By registering, you agree to our Terms & Conditions .
- +2348180191933
- Login or Register
- $ US DOLLAR
- How It Works

Basic Science JSS1 Third Term SPACE TRAVEL
Space travel : lsus.
Basic Science JSS1 Third Term
- SPACE TRAVEL
Performance Objectives
Students should be able to:
REFERENCE Precious seed BASIC SCIENCE FOR JUNIOR SECONDARY SCHOOLS BOOK
MEANING OF SPACE TRAVEL
The space outside the sun, earth, star is called outer space. Space travel is the travelling to the outer space beyond this earth. The space travellers are called astronau t. The earth is surrounded by a layer of air called atmosphere which can be divided into about 4 regions:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
Since 1957, man has been travelling to the space to find out what happens there.
Subscribe now to gain full access to this lesson note
Click here to gain access to the full notes.
- ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION (I)
- ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION (II)
- CALCULATION OF GRAVITATIONAL FORCES
- GRAVITATION AND WEIGHTLESSNESS
- THE EARTH IN SPACE
- Forces 1&2
- Chapters 19
- Category JSS1
- Author ClassNotes Edu
For Schools & Teachers
For Schools and Teacher who want to subscribe to all of the subjects, a class or term at a discounted price.

Create Your Bundle
Need many subjects? Waste no time. Select many subjects together in one subscription at a discounted price.

JSS1 Basic Science Past Questions
Section: objective.
- Which of the following is normally used to clean water closet or toilet? a) Bath sponge b) toothbrush c) insecticide d) Harpic
- If you are you are to keep your clean and tidy it will result in bad odour dandruff. True or false?
- Poor hygiene of teeth might result in tooth decay, toothache. True or false?
- Which of the following is not a food item? a) Rice b) milk c) yam d) alcohol
- We have six classes of food in an adequate diet. True or false?
- The source of earth’s energy is a) foo b) animals c) sun d) plants
- The earth is _____ million kilometers away from the sun. a) 100 b) 108 c) 50 d)80
- Animals that feed on plants are called _____ a) herbivores b) carnivores c) scavengers d) matter
- Animals that feed on flesh are called a) Scavengers b) herbivores c) carnivores d) evaporation
- The capture of sunlight energy by plants to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar is called. a) Photosynthesis b) chemosynthesis c) evaporation d) transpiration
SECTION: Essay
- List the classes of food we have
- Give three examples of solid and liquid food you know
- a) List four ways of keeping your body clean
- b) What is food?
Objective Questions
- If you fail to keep your hair clean and tidy, bad odour, dandruff might result. (a)true (b)false
- Which of the following night result from poor hygiene of the teeth? Tooth decay, toothache (a)true (b)false
- which of the following is not a food item? (a)Alcohol (b)Rice (c)milk (d)spinach
- The source of the earth's energy is (a)sun (b)plants (c)animals (d)petroleum
- Which of the following vector transmit malaria (a)mosquito (b)tsetse fly (c)blackfly (d)insects
- Which of the following is a waterborne disease (a)cholera (b)cough (c)tetanus (d)malaria
- All the living things move, grow, respire, reproduce (a)true (b)false
- Cocaine is an example of drug abuse (a)true (b)false
- A plant differs from an animal because a makes its own food (a)true (b)false
- Which of the following is not a living thing? (a)Iron (b)snail (c)earthworm (d)grasshopper
- An ant is a living things (a)true (b)false
- The following are benefits of space travel; computers, rocket or aircraft fuels. (a)true (b)false
- Problems of space travel are basic needs of life, loss of weight, high speed. (a)true (b)false
- Which of the following is present in outer space? (a)Air (b)light (c)sound (d)life
- Force of gravity cannot be carried in a spacecraft. (a)true (b)false
- Mercury has–––– number of moons. (a)1 (b)2 (c)0 (d)6
- Saturn has –––– number of moons. (a)3 (b)4 (c)7 (d)9
- Natural sources of energy include one of the following. (a)food (b)batteries (c)petroleum products (d)generator
- Which of the following is not a source of energy? (a)coal (b)smoke (c)wood (d)petroleum
- Energy is the capacity to do work. (a)true (b)false
Essay Questions

JAMB Past Questions & Answers PDF (FREE downloads, all subjects)
January 09 2024

JAMB Physics sample past questions solutions
September 01 2021

JAMB tutorials Mathematics
January 14 2019
Add a Comment
Notice: Posting irresponsibily can get your account banned!
Comments, Page 1/2
I love the outline questions.
It's good that what my daughter used for reading in examination 🖤🖤💜💜👍👍👍
You are still trying.keep it up.The questions are standard
Even a todler can answer this questions , it is so cheap.
Nice , lovely and interesting .
It is good but too easy
I hope the questions are not meant for your age group
loved is smart and easyyy
These questions have helped me. It's nice
PUT YOUR ENGLISH WELL AH MEN
Featured Posts
Latest posts.
Ecolebooks Nigeria
Home of Lesson notes and Scheme of Work
Week 5 – Jss 1 Third Term Basic Science & Technology (BST) Lesson Notes
WEEK FIVE SPACE TRAVEL
- Meaning of space travel
Purpose of space travel
Benefits of space travel
- Dangers of space travel
Meaning of space travel Space travel is the act of going to the moon or planets or orbiting the earth in a special craft called spaceship. It is also the travelling to the outer space beyond the earth. The space travelers are called ASTRONAUTS. On 21 st of July, 1969, Neil Armstrong, an American became the first human being to step into the moon. He was followed on the same day by another American named Edwin Aldrin. They stayed on the moon for 21 hours 36 minutes before they lifted up. The second moon landing took place in December 1972 when two Americans, Eugene Ceman and Harrison Schmitt stayed a total of 74hours 59 minutes on the moon surface. These astronauts wore special protective uniforms with oxygen masks for breathing. Most experiments in space are currently carried out in space station or space lab. These space stations are very large space rockets which can accommodate many people and are equipped to perform scientific experiments. Astronauts who work on these space stations usually stay for period of six months to one year after which they are replaced by other astronauts. Spaceship is moved by rockets. After leaving the earth’s atmosphere, gravity no longer pulls the spaceship to the earth. The astronauts wear special dress called suits and it help them to maintain the earths atmospheric pressure around there body throughout in space DEFINITION OF SPACE AND THE REGION’S OUTSIDE THE EARTH’S SURFACE Space refers to the region of our environment outside the earth’s crust. There are three important regions outside the earth’s surface. These are:
- The troposphere : It starts from the surface of the earth and extends to a height of about 16,000 meters. Most of the air and water vapour in our environment are found in this region. As one goes up in the troposphere, the temperature falls and it therefore becomes cooler.
- The stratosphere : It is the region directly above the troposphere. The region contains very little air. The temperature of this region does not falls as one goes up in this region
- The ionosphere : It is the upper part of the atmosphere. It contains mainly charged particles. The ionosphere is very useful to man because it enables the reflection and transmission of radio wave and signals round the world.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE OUTER SPACE
- Light from the sun passes through the outer space.
- There is no force of gravity in the outer space
- The outer space is void or empty
- Sound does not pass through the outer space, therefore the outer space is always quite
- Outer space is very large and beyond our imagination.
- It helps to watch everything that is happening in the world on the television e.g. football game, basketball game etc. at the same time the events are being carried out
- Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space
- Space travel is because of man’s curiosity it is a desire to find out the nature of life in other planets.
- The need for more knowledge of the climate and vegetation of the earth is another reason for space travel.
- The landing of equipment called satellite in space has also led to the improvement in communication
- The main benefit is the collection of scientific information about the earth and the other planets
- Production of special computers
- Production of photographic equipment such as x-ray and gamma-ray
- Production of telecommunication equipment
- Production of remote sensing equipment to guide spacecraft e.g. rocket
- Production of rocket or aircraft fuels
Dangers of space travel Space travel is risky. If anything goes wrong, one or more lives will be lost. The dangers of space travel can be caused by the following problems
- Explosion of rockets at the launch pad
- Failure of some necessary equipment in the spaceship to function well.
- Inability of the rocket to reach escape velocity
- Wrong calculation of angle, speed and time of launching
- High speed : Astronauts have to be trained in order to adopt to the high speed of space travel, so that they can think and work normally while traveling in space.
- Complicated calculation : There are lot of calculations involved before a spaceship can be launched correctly at an angle, speed and time to arrive at its destination. This is because the earth, the moon and all the planets are always in rapid motion.
- Loss of weight : The force of gravity is not felt in space, therefore it is very difficult for astronauts to stand or walk as they do on earth.
- Lack of basic need of life : The basic needs of life such as water, oxygen, food etc. are not available in the space, therefore oxygen and water must be made available in the spaceship to last for the period of the trip in space.
- Escape velocity : Rockets require escape velocity to escape from the attraction of the earth or the force of gravity
- Force of gravity : The force of gravity makes it difficult for any spacecraft to escape the earth’s surface easily. It has to be at a very high speed before the spacecraft can be allowed to leave the earth’s surface.
CLASSWORK 5
- What is a space?
- Mention the three region of space
- State 5 dangers of space travel
ASSIGNMENT 5 SECTION A
- The first man to travel to the moon is ____ (a) Neil Armstrong (b) Sir Isaac Newton (c) Maxwell Planks (d) Sir Bobby Charlton
- Which of the following is not associated with space travel (a) Basic need of life (b) force of gravity (c) electricity (d) escape velocity
- The regions outside the earth are the following except (a) troposphere (b) stratosphere (c) talkosphere (d) ionosphere
- The escape velocity is used by rocket to _______(a) overcome the force of gravity (b) escape from danger (c) hide from enemies (d) speed faster and disappear
- Which of these is not characteristic of outer space? (a) no force of gravity (b) quiet (c) empty (d) very small
- What is space travel?
- Mention three purpose of space travel
- Define troposhere
MID TERM PROJECT Using a WHITE CARDBOARD ONLY , draw and label the solar system
Related Post
All weeks – ss3 second term literature in english notes, all weeks – ss3 second term further mathematics notes, all weeks – ss3 second term french notes, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You May Like
Week 11 – ss3 second term catering craft practice (ccp) notes.
ALL SAINTS SECONDARY SCHOOL,OYIGBO
DAY AND BOARDING SCHOOL
- ICT Department
- Science Department
- Food & Nutrition
- Junior School Courses
- Senior School Courses
JSS 1 Basic Sc. 3rd term Scheme with notes & Assignment

Basic Science Scheme of work for JSS1 Third Term
1. Topic; Energy
Content; 1, meaning of energy, 2 sources of energy, 3. Forms of energy, 4. Transformation of energy, 5. Uses of energy.
2. Topic; Renewable and Non- Renewable Energy Content; 1 Meaning of Renewable and Non- Renewable Energy, 2. Examples of Renewable and Non- Renewable Energy, 3. Uses and Misuses of Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy, 4. Energy and Society
3. Topic; Forces Content: 1. Meaning of Force, 2. Types of Force, 3. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces, 4. Friction: Advantages and Disadvantages.
4. Topic; Gravitation and Weightlessness Content; 1. Meaning of Gravitation and Weightlessness, 2. The Earth in Space, 3. Space Travel, 4. Satellite
Basic Science JSS1 Third term unit 1 Topic; Energy
Energy is define as ability to do work. The unit of energy is Joule (J). Any thing is that is capable of doing work has energy. Sources Of Energy; These are sun, food, water, wind, coal, atomic reactors, crude oil products example kerosene, fuel, diesel, gas etc. A. Food- Green plants manufacture their food by the process of photosynthesis, animals eat these food and obtain energy. B. Sun- This is the primary source of energy. It supplies heat and light to the earth C. Wood- As wood burn the chemical energy in it changes to heat that is used for cooking D. Water- a fast moving river flowing through a turbine to generate mechanical energy, which changes to electrical energy, so a hydroelectric dam generates electricity through water.
Assignment; Explain briefly the following sources of energy; I. Wind, ii. Coal, iii. Crude oil products
To be submitted via e-mail : [email protected]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Recent posts.
- Notice Of School Resumption April 19, 2024
- Science Quiz Competition March 8, 2024
- ASH WEDNESSDAY February 15, 2024
- STAFF WORKSHOP January 10, 2024
- Back To School January 7, 2024
Recent Comments
- Martins George on SS 1 COMMERCE WITH ASSIGNMENT
- Balqis on JSS 2 AGRIC. SCIENCE
- osawaru praiseGOD on JSS 2 HISTORY NOTES WITH ASSIGNMENT
- osawaru praise on JSS 2 HISTORY NOTES WITH ASSIGNMENT
- Akaneme Chizoba on JSS 2 HISTORY NOTES WITH ASSIGNMENT
- Inter-House Sports
- school awards
- Uncategorized

JSS 1 Basic Science Scheme of Work ( 1st, 2nd, 3rd Term)
This JSS 1 Basic Science Scheme of Work covers the entire 1st, 2nd, and 3rd terms, offering you a well-defined roadmap to engage and empower your students. Dive into a curriculum designed to enhance science skills and ignite a lifelong love for Science learning.
JSS 1 FIRST TERM BASIC SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPICS/CONTENTS
- LIVING AND NON LIVING THINGS – I
- Meaning, Identification and Classification of Matter
- Define Matter, States of Matter
- LIVING AND NON LIVING – II
- Characteristics of living and Non Livings
- Examples, Characteristics and Importance of Plants and Animals
- LIVING AND NON LIVING THINGS – III
- Differences between Plants and Animals
- Examples, Properties, Uses and Importance of Living and Non Living
- LIVING AND NON LIVING THINGS – IV
- Classification of Non Living into Metals and Non Metals
- Examples, Properties, Uses and Importance
- HUMAN DEVELOPMENT
- Meaning of Puberty and Adolescence
- Puberty/Adolescent Changes – Physical, Social and Emotional Changes
- Personal Hygiene
Menstruation, Menstrual Cycle and Menstrual Hygiene – Myths and Facts about
Changes in Boys and Girls
V.Coping with concerns at Adolescence Pubertal Changes and Emotional Development
- FAMILY HEALTH – I
Define Sanitation and Explain its Importance and Methods used.
- – 8.FAMILY HEALTH – II
I.Define Nutrition
- Explain Balance Diet and Give Examples
- List the Classes of Food with Examples
IV. Plan an Adequate Diet for a Home.
- FAMILY HEALTH – III
I.Meaning of Drug, Drug and Substance Abuse, Addiction and Misuse
- Examples and Sources of Drugs
- Uses and Side Effects of Drugs
- REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
- Male Reproductive Organs – Internal and External
II.Functions and Cares of Male and Female Reproductive Organs
12. – 13. REVISION AND EXAMINATION
JSS 1 SECOND TERM BASIC SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK
- REVISION OF LAST TERM’S WORK
- Functions and Cares of Male and Female Reproductive Organs
- ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION – I
- Definition of Air, Soil and Water Pollution
- Causes of Air, Soil and Water Pollution, e.g. Domestic/industrial Waste, Fertilizer/ Insecticides
- Agricultural
- Non – biodegradable
- Oil Spillage
- ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION – II
- Consequences of Pollution such as Respiratory Tract Infection
- Water Borne Disease
- Destruction of Soil Organisms and Poor Plant Yield.
IV. Control Measures
- SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIs)
- Definition of STIs
- Transmission of STIs
- Signs and Symptoms of STIs
Effects of STIs, prevention of STI (Responsible Sexual Behavior, Avoid the Use of Unscreened Blood, Unsterilized Injection, Needles and Clippers)
- Behaviors that put People at Risk
VI. Finding help
- HIV/AIDS – I
- Difference between HIV/AIDS
- Mode of Transmission,
- Prevention of HIV
- Counseling and Testing
- Care and Support
- Myths and Facts about HIV/AIDS
7. – 8. ENERGY
- Meaning of Energy
- Sources of Energy
- Forms of Energy
IV. Transformation of Energy
- Uses of Energy
- RENEWABLE AND NON RENEWABLE ENERGY
- Uses and Misuse
IV. Describe how Energy Generation affects Quality of Life
- ENERGY AND SOCIETY
I.Energy for Working and Operating Appliances, Seeing, Walking, Playing, Cooking, etc.
- Energy from Hydro – Electricity for Electric Supply
- Solar Energy Generates
- Light Energy for Photosynthesis
- – 12.REVISION AND EXAMINATION
JSS 1 THIRD TERM BASIC SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK
- REVISION OFLAST TERM’S WORK
HUMAN REPRODUCTION – I
- Meaning of Menstruation, Menstrual Hygiene, Cleanliness during Menstruation
- Ovulation, Signs of Ovulation and the difficulty in predicting the Ovulation Period
- Fertilization and Conception.
- HUMAN REPRODUCTION – II
- Explain pregnancy
- Symptoms of Pregnancy and where to get help
- Growth of the Foetus (Stages, from Growth to Birth)
- Meaning and Types of Forces
- Contact and Non – Contact Forces
- Magnetic and Gravitational Force
- CALCULATIONSOF GRAVITATIONAL FORCE
- Balance and Unbalanced Forces
- Friction – Uses, Advantages and Disadvantages
- SPACE TRAVEL
- Meaning and Purpose of Space Travel
- Benefits and Dangers of Space Travel
- GRAVITATION AND WEIGHTLESSNESS
- Explain Gravitation and Weightlessness
- Effects of Gravitation on Objects
- Demonstrate the Effect of gravitational Pull on Objects
- – 8.EARTH IN SPACE
- The Solar System (Identify the Components of the Solar System)
- Rotation and Revolution of the Earth and Moon
- Description of Eclipse and Seasons
- Meaning of Satellites
- Uses of Satellites – Communication, Photography, Mapping, Geographical Information System (GIS)
- CONSEQUENCES/IMPLICATION OF TEENAGE PREGNANCY
- Physical, Social and Emotional Implication.
- Effects of Drugs and Self Medication during Pregnancy.
- Effects of Drugs Abuse on Pregnancy
- Myths and Facts about Teenage Pregnancy
VI. Finding Help
11. – 12. REVISION AND EXAMINATION
Related posts:
- JSS 1 Yoruba Language Scheme of Work ( 1st, 2nd, 3rd Term)
- JSS 1 Mathematics Scheme of Work ( 1st, 2nd, 3rd Term)
- Ogun State Schools Calendar 2023/2024 | 1st, 2nd & 3rd Term
- WAEC EXTENDS 2023 GCE REGISTRATION DEADLINE
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
18 Biggest Advantages and Disadvantages of Space Exploration
President Donald Trump announced his desire in 2018 to create a sixth branch of the U.S. military that he colloquially called the Space Force. Although Congress has yet to act on this desire to take the armed forces beyond the atmosphere of our planet, in February 2019, Trump signed Space Policy Directive 4 to have these forces organize underneath the umbrella of the U.S. Air Force.
The directive formally allows the Air Force to organize, train, and equip a corps of military space personnel for actions that take place in space. “Today I’m thrilled to sign a new order taking the next step to create the United States Space Force,” Trump said during the signing ceremony. “It’s so important. When you look at defense, when you look at all of the other aspects of where the world will be some day. I mean, this is the beginning. This is a very important process.”
The initial version of the Space Force will be overseen by a civilian undersecretary and a four-star general serving as the Chief of Staff. Although this structure is not as ambitious as having a separate branch of the military, space exploration experts feel like this is a step in the right direction.
The pros and cons of exploring space are complex simply because we have limited knowledge of what lies beyond our solar system. There are still mysteries to discover about our own planet! These are the key points to consider when we begin to look at what life might look like in the vastness of space.
List of the Pros of Space Exploration
1. It is an opportunity which is available to anyone. If you have a telescope, then you have an opportunity to start exploring space. For more than 300 years, we have looked to the stars with this technology as a way to learn more about our planet and ourselves as a species. When the Hubble space telescope was launched in 1990, it gave us our first views without atmospheric interference on what the vastness of our universe was like.
With millions of images taken and tens of thousands of papers written based on the observations made from simple telescope technologies, we have learned more about the structure of our universe, its age, and the composition of our solar system in the last 20 years than our ancestors would have ever dreamed was possible.
2. It gives us an opportunity to foster genuine cooperation. Because we are a world of nation states, the investments that we make in space exploration tend to have a patriotic feeling to them. Some efforts in this scientific area are still nationally-based, but for most projects there is a spirit of cooperation between the countries of the world who have made this realm of science a top priority. We work together as the human race to operate the international space station, fund research projects, and look outward beyond the stars to see what is there. It is one of the few areas in our lives today where we set aside our boundaries to work together toward a common good.
3. It is an effort which requires us to become innovative. The 100-year Starship Program has the ultimate goal of creating a technology that will allow us to explore space. No idea is off-limits with this project. What we have found in our quest to achieve specific goals in this area of science is that there are numerous discoveries which become possible to improve our lives here at home. Everything from athletic shoes to water purification systems came about because of our push to look beyond our planet. By tackling the technological needs to stay safe in space, we can make life better for everyone down on our planet at the same time.
4. It is an opportunity to explore something new. Although there are still regions of our planet that we rarely study because of technology limitations, the vastness of the universe is a much more significant prize. Only the Voyager spacecraft have gone beyond the first boundaries of our solar system. The information they provide us nearly four decades after their launch continues to enlighten our knowledge of the universe. There are so many unanswered questions when we think about space, especially now that scientists can determine which stars have planets orbiting around them.
Is there life somewhere else in the universe? If so, would those beings look like us? There are numerous technological barriers we must cross before we could travel for long distances in the vacuum of space, but we are getting one step closer every day.
5. It creates numerous employment opportunities in a variety of fields. There are more than 18,000 people employed in the United States by NASA, along with countless contractors, freelancers, and specialists not counted in those figures. The private company SpaceX provides about 7,000 full-time high-skill positions that support the economy. Then there are the astronauts, engineers, and flight specialists who manage the actual mechanisms of space flight to consider.
Numerous indirect employment opportunities are possible because of our efforts at space exploration too. We need caterers, designers, nutritionists, personal trainers, astronomers, scientists, and many other positions to support these activities. Even though the budget for NASA is $21 billion for FY 2020, the economic returns can be five times greater because of these activities.
6. It allows us to understand our planet better. When we can observe the full scale of our planet from a high orbital position, then we can see changes that are not always possible from the ground. It gives us a way to track the changes to our environment, study ozone depletion, and measure the impacts of a warming planet. We can provide accurate prediction models for weather patterns, observe troop movements, and install safety equipment that guards against an attack. When we take full advantage of this benefit, it becomes possible to create a place in the universe that is healthier for many years to come.
7. It gives us a new perspective on our place in the universe. It took several centuries for the scientific world (back by religious zealots) to accept the fact that the Earth was not the center of the universe. When we saw that first picture from a distance of what our planet looks like from a distant point in our solar system, it became clear to see that a small, pale blue dot in the middle of the vastness of our universe puts our daily issues into a new perspective. Until we discover otherwise, this is the only home that we have. It is up to each of us to share resources, reduce conflict, and work toward a common good.
8. It allows us to identify potential dangers before they strike. The asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars is only one source for these deadly rocks in our solar system. There may even be threats that travel through the universe to interact with our region of space from time-to-time. It would only take one significant impact to change life on our planet forever, which is why space exploration makes threat identification a top priority. If we can locate and move threatening asteroids or comets before they threaten an impact, we could stop the apocalypse before it ever gets a chance to begin.
9. It would give us access to new minerals, precious metals, and other useful items. Thanks to the asteroids which occasionally make it to the surface of our planet, we know that many of them contain iron and carbon. We also know that there is nickel, cobalt, silicon, magnesium, calcium, and several other elements present. Some might have water or oxygen contained beneath their surface. There may even be gold, platinum, and other precious metals there. We might even discover something that we’ve never encountered before.
Space exploration gives us an opportunity to access new mineral resources, allowing for the privatization of this venture. It would also give us an opportunity to start building in space because the raw materials are easy to haul and transport.
10. It gives us an opportunity to see what lies beyond in the final frontier. Unless circumstances change somehow, there will come a point in time when our species will outgrow our planet. We must begin to look for colonization opportunities in our solar system and beyond to help support the future of our race. As our scientific and technological discoveries begin to open up opportunities to visit distant stars, we can start to discover even more mysteries that will help us to answer the meaningful questions in life.
11. It could change our approach to medicine. Discovering new organic elements in space could help us to discover cures for some of our worst diseases. We really don’t know what is possible in our universe beyond the scope of basic physics. There could be untold treasures just waiting beyond our solar system to discover. Although there is always an element of risk to any exploration venture, there are great rewards often waiting for those who embrace their courage to start pressing forward. At the rate of development that we’ve seen in the 21st century, we could be looking at a very different human race in our children’s lifetimes based on the possibilities of discovery.
List of the Cons of Space Exploration
1. It could cause us harm or provide harm to other species in space. We know from experience what happens when one group of humans comes into contact with another group after generations of isolation. The diseases that transferred back and forth between Europe and the New World devastated some cultures. There were times that smallpox would kill over 90% of the local population by itself. If we encounter life on a different planet (or if they visit us), the threat of disease transmission is real. Their viruses, bacteria, and potentially unknown invaders could do as much damage to us as we could to do them. First contact would be an exciting experience, but it could also be a deadly one even though no one has any ill intent toward the other.
2. It creates high-level pollution events. We must consume fossil fuels when we launch rockets into space, which means we’re creating a significant level of pollution every time we expend fuel for exploration purposes. Even on a light load, it costs about $300,000 to fuel a rocket. Larger models could hold a half-million gallons of fuel that would be used during an entire mission. That means we are creating roughly 4 million pounds of carbon pollution with every action that we take to reach space. Then we must find a way to place these fuels safely into orbit to make our exploration efforts useful, creating even further potential problems for our atmosphere.
3. It gives us more ways to be paranoid about what others are doing. There are only five treaties which currently govern how we operate in space. Our original goal as the human race was to make it so that no one could claim a territory in orbit or our solar system that could give one nation a distinctive advantage. The creation of a Space Force could work to upset the balance that we’ve worked to create for the last 50 years. We’re already using satellites to spy on one another, monitor communications networks, and potentially target cities with weapons.
This paranoia will only increase as we push further into the stars. The only real solution to this disadvantage is to start thinking of ourselves as a planetary nation instead of one that is built on nation-states alone.
4. It will create a large amount of garbage that we must manage. Did you know that NASA tracks over a half-million pieces of space junk that orbits our planet right now? Unless we physically remove these items in some way, this garbage will linger until it falls into our atmosphere to burn up. Every item we leave behind creates a future risk for someone else. If we are going to start exploring space, then we must begin to look at ways to clean up our act before we get going. It’s bad enough that we’ve polluted our oceans with microplastics. Should a spaceship encounter that debris, it could be a deadly experience.
5. it may cause our planet to face unknown perils. A common theme in many science-fiction novels, shows, and movies is the idea that an alien race is hostile towards us. It is widely believed that water may be one of the scarcest commodities in the universe, but here we are with a planet that is more than 70% water. If we start venturing out beyond our solar system, it is entirely possible that we could encounter a species who decides that our resources are ripe for the taking. We assume that an advanced culture who could invent real-time space travel would be peaceful, but there are no guarantees. Exploring space could become an invitation for interstellar war.
6. It will always entail risk. Human beings were not meant to be in the vacuum of space. We must wear extensive protective gear to survive those conditions. Even one small leak or crack in a helmet or suit would be enough to create an adverse health condition. This issue applies to the planetary environments which we know of right now as well. Then there are the health issues to consider when the human body experiences a lack of gravity for an extended time.
NASA studied identical twins Scott and Mark Kelly when Scott took a long trip to space. Scientists monitored their bodies to see how being in a weightless environment could change the physical chemistry of a person. They discovered that genomic instability occurs, including gene expression changes, and spending a year in that environment caused a thickening of the carotid artery, DNA damage, and reduced cognitive abilities.
7. It is expensive to start exploring space. Even though the budget for NASA has not changed that much in recent years, we are spending about $200 billion per decade on our current space exploration efforts. Privatization of the industry has helped to reduce some costs, especially as SpaceX continues to work on a recoverable rocket. When you add in the costs from other countries and their space programs, our planet spends about $60 billion per year on this effort. In comparison, the United Nations suggests that it would only take half of that amount to end global hunger permanently. Should exploring space be our top priority if we’re struggling to take care of ourselves here at home?
When we examine these space exploration pros and cons, there is a certain nobleness to the idea of seeking what lies beyond the next horizon. Our society was built on the desire to explore the planet where we live. Now our culture has the itch to start pushing beyond the next boundary. Whether that means we colonize the moon, establish a community on Mars, or push toward Alpha Centauri, there is something waiting to be discovered. We’re closer than ever before to finding out what that might be.
Lesson Notes By Weeks and Term - Junior Secondary School 1

Basic Science Lesson note for JS1(Basic 7) Third Term
Basic science lesson note, lesson note on science jss1 third term.
BASIC SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY (BST) – BASIC SCIENCE LESSON NOTES JUNIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL 1
SCHEME OF WORK BASIC SCIENCE 3RD TERM
WEEK TOPIC
- Revision of last term work; Human reproduction (I) – Menstruation, ovulation, fertilization
- Human reproduction (II) – Pregnancy (conception) – signs and symptoms of pregnancy; stages of growth of the fetus
- Force – meaning and types, contact and non-contact force, magnetic and gravitational force
- Calculation of gravitational force; Balanced and unbalanced forces; Friction – meaning, uses, advantages and disadvantages
- Space travel – meaning, purpose, benefits and dangers of space travel
Mid-term project
- Gravitation and weightlessness – meaning and effect
- Earth and space – solar system, rotation and revolution, eclipse and season
- Satellite – meaning and uses
- Consequences and implications of teenage pregnancy – physical, social and emotional implication, Effects of drugs, self-medication and drug abuse during pregnancy, causes and consequences of birth defects
Examination
HUMAN REPRODUCTION (I)
Menstruation, fertilization.
Menstruation is the monthly flow or discharge of blood from the vagina of a woman at child bearing age. It is also called period. The first occurrence of menstruation is called menarche.
The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age. The periods, however may occasionally start as young as eight years old and still be considered normal.
The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is on the average of 28days. Menstruation stops occurring at menopause, which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age.
This flow of blood usually lasts between 2 to 7 days but on the average it is 5days
During pregnancy and for some time after childbirth, menstruation does not occur; this state is known as amenorrhea .
Menstrual disorders and problems associated with menstruation
- Heavy period : This is when there is an unusual and excessive flow of blood. It can also cause an extension of the bleeding to seven days.
- The absence of menstrual periods : This condition involves an absence of menstruation for 3 months or longer in a sexually mature woman who is not pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Pain and discomfort : Just before and/ or during menstruation there can be that is severe enough to interfere with normal daily activities. Such pain is usually experienced in the abdominal region and lower back as well as abdominal bloating, breast tenderness, headache, sleep problem and mood swings.
- Bleeding between menstrual periods : (Such as abnormal uterine bleeding, spotting) can be the symptom of another medicalcondition, which can vary from minor to serious. Women who experience abnormal uterine bleeding should contact a health care provider.
MENSTRUAL HYGIENE
- Choose your method of sanitation : It is essential to choose one that has the lowest absorbency rate for your flow. Frequent switching between brands can make you uncomfortable.
- Change sanitary pad regularly : Menstrual blood, once it has left the body gets contaminated with the body’s innate organisms. Therefore, the standard time to change a sanitary pad is once every six hours.
- Wash yourself regularly : When you menstruate the blood tends to enter tiny spaces like the skin between your labia or crust around the opening of the vagina and you should always wash this excess blood away. This practice also tends to beat bad odor from the vagina region.so, it is important to wash your vagina and labia well before you change into a new pad. If you cannot wash yourself before you change make sure you wipe off the areas by using toilet papers or tissues
- Don’t use soap or vaginal hygiene product : The vagina has its own cleaning mechanism that works in a very fine balance of good and bad bacteria. Washing it with soap can kill the good bacteria making way for infections. So you can use soap on the external parts but do not use it inside your vagina or vulva.
- Use the right washing techniques always : Wash or clean the area in a motion i.e. from the vagina to the anus and never wash in the opposite direction. Washing in the opposite direction can cause bacteria from the anus to enter into the vagina and urethral opening leading to infection.
- Discard your used sanitary products properly : It is essential to discard your used napkins or sanitary pads properly because they are capable of spreading infections. Wrap it very well before discarding it. It is also important that you wash your hand very well after discarding your used napkins.
- Beware of a pad rash : A pad rash is something that you might experience during the period of heavy flow.it usually occurs when the pad has been wet for a long time and rubs along the thighs causing it to chaff.to prevents this from occurring try to stay dry during your periods.
- Use only one method of sanitation at a time : Some women who have heavy flow during their periods may use several pads at a time this practice is bad because the two pads absorbs the blood and you don’t see that they are completely used up, so you are unlikely to change at regular and healthy interval. This can lead to rashes and infections.
- Have a bath regularly : Having a bath is the best thing you can do for your body during your periods. Bathing not only cleanses your body but also gives you a chance to clean your private part very well.it also helps to relieve menstrual cramps, backaches and makes you feel much better at the end of it.
- Be ready or always prepared during your periods : When you have your periods, it is important to be ready by making arrangement for extra cleaning and sanitary materials. Make sure you store them properly so that they don’t get contaminated
Ovulation is the part of the female menstrual cycle whereby a mature ovarian follicle discharges an egg (also known as an ovum, oocyte or female gamete). It is during this process that the egg travels down the fallopian tube where it may be fertilized by a sperm. The process of ovulation usually occurs between the 10 th and 19 th day into the menstrual cycle and this is the time when humans are most fertile.
Ovulation typically stops at menopause.
Note: that once a female child starts menstruating, ovulation automatically begins which means such a female child can get pregnant if there is sexual intercourse.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF OVULATION
- Change in cervical fluid or mucus : Cervical fluid or mucus that resembles” egg white “is the sign that you are near ovulation or you are ovulating. Ovulation takes place on the day a woman has the most amount of wet fluid or mucus.
- Change in basal body temperature : An increase in basal body temperature is a sign that ovulation, the cervix will be soft, high, open and wet.
- Breast tenderness and sensitivity : During ovulation the breast becomes tender and sensitive.
- Increase libido or sexual urge : During ovulation there is an increase in sexual urge in women
- Increase in the sense of vision, smell and taste : During ovulation there is an increase in the sense of vision, smell and taste
This is the fusion of the male gamete (i.e. the sperm) and the female gamete (.i.e. the ovum) to form a zygote. It occurs in the fallopian tube of the female. After fertilization the zygote grows and develops to form the young one. The process of fertilization always results to pregnancy
CLASSWORK 1
- What is ovulation?
- State 4 ovulation sign
- Define menstruation?
ASSIGNMENT 1
- An increase in basal body temperature is one of the signs and symptoms of (a) menopause (b) pregnancy (c) growth (d) puberty
- The vagina should be washed always with soap in other to make it healthy (a) true (b) false (c) maybe (d) partly correct
- The fusion of the male and female gamete to form a zygote is known as (a) conception (b) fertilization (c) menopause (d) menstruation
- Another word for menstruation is (a) period (b) pregnancy (c) fertilization (d) gamete
- Which of these statements is true of a female child who menstruates? (a) she can become pregnant (b) she will not be happy again (c) she is easily irritated with life (d) her level of assimilation decreases
- What is fertilization?
- Mention 4 signs to show that someone is pregnant
- Mention 3 menstrual disorder
HUMAN REPRODUCTION (II)
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy, stages of growth of the fetus, pregnancy (conception).
Conception is also known as pregnancy.it is the period between fertilization and the birth of the young one .In human, the period of pregnancy is about 9 months.
- Food aversions : If a woman is newly pregnant she may feel repelled by the smell of some food. She may also find that certain food she used to enjoy as suddenly completely repulsive to her.
- Mood swings : It is common to have mood swings during pregnancy due to the changes in the hormone in the body every woman respond differently to these changes.
- Abnormal bloating : Hormonal changes in early pregnancy may lead to the feeling of bloating that is similar to the feeling some women have just before their period
- Frequent urination : Shortly after a woman becomes pregnant, hormonal changes makes a chain of events that raises the rate of blood flow through the kidneys this cause your bladder to fill more quickly so you need to pee more often
- Fatigue : Pregnant women tend to always feel tired and exhausted during pregnancy and this leads to sleepiness and sluggishness
- Sore breast : The breast becomes swollen and sensitive during pregnancy due to its rising levels of hormones in their body
- Missed period : If a woman missed her period, it is an indication that she is pregnant. Although it is possible to still experience the monthly menstrual period even when a woman is pregnant
- High basal body temperature : If you have been charting your basal body temperature and you see that your body temperature has stayed elevated for 18days in a roll it is an indication that you are probably pregnant.
CARE NEEDED DURING PREGNANCY
- Get pregnancy test as soon as you miss your period
- Talk with your partner and someone else you trust
- Begin antenatal care check-ups with a medical doctor
- Follow proper antenatal care instructions which include avoiding all drugs and medicine not prescribed by a medical doctor
- Eat nourishing foods rich in protein, calcium folic acid, iodine and iron and drink plenty of water and fruit juices
- Get adequate rest and relaxation
- Do not smoke cigarettes or take alcohol
MYTHS AND FACTS ABOUT PREGNANCY
A myth refers to something that many people believe but that does not exist in the reality. It is false. On the other hand, a fact is something that is known to be true, especially that can be proved. There are myths and facts about pregnancy especially in the African traditional set up.
MYTHS ABOUT PREGNANCY
- Only pregnancy can make a woman miss her monthly period
- All pregnant women vomit
- Pregnancy makes you unclean before God
- All pregnant women have morning sickness
- Pregnant women should not dye their hair
- Pregnant women shouldn’t eat fish
- I can’t get pregnant if I have my period
- I can’t get pregnant the first time I have sex
- If I wash out my vagina after sex I won’t get pregnant
- Pregnant women should not take baths
FACTS ABOUT PREGNANCY
- Pregnant women should not carry heavy objects
- Some women may experience some bleeding and yet be pregnant
- Pregnant women should not change cat litter
- Pregnant women should not drink alcohol
- You can be pregnant for over a year
Each month a group of eggs (called oocytes) is recruited from the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Normally, one follicle in the group is selected to complete maturation. This dominant follicle suppresses all the other follicles in the group, which stop growing and degenerate.
The mature follicle opens and releases the egg from the ovary (ovulation). Ovulation generally occurs about two weeks before a woman’s next menstrual period begins. After ovulation, the ruptured follicle develops into a structure called the corpus lustrum, which secretes progesterone and estrogen. The progesterone helps prepare the endometrium (lining of the uterus) for the embryo to implant.
On average, fertilization occurs about two weeks after your last menstrual period. When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating around it to prevent other sperm from entering. At the moment of fertilization, a baby’s genetic make-up is complete, including its sex.
If a Y sperm fertilizes the egg, the baby will be a boy; if an X sperm fertilizes the egg, and the baby will be a girl.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone present in your blood from the time of conception. It is produced by cells that form the placenta and is the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. However, it usually takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins dividing rapidly into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days. The fertilized egg (called a blastocyst) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus where its next job is to attach to the endometrium (a process called implantation). Before this happens, the blastocyst breaks out of its protective covering. When the blastocyst establishes contact with the endometrium, an exchange of hormones helps the blastocyst attach. The endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix is sealed by a plug of mucus.
Within three weeks, the blastocyst cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo, and the baby’s first nerve cells have already formed. Your developing baby is called an embryo from the moment of conception to the eighth week of pregnancy. After the eighth week and until the moment of birth, the developing baby is called a fetus.

The development stages of pregnancy are called trimesters or three-month periods, because of the distinct changes that occur in each stage.
STAGES OF GROWTH: MONTH BY MONTH
As the fertilized egg grows, a water-tight sac forms around it gradually; filling it with fluid. This is called the amniotic sac, and it helps cushion the growing embryo.
The placenta also develops. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers nutrients from the mother to the baby, and transfers wastes from the baby.
A primitive face will take form with large dark circles for eyes. The mouth, lower jaw, and throat are developing. Blood cells are taking shape, and circulation will begin. The tiny “heart” tube will be at 65 times a minute by the end of the fourth week. By the end of the first month, the baby is about 1/4 inch long – smaller than a grain of rice!
The baby’s facial features continue to develop. Each ear begins as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds that eventually grow into arms and legs are forming. Fingers, toes and eyes are also forming. The neural tube (brain, spinal cord and other neural tissue of the central nervous system) is well formed. The digestive tract and sensory organs begin to develop. Bone starts to replace cartilage.
The head is large in proportion to the rest of the baby’s body. By the end of the second month, your baby is about 1 inch long and weighs about 1/30 of an ounce. At about 6 weeks, your baby’s heart beat can usually be detected. After the 8th week, your baby is called a fetus instead of an embryo.
The baby’s arms, hands, fingers, feet, and toes are fully formed. The baby can open and close its fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails are beginning to develop and the external ears are formed. The beginnings of teeth are forming. The baby’s reproductive organs also develop, but the baby’s gender is difficult to distinguish on ultrasound.
By the end of the third month, your baby is fully formed. All the organs and extremities are present and will continue to mature in order to become functional. The circulatory and urinary systems are working and the liver produces bile. At the end of the third month, your baby is about 4 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce. Since the baby’s most critical development has taken place, the chance of miscarriage drops considerably after three months.
The baby’s heartbeat may now be audible through an instrument called a Doppler. The fingers and toes are well-defined. Eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails, and hair are formed. Teeth and bones become denser. The baby can even suck his or her thumb, yawn, stretch, and make faces.
The nervous system is starting to function. The reproductive organs and genitalia are now fully developed, and the doctor can see on ultrasound if the baby is a boy or a girl. By the end of the fourth month, the baby is about 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces.
One may begin to feel the baby move, since he or she is developing muscles and exercising them. This first movement is called quickening .
Hair begins to grow on the baby’s head. The baby’s shoulders, back, and temples are covered by a soft fine hair called lanugo . This hair protects the baby and is usually shed at the end of the baby’s first week of life. The baby’s skin is covered with a whitish coating called vernix caseosa. This “cheesy” substance is thought to protect baby’s skin from the long exposure to the amniotic fluid. This coating is shed just before birth. By the end of the fifth month, the baby is about 10 inches long and weighs from 1/2 to 1 pound.
The baby’s skin is reddish in color, wrinkled, and veins are visible through the baby’s translucent skin. Baby’s finger and toe prints are visible. The eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
Baby responds to sounds by moving or increasing the pulse. One may notice jerking motions if baby hiccups. If born prematurely, the baby may survive after the 23rd week with intensive care. By the end of the sixth month, the baby is about 12 inches long and weighs about 2 pounds.
The baby will continue to mature and develop reserves of body fat. The baby’s hearing is fully developed. He or she changes position frequently and responds to stimuli, including sound, pain, and light. The amniotic fluid begins to diminish.
At the end of the seventh month, the baby is about 14 inches long and weighs from 2 to 4 pounds. If born prematurely, the baby would be likely to survive after the seventh month.
The baby will continue to mature and develop reserves of body fat. One may notice that the baby is kicking more. Baby’s brain is developing rapidly at this time, and the baby can see and hear.
Most internal systems are well developed, but the lungs may still be immature. The baby is about 18 inches long and weighs as much as 5 pounds.
The baby continues to grow and mature: the lungs are nearly fully developed.The baby’s reflexes are coordinated so he or she can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light, and touch. Baby is definitely ready to enter the world!
One may notice that the baby moves less due to tight space. The baby’s position changes to prepare itself for labor and delivery. The baby drops down in the pelvis. Usually, the baby’s head is down toward the birth canal. The baby is about 18 to 20 inches long and weighs about 7 pounds.
CLASSWORK 2
- What is pregnancy?
- Give four facts about pregnancy
ASSIGNMENT 2
SECTION A
- The following are not symptoms of pregnancy in human except (a) fighting (b) fatigue (c) crying (d) walking
- The ideal pregnancy duration in human is (a) 6 months (b) 7 months (c) 8 months (d) 9 months
- The fluid that cushions the growing embryo is called (a) water (b) mineral (c) amniotic fluid (d) baby fluid
- Pregnancy can be detected with any of these symptoms except (a) nausea (b) fatigue (c) food aversion (d) menstruation
- Carefully state the difference between fertilization and conception
- Mention any four signs and symptoms of pregnancy
- Mention three ways of detecting pregnancy
Types of Force
Contact and non-contact force, magnetic and gravitational force, meaning of force.
A force can be defined as any action that makes or tries to move, stop or alter the speed of a body in a given direction. Force can also be said to mean a push or a pull. The unit of force is Newton (N). Force is given by the formula:
Force (F) = Mass (m) x Acceleration (a)
There are two types of force namely:
- Contact force
- Non-contact
- CONTACT FORCES: These are forces which sources are in contact with the body to which they are applied. The contact forces could be direct or indirect. Examples of contact forces are: push, pull, tension, friction, upthrust
- NON- CONTACT FORCES: These are forces which the sources do not require contact with the body they are applied. These forces act through a region in space called field. They are therefore also called force fields . Examples include magnetic force, gravitational force and electric force
- MAGNETIC FORCE: In a bar magnetic, there is North Pole end south pole end. The like poles repel each other while unlike poles attract each other .
Magnets can attract other magnets, iron fillings or any other metallic materials. This phenomenon show that a magnetic force acts over an area around the magnet. Thus a magnetic force is called a field force which acts over an area.
- GRAVITATIONAL FORCE: The force which the earth attracts all objects to itself is called the force of gravity or gravitational force . This is the reason why objects above the earth fall down to the earth.
- ELECTRIC FORCE: Electric force field exists between two electric charges. Unlike charges attract each other while like charges repel each other .
CLASSWORK 3
- What is force? Give the SI unit
- State two contact force
ASSIGNMENT 3
- The correct SI unit of force is (a) Joules (b) Watt (c) Newton (d) Metre
- Which of the following statement is false(a) a force changes the shape of a body (b) forces may be balanced or unbalanced (c) a force cannot change the direction of a moving body (d) a force changes the speed of object
- The gravitational force can be found (a) on the earth (b) in the moon (c) around the planets (d) in the galaxy
- The magnetic force is also known as _________(a) pulse ( b) electrical (c) field force (d) gravitational force
- Which of the following is a type of force (a) electrical (b) heat (c) rotating (d) reversible
- Mention three non-contact force that you know
- State two importance of force
- State the difference between contact and non-contact force
CALCULATION OF GRAVITATIONAL FORCE
Calculation of gravitational force
Balanced and unbalanced forces
- Frictional force
Uses/Advantages
Disadvantages, calculation of work done against gravity.
Suppose you lift an object of mass 1kg from the ground to a height of 1m, the work done in lifting the abject is calculated by using the formula; Mgh
Mgh = 1 x 1 x 9.8 joules (g = 9.8m/s 2 )
Joule is the unit of work done.
When an object is stationary, the forces acting on it are balanced forces. The sum of such forces acting on the body is zero and they act in opposite direction.
When an object is in motion (moving), the forces acting on it are unbalanced. The sum of such forces is not zero. Such forces are either acting in it are direction or the same direction but are not equal in value. Unbalance forces cause a body to accelerate.
GENERAL EFFECT OF A FORCE
- A force causes motion of an object
- A force causes moving object to come to rest (stop)
- A force changes the speed of a body in motion
- A force causes changes in the direction of motion.
The S.I unit of force is the Newton, N. The force acting on an accelerating body of mass, m, is given by,
F = ma
Force acts in a specific direction. The direction of the action of a force is usually indicated by an arrow, or depending on the direction
Friction force
Frictional force is the force that act between the surfaces of solid objects and tends to oppose their motion over each other
- It helps in walking
- It helps in carrying objects
- It helps in grinding
- It makes nails stay on the wall
- Car brakes work by friction
- It causes wear and tear of machine parts of machine
- It causes loss of energy
- It produces unpleasant noise
- It makes machine hot and inefficient
METHODS OF REDUCING FRICTION
- By lubricating surfaces with oil or grease
- Use of the ball bearing
CLASSWORK 4
- Define frictional force?
- Enumerate two advantages of friction
- Highlight two disadvantages of friction
ASSIGNMENT 4
- Which of the following forces requires contact for its action (a) gravitational force (b) frictional force (c) magnetic forces (d) electrical force
- The sum of balanced forces is (a) zero (b) greater than zero (c) less than zero (d) about one
- The S.I unit of force is (a) Kilogram (b) Watt (c) Newton (d) Power
- All of the following are correct except one (a) forces causes motion (b) forces cause change in the direction of motion (c) forces stops motion (d) force is always parallel
- One of the following force is non-contact force (a) electric force (b) push (c) tension (d) push
- Calculate the force acting on a body of mass 0.6kg (g=9.8ms -2 ; f=mg)
- What is the name of the instrument used to measure the weight of a body?
SPACE TRAVEL
Meaning of space travel, purpose of space travel, benefits of space travel, dangers of space travel.
Space travel is the act of going to the moon or planets or orbiting the earth in a special craft called spaceship. It is also the traveling to the outer space beyond the earth.
The space travelers are called ASTRONAUTS. On 21 st of July, 1969, Neil Armstrong, an American became the first human being to step into the moon. He was followed on the same day by another American named Edwin Aldrin. They stayed on the moon for 21 hours 36 minutes before they lifted up. The second moon landing took place in December 1972 when two Americans, Eugene Ceman and Harrison Schmitt stayed a total of 74hours 59 minutes on the moon surface. These astronauts wore special protective uniforms with oxygen masks for breathing.
Most experiments in space are currently carried out in space station or space lab. These space stations are very large space rockets which can accommodate many people and are equipped to perform scientific experiments. Astronauts who work on these space stations usually stay for period of six months to one year after which they are replaced by other astronauts.
Spaceship is moved by rockets. After leaving the earth’s atmosphere, gravity no longer pulls the spaceship to the earth. The astronauts wear special dress called suits and it help them to maintain the earths atmospheric pressure around there body throughout in space
DEFINITION OF SPACE AND THE REGION’S OUTSIDE THE EARTH’S SURFACE
Space refers to the region of our environment outside the earth’s crust. There are three important regions outside the earth’s surface. These are:
- The troposphere : It starts from the surface of the earth and extends to a height of about 16,000 meters. Most of the air and water vapour in our environment are found in this region. As one goes up in the troposphere, the temperature falls and it therefore becomes cooler.
- The stratosphere : It is the region directly above the troposphere. The region contains very little air. The temperature of this region does not falls as one goes up in this region
- The ionosphere : It is the upper part of the atmosphere. It contains mainly charged particles. The ionosphere is very useful to man because it enables the reflection and transmission of radio wave and signals round the world.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE OUTER SPACE
- Light from the sun passes through the outer space.
- There is no force of gravity in the outer space
- The outer space is void or empty
- Sound does not pass through the outer space, therefore the outer space is always quite
- Outer space is very large and beyond our imagination.
- It helps to watch everything that is happening in the world on the television e.g. football game, basketball game etc. at the same time the events are being carried out
- Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space
- Space travel is because of man’s curiosity it is a desire to find out the nature of life in other planets.
- The need for more knowledge of the climate and vegetation of the earth is another reason for space travel.
- The landing of equipment called satellite in space has also led to the improvement in communication
- The main benefit is the collection of scientific information about the earth and the other planets
- Production of special computers
- Production of photographic equipment such as x-ray and gamma-ray
- Production of telecommunication equipment
- Production of remote sensing equipment to guide spacecraft e.g. rocket
- Production of rocket or aircraft fuels
Space travel is risky. If anything goes wrong, one or more lives will be lost.
The dangers of space travel can be caused by the following problems
- Explosion of rockets at the launch pad
- Failure of some necessary equipment in the spaceship to function well.
- Inability of the rocket to reach escape velocity
- Wrong calculation of angle, speed and time of launching
- Explosion of rockets in flight
PROBLEMS OF SPACE TRAVEL
- High speed : Astronauts have to be trained in order to adopt to the high speed of space travel, so that they can think and work normally while traveling in space.
- Complicated calculation : There are lot of calculations involved before a spaceship can be launched correctly at an angle, speed and time to arrive at its destination. This is because the earth, the moon and all the planets are always in rapid motion.
- Loss of weight : The force of gravity is not felt in space, therefore it is very difficult for astronauts to stand or walk as they do on earth.
- Lack of basic need of life : The basic needs of life such as water, oxygen, food etc. are not available in the space, therefore oxygen and water must be made available in the spaceship to last for the period of the trip in space.
- Escape velocity : Rockets require escape velocity to escape from the attraction of the earth or the force of gravity
- Force of gravity : The force of gravity makes it difficult for any spacecraft to escape the earth’s surface easily. It has to be at a very high speed before the spacecraft can be allowed to leave the earth’s surface.
CLASSWORK 5
- What is a space?
- Mention the three region of space
- State 5 dangers of space travel
ASSIGNMENT 5
- The first man to travel to the moon is ____ (a) Neil Armstrong (b) Sir Isaac Newton (c) Maxwell Planks (d) Sir Bobby Charlton
- Which of the following is not associated with space travel (a) Basic need of life (b) force of gravity (c) electricity (d) escape velocity
- The regions outside the earth are the following except (a) troposphere (b) stratosphere (c) talkosphere (d) ionosphere
- The escape velocity is used by rocket to _______(a) overcome the force of gravity (b) escape from danger (c) hide from enemies (d) speed faster and disappear
- Which of these is not characteristic of outer space? (a) no force of gravity (b) quiet (c) empty (d) very small
- What is space travel?
- Mention three purpose of space travel
- Define troposhere
MID TERM PROJECT
Using a WHITE CARDBOARD ONLY , draw and label the solar system
GRAVITATION AND WEIGHTLESSNESS
Gravitation.
Gravitation is a force that has effect on the stability of a body.
If an object is tossed up the air, it will full back to the ground because the earth exerts an attraction on it. This attraction is called gravitational attraction.
The gravitational attraction / force between any two object increases as the two objects approach each other.
The earth has a great gravitational full because it has a great mass. The gravitation pull of the earth is always directed to the center.
WEIGHTLESSNESS
Weightlessness is a feeling of being weightless. It does not mean having no weight. As someone move away from the surface of the progressively reduces. In the outer surface of the earth, a person or body has no weight because the gravitational pull of the earth is no longer acting there.

Effect of gravitation on objects
- Stability of the earth : Gravitation helps every object in the earth include man to remain stable
- Weight : The weight of an individual is a measure of the gravitational pull of the earth on that person
- Revolution of the moon round the earth : The moon is able to revolve round the earth because the gravitational pull of the earth attracts it
- Balance of planets in our solar system : The sun and all the planets in our solar system exercise gravitational pulls on one another and mutually balance on another in space
- Work is done against gravity in lifting an object form the earth : Lifting an object from the ground involves opposing gravitational pull, therefore work is done against gravitational attraction of the earth
CLASSWORK 6
- Define gravitational pull
- What is weightlessness?
- The earth’s gravitational pull on an object is represented by that object’s (a) weight (b) size (c) volume (d) materials
- The ability of an object to remain stable on earth is due to ______(a) gravitational pull (b) weightlessness (c) moon and earth sizes (d) its height
- Gravitational force is a force of (a) separation (b) attraction (c) friction (d) opposition
- The earth has a large gravitational pull on object because the earth (a) has plants and animals (b) is a planet (c) is large in size (d) revolves
- When a metal ball of 20kg and a wooden ball of 10kg are dropped from the some height(a) the metal ball reach the ground before wooden ball (b) both balls will reach the ground at the same time (c) the wooden ball falls faster than metal ball (d) the metal ball null full sideways
- Explain weightlessness
- State four effects of gravity on an object.
WEEKS SEVEN AND EIGHT
EARTH AND SPACE
Solar system, rotation and revolution.
The sun and all the bodies orbiting round it makes up the solar system . The planets and their moons are the main bodies that revolve round the sun.
Other bodies in the solar system are asteroids, comets, and meteoroids .
THE PLANETS
Nearest to the sun is mercury, the smallest of the planets. Then come Venus, Earth, Mass, Jupiter [the biggest planet], Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. The distance across the solar system is about 12000million kilometers.
Rotation : This is the movement of a planet about its axis. Rotation of the earth brings about night and day.
Revolution : This is movement of a planet round the sun in the solar system. The Earth revolves round the sun giving rise to seasons. The earth takes approximately 365 days to revolve round the sun.
The earth is the third planet from the sun and it is the only known planet in the universe that harbors living things. The earth contains water which in addition to the oxygen assists in supporting life on earth.
The earth does not produce light hence it is said to be non-luminous.
While those heavenly bodies that give out light, such as the stars and the sun are said to be luminous.
The earth has only one satellite called the moon. The moon revolves round the earth. The earth rotates about its axis giving rise to day and night.
The sun is the single biggest star in the universe that supplies all planets light and heat. The sun does not rotate. Earth revolves round the sun giving rise to seasons. The earth takes approximately 365 days to revolve round the sun. There is no water or atmosphere in the sun.
The moon is the only earth satellite that revolves round its axis. The moon gives a reflection of light from the sun and supplies the earth with moon light. The moon is non- luminous and has no life on it.
Eclipse is the full or partial blocking of light from one celestial body by another celestial body
Types of eclipse
- Eclipse of the sun: This occurs when the moon moves between the sun and the earth and all are exactly in a straight line. Eclipse of the moon: It occurs when the earth is between the sun and the moon and the three are exactly on a straight line.
NOTE : There is nothing like eclipse of the earth.
Climate and Seasons
Climate can be defined as the average weather condition of a particular area for a given period of time.
Seasons : The revolving of the earth about the sun gives rise to seasons.
Different parts of the surface of the earth have the sun shining on them at different times of the year.
There is a time when there are shorter days and longer nights during some months in a year, and also shorter nights and longer days during some other months.
There are also some months during which the days and nights are equal in duration. This happens because the earth moves in an orbit around the sun. The earth tilts in opposite direction twice a year, hence, giving rise to two seasons –Rainy and Dry seasons
CLASSWORK 7&8
- What is solar system?
- How many planets do we have? Mention them
- What is climate?
ASSIGNMENT 7&8
- The sun and all the bodies orbiting round it makes up the (a) solar system (b) galaxy (c) meteoroids (d) comets
- How many planets do we have (a) 1 (b) 5 (c) 9 (d) 12
- The third planet after the earth from the sun is (a) mass (b) mercury (c) Jupiter (d) Saturn
- The average weather condition of a particular area for a given period of time is (a) weather (b) season (c) climate (d) session
- Other bodies in the solar system include the following except(a) asteroid (b) comets (c) water (d) meteoroids
- The revolving of the earth about the sun gives rise to(a) day (b) night (c) seasons (d) sun
- Which of the following pairs are not both planets (a) Mercury and Saturn (b) Earth and Moon (c) Venus and Mars (d) Jupiter and Pluto
- Rotation of earth about its axis causes(a) climate (b) season (c) day and night (d) evening
- ………. is the full or partial blocking of light from one celestial body by another celestial body (a) rotation (b) revolution (c) eclipse (d) climate
- Which of the following is odd? (a) Mercury, Venus and Earth (b) Saturn, Uranus and Pluto (c) Earth, Mars and Jupiter (d) Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus
- Differentiate between climate and season?
Satellite is a body that orbits or moves round a planet e.g. the moon is a satellite of the earth.
Thus, the satellites or moons of the planet in our solar system are shown below
PLANET NO OF SATELLITE
Mercury None
Venus None
Earth 1
Mass 2
Jupiter 12
Saturn 9
Uranus 5
Neptune 2
Pluto None
NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL SATELLITES
The moons that orbit the planets in solar system are natural satellite while artificial satellite are moon made bodies, which were launched by various countries, and now orbiting the earth e.g.
COUNTRY YEAR OF FIRST LAUNCH FIRST SATELLITE
USSR 1957 Sputnik 1
USA 1958 Explorer 1
Australia 1964 Blue streak
France 1965 Asterix
Japan 1970 Osumi
China 1970 Dong fang hang 1
United Kingdom 1971 Prospero X-3
India 1979 Rohini 1
Israel 1988 Ofeg 1
Nigeria 2003 SAT 1
Types and Uses of satellite
- Bio satellites : These are used to carry living organism especially for scientific experimentation
- Observation satellites : They are used for geographical studies, photographing of areas, map marking
- Weather satellites : These are used to monitor the weather conditions in the atmosphere and supply the information to ground stations
- Communication satellites : They are designed purposely to send information quickly from one place to another
- Reconnaissance satellites : They are used for military or intelligence purposes, such as observing enemy location or troop movements
- Space station satellites : They are designed for human being to live on in outer space. They are only designed for periods of weeks, months or years
- Navigational satellites : These used radio time signals, it enable mobile receivers on the ground to determine their exact location
CLASSWORK 9
- Give the number of satellite for the following planets (i) Neptune (ii) Jupiter (iii) Uranus
ASSIGNMENT 9
- The heavenly body that moves round the planet is called (a) earth (b) sun (c) satellite (d) stars
- Identify the planet with the least number of satellite in the following (a) earth (b) Saturn (c) Venus (d) Jupiter
- The following are examples of planet except ______ (a) moon (b) earth (c) mass (d) Jupiter
- Which of these satellites is for monitoring the dry and wet season of a particular area? (a) astronomical satellite (b) weather satellite (c) bio satellites (d) communication satellite
- Which of the following is not a use of satellite? (a) communication (b) photograph (c) weather monitoring (d) driving
- Highlight three uses of satellites
- Briefly explain the effect of artificial satellites in improving the world
Meaning of teenage pregnancy
Causes of teenage pregnancy, consequences and implications of teenage pregnancy.
- Physical, social and emotional implication
- Effects of drugs, self-medication and drug abuse during pregnancy
Causes and consequences of birth defects
Teenage pregnancy is defined as a pregnancy in a young woman who has not reached her 20 th birthday when the pregnancy ends, regardless of whether the woman is married or is legally an adult. Worldwide, rates of teenage pregnancy range from 143 per 1000 in some sub-Saharan African countries to 2.9 per 1000 in South Korea.
Pregnant teenagers face many of the obstetrics issues as women in their 20s and 30s. However, there are additional medical concerns for mothers age 14 or younger, especially if they live in a developing country. For mothers between 15 and 19, risks are associated more with socio-economic factors than with the biological effects of age.
There are many factors that cause teenage pregnancy. These include:
- Social belief : In some societies, early marriage and traditional gender roles are important factors in the rate of teenage pregnancy. For example, in some Sub- Saharan African countries, early marriage is often seen as a blessing because it is a proof of the young woman’s fertility. In the Indian sub-continent, early marriage and pregnancy is more common in traditional rural communities compared to the rate in cities.
- Lack of sexuality education : The lack of education on safe sex, whether it is from parents, school or otherwise is a cause of teenage pregnancy. Many teenagers are not taught about methods of birth control and how to deal with peers who pressure them into having sex before they are ready.
- Lack of use of contraceptive methods : The use of a method with a high failure rate is a factor in teenage pregnancy
- Use of drugs and alcohol : Inability to reduce drugs and alcohol may possibly encourage unintended sexual activity. Teenagers who engage in drug use are more likely to engage in sex. The drugs with the strongest evidence linking to teenage pregnancy are cannabis, alcohol and amphetamines including “ecstasy”
- Poverty : Poverty is associated with increased rates of teenage pregnancy. Economically, poor countries have far more teenage mothers compared with economically rich countries.
Adolescent pregnancy refers to pregnancy in a girl between the ages of 10 to 19. Adolescent pregnancy is usually unwanted and unintended. It can be dangerous for both the mother and the unborn child.
The consequences of adolescent pregnancy and delivery include the following:
- It can lead to induced hypertension which can cause heart failure and death of both the mother and the child
- It can also lead to premature labour and spontaneous abortion
- Health risks include infection, incomplete abortion, injuries to genital organs etc.
- Termination of education
- Life plans and career goals are disrupted
- Feeling of loss of childhood and adapting to adulthood
- Forced marriage
IMPLICATIONS OF TEENAGE PREGNANCY
Teenage pregnancy is usually unintended and unwanted. It can be dangerous both to the mother and the unborn child. The implication of teenage pregnancy can be categorized into four. These are:
- Health implication
- Unsafe abortion
- Social economic implication
- Emotional implication
1. Health implication: Teenage pregnancy could result in a lot of health risks. Some of these include:
i. Pregnancy induced hypertension, which can cause heart failure and death of both the mother and child
ii. Premature labour or spontaneous abortion
iii. Iron deficiency anemia which reduces the chances of surviving and excessive bleeding
iv. Incomplete abortions
v. Infections and injuries to genital organs
2. Unsafe abortion: Adolescents are the most likely to seek abortions from untrained and unqualified health care providers. They may also attempt induced abortion. Unsafe abortion can also lead to a number of health risks and loss of life
3. Socio-economic implications: These include the following:
i. Termination of education
ii. Disruption of life plan and career goals
iii. Early and forced marriage due to pregnancy
iv. Stigmatization and isolation from peers
v. low self esteem
vi. Few job opportunities, low income and poverty
4. Emotional or psychological implication : Some of these are:
i. loneliness and depression
ii. Feeling of guilt and fear
iii. Feelings of insecurity
iv. Emotional or psychological imbalance as a result of loss of childhood and adapting to adulthood
A birth defect is a problem that occurs when a baby is developing in the uterus (womb). Birth defects can be minor or severe.
The causes of birth defect include the following:
- Genetics: These are abnormalities transferred by parents to their children. Genetic birth defects happen at conception and often cannot be prevented
- Non genetic: These are caused by harmful habits or dangerous exposures of the pregnant mothers. Some of these habits or dangerous exposures are:
- Using illegal drugs
- Taking alcohol
- Exposure to toxic chemicals
- Untreated bacterial or viral infections
The most common types of functional or developmental birth defects include:
- Down syndrome – causes delay in physical and mental development
- Sickle cell disease
- Cystic fibrosis – this damage the lungs and the digestive system
CLASSWORK 10
- Explain “teenage pregnancy” in your understanding
- Enumerate four major causes of teenage pregnancy
ASSIGNMENT 10
- The following factors EXCEPT ONE can lead to teenage pregnancy (a) social belief (b) ignorance of sexuality (c) social problem (d) rapid progress
- Which of the following is the consequence of adolescent pregnancy? (a) Sexual pleasure (b) termination of education (c) happy marriage (d) proper education
- The following will not cause of birth defect except (a) smoking (b) illegal drugs (c) balanced diet (d) bacterial infection
- Teenage pregnancy should be discouraged in the twenty first century (a) true (b) false (c) disagree (d) maybe
- Pregnancy by human female under the age of twenty is called ____(a) child pregnancy (b) female pregnancy (c) under age pregnancy (d) teenage pregnancy
- Give three implications of teenage pregnancy
- Enumerate three causes of teenage pregnancy
WEEK ELEVEN
WEEK TWELVE
Literature in English Lesson note SS2 Third Term
Third term scheme of work for agric science jss 2 (basic 8), lesson note on basic technology jss 3 second term, first term scheme of work for christian religious studies ss1.

Lesson Note on English…

Mathematics Lesson Note JSS1…
Second term scheme of….

Toddler Scheme of Work…
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Privacy Overview
Earth in Space
Back to: BASIC SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY JSS 1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about the earth in space. Enjoy the class!

The solar system
The planet earth, on which we live, is moving through space all the time. It is going around the sun. In doing this it carries us all through space. The earth travels through space but we do not realize this because the air around the earth is carried along with it. The sun together with all the bodies which revolves around it makes up the solar system.
The solar system consists of the sun, nine planets and their moons along with dwarf planets, comets and asteroids, which revolve around the sun. The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, the dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies.
The solar system is divided into inner and outer parts. The inner part contains the Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars while the outer part contains Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The two parts are demarcated by the asteroid belt.
The nine planet
The Sun is, at present, about 70% hydrogen and 28% helium by mass, everything else (“metals”) amounts to less than 2%. This changes slowly over time as the Sun converts hydrogen to helium in its core. The Sun’s magnetic field is very strong (by terrestrial standards) and very complicated. Its magnetosphere (also known as the heliosphere) extends well beyond Pluto.
The Sun is the heart of our solar system and its gravity is what keeps every planet and particle in orbit. This yellow dwarf star is just one of the billions like it across the Milky Way galaxy. Our Sun is a normal main-sequence G2 star, one of more than 100 billion stars in our galaxy.
The planet closest to the Sun, Mercury is the smallest and fastest planet in the solar system; whipping around the Sun every 88 Earth days. Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun but, perhaps surprisingly, it does not have the highest temperatures.
It is the second planet from the Sun and the sixth-largest. Together with Mercury, they are the only planets without a satellite, even though Mercury is closer to the sun, Venus is the hottest planet.
The place we call home, Earth is the third rock from the sun and the only planet with known life on it, and lots of it too! Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the fifth largest planet in the Solar System with the highest density. It is currently the only known location where life is present.
It is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet with a thin atmosphere, having the surface features reminiscent both of the impact craters of the Moon, and the valleys, deserts and polar ice caps of Earth. It is the most widely searched planet for life.
It is named after the principal Roman god, the equivalent of the Greek god Zeus. Jupiter is one of the five visible planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Saturn), being the fifth most distant from the Sun at an average distance of 5.2 AU, its closest approach is at 4.9 AU and at its farthest 5.4 AU.
It is the sixth planet from the sun, with the largest planetary rings in the Solar System. It is the second-largest planet after Jupiter, and recently, with many other moons being discovered, it surpassed the number of Jupiter’s moons and is now considered the planet with the most numerous satellites.
It is the seventh planet from the Sun, around 1.8 billion miles or 2.9 billion kilometres distance away. … Venus also does this but Uranus is the only known planet to rotate on its side. It takes Uranus 84 years to complete an orbit of the Sun, the longest from all the planets in the solar system.
It is the fourth largest and the farthest planet of the Solar System with the most powerful wind speeds out of all the planets. It is the smallest of the gas giants and is the first planet to be discovered by mathematical predictions in 1846.
It is the smallest planet and the farthest planet from the sun.
In our next class, we will be talking more about the Earth in Space . We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
Share this lesson with your friend!
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
1 thought on “Earth in Space”
How come Uranus is the slowest when Neptune and Pluto are farther
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
ClassNotes.ng is an Afrilearn brand.
- 08051544949
- [email protected]
- Teach for CN
- Testimonials
- Terms of use
- Privacy Policy
Weekly Newsletter
WhatsApp us
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Everything you need to know about space travel (almost)
We're a long way from home...
Paul Parsons
When did we first start exploring space?
The first human-made object to go into space was a German V2 missile , launched on a test flight in 1942. Although uncrewed, it reached an altitude of 189km (117 miles).
Former Nazi rocket scientists were later recruited by both America and Russia (often at gunpoint in the latter case), where they were instrumental in developing Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) – rockets capable of carrying nuclear weapons from one side of the planet to the other.

It was these super-missiles that formed the basis for the space programmes of both post-war superpowers. As it happened, Russia was the first to reach Earth orbit, when it launched the uncrewed Sputnik 1 in October 1957, followed a month later by Sputnik 2, carrying the dog Laika – the first live animal in space.
The USA sent its first uncrewed satellite, Explorer 1, into orbit soon after, in January 1958. A slew of robotic spaceflights followed, from both sides of the Atlantic, before Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin piloted Vostok 1 into orbit on 12 April 1961, to become the first human being in space . And from there the space race proper began, culminating in Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin becoming the first people to walk on the Moon as part of NASA's Apollo programme .
Why is space travel important?
Space exploration is the future. It satisfies the human urge to explore and to travel, and in the years and decades to come it could even provide our species with new places to call home – especially relevant now, as Earth becomes increasingly crowded .
Extending our reach into space is also necessary for the advancement of science. Space telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope and probes to the distant worlds of the Solar System are continually updating, and occasionally revolutionising, our understanding of astronomy and physics.
- Subscribe to the Science Focus Podcast on these services: Acast , iTunes , Stitcher , RSS , Overcast
But there are also some very practical reasons, such as mining asteroids for materials that are extremely rare here on Earth.
One example is the huge reserve of the chemical isotope helium-3 thought to be locked away in the soil on the surface of the Moon . This isotope is a potential fuel for future nuclear fusion reactors – power stations that tap into the same source of energy as the Sun. Unlike other fusion fuels, helium-3 gives off no hard-to-contain and deadly neutron radiation.
However, for this to happen the first challenge to overcome is how to build a base on the Moon. In 2019, China's Chang’e 4 mission marked the beginning of a new space race to conquer the Moon, signalling their intent to build a permanent lunar base , while the NASA Artemis mission plans to build a space station, called Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway , providing a platform to ferry astronauts to the Moon's surface.
Could humans travel into interstellar space and how would we get there?
It’s entirely feasible that human explorers will visit the furthest reaches of our Solar System. The stars, however, are another matter. Interstellar space is so vast that it takes light – the fastest thing we know of in the Universe – years, centuries and millennia to traverse it. Faster-than-light travel may be possible one day, but is unlikely to become a reality in our lifetimes.
It’s not impossible that humans might one day cross this cosmic gulf, though it won’t be easy. The combustion-powered rocket engines of today certainly aren’t up to the job – they just don’t use fuel efficiently enough. Instead, interstellar spacecraft may create a rocket-like propulsion jet using electric and magnetic fields. This so-called ‘ ion drive ’ technology has already been tested aboard uncrewed Solar System probes.

Another possibility is to push spacecraft off towards the stars using the light from a high-powered laser . A consortium of scientists calling themselves Breakthrough Starshot is already planning to send a flotilla of tiny robotic probes to our nearest star, Proxima Centauri, using just this method.
Though whether human astronauts could survive such punishing acceleration, or the decades-long journey through deep space, remains to be seen.
How do we benefit from space exploration?
Pushing forward the frontiers of science is the stated goal of many space missions . But even the development of space travel technology itself can lead to unintended yet beneficial ‘spin-off’ technologies with some very down-to-earth applications.
Notable spin-offs from the US space programme, NASA, include memory foam mattresses, artificial hearts, and the lubricant spray WD-40. Doubtless, there are many more to come.
Read more about space exploration:
- The next giant leaps: The UK missions getting us to the Moon
- Move over, Mars: why we should look further afield for future human colonies
- Everything you need to know about the Voyager mission
- 6 out-of-this-world experiments recreating space on Earth
Space exploration also instils a sense of wonder, it reminds us that there are issues beyond our humdrum planet and its petty squabbles, and without doubt it helps to inspire each new generation of young scientists. It’s also an insurance policy. We’re now all too aware that global calamities can and do happen – for instance, climate change and the giant asteroid that smashed into the Earth 65 million years ago, leading to the total extinction of the dinosaurs .
The lesson for the human species is that we keep all our eggs in one basket at our peril. On the other hand, a healthy space programme, and the means to travel to other worlds, gives us an out.
Is space travel dangerous?
In short, yes – very. Reaching orbit means accelerating up to around 28,000kph (17,000mph, or 22 times the speed of sound ). If anything goes wrong at that speed, it’s seldom good news.
Then there’s the growing cloud of space junk to contend with in Earth's orbit – defunct satellites, discarded rocket stages and other detritus – all moving just as fast. A five-gram bolt hitting at orbital speed packs as much energy as a 200kg weight dropped from the top of an 18-storey building.

And getting to space is just the start of the danger. The principal hazard once there is cancer-producing radiation – the typical dose from one day in space is equivalent to what you’d receive over an entire year back on Earth, thanks to the planet’s atmosphere and protective magnetic field.
Add to that the icy cold airless vacuum , the need to bring all your own food and water, plus the effects of long-duration weightlessness on bone density, the brain and muscular condition – including that of the heart – and it soon becomes clear that venturing into space really isn’t for the faint-hearted.
When will space travel be available to everyone?
It’s already happening – that is, assuming your pockets are deep enough. The first self-funded ‘space tourist’ was US businessman Dennis Tito, who in 2001 spent a week aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for the cool sum of $20m (£15m).
Virgin Galactic has long been promising to take customers on short sub-orbital hops into space – where passengers get to experience rocket propulsion and several minutes of weightlessness, before gliding back to a runway landing on Earth, all for $250k (£190k). In late July 2020, the company unveiled the finished cabin in its SpaceShipTwo vehicle, suggesting that commercial spaceflights may begin shortly.
Meanwhile, Elon Musk’s SpaceX , which in May 2020 became the first private company to launch a human crew to Earth orbit aboard the Crew Dragon , plans to offer stays on the ISS for $35k (£27k) per night. SpaceX is now prototyping its huge Starship vehicle , which is designed to take 100 passengers from Earth to as far afield as Mars for around $20k (£15k) per head. Musk stated in January that he hoped to be operating 1,000 Starships by 2050.
10 Short Lessons in Space Travel by Paul Parsons is out now (£9.99, Michael O'Mara)
- Buy now from Amazon UK , Foyles , WH Smith and Wordery
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
itsmyschoollibrary
Your lesson notes in a blink, js1 basic science and technology scheme of work for first term, second term, and third term..
Basic Science And Technology Scheme Of Work For JSS 1 First Term, Second Term, And Third Term.
Basic science is a subject that covers knowledge of living and non-living things of the environment. It was mainly focused on life, chemical, and physical science. However, recently, technological aspect of science has been incorporated into it, making the subject to stand as Basic Science And Technology. Most teachers and students are aware of these changes but for parents who are seeing or hearing it for the first time, should not be confused. So as you go through the topics in the scheme given below, you will see topics relating to computer studies, technical drawings, and basic science. These three subjects have become one now known as Basic Science And Technology, abbreviated as B.S.T. So, as we stay back home for the COVID 19, this scheme should be able to guide you teach your wards the contents of this subject. Below is the scheme of work for Basic Science And Technology for junior secondary one. It contains topics, subtopics, learners and teacher’s activities. I do hope you find it useful.
BASIC SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY JSS 1 FIRST TERM
1 LEARNING ABOUT OUR ENVIROMENT Living things and non living things. a. Meaning b. Characteristics c. Differences d. Examples e. Importance Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should take learners on nature walk to collect different samples of matter, lead learners on discussion on the three states of matter. That is, solid, liquid and gaseous state. Learners Activities : The learners are to observe the collective specimens and group them into living and non-living things as instructed by the teacher. 2 COMMUNITY HEALTH a. Meaning of Community Health b. Sanitation c. Nutrition d. Balance diet Teacher’s Activities : The teacher should present and discuss picture of healthy and unhealthy life styles and environment. Explain how heredity, environment and life style affects individual.
Learners Activities : The learners should Listen attentively to the teacher’s explanations on ways of dispensing sewage and refuse in the home. They should also narrate to the teacher how they dispose these waste. 3 COMMUNITY HEALTH II a. Determinant of health b. Characteristics of healthy person c. Drugs and substances abuse. d. Examples and effects of drugs. Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should explain in the concept of the lesson listed above as she allow learners to take part in the it 4. PHYSICAL FITNESS AND BOFY CONDITIONING a. Meaning of physical fitness b. Components of physical fitness c. Characteristics of physical fitness d. Factors that can affect our physical fitness e. Exercises to develop our endurance and flexibility. Activities : The teacher should lead explanation and discussion on the components of physical fitness, engage the learners on some exercises that help in developing strength, agility, endurance and flexibility, should also state the precautions to be taken before and during performing exercise as she demonstrate before the learners. 5. ATTHLETICS (TRACK AND FIELD EVENT) a. Definition of the term Athletics. b. Components of Athletics c. Describe basic skills in Discus and short-put. d. Rules and regulation in Discus and short-put. Teacher’s Activities: Should give detail explanation on the skills and technique involved in Short-Put and Discus. Learners Activities: They should watch the teacher demonstrating the various skills. Note that it is necessary to do some warming up before engaging in any of these events. 6. SPORTS AND GAM ES a. Basic skills in Volley ball and Soccer b. Rules and regulations in Volley ball and soccer c. Officials and their duties/facilities and equipments. Teacher’s Activities : The teacher should describe the sports Volleyball and soccer, demonstrate the technique and skills involved in playing the game, explain the rules and regulations involved in the game while learners listen, participate, and adhere to these rules given by the teacher. Aids : The teacher would need a drawn and labeled Court/Pitch to facilitate this lesson. 7. UNDERSTANDING TECHNOLOGY a. Meaning of basic Technology related occupation b. Importance of technology c. Properties of materials d. Identification of woods materials and ceramics. e. Physical properties of wood, metals and ceramics. f. Type of wood, ceramics and metals Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should explain to the learners that technology is universal and give illustrating reasons why both males and females should be encouraged to study technology. Learners Activities: The learners should state the of importance of technology in our everyday life. Aids : The teacher should get role model of males and females in technology even if is a cell phone repairer. 8 BASIC COMPUTER OPERATIONS AND CONCEPTS a. Early counting devices b. Mechanical and electro-mechanical devices c. Electronic counting device d. Generation of Computers e. Computer system
Teacher’s Activities : The teacher is to lead the learners to a suitable Computer laboratory for exploration, guide them to identify ways of taking good care of the Computer room/laboratory. Learners Activities : They should participate in class discussions and take precautions as they visit the computer lab. 9 ENVIROMENTAL POLLUTION I a. Definition, meaning of pollution b. Types, e.g. soil, water and air. c. Causes d. Experiment/practical e. Demonstration in the class f. Effect g. Control measures. Teacher : Lead students on discussion on soil and water pollution, Carry out activities on water boiling, filtration, flower planting, film watching and recording of soil pollution from visited sites. Guides learners to investigate the effect of pollution in soil, plants, animal, and environments. 10 PATHOGENS DISEASES AND THEIR PREVENTION a. Meaning of pathogens diseases b. Diseases caused by pathogens c. List different types of pathogen diseases d. List the preventive measures i. Adequate Nutrition and Exercise ii. Clean environment iii. good hygiene iv. Immunization, vaccination v. Proper disposal of refuse and sewage. Teacher’s Activitie s: The teacher should lead learners to discuss how diseases are caused by pathogen, give detail explanation on how to prevent diseases, raise questions on prevention of diseases, state the effects of diseases on health. 11 ENERGY a. Meaning of Energy b. Sources of Energy c. Forms of Energy d. Experimental/Practical showing Learners a panel of solar energy e. Transformation of Energy f. Uses of Energy Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should Lead learners to state the sources of energy known to them, provide some materials for activities to illustrate forms of energy as he/she must have discussed with them. Learners Activities: The learners should state sources of energy, describe the actions as indicated on the chart presented by the teacher. 12 SAFETY a. Safety guideline for pedestrian b. Safety guideline for cyclist and motor cyclist c. Safety guideline for motorist. Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should state the meaning of pedestrian, safety guidelines for pedestrian e.g. walking on the left hand side facing oncoming vehicle and allow learners state their experience on the pedestrian route. 13 Revision Revision 14 Examination Examination
BASIC SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY JSS1 SECOND TERM 1. WORKSHOP SAFETY, a. Causes of workshop accident b. Types of workshop accident c. Safety devices in workshop d. Safety rules and regulation Teacher Activities: The teacher should explain the meaning and causes of workshop accidents, lead the class on discussion on types of activities that occur in work shop places. Learners Activities : listen, Practice some workshop accidents preventive measures as directed by the teacher. 2 WORKSHOP II a. Computer Management ethics. b. Laboratory rules and regulation. Activities : The teacher should lead the learners to observe safety rules and regulations whenever in workshop places. Instructional aids such as Safety devices, e.g. fire extinguishers, sand bucket. 3 CONTACT AND NON-CONTACT SPORT a. Meaning of contact and non-contact sports. b. Types of contant and non-contant sports e.g. wrestling, judo, swimming gymnastics e.t.c c. Practical talking students to swimming pools. d. Basic skills in contact and non-contact sports. e. Benefit of contact and non-contact sports. f. Officials and their duties.
Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should define the term contact and non-contact sport, list examples of them, demonstrate the various skills involved in the contant and non-contact sport, list safety measures in contact and non-contact sports, enumerate the benefit derived from contact and non-contact sport. 4 RENEWABLE AND NON RENEWABLE ENERGY a. Meaning b. Example c. Uses and misuse d. Energy and society e. Importance Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should initiate and lead discussion on renewable and non-renewable energy. Learners Activities: They are to Participate in discussions and note the main ideas. 5. FORCES I a. Meaning and types of forces b. Contact and non contact forces c. Magnetive and gravitational force Activities : The teacher should guide the learners through the activities of pushing and pulling, squeezing, bending and stretching of objects. Aids : The teacher should make available chart showing contact and non-contact forces. 6 FORCES II a.Calculation of gravitational force b. Balance and un-balance force c. Friction, uses advantages and disadvantages d. Provide chart showing contact and non-contact force Activities : The teacher should guide the learners to calculate gravitational force using the formula GF=mgh
7 MATERIAL PROCESSING 1. Identification of materials and properties. a. Wood, metal ceramics Activities: The teacher is to guide the learners to identify building materials, explain the uses of the different building materials while the learners pay attention to lesson. 8 APPLICATION OF IT IN EVERY DAY LIFE a. Use of IT b. Communication c. Timing and control d. Organization processing/Management e. IT and society Teacher’s Activities: Prepare charts to identify it uses in every day life, Show video clips of IT uses in every day life Learners: Watch video and note how IT influences daily lives of people, Participates in class discussion. 9 BUILDING MATERIALS a. Common building materials b. Uses of the building materials. Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should explain the meaning of building materials, guide learners to identify building materials and the various types. 10 DRAWING INSTRUMENTS a. Drawing instruments and materials. b. Basic techniques of handling instruments and materials c. Practical: teacher demonstrating and students practice appreciable techniques of handling instruments. d. Uses and care of drawing instruments and materials. Activities: The teacher should explain the concept of drawing instruments, display drawing instrument and materials, guide learners to identify and name drawing instruments and materials. Learners : The learners should Use various drawing instruments to construct shapes under the guidance of the teacher. 11 Revision Revision 12 Examination Examination
BASIC SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY JSS 1 THIRD TERM 1 SCIENCE DEVELOPMENT I a. Gravitation and weightlessness b. The earth space c. Identification of component of solar energy d. Rotation and revolution of the earth Teacher’s Activit i es : The teacher should demonstrate the effect of gravitational pull objects, lead the learners to demonstrate the effect of gravitational objects and the moon Learners Activities: They are to w atch and comment on films/picture clippings, participates in class and group work discussions, carry out demonstrations on gravitational activities on weighing themselves and recording of individual weight.
2 SCIENCE DEVELOPMENT II a. Space travel b. Satellite c. Benefits and danger of space travel 3 TOOLS, MACHINES AND PROCESSES a. Workshop hand tools . Measuring tool . Setting and marking out tools . Driving tools . Burning tools . Holding tool devices . Cutting and pairing . Care and maintenance of all Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should lead class discussion on measuring and types of maintenance practice, demonstrate different methods of caring and maintaining workshop tools and machines. Learners Activities: Understand simple maintenance of tools and machines, e.g. Regular cleaning, oiling and greasing of simple machines and tools. The learners should watch and practice this too at their respective homes. 4 METAL WORK AND TOOL . Marking out tools . Measuring tools and gauges . Driving and cutting tool . Care maintenance . Display wood work hand tools. Activities : The teacher should show a demonstration on the use of the various hand tools and learners should watch and partake in the demonstration. 5. BOARD PRACTICE a. Basic board practice b. Setting drawing paper on the board c. Sharpening pencil to conical points and knife edge using the tee and set squares for drawing border, horizontal and practical lines. Teacher’s Activities: Demonstrate correct techniques for : Setting drawing paper on the board, Sharpening pencil to conical point, Positioning and drawing the little board Learners Activities: They should watch the teacher’s demonstration and practice free hand sketching, Practice the technique. 6 FREE HAND a. Basic free hand techniques of drawing line, curves, circles and irregular shapes. b. Practical inclusive Teacher’s Activities : Demonstrate correct techniques of free hand sketching, assign free hand drawing tools. Learners Activities: Watch the teacher’s demonstrations. 7 INFORMATION TRANSMISSIONS 1. Meaning of information transmission Teacher’s Activities: Bring chart/picture of modern tool and for transmitting information, mention ancient methods of information transmission, mention the modern method of transmission information, lead learners to identify these tools. Learners Activities: Follow the guidance of the teacher to classify information by mode of transmission. 8 DATA PROCESSING a. Definition of data processing b. Data processing cycle c. Stage d. Importance of Computer as a tool for data processing Teacher’s Activities: Lead learners to define and identify data processing cycle/stages, discuss what each stage involves. Learners Activities: Partake in the class discussion and copy the board summary into their note book. 9 RECREATIONAL LEISURE AND DANCE ACTIVITIES a. Meaning of recreational leisure and dancing activities b. Differences between Dance, leisure and recreational c. Benefits of recreational leisure and dancing. Teacher’s Activities: T he teacher should invite traditional dancers to demonstrate some dancing skills. Outline the benefits of recreational activities and dancing. 10 RECREATIONAL, LEISURE/DANCING ACTIVITIES a. Demonstration of some local dances step. b. Invites a traditional dancer to demonstrate some dancing skills. c. Dancing competitions should be organized. Teacher’s Activities : Explain the meaning of recreation, leisure and dance, guide the learners to identify the various components of recreation and dance. Learners Activities: Listen to the teacher’s explanations and Practice some local dance. 11 FOOD AND NUTRITION a. Meaning of food, and types of food. b. Classes of food and importance Teacher’s Activities: The teacher should explain the meaning of food and Nutrition, group food into different classes, explain the importance of food to the learners and the learners should in turn participate in the lesson activities by listening attentively to the teacher. 12 Revision Revision 13 Examination Examination
Please do note that well developed lesson contents on this subject will be made freely available soon. So do stay connected!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from itsmyschoollibrary.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

10 Benefits of Space Exploration. (Including Medical and Economical)
On April 12, 1961, the Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to journey to outer space. The age of space exploration started that day.
But why are we so interested in spending so much time, money, and resources to visit chunks of rock that are most likely empty? Why purposely go to environments that are dangerous and even deadly to humans?
Well, the answer is simple.
The benefits of space exploration outweigh the dangers of it. Becoming a space-faring civilization is the most important goal we must achieve for humanity to survive long-term .
In this article, we’ll the major 10 benefits of space exploration. These include medical, technological, and economic benefits. They are listed in no particular order of importance.
Economic benefits of space exploration
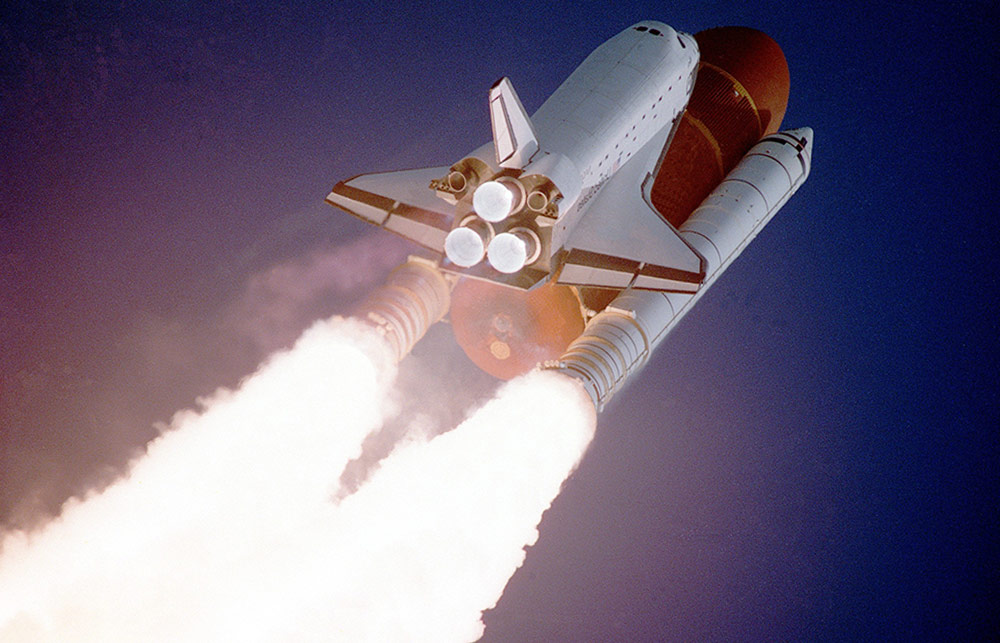

10. Creation of STEM Jobs
NASA employs more than 18,000 people. SpaceX more than 12,000. And that’s not counting outside contractors with whom those numbers at least double.
A lot of those jobs are positions for engineers, data analysts, mathematicians, physicists, astronomers, doctors, biologists, geologists, etc.
Space exploration is one of the industries that require the largest percentage of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) jobs.
These positions require highly qualified people to fill them but are also some of the highest-paid jobs in the market. The average entry-level STEM job pays approximately 26% higher than non-STEM fields for college graduates.
So, in summary, the growing space industry creates high-paying jobs.
9. Space mining and asteroid capturing
In space, there are many valuable resources in big quantities that are scarce on Earth. For example, the asteroid Pysche 16 is estimated to contain over $700 quintillion dollars worth of gold. Enough to give each person on Earth more than $100 billion dollars. And that’s not even close to being the most valuable object.
Economists have predicted the space mining industry will create the first trillionaire.
But the real benefit for the advancement of humankind might come from a much more unlikely substance. Water.
Learning to capture asteroids full of ice and crashing them safely, could help us solve one of the biggest challenges of inhabiting planets. The lack of liquid water.
8. Space tourism industry
The biggest dream some of us have is being able to take a trip to outer space. It is the ultimate destination. And because unfortunately, not many people can become astronauts, the rest of us will have to wait until the space tourism industry develops a bit more. It is still too expensive to go to space .
In 2021, a trip in one of the first trips offered by Blue Origin, the space company created by Jeff Bezos, was auctioned. The winner paid $28 million for the privilege to be one of the first space tourists.
As reusable rockets improve, the costs of these trips will become significantly lower. Hopefully one day they’ll be within the reach for all of us.
The space tourism industry will indubitably create tens of thousands of jobs. From travel agents to pilots, to manufacturing jobs in the factories that make the rockets.
Medical benefits of space exploration
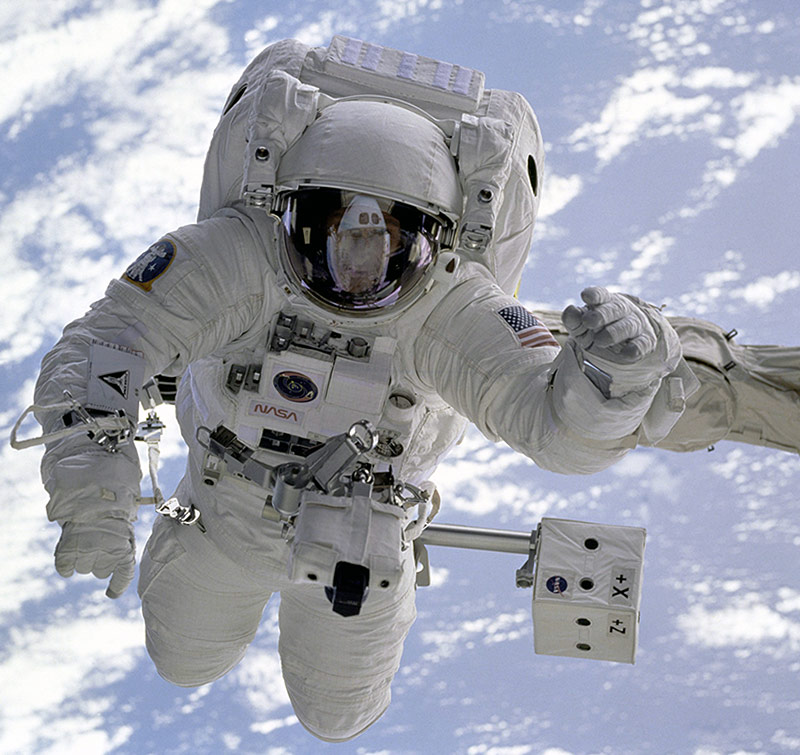

7. Learning more about the human body
Studying the effects of space travel has helped us better understand the human body. For example, analyzing the effects of zero-gravity on blood circulation led to many discoveries on how arteries age and how to prevent some types of heart failure.
The experiments and measurements of bone strength and bone loss in astronauts have helped doctors better understand osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
The medical benefits of space exploration extend to pretty much every area of the human body. From muscle physiology to mental health.
6. Improving medical assistance in remote areas
One of the biggest challenges of space travel is solving problems when you can’t send any new equipment, experts, or any other help. You have to fix things with whatever is available on the ship.
So what happens when there’s a medical emergency on a spaceship?
This question has led doctors and engineers to develop tools and machines that can perform medical procedures and diagnostics remotely.
That same technology has many applications on Earth too. It allows doctors to assist patients that are located in remote rural areas or villages that are difficult to access.
5. Development of new medical procedures
All this knowledge that has been collected has yielded many developments in medical procedures.
Some examples of medical advancements that have been created thanks to space exploration are:
- Heart pumps
- Programmable pacemakers
- Fiber-optic catheters to perform laser angioplasty
- Digital imaging breast biopsy used to detect breast cancer
- Fetus monitoring transmitters
- Cooling suits made to lower a person’s temperature
The NASA spinoff site keeps track of some of the health and medicine advancements that have been made possible thanks to space exploration.
Other benefits of space exploration
4. development of new technologies.
The space race is one of the eras that has birthed the most technological advancements in the shortest period of time. It is probably only third behind both world wars. Throughout the years, companies have found consumer uses for many of these developments. To this day we still use them in our day-to-day lives without even knowing that some NASA engineers originally developed them for the Apollo program that took humankind to the Moon.
Listing all the technologies that have been derived from space exploration would be impossible, but here are some notable examples.
- Vacuum sealed food.
- Shock-absorbing sneaker soles. That’s right, the comfy running soles were originally developed for astronaut spacesuits.
- Fireproof materials used in firefighter uniforms
- Quake-proofing technology used in bridges and buildings to resist Earthquakes
- Heat-repellent blankets. There’s a reason why they are also known as “space blankets”. Fun fact, they can also double as DIY telescope covers.
- Rechargeable hearing aids
- Autonomous drone navigation
- Modern vacuum cleaners
- The lenses used in “action cameras”
- Water purification technology
As you can see, it is important for us to keep pushing the limits of space exploration. Who knows what kind of new technologies could be developed that will make our lives easier in the future.
3. Inspire the next generation
Space exploration sparks the curiosity of children who will become the next Elon Musk, Neil Armstrong, Sally Ride, or Guion Bluford.
It inspires students to dream and gets them interested in science and technology.
Not only is this good for them as STEM jobs can secure them a comfortably future, but it also helps humanity. It is through invention, research, and knowledge that humanity will be able to overcome the big challenges it will be facing in the future.
2. Protecting Earth
We only have one planet where we can live without the help of spacesuits. It would be nice to keep it in good condition until we can figure out a way to find other habitable planets or terraform others.
To do that, we need to learn more about the dangers of space. We know about extinction events like asteroids, but that’s not the only potential threat to our survival. Solar flares, radiation, magnetic pole changes, and greenhouse effects are just some of the challenges Earth might face at some point.
Exploring space is the only way we will learn more about them so we can develop strategies and technology that could help save us from such events.
1. Increase humanity’s odds of survival
There’s one thing we are certain of about when it comes to space. If we – humanity – don’t become a space-faring civilization. We will become extinct sooner or later.
Earth will eventually become uninhabitable and will probably be devoured by the Sun as it expands during the later years of its life cycle. And that’s hoping nothing else happens before, like an asteroid impact, an ice age, atmospheric loss, climate change, or any other potential threats that could wipe us out, to put it bluntly.
Space exploration is not a luxury for the richest nations. It should be a worldwide priority and every country needs to come together in this effort. It is simply the only way we can hope to survive as a species.
We don’t know if we have millions of years or hundreds of years before any of these events happen. So it’s better to get started today.
- Space exploration can be the doorway to many growth industries such as asteroid mining or space tourism.
- Many medical advancements have been made possible thanks to the aerospace industry.
- Space exploration is critical and the only path to the survival of the human race.
Elena is a Canadian journalist and researcher. She has been looking at the sky for years and hopes to introduce more people to the wonderful hobby that is astronomy.
Related Posts

What Happened to the Mars Helicopter? (Ingenuity)

What is the Purpose of the International Space Station?

Who Owns The International Space Station?

Is There Gold On The Moon? Yes! And Here’s Why It Matters.

Is There Gold On Mars? Yes! And The Discovery Was Very Curious…
Have We Landed On Venus?
- Buying Guides
- Telescope Accessories
- Magnification Calculator
- Field of View Calculator
- Constellations
- Solar System
- Space Exploration
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

COMMENTS
The purpose of space travel include the following: Exploration: To be human is to be an explorer. It is part of who we are: since the first tribes left the African savanna and spread into Europe and Asia, we have had the need to explore the unknown. Now humans have visited or settled every corner of the globe.
MEANING OF SPACE TRAVEL. The space outside the sun, earth, star is called outer space. Space travel is the travelling to the outer space beyond this earth. The space travellers are called astronaut. The earth is surrounded by a layer of air called atmosphere which can be divided into about 4 regions: Troposphere. Stratosphere.
Proponents of space travel have noted the rich amount of precious metals that exist in space. For example, in 2021, NASA discovered a asteroid called "16 Psyche" which has more gold on it than the value of the global economy, about $10,000 quadrillion (the global economy is about $84.5 trillion). ... The calculations of the benefits of space ...
Benefits of Satellite 1. It can cover a large geographical area 2. High band width 3. Easy to use 4. Always on connection 5. Uses multitude device Space Travel Space travel means going to the moon or planets or orbiting the earth in a special craft called Space Craft or Spaceship
The following are benefits of space travel; computers, rocket or aircraft fuels. (a)true (b)false; Problems of space travel are basic needs of life, loss of weight, high speed. (a)true (b)false; Which of the following is present in outer space? (a)Air (b)light (c)sound (d)life; Force of gravity cannot be carried in a spacecraft. (a)true (b)false
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the study of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with tel...
Week 5 - Jss 1 Third Term Basic Science & Technology (BST) Lesson Notes. Space travel is the act of going to the moon or planets or orbiting the earth in a special craft called spaceship. It is also the travelling to the outer space beyond the earth. The space travelers are called ASTRONAUTS.
Basic Science JSS1. Third term unit 1. Topic; Energy. Energy is define as ability to do work. The unit of energy is Joule (J). Any thing is that is capable of doing work has energy. Sources Of Energy; These are sun, food, water, wind, coal, atomic reactors, crude oil products example kerosene, fuel, diesel, gas etc.
We have now entered the decade of results. With more than 20 years of experiments now conducted on the station, more breakthroughs are materializing than ever before. Explore 15 of the ways the space station is benefiting humanity. 1. Producing the next generation of medical scanning technology. In their quest to study neutron stars, the team ...
Space travel jss1 . 0% average accuracy. 0 plays. 7th grade . Science. 15 minutes ago by . Olorunnifemi Akobi . 0 Save Share Edit Copy and Edit. LESSON. NEW. SUPER DRAFT. Space travel jss1 .
Posted on August 5, 2023. This JSS 1 Basic Science Scheme of Work covers the entire 1st, 2nd, and 3rd terms, offering you a well-defined roadmap to engage and empower your students. Dive into a curriculum designed to enhance science skills and ignite a lifelong love for Science learning. JSS 1 FIRST TERM BASIC SCIENCE SCHEME OF WORK.
From its orbit 402 kilometers (250 miles) above Earth, the International Space Station collects a variety of data and imagery that benefit humanity. More than 3.5 million photographs of Earth have contributed to research on our atmosphere and climate change, monitoring of and response to natural disasters such as flooding and volcanic eruptions ...
Space exploration gives us an opportunity to access new mineral resources, allowing for the privatization of this venture. It would also give us an opportunity to start building in space because the raw materials are easy to haul and transport. 10. It gives us an opportunity to see what lies beyond in the final frontier.
WEEK FIVE. SPACE TRAVEL. MEANING OF SPACE TRAVEL The space outside the sun, earth, star is called outer space. Space travel is the travelling to the outer space beyond this earth. The space travellers are called astronau t. The earth is surrounded by a layer of air called atmosphere which can be divided into about 4 regions: Troposphere ...
WEEK FIVE. SPACE TRAVEL. Meaning of space travel; Purpose of space travel; Benefits of space travel; Dangers of space travel; Meaning of space travel. Space travel is the act of going to the moon or planets or orbiting the earth in a special craft called spaceship. It is also the traveling to the outer space beyond the earth.
The solar system. The planet earth, on which we live, is moving through space all the time. It is going around the sun. In doing this it carries us all through space. The earth travels through space but we do not realize this because the air around the earth is carried along with it. The sun together with all the bodies which revolves around it ...
Everything you need to know about space travel (almost) - BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Space exploration unites the world to inspire the next generation, make ground-breaking discoveries, and create new opportunities. Technologies and missions we develop for human spaceflight have thousands of applications on Earth, boosting the economy, creating new career paths, and advancing everyday technologies all around us.
Basic Science And Technology Scheme Of Work For JSS 1 First Term, Second Term, And Third Term. Basic science is a subject that covers knowledge of living and non-living things of the environment. It was mainly focused on life, chemical, and physical science. However, recently, technological aspect of science has been incorporated into it, making…
It is the need to find out what exists there in outer space that led man to begin the activities of space exploration through space travel. Space travel means to make a journey far beyond the earth's atmosphere into outer space. Space travel by man started on October 4, 1957 when a rocket driven Russian space craft called Sputnik carried men ...
The medical benefits of space exploration extend to pretty much every area of the human body. From muscle physiology to mental health. 6. Improving medical assistance in remote areas. One of the biggest challenges of space travel is solving problems when you can't send any new equipment, experts, or any other help.
He created this foam to absorb the energy of plane crashes and increase survival rates, but it didn't just save lives, it made sitting for hours in flight more comfortable. Now memory foam can ...
ISECG - Benefits Stemming from Space Exploration 1. Introduction . For more than fifty years, humans have explored space, and this has produced a continuing flow of societal benefits. By its very nature, space exploration expands the envelope of human