

Tourism in Cambodia
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Tourism in Cambodia is big business. But why is tourism so important here and how should it be managed? Read on to find out…
Cambodia, with its profound history and enigmatic landscapes, is a magnet for travellers seeking both heritage and nature. From the awe-inspiring temples of Angkor Wat to the untouched beaches of Sihanoukville, the country showcases a rich tapestry of experiences. In this article, I will explore the myriad facets of Cambodia’s tourism sector, illuminating its diverse attractions and cultural depth.
Geography of Cambodia

Cambodia is a Southeast Asian country located in the southern part of the Indochinese Peninsula. It shares borders with Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the northeast, Vietnam to the east, and the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. Here is a brief overview of Cambodia’s geography :
- Landforms: Cambodia’s terrain is characterized by low-lying plains, river valleys, and a central plain known as the Cambodian Plain or the Central Lowlands. The Mekong River, one of Southeast Asia’s major waterways, flows through the eastern part of the country, providing fertile soil and playing a crucial role in Cambodia’s agriculture.
- Cardamom Mountains: In the southwestern part of Cambodia lies the Cardamom Mountains, a range that stretches parallel to the Gulf of Thailand. These mountains are covered with dense forests and are home to various wildlife species, including endangered ones like tigers and Asian elephants.
- Densely Forested Areas: Large parts of Cambodia are covered by forests, particularly in the northern and eastern regions. These forests are rich in biodiversity, with diverse flora and fauna, including rare species like the giant ibis and the Asian black bear.
- Tonle Sap Lake: In the central part of the country, there is the Tonle Sap, which is Southeast Asia’s largest freshwater lake. It is unique because its flow changes direction depending on the season. During the rainy season, the lake expands significantly, while during the dry season, it drains into the Mekong River.
- Coastal Areas: Along Cambodia’s southern coastline, there are sandy beaches and several offshore islands in the Gulf of Thailand. Popular tourist destinations like Sihanoukville and Kep are located in this region, attracting visitors with their beautiful beaches and tropical landscapes.
- Climate: Cambodia has a tropical monsoon climate with two distinct seasons. The rainy season usually lasts from May to October, characterized by high humidity and frequent rainfall. The dry season runs from November to April and brings drier and cooler weather.
Overall, Cambodia’s geography offers a diverse landscape, ranging from fertile plains to mountainous regions and coastal areas. This diversity contributes to the country’s natural beauty, rich biodiversity, and varied agricultural resources.
Tourism Industry in Cambodia:
Cambodia, a vibrant nation nestled in the heart of Southeast Asia, has witnessed a remarkable growth in its tourism industry over the past few decades. This paper aims to examine the country’s tourism sector, exploring its historical significance, popular tourist destinations, policy framework, and economic impacts. By doing so, a comprehensive understanding of Cambodia’s tourism industry can be gained.
Cambodia’s rich historical legacy, prominently exemplified by the majestic temples of Angkor Wat, has been instrumental in shaping its tourism landscape. Angkor Wat, a UNESCO World Heritage site, stands as a testament to the once-mighty Khmer Empire and attracts tourists from across the globe. Furthermore, Cambodia’s tumultuous past, including the tragic era of the Khmer Rouge regime, has generated interest among history enthusiasts and visitors seeking a deeper understanding of the nation’s complex history.
Beyond Angkor Wat, Cambodia offers an array of captivating destinations that contribute to its allure as a tourist hotspot. The bustling capital city of Phnom Penh showcases a blend of French colonial architecture and traditional Khmer heritage. The coastal city of Sihanoukville entices beach lovers with its pristine beaches and lively atmosphere, while the tranquil riverside town of Battambang offers an authentic glimpse into rural Cambodian life. Other notable attractions include the ancient temple complex of Preah Vihear, the wildlife-rich Cardamom Mountains, and the picturesque islands of Koh Rong and Koh Rong Samloem.

Recognizing the importance of the tourism sector, the Cambodian government has implemented various policies and initiatives to foster its growth. These include infrastructure development, visa facilitation measures, and the preservation of cultural and natural heritage sites. The Ministry of Tourism plays a pivotal role in promoting Cambodia as a tourist destination and has been actively engaging in partnerships and collaborations with international organizations and tour operators to enhance the industry’s sustainability and competitiveness.
The tourism industry has emerged as a vital contributor to Cambodia’s economy. Its rapid growth has led to the creation of employment opportunities, particularly in the service sector, thereby improving livelihoods and reducing poverty. Additionally, tourism revenues have supported the development of infrastructure, healthcare, and education systems, indirectly benefiting local communities. However, challenges such as seasonal fluctuations, environmental sustainability, and equitable distribution of tourism benefits persist and necessitate continued efforts for inclusive growth.
The tourism industry in Cambodia showcases the country’s rich cultural heritage, breathtaking landscapes, and hospitable communities. With its historical significance, diverse tourist destinations, proactive policies, and positive economic impacts, Cambodia has positioned itself as a prominent player in the Southeast Asian tourism landscape. While ongoing challenges persist, the sustained growth of the tourism sector holds immense potential for further socioeconomic development and the preservation of Cambodia’s unique identity.
Statistics about Tourism in Cambodia:
Now lets highlight a few ket statistics about tourism in Cambodia:
- Tourist Arrivals: In 2019, Cambodia welcomed approximately 6.61 million international tourist arrivals.
- Tourism Revenue: The tourism sector contributed around $4.92 billion in revenue to Cambodia’s economy in 2019.
- Economic Impact: Tourism accounted for about 12.1% of Cambodia’s GDP in 2019.
- Employment: The tourism industry provided employment for around 630,000 people in Cambodia in 2019, representing approximately 12.7% of total employment.
- Main Source Markets: The top five source markets for international tourists visiting Cambodia in 2019 were China, Vietnam, Thailand, South Korea, and the United States.
- Angkor Wat Visitors: Angkor Wat, the famous UNESCO World Heritage site, attracted more than 2.2 million visitors in 2019.
- Tourism Growth: Between 2010 and 2019, Cambodia experienced an average annual growth rate of approximately 10.3% in international tourist arrivals.
- Average Length of Stay: The average length of stay for international tourists in Cambodia was around 6.7 days in 2019.
- Accommodation Capacity: Cambodia had a total of around 1,067 registered hotels and guesthouses with over 64,000 rooms available in 2019.
- Eco-Tourism Potential: Cambodia has a significant potential for eco-tourism with its diverse natural landscapes, including national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and ecotourism sites.
Most Popular Tourist Attractions in Cambodia
Here are some of the major tourist attractions in Cambodia:
Angkor Archaeological Park:
- The Angkor Archaeological Park is an unparalleled treasure trove of ancient ruins and religious structures that testify to Cambodia’s glorious past. Nestled amidst lush jungles near the city of Siem Reap, this UNESCO World Heritage site encompasses over 400 square kilometers. Its centerpiece, Angkor Wat, is the world’s largest religious monument and an iconic symbol of Cambodia. Built during the Khmer Empire’s zenith in the 12th century, Angkor Wat displays intricate bas-reliefs, towering spires, and an awe-inspiring architectural design. Other notable temples within the park include Bayon, Ta Prohm, and Preah Khan, each exhibiting distinct architectural styles and historical significance.
Royal Palace in Phnom Penh:
- Situated in the capital city of Phnom Penh, the Royal Palace represents the pinnacle of Cambodia’s royal heritage. Serving as the official residence of the King since the mid-19th century, this magnificent complex showcases a fusion of traditional Khmer architecture and European influences. Its centerpiece, the Silver Pagoda (Wat Preah Keo Morokat), houses a renowned collection of Buddhist artifacts, including the Emerald Buddha. Visitors can explore the opulent Throne Hall, the Moonlight Pavilion, and the manicured gardens, gaining insights into Cambodia’s royal legacy and contemporary monarchy.
Killing Fields Memorial:

- While Cambodia’s cultural attractions evoke admiration, it is vital to acknowledge the country’s tragic history as well. The Killing Fields Memorial, located in Choeung Ek, stands as a poignant reminder of the Khmer Rouge regime’s atrocities during the late 1970s. This somber site encompasses mass graves and a memorial stupa containing the remains of victims. A visit to the memorial provides visitors with a solemn opportunity to reflect upon the past, pay tribute to the lives lost, and gain a deeper understanding of Cambodia’s journey toward healing and reconciliation.
Beaches of Sihanoukville:
- Nestled along Cambodia’s southwestern coast, the pristine beaches of Sihanoukville offer a serene retreat for tourists seeking relaxation and natural beauty. Renowned for its white sandy shores, azure waters, and vibrant marine life, this coastal paradise is an emerging tourist destination. Koh Rong and Koh Rong Samloem islands, located near Sihanoukville, boast idyllic beachfronts and provide opportunities for diving, snorkeling, and island hopping. Visitors can also indulge in local seafood cuisine and immerse themselves in the laid-back atmosphere that characterizes this coastal gem.
Cambodia’s popular tourist attractions encompass a wide array of cultural, historical, and natural wonders that captivate travelers. From the awe-inspiring ancient temples of the Angkor Archaeological Park to the poignant reminders of the country’s turbulent past at the Killing Fields Memorial, visitors are invited to explore the profound layers of Cambodia’s identity. Additionally, the Royal Palace in Phnom Penh showcases the nation’s regal heritage, while the beaches of Sihanoukville offer an oasis of tranquility along the country’s picturesque coastline. By experiencing these diverse attractions, tourists can gain a deeper appreciation of Cambodia’s rich tapestry of traditions, resilience, and natural beauty.
Most Popular Types of Tourism in Cambodia:
There are many different types of tourism in Cambodia, here are the most common:
- Cultural Tourism: Cultural tourism serves as the cornerstone of Cambodia’s tourism industry. The world-famous Angkor Archaeological Park, home to the magnificent Angkor Wat temple complex, is a UNESCO World Heritage site and a key attraction for cultural enthusiasts. Visitors are captivated by Cambodia’s rich Khmer heritage, traditional dance performances, and local arts and crafts. Cultural tourism not only promotes national identity but also contributes to community development and cultural preservation.
- Historical Tourism: Cambodia’s turbulent history, including the Khmer Empire, the tragic era of the Khmer Rouge, and subsequent rebuilding efforts, attracts history enthusiasts seeking to understand the nation’s past. The Killing Fields of Choeung Ek and the Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum in Phnom Penh are poignant reminders of the Khmer Rouge regime and provide visitors with a solemn and educational experience. Historical tourism plays a vital role in Cambodia’s reconciliation process, preserving collective memory and fostering empathy.
- Ecotourism: The abundant natural resources and diverse ecosystems of Cambodia have nurtured the growth of ecotourism. Visitors are drawn to the country’s pristine national parks, such as Virachey and Bokor, where they can engage in activities like trekking, wildlife spotting, and exploring indigenous communities. Ecotourism initiatives prioritize environmental conservation, sustainable livelihoods for local communities, and the protection of endangered species, reinforcing Cambodia’s commitment to ecological preservation.
- Adventure Tourism: Adventure tourism in Cambodia is gaining popularity, particularly among thrill-seekers looking for adrenaline-pumping experiences. The country offers activities such as zip-lining, off-road cycling, and jungle trekking, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in Cambodia’s natural wonders while enjoying adventurous pursuits. Adventure tourism contributes to diversifying Cambodia’s tourism offerings and attracting a younger demographic of travelers seeking unique and exhilarating experiences.
- Religious Tourism: Religious tourism in Cambodia revolves around the spiritual significance of Buddhist temples and religious sites. Besides the iconic Angkor Wat, the country boasts numerous other ancient temples, such as Bayon and Preah Vihear, which attract pilgrims and spiritual seekers alike. Visitors can participate in meditation retreats, engage with Buddhist monks, and witness religious ceremonies, fostering cultural exchange and spiritual exploration.
- Beach Tourism: Cambodia’s coastline, notably the seaside town of Sihanoukville and the islands of Koh Rong and Koh Rong Samloem, draws beach enthusiasts seeking relaxation and tropical beauty. Beach tourism complements Cambodia’s cultural and historical offerings by providing visitors with a chance to unwind, enjoy water sports, and experience the laid-back coastal lifestyle. Development in this sector aims to balance tourism infrastructure expansion with environmental protection.
- Conclusion: Cambodia’s tourism industry encompasses a diverse range of popular tourism types, each contributing to the country’s economic growth, cultural preservation, and environmental sustainability. By leveraging its cultural heritage, historical significance, natural beauty, and adventurous opportunities, Cambodia continues to attract visitors from around the globe. The promotion of sustainable tourism practices is crucial to ensuring the long-term viability of Cambodia’s tourism industry, as it strives to preserve its unique attractions for future generations.
Impacts of Tourism in Cambodia

Tourism in Cambodia has emerged as a significant economic sector in the country, contributing to the country’s development and providing numerous employment opportunities. However, like any tourism destination, Cambodia experiences a range of impacts associated with the industry. This paper delves into the social, environmental, and economic consequences of tourism in Cambodia, shedding light on the overall effects on the nation.
Social Impacts of tourism in Cambodia
Positive Impacts:
Cultural Exchange and Preservation: Tourism in Cambodia facilitates cultural exchange between visitors and local communities, fostering an appreciation for Cambodia’s rich heritage. This interaction often leads to the preservation and promotion of traditional arts, crafts, and cultural practices.
Employment Opportunities: Tourism in Cambodia generates employment opportunities, particularly in the hospitality and service sectors, offering local residents income and improved livelihoods.
Negative Impacts:
Social Disruption: Rapid tourism growth can cause social disruption by altering the dynamics and values of local communities. The influx of tourists may lead to changes in traditional lifestyles, increased competition for resources, and social inequalities.
Exploitation and Cultural Appropriation: Unregulated tourism in Cambodia can lead to the commodification of culture and exploitation of local communities. Cultural appropriation and misrepresentation may occur, diluting authentic cultural experiences.
Environmental Impacts of tourism in Cambodia
Positive Impacts:
Conservation Efforts: Tourism in Cambodia can provide incentives for the conservation of natural resources and protected areas. Revenue generated from ecotourism initiatives can be reinvested in environmental preservation efforts, contributing to biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Environmental Awareness: Visitors to Cambodia often gain a deeper understanding of environmental challenges, leading to increased awareness and support for conservation initiatives.
Negative Impacts:
Overexploitation of Resources: Uncontrolled tourism in Cambodia can strain local ecosystems, resulting in habitat destruction, deforestation, and pollution. Overconsumption of water, energy, and waste generation can degrade natural resources and disrupt fragile ecosystems.
Carbon Footprint: The transportation and accommodation infrastructure required to support tourism in Cambodia can contribute to increased carbon emissions and climate change.
Economic Impacts of tourism in Cambodia
Positive Impacts:
Employment and Income Generation: Tourism in Cambodia is a significant source of employment, particularly for the local workforce. Jobs in the tourism sector provide income opportunities, alleviate poverty, and contribute to the overall economic growth of the country.
Foreign Exchange Earnings: Tourism generates foreign exchange through visitor expenditures, which contributes to the balance of payments and helps strengthen the national economy.
Leakages and Dependency: Leakage occurs when a significant portion of tourism revenue leaves the host country, benefiting foreign investors rather than the local economy. Overdependence on tourism can make the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in the industry.
Seasonal Employment: The tourism industry often exhibits seasonality, leading to fluctuations in employment opportunities. This can result in instability and unemployment during the off-peak season.
Tourism in Cambodia has brought about numerous social, environmental, and economic impacts, both positive and negative. While the industry has contributed to cultural preservation, employment generation, and economic growth, it has also posed challenges such as social disruption, environmental degradation, and economic vulnerabilities.
To maximize the benefits and minimize the negative consequences, sustainable tourism development strategies, including responsible tourism practices, community involvement, and environmental conservation efforts, are crucial. These measures can help ensure that tourism in Cambodia continues to play a positive role in the country’s development while preserving its unique cultural and natural heritage.

Crime and Safety in Cambodia
Cambodia has made significant progress in terms of safety and security in recent years, but tourism in Cambodia still faces some challenges related to crime. Here is an overview of crime and safety in Cambodia:
- Petty Crime: Like many tourist destinations, Cambodia experiences incidents of petty crime such as pickpocketing, bag snatching, and theft in crowded areas, markets, and tourist sites. Visitors are advised to remain cautious and take necessary precautions to safeguard their belongings.
- Scams: Some common scams in Cambodia involve overcharging for services, counterfeit goods, and fake charity organizations targeting tourists. Exercise caution when dealing with unfamiliar vendors or individuals asking for money.
- Violent Crime: While violent crime is relatively low in Cambodia, there have been instances of armed robberies, assaults, and burglaries, especially in urban areas. These crimes often occur in dimly lit streets or remote locations. It is advisable to avoid traveling alone at night and remain aware of your surroundings.
- Drug-related Crime: Cambodia has been used as a transit route for drug trafficking, primarily involving illicit substances like methamphetamine. Engaging in drug-related activities can lead to severe penalties, including lengthy prison sentences or even the death penalty.
- Terrorism: Cambodia is not considered a high-risk country for terrorism. However, global threats can affect any nation, so it’s always prudent to stay updated on travel advisories and follow any security instructions provided by local authorities.
- Traffic Safety: Road accidents are a significant concern in Cambodia due to factors like poor infrastructure, reckless driving, and inadequate enforcement of traffic laws. Exercise caution when crossing roads, consider hiring experienced drivers, and use reliable transportation services.
- Landmines: Cambodia still has areas affected by landmines and unexploded ordnance from past conflicts. It is crucial to stay on well-traveled paths and avoid venturing into unknown or unmarked areas.
- Keep your valuables secure and be vigilant in crowded places.
- Use reliable transportation services and licensed taxis.
- Respect local customs, laws, and regulations.
- Avoid excessive displays of wealth or valuable jewelry.
- Stay updated on travel advisories from your government or embassy.
FAQs about Tourism in Cambodia
Now that we know a bit more about tourism in Cambodia, lets answer some of the most common questions on this topic:
Q: Is Cambodia a safe country for tourists?
A: Yes, Cambodia is generally a safe country for tourists. However, like in any other destination, it’s important to exercise common sense and take necessary precautions, such as avoiding isolated areas at night and keeping an eye on your belongings.
Q: What is the best time to visit Cambodia?
A: The best time to visit Cambodia is during the dry season, which runs from November to April. This period offers pleasant temperatures and lower chances of rainfall, making it ideal for exploring the famous temples of Angkor and enjoying outdoor activities.
Q: Do I need a visa to visit Cambodia?
A: Yes, most visitors to Cambodia need a visa. However, citizens from certain countries are exempt from obtaining a visa or can obtain one on arrival. It’s recommended to check with the Cambodian embassy or consulate in your country for the most up-to-date visa requirements.
Q: What currency is used in Cambodia?
A: The official currency of Cambodia is the Cambodian Riel (KHR). However, US dollars are widely accepted and often preferred for larger transactions, especially in popular tourist areas. It’s advisable to carry a mix of both currencies when traveling in Cambodia.
Q: What are the must-visit destinations in Cambodia?
A: Cambodia offers a wealth of attractions, but some must-visit destinations include the ancient temples of Angkor in Siem Reap, the capital city of Phnom Penh with its rich history, and the beautiful coastal areas like Sihanoukville and Koh Rong.
Q: Is it necessary to take malaria medication when visiting Cambodia?
A: Malaria is present in certain parts of Cambodia, especially in rural areas. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or travel medicine clinic before your trip to determine if malaria medication is necessary and to take appropriate precautions against mosquito bites.
Q: What is the local cuisine like in Cambodia?
A: Cambodian cuisine is known for its blend of flavors and influences from neighboring countries. Some popular dishes include fish amok (steamed fish in coconut curry), lok lak (marinated beef stir-fry), and num banh chok (rice noodles with fish-based curry). Don’t miss trying the delicious fruit shakes and fresh tropical fruits too!
Q: Can I use credit cards in Cambodia?
A: Credit cards are widely accepted in major hotels, restaurants, and larger establishments in Cambodia, particularly in popular tourist areas. However, it’s advisable to carry some cash, especially in more remote locations and smaller establishments where cash transactions are more common.
Q: What should I wear when visiting religious sites in Cambodia?
A: When visiting religious sites, such as temples or pagodas, it’s important to dress modestly and respectfully. Both men and women should cover their shoulders and wear clothing that covers their knees. Carrying a scarf or shawl to cover up when necessary is also recommended.
Q: Are there any cultural customs or practices I should be aware of in Cambodia?
A: Yes, there are a few cultural customs to keep in mind. It’s polite to remove your shoes before entering someone’s home or a place of worship. Additionally, it’s considered respectful to avoid touching someone’s head, as it is considered sacred in Cambodian culture. Showing respect to elders and monks is also appreciated.
To Conclude: Tourism in Cambodia
Cambodia, where history whispers through ancient temples and untouched nature flourishes, reaffirms its stature as a Southeast Asian marvel. As our exploration draws to a close, spanning its archaeological wonders to verdant landscapes, the magnetic appeal of Cambodian tourism is undeniable. For those seeking a voyage anchored in cultural depth and scenic splendour, Cambodia stands as an evocative testament to the region’s rich heritage.
If you enjoyed this article about tourism in Cambodia, I am sure you will love these too:
- The Killing Fields in Cambodia- 3 reasons NOT to visit
- 30 Fun Facts About Vietnam
- Tourism in Laos
- 13 things you don’t know about the country of Egypt 10 worst examples of pollution on the beach in the world
Liked this article? Click to share!
Home — Essay Samples — Geography & Travel — Tourism — The Positive and Negative Impacts of Tourism on Cambodia
The Positive and Negative Impacts of Tourism on Cambodia
- Categories: Tourism
About this sample

Words: 1042 |
Published: Jul 10, 2019
Words: 1042 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read
Table of contents
Positive effects of tourism in cambodia, negative effects of tourism in cambodia, positive and negative impacts of tourism on the environment of cambodia, works cited.
- Conservation Efforts: Revenue generated from tourism has been channeled into conservation initiatives aimed at protecting Cambodia's natural and cultural heritage sites. This includes funding for the preservation of historical temples like Angkor Wat and the conservation of biodiversity in national parks.
- Reforestation: In some regions, tourism-driven conservation projects have led to reforestation efforts, helping to restore damaged ecosystems and combat deforestation.
- Deforestation: The growth of tourism has contributed to deforestation in Cambodia, particularly in areas near popular destinations like Siem Reap. Forests are cleared to make way for infrastructure development, such as hotels and roads, resulting in habitat loss for numerous plant and animal species.
- Pollution: Increased tourist activities have led to higher levels of pollution, including water pollution from sewage and waste disposal. This pollution can harm aquatic ecosystems and water quality, affecting both wildlife and local communities.
- Habitat Destruction: Construction of tourist facilities, such as resorts and golf courses, often involves the destruction of natural habitats. This can disrupt the ecosystems that support Cambodia's unique and diverse wildlife.
- Overuse of Natural Resources: The demand for water, energy, and other resources in tourist areas can strain local supplies, leading to over-extraction of resources and exacerbating scarcity in already vulnerable regions.
- Soil Erosion: Activities related to tourism, such as hiking and off-road vehicle tours, can contribute to soil erosion, further degrading natural landscapes.
- Wildlife Exploitation: The demand for wildlife-based tourism activities, such as elephant rides and visits to wildlife sanctuaries, can contribute to the illegal wildlife trade and the mistreatment and endangerment of animals.
- Nhean, P. (2013). 'The Kingdom of Wonder': Cambodia's Destination Branding. In R. Raj & G. Musa (Eds.), Tourism Development in Asia (pp. 139-153). Channel View Publications.
- Royal Government of Cambodia (RGC). (2012). Cambodia Tourism Marketing Strategy 2012-2020. Ministry of Tourism, Cambodia.
- World Travel and Tourism Council. (2016). Travel & Tourism Economic Impact 2016 Cambodia. World Travel and Tourism Council.
- Meng, K., & Nhean, P. (2018). Chinese Tourists Driving Southeast Asia Airport Boom. Nikkei Asian Review.
- Ma, A., & Cripps, K. (2017). Angkor Wat: Tourists behaving badly at Cambodia's sacred site. CNN Travel.
- Fifield, A. (2018). Cambodia’s Chinese tourism boom sparks concerns over impact. Financial Times.
- World Bank. (2019). Cambodia: Maximizing the Benefits of Tourism for Inclusive Development. World Bank Group.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Geography & Travel

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1267 words
1 pages / 639 words
1 pages / 665 words
6 pages / 3010 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Tourism
Adventure tourism has emerged as a popular and thriving sector within the broader travel industry. This essay delves into the dynamics of adventure tourism, exploring its appeal, benefits, and challenges. Through an in-depth [...]
As the first rays of dawn painted the horizon with hues of orange and pink, I stood before the enigmatic time machine, my heart racing with anticipation. For I, a mere mortal, possessed the extraordinary ability to traverse the [...]
Exploring foreign lands has always been a fascinating aspect of human curiosity. It is a desire to discover new cultures, traditions, and landscapes that are different from one's own. The experience of traveling to foreign lands [...]
Traveling has always been a significant part of my life. From a young age, I have been fortunate enough to explore different cultures, experience new traditions, and immerse myself in the beauty of our world. My passion for [...]
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. Tourism may be international, or [...]
Mankind in the twenty-first century lives in a media-immersed world. Media has been a part of our lives for decades. Since humanity needed a medium to convey information, media have been developed with advance in technology and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Enabling ecotourism development in Cambodia
Maurice andres rawlins, elisabeth steinmayr, werner kornexl.
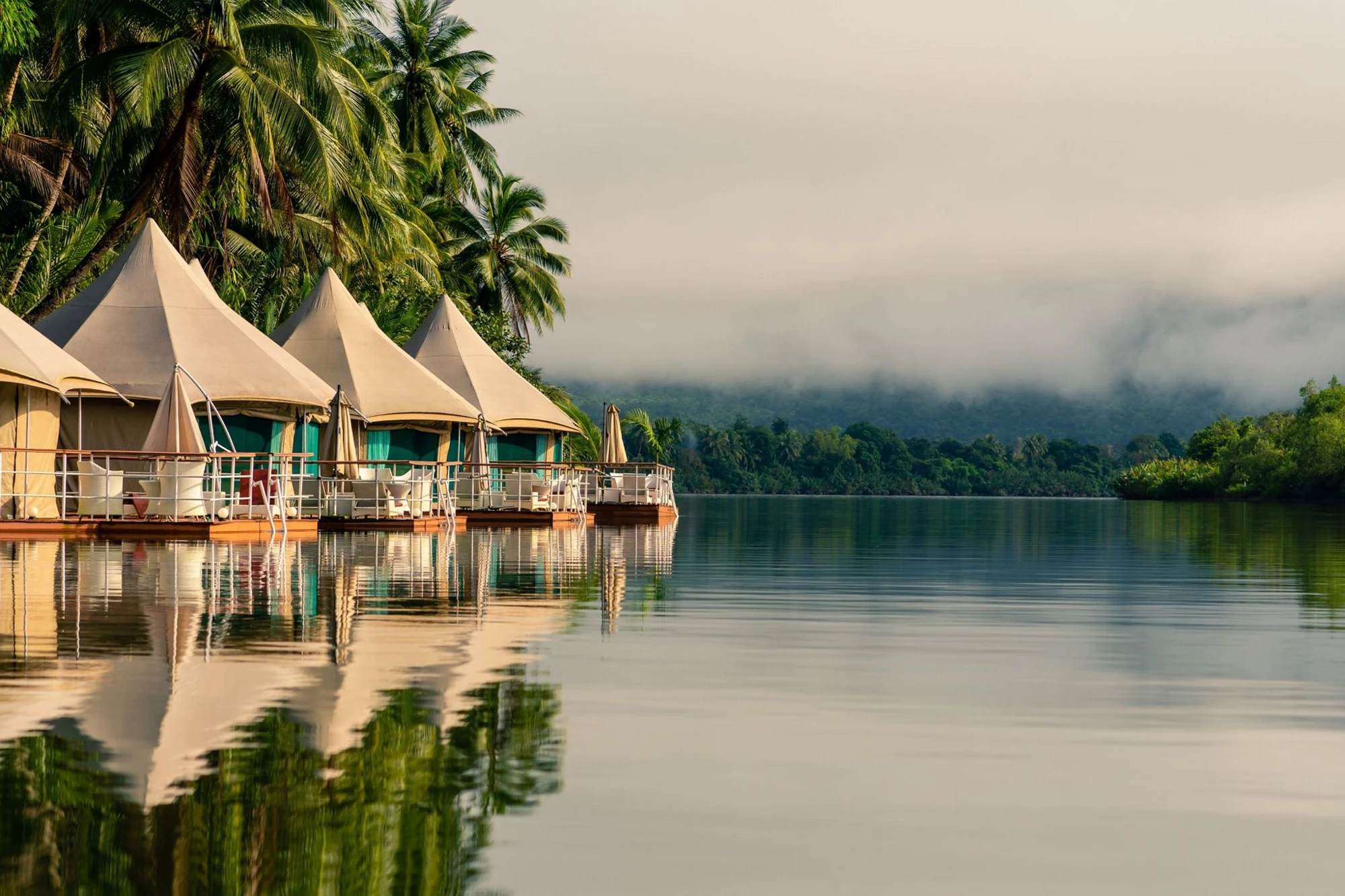

Iconic Cambodian landscapes, such as the Cardamom Mountains have a wealth of natural assets that allow for new and exciting multi-day tourism itineraries for domestic and international markets. In addition, the remoteness of Cambodia’s picturesque forested landscapes also entices the mid to high-end tourist market, who are looking to unwind and unplug.
Cambodia’s tourism industry is a key contributor to its economic growth. It provides a sizable contribution to Cambodia’s economy (21 percent of GDP in 2019) , which has been on the rise for the past ten years. The ecotourism sector was a notable part of this and, in recent years, was showing signs of even greater growth than the rest of the tourism industry.
A recent slowdown in the growth of tourism in Cambodia , however, points to a need to diversify the sector. Angkor Wat in Siem Reap has been the main attraction to Cambodia, and while the iconic temples still draw crowds, statistics show that growth in arrivals to Angkor sites is slowing. Experts suggest that the decelerated growth of tourist arrivals is due to fewer Chinese tourists visiting Siem Reap. Instead, these tourists are increasingly drawn to Cambodia’s coastal areas. Another reason is that higher competition from neighboring countries, especially Vietnam, is drawing Chinese and South Korean tourists away from Siem Reap.
Trends of increased visitors to ecotourism sites in Cambodia indicate that ecotourism is a product that could be further developed to harness its potential, and the Cambodian government wants to capitalize on this potential. Developing tourism can also create much-needed revenues to help manage Cambodia’s extensive protected area (PA) network and protect important economic services provided by forests in the PAs.
“Invest now in ecotourism development to: DIVERSIFY Cambodia’s tourism product with ecotourism offerings; CREATE jobs and STIMULATE rural economies; and PROTECT the forest assets that underpin ecotourism” is one of the main key messages that has been formulated in a newly released World Bank advisory report on Enabling Ecotourism Development in Cambodia ; a report which has been developed to support the Royal Government of Cambodia in the sustainable development of ecotourism. One of the main tenets promoted in the report is around investing and diversifying the country’s tourism, which is part of the Bank’s broader strategy for sustainable management of the country’s natural capital and strengthening its links to the economy.
COVID-19 is an additional reason for diversifying the country’s tourism offerings. “BUILD BACK BETTER after COVID-19 in the tourism sector by investing in ECOTOURISM” is another key message being promoted in the World Bank’s advisory report. As more people become unemployed due to the fallout of COVID-19, they are more likely to turn to illegal activities to supplement incomes, such as illegal wildlife trafficking and logging, and clearing forests for agriculture. The promotion of ecotourism development in Cambodia is, therefore, an essential element of Cambodia’s post-COVID-19 recovery strategy. It is also an essential ingredient that can pave the way towards the building back of a more resilient economy, which in turn can boost sustainable livelihoods and rural job creation for the Cambodian people.
In response to the need to diversify Cambodia’s tourism product and respond to the COVID-19 through the development of ecotourism, this new World Bank report provides five key recommendations each with strategic actions for:
- Mitigating the impacts of COVID-19 on the ecotourism industry.
- Strengthening regulatory frameworks for ecotourism.
- Strengthening key institutions and partnerships for ecotourism development.
- Strengthening ecotourism destination planning, management, and marketing.
- Enabling and supporting the private sector in tourism.
The World Bank will support the Royal Government of Cambodia on implementing these recommendations and developing its ecotourism sector through the Cambodia Sustainable Landscape and Ecotourism Project (CSLE) . The analytical work on ecotourism will also be expanded to Cambodia’s coastal areas with funding from the PROBLUE trust fund and will inform a regional approach for ecotourism development with funding from the PROGREEN trust fund .
- Environment
- East Asia and Pacific
- COVID-19 (coronavirus)

Senior Environmental Specialist

Junior Professional Officer

Senior Natural Resources Management Specialist
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
- Development Policy Centre
- Australian Aid Tracker
- Aid Profiles
- PNG Databases
- Publications

Navigating uncertainty: Cambodian tourism businesses and the pandemic

Streets crowded with tuk-tuks carrying visitors to Angkor Wat; bustling restaurants and bars; hotels and guesthouses pre-booked for the Water Festival – these scenes vanished when the COVID-19 pandemic stopped international and domestic tourists from visiting Cambodia’s sights.
Although the country’s public health situation was comparably unscathed throughout 2020 – Cambodia recorded only 331 active cases and no deaths by November 2020 – movement restrictions decreased household incomes by 30 to 60%. The situation escalated in 2021 when Cambodia went from a few cases to more than 60,000 by mid-July 2021.
Contributing over 70% of jobs and 58% of GDP in 2018, Cambodia’s micro-, small and medium-size enterprises (MSMEs) have been profoundly affected by the pandemic. The tourism industry, Cambodia’s second-largest driver of economic growth and where many MSMEs work, is especially in crisis. In 2019, tourism generated about US$4.9 billion, nearly 20% of the country’s GDP , while COVID-affected 2020 saw international tourism revenue plummet nearly 80%, to US$1.023 billion.
In 2020 and 2021, to understand the impact of COVID-19 on small businesses in the region, The Asia Foundation collaborated with local partners in carrying out multiple surveys of MSMEs in tourism, handicrafts, manufacturing and other industries across Cambodia, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Timor-Leste.
In July and November 2020 and in April 2021, we also surveyed registered and unregistered businesses in Cambodia’s tourism sector. The surveys indicated that 99% had been affected by the pandemic and lockdowns, with over 50% severely affected in April 2021. As COVID-19 restrictions were extended, the situation worsened: 54% of respondents reported cash flow problems in November 2020, increasing to 83% by April 2021.
The surveys revealed a link between national COVID-19 caseloads, perceptions around business survivability, and adaptation efforts. In Cambodia, a slight majority of surveyed businesses considered COVID-19 a threat to their operations in July and November 2020, when caseloads were low, but by April 2021 more than three-quarters of businesses viewed the pandemic as a serious threat.
In July 2020, 40% of Cambodian tourism businesses reported pandemic-related layoffs, while 60% had held steady. Only 16% reported letting staff go between July and November. Instead, many had decreased employee hours or were rotating hours to keep workers. However, by April 2021, facing greater restrictions and a worsening public health crisis, 33% of Cambodian tourism businesses reported having laid off employees – twice as many as in November.
Idled tourism workers sought any short-term work opportunities to make ends meet. In Siem Reap, the gateway to Angkor Wat and other attractions, many women – who were disproportionately affected by layoffs – left the city, hoping to find jobs in the garment industry in Phnom Penh. Unfortunately, COVID-19 containment measures caused the garment factories to close.
After the first lockdown in April 2020, street vendors, taxi drivers, and tuk-tuk drivers felt less affected by the pandemic because domestic tourism and daily life continued. However, as pandemic restrictions grew and activity declined, many male tuk-tuk drivers turned to construction work – only to see worksites close in April 2021 lockdowns, leaving some with only half that month’s salary in hand.
Many Cambodian tourism MSMEs were unable to adapt their business models to digital methods. Only 8% reported doing increased business online by April 2021. Some food-related businesses, such as restaurants and street vendors in Phnom Penh, generated income through online delivery platforms. However, online is not an option for tourism businesses that cannot offer takeout food or virtual services.
Since the crisis began, Southeast Asian governments have provided a range of packages to support businesses in weathering the pandemic. However, communication about assistance and how to access it has often been inadequate.
Cambodia has provided direct support, such as cash for laid-off workers, and indirect support, such as debt restructuring. Unregistered businesses do not currently qualify for support, yet they make up a large share of employers and workers.
Although Cambodia was relatively successful in disseminating information to registered businesses compared to other countries in the region, only about 50% of MSMEs surveyed had enrolled and received needed assistance. Some said they lacked information on the programs, especially process and eligibility details, while others found the application procedures difficult to navigate.
The initial optimism of many Southeast Asian MSMEs for a 2021 economic recovery has been dampened by the latest wave of COVID-19. Despite this, Cambodia may see a quicker return to normal due to one of the highest vaccination rates in the region.
Governments must prioritise vaccine rollout, and plan for an uncertain future, in order to mitigate the economic fallout of COVID-19 containment strategies. Financial assistance for MSMEs can help negate the worst of the effects and prolong business survival. But to be effective, coverage needs to include both registered and unregistered businesses.
Beyond existing support mechanisms, governments must provide targeted and tailored assistance for women, young people, and contract and informal workers – those most adversely affected by the economic fallout. A strong and inclusive economic recovery will require more than online access and minor business adaptations – it will demand greater attention to these differential dynamics, better communication and outreach to MSMEs, and larger safety nets while scaling up vaccination.
Read the Cambodia surveys . Read the latest GovAsia issue 1.3 about the impact of COVID-19 on MSMEs across Southeast Asia . Find individual country survey reports .
This post is part of a collaborative series with The Asia Foundation .

This article draws on research exploring the impacts of COVID-19 on Cambodian MSMEs in the tourism sector and households in Cambodia. The research was completed in partnership with Angkor Research and Consulting, Centre for Policy Studies, and Future Forum, and was funded under a partnership between The Asia Foundation’s United States Congressional Appropriation; Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT), Australia; and Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade (MFAT), New Zealand through the Ambassador Fund. The views expressed are those of the authors only.
Related posts:
- COVID-19 in Vietnam: holding our breath in wave four
- Fiji's new budget: significant fiscal challenges
- One-third of Pacific businesses doubt they will survive COVID-19
- Fiji’s next budget should focus on crisis mitigation and economic recovery
- COVID-19 takes hold in the Pacific

Men Pechet is a Program Manager in The Asia Foundation’s Cambodia Office.

Marly Augustine
Marly Augustine is a consultant with The Asia Foundation’s Governance, and Evaluation and Learning Units.
Leave a Comment X
Sign me up for the fortnightly newsletter!
Don't subscribe All new comments Replies to my comments Notify me of followup comments via e-mail. You can also subscribe without commenting.
Share on Mastodon
- ABOUT AQUARII
- MEET THE TEAM
- PARTNERSHIPS
- LIBRARY OF LAWS
- MARKET INFORMATION
- EVENTS & PUBLICATIONS
- BIZ-DIRECTORY
- CLASSIFIEDS
- Market Info
- Doing Business in Cambodia
State of the Tourism Industry in Cambodia in 2023: Opportunities and challenges
The tourism industry in Cambodia is one of the key drivers of its economy, accounting for approximately 12% of GDP and employing over 600,000 people pre-pandemic, of which 60 per cent were women ( source ). The country is home to a wealth of cultural and natural attractions, including the world-famous Angkor Wat temple complex, as well as stunning beaches, rainforests, and national parks.
Overall, the state of the tourism industry in Cambodia in 2023 is positive. The sector is recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic and is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. In recent analysis, we find Cambodia’s economic prospects to be quite promising, with a forecasted growth rate of 5.5% in 2023 and a further uptick to 6.0% in 2024. This growth trajectory is underpinned by several key factors, as highlighted in the report released by the Asian Development Bank (ADB). ( source )
However, the tourism industry in Cambodia and its key stakeholders could do more to diversify the industry and attract higher-spending tourists. In this article, we discuss the state of the tourism industry in Cambodia, as well as the opportunities and challenges facing the sector in the post-pandemic era. For more in-market information, view our business and investment resources here or contact us today.
What is the state of the tourism industry in Cambodia in 2023?
Jyotsana Varma, ADB Country Director for Cambodia, said that despite prevailing global economic challenges, Cambodia’s economy demonstrated resilience in 2022, primarily attributed to the ongoing recovery in the tourism sector. Varma points out that Cambodia’s economic outlook is favorable, characterized by robust growth, a narrowing current account deficit, and a controlled inflation rate projected at 3.0% in 2023 and 4.0% in 2024. ( source )
The Asian Development Outlook (ADO) for April 2023 underscores the pivotal role of the tourism sector, which is expected to grow by an impressive 7.3% in 2023, followed by a slightly moderated growth rate of 6.8% in 2024. To maintain this positive trajectory, the report emphasizes Cambodia’s commitment to increasing green investments, a strategic move aimed at unlocking long-term growth potential.
In reviewing Cambodia’s economic performance in 2022, the ADO report reveals an estimated growth rate of 5.2%. This growth was primarily driven by rising external demand for Cambodian products and tourism services. The revival of demand in sectors such as food, accommodation, local trade, transport, and communications contributed significantly to this growth. Notably, international visitor arrivals saw a remarkable rebound, surging from approximately 200,000 in 2021 to about 2.3 million in 2022 as travel confidence was restored. ( source )
However, it’s essential to acknowledge certain challenges and considerations. The report anticipates a deceleration in the growth of exports, particularly in the garment, footwear, and travel goods sectors, due to subdued external demand in key markets like the United States and Europe. Nevertheless, Cambodia’s industrial sector remains on a positive trajectory, thanks to policy reforms and trade agreements. Industrial output is expected to grow by 5.8% in 2023, accelerating to 7.8% in 2024.
Meanwhile, the construction sector’s growth is expected to remain relatively sluggish, while agriculture is projected to grow by 1.1% in 2023 and 1.2% in 2024, with a particular boost from crop production for exports.
What will be the challenges for the tourism industry in Cambodia in 2023?
In terms of potential risks, factors such as weaker growth in the United States and Europe, high levels of private debt, fluctuations in tourist arrivals and foreign direct investment, elevated energy prices, and potential disruptions in agriculture due to extreme weather events will play a big role in the future of the tourism industry in Cambodia in 2023 and beyond.
How can the tourism industry in Cambodia diversify its offerings?
As Cambodia strives to diversify and expand its tourism industry beyond the iconic Angkor Wat and the constraints of a short peak season, it can draw valuable insights from the experiences of neighboring countries in Southeast Asia. Let’s explore how regional success stories, such as Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, have diversified their tourism offerings and how Cambodia can apply similar strategies.
What lessons can the tourism industry in Cambodia learn from regional nations?
Looking beyond just the ‘honeypot’ of Angkor Wat, there are a number of lessons Cambodia can learn from its neighbors in the ASEAN.
With its vast archipelago, it has successfully diversified its tourism portfolio by promoting ecotourism and celebrating its rich cultural diversity. Cambodia can follow suit by highlighting and promoting its stunning natural landscapes, such as the Cardamom Mountains, Bokor National Park, and Ream National Park, as well as its diverse culture, museums, and traditional villages. Indonesia has also encouraged public-private partnerships to develop tourism infrastructure and services. Cambodia can collaborate with private enterprises to create new attractions, accommodations, and experiences. This collaboration can be incentivized through mechanisms like tax breaks.
Malaysia first began expanding its market by targeting niche markets such as medical tourism and culinary tourism. Cambodia can identify and develop niche markets that align with its strengths, such as wellness and spa tourism, adventure tourism in the Cardamom Mountains, or culinary tours showcasing its unique cuisine. Malaysia then promoted cultural festivals, such as Thaipusam and Hari Raya Aidilfitri, to attract tourists worldwide. Cambodia can promote its own cultural festivals and events, like the Water Festival or Bon Om Touk, as cultural attractions that draw visitors outside of peak season.
Thailand has successfully rebranded itself as a year-round destination, showcasing different regions and activities throughout the year. Cambodia can follow this approach by shedding the traditional peak season label and promoting activities suited for each season, as mentioned earlier. Furthermore, investing in infrastructure, like Thailand’s extensive network of airports, can improve accessibility to different parts of Cambodia. Thailand invests heavily in marketing campaigns that highlight its diverse attractions. Cambodia can allocate resources to robust marketing efforts showcasing its year-round appeal and unique offerings, much like Thailand’s successful campaigns.
Incorporating these strategies, Cambodia can diversify its tourism industry and extend its appeal beyond Angkor Wat and the traditional peak season. By embracing its natural beauty, cultural richness, and vibrant F&B scene, Cambodia can position itself as an all-year-round travel destination, stimulate economic growth, and provide opportunities for its people. Specific initiatives, such as promoting festivals, niche markets, and infrastructure development, can be instrumental in achieving this transformation. The lessons from its regional counterparts offer valuable guidance on Cambodia’s path to unlocking its tourism potential.
How much has the tourism industry in Cambodia grown?
The sector is only second to the garment sector with the largest number of women employed. In terms of hotels and accommodation, as of 2020, a total of 1,028 hotels provide 44,428 rooms residing in 25 provinces across Cambodia.13 Another accommodation type is the guesthouse, in which 2,755 units are divided into 35,791 rooms are available for tourists.14 As the tourism industry grows and demand for accommodation spike over the year, the number of hotels and guesthouses also increase. In 1998, there were only 216 hotels and 147 guesthouses. It shows a growth rate of 386 percent and 1.740 percent for hotels and guesthouses, respectively. ( source )
How has the tourism industry in Cambodia recovered following COVID-19?
The COVID-19 pandemic had a devastating impact on Cambodia’s tourism industry, with international visitor arrivals plummeting by over 90% in 2020. However, the sector has since begun to recover, with international arrivals reaching over 2.3 million in 2022, ( source ) an increase of over 1,000% from the previous year.
The recovery of Cambodia’s tourism industry is expected to continue in 2023, with the government forecasting international arrivals to reach 4.5 million. This growth is being driven by a number of factors, including the relaxation of travel restrictions, the increasing availability of flights to Cambodia, and the government’s ongoing promotion of the country as a tourist destination.
How has the government helped with the recovery of the tourism industry in Cambodia?
The government has taken proactive steps to initiate both short and long-term strategies aimed at revitalizing the tourism industry. These measures encompass a range of initiatives designed to support tourism-related businesses and bolster the sector’s overall resilience.
Among the measures implemented are tax and fee exemptions, along with financial support and loans extended to businesses operating in the tourism sector. Furthermore, there have been concerted efforts to facilitate vaccination campaigns for employees within the tourism industry and to enhance their capacity. Infrastructure development also forms a vital component of these recovery initiatives.
For example, a policy granting monthly tax exemptions to all hotels and guesthouses in Siem Reap was introduced in February 2020. This tax exemption policy, which specifically targets tourism-related accommodations, has been extended until March 2023, providing continued relief to the sector.
Additionally, in May 2022, the government launched the Tourism Recovery Co-financing Scheme (TRCS), amounting to $150 million. This financial support is derived from a $75 million contribution by the Royal Government of Cambodia (RGC), channeled through the Small and Medium Enterprise Bank of Cambodia (SME Bank), complemented by an equal $75 million contribution from Participating Financial Institutions (PFIs). Under this scheme, enterprises in the tourism sector impacted by the COVID-19 crisis have the opportunity to apply for loans from select financial institutions partnering with SME Bank. These loans come with concessional interest rates, further aiding the sector’s recovery.
The government is also investing in tourism infrastructure, such as roads, airports, and hotels. This investment is helping to make Cambodia more accessible and attractive to tourists. For example, the government is currently constructing a new international airport in Siem Reap, the gateway to Angkor Wat ( read more )
To provide a structured framework for the revival of Cambodia’s tourism, the government has devised the Roadmap for Recovery of Cambodia Tourism during and post COVID-19. This roadmap serves as a comprehensive guide, with the overarching objectives of fortifying the tourism sector in the aftermath of the pandemic, mitigating adverse effects, and establishing Cambodia as a secure and appealing destination in the post-pandemic era.
The roadmap unfolds in three distinct phases:
- Phase 1: Crisis Management in the New Normal Phase and Planning for Recovery (2020-2021): During this initial phase, the focus was on navigating the challenges posed by the pandemic and laying the groundwork for future recovery efforts.
- Phase 2: Recovery of the Tourism Sector in Cambodia in the Post-COVID (2022-2023): This phase, currently underway, is dedicated to the active rejuvenation of Cambodia’s tourism sector, aiming for a robust and sustainable revival.
- Phase 3: Preparation for the New Future of the Tourism Sector in Cambodia (2024-2025): In this final phase, the emphasis will be on future-proofing the tourism industry, ensuring its resilience, and positioning it for long-term growth and success.
These phases collectively form a strategic roadmap that guides Cambodia’s efforts to revitalize its tourism industry, adapting to the evolving landscape shaped by the challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic.
What is the government planning for the future of the tourism industry in Cambodia?
The Ministry of Tourism (MoT) has launched a new strategic initiative titled ‘Uniting for a Collective Vision,’ with the goal of elevating Cambodia’s global standing as a premier tourism destination.
Minister of Tourism Sok Soken articulated that this strategic endeavor aims to streamline and amplify efforts toward transforming Cambodia into a globally competitive, sustainable, and inclusive tourist destination. ( source ).
Soken emphasized that adopting a shared language and mindset to plan, execute, and monitor this initiative will yield five significant advantages.
Firstly, it fosters ‘clarity of purpose,’ ensuring comprehensive comprehension of the strategy’s essence, objectives, and action plan across all ministries. Secondly, it promotes ‘unified decision-making’ by employing a common language, leading to more efficient and effective decision-making processes grounded in a unified analytical framework.
Thirdly, it encourages ‘strengthened collaboration’ by establishing a platform for open dialogue and robust feedback, harnessing collective expertise and diverse perspectives within the ministry. Fourthly, it focuses on ‘trust-building,’ as shared language and information cultivate a sense of trust and alignment, enabling the team to rely on one another and enhance overall work performance.
Lastly, it targets the ‘synchronization of projects and activities,’ optimizing resource allocation, minimizing redundancy, and ensuring that endeavors complement each other.
How is the tourism industry in Cambodia developing in 2023?
While Cambodia’s tourism industry is recovering, there is still room for improvement. One of the key challenges facing the tourism industry in Cambodia is the need to diversify its offerings. Currently, the majority of tourists to Cambodia visit Angkor Wat and other cultural attractions. However, the country has much more to offer, including beaches, rainforests, and national parks.
The Cambodian government is working to promote these new tourism destinations, but more needs to be done to make them more accessible and attractive to tourists. For example, the government could invest in developing new infrastructure and tourist facilities in these areas.
Another challenge facing Cambodia’s tourism industry is the need to attract higher-spending tourists. Currently, the majority of tourists to Cambodia are budget travelers. However, the country has the potential to attract more high-end tourists by developing luxury resorts and spas, as well as offering more unique and experiential activities.
How can the tourism industry in Cambodia better capitalize on new tourism trends?
There are a number of ways in which the tourism industry in Cambodia could better capitalize on opportunities. Some of these are:
- Focus on sustainable tourism. Sustainable tourism is a growing trend, with more and more travelers looking for ways to reduce their environmental impact. Cambodia can capitalize on this trend by developing sustainable tourism products and services, such as eco-lodges and community-based tourism programs.
- Promote Cambodia’s unique culture and heritage. Cambodia has a rich and unique culture and heritage, which can be a major draw for tourists. The tourism industry in Cambodia could do more to center the tourism industry in Cambodia around this culture and heritage through marketing campaigns and international events.
- Develop new and innovative tourism products and experiences. Cambodia needs to develop new and innovative tourism products and experiences to attract more visitors and keep them coming back for more. For example, there could be further development of new hiking trails in national parks, or create new cultural festivals.
- Improve tourism infrastructure and services. Cambodia could improve its tourism infrastructure and services to make it easier and more enjoyable for tourists to visit the country. For example, more investment could be channeled into developing better roads and transportation networks, and improving the quality of hotels and restaurants.
- Target specific tourist markets. Cambodia needs to target specific tourist markets with its marketing campaigns. For example, the tourism industry in Cambodia could target high-end tourists by developing luxury resorts and spas, or target eco-tourists by promoting sustainable tourism products and services.

OUR PREFERRED PARTNERS

SHORTCUTS
- Business Directory
- Classifieds
WORK WITH US
- Partnerships
- Career Opportunities
- Internship Application
HAVE A QUESTION?
- [email protected]
- +855 (0) 85 32 11 21
"Connecting Businesses, Creating Opportunities and Growing Partnerships"
@2023 aquarii. all rights reserved. use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms of service and privacy policy ., thank you for requesting the report.
Please download The report here!
In Business
Transforming the future of work with soft skills
Factory Improvement Toolset (FIT)
Upgrading factories through a sustainable, scalable approach
Community-Based Enterprise Development (C-BED)
Supporting vulnerable and marginalized communities
Ready for Business (R4B)
Enabling youth entrepreneurs

Small Business Competitiveness Programme (SBC)
Supporting micro and small tourism entrepreneurs
Growing the cooperative movement
Access to requires approval from the ILO and your national employer organization. Please request access and we will be in touch shortly with further information.
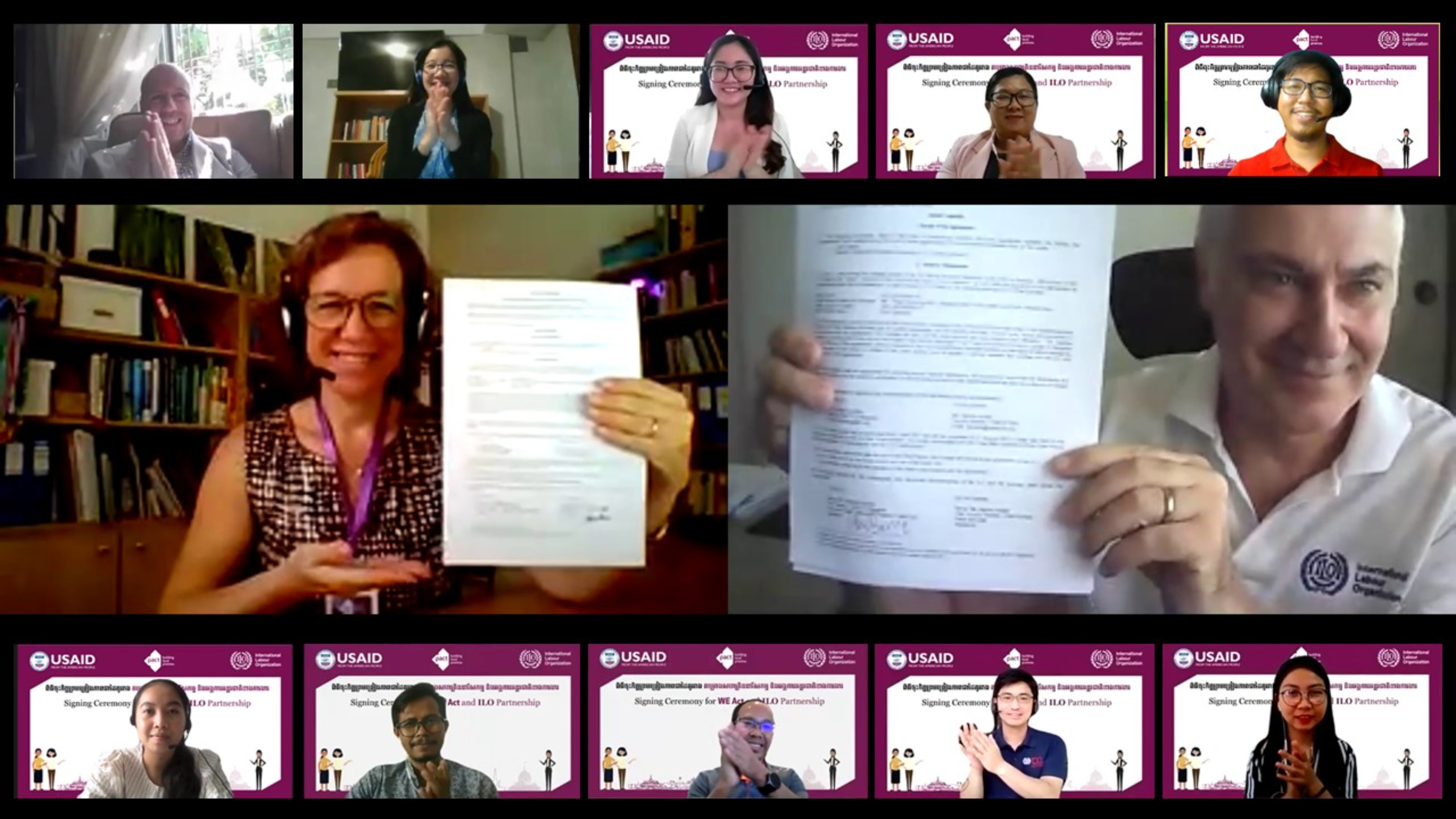
Building a stronger and more sustainable tourism sector in Cambodia
The COVID-19 pandemic has halted the tourism industry in Cambodia. The ILO and Cambodia’s Ministry of Tourism are collaborating on entrepreneurship trainings in order to recover sustainably, improve working conditions and build back better.

On 25th to 27th of January 2021, the ILO and Cambodia’s Ministry of Tourism (MoT) organized a three-day training for facilitators on entrepreneurship in the tourism sector. The training on the ‘Methodology of Training on Entrepreneurship in the Tourism Sector’ brought together 45 participants (15 females) who learned key business and entrepreneurial skills to build back the industry.
Due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and travel restrictions, Cambodia’s tourism sector has been heavily impacted. Strengthening the capacity and conditions of SMEs in the industry is crucial for sustainable recovery as the ministry looks to restart tourism after the crisis. The training, held in Phnom Penh, taught ILO’s Community-Based Enterprise Development (C-BED) programme, an innovative business development project for aspiring entrepreneurs in underserved communities. The peer-learning programme teaches critical steps to build and develop a business, as well as strengthening decision-making, planning and finances. The activity-based learning methods of training builds on the experience of fellow participants which ensures flexibility to the evolving needs of industry and workers during difficult times.
Participants learned how to facilitate their own sessions and pass on vital entrepreneurial skills to the wider tourism community. By expanding the quantity and quality of professional entrepreneurial skills in the industry, the tourism sector can recover and become more resilient in the future.

MoT and ILO acknowledged this training was aligned with and contributed to achieving the Strategic Plan for Tourism Human Resource Development 2017-2025, especially the Strategic Plan for Restarting Tourism 2021-2025. The participants of this training programme will deliver practical skills and knowledge to tourism business operators in different provinces with using the new training method of activity-based learning. MoT and ILO will continue working together to sustainably improve entrepreneurship in the tourism sector along with the ongoing direction and action plan for future.
This activity was supported by the Decent Employment for Youth in Cambodia programme, which is a UN joint programme primarily funded by Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), as well as the ILO/Japan Fund for Building Social Safety Nets in Asia and the Pacific (SSN Fund).
To learn more about C-BED and activity-based learning, click here .
More updates

Cambodia boosts youth entrepreneurship through vocational trainings
The ILO and Pact Cambodia collaborate on entrepreneurship and soft skills for 1,500 Cambodian youth and women
Equipping online facilitation skills to better support MSMEs during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic
- Media OutReach News
- Business Startup
- Banking & Finance
- Construction & Maintenance
- Hospitality & Tourism
- IT & Communications
- Legal & Accounting
- Marketing & Media
- Medical & Pharmaceutical
- People & Skills
- Property & Accommodation
- Safety, Security & Insurance
- Transportation & Logistics
- Business Chambers & Associations
- Embassies & Consulates
- Government Ministries
- Starting a Business in Cambodia
- Banking & Finance in Cambodia
- Construction & Maintenance in Cambodia
Hospitality & Tourism in Cambodia
- IT & Communications in Cambodia
- Legal & Accounting in Cambodia
- Marketing, Media & Advertising in Cambodia
- Medical & Pharmaceutical in Cambodia
- People & Skills in Cambodia
- Education in Cambodia
- Property & Accommodation in Cambodia
- Cambodian Safety, Security & Insurance
- Cambodian Transportation & Logistics
- Cambodia’s Major Industries
- Business Chambers & Associations in Cambodia
- Infrastructure & Utilities in Cambodia
- Business Networking in Cambodia
- NGO’s in Cambodia
- Royal Government Ministries in Cambodia
- Doing business outside Phnom Penh
- Business Profiles
- Cambodia Properties

TAX UPDATE: Annual Tax And Accounting Compliance Obligations – With DFDL

Artificial Intelligence And The Future Of Bancassurance In Cambodia

Panel Discussion On Tax, Accounting And Auditing In Cambodia’s Food Industry

Bancassurance In Cambodia – AmCham Workshop 2024
New airline about to take off, obtaining a work permit in cambodia, how to obtain cambodian citizenship, media outreach, new blood bank looks to stock up for national needs, cambodia tourism: hospitality & tourism in cambodia.
If you are looking at taking a holiday in Cambodia and visiting for business or pleasure, or maybe you are looking to join the burgeoning tourism industry, then this guide covers all your bases for the hospitality and tourism industry in Cambodia.
We have pulled together a summary of tourism industry tips in Cambodia and the various facilities available to an individual and corporate users, plus information relating to travelling into and around the country.
If you can’t find your answer here, just ask us at B2B and we’ll point you in the right direction.
Updated May 2020
How important is tourism to Cambodia?
- Prime Minister Hun Sen announced that Cambodia attracted 4.5 million tourists over the course of 2014 at the opening of the World Conference on Tourism and Culture. He added at the time “The projection for 2020 is 7.5 million inbound tourists that generate $5 billion in terms of revenues and 80,000 jobs. In addition, Cambodia’s tourism campaign of “Cambodia: Kingdom of Wonder” and the competition movement of “Clean City, Clean Resort, Good Service” has greatly helped promote Cambodia’s prestige in the region and in the world.
- Tourism statistics show that Cambodia has seen an increase in tourism every year from 2013-2019. Data shows the total number of tourists to the Kingdom as 2016 (5,011,712), 2017 (5,602,157), 2018 (6,201,077), 2019* (6.7 million* estimated).
- In 2019, Cambodia earned around $4.91 billion from international tourism.
- Siem Reap and Angkor Wat have repeatedly won international travel and destination awards.
- The coast of Cambodia has seen rapid growth and development along Sihanoukville, Kep, Kampot and on the islands.
- All key regional hubs have tourism development and strategic plans in place or in the process of being drawn up, which include the identification of tourist attractions, improving infrastructure and access.
- Current airports, roads and seaports are seeing enhancements and new facilities are being built to attract more domestic, regional and international tourists.
When are Cambodia’s tourism seasons?
- Tourism in Cambodia is seasonal with the “high season” running from November to March when it’s dry and there is relatively cooler weather.
- July and August are also popular with Western tourists because of the school summer holidays while June and September are traditionally the quietest months.
- If you are setting up a tourist-reliant business make sure you factor in the low season and the lack of income impact into your business plan.
- The low season is being marketed by some vendors as “green season” and doesn’t appear to scare away regional Asian travelers as much as some might first suspect.
- The number of public holidays in the Kingdom of Cambodia is high, although these were reduced in 2020, they still have an impact on business operations and travel and some regions are inundated with local visitors for specific holidays like Khmer New Year (April), and Water Festival (October).
What are the tourism trends taking place in the Kingdom of Cambodia?
- Cambodia benefits from being part of the Indochina/Southeast Asia circuit—an enticing set of affordable destinations for many contemporary explorers.
- Yet, due to this, short stays have been the norm in Cambodian tourism, as visitors tend to cram as many neighbouring countries as possible into a few weeks of yearly vacation time.
- Furthermore, reliance on regional tourism infrastructure has a direct impact on Cambodian tourism as when the surrounding region is unsettled, such as during the Thai coup or Vietnamese anti-Chinese riots in 2014, or from pandemics, Cambodian tourism is adversely affected, regardless of whether or not regional events have any actual ramifications on the country.
- There has been an increase in the number of direct long-haul flights coming into Cambodia from worldwide destinations since 2018 as well as connecting flights to regional hubs.
- Cambodia has decreased its reliance on transfers from nearby regional hubs, such as Bangkok, Ho Chi Minh, Singapore, Kuala Lumpur and Hong Kong but these are still vital to tourism.
- As more direct long-haul flights increase, this problem will lessen and the airports are seeing upgrades to allow for larger capacities and longer runways to accept long haul flights from larger aircraft.
- Tourism continues to increase and is spreading further afield than the traditional tourist hotspots of Siem Reap, Phnom Penh and the coast.
- The private sector — through mechanisms like the Cambodia Tourism Federation — is finding platforms to better advertise some of the diversity of Cambodia as a destination.
- The private sector and the Ministry of Tourism jointly try and organise a calendar of yearly events (such as festivals, fairs and exhibitions) that will help to further promote Cambodia with both tourists and business people alike.
- Visitors to Kampot, Kep and Battambang are also seeing a rise.
- Cruise trip services, and water-based expeditions and golf tourism are also increasing as is eco-tourism.
Which demographic makes up the majority of tourists to Cambodia?
- Cambodia’s hospitality and tourism industry has already moved from focusing on only backpackers and expanded their target market on other visitors. There has been a significant increase in middle income and upper-income visitors, especially families, to visit Cambodia.
- Visitors from America, the UK, Europe and Australia continue to steadily flow into Cambodia. However, the largest group of visitors have been from China and there has been a boom in Asian tourists.
- The strongest Asian tourist arrivals to Cambodia are the Chinese, the Vietnamese, Laotians, South Koreans, Malaysians and the Japanese.
- The biggest group of non-Asian tourists are from the USA, UK, and France.
- The recent boom in Asian mass tourism is sometimes misleading in terms of the Cambodian tourism industry’s development though – as it doesn’t encourage trickle-down wealth to the local market, as generally expected from responsible tourism growth.
- Inter-Asian tourism agencies often create their own tourism infrastructure inside Cambodia – limiting the flow of wealth to the local market.
- Chinese tour groups, for instance, generally take Chinese owned and operated chartered tours, stay at Chinese owned or endorsed hotels, eat at Chinese restaurants, and gamble at Chinese endorsed casinos.
- This means the local economy doesn’t benefit to the extent it does with a more independent traveller.
Where does Cambodia’s future in tourism lie?
- With the integration of ASEAN, it has been predicted Cambodia will increasingly become used as a business destination.
- The adoption of the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) blueprint and the ASEAN Training Standards are improving the tourism industry.
- Cheaper and better conference facilities in the main Cambodian cities, and an increasing number of direct flights from international business hubs, including Singapore and Hong Kong, add to this trend.
- Improvements in making visas available online and improving digital frameworks allow tourists to more easily visit Cambodia.
- The Cambodia Tourism Marketing Strategy 2015-2020 report projected there would be 7.5 million foreign visitors annually by 2020 with forecasts suggesting up to 15 million arrivals in 2030, bringing in an estimated $10 billion and creating up to 2 million jobs.
- The Cambodian government is trying to tackle zero-dollar tourism.
What affects will Cambodia’s entry into ASEAN have on tourism?
- The ten ASEAN countries (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) all have different visa policies but the implementation of the visa for ASEAN will make travel easier.
- People will be able to move freely around the region, meaning there is open immigration for workers.
- This is likely to increase competition for labour more so than already exists, and drive up costs of hiring and retaining tourism professionals within Cambodia.
How is tourism changing in Cambodia?
- Tourism has rapidly changed in Cambodia with the influx of visitors contributing greatly to the changing face of the country.
- The number of tourism industry competitors is increasing at a rapid rate, but this may be a good thing.
- It means businesses must set their own benchmarks; improve their design, create events, and increase visibility, continually.
- Investing in branding and finding a unique selling point that sets you apart from the rest are two elements that will help you to succeed in hospitality in Cambodia. It is important to remain adaptable, and open to changing trends.
- Phnom Penh’s boutique hotel boom is a great example of popular and recent diversification in the midrange hospitality market.
- Boutique hotels priced between $50 and $120 a night are widely available in Phnom Penh (and Siem Reap), and typically offer a more personal service than the major brands.
- Demand has changed, and continues to change, with tourists expecting a wider range of experiences and standards of service.
- High-end resorts and luxury hotels are more frequent across the country including in the jungles, on the islands and in the major cities which have also seen more international hotel brands enter the Cambodian market.
Is there a shortage of skilled tourism professionals in Cambodia?
- As the tourism industry in Cambodia continues to expand, the supply of experienced, talented staff struggles to keep pace with growing demand, however the government and corporate initiative to train professional tourism staff are trying to address this.
- This remains true despite the existence of several high-end and mid-range training schools training tourism professionals in Cambodia.
- Additionally, the hospitality industry faces competition from growing sectors such as banking, sales and , digital and telecommunications where service-oriented staff are in high demand, and where these companies are able to afford higher salaries as incentives to staff.
- Staff poaching in the tourism and hospitality industry is rife in Cambodia, as it is elsewhere in the region. This will only increase with the conglomeration of ASEAN labour markets.
- For business owners, dealing with this problem is not just about remuneration, it’s also about selection, training and development; offering staff incentives and a clear career path and promotions.
- In the hospitality industry you need to be very proactive in retaining and developing talent.
- The Cambodian government announced in 2019 its intention to grow the workforce in the tourism industry to 1 million people, with the estimates at the time being 800,000 people employed in the sector.
- Since 2016, more Cambodian hospitality and tourism companies have been seeking ASEAN’s Mutual Recognition Arrangement on Tourism Professionals, which sets out guidelines for how to train and evaluate staff.
How is the internet impacting tourism in Cambodia?
- The rapid ascent of Cambodia’s inbound tourism market coincided with a staggering increase in the rate of internet use and travel apps available.
- The frequent use and reliance on Facebook and other social networking platforms and travel sites such as TripAdvisor, Airbnb, travel booking sites etc means Cambodia receives free tourism promotional material which is spread across these online channels.
- This can be a double-edged sword, with the potential for unmoderated criticism to be widely spread also.
- Businesses operating in the tourism and hospitality industry need to monitor social media, and make use of digital trends in their industries.
- As long as services are well-rated, even the smallest bed and breakfast can compete in free advertising online.
- Click-through booking websites also put power into the consumer’s hands.
- The largest of these sites, agoda.com and booking.com, now link to thousands of hotels in Cambodia.
- Do due diligence into the costs as these online systems and tools can charge between 10 and 20% commission – add to that a 2.5% credit card charge and 10% VAT and it soon adds up.
What software solutions are available in the Cambodian tourism industry?
- Software solutions catering to the hospitality industry can also be a big help to those setting up in Cambodia.
- Information systems allow data from different elements of the company, such as front-end, back-office and restaurant to be compiled and analysed.
- Other features include inventory control, reservations, guest comments, and room vacancy.
- International hotel management software and reservation systems are relatively borderless and can be implemented in Cambodia.
Tourism Top Tips: Cambodia
Here we call on experts in Cambodia to share what they have learnt about being a success in Cambodia’s fiercely competitive hospitality and tourism sector.
Make sure you take time to plan ahead
- Gone are the days when all it took was hiring a small shop house, putting a few rattan chairs outside and a noticeboard with a name outside to make a few bucks.
- Cambodia has evolved and the capital (Phnom Penh) and other urban areas now offer a wealth of choices for the diverse wealth of tourists that today visit the country.
- However, many foreign investors still fail to acknowledge the need to carry out strategic planning to survive in this over-saturated market.
- Many tourism and hospitality services go bankrupt in Cambodia before they open because they underestimate what you have to do in Cambodia to make things work.
- Demand has changed and tourists expect more from their experiences visiting Cambodia.
Stand out from the crowd
- Competition is fierce in Cambodia and now you have to be innovative and do something different to make yourself stand out from the crowd.
- Investing in branding and finding a unique selling point that sets you apart from the rest are two elements that will help in hospitality.
- There’s no easy money, including in Cambodia. If you have a good idea, are prepared to work like crazy and have enough cash to invest in the business – only then can you succeed.
- While succeeding in Phnom Penh, is easier than say Europe, people still misjudge it and think it’s even easier here than it is.
Always play fair
- A large pool of skilled hospitality workers are lacking despite several high-end training schools so recruiting and retaining good staff is vital.
- Easy ways to achieve these are to pay a fair salary, take time hiring the correct person and then training them.
- Continued training is essential and incentives also offer benefits to employees, such as health insurance and social activities.
Be prepared for some challenges
- Cambodia’s reliance on the region has a direct impact on tourism.
- Being part of a larger trip to Indochina means when the surrounding region is unsettled, such as a pandemic or a coup, it also affects Cambodia.
- This impact is regardless of whether or not it has any ramifications on Cambodia itself, although as we said- more direct flights to Cambodia and the types of tourists are changing.
- Don’t underestimate the actual cost involved to set up a venture in Cambodia and the time that it will take to start making a respectable profit.
Accommodation and facilities available in Cambodia
No matter how you like to travel, Cambodia will always have a place to cater for your needs; from $5 backpackers beds to $2000 a night 5-star luxury resorts.
Increasingly too, the Kingdom of Cambodia is offering facilities for corporate events and business travellers.
What type of accommodation is available in Cambodia?
- Phnom Penh and Siem Reap have the largest variety of hotels and guesthouses and are each home to a range of internationally branded hotels such as Raffles, Le Méridien, Sofitel and Rosewood.
- Luxury Hotels in Cambodia has been selected in the much anticipated Condé Nast Traveler’s Readers Choice Awards.
- New international hotel brands, including well known and premium luxury brands, continue to expand into Cambodia eg: Shangri-La, Rosewood, Hilton etc.
- Many hotels, particularly in Phnom Penh, target the business market and provide additional services such as business lounges, meeting facilities and secretarial assistance.
- Internet access is improving continuously and the majority of hotels, as well as restaurants and cafés, offer free Wi-Fi services.
- The breadth and quality of services vary considerably as some areas of Cambodia, such as Siem Reap and coastal areas, have developed more quickly than others.
- In many cases, good rates can be secured via online booking sites such, although booking directly through a hotel can still be the cheapest option and asking for discounts is not uncommon.
- Boutique hotels priced between US$30 and US$120 a night are widely available in Phnom Penh and Siem Reap, and on the coast and typically offer a more personal service than the major brands.
- Accommodation in Cambodia is cheap in comparison to many of its neighbours, especially Hong Kong and Singapore and even Thailand.
- By comparison, a decent guesthouse in Cambodia can cost between $15 and $20 a night.
- Sihanoukville has some upscale hotels, but the city has changed rapidly. Elsewhere in the country, hotel facilities have a great range and higher-end resorts in areas such as Kompong Thom, Koh Kong, Kep and even on top of Bokor Mountain in Kampot Province are available.
- The average quality of service across the hospitality industry in Cambodia is evolving and at high-end resorts and hotels, it can be world-class.
- A massive number of restaurants and cafes open up every year in Phnom Penh alone. It’s fiercely competitive in an industry that works on very little profit with ever-increasing running costs.
Are corporate facilities available in Cambodia?
- The rapid growth of the Cambodian tourism market in recent years has not failed to catch the attention of international companies seeking a destination for MICE (Meetings, Incentive trips, Conferences and Events).
- Many tour operators in Cambodia now arrange MICE trips and events, usually receiving clients through travel companies or organisers based in clients’ home countries.
- Seminars, conventions, exhibitions, incentive trips and reward vacations, all help boost Cambodia as a place where business people come for more than just the scenery.
- Phnom Penh’s Diamond Island Convention Center and Angkor CoEX in Siem Reap each has the capacity for Conventions and Exhibitions.
- International chains such as Raffles and Sofitel are present in both Phnom Penh and Siem Reap and offer exclusive MICE inclusive packages.
- The third MICE-ready locale in Cambodia is Sihanoukville, with large international-standard hotels available and under construction as the city landscape is changing fast.
What sort of tour companies exist in Cambodia?
- Tour companies and guides, of which there are many, range considerably in price, quality, languages and services offered.
- Many upscale overseas tour operators now offer itineraries in Cambodia, teaming up with local ground operators to provide high-quality tours for discerning customers.
- Higher-end tours provide unique room and board as well as adventures and exotic methods of transportation such as taking an ATV through the jungle.
- Off-road motorcycle and mountain bike trips, ranging from a couple of days or longer, are offered by several operators.
- Eco-tourism and adventure tourism is becoming an increasingly popular speciality.
- The temples of Angkor are still the biggest attraction and visitors will often add a few days in Phnom Penh or at the beach.
- Ongoing improvements to road networks have significantly reduced travel times and the once remote areas such as Mondulkiri and Ratanakiri are now finding their way onto several tour operators’ maps.
Is it easy to travel around Cambodia?
- The most common means of transport for short distances and (especially for Cambodian people) is the moto or motodop, known in English as a moped.
- Other forms of inner-city transport include Cambodian remorque tuk-tuks, which are carriages pulled by a moto, and traditional cyclos which are three-wheeled bicycles with a passenger seat at the front. Since around 2018 smaller, often electric, tuk-tuks from elsewhere in Asia have become more common.
- Cyclos are rarely seen outside Phnom Penh and, with their numbers in decline, are now used mainly by tourists and the elderly.
- Prices vary for motos and tuk-tuks depending on the number of passengers, distance travelled, destination and time of day, with short moto trips costing from around 3000 Riel (US$0.75).
- Taxis are becoming more common in urban centres and can be cheaper than taking a tuk-tuk or moto.
- Metered taxi firms do operate in Phnom Penh and other major cities.
- Taxis (corporate and private) are also frequently used for cross-country travel and can be quite affordable especially if you are travelling in a group.
- Buses and minibuses are a common means of transport between cities. Larger coaches travel between the major urban centres while more remote locations are generally serviced by smaller minibuses. Minibuses can be found at Phnom Penh’s larger markets.
- The rail system is being rehabilitated, with a few sections of track in operation between Phnom Penh, Kampot and Sihanoukville as well as between Phnom Penh towards Poipet for passengers and used to haul freight. There are plans to build on this and connect to Thailand.
- Passenger boats operate between Phnom Penh and Siem Reap but are fairly expensive in comparison to the bus. Within Phnom Penh, boat taxi services were also introduced in 2019. Ferries are used for river crossings.
- Ridesharing apps have become more dominant in Cambodia since 2017. Initially Uber (since bought out by Grab), PassApp, WeGo and more all compete and have transformed how people commute.
Airport Essentials in Cambodia
Cambodia has three operational international airports in 2020: Phnom Penh, Siem Reap and Sihanoukville. There are several more regional and private airports across Cambodia but the entire airport network is undergoing improvements and new airports are being constructed.
What is new in the Cambodian air travel sector?
- In a bid to boost tourism and cater for the ever-increasing number of visitors to the country, the Phnom Penh and Siem Reap international airports were initially upgraded in 2014 and have seen more since. The development saw an extension of parking lots and terminals, including more check-in and immigration counters and new baggage handling systems.
- In 2018, the three international airports, for the first time, hit a milestone of 10 million passengers.
- Sihanoukville Airport also has undergone improvements and the runway is being extended in 2020. In addition, the facilities improved and the airport’s capacity has been increased.
- Airline offices are commonly found in downtown Phnom Penh and Siem Reap, or at the airports themselves. The actual services available at each office will vary – keep in mind too that customer service lines are not always open in Cambodia, staff may not always speak English and consequently, calls may need to be made to Singapore, Malaysia or Thailand for international airlines.
- A local travel agent will usually be able to help if the airline is unresponsive.
- Cambodia Angkor Air is the national flag carrier. However, a number of new Cambodian-based airlines (often with Chinese backing) have opened up since 2017. These include JC Airlines, Lanmei Airlines, and Cambodia Airways.
- Tourism and hospitality are regulated by the Ministry of Tourism and the Ministry of Economics and Finance.
- There are two industry associations operating in Cambodia: the Cambodia Restaurant Association and the Cambodia Hotel Association. They represent the industry to the government.
- New airports are being constructed, with a new Phnom Penh Airport starting its 1st phase in 2019 (expected to be completed by July 2022), the Dara Sakor International Airport is being built in the southwestern province of Koh Kong (due for 2023) and the new Siem Reap airport is also due in 2023 with more regional hubs being investigated.
Can I get a Cambodian Visa at the airport?
- Visitors to Cambodia can get a visa on arrival at the airports, simply by filling in a form, providing two passport photos and paying the requisite fee.
- A basic tourist visa (Type “T” – Strictly non-working visa) and is valid for a month and can be extended for one more month. As of October 2014, you can now apply online for a tourist evisa: www.evisa.gov.kh
- The Cambodian Foreign ministry warns visitors of the many fraudulent visa websites as: cambodiaevisa.com, welovecambodia.com, evisacambodia.com, cambodiaonarrival.com, eVisa-Cambodia.com etc.
- Business visas, which are now referred to as an ordinary visa (E class), can be extended indefinitely by up to one year at a time without any requirement to leave the country. The visas for travelling and working do change so its best to check before booking.
- Having a job or a business is not required to obtain a business visa, however, should one wish to change from a tourist visa to a business visa they must first leave and then re-enter the country. Other changes were also added in 2017. You can find out more here or contact your embassy or the Cambodian Department of Immigration.
- The new FPCS was enforced in 2020, and Foreigners must register on the FPCS (Foreigners Present in Cambodia System) for visa extensions and as tourists.
Where can I find flight schedules to and from Cambodia?
- Most flights arriving into, or departing from, Cambodia operate during the working day, though there are also several late evening departures to countries such as Japan, Korea and China.
- There are dozens of airlines operating flights to Cambodia including regional operators such as AirAsia, Bangkok Airways, Silk Air, and international airlines such as Thai Airways International, Emirates and Qatar Airways.
- Flight schedules can be found on airline websites and Cambodia Airport’s website .
Am I liable for any tax or customs excise when entering Cambodia?
- Upon arrival in Cambodia, travellers must fill in a customs declaration form and submit it to the customs official.
- In cases where self-selection routes are operated, passengers have the option of making their customs declaration in either the Red Channel or the Green (nothing to declare).
- Outbound passengers should note that the export of antiquities requires a permit from the Ministry of Culture and Fine Arts as well as an export permit from the General Department of Customs and Excise.
What do I need to think about when I start a new business in the industry?
- Do a feasibility study : Dozens of restaurants close every year in the capital of Phnom Penh due to a lack of long term planning.
- Pick concept and target market carefully : Look at your prospective market and target your business very specifically.
- Choose the location carefully : In hospitality and tourism, location is key. Based on your concept and target market, choose the location that’s right for you.
- Plan projected budget meticulously : Make sure registration and legal fees are factored in. Add an extra 15% of leeway into your projected amount of capital and time.
- Prepare for growth: The hospitality and tourism market is poised for enormous growth in the near future. If you don’t prepare for growth, you risk your competitors overtaking you.
- Account for seasonality : From March to June you can expect a significant drop in the number of visitors to the country. Account for this in your business plan.
How do I apply for a tourism vendor licence in Cambodia?
- The Ministry of Tourism launched a new online system in April 2015 for the registration of tourism-related businesses and tour guides.
- The intention of the new process is to increase the efficiencies of the licence inspection process and increase government revenues through compliance.
- To aid tax collection and accountability, each business will now be issued an ID and Quick Response Code.
- Businesses and tour guides can now visit www.cambodiatourismindustry.org to submit their online applications.
- Each new licence will be issued three days after submission. The system will notify businesses a month before their licence is up for yearly renewal.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
EDITOR PICKS
- All time popular

Cambodia Gears Up For Four-Day Celebration Of Khmer New Year In...

POPULAR POSTS

NagaCorp Records $145M Gross Gaming Revenue For Q1 2024

Mediam By Aleph Becomes An Official Google Media Sales Representative In...

RMA Cambodia Plc. To Organise Three-Day ‘Business Partners Expo 2024’ At...
- Advertising
- Realestate.com.kh
- Cambodia Property
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Introduction of ICT for Sustainable Development of the Tourism Industry in Cambodia

Related Papers
Helena Grunfeld
Information and communication technologies (ICTs) are widely used in tourism and tourists tend to take for granted that they can use the Internet for most of their travel arrangements, even when travelling to countries in the developing world. But not all tourism operators have the resources, whether financial or skills, to benefit from the use of ICT, and there is a risk that this could exclude them from itineraries. While it has the potential to contribute to pro-poor tourism, ICT can thus also have the opposite effect, unless concerted action is taken to include small poor operators into some form of Internet presence. This is the conclusion drawn from an exploratory study conducted among small tourism operators in the Siem Reap region of Cambodia. The paper concludes with a proposal of an Internet platform promoting pro-poor tourism in the area and suggests that the Cambodian government has an important role to play in facilitating use of the Internet by this segment of the tour...
Okafor Christian I. (Advisor on Durable Solution) Ph.D., M.Sc., B.Tech., Dip, MNITP, FIMC, CMC.
Speaking of competitiveness has become frequent nowadays, because it is one of the central concerns of governments and industries of all countries. In a world increasingly global and competitive it is essential that companies develop a strategic management in order to follow the complexity of the environment, the trends and competitiveness of the market to gain competitive advantages. This paper reviewed destination competitiveness as it affect tourism and the enablement of technology as a vehicle of transformation. The importance of ICTs for enhancing the competitiveness of tourism enterprises in developing countries is tremendous. ICTs can help them organize their tourism offer, and the Internet provides new opportunities for tourism providers to actually target markets worldwide. This has impacted on the way in which regional tourism destinations are promoted. The method of promoting regions via the development of regional tourist destination websites or portals using Internet technologies is increasingly being adopted both in Australia and around the world. Many tourism enterprises in developing countries have not yet been able to adopt ICTs, even though their application could offer competitive advantages. It develops the proposition that use of such technologies can be a practical approach which destinations may use to mitigate some of tourism's negative impacts. Adopting a destination-focused perspective and through the undertaking of a worldwide study, this research examined how ICT can be used in the management of sustainable tourism.
COMPUTING AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS
IRPN: Innovation & International Management (Topic)
Iris Mihajlovic
Technological development and tourism is close connected since exponential growth is realized in both areas in last 50 years. Information and communication technology influence on global scale on tourism development, and tourism development change the business practice and development strategies. Three new systems has dramatically influence on tactical and strategic level of doing business, computer reservation systems, global distribution system and Internet. Technological changes are obvious in three directions: radical changes in existing industries, development of new industries, incentive of new market development and industries which are not in direct connection with new technologies. The aim of this paper is to point on new technologies development on tourism thru overview of previous research.
Journal of Internet Computing and Services(JICS)
deepanjal shrestha
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has revolutionized the world and has profound impact on the social and economic development of a country. Implementation, practice and accessibility of ICT is viewed as an integral part of any countries' strategy today. These new technologies are becoming popular due to their ability to produce, distribute and provide instant access to massive information in no time. ICT has pervaded almost every aspect of human endeavor that may include health, education, economics, governance, entertainment etc. Tourism is one such vital industry that find enormous application of ICT in its strategic and operational level, to promise long term benefits and enhance economic growth. Tourism industry in western world and some developed countries of Asia have applied ICT for more than 30 years, and have gained tremendous benefits. Nepal which is also growing as one of the favourite tourist destinations lacks proper implementation of ICT in this industry. In our study we examined how the ICT can play a vital role in developing the tourism industry of Nepal. This study is an exploratory research based on primary data collected from tourist visiting Nepal, supported by information from tour operators, government agencies, NGOs and INGOS. A framework is devised on the basis of data and information collected and finally, discussions elaborate on the prospect and challenges of implementation of ICT in tourism industry of Nepal. ☞ keyword : ICT, information access, internet, data center, tourism industry.
SHS Web of Conferences
Wanchalerm Poldee
SSRN Electronic Journal
Deepmala Shrestha
Gajendra Sharma
Nepal is a country blessed with natural beauty, diverse culture, majestic Himalayas, religious destination which attracts thousands of tourists every year making the tourism industry progressive to flourish. Information Communication Technology (ICT) proves to be an effective tool for strengthening the tourism industry. Thus, the purpose of this research study is to analyze about the past scenario of tourism industry, advent of ICT in tourism industry, positive impacts of ICT in tourism industry through in-depth interview with tourism experts and people who have worked for tourism since decades. This study is a form of qualitative research where narrative inquiry has been selected and the scenario has been analyzed through themes developed from the narratives. The result reveals that the emerging technology brings positive impacts to tourism industry assisting branding, promotion of the country, enhancing networks through communication and easily booking tours. The proper utilizatio...
RELATED PAPERS
Julio Oramas
Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience
Uriel Fernando Rodriguez Aguirre
Ayu Vijayanti
Contact Lens and Anterior Eye
Niraj Mandal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Albar Fabian Ardo Albar
Muhammad Shobur
Mohamed Hassan
Stefano Vanin
The Missouri Review
David Groff
Uncertainty principle incongruity
fernando mancebo
Fertility and Sterility
Négociations
Dean G Pruitt
Sustainability
Muhamad Rizki
Yale Journal on Regulation
eva marlina fatmawati
Revista U.D.C.A Actualidad & Divulgación Científica
juan david vargas triana
Proceedings. Frontiers '99. Seventh Symposium on the Frontiers of Massively Parallel Computation
Rupak Biswas
jhkghjf hfdgedfg
澳洲毕业证书 学历学位证
Saturnin ZOETYANDE
Tereza Mošnerová
Journal of Fungi
Radivoje Jevtic
Revista Mosaicum
Dionisia Margarita Gaspar Ruiz
See More Documents Like This
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The total number of inbound tourists to these GMS countries was 73.6 million in 2019 with the total shared between Thailand 39.8 million, Viet Nam 18.0 million, Cambodia 6.6 million, Lao PDR 4.8 million and Myanmar 4.36 million. 4. Cambodia's Tourism Profile Pre COVID-19. Tourism is a priority sector in the Cambodian government's ...
Tourism Revenue: The tourism sector contributed around $4.92 billion in revenue to Cambodia's economy in 2019. Economic Impact: Tourism accounted for about 12.1% of Cambodia's GDP in 2019. Employment: The tourism industry provided employment for around 630,000 people in Cambodia in 2019, representing approximately 12.7% of total employment.
This comprehensive strategy emphasizes cultural and ecotourism, representing the bedrock of Cambodia's tourism industry and serving as the cornerstone for long-term destination development (RCG, 2012). The employment potential of tourism in Cambodia is substantial, with the RGC projecting the creation of approximately 800,000 jobs by 2020.
A Study On Cambodia Tourism Essay. Cambodia is not an isolated case: tourism is a key sector in many of the least developed countries (LDCs), a grouping officially recognized by the United Nations in 1971. Still, their. overall share in international tourism is small, accounting for less than 1% of global tourism. receipts.
Tourism In Cambodia Essay. 965 Words4 Pages. Tourism in Cambodia In Cambodia, tourism is known as a key sector of industry income since it has played as a vital role to develop economic of Cambodia. According to Ministry of Tourism in 2016, Cambodia had welcome about 5,011,712 visitors rose by 5% in which include 2 million of ASEAN population ...
Pub Street in the Cambodian tourist gateway of Siem Reap empty during COVID-19 lockdown on April 22, 2020. Nearly half of tourism-related businesses in Cambodia have been forced to close their ...
Cambodia's tourism industry is a key contributor to its economic growth. It provides a sizable contribution to Cambodia's economy (21 percent of GDP in 2019), which has been on the rise for the past ten years. The ecotourism sector was a notable part of this and, in recent years, was showing signs of even greater growth than the rest of the ...
The tourism industry, Cambodia's second-largest driver of economic growth and where many MSMEs work, is especially in crisis. In 2019, tourism generated about US$4.9 billion, nearly 20% of the country's GDP, while COVID-affected 2020 saw international tourism revenue plummet nearly 80%, to US$1.023 billion.
The annual tourism growth rate in Cambodia is among the highest in the world; however, tourist industry impact on Cambodian's economy is quite low. The purpose of our study is to analyse the strengths and weaknesses of the Cambodian tourism market so that a framework can be established to help the country's policy-makers formulate strategies to use its resources effectively to create ...
Cambodia's tourism industry is a key contributor to its economic growth. However, a recent slowdown in the growth of tourism points to a need to diversify Cambodia's tourism sector. Cambodia's spectacular and pristine natural assets are exactly what ecotourists look for and the opportunities for supporting the expansion of this industry are great.
This paper provides an overview of the historical development of the Cambodian political economy and the role of tourism in shaping it since the early 1990s when Cambodia opened its door to the world. The paper provides a general overview of tourism products and the government's policies in tourism development in Cambodia and then examines the perceived impacts of tourism on socio-economic ...
The tourism industry in Cambodia is one of the key drivers of its economy, accounting for approximately 12% of GDP and employing over 600,000 people pre-pandemic, of which 60 per cent were women (source).The country is home to a wealth of cultural and natural attractions, including the world-famous Angkor Wat temple complex, as well as stunning beaches, rainforests, and national parks.
The tourism industry in Cambodia is on the brink of a significant transformation as it eagerly anticipates the "2024 China-Cambodia Year of People-to-People Exchange" event, scheduled to take place in Siem Reap province. This event is poised to play a pivotal role in promoting and attracting more Chinese and foreign tourists to the country.
According to the Roadmap for Recovery of Cambodian Tourism During and Post COVID-19, the government envisions a reformed tourism sector that emphasizes quality, safety, and sustainability, while ...
Jan 28, 2021. The COVID-19 pandemic has halted the tourism industry in Cambodia. The ILO and Cambodia's Ministry of Tourism are collaborating on entrepreneurship trainings in order to recover sustainably, improve working conditions and build back better. On 25th to 27th of January 2021, the ILO and Cambodia's Ministry of Tourism (MoT ...
September 1, 2021. by The Diplomat. Nearly half of tourism-related businesses in Cambodia have been forced to close their doors due to the compounding impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new survey report published by the Asia Foundation last week. Based on surveys conducted with around 1,000 tourism-related small and medium ...
5. Cambodia is a land of potentials, bouncing back from being colonized by the French in 1884 and from years of dejection from three civil wars in 1970, 1975 and a genocide period after 1975. The Land of Wonder has shown tremendous growth in many industries, particularly with its tourism industry, according to a research done by Emma Ericson ...
Accommodation and facilities available in Cambodia. No matter how you like to travel, Cambodia will always have a place to cater for your needs; from $5 backpackers beds to $2000 a night 5-star luxury resorts. Increasingly too, the Kingdom of Cambodia is offering facilities for corporate events and business travellers.
The situation of tourism industry in Cambodia is not far from tourism industry in China. The study by Jennifer X.M, Buhalis D., and Haiyan S. on the ICTs and Internet adoption in Chaina's Tourism Industry, reflected the comparable situation in the tourism industry in Cambodia.
To begin with, this essay will briefly unfold the physical and cultural characteristics of Cambodia and Siem Reap. The challenges and opportunities in Siem Reap will be covered. This essay also will answer the question of how the tourism industry has shaped the local, natural and social environment in Siem Reap.
Essay On Advantages And Disadvantages Of Tourism In Cambodia. Tourism which is the most common sector for the economic growth has many definitions due to the context. According to WTO (1996) states that "tourism refers to the consumption of tourists, to the production units supplying goods and services particularly to tourists, or even to a set ...
People working in the tourism sector have an advantage in that one gets to meet many new people from different parts of the world or country, which enhances social interaction, and creation of links with them. Order custom essay Advantages of Tourism in Cambodia with free plagiarism report. 450+ experts on 30 subjects Starting from 3 hours ...
Cambodia Genocide Essay. Throughout history, the world has bared witness to many genocides. Even in today's current era, there are people trying to eliminate certain races in several countries. Among these genocides of the past, is a country in Southeast Asia called Cambodia. In the 1960's, this fairly large country that is roughly the size ...