged to A3 size to provide adequate space for writing.)
Short Activity: Easier – Students match statements to each ecosystem and write them in each box. Medium – Students add titles, then match statements to each ecosystem and write them in each box. Harder – Students add titles and write their own sentences about each ecosystem in the box. Extension – Students label the different ecosystems on the map, including drawings of animals found in each one.
Extended Writing Activity: Easier – Students write an information text about Brazil’s ecosystems, including an introductory paragraph. Harder – Students write an information text about Brazil’s ecosystems, including sub-headings and an introductory paragraph.
If you like this resource, we would appreciate a review! We will happily send you a free resource in return for a review or useful suggestions/feedback. Contact us at [email protected] .
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 58%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Exploring Brazil - KS2
**Exploring Brazil** is a Geography unit designed for students in KS2 (Y4-6). The planning overview, topic title page and vocabulary page can be downloaded for free [here](https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/exploring-brazil-ks2-planning-overview-12391039). Lessons include: **L1** – Identifying the countries and capitals of South America **L2** – Writing a Brazil fact file **L3** – Using 4 and 6-figure grid references to locate Brazilian cities **L4** – Identifying the human and physical features of Brazil **L5** – Exploring Brazil’s ecosystems **L6** – Investigating Brazil’s weather and climate Each lesson includes a presentation and differentiated activities/worksheets. [](http://) If you like this resource, we would appreciate a review! We will happily send you a free resource in return for a review or useful suggestions/feedback. Contact us at [email protected].
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Fantastic lesson which saved me a lot of time.
TeachItForward
Thank you for the 5-star review - most appreciated! If you would like to try another resource for free at some point get in touch at [email protected]. Ed :)
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Great resource, thank you.
Thank you so much for the lovely review - I'm glad you liked this lesson. If you would like to try another resource for free at some point get in touch! ([email protected]). Ed :)
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Rio de Janeiro is a city in the country of Brazil. Brazil is the biggest country on the continent of South America. Brazil is nearly as big as the continent of Europe! The River Amazon flows ...
Brazil is the largest country in South America and the fifth largest nation in the world. It forms an enormous triangle on the eastern side of the continent with a 4,500-mile (7,400-kilometer) coastline along the Atlantic Ocean. It has borders with every South American country except Chile and Ecuador. The Brazilian landscape is very varied.
Brazil's geography. Brazil is the largest country in South America and the fifth largest nation in the world. It forms an enormous triangle on the eastern side of the continent with a 7,400km coastline along the Atlantic Ocean. It has borders with every South American country except Chile and Ecuador. The Brazilian landscape is very varied.
Here are some interesting Brazil Facts which were chosen and researched by kids especially for kids. Capital: Brasilia, with 5 million inhabitants is the country's fourth largest city. The largest city in Brazil is Sao Paulo with about 23 million inhabitants. Literacy: More than 91% of the people can read and write.
Join us today as we travel to Brazil! We're a homeschooling family, and we learn together about one new country every week. This week: Brazil.Learn the coole...
doc, 479 KB. pptx, 6.78 MB. This is the free planning overview for Exploring Brazil, a comprehensive unit of work about the geography of Brazil. A vocabulary page and topic title page are also included. The unit is is designed for students in KS2 from Y4 to Y6 and includes a variety of engaging lessons, differentiated activities and worksheets.
In this category you'll find teaching materials and learning resources to help you put together an engaging Brazil topic for KS2 children. Children will learn all about the different aspects of the amazing country of Brazil with our engaging collection of resources on the topic. Explore teaching materials covering Brazil's geography, events ...
Why do people visit Brazil? In this lesson we will recap our knowledge of the seven continents in the world, before zooming into South America and locating Brazil. We will explore some of the reasons people visit Brazil, focusing on natural areas of beauty as well as cultures and festivals that tourists come to experience.
What is distinctive about Brazil's toco toucan? Pupils will learn about some of the unique features of Brazil, including its wildlife, produce and sporting achievements in our National Geographic Kids' Geography primary resource sheet. The teaching resource can be used in study group tasks, as a printed handout for each pupil, or for ...
This fantastic teaching and learning pack includes an informative PowerPoint covering Brazil's geography for KS2. The PowerPoint will introduce your pupils to the human and physical features of Brazil, such as the climate, carnivals and famous Brazilian landmarks, such as The statue of Christ the Redeemer in Rio de Janeiro. Also included in this Brazil Geography for KS2 resource pack, are ...
Rio de Janeiro is one of the largest cities in Brazil and was the country's capital city until 1960. Even though it is no longer the official capital city of Brazil, Rio de Janeiro is still famous for its many landmarks and beautiful landscapes. This Fact File includes key information about the area - such as currency, language and population - while also containing more in-depth details of ...
Exploring Brazil is a Geography unit designed for students in KS2 (Y4-6).. The planning overview, topic title page and vocabulary page can be downloaded for free here.Lessons include: L1 - Identifying the countries and capitals of South America. L2 - Writing a Brazil fact file. L3 - Using 4 and 6-figure grid references to locate Brazilian cities. L4 - Identifying the human and physical ...
How is the weather in Brazil different than the UK? 20m video. Lesson . 8
Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world by area and the sixth most populous country in the world. Find out more with BBC Bitesize. For students between the ages of 11 and 14.
In the list of world tourist destinations, in 2018, Brazil was the 48th most visited country, with 6.6 million tourists (and revenues of 5.9 billion dollars). Natural areas are its most popular tourism product, a combination of ecotourism with leisure and recreation, mainly sun and beach, and adventure travel, as well as cultural tourism.
Exploring Brazil is a Geography unit designed for students in KS2 (Y4-6). The planning overview, topic title page and vocabulary page can be downloaded for free here. Lessons include: L1 - Identifying the countries and capitals of South America. L2 - Writing a Brazil fact file. L3 - Using 4 and 6-figure grid references to locate Brazilian ...
Start exploring Brazil with Lonely Planet's video guide to getting around, when to go and the top things to do while you're there. For more travel tips, head...
In this lesson Jack explores Brazil and South America. We discuss the location and climate. Children will gain the opportunity to learn about the famous landmarks. We take a look at the food associated with Brazil and South America. Children will learn about the culture and the people. The video lesson can be paused and navigated to allow ...
In this Exploring Brazil KS2 Geography planning pack for Year 5 and Year 6, your class will find out about all the different aspects of this amazing country. Share this: They will begin by using their map skills to locate Brazil, and then go on to explore the physical geography of the country, including an in-depth look at the Amazon rainforest.
Teach children all about Brazil with this country profile. The first page includes key facts about Brazil's capital city, language, population and currency, as well as a map to show the location of Brazil within South America. The second page gives more information about the history of Brazil, its climate and biodiversity and growing tourism ...
Reading Comprehension: Brazil. Subject: Guided reading. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. pdf, 387.53 KB. Children will be fascinated to discover exciting facts about Brazil. There are 2 levels of questions to suit all learners: A red border for simpler questions.
The official language of Brazil is Portuguese. The capital of Brazil is Brasilia, but the largest city is Sao Paulo. The Brazilian population was 209 million in 2017. The currency in Brazil is the 'real'. One 'real' is divided up into 100 'centavos' (like our pence). Brazil has 26 states and one federal district - the federal ...
pptx, 116.65 KB. This lesson is part of Exploring Brazil, a Geography unit designed for students in KS2 (Y4-6), but can also be taught as a stand alone lesson. The presentation introduces students to Brazil's six main biomes including the tropical rainforest, caatinga (desert), Pantanal wetlands, cerrado (savannah) and Atlantic Forest.