Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

COVID-19 international travel advisories
If you plan to visit the U.S., you do not need to be tested or vaccinated for COVID-19. U.S. citizens going abroad, check with the Department of State for travel advisories.
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S.
- As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
- As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
U.S. citizens traveling to a country outside the U.S.
Find country-specific COVID-19 travel rules from the Department of State.
See the CDC's COVID-19 guidance for safer international travel.
LAST UPDATED: December 6, 2023
Have a question?
Ask a real person any government-related question for free. They will get you the answer or let you know where to find it.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The U.S. restricts travel from 8 countries as omicron variant spreads

Travelers exit the International Arrivals area at Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, on Monday. The Biden administration is banning travel for non-U.S. citizens from several African countries over concerns about the omicron variant. Jim Watson/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Travelers exit the International Arrivals area at Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, on Monday. The Biden administration is banning travel for non-U.S. citizens from several African countries over concerns about the omicron variant.
The U.S. is enacting travel bans in an effort to limit the spread of the new omicron variant of the coronavirus, which the World Health Organization warns poses a "very high" global risk .

Coronavirus Updates
As omicron spreads, studies suggest that travel bans alone don't do much good.
Starting Monday, President Biden has imposed travel restrictions for non-U.S. citizens from the following eight countries:
- South Africa

The Coronavirus Crisis
Biden says omicron variant is cause for concern but not panic.
The European Union , Canada, United Kingdom, and Israel have announced travel restrictions from southern African countries as well.
Some health officials and public health experts caution that travel restrictions alone may not be effective in controlling the spread of infectious disease , and could even have harmful effects, like exacerbating xenophobia and deterring countries from being transparent about the state of the virus in the future.
The variant was first reported last week in South Africa, where vaccination rates are about 24% .
Cases of the omicron variant have since been confirmed in Botswana, the United Kingdom, Italy, Germany, Belgium, Israel, the Netherlands, Australia and Hong Kong.
Biden is encouraging children and adults to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
"This pandemic will not end until we have global vaccinations," he said last week in a statement .
In an address on Monday, he said the variant is "a cause for concern — not a cause for panic."
Tien Le is an intern on NPR's News Desk.
This story originally appeared on the Morning Edition live blog .
- president biden
- coronavirus
- World Health Organization

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Fact Sheets
Frequently Asked Questions: Guidance for Travelers to Enter the U.S.
Updated Date: April 21, 2022
Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request. On April 21, 2022, DHS announced that it would extend these requirements. In determining whether and when to rescind this order, DHS anticipates that it will take account of whether the vaccination requirement for non-U.S. air travelers remains in place.
These requirements apply to non-U.S. individuals who are traveling for essential or non-essential reasons. They do not apply to U.S. citizens, Lawful Permanent Residents, or U.S. nationals.
Effective November 8, 2021, new air travel requirements applied to many noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily. These travelers are also required to show proof of COVID-19 vaccination. All air travelers, including U.S. persons, must test negative for COVID-19 prior to departure. Limited exceptions apply. See CDC guidance for more details regarding air travel requirements.
Below is more information about what to know before you go, and answers to Frequently Asked Questions about cross-border travel.
Entering the U.S. Through a Land Port of Entry or Ferry Terminal
Q. what are the requirements for travelers entering the united states through land poes.
A: Before embarking on a trip to the United States, non-U.S. travelers should be prepared for the following:
- Possess proof of an approved COVID-19 vaccination as outlined on the CDC website.
- During border inspection, verbally attest to their COVID-19 vaccination status.
- Bring a Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative compliant border crossing document, such as a valid passport (and visa if required), Trusted Traveler Program card, a Department of State-issued Border Crossing Card, Enhanced Driver’s License or Enhanced Tribal Card when entering the country. Travelers (including U.S. citizens) should be prepared to present the WHTI-compliant document and any other documents requested by the CBP officer.
Q. What are the requirements to enter the United States for children under the age of 18 who can't be vaccinated?
A: Children under 18 years of age are excepted from the vaccination requirement at land and ferry POEs.
Q: Which vaccines/combination of vaccines will be accepted?
A: Per CDC guidelines, all Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved and authorized vaccines, as well as all vaccines that have an Emergency Use Listing (EUL) from the World Health Organization (WHO), will be accepted.
Accepted Vaccines:
- More details are available in CDC guidance here .
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your dose of an accepted single-dose COVID-19 vaccine;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after your second dose of an accepted 2-dose series;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received the full series of an accepted COVID-19 vaccine (not placebo) in a clinical trial;
- 2 weeks (14 days) after you received 2 doses of any “mix-and-match” combination of accepted COVID-19 vaccines administered at least 17 days apart.
Q. Is the United States requiring travelers to have a booster dose to be considered fully vaccinated for border entry purposes?
A: No. The CDC guidance for “full vaccination” can be found here.
Q: Do U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land POEs and ferry terminals?
A: No. Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or Lawful Permanent Residents (LPRs). Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: Is pre- or at-arrival COVID testing required to enter the United States via land POEs or ferry terminals?
A: No, there is no COVID testing requirement to enter the United States via land POE or ferry terminals. In this respect, the requirement for entering by a land POE or ferry terminal differs from arrival via air, where there is a requirement to have a negative test result before departure.
Processing Changes Announced on January 22, 2022
Q: new changes were recently announced. what changed on january 22.
A: Since January 22, 2022, non-citizens who are not U.S. nationals or Lawful Permanent Residents have been required to be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States at land ports of entry and ferry terminals, whether for essential or nonessential purposes. Previously, DHS required that non-U.S. persons be vaccinated against COVID-19 to enter the United States for nonessential purposes. Effective January 22, all non-U.S. individuals, to include essential travelers, must be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request. DHS announced an extension of this policy on April 21, 2022.
Q: Who is affected by the changes announced on January 22?
A: This requirement does not apply to U.S. citizens, U.S. nationals, or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. It applies to other noncitizens, such as a citizen of Mexico, Canada, or any other country seeking to enter the United States through a land port of entry or ferry terminal.
Q: Do U.S. citizens need proof of vaccination to return to the United States via land port of entry or ferry terminals?
A: Vaccination requirements do not apply to U.S. Citizens, U.S. nationals or U.S. Lawful Permanent Residents. Travelers that exhibit signs or symptoms of illness will be referred to CDC for additional medical evaluation.
Q: What is essential travel?
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for “essential travel.” Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers). Under current policy, there is no exception for essential travel.
Q: Will there be any exemptions?
A: While most non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States will need to be vaccinated, there is a narrow list of exemptions consistent with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order in the air travel context.
- Certain categories of individuals on diplomatic or official foreign government travel as specified in the CDC Order
- Children under 18 years of age;
- Certain participants in certain COVID-19 vaccine trials as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals with medical contraindications to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine as specified in the CDC Order;
- Individuals issued a humanitarian or emergency exception by the Secretary of Homeland Security;
- Individuals with valid nonimmigrant visas (excluding B-1 [business] or B-2 [tourism] visas) who are citizens of a country with limited COVID-19 vaccine availability, as specified in the CDC Order
- Members of the U.S. Armed Forces or their spouses or children (under 18 years of age) as specified in the CDC Order; and
- Individuals whose entry would be in the U.S. national interest, as determined by the Secretary of Homeland Security.
Q: What documentation will be required to show vaccination status?
A: Non-U.S. individuals are required to be prepared to attest to vaccination status and present proof of vaccination to a CBP officer upon request regardless of the purpose of travel.
The current documentation requirement remains the same and is available on the CDC website . Documentation requirements for entry at land ports of entry and ferry terminals mirror those for entry by air.
Q: What happens if someone doesn’t have proof of vaccine status?
A: If non-U.S. individuals cannot present proof of vaccination upon request, they will not be admitted into the United States and will either be subject to removal or be allowed to withdraw their application for entry.
Q: Will incoming travelers be required to present COVID-19 test results?
A: There is no COVID-19 testing requirement for travelers at land border ports of entry, including ferry terminals.
Q: What does this mean for those who can't be vaccinated, either due to age or other health considerations?
A: See CDC guidance for additional information on this topic. Note that the vaccine requirement does not apply to children under 18 years of age.
Q: Does this requirement apply to amateur and professional athletes?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions.
Q: Are commercial truckers required to be vaccinated?
A: Yes, unless they qualify for one of the narrow CDC exemptions. These requirements also apply to bus drivers as well as rail and ferry operators.
Q. Do you expect border wait times to increase?
A: As travelers navigate these new travel requirements, wait times may increase. Travelers should account for the possibility of longer than normal wait times and lines at U.S. land border crossings when planning their trip and are kindly encouraged to exercise patience.
To help reduce wait times and long lines, travelers can take advantage of innovative technology, such as facial biometrics and the CBP OneTM mobile application, which serves as a single portal for individuals to access CBP mobile applications and services.
Q: How is Customs and Border Protection staffing the ports of entry?
A: CBP’s current staffing levels at ports of entry throughout the United States are commensurate with pre-pandemic levels. CBP has continued to hire and train new employees throughout the pandemic. CBP expects some travelers to be non-compliant with the proof of vaccination requirements, which may at times lead to an increase in border wait times. Although trade and travel facilitation remain a priority, we cannot compromise national security, which is our primary mission. CBP Office of Field Operations will continue to dedicate its finite resources to the processing of arriving traffic with emphasis on trade facilitation to ensure economic recovery.
Q: What happens if a vaccinated individual is traveling with an unvaccinated individual?
A: The unvaccinated individual (if 18 or over) would not be eligible for admission.
Q: If I am traveling for an essential reason but am not vaccinated can I still enter?
A: No, if you are a non-U.S. individual. The policy announced on January 22, 2022 applies to both essential and non-essential travel by non-U.S. individual travelers. Since January 22, DHS has required that all inbound non-U.S. individuals crossing U.S. land or ferry POEs – whether for essential or non-essential reasons – be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide related proof of vaccination upon request.
Q: Are sea crew members on vessels required to have a COVID vaccine to disembark?
A: Sea crew members traveling pursuant to a C-1 or D nonimmigrant visa are not excepted from COVID-19 vaccine requirements at the land border. This is a difference from the international air transportation context.
Entering the U.S. via Air Travel
Q: what are the covid vaccination requirements for air passengers to the united states .
A: According to CDC requirements [www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/noncitizens-US-air-travel.html | Link no longer valid], most noncitizens who are visiting the United States temporarily must be fully vaccinated prior to boarding a flight to the United States. These travelers are required to show proof of vaccination. A list of covered individuals is available on the CDC website.
Q: What are the COVID testing requirements for air passengers to the United States?
A: Effective Sunday, June 12 at 12:01 a.m. ET, CDC will no longer require pre-departure COVID-19 testing for U.S.-bound air travelers.
- Border Security
- Transportation Security
- Airport Security
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
'No point in getting irate, the queue will still be there': International tourists arrive to long lines
A rush of international travelers headed into the United States Monday as the COVID-19 travel ban ended and people from dozens of countries begin flooding in, more than 600 days since they were barred from entry.
That's more than 86 weeks. Nearly 20 months. Enough time for grandchildren to be born , or for couples to lose track of the number of nights they fell asleep to FaceTime calls with their partner. Long enough to lose hope in a U.S. vacation or honeymoon after having to delay plans over and over.
Lines began forming at the Canada and Mexico borders well before daybreak, and eager travelers boarded flights from Europe, including dueling departures from London's Heathrow airport. The U.S.-Mexico border is typically the world's busiest border crossing, with about 350 million people crossing annually.
► US drops travel ban Nov. 8: Expect bottlenecks at airports under strict entry rules
►Vacation travel: Hawaii opening for fully vaccinated international travelers, but some virus restrictions linger
Learn more: Best travel insurance
The new U.S. entry requirements require foreign air passengers to test negative for the coronavirus before boarding a plane to the country and, if they are 18 or older , show proof of full vaccination. Travelers entering the U.S. on land or by ferry for nonessential reasons must show proof of vaccination. Although federal officials had warned of the potential for long lines at entry points, there seemed to be few delays as visitors arrived by land and air.
It's a long-awaited moment for travelers from more than 30 countries. The U.S. initiated its first COVID-19-related travel ban on China in February 2020 . By the end of March, it had added travel bans on the United Kingdom , Ireland, Iran and 26 countries in the European Schengen Area . Brazil, India and South Africa were later added to the list.
Want more? Sign up for USA TODAY's Travel newsletter to receive updates directly to your inbox and follow us on Twitter .
Federal officials warned of delays: 'No staff around to help'
The smooth sailing for international travelers at JFK Airport ended Monday afternoon as arrivals ramped up after a relatively quiet morning. Passengers arriving from England on Virgin Atlantic reported lines of up to two hours to clear Customs and Border Protection processing due to the arrival of multiple flights from the United Kingdom. CBP officials had warned lines would grow from recent levels given the return of international passengers.
Paul Richards, the 58-year-old head of safeguarding for Stoke City F.C., arrived on a Virgin Atlantic flight from London at 3:35 p.m. ET for vacation and to celebrate his son's 21st birthday. He ultimately waited about two hours before being cleared into the country.
"No point in getting irate, the queue will still be there,'' he said as he waited.
Marc Evans, a 42-year-old police officer, flew from Manchester, England, with his wife and two children to visit family for the first time in 20 months, ultimately waiting more than an hour.
"It was apparently a PR stunt to show the USA was back open but seems they weren't concerned about the queues at customs," Evans said via Twitter message, noting that they have a friend waiting to pick them up at the airport.
Evans said he was frustrated as his family has been told to wait as other families with children have been able to jump the queue. There are "no staff around to help," he said.
But the problem extends beyond a pesky wait, according to Evans. "Other people were getting connecting flights and told to stay in line," he said.
— Morgan Hines, Dawn Gilbertson, USA TODAY
'What happens here, only happens here': McCarran welcomes tourists
When the first U.K. passengers arrived in Las Vegas on Monday afternoon, McCarran International Airport made sure to give them a "fabulous Las Vegas welcome," complete with waving showgirls as the plane taxied to its gate and free T-shirts and hats promoting the city's new slogan, "What happens here, only happens here."
Karl Watson, 37, of London plans to spend his week in Nevada visiting national parks and watching a Bryan Adams performance. But his first stop? A bar.
"First of all, I'm going to get really drunk," he said.
Watson said getting through customs and security was a long process, with the lines taking more than an hour to get through, but the Las Vegas airport was still "buzzing" with excitement when the plane landed.
"Everyone on the plane was cheering when the plane landed," Watson said. "Usually when people clap I'm like, shut up, you don't do that when a bus parks. But this time, it was exciting. It was really cool."
"It's just such a fun place. Vegas never stops," added Ann Kirk, 64 of Birmingham, England who landed in Las Vegas with her husband Mark.
The two plan to spend five weeks in the U.S., but that's nothing compared to two- or three-month vacations they used to take before the travel ban. The couple usually spends most of their time at a home they own in Lake Havasu City in Arizona, and already have their next visit planned for February.
"It's the warmth. The heat. The sunshine," Mark Kirk, 62, said.
"We've really missed it," Ann Kirk added.
— Bailey Schulz, USA TODAY
Changes affect most air travelers
Arriving at Hartsfield-Jackson's Atlanta International Airport from Korea, Seongbin Woo, 26, said his travel experience for his first U.S. visit was "not that smooth," largely because he had to rush to get test results back before departing Seoul. Although Korean nationals were not banned from travel to the U.S., anyone arriving as of Monday must follow new protocols, including showing proof of vaccination.
"I heard that everyone here is not wearing masks, so it's good for me because I am tired of masks," he said. He added he is still concerned about getting sick.
Ivana Pedroso, 30, tearily reunited with her parents as they arrived from Sao Paulo, Brazil. Pedroso lives in Greensboro, North Carolina, where she's a graduate student at North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University. She had been able to visit Brazil several times, but this is the first time her parents will see the house she bought.
"It's great. Exciting. I have been waiting for this moment for two years because she doesn't know my house," Pedroso said. "They don't know where I live. So I've been waiting for this moment for two years."
Pedroso said her parents will stay for her graduation in December, on a trip they've been rescheduling for two frustrating years. Her parents said the flights and border control checks went smoothly, and they were confident they would be safe.
"She was a little bit nervous, but since they followed the protocols and all the companies, Delta Airlines and the airport followed the protocols with COVID, everything was OK," Pedroso said of her mom. "Sanitizers and masks all the time. They're good."
Waiting for "my guy," Deb Halleck, 61, wore a Manchester United jersey waiting for Stephen Donnelly to arrive in Atlanta from England via Amsterdam. Wearing a similar jersey, Donnelly strode through the terminal and swept her into a hug that seemed to make time stop. The two had been friends for years but this summer realized they wanted more.
"We've just been friends and recently, more than that, so just excited," Halleck said moments before he arrived. "I can't wait."
Since July, they've talked on the phone every day and FaceTimed. Every week they make dinner together, long distance, and share a meal. Donnelly also buys her flowers and takes a picture and sends them to her weekly. Donnelly, 62, said the mood was apprehensive on the plane due to the new rules, but was happy to finally be in the U.S. with Halleck.
What are their plans now? "She's in charge. I just go with the flow," Donnelly said.
By late afternoon the arrivals terminal at Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport began filling with loved ones awaiting passengers on a string of flights from cities like Amsterdam, Frankfurt and London, along with other places not previously banned.
All eyes were either staring down the corridor at the sliding doors coming from customs or glued to their phones. Locals eagerly checked to see how much longer it would take for their family, friends and significant others to make it through customs.
One woman remained dedicated to holding up a sign that said #HappyMama while another family, whose kids had been holding up "Welcome Home" signs set them down, sitting in the floor to wait. They had waited this long. What's a little longer?
— Eve Chen, USA TODAY
Romance reignited and 'already have Disneyland booked'
At LAX, the happy emotions ran the gamut — hugs and kisses, laughter and tears — when Damia Suuck, 20, of Claremont, California, saw her German boyfriend, Eric Reuschel, 19, for the first time in almost a year as he came off the plane from Frankfurt.
"We were waiting, waiting. We booked so many tickets," said Suuck, who was waiting at LAX with her mother, Fadia Suuck.
Damia Suuck, who has German and American citizenship, was able to visit her boyfriend in Germany last Christmas, but Monday was the first day he could visit the U.S. They began dating about two years ago when she was living briefly in Germany.
"We haven't seen each other in almost 12 months, so to meet again, I can't explain it. It's crazy," said Reuschel.
Their plans for Reuschel's one-month visit?
"We already have Disneyland booked. That was No. 1," Damia Suuck said.
— Bill Keveney, USA TODAY
Scattered delays create a 'stressful' experience
Julien Yomtov of Paris said he faced several frustrating delays leaving France – first at security and then again when the plane's departure was delayed an hour. He said he's excited to get back to Las Vegas, traveling via Los Angeles, to play in the World Series of Poker, which he normally does annually with his brother.
"The experience was stressful because the employees are (not) ready to welcome so many travelers," he told USA TODAY via Whatsapp. "Hope in LAX it will be easier."
Although Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport is one of the busiest airports in the world, the international terminal's arrival hall on Monday, which was almost tranquil and relatively empty through early afternoon. Many fellow passengers made connections to other cities, and those who made Atlanta their final destination described their trips as smooth and even "better than before."
— Bailey Schulz, Eve Chen, USA TODAY
Trip delayed four times
In Los Angeles, Jan Hutten tiptoed up to his sister-in-law Jeannette Gross for a surprise hug, kicking off a family reunion three years in the waiting. His wife Henny followed with a hug of her own, grasping her sister as the Huttens arrived from Amsterdam for a three-week visit. The two had tried to visit four times previously, but had to keep rescheduling due to the ongoing travel ban.
Gross and her son, Gary Loth live in Valencia, north of Los Angeles, and will be taking the Huttens for sushi and Mexican food in sunny Los Angeles — a welcome change from the rainy weather they left behind.
"Fantastic! Finally," Henny Hutten said in Dutch, her native language, when asked how it felt to get together with her sister after having to settle for Skype calls in the three years since they last saw each other.
"I'm very happy to see her," Gross said, adding they usually get together once a year. The separation "was very painful, not being able to hug her. We Skyped, but it's not the same."
Henny Hutten offered a one-word response when asked about the sibling separation: "Terrible!"
The Huttens were supposed to visit in April 2020 to celebrate Gross's retirement. That was the first COVID-related postponement. After more reservations and cancellations, Gross quickly texted her sister when the Nov. 8 opening was announced.
"I said, ‘Change your flight. We're opening up.' She did. She got right on the ball," Gross said.
Families begin to reunite: 'Everything is so exciting'
Simone Thies of Cologne, Germany, is flying in to see her fiancé, who she has seen just twice since the ban began-- once during a trip to Aruba in June, and again when he visited her in Germany in August. Before those trips, they had been separated a year. Thies stayed overnight in a Düsseldorf hotel near the airport before catching her Delta flight, headed ultimately to Lincoln, Nebraska.
"I want to avoid stress because everything is so exciting," she said.
Getting through the line at the Düsseldorf airport was quick — "5 minutes at most," she said — but she had one more stop in Paris before crossing the Atlantic.
There, she had to show her passport, proof of vaccination and results of her negative coronavirus test. Even as the first person in line, the wait took about 20 minutes because one employee was still learning which documents to check, she said.
"The line is very long, but (I'm) done for now," she said before departing.
Alan Marques said the border closure for tourists nearly ended his relationship with his boyfriend, who is a flight attendant. They've been together four years, but hadn't seen each other in four months, until Marques, 33, flew in from Sao Paulo to Atlanta on Monday. He said the separation has been "very difficult and distressing," because his boyfriend's visits to Brazil have only been for a few hours, instead of the days they are used to.
How does it feel to be properly reunited? "So good," he said.
Mexico border busy ... then quiet
After a busy few hours after midnight ET at the El Paso-Ciudad Juárez border crossing in Texas, the normally bustling border crossing fell quiet. Traffic was minimal at crossings between El Paso and Ciudad Juárez and passenger vehicles zipped up the El Paso's Bridge of the Americas freely, no line to stop them.
"I've sold hardly anything," said newspaper salesman José Fierro, whose rack was still filled with El Diario newspapers and PM tabloids at 8 a.m. He had been there on the curb since 3 a.m., he said. There was 6 a.m. traffic, then nothing. "Everyone crossed yesterday, panicked about how the lines were going to be today."
Constantino Castellanos, 68, and his wife, Lizbeth, 62, bought quesadillas at the foot of the Bridge of the Americas, a street vendor handing over a Styrofoam tray wrapped in plastic.
They could take their time. The bridge – usually a wall of slow-moving cars and trucks – was an empty ribbon of asphalt. The border had been closed to tourists or people visiting family, although a wide variety of essential workers had been permitted to cross during the closure. During that time, Mexican nationals holding tourist cards were banned from traveling over the land border; air travel between points in the interior of both countries never ceased.
"It's been two years," said Lizbeth Castellanos. "We're going to Marshalls and Walmart."
The crossing reopened at just after midnight Eastern time. At 6 a.m. Eastern, U.S. Customs and Border Protection reported no significant crossing delays at either the Mexico or Canada borders.
Susana Hernández of Juárez was crossing for the first time since the pandemic restrictions to buy clothes in El Paso for her business. She smiled and flashed her vaccine card.
"We're happy," she said. "We're home, we feel like we're back home."
Cross-border traffic of essential travelers between El Paso and Juárez reached nearly 800,000 crossings of passenger vehicles in August, according to the Border Region Modeling Project at the University of Texas at El Paso.
"Nobody anticipated that this pandemic would last as long as it has, in terms of travel restrictions," said Hector Mancha, U.S. Customs and Border Protection director of field operations in El Paso. "People have not crossed over and visited with family in going on two years... Unfortunately, the pandemic has kept us from (reopening). I think it's overdue."
— Lauren Villagran, Martha Pskowski , El Paso Times
'Welcome back world'
Times Square was relatively quiet Monday morning as the city that never sleeps prepared to welcome vaccinated international tourists back to the U.S.
Around 8:45 a.m., the Times Square Alliance unfurled a "Welcome Back World" sign on the Red Steps in Times Square.
The Steps, considered an iconic New York landmark for tourists, had about 190,000 people walk by them each day before the pandemic, according to the Times Square Alliance, the not-for-profit group that maintains it. At the pandemic's worst, that number dropped to 30,000, and New York businesses hope the flood of tourists will boost their finances.
TJ Witham, the vice president of communications for the Times Square Alliance, told USA TODAY the alliance chose the red steps as it is an "iconic meeting place" for people visiting the Big Apple.
Chris Dickson, a 41-year-old bus scheduler from Newcastle, England, flew to New York City on Monday for 48 hours, using credit from a British Airways trip he'd had to cancel seven months ago.
Dickson planned to drop his bag at his Brooklyn hotel and start exploring the city he last visited more than two years ago.
"I just wanted to come to America at the first opportunity,'' he said. "I'm going to walk across the Brooklyn Bridge, I'm going to go through Central Park, I'm going to do some running, some jogging in that area. I'm just going to enjoy the weather and enjoy being back in America.''
Mainda Kiwelu, 45, arrived in New York on the second British Airways flight of the day. She said this was her first trip to the U.S. in about five or six years, and was hoping to visit the Brooklyn Bridge and Central Park later this week, after work meetings.
"The flight was ok," Kiwelu said. "It was just a bit nerve-wracking sort of doing all the logistics for the travel and making sure the vaccination certificate, app, everything works."
Dueling takeoffs from London to New York
A pair of simultaneous flights left London's Heathrow airport early Monday morning, taking off on parallel runways and following similar flight paths for New York's JFK International Airport. British Airways Flight 1 and Virgin Atlantic Flight 3 took off at 3:51 a.m. ET and landed within minutes of each other. The airlines are rivals but teamed up to commemorate the reopening of foreign travel to the U.S., and British Airways' CEO was aboard his company's flight, which touched down about 11 a.m. ET
American Airlines, which is a BA travel partner, saw bookings from London to US surge 70 percent in the past week, with a lot of the travel for remainder of 2021, said Chief Revenue Officer Vasu Raja.
Clive Wartten, who runs a business-travel group in the UK, arrived on the British Airways flight and was headed for a run in Central Park before meetings with colleagues. Wartten planned to fly home Tuesday night.
"It just feels good to be back on an airplane," he said. "There was a real buzz at the airport and aboard the aircraft, lots of cheering when we took off. It was a bit of a holiday party flight."
Wartten, who is the CEO of the Business Travel Association, later tweeted that he made it from the plane to one of New York's famed yellow taxis in just seven minutes.
"This is a big step for us to come back and open business travel with our US friends," he told USA TODAY while passing through the terminal.
British Airways CEO Sean Doyle has been pushing the Biden administration to ease travel restrictions between the UK and the US for months because it is one of the busiest travel corridors in the world. At one point during the spring, he said, the second runway at Heathrow was closed because the airport hadn't seen such a limited number of flights since World War II.
"This has been a crisis like no other,'' he said Monday after arriving in New York.
Doyle believes the border reopening took too long – the UK and European Union started welcoming US tourists back over the summer – but on Monday said he didn't want to dwell on the past. Instead, he gushed about what the reopening means to British Airways and its passengers.
"The North Atlantic is very important to British Airways and today's a very, very important turning point and milestone in the future of the country,'' he said.
Is he worried travel restrictions could return if COVID cases spike on either side of the Atlantic?
"You always have to keep an eye on things,'' he said. "But I do think that we're seeing a sort of pragmatic framework emerge across a number of jurisdictions.''
He said he hopes that that framework – basing entry requirements on vaccination and testing – remains despite any COVID trends going forward.
— Dawn Gilbertson, Morgan Hines, USA TODAY
Anticipation at airports
Ahead of the British Airways first flight arrival, family members waited in the Terminal 7 arrivals area at New York's John F. Kennedy International Airport, which is decked out with balloons and New York symbols including the back half of a taxicab filled with a floral arrangement and NYC-themed cookies.
Louise Erebara, from Danbury, Connecticut, arrived at the airport with her family early to welcome her sister and her sister's husband after 730 days apart.
"It's everything, we can't thank British Airways enough," a choked-up Erebara said, noting the airline paid for her relatives' flight. "They want to reunite ex-pats and they're doing it."
In Atlanta, Ari Bell, waited anxiously for her fiancé to arrive from the UK after 21 months apart. They've bridged the distance with Snapchat, video calls and texts, and she was waiting to surprise him at the airport as he starts a three-week visit that will include his first-ever Thanksgiving.
"He actually came over for a quick job interview in February, right before the shutdown, got back to London and then that March, everything closed up. So we've just kind of been hanging on a string," Bell said. "It was a little bit confusing to get him here, just because he didn't know he needed a negative (test) so that three days prior we actually had to make that last minute. And he came back negative. He's already fully vaccinated. I'm vaccinated. I got my booster yesterday, just in case — I'm just excited to see him."
Bell said she's excited to just watch a movie together — for months, they've been watching movies simultaneously but separated by the Atlantic Ocean.
"We're homebodies. We like to game together. But yeah, that's mostly what we're looking forward to — just being in the same space together," she said. "This is going to be our first Thanksgiving together, his first Thanksgiving period. He's never celebrated. So we're actually gonna make the big meal and have all my family come over. He's a little nervous. But you know, he loves my dad. They're both ex-army. So they get along great."
And Rosa Chorra, 37, eagerly awaited her parents' arrival from Spain, waiting with her 10-month-old Aurora for their plane to land in Atland. Chorra's parents missed her pregnancy and granddaughter's birth, although Chorra was able to take Aurora to visit them three months ago. She said she missed having the help they could have provided with a newborn.
"It was absolutely horrible. I think it's been the hardest time of my life. I mean, when she was born, the first months that are the hardest, and it's been tough," Chorra said.
— Dawn Gilbertson, Morgan Hines, Eve Chen, USA TODAY
Headed to Disney World
For UK resident Emma Barbour and her family, the border reopening means one thing: Florida's Disney World with their 10-year-old daughter.
They usually come annually, but put those plans on hold after 2019, and rescheduled this trip three times as they waited for the Biden administration to lift the ban. Barbour, 41, said the airports were busy but staff seemed cheerful despite long lines.
"We honestly wouldn't travel if we felt unsafe or nervous, we are fully vaccinated and will wear our masks. I definitely won't let it tarnish our time there by worrying about it," she said from Paris as they waited to board their Atlanta-bound flight.
The British are coming
Sam Nagy and his family are headed to Florida, to the Universal Orlando Resort, their first trip to the U.S. since 2018. He said lines at the Manchester, England, airport were smooth, raising his hopes for the family vacation they've rescheduled four times already.
"That once-a-year trip is so much more to us than just a vacation, it honestly feels like it's ‘home' as cliché as that may be to say," said Nagy.
Paul Richards is flying from London to New York on Virgin Atlantic and described the airport scene as chaotic, with long check-in lines this morning. He is headed to New York City for vacation to celebrate his son's 21st birthday.
"They are working really hard to get people through, however, some passengers hadn't completed the attestation forms or just stood in the wrong queue,'' he said. "Once through check in, security was pretty slick.''
— Dawn Gilbertson, USA TODAY
Lines at the Canada-US border
At th Sweetgrass, Montana, border crossing, wait times climbed to 240 minutes -- four hours — according to U.S. Customs and Border Protection. Normal wait time is about 45 minutes.
Windsor, Ontario, Mayor Drew Dilkens said a Canadian travel requirement – having negative polymerase chain reaction test that can cost $200 – is likely to prevent many who want to drive from Ontario to Michigan from doing so.
He explained the testing provision doesn't make sense for day-trippers nor does it provide the kind of health assurance the government thinks it does because someone could easily contract the virus during their visit.
He wants to see that requirement lifted.
— Frank Witsil, Detroit Free Press
How did the international travel ban start?
The travel ban barred most foreign nationals who had been in the listed countries in the past 14 days from entering the U.S., regardless of vaccination status. The country also cut off nonessential travel across the U.S. land borders with Mexico and Canada in March 2020.
It wasn't until September that the White House announced that it would end the travel ban for fully vaccinated travelers – months after many other nations reopened to U.S. tourists.
The new U.S. entry requirements, which went into effect Monday, require foreign air passengers to test negative for the virus before boarding a plane to the country and, if they are 18 or older , show proof of full vaccination. Travelers entering the U.S. on land or by ferry for nonessential reasons also need to show proof of vaccination.
As airports and border crossings get adjusted to the new travel rules, international travelers should prepare for lines .
The first flight from a country listed the travel ban is set to fly into Chicago from Dublin just before 7 a.m. CT, according to flight tracker Flight Aware and flight-data firm OAG.
Plenty more will follow; there are more than 2 million international flights scheduled to arrive in the U.S. next month, compared to just 728,820 in December of 2020, according to OAG and Flight Aware.
► US drops travel ban: Expect bottlenecks at airports under strict entry rules
Watch CBS News
U.S. lifts travel ban for specific countries. Here's an overview of the changes.
Updated on: November 8, 2021 / 7:10 PM EST / AP
More than a year and a half after COVID-19 concerns prompted the U.S. to close its borders to international travelers from countries including Brazil, China, India, South Africa, the United Kingdom and much of Europe, restrictions are shifting to focus on vaccine status.
Beginning Monday, bans on travel from specific countries are over . The U.S. will allow in international travelers, but they must be vaccinated — with a few exceptions.
The U.S. is also reopening the land borders with Canada and Mexico for vaccinated people. Most trips from Canada and Mexico to the U.S. are by land rather than air.
Here are some questions and answers about the changes:
Why are these changes happening?
The goal is to restore more normal travel while limiting the spread of COVID-19, the government says. The travel industry and European allies have pushed for an end to country-specific bans. Americans have been allowed to fly to Europe for months, and Europeans have been pushing the U.S. to change its policies.
In 2019, before the pandemic, about one-fifth of the roughly 79 million visitors to the U.S. came from Europe.
What are the main requirements?
All adult foreign nationals traveling to the U.S. must be fully vaccinated before boarding their flight. Like before, travelers will still have to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test taken within 72 hours of departure to the U.S.
Does everyone need to be vaccinated?
Yes, with some exceptions. Children under 18 don't need to be vaccinated but they do need to take a COVID-19 test. Kids 2 and younger are exempt from testing requirements.
What about adults who aren't vaccinated?
Since half the world remains unvaccinated, and vaccine distribution has been so skewed to rich countries, the Biden administration is leaving a loophole for people who live in countries where vaccines are scarce. That list includes about 50 countries where fewer than 10% of people have been vaccinated. Travelers from those countries will need permission from the U.S. government to come, and it can't be just for tourism or business travel.
The U.S. government says it will permit unvaccinated international visitors to enter the country if there is a humanitarian or emergency reason, such as an emergency medical evacuation. Those exceptions will be applied "extremely narrowly" and will require approval from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. There could also be a medical exception, with documentation from a doctor.
What will Americans have to do?
Americans who are unvaccinated have to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test within one day of international travel. If you're vaccinated, you need to take a test within three days of your departure, for both Americans and citizens of other countries. This does not apply to flights within the U.S.
Who is going to enforce the vaccine rules?
The airlines. They will have to verify vaccine records and match them against ID, and if they don't, they could face fines of up to nearly $35,000 per violation. Airlines will also collect information about passengers for contact-tracing efforts. There will be CDC workers spot-checking travelers for compliance in the U.S.
Which vaccines will you let it in?
Most but not all of them . Any COVID-19 vaccine approved for emergency use by the World Health Organization, which include the Pfizer, Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines used in the U.S. as well as most used overseas, such as AstraZeneca and China's Sinovac. Not currently allowed is Russia's Sputnik V vaccine, which is authorized in 70 countries. The WHO is reviewing Sputnik but hasn't approved it.
What if you drive in from Mexico or Canada?
The land borders have only been open for "essential" travel. Now, anyone can come, if they're vaccinated against COVID. Be prepared to show proof of the shot to Customs and Border Protection agents. Children are exempt from the requirement.
How will this affect travel?
While the administration is characterizing this as a reopening, some people who were technically allowed to fly to the U.S. earlier in the pandemic are now blocked because of their vaccination status. Other roadblocks to normal travel resuming are big delays in issuing U.S. visas, which people in most countries need to visit the U.S. for business and tourism, and restrictions in other countries that make travel difficult.
Even though people coming from China will now be allowed into the U.S., for example, not many are expected to travel because of restrictions at home. Before the pandemic, Chinese tourists were a lucrative market for the U.S. travel industry.
Industry experts do expect a big influx in people flying from Europe, and hope that a broader recovery in travel follows as more people globally get vaccinated, U.S. visa processing speeds up, other countries lift their own restrictions and people feel less scared about getting COVID because of travel.
- United Kingdom
More from CBS News

Scotland halts prescription of puberty blocking hormones for minors

Supreme Court to weigh bans targeting homeless encampments

What to know as India's 2024 election gets underway

Gold bars and coins vs. gold stocks: Which is better for investors right now?
clock This article was published more than 2 years ago

Travel ban will end Nov. 8 for international visitors who show proof of vaccination, negative coronavirus test
Children under 18 do not have to show proof of vaccination but will be required to show proof of a negative test.

Vaccination will not be required for children under age 18 to travel to the United States once officials lift a ban on international visitors, but they will have to show proof of a negative coronavirus test before boarding a flight, according to rules outlined Monday by the Biden administration.
With about two weeks to go before the United States lifts a travel ban on visitors from 33 countries, federal health officials offered more specifics for travelers and airlines before restrictions are lifted Nov. 8. Although vaccination won’t be required for children, most non-U.S. citizens and nonimmigrants arriving by air will have to show both proof of vaccination and proof of a negative coronavirus test taken within three days of departure.
“With science and public health as our guide, the United States has developed a new international air travel system that both enhances the safety of Americans here at home and enhances the safety of international air travel,” the White House said in a statement.
Federal health officials said the exception was made for children because many do not have access to or are not yet eligible for the vaccines. However, children must still be tested before traveling to the United States. Those traveling with vaccinated adults must be tested within the previous three days, while those traveling with unvaccinated adults or who are traveling alone must show proof of a negative test taken one day before their flight.
The new rules don’t require U.S. citizens and legal permanent residents to be vaccinated but do outline different testing requirements depending on their vaccine status. Those who have been vaccinated must show proof of a negative test taken within of their departure. Those who are unvaccinated must show proof of a test taken one day before their departure.
It will be up to airlines to verify a person’s vaccination and testing status, officials said. Many airlines already have systems that allow travelers to upload proof of a negative test and vaccine status. In addition, international visitors will have to provide information for how they can be reached in the United States for contact-tracing efforts.
“These are strict safety protocols that follow the science and public health to advance the safety of Americans here at home and the safety of international air travel,” a senior White House official said in a briefing with reporters.
The Biden administration announced in September that it was replacing the travel ban on international visitors with a system that would rely on vaccination, testing and contact tracing for visitors wishing to come to the United States.
U.S. announces end to travel ban on international visitors
The announcement was welcomed by the travel industry, which has been pushing the government for more than a year to lift the travel ban on travelers from 33 countries. With the ban in place, industry representatives feared the United States was losing ground to Europe, which began to ease travel restrictions for Americans this summer. Canada opened its borders on Aug. 9 to visitors from the United States who had been vaccinated.
Kevin M. Burke, president of Airports Council International-North America, said the new protocols will help the nation safely and securely reopen its borders.
“We appreciate the Biden administration’s commitment to working with industry on these complex challenges and we look forward to our ongoing work as the November 8 reopen date nears,” he said in a statement.
Since the announcement in September, the administration has slowly been laying the groundwork for lifting the ban. That included the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention deciding which vaccines would be accepted, specifying that travelers must have received those with full or emergency approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or the World Health Organization.
Fully vaccinated travelers can come to the U.S. even if their doses are mixed
In January, President Donald Trump announced a plan to end the travel ban, saying it was unnecessary because of his administration’s policy that required international travelers to provide proof of a negative test before boarding U.S.-bound flights. But within days of taking office, the Biden administration reinstated the ban and added South Africa, and later India, to the list, citing the need to control the spread of coronavirus variants.
In June, the White House formed working groups to help determine when to lift rules that banned international visitors from certain countries.
Under the restrictions, most foreign nationals who have been in the United Kingdom, several European Union countries, Brazil or China in the previous 14 days are not permitted to enter the United States. India was added to the list in May.
The White House also announced this month it was easing pandemic-related restrictions on overland border crossings from Canada and Mexico. Officials said Monday they would release additional information about requirements that people coming to the United States via land borders must follow.
The updated policy offers limited exceptions for individuals enrolled in certain coronavirus vaccine clinical trials and those who shouldn’t get vaccinated for medical reasons. Those who need to travel for emergency or humanitarian reasons and have a letter issued by the U.S. government verifying their need to travel also may be exempted.
In addition, those with non-tourist visas coming to the United States from countries where there is low vaccine availability as determined by the CDC may be allowed to travel to the United States. Those who receive exemptions but intend to stay for more than 60 days may be required to get vaccinated once in the United States.
More coverage: Air travel, transit, railroads
High-speed rail: Las Vegas-S. California project gets $3 billion federal grant
Merger: JetBlue, Spirit case in the hands of a federal judge
Air travel: Alaska Airlines reaches deal to buy Hawaiian Airlines for $1.9 billion
Maryland: Moore administration targets $2 billion cut to transportation projects
Air safety: Air traffic controller’s decision-making spotlighted in near-miss files


COVID-19 Restrictions on U.S. Visas and Entry
This page tracks U.S. visa and entry restrictions related to COVID-19. See NAFSA's Coronavirus Critical Resources Page for related information and resources.
Page Contents
- COVID Vaccine Requirement for Nonimmigrant Air Travelers End May 11 (updated 05/10/2023)
- Geographic Proclamations No Longer in Effect (updated 12/31/2021)
- General Resumption of Visa Services (updated 10/21/2022)
- COVID-19 Surge Impacts Nonimmigrant Visa Appointments in China (updated 1/12/2023)
- Expansion of Renewal Visa Interview Waivers (updated 12/27/2022)
- Vaccination requirements for individuals traveling through land ports of entry at the Canadian and Mexican borders scheduled to end at 12:01 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on May 12, 2023. (updated 05/10/2023)
- Mask Mandate Vacated (updated 4/18/2022)
- CDC Terminates COVID Test Requirement for Passengers Flights Originating in PRC ( updated 03/10/23) )
- COVID Viral Tests No Longer Required for Boarding All U.S.-Bound Flights Effective June 12, 2022 (updated 06/11/2022)
COVID Vaccine Requirement for Nonimmigrant Air Travelers
From November 8, 2021 through May 11, 2023, Presidential Proclamation 10294 of October 25, 2021, Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic , required all "noncitizens who are nonimmigrants" entering the United States through an air POE to show proof that they were fully vaccinated with an acceptable COVID vaccine. Presidential Proclamation of May 9, 2023, Revoking the Air Travel COVID-19 Vaccination Requirement , revokes Proclamation 10294's vaccination requirement effective 12:01 a.m. eastern daylight time on May 12, 2023.
For details, see NAFSA's page: COVID Vaccine and Test Requirements for U.S. Entry .
Geographic COVID-19 Proclamations No Longer in Effect
There are currently no geographic COVID-19 entry ban proclamations in effect.
- See NAFSA's page COVID Vaccine and Test Requirements for U.S. Entry for other current COVID-19 entry requirements and restrictions.
- See NAFSA's page Archive: Geographic COVID-19 Proclamations Affecting Entry from Certain Countries for historical information on revoked geographic COVID-19 proclamations.
U.S. Consular and Visa Services
The Department of State Visa Office does not maintain a COVID-19 portal page with information dedicated to U.S. visas, although the DOS travel.state.gov website does list COVID-19-related news alerts on its U.S. Visa News page . This NAFSA page has highlights from that and other sources.
Advocacy on Visa Delays
Senators ask dos to address visa backlog for international students.
On August 10, 2021, U.S. Senator Alex Padilla (D-Calif.) led a group of 23 Senators in calling on Secretary of State Antony Blinken and the State Department to address the backlog of visas for international students, which grew significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic. Read NAFSA's press release .
NAFSA Meets With Department of State Regarding Consular Operations
On July 12, 2021, Esther Brimmer, DPhil, NAFSA's executive director and CEO, met with U.S. State Department Acting Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary for Consular Affairs, Edward Ramotowski, to discuss growing concerns regarding limited visa appointment availability and processing delays affecting international students and scholars planning to arrive on U.S. campuses this fall. NAFSA members can read a meeting summary .
General Resumption of Visa Services
The Department of State suspended routine visa services worldwide in March 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. On July 13, 2020, DOS tweeted the following update from @TravelGov: " US embassies and consulates are beginning the phased resumption of routine visa services. The dates for each embassy or consulate will depend on local conditions. We are unable to provide details for each location. Please monitor the embassy or consulate website for updates. "
Read DOS' October 21, 2022 Update on Worldwide Visa Operations , transcribed below, for a DOS progress report.
" Update on Worldwide Visa Operations Last Updated: October 21, 2022 Worldwide Visa Operations Are Recovering Faster than Expected from the COVID-19 Pandemic The Department of State is successfully lowering visa interview wait times worldwide, following closures during the pandemic. We’ve doubled our hiring of U.S. Foreign Service personnel to do this important work, we are recovering faster than projected, and this year we will reach pre-pandemic processing levels. Backlogs and Wait Times – How We Got Here As for many service providers, the COVID-19 pandemic forced profound reductions in the Department’s visa processing capacity in two main ways. First, restrictions on travel to the United States, and local restrictions on public places like our overseas consular waiting rooms, curbed our ability to see visa applicants. As most applicants are required by U.S. law to appear in person, these restrictions forced a reduction in the number of visa applications the Department could process. Second, as revenue from the application fees that fund visa processing operations was cut nearly in half, the Department was forced to leave more than 300 overseas consular officer positions unfilled in 2020 and 2021. This further reduced the number of visa applications we could process. Where We Are Now Since COVID-19 restrictions have been lifted, we are back in business worldwide. Ninety-six percent of our embassies and consulates are again interviewing visa applicants, and we are processing nonimmigrant visa applications at 94 percent of pre-pandemic monthly averages and immigrant visa applications at 130 percent. In the past 12 months (through September 30, 2022), we processed 8 million non-immigrant visas, well above our best-case projections. We are well on the way to meeting and exceeding pre-pandemic visa processing capacity. Improved efficiency through Interview Waivers During the pandemic, the Department of State coordinated with the Department of Homeland Security to waive in-person interviews for several key visa categories, including for many students and temporary workers integral to supply chains. In addition, applicants renewing nonimmigrant visas in the same classification within 48 months of their prior visa’s expiration are now eligible to apply without an in-person interview in their country of nationality or residence. This has already reduced the wait time for an interview appointment at many embassies and consulates. We estimate 30 percent of worldwide nonimmigrant visa applicants may be eligible for an interview waiver, freeing up in-person interview appointments for those applicants who still require an in-person interview. Building on Success Our focused efforts during the pandemic recovery period have yielded substantial results in facilitating travel to the United States. Here are just some of our successes in the last year: We reduced the immigrant visa (IV) backlog and reunited families: As of October 2022, our consular sections worldwide have reduced the overall IV interview scheduling backlog by 25 percent (nearly 135,000 applicants), from its peak in July 2021. Our embassies in El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras eliminated an IV backlog of 22,000 applicants, and our consulate in Ciudad Juarez reduced the IV backlog for Mexican applicants by nearly 44 percent. We set records for student and academic exchange visitor visas. Consular sections worldwide adjudicated more student visas in July 2022 than in any other month since 2016, with nearly 180,000 F, M, and academic J visas processed. We exceeded pre-pandemic levels of visa processing for seasonal agricultural and nonagricultural workers who are vital links in the nation’s food supply chain and help ease labor shortages and inflation, with more than 395,000 H-2 visas issued in fiscal year 2022. We issued thousands of crewmember visas essential for maintaining the global supply chains that support both the U.S. and global economy. By Summer 2022, the issuance rates of crewmember visas were comparable to pre-pandemic levels. We issued all available E-3 visas in FY 2022, the immigrant visa category most sought by healthcare workers, who are crucial to the health and wellbeing of our communities. We issued 54,334 Diversity Visas during the DV-2022 program year. That is the highest number of DVs issued in 25 years, and all available DV numbers were exhausted when that total was combined with the domestic adjustments of status approved by USCIS under the DV program. For Those Navigating Long Interview Wait Times Our goal is to provide a visa interview for every applicant who requires one, worldwide, in a reasonable timeframe. Although our processing capacity is rebounding faster than projected, we know that visa applicants still face lengthy wait times at some embassies and consulates. We urge any visa applicant who can travel to another embassy or consulate with shorter wait times to consider doing so. There is no penalty for applying anywhere appointments are available, even outside your home country. For the latest information about wait times, see https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas.html ."
To find embassy or consulate websites, go to https://www.usembassy.gov/ . The embassy links get you to the right embassy website, but you will have to do some clicking to find relevant COVID-19 information, as each embassy website is structured a bit differently.
COVID-19 Surge Impacts U.S. Mission China Visa Appointments
Update from U.S. Mission China Consular Services for December 15, 2022
"Due to the operational impacts caused by the surge of COVID-19 infections across China, U.S. Embassy Beijing and U.S. Consulate General Shanghai are providing passport and emergency citizen services only. U.S. Consulates General Wuhan, Shenyang, and Guangzhou will only be providing emergency consular services until further notice. Please go to https://china.usembassy-china.org.cn/services/ for more information on emergency consular services. All routine Visa Services, with the exception of some previously scheduled for Consulate General Shanghai — are temporarily suspended; all regularly scheduled appointments at Embassy Beijing and the other Consulates General have been canceled."
Update from U.S. Mission China for December 27, 2022
"Consular Sections at the U.S. Embassy in Beijing, and Consulates Guangzhou and Shenyang will resume routine consular services on January 3. Consulate General Wuhan has resumed providing limited U.S. citizen services. Shanghai will continue operating in emergency operations status until further notice. Please note that the number of appointments available for routine services will be based on staffing."
Expansion of Visa Interview Waivers
In a December 23, 2022 announcement , DOS extended until December 31, 2023 the discretionary authority given to consular officers to waive the in-person interview requirement for certain "F, M, and Academic J Visa Holders" and "Petition-Based H, L, O, P, and Q Visa Holders."
See NAFSA's page for additional details .
Controls at Land Ports of Entry on Canadian and Mexican Borders
From January 22, 2022 through May 11, 2023, all noncitizens who are nonimmigrants had to show proof that they were fully vaccinated with an acceptable COVID-19 vaccine under the same vaccine standards as air travelers. Unlike air travel, however, travelers entering through land or ferry ports of entry were never subject to a pre-entry COVID-19 testing requirement. The U.S.-Canada-Mexico COVID restrictions ceased to have effect as of 12:01 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) on May 12, 2023, under a pair of Federal Register Notice published on May 10, 2023. Canada notice | Mexico notice .
Airports and Flights
Mask mandate vacated.
Executive Order 13988 of January 21, 2021 , titled Executive Order on Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel, directed relevant agencies to incorporate, to the extent feasible, CDC recommendations on public modes of transportation and at ports of entry to the United States, including recommendations such as mask-wearing, physical distancing, appropriate ventilation, timely testing, and possibly self-quarantine after U.S. entry. See NAFSA's page on Executive Order 13988 for details.
CBP announced that on February 2, 2021 it began "enforcing the requirement that travelers wear face masks at all air, land and sea ports of entry in the United States in accordance with President Biden's Executive Order on Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Order Regarding the Requirement for Persons to Wear Masks While on Public Conveyances and at Transportation Hubs...With limited exceptions, travelers must wear a face mask while physically present at a U.S. air, land, or sea port of entry. CBP Officers will require travelers to temporarily lower their mask during the inspection process to verify their identity."
However, On April 18, 2022, a Federal District Court judge in Tampa, Florida issued a ruling that the "Mask Mandate exceeds the CDC's statutory authority and violates the procedures required for agency rulemaking under the APA. Accordingly, the Court vacates the Mandate and remands it to the CDC." The case was Health Freedom Defense Fund, Inc. et al. v. Biden. Case 8:21-cv-01693-KKM-AEP.
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) followed up with an April 18, 2022 statement saying: "Due to today’s court ruling, effective immediately, TSA will no longer enforce its Security Directives and Emergency Amendment requiring mask use on public transportation and transportation hubs. TSA will also rescind the new Security Directives that were scheduled to take effect tomorrow. CDC continues to recommend that people wear masks in indoor public transportation settings at this time."
CDC Terminates COVID Test Requirement For PRC Travelers
The Centers for Disease Control announced on March 10, 2023, that:
"On March 10, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) rescinded the Order titled “ Requirements for Negative Pre-Departure COVID-19 Test Result or Documentation of Recovery from COVID-19 for Aircraft Passengers Traveling to the United States from the People’s Republic of China .”
This rescission takes effect for flights departing to the United States from the People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Designated Airports* at or after 3:00pm ET (8:00pm GMT) on March 10, 2023 , and will be published in the Federal Register.
This means that starting March 10, 2023 at 3pm ET, air passengers will no longer need to get tested and show the negative COVID-19 test result, or show documentation of recovery from COVID-19, prior to boarding a flight to the U.S. from the People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong, and Macau, or through a Designated Airport.
* Designated Airports included Incheon International Airport (ICN) in Seoul, Republic of Korea; Toronto Pearson International Airport (YYZ) in Canada; and Vancouver International Airport (YVR) in Canada.
View the Rescission [PDF – 5 pages] ."
The requirement had applied to air passengers regardless of nationality and vaccination status, if they wanted to enter the United States on a flight:
- originating from the PRC, Hong Kong, or Macau; or
- transiting Incheon International Airport, Toronto Pearson International Airport, or Vancouver International Airport on their way to the United States, if they have been in the PRC in the last 10 days.
Covered travelers had to take an acceptable COVID test ("such as a PCR test or an antigen self-test administered and monitored by a telehealth service or a licensed provider and authorized by the Food and Drug Administration or the relevant national authority") no more than 2 days before their departure to the United States, and the traveler must show a negative test result to the airline upon departure.
CDC Rescinds Order Requiring all Passengers on U.S.-Bound Flights to Have COVID-19 Viral Test, Effective June 12, 2022
Proclamation 10294 of October 25, 2021 did not institute new negative COVID-19 test requirements. Rather, in addition to being subject to the proof of vaccination requirements instituted by Proclamation 10294, nonimmigrants who were entering the United States through an air port of entry prior to June 12, 2022 were also subject to CDC rules that required all travelers ( regardless of citizenship ) to present proof of receiving a negative pre-departure viral test result for COVID-19. Nonimmigrants subject to Proclamation 10294 of October 25, 2021 must, however, still show both proof of being fully vaccinated (or qualify under one of the narrow exceptions) in order to enter the United States.
Update from the CDC website :
"As of 12:01AM ET on June 12, 2022 , CDC will no longer require air passengers traveling from a foreign country to the United States to show a negative COVID-19 viral test or documentation of recovery from COVID-19 before they board their flight. For more information, see Rescission: Requirement for Negative Pre-Departure COVID-19 Test Result or Documentation of Recovery from COVID-19 for all Airline or Other Aircraft Passengers Arriving into the United States from Any Foreign Country ."
See NAFSA's page COVID Vaccine and Test Requirements for U.S. Entry for additional details.
Related Content
Regulatory resources.
Places the U.S. Government Warns Not to Travel Right Now
You may want to reconsider traveling to these countries right now.
Do Not Travel to These Countries

Getty Images
Crime, civil unrest and terrorism are common risk factors for countries that end up on the State Department's "Do Not Travel" advisory list.
In 2024, tourism across the globe is “well on track” to return to pre-pandemic levels, according to projections by UN Tourism.
Global conflicts and natural disasters , ranging from a series of coups across Africa to catastrophic earthquakes in the Middle East affected international travel patterns throughout 2023. Still, international tourist arrivals reached 87% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023, according to estimates by UN Tourism .
In January 2024 alone, about 4.6 million U.S. citizens left the country for international destinations, 17% higher than the same month in 2019, according to the International Trade Administration . But some destinations warrant more caution than others.
On Oct. 19, 2023, following the outbreak of war between Israel and Gaza and flaring tensions in the region, the U.S. State Department issued a worldwide caution advisory due to “increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests.” Prior to this update, the most recent worldwide caution advisory was issued in 2022 after a U.S. strike killed Ayman al-Zawahiri, Osama bin Laden’s successor as leader of Al Qaeda, causing “a higher potential for anti-American violence.” The worldwide caution advisory remains in effect.
The U.S. State Department also issues individual travel advisory levels for more than 200 countries globally, continually updating them based on a variety of risk indicators such as health, terrorism and civil unrest. Travel advisory levels range from Level 1, which means exercise normal precautions, to Level 4, which means do not travel there.
About 10% of countries – 19 total – have a Level 4: “Do Not Travel” advisory as of Mar. 4. In Level 4 countries, the U.S. government may have “very limited ability” to step in should travelers’ safety or security be at risk, according to the State Department. Crime, civil unrest, kidnapping and terrorism are common risk factors associated with Level 4 countries.
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list.
Places With a Level 4 Travel Advisory
These are the primary areas the U.S. government says not to travel to right now, in alphabetical order:
Jump to Place: Afghanistan Belarus Burkina Faso Central African Republic Myanmar (formerly Burma) Gaza Haiti Iran Iraq Libya Mali Mexico North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) Russia Somalia South Sudan Sudan Syria Ukraine Venezuela Yemen
Afghanistan: The Central Asian country is wrestling with “terrorism, risk of wrongful detention, kidnapping and crime,” according to the State Department. U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for wrongful detention and kidnapping. In 2022, the government reinstituted public floggings and executions, and women’s rights are disappearing under Taliban control. The U.S. Embassy in Kabul halted operations in August 2021. Since the Taliban took control , many forms of international aid have been halted . Meanwhile, in 2023, some of the year’s deadliest earthquakes killed more than 2,400 in Afghanistan while the country continues to face a years-long extreme drought.
Belarus: Belarus, which shares a western border with Russia and a southern border with Ukraine, has been flagged for “Belarusian authorities’ continued facilitation of Russia’s war against Ukraine, the buildup of Russian military forces in Belarus, the arbitrary enforcement of local laws, the potential of civil unrest, the risk of detention, and the Embassy’s limited ability to assist U.S. citizens residing in or traveling to Belarus.” The U.S. Embassy in Minsk halted operations in February 2022.
Burkina Faso: Terrorism, crime and kidnapping are plaguing this West African nation. Terrorist attacks may target hotels, restaurants and schools with little to no warning, and the East and Sahel regions of the country are under a state of emergency. In late November 2023, hundreds died in clashes between state security forces and rebels near the country’s border with Mali. In June, more than 2 million people in Burkina Faso were displaced due to “violence linked to al-Qaida and the Islamic State group.”
Central African Republic: While there have not been specific incidents of U.S. citizens targeted with violence or crime, violent crime and sudden closure of roads and borders is common. The advisory states that “Embassy Bangui’s limited capacity to provide support to U.S. citizens, crime, civil unrest, and kidnapping” is a factor in its assessment. Recent data from UNICEF suggests the country has the worst drinking water accessibility of all countries in 2022.
Myanmar (Formerly Burma): Armed conflict and civil unrest are the primary reasons to not travel to this Southeast Asian country, which experienced a military coup in early 2021. Limited health care resources, wrongful detentions and “areas with land mines and unexploded ordnance” are also listed as risk factors. After Ukraine and Israel, Myanmar had the highest conflict-related death toll in 2023.
Gaza : Hamas, a foreign terrorist organization as designated by the State Department, controls much of the Gaza Strip, which shares borders with both Israel and Egypt. On Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas fighters broke across the border into Israel, killing hundreds of civilians and soldiers in a brazen attack that stunned Israelis. On Oct. 10, Israel hit the Gaza Strip with “the fiercest air strikes in its 75-year conflict” according to Reuters . The conflict has since escalated into war between Israel and Hamas, with regular Israeli airstrikes leading to extensive civilian casualties in Gaza. As of mid-December, nearly 85% of Gaza’s population were displaced from their homes, according to UN estimates . The region continues to face shortages of food , water, electricity and medical supplies , with conditions deemed “far beyond a humanitarian crisis.” The State Department warns of terrorism and armed conflict within Gaza’s borders.
Haiti: In July 2023, the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Port-au-Prince in response to the increased risk of kidnapping and violent crime in the country , as well as armed conflict between gangs and police. The travel advisory states that cases of kidnapping “often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings.” The travel advisory also states that “U.S. citizens in Haiti should depart Haiti as soon as possible” given “the current security situation and infrastructure challenges.” A series of gang attacks in late September 2023 caused thousands to flee their homes, and many aid groups have been forced to cut or suspend operations amid escalating violence in recent months.
Iran: Terrorism, kidnapping and civil unrest are risk factors for all travelers to Iran, while U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for “arbitrary arrest.” U.S.-Iranian nationals such as students, journalists and business travelers have been arrested on charges of espionage and threatening national security. Executions in Iran rose sharply between 2021 and 2022, bringing the country’s total to nearly 580 people over the year, according to a report by Amnesty International released in May 2023.
Iraq: The State Department cites “terrorism, kidnapping, armed conflict [and] civil unrest” as cause for the country’s Level 4 distinction. Iraq’s northern borders, and its border with Syria, are especially dangerous. Since the escalation of conflict in neighboring Israel in October, there has been an increase in attacks against Iraqi military bases, which host U.S. troops and other international forces. In October 2023, non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members were ordered to leave the U.S. embassy in Baghdad.
Libya: Following the end of its dictatorship over a decade ago, Libya has been wrought with internal conflict between armed groups in the East and West. Armed conflict, civil unrest, crime, kidnapping and terrorism are all risk factors. U.S. citizens have been targets of kidnapping for ransom, with terrorists targeting hotels and airports frequented by Westerners. The U.S. Embassy in Tripoli halted operations in 2014. In mid-September 2023, floods, which some say were intensified by climate change , killed thousands in eastern Libya. Clashes between armed factions escalated across the country in the latter half of 2023, including in the capital city of Tripoli and in Benghazi.
Mali: After experiencing military coups in 2020 and 2021, crime, terrorism and kidnapping are all prevalent threats in this West African landlocked nation. In July 2022, non-emergency U.S. government employees and their families were ordered to leave the country due to higher risk of terrorist activity. A U.N. report in August 2023 said that military groups in the country, including both Mali security forces and possibly Russian Wagner mercenaries, were spreading terror through the use of violence against women and human rights abuses. Democratic elections were supposed to occur in February 2024, but Mali’s military junta postponed the plans indefinitely. In December, the U.N. officially ended a decade-long peacekeeping presence in the country, which had been among the agency’s deadliest missions, with hundreds of the mission personnel killed since 2013.
Mexico: Each state in Mexico is assessed separately for travel advisory levels. Six of the 32 states in Mexico are designated as Level 4: Colima, Guerrero, Michoacan, Sinaloa, Tamaulipas and Zacatecas. Crime and kidnapping are listed as the primary risk factors throughout the country. Nearly 112,000 people were missing across the country as of October, a number the U.N. has called “alarming.”
North Korea (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea): U.S. passports are not valid for travel “to, in, or through” this country, home to one of the world's longest-running dynastic dictatorships. The travel advisory states that the Level 4 distinction is due to “the continuing serious risk of arrest and long-term detention of U.S. nationals.” In July 2023, a U.S. soldier fled across the border into North Korea, where he is believed to be in North Korean custody, the first American detained in the North in nearly five years. He was returned to U.S. custody in September 2023.
Russia: The travel advisory for Russia cites its invasion of Ukraine , harassment of U.S. citizens by Russian government officials and arbitrary law enforcement as a few of the reasons for the Level 4 designation. Chechnya and Mount Elbrus are specifically listed as Level 4 regions. Terrorism, civil unrest, health, kidnapping and wrongful detention are all noted as risks.
Russia Invades Ukraine: A Timeline

Somalia: A severe drought resulting from five failed rainy seasons in a row killed 43,000 people in 2022, and caused a famine amid conflict with Islamist insurgents . Violent crime is common throughout Somalia , pirates frequent its coast off the Horn of Africa, and medical facilities, where they exist, have limited capacity. Crime, terrorism, civil unrest, health and kidnapping are all risk factors. In January 2024, some passengers aboard a U.N.-contracted helicopter were taken hostage by al-Shabaab militants after the vehicle crashed in central Somalia.
South Sudan: Crime, kidnapping and armed conflict are the primary risk factors for South Sudan, which separated from Sudan in 2011, making it the world’s newest country . Weapons are readily available, and travelers have been victims of sexual assault and armed robbery.
Sudan: The U.S. evacuated its embassy in Khartoum in April 2023, and the country closed its airspace due to the ongoing conflict in the country, only permitting humanitarian aid and evacuation efforts. Fighting has escalated in the region between two warring generals seeking to gain control after a military coup in 2021 ousted the country’s prime minister. Civil unrest is the primary risk factor for Africa’s third largest country by area. Crime, terrorism, kidnapping and armed conflict are also noted. The International Criminal Court began investigating alleged war crimes and violence against African ethnic groups in the country in 2023. Millions have fled their homes due to conflict, and the U.N. has said its efforts to provide aid have been hindered by a lack of support, safety and resources. As recently as December 2023, the United Nations warned of catastrophic famine , with millions of children at-risk for malnutrition .
Syria: The advisory states that “No part of Syria is safe from violence,” with terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, armed conflict and risk of unjust detention all potential risk factors. U.S. citizens are often a target for kidnappings and detention. The U.S. Embassy in Damascus halted operations in 2012. Fighting in neighboring Israel has escalated since October, and the conflict has spilled over into Syria, where the U.S. has carried out air strikes following drone and rocket attacks against American troops in Syria and Iraq, triggered by the Israel-Hamas war.
Ukraine: Russian setbacks in their invasion of Ukraine buoyed hopes in Ukraine in 2023. However, Ukraine is a Level 4 country due to Russia’s invasion, with crime and civil unrest also noted as risk factors. The country’s forces shot down two Russian fighter jets on Christmas Eve 2023, in a move Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said “sets the right mood for the entire year ahead.”
Venezuela: Human rights abuses and lack of health care plague this South American nation, which has been in a political crisis since 2014. In 2019, diplomatic personnel were withdrawn from the U.S. Embassy in Caracas. Threats in the country include crime, civil unrest, kidnapping, wrongful detention and poor health infrastructure.
Yemen: Six of the nine risk factors defined by the State Department – terrorism, civil unrest, health risks, kidnapping, armed conflict and landmines – are all present in Yemen. Despite private companies offering tourist visits to the Yemeni island of Socotra, the U.S. government argues those arranging such visits “are putting tourists in danger.” Civil war and cholera are also both present throughout the country. The U.S. Embassy in Sanaa halted operations in 2015. The country has experienced a relative lull in the civil war fighting, but as peace negotiations have gotten traction, flare ups in the fighting have jeopardized progress. Most recently, the U.S. and U.K. have carried out a series of airstrikes in the country, targeting Iran-backed Houthi sites.
Other Countries to Watch
Since Jan. 1, the State Department has updated travel advisories for 17 different countries as well as for the West Bank and Gaza, adding information about specific regions or risk factors, or simply renewing an existing advisory. Travel advisory levels can change based on several factors in a nation, such as increased civil unrest, policies that affect human rights or higher risks of unlawful detention.
The State Department has given about 25 countries an assessment of Level 3, meaning it recommends people “reconsider travel” to those destinations.
On Oct. 14, one week after the deadly Hamas attack on Israel, Israel and the West Bank were both moved from Level 2 to Level 3, while Gaza remains at Level 4. The region’s travel advisory was updated in November to reflect travel restrictions for certain government employees who have not already left the area, and it was updated again on Jan. 3.
Following the outbreak of the Israel-Hamas war in early October, the U.S. State Department raised Lebanon ’s travel advisory level from a Level 3 to a Level 4 level due to “the unpredictable security situation related to rocket, missile, and artillery exchanges” between Israel and Hezbollah or other militant groups. In December, the U.S. Embassy in Beirut returned to normal staffing and presence, and on Jan. 29, the country was moved back to Level 3. Crime, terrorism, armed conflict, civil unrest, kidnapping and unexploded landmines are listed as the country’s primary risk factors. However, the country’s borders with Syria and with Israel, as well as refugee settlements within Lebanon, are specifically noted as Level 4 regions.
China became a Level 3 country in late 2020, with an update in December 2022 citing “the surge in COVID-19 cases, arbitrary enforcement of local laws, and COVID-19-related restrictions” as the reason for the advisory. In June 2023, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR) was moved from the Level 3 to the Level 2 list, but travelers are still advised to be cautious in the area due to “arbitrary enforcement of local laws.” Meanwhile, Macau remains at Level 3.
Following an attempted coup in August 2023, Niger was elevated to Level 4 in August and the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Niamey. In early January 2024, the overall risk level for the country was lowered back to Level 3. Despite the new classification, the State Department still asks non-emergency government personnel and eligible family members to depart the country.
In mid-December 2023 there was an explosion at Guinea’s main fuel depot which has since affected access to health care and basic goods and services. The country was subsequently designated a Level 3 nation after having previously been Level 2. Concerns about civil unrest, health, crime and fuel shortages impacting local infrastructure were listed as the primary risk factors contributing to the change.
Several Level 3 countries are among the worst countries for human trafficking, as designated by the State Department’s annual Trafficking in Persons Report . Level 3 countries on this list include Papua New Guinea, Guinea Bissau, China and Chad. There are also nine Level 4 countries designated as among the worst for human trafficking: Afghanistan, Belarus, Iran, Myanmar, North Korea, Russia, Syria, South Sudan and Venezuela.
Over 70 countries are currently at Level 2, meaning the State Department recommends travelers “exercise increased caution” when traveling to those destinations.
Botswana became the newest Level 2 country on Feb. 26 after having previously been Level 1, with crime noted as the primary risk factor.
France, which saw nationwide protests throughout 2023, has civil unrest and terrorism noted as risk factors for its Level 2 status, and Sweden’s Level 2 status is associated with risks of terrorism.
The Level 2 travel advisory for the Bahamas was updated in January to reflect water safety concerns. The advisory warns that “activities involving commercial recreational watercraft, including water tours, are not consistently regulated” and notes that government personnel are “not permitted to use independently operated jet-ski rentals on New Providence and Paradise Islands.” It also warns visitors to be mindful of sharks, weather and water conditions. The advisory also says that crime is a primary risk factor with gang-on-gang violence contributing to high homicide rates in some areas. Visitors are asked to “be vigilant” and to not physically resist robbery attempts.
Bangladesh 's Level 2 travel advisory was updated in October 2023 to add a note about the country’s general election , which took place Jan. 7, 2024. The advisory states “demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence.” The U.S. has since claimed the country’s election was not free nor fair.
In November 2023, several Level 2 travel advisories were updated with new cautionary information. The advisory for Ghana was updated to reflect threats against LGBTQI+ travelers specifically, noting “anti-LGBTQI+ rhetoric and violence have increased in recent years.” Meanwhile, the advisory for South Africa was updated in February to note that routes recommended by GPS may be unsafe with higher risk for crime.
Turkmenistan was moved off of the Level 2 list to become the newest addition to the Level 1 list on Jan. 22, meaning normal precautions are recommended but there are no risk factors causing travelers to practice increased caution.
The State Department asks travelers to pay attention to travel advisory levels and alerts , review country information pages for their destinations and read related country security reports before going abroad.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Russia , Ukraine , Travel , Coronavirus , Travel Tips , Israel , Gaza , violence , Civil War , crime , kidnapping
Recent Articles

Best Countries

National News

Best Countries Rankings
- # 1 Switzerland
- # 5 Australia
- # 5 United States
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
Switzerland is world's best country.
Julia Haines Sept. 6, 2023

Photos: Best Countries Around the World
Sept. 6, 2023

The 25 Best Countries in the World
Elliott Davis Jr. Sept. 6, 2023

China Hosts Foreign Naval Officials Amid South China Sea Tensions
Reuters April 20, 2024

Taiwan Says It Will Discuss With US How to Use New Funding


Million Dollar Sense
20 Wonderful Facts About The Time Alcohol Was Banned In America
Posted: April 20, 2024 | Last updated: April 20, 2024

#1. The Rise of Speakeasies
Speakeasies flourished during Prohibition, with an estimated 100,000 operating in New York City alone. These clandestine establishments often required patrons to enter through hidden entrances or provide secret passwords, adding an element of excitement and exclusivity to the nightlife. While speakeasies still exist, you likely won’t be arrested for drinking in one.

#2. Bootlegging
Bootlegging became a lucrative business during Prohibition, with bootleggers smuggling alcohol from Canada, producing moonshine in rural areas, and distributing it through underground networks. Notorious gangsters like Al Capone amassed vast fortunes through bootlegging operations.

#3. Flappers and Social Rebellion
Flappers, emblematic of the Roaring Twenties, defied traditional gender norms with their short hair, short skirts, and love of jazz music and dance. They frequented speakeasies, defied the alcohol ban, smoked cigarettes openly, and challenged societal expectations of female behavior.

#4. Organized Crime Syndicates
Prohibition gave rise to powerful organized crime syndicates that controlled the illegal alcohol trade through violence, corruption, and intimidation. Gangsters like Al Capone and Bugs Moran became household names, dominating cities like Chicago with their criminal empires.

#5. Raid and Enforcement
Law enforcement agencies struggled to enforce Prohibition laws effectively due to widespread corruption and public opposition. While raids on speakeasies were common, they often resulted in temporary closures rather than permanent shutdowns, as operators quickly resumed business elsewhere.

#6. Cultural Impact
The Prohibition Era had a profound influence on American culture, shaping the way people socialized, consumed entertainment, and expressed themselves. It led to the creation of iconic cocktails like the martini and the Manhattan, as well as the rise of jazz music and dance clubs.

#7. Women’s Rights and Suffrage
Women played significant roles in the temperance movement, advocating for Prohibition as a means to protect families from the harmful effects of alcohol abuse. The Women’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) led the charge for Prohibition, believing it would lead to social reform and improve public health.

#8. Speakeasy Culture in Urban Centers
Major cities like New York, Chicago, and San Francisco became hubs of speakeasy culture, with underground bars catering to a diverse clientele. Speakeasies ranged from lavish nightclubs frequented by the elite to dingy basement dives hidden from public view.

#9. The Volstead Act and Enforcement Challenges
The Volstead Act, which enforced Prohibition nationwide, faced widespread resistance and defiance from the public. Many Americans continued to drink alcohol despite its prohibition, leading to a spike in prices on the black market and an increase in organized crime.

#10. The Great Gatsby Era
F. Scott Fitzgerald’s novel “The Great Gatsby” captured the decadence and excess of the Prohibition Era, depicting the opulent lifestyles of the wealthy elite and their indulgence in lavish parties fueled by illegal alcohol. The novel remains a timeless portrayal of the era’s allure and disillusionment.

#11. Speakeasy Passwords and Secrecy
To gain entry to speakeasies, patrons often had to provide a secret password or know someone on the inside. This added an element of intrigue and exclusivity to the underground nightlife scene, fostering a sense of camaraderie among regulars. Speakeasies were only as successful as the secret-keeping abilities of their patrons. If a speakeasy got too popular, there was a real risk of a raid from law enforcement.

#12. Moonshine and Homemade Liquor
In rural areas, individuals turned to homemade moonshine and illicitly distilled liquor as alternatives to commercially produced alcohol. Moonshiners operated clandestine stills hidden deep in the woods to avoid detection, risking arrest and confiscation of their equipment.

#13. Celebrity Involvement and Scandals
Celebrities of the era, including actors, musicians, and politicians, were not immune to the allure of speakeasies and illegal alcohol. Their involvement in scandals and arrests added to the mystique surrounding Prohibition-era culture, fueling public fascination and gossip.

#14. Repeal of Prohibition
The end of Prohibition came with the ratification of the 21st Amendment in 1933, which repealed the 18th Amendment and restored the legal sale and consumption of alcohol in the United States. The repeal marked the end of a tumultuous era and ushered in a new chapter in American history.

#15. Legacy of Prohibition
Despite its repeal, Prohibition left a lasting legacy on American society, shaping attitudes toward alcohol, law enforcement, and government regulation. The era remains a fascinating chapter in the nation’s history, reflecting the complexities of social change and moral reform.

#16. Impact on Music and Entertainment
Prohibition fueled the growth of underground music and entertainment scenes, with jazz clubs and speakeasies becoming hotbeds of creativity and rebellion. Musicians like Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington found widespread acclaim in these venues, providing a soundtrack to the era’s defiance.

#17. Literary Reflections
Writers of the Prohibition Era, such as Ernest Hemingway and Dorothy Parker, captured the spirit of the times in their works, exploring themes of decadence, disillusionment, and societal upheaval. Their writings offered insights into the human experience during this tumultuous period.

#18. Social Stratification and Exclusivity
Access to speakeasies often depended on social status and connections, leading to a stratified nightlife culture where the wealthy rarely rubbed shoulders with the working class. The allure of exclusivity drove demand for membership clubs and private events, further segregating patrons based on wealth and influence.

#19. Public Health Concerns
Prohibition was initially framed as a public health measure aimed at reducing alcohol-related harm, but it ultimately led to unintended consequences. The rise of illicit alcohol production and distribution resulted in widespread adulteration and contamination, posing significant risks to public health.

#20. Legacy of Resistance
Prohibition sparked widespread resistance and civil disobedience among the American public, challenging the authority of the government and law enforcement agencies. Bootleggers, speakeasy operators, and ordinary citizens openly defied Prohibition laws, leading to a culture of rebellion and defiance that shaped the era’s identity.
Like our content? Be sure to follow us .

15 Everyday Things Baby Boomers Had 40 Years Ago That Are Luxuries Now
As we ride the waves of technological progress, manufacturing efficiencies and cheap supply chains, some everyday aspects that were once standard now seem like relics of a bygone era. Let us take a nostalgic trip down memory lane as social media users reminisce about luxuries that were once ordinary.

27 Activities to Avoid After Age 75
In this article, we look at common activities that seniors might need to approach carefully or skip entirely to lower the risk of injury or other problems. By recognizing these potential risks and making smart choices, older adults can focus on staying safe and enjoying life as they grow older.
More for You
20 of the world's richest people who you might not know are LGBTQ+
Stephanie Sparks, former pro golfer and Golf Channel host, dead at 50
‘CSI: Vegas' and ‘So Help Me Todd' Canceled at CBS
Target will 'greatly reduce' items on shelves for sale in its stores next year
7 CDs You Probably Owned, Threw Out and Now Are Worth Bank
These Are the Top Curb Appeal Updates for 2024, According to Experts
Patrick Mahomes explains why he may not play in the NFL for as long as Tom Brady
Biden revises Title IX protections for pregnancy, trans people and assault victims
Tenney hits fellow Republicans for failure to advance border bill out of committee
This couple bought a rundown abandoned house for $1.5 million and plan to make it their forever home: Take a look inside
James Bond Trailer Featuring Henry Cavill Receives 2.3M Views Despite Being an AI Fake | THR News Video
Average US annual salary by age revealed – see how you compare
14 Aging Cartoons That Make Getting Older a Whole Lot Funnier
Why You Should Stick to the One-Tenth Rule When Buying a Car
Armand Duplantis breaks pole vault world record for 8th time
Tech trick: How to tell who’s calling when you don’t recognize the phone number
Ex-Patriots star 'not surprised' Bill Belichick's time with team ended: 'We weren’t getting any production'
3 Reasons Why I Regret Buying the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090
39-year-old left full-time job to grow her side hustle—now she makes $279,000 a year without working 'all the time'
‘We’re in trouble’: Pollster reacts to his discussion with young voters
Trans care restrictions force some families to travel hours, spend hundreds for treatment
Misty Stamm was working tirelessly to figure out the details: waking up early, the hourslong drives, booking hotels and finding doctors who could legally administer gender-affirming hormone therapy to her 16-year-old transgender daughter.
Stamm is living in one of the 24 states where legislation is restricting gender-affirming health care for transgender youth, so she and parents like her must make long, expensive trips out of their home states to find the care their children need, according to a new report from the Campaign for Southern Equality Research and Policy Center.
“If we didn't have the care, I don't think she'd be alive,” said Stamm.
Stamm, who lives in Tennessee, drove five hours to get her daughter to a gender clinic in Ohio when her family first started considering care options. She wanted her daughter to be seen by a physician in person.
With new gender-affirming care restrictions set to go into effect soon in Ohio, Stamm and her daughter have since turned to a telehealth provider in Virginia.
However, they still have to drive two hours to Virginia for the online appointment, as to not break Tennessee law, which also bans telehealth providers from providing care and treatments like puberty blockers and hormone therapies to a minor located in the state.
Stamm told ABC News that the time, effort and money they’re spending to access care is worth it.
When she came out as transgender at 13, “the mental health issues stopped completely,” said Stamm. “That affirmed to us that this was the right thing.”
Stamm's daughter had been in counseling and therapy since she was in fifth grade, struggling with her mental health and experiencing depression, anxiety and suicidal ideations.
At age 14, Stamm's daughter received puberty blockers to temporarily pause the development of physical sex characteristics. As her daughter grew older, the family and physicians together decided to move forward with hormone therapy. Throughout this process, they said, psychologists and therapists were consulted and were required for approvals.
“There's no talk of surgery or anything like that,” said Stamm. “That's a decision that she can make when she is an adult.”
Meanwhile, her mental health has progressed exponentially – Stamm said her daughter has since been released by her therapist and is only seen occasionally, as needed.
"She's just doing so well, and if we didn't have access -- we have to have it. She has to have it."
MORE: Report: LGBTQ content drove book banning efforts in 2023
Gas, airfare, lodging and other expenses to cross state lines and access gender-affirming care could cost hundreds to thousands of dollars, the Southern Equality report states.
Stamm says she and her husband have spent likely thousands of dollars in travel costs to get care and are anxiously awaiting the day their daughter turns 18 so she can access care more freely.
The report from Southern Equality Research and Policy Center found that it could take almost 20 hours of driving roundtrip for some families across the South and Midwest to reach a state where trans youth care is legally accessible.
Families with transgender children across southern Florida, Louisiana, Missouri and Texas are the hardest hit, according to the report -- they would need to take a more than eight-hour car ride one way to get to a clinic that serves trans youth.
For Jennifer, an Austin, Texas, resident who asked to go by a pseudonym for safety concerns, said the health care bans in her state threw her family into logistical and financial chaos.
Her 15-year-old daughter’s appointments to begin hormone therapy were canceled before the law in Texas even went into effect. When they sought out care in Louisiana, providers also were canceling appointments.
She sought out the help of local advocacy groups to help her family find a provider in Texas' neighbor to the west, New Mexico.
However, the costs continue to mount: “We are in a position that we could afford to buy plane tickets and stay in a hotel for a couple of nights and pay all of the out-of-pocket expenses for the medical care,” said Jennifer. “For a lot of people, that's probably not an option.”
Though telehealth has expanded opportunities for access to care, policies like those in Tennessee restrict these appointments for prescriptions from happening in the state and force some families like the Stamms to cross borders for online appointments.

Tennessee Gov. Bill Lee, who signed the gender-affirming care ban , has defended the bill against legal challenges.
"Tennessee is committed to protecting children from permanent, life-altering decisions," said Lee in a post on social platform X after the Justice Department argued the law violates the Fourteenth Amendment's Equal Protection Clause.
Supporters of gender-affirming medical care bans argue that children should wait until they’re older to make these medical decisions, and that there needs to be more research on the impact of these procedures on patients.
In the state’s court filings in opposition to a lawsuit against the ban, the state invokes Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization – the decision which overturned Roe v. Wade and ended federal protections for abortion rights.
The state argues that Dobbs allows states “to regulate medical treatments” and that it does not discriminate against transgender people because “not all transgender individuals use puberty blockers, hormones, or surgery.”
“This Court should acknowledge divergent views and hold that the responsibility to choose between them rests with the people acting through their elected representatives,” read the state’s filing.
The Tennessee Legislature is now considering a bill that could make it a felony to help a minor access gender-affirming care out-of-state without parental consent.
MORE: Kansas governor vetoes gender-affirming trans youth care ban
Transgender care for people under 18 has been a source of contention for state politicians in recent years, impacting a group estimated to make up less than 1.5% of the population ages 13-17, according to an estimate from researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles .
Often due to discrimination, stigma, and gender-related stress, trans youth are at increased risk for poor mental health and suicide, substance use, experiencing violence, and other health risks, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Major national medical associations, including the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Medical Association, the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, and more than 20 others have argued that gender-affirming care is safe, effective and medically necessary.
“Allowing them to live in their identity is what saves their mental health,” Jennifer said in response to criticism over transgender medical care.
As families continue to seek out avenues for care, Jennifer and Stamm want lawmakers to know that they're just a "normal, regular family."
“I want them to see us as people,” Jennifer said. “We are their neighbors, we are people who teach their kids in school. We are people they work with.”
Stamm adds, "She's just a regular kid, just trying to be a regular kid. … This has just presented so many challenges for her and we feel isolated. Our circle is tight and small ... Hopefully, people will be a little bit more empathetic to what we're going through. And how ridiculous all of this is."
Related Topics
Up next in news—.

School shooting survivors share their stories, from Columbine to Oxford High

Heart-pounding beach rescue caught on camera

Hiker speaks out after being rescued from California cliff

Skier who survived violent chair lift ride in high winds speaks out
Shop editors picks, sponsored content by taboola.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What the data says about abortion in the U.S.
Pew Research Center has conducted many surveys about abortion over the years, providing a lens into Americans’ views on whether the procedure should be legal, among a host of other questions.
In a Center survey conducted nearly a year after the Supreme Court’s June 2022 decision that ended the constitutional right to abortion , 62% of U.S. adults said the practice should be legal in all or most cases, while 36% said it should be illegal in all or most cases. Another survey conducted a few months before the decision showed that relatively few Americans take an absolutist view on the issue .
Find answers to common questions about abortion in America, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Guttmacher Institute, which have tracked these patterns for several decades:
How many abortions are there in the U.S. each year?
How has the number of abortions in the u.s. changed over time, what is the abortion rate among women in the u.s. how has it changed over time, what are the most common types of abortion, how many abortion providers are there in the u.s., and how has that number changed, what percentage of abortions are for women who live in a different state from the abortion provider, what are the demographics of women who have had abortions, when during pregnancy do most abortions occur, how often are there medical complications from abortion.
This compilation of data on abortion in the United States draws mainly from two sources: the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Guttmacher Institute, both of which have regularly compiled national abortion data for approximately half a century, and which collect their data in different ways.
The CDC data that is highlighted in this post comes from the agency’s “abortion surveillance” reports, which have been published annually since 1974 (and which have included data from 1969). Its figures from 1973 through 1996 include data from all 50 states, the District of Columbia and New York City – 52 “reporting areas” in all. Since 1997, the CDC’s totals have lacked data from some states (most notably California) for the years that those states did not report data to the agency. The four reporting areas that did not submit data to the CDC in 2021 – California, Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey – accounted for approximately 25% of all legal induced abortions in the U.S. in 2020, according to Guttmacher’s data. Most states, though, do have data in the reports, and the figures for the vast majority of them came from each state’s central health agency, while for some states, the figures came from hospitals and other medical facilities.
Discussion of CDC abortion data involving women’s state of residence, marital status, race, ethnicity, age, abortion history and the number of previous live births excludes the low share of abortions where that information was not supplied. Read the methodology for the CDC’s latest abortion surveillance report , which includes data from 2021, for more details. Previous reports can be found at stacks.cdc.gov by entering “abortion surveillance” into the search box.
For the numbers of deaths caused by induced abortions in 1963 and 1965, this analysis looks at reports by the then-U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, a precursor to the Department of Health and Human Services. In computing those figures, we excluded abortions listed in the report under the categories “spontaneous or unspecified” or as “other.” (“Spontaneous abortion” is another way of referring to miscarriages.)
Guttmacher data in this post comes from national surveys of abortion providers that Guttmacher has conducted 19 times since 1973. Guttmacher compiles its figures after contacting every known provider of abortions – clinics, hospitals and physicians’ offices – in the country. It uses questionnaires and health department data, and it provides estimates for abortion providers that don’t respond to its inquiries. (In 2020, the last year for which it has released data on the number of abortions in the U.S., it used estimates for 12% of abortions.) For most of the 2000s, Guttmacher has conducted these national surveys every three years, each time getting abortion data for the prior two years. For each interim year, Guttmacher has calculated estimates based on trends from its own figures and from other data.
The latest full summary of Guttmacher data came in the institute’s report titled “Abortion Incidence and Service Availability in the United States, 2020.” It includes figures for 2020 and 2019 and estimates for 2018. The report includes a methods section.
In addition, this post uses data from StatPearls, an online health care resource, on complications from abortion.
An exact answer is hard to come by. The CDC and the Guttmacher Institute have each tried to measure this for around half a century, but they use different methods and publish different figures.
The last year for which the CDC reported a yearly national total for abortions is 2021. It found there were 625,978 abortions in the District of Columbia and the 46 states with available data that year, up from 597,355 in those states and D.C. in 2020. The corresponding figure for 2019 was 607,720.
The last year for which Guttmacher reported a yearly national total was 2020. It said there were 930,160 abortions that year in all 50 states and the District of Columbia, compared with 916,460 in 2019.
- How the CDC gets its data: It compiles figures that are voluntarily reported by states’ central health agencies, including separate figures for New York City and the District of Columbia. Its latest totals do not include figures from California, Maryland, New Hampshire or New Jersey, which did not report data to the CDC. ( Read the methodology from the latest CDC report .)
- How Guttmacher gets its data: It compiles its figures after contacting every known abortion provider – clinics, hospitals and physicians’ offices – in the country. It uses questionnaires and health department data, then provides estimates for abortion providers that don’t respond. Guttmacher’s figures are higher than the CDC’s in part because they include data (and in some instances, estimates) from all 50 states. ( Read the institute’s latest full report and methodology .)
While the Guttmacher Institute supports abortion rights, its empirical data on abortions in the U.S. has been widely cited by groups and publications across the political spectrum, including by a number of those that disagree with its positions .
These estimates from Guttmacher and the CDC are results of multiyear efforts to collect data on abortion across the U.S. Last year, Guttmacher also began publishing less precise estimates every few months , based on a much smaller sample of providers.
The figures reported by these organizations include only legal induced abortions conducted by clinics, hospitals or physicians’ offices, or those that make use of abortion pills dispensed from certified facilities such as clinics or physicians’ offices. They do not account for the use of abortion pills that were obtained outside of clinical settings .
(Back to top)
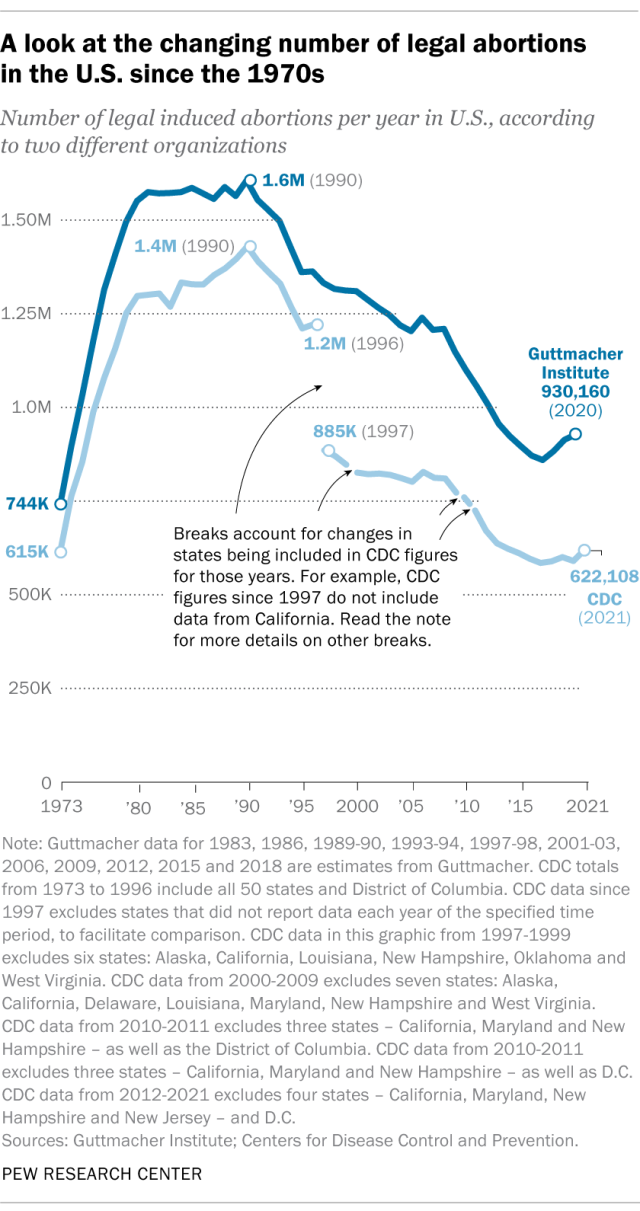
The annual number of U.S. abortions rose for years after Roe v. Wade legalized the procedure in 1973, reaching its highest levels around the late 1980s and early 1990s, according to both the CDC and Guttmacher. Since then, abortions have generally decreased at what a CDC analysis called “a slow yet steady pace.”
Guttmacher says the number of abortions occurring in the U.S. in 2020 was 40% lower than it was in 1991. According to the CDC, the number was 36% lower in 2021 than in 1991, looking just at the District of Columbia and the 46 states that reported both of those years.
(The corresponding line graph shows the long-term trend in the number of legal abortions reported by both organizations. To allow for consistent comparisons over time, the CDC figures in the chart have been adjusted to ensure that the same states are counted from one year to the next. Using that approach, the CDC figure for 2021 is 622,108 legal abortions.)
There have been occasional breaks in this long-term pattern of decline – during the middle of the first decade of the 2000s, and then again in the late 2010s. The CDC reported modest 1% and 2% increases in abortions in 2018 and 2019, and then, after a 2% decrease in 2020, a 5% increase in 2021. Guttmacher reported an 8% increase over the three-year period from 2017 to 2020.
As noted above, these figures do not include abortions that use pills obtained outside of clinical settings.
Guttmacher says that in 2020 there were 14.4 abortions in the U.S. per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44. Its data shows that the rate of abortions among women has generally been declining in the U.S. since 1981, when it reported there were 29.3 abortions per 1,000 women in that age range.
The CDC says that in 2021, there were 11.6 abortions in the U.S. per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44. (That figure excludes data from California, the District of Columbia, Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey.) Like Guttmacher’s data, the CDC’s figures also suggest a general decline in the abortion rate over time. In 1980, when the CDC reported on all 50 states and D.C., it said there were 25 abortions per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44.
That said, both Guttmacher and the CDC say there were slight increases in the rate of abortions during the late 2010s and early 2020s. Guttmacher says the abortion rate per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44 rose from 13.5 in 2017 to 14.4 in 2020. The CDC says it rose from 11.2 per 1,000 in 2017 to 11.4 in 2019, before falling back to 11.1 in 2020 and then rising again to 11.6 in 2021. (The CDC’s figures for those years exclude data from California, D.C., Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey.)
The CDC broadly divides abortions into two categories: surgical abortions and medication abortions, which involve pills. Since the Food and Drug Administration first approved abortion pills in 2000, their use has increased over time as a share of abortions nationally, according to both the CDC and Guttmacher.
The majority of abortions in the U.S. now involve pills, according to both the CDC and Guttmacher. The CDC says 56% of U.S. abortions in 2021 involved pills, up from 53% in 2020 and 44% in 2019. Its figures for 2021 include the District of Columbia and 44 states that provided this data; its figures for 2020 include D.C. and 44 states (though not all of the same states as in 2021), and its figures for 2019 include D.C. and 45 states.
Guttmacher, which measures this every three years, says 53% of U.S. abortions involved pills in 2020, up from 39% in 2017.
Two pills commonly used together for medication abortions are mifepristone, which, taken first, blocks hormones that support a pregnancy, and misoprostol, which then causes the uterus to empty. According to the FDA, medication abortions are safe until 10 weeks into pregnancy.
Surgical abortions conducted during the first trimester of pregnancy typically use a suction process, while the relatively few surgical abortions that occur during the second trimester of a pregnancy typically use a process called dilation and evacuation, according to the UCLA School of Medicine.
In 2020, there were 1,603 facilities in the U.S. that provided abortions, according to Guttmacher . This included 807 clinics, 530 hospitals and 266 physicians’ offices.
While clinics make up half of the facilities that provide abortions, they are the sites where the vast majority (96%) of abortions are administered, either through procedures or the distribution of pills, according to Guttmacher’s 2020 data. (This includes 54% of abortions that are administered at specialized abortion clinics and 43% at nonspecialized clinics.) Hospitals made up 33% of the facilities that provided abortions in 2020 but accounted for only 3% of abortions that year, while just 1% of abortions were conducted by physicians’ offices.
Looking just at clinics – that is, the total number of specialized abortion clinics and nonspecialized clinics in the U.S. – Guttmacher found the total virtually unchanged between 2017 (808 clinics) and 2020 (807 clinics). However, there were regional differences. In the Midwest, the number of clinics that provide abortions increased by 11% during those years, and in the West by 6%. The number of clinics decreased during those years by 9% in the Northeast and 3% in the South.
The total number of abortion providers has declined dramatically since the 1980s. In 1982, according to Guttmacher, there were 2,908 facilities providing abortions in the U.S., including 789 clinics, 1,405 hospitals and 714 physicians’ offices.
The CDC does not track the number of abortion providers.
In the District of Columbia and the 46 states that provided abortion and residency information to the CDC in 2021, 10.9% of all abortions were performed on women known to live outside the state where the abortion occurred – slightly higher than the percentage in 2020 (9.7%). That year, D.C. and 46 states (though not the same ones as in 2021) reported abortion and residency data. (The total number of abortions used in these calculations included figures for women with both known and unknown residential status.)
The share of reported abortions performed on women outside their state of residence was much higher before the 1973 Roe decision that stopped states from banning abortion. In 1972, 41% of all abortions in D.C. and the 20 states that provided this information to the CDC that year were performed on women outside their state of residence. In 1973, the corresponding figure was 21% in the District of Columbia and the 41 states that provided this information, and in 1974 it was 11% in D.C. and the 43 states that provided data.
In the District of Columbia and the 46 states that reported age data to the CDC in 2021, the majority of women who had abortions (57%) were in their 20s, while about three-in-ten (31%) were in their 30s. Teens ages 13 to 19 accounted for 8% of those who had abortions, while women ages 40 to 44 accounted for about 4%.
The vast majority of women who had abortions in 2021 were unmarried (87%), while married women accounted for 13%, according to the CDC , which had data on this from 37 states.
In the District of Columbia, New York City (but not the rest of New York) and the 31 states that reported racial and ethnic data on abortion to the CDC , 42% of all women who had abortions in 2021 were non-Hispanic Black, while 30% were non-Hispanic White, 22% were Hispanic and 6% were of other races.
Looking at abortion rates among those ages 15 to 44, there were 28.6 abortions per 1,000 non-Hispanic Black women in 2021; 12.3 abortions per 1,000 Hispanic women; 6.4 abortions per 1,000 non-Hispanic White women; and 9.2 abortions per 1,000 women of other races, the CDC reported from those same 31 states, D.C. and New York City.
For 57% of U.S. women who had induced abortions in 2021, it was the first time they had ever had one, according to the CDC. For nearly a quarter (24%), it was their second abortion. For 11% of women who had an abortion that year, it was their third, and for 8% it was their fourth or more. These CDC figures include data from 41 states and New York City, but not the rest of New York.
Nearly four-in-ten women who had abortions in 2021 (39%) had no previous live births at the time they had an abortion, according to the CDC . Almost a quarter (24%) of women who had abortions in 2021 had one previous live birth, 20% had two previous live births, 10% had three, and 7% had four or more previous live births. These CDC figures include data from 41 states and New York City, but not the rest of New York.
The vast majority of abortions occur during the first trimester of a pregnancy. In 2021, 93% of abortions occurred during the first trimester – that is, at or before 13 weeks of gestation, according to the CDC . An additional 6% occurred between 14 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, and about 1% were performed at 21 weeks or more of gestation. These CDC figures include data from 40 states and New York City, but not the rest of New York.
About 2% of all abortions in the U.S. involve some type of complication for the woman , according to an article in StatPearls, an online health care resource. “Most complications are considered minor such as pain, bleeding, infection and post-anesthesia complications,” according to the article.
The CDC calculates case-fatality rates for women from induced abortions – that is, how many women die from abortion-related complications, for every 100,000 legal abortions that occur in the U.S . The rate was lowest during the most recent period examined by the agency (2013 to 2020), when there were 0.45 deaths to women per 100,000 legal induced abortions. The case-fatality rate reported by the CDC was highest during the first period examined by the agency (1973 to 1977), when it was 2.09 deaths to women per 100,000 legal induced abortions. During the five-year periods in between, the figure ranged from 0.52 (from 1993 to 1997) to 0.78 (from 1978 to 1982).
The CDC calculates death rates by five-year and seven-year periods because of year-to-year fluctuation in the numbers and due to the relatively low number of women who die from legal induced abortions.
In 2020, the last year for which the CDC has information , six women in the U.S. died due to complications from induced abortions. Four women died in this way in 2019, two in 2018, and three in 2017. (These deaths all followed legal abortions.) Since 1990, the annual number of deaths among women due to legal induced abortion has ranged from two to 12.
The annual number of reported deaths from induced abortions (legal and illegal) tended to be higher in the 1980s, when it ranged from nine to 16, and from 1972 to 1979, when it ranged from 13 to 63. One driver of the decline was the drop in deaths from illegal abortions. There were 39 deaths from illegal abortions in 1972, the last full year before Roe v. Wade. The total fell to 19 in 1973 and to single digits or zero every year after that. (The number of deaths from legal abortions has also declined since then, though with some slight variation over time.)
The number of deaths from induced abortions was considerably higher in the 1960s than afterward. For instance, there were 119 deaths from induced abortions in 1963 and 99 in 1965 , according to reports by the then-U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, a precursor to the Department of Health and Human Services. The CDC is a division of Health and Human Services.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published May 27, 2022, and first updated June 24, 2022.

Support for legal abortion is widespread in many countries, especially in Europe
Nearly a year after roe’s demise, americans’ views of abortion access increasingly vary by where they live, by more than two-to-one, americans say medication abortion should be legal in their state, most latinos say democrats care about them and work hard for their vote, far fewer say so of gop, positive views of supreme court decline sharply following abortion ruling, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
US will not take part in any Israeli retaliatory action against Iran
- Medium Text
- LATEST DEVELOPMENTS
- Blinken and Austin speak to counterparts
- UN's Gutteres calls for de-escalation
- US says Iran will be held accountable
- Israel lifts some security measures
LITTLE SERIOUS DAMAGE

MOTIVATIONS FOR ATTACK DEBATED
Coming soon: Get the latest news and expert analysis about the state of the global economy with Reuters Econ World. Sign up here.
Reporting by James MacKenzie and Maayan Lubell in Jerusalem, Parisa Hafezi in Dubai, Jeff Mason and Daphne Psaledakis in Washington, Suleiman al-Khalidi in Amman and Nidal al-Mughrabi and Adam Makary in Cairo; Writing by Michael Georgy, Angus McDowall, David Morgan and Patricia Zengerle and Lincoln Feast; Editing by William Mallard, Sharon Singleton, William Maclean, Lisa Shumaker and Michael Perry
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Jeff Mason is a White House Correspondent for Reuters. He has covered the presidencies of Barack Obama, Donald Trump and Joe Biden and the presidential campaigns of Biden, Trump, Obama, Hillary Clinton and John McCain. He served as president of the White House Correspondents’ Association in 2016-2017, leading the press corps in advocating for press freedom in the early days of the Trump administration. His and the WHCA's work was recognized with Deutsche Welle's "Freedom of Speech Award." Jeff has asked pointed questions of domestic and foreign leaders, including Russian President Vladimir Putin and North Korea's Kim Jong Un. He is a winner of the WHCA's “Excellence in Presidential News Coverage Under Deadline Pressure" award and co-winner of the Association for Business Journalists' "Breaking News" award. Jeff began his career in Frankfurt, Germany as a business reporter before being posted to Brussels, Belgium, where he covered the European Union. Jeff appears regularly on television and radio and teaches political journalism at Georgetown University. He is a graduate of Northwestern University's Medill School of Journalism and a former Fulbright scholar.

World Chevron
At least two people are dead and six others injured in a shooting at a block party in Memphis, Tennessee, on Saturday, according to police.
South Korea on Sunday protested Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida's offering to Tokyo's Yasukuni Shrine with "deep disappointment" and urged Japanese leaders to show repentance for the country's wartime past.

Two Japanese navy helicopters crashed into the sea during a training exercise, killing at least one of the eight crew members on board, the defence minister said on Sunday.
- Share full article
Advertisement
The U.S. issues new travel guidelines, warning that Iran will avenge the killings of senior commanders.
The State Department has barred its employees from traveling to large parts of Israel. Iran has repeatedly vowed to strike back over the deadly bombing this month of an Iranian Embassy complex in Syria.

By Liam Stack and Eric Schmitt
- April 12, 2024
Several countries including the United States have issued new travel guidelines for Israel and the surrounding region, as the Israeli military said its forces were “highly alert” for a possible Iranian strike in retaliation for the killings of several commanders.
Iran has repeatedly vowed to strike back at Israel over the bombing of an Iranian Embassy complex in Damascus, Syria, this month that killed three generals and four other military officers. An American official said on Friday that Washington expects an attack by Iran against Israel that would be bigger than recent attacks in the long shadow war between the two countries, but not so big that it would draw the United States into war. The official spoke on condition of anonymity because of the sensitivity of the matter.
The U.S. State Department on Thursday barred its employees from traveling to large parts of Israel, the first time the U.S. government had restricted the movement of its employees in this way since the war in Gaza began more than six months ago.
On Thursday, Britain told its citizens that they “should consider leaving” Israel and the Palestinian territories “if it is safe to do so.” On Friday, India told its citizens “not to travel to Iran or Israel till further notice,” while France advised people not to travel to Israel, Iran or Lebanon and evacuated the families of French diplomats from Iran.
Asked about the U.S. travel warning , Matthew Miller, the State Department spokesman, said at a news briefing Thursday: “We have seen Iran making public threats against Israel in the past few days.” He declined to provide details about any specific information that prompted the warning.
The new guidelines bar U.S. government employees and their families from traveling to locations outside the Tel Aviv, Jerusalem and Beersheba metropolitan areas “out of an abundance of caution” until further notice. The State Department said U.S. personnel could move among those areas for personal travel.
The top American military commander for the Middle East, Gen. Michael E. Kurilla, traveled to Israel to coordinate a response to possible Iranian retaliation, U.S. officials said.
“Our enemies think that they will divide Israel and the United States,” the Israeli defense minister, Yoav Gallant, said in a statement on Friday after meeting with General Kurilla. “They are connecting us and are strengthening the relationship between us.”
If Iran attacks, he added, “we will know how to respond.”
On Thursday, the Israeli military’s chief spokesman, Rear Adm. Daniel Hagari, said that the armed forces were “highly alert and prepared” for any action Iran might take, even as the timing and scale of any response remained unclear. Analysts say that Tehran, which has long used a network of proxy forces to project power across the Middle East, wants to avoid igniting a full-fledged war that could drag in the United States and threaten the survival of Iran’s regime.
“For years, and even more so during the war, Iran has been financing, directing and arming its proxies — in Lebanon, Gaza, Syria, Iraq and Yemen — to attack the state of Israel,” he said. “An attack from Iranian territory would be clear evidence of Iran’s intentions to escalate the Middle East and stop hiding behind the proxies.”
Liam Stack is a Times reporter covering the Israel-Hamas war from Jerusalem. More about Liam Stack
Eric Schmitt is a national security correspondent for The Times, focusing on U.S. military affairs and counterterrorism issues overseas, topics he has reported on for more than three decades. More about Eric Schmitt

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Office of the Spokesperson. April 19, 2021. State Department Travel Advisory Updates. In order to provide U.S. travelers detailed and actionable information to make informed travel decisions, the Department of State regularly assesses and updates our Travel Advisories, based primarily on the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC ...
× External Link. You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State. Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein.
The U.S. lifted restrictions Monday on travel from a long list of countries including Mexico, Canada and most of Europe, allowing tourists to make long-delayed trips and family members to ...
Key Points. The U.S. on Monday will lift a pandemic travel ban on international visitors from more than 30 countries after 19 months. New rules will replace the ban, requiring international ...
What to Know: U.S. Travel Restrictions. Lauren Hard 📍 Reporting from New Jersey. Reuters. The new policy ends an 18-month ban on nonessential travel from 33 countries, including China, Brazil ...
The development follows a September announcement in which the White House said that, come November, it will lift the 18-month ban on visitors from the European Union, China, Iran, South Africa ...
The halt to the 18-month ban on travel from 33 countries includes members of the European Union, China, Iran, South Africa, Brazil and India. ... but North America is the second biggest ...
The White House on Friday will lift COVID-19 travel restrictions for fully vaccinated international visitors starting Nov. 8, ending historic restrictions that had barred much of the world from ...
COVID-19 testing and vaccine rules for entering the U.S. As of May 12, 2023, noncitizen nonimmigrant visitors to the U.S. arriving by air or arriving by land or sea no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated against COVID-19. As of June 12, 2022, people entering the U.S. no longer need to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test .
The U.S. is enacting travel bans in an effort to limit the spread of the new omicron variant of the coronavirus, which the World Health Organization warns poses a "very high" global risk.
0:00. 2:02. The U.S. is launching a new travel system on Nov. 8. Vaccinated foreign air travelers will need to show proof of full vaccination and test for COVID-19. The new travel system also adds ...
A: Under the prior policy, there was an exception from temporary travel restrictions for "essential travel." Essential travel included travel to attend educational institutions, travel to work in the United States, travel for emergency response and public health purposes, and travel for lawful cross-border trade (e.g., commercial truckers).
Starting Monday, inbound travelers to the U.S., including citizens, have to make time and budget for Covid tests closer to their departure date.
Yes, as of 12:01 a.m. ET on December 31, the travel bans are lifted. The bans announced on November 26 barred entry into the US of noncitizens coming from eight countries in southern Africa.
It's a long-awaited moment for travelers from more than 30 countries. The U.S. initiated its first COVID-19-related travel ban on China in February 2020. By the end of March, it had added travel ...
U.S. lifts international travel ban 02:13. More than a year and a half after COVID-19 concerns prompted the U.S. to close its borders to international travelers from countries including Brazil ...
With about two weeks to go before the United States lifts a travel ban on visitors from 33 countries, federal health officials offered more specifics for travelers and airlines before restrictions ...
As for many service providers, the COVID-19 pandemic forced profound reductions in the Department's visa processing capacity in two main ways. First, restrictions on travel to the United States, and local restrictions on public places like our overseas consular waiting rooms, curbed our ability to see visa applicants.
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list. Places With a Level 4 Travel ...
The travel ban will not apply to American citizens or lawful permanent residents, officials said. But they will need to show a negative coronavirus test before coming to the United States.
The travel restrictions do not ban flights or apply to U.S. citizens and lawful U.S. permanent residents. ... Airlines for America, an industry trade group, said it was "in communication with the ...
They frequented speakeasies, defied the alcohol ban, smoked cigarettes openly, and challenged societal expectations of female behavior. #4. Organized Crime Syndicates. Prohibition gave rise to ...
For Jennifer, an Austin, Texas, resident who asked to go by a pseudonym for safety concerns, said the health care bans in her state threw her family into logistical and financial chaos. Her 15-year-old daughter's appointments to begin hormone therapy were canceled before the law in Texas even went into effect.
The 18-month travel ban on travelers from Europe, China, Iran, South Africa, Brazil and India has been crippling for the industry, which suffered a $500 billion loss in travel expenditures in 2020 ...
The CDC says that in 2021, there were 11.6 abortions in the U.S. per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44. (That figure excludes data from California, the District of Columbia, Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey.) Like Guttmacher's data, the CDC's figures also suggest a general decline in the abortion rate over time.
President Joe Biden warned Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu the U.S. will not take part in a counter-offensive against Iran, an option Netanyahu's war cabinet favors after a mass drone and ...
For Americans eager to resume international travel, here are the countries that currently allow U.S. citizens to enter, though there may be restrictions, including vaccine requirements.
The U.S. issues new travel guidelines, warning that Iran will avenge the killings of senior commanders. The State Department has barred its employees from traveling to large parts of Israel.