UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Wildlife is our world heritage, unwto/chimelong.
- UNWTO/Chimelong Initiative
- WHY WILDLIFE?
- UNWTO/CHIMELONG ACTIVITIES
- INITIATIVE RESOURCES - CONTACTS

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Why Wildlife?
- Asia and the Pacific
Wildlife tourism refers to the observation and interaction with local animal and plant life in their natural habitats.
It encompasses segments such as eco-tourism, safari tours and mountain tourism among others. Wildlife watching tourism occurs mainly in protected areas. Nature, national parks and wildlife are considered the most important tourism assets for tourists travelling for instance to Africa.

A WWF report shows that 93% of all natural heritage sites support recreation and tourism and 91% of them provide jobs. For instance, in Belize, more than 50% of the population are said to be supported by income generated through reef-related tourism and fisheries.
Wildlife represents biodiversity, essential for our health and the well-being of the whole planet.
Wildlife represents biodiversity, essential for our health and the well-being of the whole planet. We live in an interconnected ecological system, where each macro- and microorganism, whether animal, plant or fish affects the other. Alteration of the natural habitat of any organism will trigger a dynamo effect, so non-equilibrium in the ecological system as a whole endangers the life cycle of many species. Around 40,000 species of animals, fungi and plants benefit humans. More than the third of our pharmaceuticals originate from wild plants
Wildlife remains a major concern for the international, regional and local communities. Among the multiple risks that menace wildlife are: diseases, climate change and actions of human nature, such as poaching and illegal trafficking. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List Index:

- Amphibians are declining most rapidly in Latin America and the Caribbean, partly due to the chytrid fungal disease,
- The greatest extinction risks for birds and mammals are found in South-Eastern Asia, mainly owing to the conversion of lowland forests.
- 7,000 species of animals and plants have been detected in illegal trade, and the list of species under international protection continues to grow.
Policy measures and higher sensitization of the general public and of specific stakeholders like media professionals appear as needed paths to ensure protection of wildlife and therefore of biodiversity. The engagement of printed, audiovisual and electronic and online media outlets in advocating wildlife as an essential component of biodiversity and as an added potential to tourism development by reporting professionally, accurately and comprehensively on this topic remains a major goal. The increased capacity of the media will enable a framework of action together with governments and civil society to improve wildlife and biodiversity protection.
A WWF report shows that 93% of all natural heritage sites support recreation and tourism and 91% of them provide jobs
Wildlife in the Agenda 2030
Besides been mentioned in the SDGs, wildlife and biodiversity have been placed at the core of most of the discussions of the Agenda 2030. The recent UN Biodiversity Conference (December 2016) was integrated by two Working Groups. Working Group I (WG I) addressed cooperation with other conventions and organizations; a global multilateral benefit-sharing mechanism under the Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization; and socioeconomic considerations, liability and redress, risk assessment and risk management, and unintentional transboundary movement of living modified organisms (LMOs) under the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety.
The Working Group II (WG II) approved conference room papers (CRPs) on sustainable wildlife management, recommendations from the UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII), and climate-related geo-engineering. WG II further addressed marine debris and underwater noise, marine spatial planning, biodiversity in cold-water areas and pollinators.
Reasons for wildlife protection and conservation
For those still not convinced about the potential of wildlife, lets remind some of the benefits:
- Biodiversity: In nature, different species are connected through various food webs. The disappearance of one species could influence several others down the line.
- Agriculture: Promoting wildlife conservation could help secure future food supplies.
- Research: There may be many undiscovered plants and animals in the wild. 50 percent of the drugs available in the United States were originally developed from microbial organisms, plants, and animals.
- Economics of Eco-Services: ecosystem activities have an effect on the quantity and quality of fresh water accessible to humans.
- Ecotourism: enjoying African ecosystems has been a tremendous stimulus for economies within Africa.
- Environmental Indicators: various animals can serve as indicators for other environmental problems is one of the rarely discussed benefits of wildlife conservation. The loss of peregrine falcons and bald eagles was one of the factors that alerted scientists to the toxicity of DDT, unnoticed for longer in a less diverse ecosystem.
- Education: Studying animals and their habitats can be a valuable learning experience for students of all ages.
- Psychological Benefits: Ecotourists experience a tremendous sense of wonder, contentment, and fulfillment from their wildlife encounters.
Challenges in the wildlife global cause

- Trafficking in wildlife and their parts is a criminal international trade worth an estimated $20 billion a year
- Several iconic species —including elephants, rhinos, and tigers, as well as many lesser known species — toward the precipice of extinction
- Examples: The loss of African elephants: 100,000 over the past three years (96 elephants a day, with only 400,000 remaining in the wild across all of Africa).
- Fewer than 30,000 wild rhinos survive.
- A mere 3,200 wild tigers survive in the forests of Asia, including only 1,000 breeding females.
Areas of work , three central goals:
- Stopping the killing;
- Stopping the trafficking; and
- Stopping the demand
Download PDF
- Download the UNWTO Briefing Paper 'Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa'

Why Wildlife Tourism Isn’t Always A Good Thing
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Wildlife tourism refers to any tourism that involves wildlife- from swimming with dolphins to volunteering at a turtle conservation centre. The wildlife tourism industry is diverse, taking many different shapes and forms. However, the wildlife tourism industry is also very controversial and has been subject to a lot of negative media coverage in recent years.
In this article I will teach you about what wildlife tourism is and I will introduce you to the different types of wildlife tourism that occur around the world. I will also explain to you why this is a very important industry and the many advantages of wildlife tourism. Lastly, I will outline some of the negative aspects that are associated with wildlife tourism and provide suggestions on how wildlife tourism can be responsible.
What is wildlife tourism?
Zoos and aquariums, animal rescue centres and sanctuaries, birdwatching, whale watching, hunting and fishing, swimming with dolphins, playing with lions and tigers, cuddling a panda, elephant riding, shark cage diving, gorilla trekking, monkey forests, ostrich riding, conservation, breeding porogrammes, economic benefits, job creation, mistreatment of the animals, introduction of disease, wild animals can be dangerous, changes in animal behaviour, reduced breeding success, do your research before you go, don’t get too close, sanctuaries and rescue centres are better than zoos, don’t mess with nature, animal souvenirs, eat carefully, raise awareness about wildlife tourism, wildlife tourism: further reading.

Put simply, wildlife tourism is tourism that involves wildlife. But the important question is, what is wildlife? And when does a wild animal stop being ‘wild’?
Most types of animal tourism involves the use of animals that are or were once living in the wild. Whether its a stray cat who was taken into a shelter, or a zoo-based rhinoceros that was rescued from poachers, unless bred in captivity, the majority of animals that we see in the tourism industry come from the wild.
As such, wildlife tourism, in its broadest sense, encounters all types of tourism that involves animals. Types of wildlife tourism can then be segregated into two categories: animals in captivity and animals in the wild.
Types of wildlife tourism
There are many different types of wildlife tourism.
The United Nations estimates that tourism involving wildlife accounts for around 7% of all tourism around the world. However, they exclude animals in captivity, so unreality this figure is likely much higher. From safaris in Tanzania to diving at then Great Barrier Reef, there are plenty of ways that tourists can watch and get up close and personal with wildlife.
Below, Have outlined the most commonly found types of wildlife tourism around the world, with examples.

A safari takes place in an animal’s natural habitat. Safari’s usually involve the use of a small safari vehicle and a ranger, who will drive tourists to areas where there are likely to be animals.
Safari is traditionally associated with Africa, but can also be found in other parts of the world.
Popular safari destinations: Tanzania; Kenya; South Africa

A zoo or an aquarium is a place where animals are kept captivity, usually in cages. Zoos are renowned for having small enclosures and for domesticating animals.
Some zoos and aquariums have important research projects and breeding programmes. Many will also take on rescue animals or marine life.
Popular zoos: San Diego Zoo; Singapore Zoo; Australia zoo, London Zoo
Popular aquariums: Georgia aquarium; Marine Life Park, Sentosa, Singapore; Dubai Mall Aquarium

Many farms around the world have been commercialised to allow visitors in to see the animals. They may include feeding experiences and the opportunity to interact with the animals, such as stocking the rabbits or riding the horses.
Farms are usually small, independently owned businesses that are not famous around the world, but that are well known within the local area.

Animal rescue centres and sanctuaries are businesses who rescue animals and then care for them.
Oftentimes they will look like a zoo, and may be commercialised in a similar way. However, the funds made should be reinvested into the business, rather than for profitable gain.
Popular animal rescue centres and sanctuaries: Elephant Nature Park, Thailand; Lonely Pine Koala Sanctuary, Australia; Sloth Sanctuary of Costa Rica ; The David Sheldrick Wildlife Trust, Kenya; Panda Research Centre,Chengdu, China

Birdwatching, also referred to as birding, occurs in a bird’s natural habitat. It involves watching the birds, often from a distance with the use of binoculars.
It can also involve the use of a webcam, facilitating virtual tourism .
Popular birdwatching destinations: The Gambia ; The Galapagos; The Pantanal, Brazil

Whale watching usually occurs on tours, when tourists will be taken out to sea on a boat in search of whales. There will usually be a guide who will provide details about the whales and who is able to spot them easily through a trained eye.
Popular what watching destinations: Australia; Iceland; South Africa ; Canada

Hunting is the practice of pursuing and capturing or killing wild animals. Many animals are hunted for enjoyment throughout the world, from deer to pigeon to bears.
Hunting can be both legal and illegal depending on where it takes place and what is being hunted.
Likewise, fishing is a popular activity around the globe. Some people fish for enjoyment and return the fish to the water once caught and others eat or sell the fish.
Popular hunting animals: Deer; pigeon; rabbit; bears

Diving is a popular form of wildlife tourism, enabling tourists to experience life beneath the sea.
Many people will undertake PADI courses or similar to enable them to dive deeper and swim further.
Popular dive sites: the Great Barrier Reef, Australia; The Red Sea,Egypt ; Blue Hole,Belize, Gili Islands, Bali
Wildlife encounters
Many people are keen to get up close and personal with wildlife.
Back in the 2000’s everyone was doing it. If you had a photo of you and a baby tiger as your Facebook profile picture you were one of the cool kids. Upload that same photo today and you will likely experience a barrage of abuse from your nature-loving friends and connections.
Some types of wildlife encounters are great. Take volunteer work, for example. There are many conservation projects around the world that are desperate for volunteer tourists to help run their operations.
However, most animals encounters are not so good. Animals are often drugged or abused to keep them calm around the tourists. They are kept in inhumane conditions and treated unethically- I mean, would you want to walk up and down the road all day long with people on your back?!
Here are some the most common wildlife encounters around the world:

You can swim with dolphins in the wild in a handful of places around the world.
It is more common, however, to swim with dolphins that are in enclosures. These animals are taken out of their natural habitats and asked to perform trips and entertain tourists.
Popular places to swim with dolphins: USA, Mexico, Bahamas , Portugal.

There are plenty of places that allow you to have an up close and personal experience with lions and tigers.
Naturally, these are dangerous animals, so that instantly raises alarm bells to me. Oftentimes these animals are drugged and abused to ensure that they ‘perform’ for the tourist.
Popular places to play with lions and tigers: Thailand, India , South Africa

Cuddling a panda is a thing of the past unless you are a volunteer tourist (and still many would argue even this is unethical). The last commercial activity which enabled you to cuddle and have your photograph taken with a panda stopped operations in 2018.
However, there are still plenty of opportunities to visit the famous giant pandas, most of which are in China .
Popular places to visit pandas: China

Elephant riding is most commonly found in Asia. Elephants are used to carry tourists around as a leisure activity. There have been many ethical debates about this, which has resulted in a reduction of elephant rides taken around the world.
Now, many elephant organisations are trying to appeal to tourists who take a more ethical approach by transforming their organisation into an ‘elephant sanctuary. Whilst these are sometimes genuine, with ethical practices, some are not so- they simply disguise their unethical approaches by giving themselves the title ‘sanctuary’.
Popular elephant riding destinations: Thailand , Cambodia, India

A cat cafe is a venue that houses a variety of cats, whilst also serving basic food and beverages. People pay an entrance fee or hourly rate to sit with the cats. You can play with the cats and stroke them. Cat cafes are most commonly found in Asia and are particularly popular in Japan, although you can also find them in other parts of the world.
Some cat cafes claim to be rescue centres or sanctuaries, but most operate on a for-profit business. Some do not allow young children in, for fear off them scaring or hurting the animals. Others have no such rules. A cafe is obviously not a natural place for a cat to live, and some argue that the concept in unethical.
Popular destinations with cat cafes: Japan, Thailand ,

Shark cage diving is essentially underwater diving or snorkelling whilst inside a cage. A process called chumming ( baiting the sharks with minced fish) is used to lure the sharks towards the cage.
Shark cage diving can be dangerous both for the person inside the cage and for the shark. The methods are also questionable. Encouraging the sharks to behave in a way that they wouldn’t usually will lead to lasting behavioural changes, which will inevitably have a knock on effect on other marine life and the wider ecosystem.
Popular shark cage diving destinations: South Africa, Florida

Gorilla trekking occurs in remote areas on the African continent . The concept is quite simple- tourists go hiking in search of gorillas.
Gorilla trekking is a unique experience, and tours are pricey. Tourists generally keep their distance and there have been few negative impacts reported.
However, there is always potential for abuse. Careful regulation and monitoring needs to remain in place to ensure that the gorillas are not tempted into certain areas with food or disturbed by the presence of trekkers.
Popular gorilla trekking destinations: Rwanda, Uganda

A monkey forest is a wooded area where monkeys live. This could be the monkeys’ natural habitat, but more likely they have been placed there intentionally.
Visitors will usually pay an entrance fee. They are then free to roam around the forested area and interact with the monkeys. Some monkey forest areas are relatively natural, whereas others may have monkey shows or circuses.
It can be dangerous to visit a monkey forest. As a result of human interaction and loss of natural habitat and feeding grounds monkey often become vicious. It is common for them to bite tourists, which then requires the person to visit a hospital for a rabies jab.

Ostrich riding occurs mostly on ostrich farms and was a popular tourist activity until fairly recently. In 2017, ostrich riding was banned in South Africa, which is where it most commonly occurred.
Ostrich riding as a form of wildlife tourism was/is unethical. This is because the weight of the tourist can seriously hurt the ostrich. It is also not good to make the ostrich spend its day running up and down with people on its back.
Popular places to ride an ostrich: South Africa
Benefits of wildlife tourism
Wildlife tourism can be a great thing. There are many positive impacts of wildlife tourism including; conservation, research, breeding programmes and economic benefits.
For many wildlife tourism businesses, conservation is their top priority. In fact, most places where the focus is conservation would rather not have any tourists come to visit at all, however it is the tourists that pay the bills and allow their business to operate.
Wildlife tourism businesses can be fantastic for conservation and can raise a lot of money. These types of businesses are usually charities or trusts. They do not make a profit and their intentions are wholesome.

Wildlife tourism also facilitates important research. Research can help us to further understand the animals and therefore to better cater for them, both in the wild and in captivity.
Many wildlife tourism projects have successful breeding programmes. From Siberian tigers and pandas in China to koalas in Australia to lions in Botswana, there are successful breeding programmes underway around the world.
Many of these programmes would not be able to operate without the money raised from tourists.
There are many positive economic impacts of wildlife tourism.
Wildlife tourism brings tourists to a given area, and they bring money with them! They spend money on hotels, on food and on transport.
This money can then be reinvested into the economy and spent on areas such as healthcare and education.
Another economic advantage of wildlife tourism that is worth mentioning is job creation. Whatever type of wildlife business it is, it will require staff. This helps to boost employment figures in the area as well as helping the boost the overall economic prospects resulting from wildlife tourism.
Disadvantages of wildlife tourism
Sadly, there are also many disadvantages of wildlife tourism. Whilst there is great potential for wildlife tourism to do good, many businesses are poorly managed and demonstrate unethical practices. This most commonly includes; the mistreatment of animals, introduction of disease, dangerous behaviour, changes in the animal’s behaviour and reduced breeding success.
Mistreatment of animals is common, especially in developing countries.
Fortunately, there is a lot more awareness of this nowadays than there once was. Recent years have seen many laws and regulations introduced in the name of animal welfare all over the world. This has helped to reduce the mistreatment of animals in the wildlife tourism business.
Nevertheless, mistreatment does still occur and it is pretty common. There are still circuses that use animals and attractions that make animals perform tricks for tourists. From elephant camps in Thailand to monkeys dressed as babies in Morocco, there are many examples of mistreatment around the world.

Since the COVID-19 pandemic, I think that all understand animals can pass disease onto humans. And this also works the other way around.
When tourists are allowed to have close interaction with animals there is a risk of them passing on illnesses that the animals do not have immunity to. A common cold might not be a big deal for a human, but it could kill a lion cub, for example.
Many of the people who work in animal tourism are not trained in this field and could unintentionally introduce disease either to humans or to the animals that they are working with.
Animals are unpredictable and can be dangerous. Elephants can easily trample people, sharks can bite and monkeys can give a person rabies.
Using animals in a tourism setting can have serious implications for its welfare and wellbeing.
How would you respond if you were locked in a cage and only let out to perform tricks? I bet your behaviour would change!
These behavioural changes can be unpredictable and dangerous, for both the tourist and the animal.
When animals are taken away from their usual habitat and exposed to tourists they may have trouble breeding.
For businesses that claim to be conservation centres, this can actually have the opposite effect. Instead of protecting the species it can exemplify and exhasberate its extinction.
Responsible wildlife tourism

The moral of the story here is this- wildlife tourism can be great, but it needs great management. When wildlife tourism is bad, it is very bad.
Wildlife tourism businesses need to operate under sustainable tourism practices. In recent years we have seen many wildlife tourism organisations change their practices. This is perhaps most common in Thailand, where many elephant riding companies have become sanctuaries.
But it’s not just down to the business, it’s down to us tourists too! Here are some of the things that can do to ensure responsible wildlife tourism.
This is sometimes easier said than done, because there isn’t always a great deal of information available about every wildlife tourism attraction. Nonetheless, you should always try to research the place that you are considering visiting before you do so.
There are many wildlife conscious people around in today’s world, and if it is a major attraction that you are thinking about going to then there will be reviews on Trip Advisor and other review sites. And if there is mistreatment of the animals then you will most likely find information about it here.
If the reviews are bad then I urge you not to go. Yes, you might get to have a cuddle with a lion cub, that’s cute. But think about the picture picture here.
Getting too close to animals can have a number of negative impacts. It can scare the animals, it can cause changes to their behaviour, it can cause them to stop breeding or relocate town area that is less safe. It can also be dangerous.
Be sensible and keep your distance from animals.
If you really want an animal experience, you should choose to visit a sanctuary or research centre rather than a zoo. From the outside, the differences might not be that obvious, but from the inside the differences are big.
The treatment of the animals should be better, to start with. Plus sanctuaries have underlying motives that are not about making money. They are there to protect, rehabilitate and conserve the species, not to exploit it. For these types of organisations, allowing visitors is a means of making enough money to support the conservation project, not a way to get rich as the expensive of a poor animal(s).
Beware, however. Some places label themselves as sanctuaries, when there is in reality little conservation involved. It is simply cover up for their less altruistic intentions. This is why doing your research is important- don’t just read what you see on the tin!
Let nature be nature. Don’t put clothes on animals, don’t feed them and don’t interfere with them.
All of these things lead to instant and progressive changes in animal behaviours. The wildlife that you are seeing today won’t be the same in 10 or 20 or 30 years if you keep messing with it.
Be mindful of souvenirs that you are buying. Sometimes souvenirs are made with ivy or animal fur, for example. This has inevitably involved the death of an animal. So be careful when you go shopping and think before you buy.
There’re also a number of destinations that use wildlife in their food and drink.
In Vietnam, for example, many backpackers think it is funny to drink snakes blood or drinks theatre made bu drowning live snakes in them. There is nothing funny our cool about killing a snake. End of.
In countries such as China and Japan, it is common to see (often endangered) shark on the menu un restaurants. And in Iceland you can eat whale or puffin. I’m not a vegetarian, but I draw the line on eating endangered animals, and you should too.
The most important thing you can do is raise awareness.
If you visit wildlife attraction that you think is doing a great job, write a review on Trip Advisor, tell your friends. Every little helps to support their cause.
Likewise, if you see an attraction that is operating unethically, then you should definitely speak out. This is especially important with smaller, lesser known attractions. If nobody tells you, then you don’t know, right?
I hope you have enjoyed reading this article about wildlife tourism and that you have learnt something new today! If you want to learn a bit more, then I recommend the following:
- Wildlife Tourism – A landmark contribution to the rapidly growing field of wildlife tourism, especially in regard to its underpinning foundations of science, conservation and policy.
- Wildlife Tourism Futures: Encounters with Wild, Captive and Artificial Animals – An excellent book focussing on future wildlife tourism development and management; the experiential value, educational components and ethical relevance of tourism-animal encounters; and the technology applied to wildlife tourism.
- Marine Wildlife and Tourism Management: Insights from the Natural and Social Sciences – This book demonstrates that through scientific approaches to understanding and managing tourist interactions with marine wildlife, sustainable marine tourism can be achieved.
Liked this article? Click to share!
Growing Wildlife-Based Tourism Sustainably: A New Report and Q&A

Copyright: Sanjayda, Shutterstock.com
STORY HIGHLIGHTS
- While wildlife and biodiversity are increasingly threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and a lack of funding for protection, nature-based tourism is on the rise and could help provide solutions for these issues.
- The publication Supporting Sustainable Livelihoods through Wildlife Tourism highlights successful wildlife tourism programs in seven countries in Africa and Asia that can be used as models to promote conservation and boost economies.
- World Bank lead economist Richard Damania answers questions on the drivers, innovations and challenges for wildlife tourism, and why the World Bank Group and governments should support sustainable tourism strategies.
Wildlife tourism is a powerful tool countries can leverage to grow and diversify their economies while protecting their biodiversity and meeting several Sustainable Development Goals. It is also a way to engage tourists in wildlife conservation and inject money into local communities living closest to wildlife. Success stories and lessons learned from nature-based tourism are emerging from across the globe.
“Here is a way of squaring the circle: provide jobs and save the environment,” said World Bank lead economist Richard Damania, who has extensive experience in understanding the link between tourism and the economy . In 2016, travel and tourism contributed $7.6 trillion, or 10.2%, to total GDP, and the industry provided jobs to one in 10 people, according to the World Travel & Tourism Council .
While nature-based tourism, which includes wildlife tourism, has been expanding rapidly in the last decade or so due to increased demand and opportunities, wildlife and biodiversity are increasingly threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and a lack of funding for protection.
Which is why more than ever countries need to look to concrete examples of well-planned, sustainably-run tourism operations that have led to increased investments in protected areas and reserves, a reduction in poaching, an increase in the non-consumptive value of wildlife through viewing , and opportunities for rural communities to improve their livelihoods through tourism-related jobs, revenue-sharing arrangements, and co-management of natural resources.
A recently-released publication— Supporting Sustainable Livelihoods through Wildlife Tourism —developed by the World Bank Group and the Global Wildlife Program , funded by the Global Environment Facility , showcases sustainable wildlife tourism models that can be applied to developing countries, and offers solutions and case studies to bring insight into this sector as a mechanism for inclusive poverty reduction and global conservation.
The Global Wildlife Program spoke with Damania to learn more about the growth, challenges, and innovations in wildlife-based tourism.

Copyright: Wandel Guides, Shutterstock.com
Why should the World Bank support conservation endeavors, and how does wildlife tourism help support our mission?
Enlightened self-interest is one obvious reason why we need to promote wildlife tourism. It provides the most obvious way to reconcile the interests of nature with the imperative for development and growth. Tourism simultaneously creates jobs while, when done well, protects natural habitats.
Prudence and precaution are another reason why investments in nature-based tourism ought to be promoted. The science of “ planetary boundaries ” warns us that many fragile natural environments and ecosystems are reaching their limits and in some cases, the hypothesized safe boundaries have been crossed. Further damage will imply that we lose important ecosystem services such as watershed and soil protection with damaging consequences for development.
But, in my mind, perhaps the most important reason is humanity’s moral and ethical imperative as stewards of global ecosystems. Simply because humanity has the ability to destroy or convert ecosystems and drive species to extinction does not make it ethically justifiable. There needs to be an ethical balance and that is where ecotourism comes in. We need jobs and economic growth, but here is a way to get jobs and growth in ways that meet our moral and ethical obligation.
What have been the drivers behind a burgeoning nature-based/wildlife-based tourism sector?
I think there are two things that drive it: as habitats diminish there is more scarcity and their value goes up. Everyone wants to see the last remaining habitats of wild gorillas for instance, or the few remaining wild tigers in India. In sum scarcity confers economic value.
Another force driving demand is the internet and rising lifestyles—you can learn about animals and habitats you might not have known existed, and more people have the ability to visit them. So, you have supply diminishing on one hand, and demand rising on the other hand which creates an opportunity for economic progress together with conservation.
What is your advice to governments and others who are developing or expanding on a nature or wildlife-based tourism strategy?
Tourism benefits need to be shared better . There is a lack of balance with too many tourists in some places, and none elsewhere. Some destinations face gross overcrowding, such as South Africa’s Krueger National Park or the Masai Mara in Kenya where you have tourists looking at other tourists, instead of at lions. We need to be able to distribute the demand for tourists more equally. The Bank has a role to play in developing the right kind of tourism infrastructure.
Those living closest to nature and wildlife must also benefit . The local inhabitants that live in the national parks or at their periphery are usually extremely poor. Having tourism operations that can benefit them is extremely important for social corporate reasons, but also for sustainability reasons. If the benefits of tourism flow to the local communities, they will value the parks much more.
We also need to be mindful of wildlife corridors . We know that dispersion and migration are fundamental biological determinants of species survival. Closed systems where animals cannot move to breed are not sustainable in the long run. As we break off the corridors because of infrastructure and increasing human populations we are putting the ecosystems on life support.
There are some who believe we can manage these closed ecosystems, but it takes an immense amount of self assurance in science to suggest this with confidence, and it is unclear that one can manage ecosystems that we do not adequately understand. A measure of caution and humility is needed when we are stretching the bounds of what is known to science.
What are some of the innovative partnerships that are helping the wildlife-based tourism businesses in developing countries?
One very successful model that has combined wildlife conservation and management and community benefits and welfare is the Ruaha Carnivore Project in Tanzania, part of Oxford University’s Wildlife Conservation Research Unite ( WildCRU ). They use a payment for ecosystem services (PES) scheme and do all the right things.
Another example are the community conservancies in Namibia. The community manages the land for wildlife and there are a variety of profit sharing commercial tourism arrangements—although not everything always works fairly or perfectly. Incentives matter deeply and communities need to be guided and need technical assistance in setting up commercial arrangements.
The Bank needs to understand these better and find ways of scaling those up. The IFC has a very good role to play here as well.
To learn more and to explore numerous examples of community involvement in wildlife tourism from Botswana, India, Kenya, Malawi, Namibia, South Africa and Uganda, read the report Supporting Sustainable Livelihoods through Wildlife Tourism or find a one-page fact sheet here .
The Global Wildlife Program (GWP) is led by the World Bank and funded by a $131 million grant from the Global Environment Facility (GEF). The program is working with 19 countries across Africa and Asia to promote wildlife conservation and sustainable development by combatting illicit trafficking in wildlife, and investing in wildlife-based tourism.
- Full Report: Supporting Sustainable Livelihoods through Wildlife Tourism
- Fact Sheet on Key Messages
- Report: Twenty Reasons Sustainable Tourism Counts for Development
- Report: Women and Tourism: Designing for Inclusion
- Blog: Africa can Benefit from Nature-based Tourism in a Sustainable Manner
- Feature: Ramping up Nature-Based Tourism to Protect Biodiversity and Boost Livelihoods
- Website: Global Wildlife Program
- Website: Environment
- Website: Competitiveness
- Global Environment Facility
Introduction: Wildlife Tourism Management and Phenomena: A Web of Complex Conceptual, Theoretical and Practical Issues
- First Online: 16 June 2017
Cite this chapter

- Ismar Borges de Lima 6 , 7 &
- Ronda J. Green 8 , 9
Part of the book series: Geoheritage, Geoparks and Geotourism ((GGAG))
2356 Accesses
4 Citations
This introductory chapter highlights the major conceptual and practical issues regarding wildlife tourism worldwide. A series of events have brought concerns that the status and conditions of wild animals in the tourism needs further critical discussion, with current study cases being in the spotlight for analysis. There is a web of complexities permeating the field of wildlife tourism in terms of planning and management, not to mention the ethical issues. The current state of wildlife tourism draws attention to the need of in-depth reflections and insights on the use of animals as attractions as well as the needs and attitudes of tourism personnel and visitors. A change in perception of the natural world on the whole is needed, from a fully utilitarian view to a more compassionate one. The Earth is not home only for humans, so we need to break away from a predominantly anthropocentric view in our society. Indeed, within these epistemological and philosophical frames, ‘ecological’ and ‘conservation’ aspects have been regarded as fundamental for bringing a certain consensus to the equation on a morally acceptable human-nature relation for the 21st Century. This introductory chapter begins by presenting conceptual and disciplinary approaches to environmental social sciences, as well as human and political ecology, pertinent to this volume. It then presents some of the polemic cases involving wildlife and visitors, such as Cecil the lion, the tigers in the Thai Buddhist Temple, and, the killing of gorilla Harambe. The chapter concludes by presenting a summary of each chapter providing unique and original content to making this volume an exciting reading experience to update the readers' knowledge and understanding of the current state of wildlife tourism and issues facing it, as part of the bigger picture of our practical and ethical viewpoints of humans and the rest of nature on our planet.
This book gathers a great selection of case studies that fill gaps in the literature on wildlife tourism, by critically and insightfully informing the readers on theoretical and practical issues with regards to human and wild animal encounters, and the ways to approach, understand and manage this complex and intricate relationship.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Actman J (2016) Cecil the lion died one year ago—here’s what’s happened since. Wildlife Watch News. National Geographic (May, 2016). Retrieved from, http://news.nationalgeographic.com/2016/06/cecil-african-lion-anniversary-death-trophy-hunting-zimbabwe/ . Accessed on 8 Dec 2016
Altschiller D (2011) Animal-assisted therapy. Health and medical issues today. Greenwood, Oxford, UK
Google Scholar
Armstrong P (2011) The gaze of animals. In: Taylor N, Signal T (eds) Theorizing animals: re-thinking humanimal relations. Brill, Leiden & Boston, pp 175–201
Chapter Google Scholar
Archer J (1988) The behavioural biology of aggression. Cambridge University Press, Melbourne
Bauer J, Giles J (2002) Recreational hunting: an international perspective. Wildlife Tourism Research Report Series n. 13. Cooperative Research Centre for Sustainable Tourism—CRC, Queensland, Australia
BBC (2016) Thai Tiger Temple’s long history of controversy. Asia section (June 1, 2016). Retrieved from http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-36423321 . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
Beatson P (2011) Mapping human animal relations. In: Taylor N, Signal T (eds) Theorizing animals: re-thinking humanimal relations. Brill, Leiden & Boston, pp 21–58
Bertelsmeier C, Bonnaud E, Gregory S, Courchamp F (2012) Applied ecology. In: Hastings A & Gross L (eds), Encyclopedia of theoretical ecology. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles
Brando S (2016) Wild animals in entertainment. In: Bovenkerk B, Keulartz FWJ (eds) Animal ethics in the age of humans: blurring boundaries in human-animal. Springer, Cham, pp 295–318
Cambronne A (2013) Deerland: American hunt for ecological balance and the essence of wilderness. Nature. Lyon Press, New York
Chandler CK (2012) Animal assisted therapy in counseling. Routledge, New York
Cunningham W, Cunningham M (2005) Environmental Science. McGraw-Hill Education, New York
Cusack O (1988) Pets and mental health. Routledge, London
de Lima IB (2009) Utilitarian and abstract rhetorics in ecotourism and social constructionism: the power of language. Int J Manag Decis Mak 10(231):2009
Duffy R, Moore L (2011) Global regulations and local practices: the politics and governance of animal welfare in elephant tourism, Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 19(4-5):589–604
EcoWatch (2016) Five times animals have been killed in zoos due to human encounters. Animals (June 3, 2016). Retrieved from http://www.ecowatch.com/5-times-animals-have-been-killed-in-zoos-due-to-human-encounters-1891162359.html . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
Engel TB, Galloway ML, Bull MP (1994) The horse, the handicapped and the riding team in a therapeutic program. A training manual for volunteers. University of Virginia, USA
Festa-Bianchet M, Apollonio M (eds) (2003) Animal behaviour and wildlife conservation. General introduction. Island Press, London, pp 3–12
Franklin A (1999) Animals and Modern Cultures: A sociology of human-animal relations in modernity. Sage Publications, London
Frost W (ed) (2011) Zoos and tourism: conservation, education, entertainment? Channel View Publications, Ontario
Green RJ, Higginbottom K (2001) The Negative Effects of Wildlife Tourism on Wildlife. Wildlife Tourism Research Report Series No. 5, status assessment of wildlife tourism in australia series, CRC for sustainable tourism, Queensland, Australia
Green RJ, Wood P (2015) Australian wildlife and research network. In: Slocum SL, Kline C, Holden A (eds) Scientific tourism: researchers as travellers. Taylor and Francis, New York, pp 164–180
Hastings A, Gross L (eds) (2012) Encyclopedia of theoretical ecology. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles
Higginbottom K (2004) Wildlife tourism: impacts, management and planning. CRC sustainable tourism & common ground, UniversityPress.com, Altona, Victoria, Australia
Higginbottom K, Northrope C, Green RJ (2001) The positive effects of wildlife tourism on wildlife. wildlife tourism research report series No. 6, status assessment of wildlife tourism in australia series, CRC for sustainable tourism, Queensland, Australia
Holden A (2016) Environment and tourism. Routledge, New York
Hughes M, Carlsen (2008) Human-wildlife interaction guidelines in Western Australia. J Ecotourism 7(2–3):147–159
Article Google Scholar
Humphrey SR, Bain JR (1990) Endangered animals of Thailand. Sandhill Crane Press Inc, Gainesville, Florida, USA
IISC (2016) Indian Institute of Science. Centre for Ecological Science. National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries and Biosphere Reserves in India. Retrieved from, http://ces.iisc.ernet.in/envis/sdev/parks.htm . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
Ingold T (1988) Introduction. In: Ingold T (ed) What is an animal? Unwin Hyman, London, pp 1–16
Kemmerer L (2011) Theorizing others. In: Taylor N, Signal T (eds) Theorizing animals: re-thinking humanimal relations. Brill, Leiden & Boston, pp 59–86
Khullar DR (2016) Geography: fundamentals of physical geography and physical environment. New Saraswati House, New Delhi
Knight C, Sullivan M (2016) Gorilla killed after 3-year-old falls into zoo enclosure. Cincinnati.com. Retrieved from, http://www.cincinnati.com/story/news/2016/05/28/police-child-taken-hospital-after-falling-into-gorilla-pen/85095094/ . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
Krichner J (2009) The balance of nature: ecology’s enduring myth. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Kontogeorgopoulos N (2009) Wildlife tourism in semi-captive settings: A case study of elephant camps in Northern Thailand. Current Issues in Tourism 12:429–44
Lair RC (1999) Gone astray: the care and management of the Asian elephant in domesticity. FAO. Forestry Department, Rome, Italy, and Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific (RAP). Dharmasam Co, Bangkok, Thailand. Available online. Retrieved from, http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/AC774E/AC774E00.HTM . Accessed on 11 Dec 2016
Lindenmayer D, Burgman MA (2005) Practical conservation biology. Csiro Publishing, Collingwood
Markwell K (2015) Animals and tourism: understanding diverse relationships. Channel View Publications, Ontario
Melkania NP (1998) Towards an integrated conservation strategy. In: Singh V, Sharma ML (eds) Mountain ecosystems: a scenario of unsustainability. Indus Publishing Company, New Delhi, pp 89–100
Miller JR, Lerner RM, Schiamberg LB, Anderson PM (eds) (2002) Encyclopedia of human ecology A-H. ABC Clio, Santa Barbara, CA, USA & Oxford, UK
Mills DS, Marchant-Forde JN (eds) (2010) The encyclopedia of applied animal behaviour and welfare. CABI, London
Moran EF (2010) Environmental social science: human—environmental interactions and sustainability. Wiley, Oxford
Book Google Scholar
Moscardo G, Saltzer R (2005) Understanding tourism wildlife interactions: visitor market analysis. Technical Report. Cooperative Research Centre for Sustainable Tourism—CRC, Queensland, Australia
Newman JL (2013) Encountering gorillas: a chronicle of discovery, exploitation, understanding and survival. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Lanham
Novelli M, Humavindu MN (2005) Wildlife tourism: wildlife use vs local gain: trophy hunting in Namibia. In: Novelli M (ed) Niche tourism: contemporary issues, trends and cases. Elsevier Buttlerworth-Heinemann, Burlington, pp 171–182
Pickover M (2005) Animal rights in South Africa. Double Storey, Cape Town
Raina AK (2005) Ecology, wildlife and tourism development: principles, practices and strategies. Sarup & Sons, New Delhi
Ramsey A (2016) What really happened at Thailand’s Tiger Temple? News Features online. Aljazeera. Retrieved from, http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/features/2016/06/happened-thailand-tiger-temple-160605074332073.html . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
Reardon M (2012) Shaping Kruger: animal behaviour, ecology and management in Africa’s Premier Game Park. Struick Nature. Random House, Cape Town
Reynolds JE, Redfern JM, Shulstad RN (eds) (1974) Readings in natural resource economics. Committee on Soil and Water Conservation of the Agricultural Board. MSS Information Corporation, New York, pp 111–133
Romo R, Sholchet C (2013) Costa Rica to close zoos, release some animals. CNN Online. Regions. Retrieved from, http://edition.cnn.com/2013/08/07/world/americas/costa-rica-zoo-cages/ . Accessed 12 Dec 2016
Roterman N (2016) Two lions killed to save suicidal young man in Chilean Zoo. Retrieved from, http://www.latintimes.com/two-lions-killed-save-suicidal-young-man-chilean-zoo-386300 . Accessed on 4 Dec 2016
Rowan R, Knowlton N, Baker A, Jara J (1997) Landscape ecology of algal symbionts creates variation in episodes of coral bleaching. Nature 388:265–269
Article CAS Google Scholar
Semeniuk AD, Haider W, Cooper A, Rothley KD (2010) A linked model of animal ecology and human behavior for the management of wildlife tourism. Ecol Model 221(2010):2699–2713
Shapiro K (2002) The state of human-animal studies: solid, at the margin! Soc Anim 10:330–337
Shapiro K, Copeland MW (2005) Toward a critical theory of animal issues in fiction. Soc Anim 13:343–347
Smith M, Duffy R (2003) The ethics of tourism development. Routledge - Taylor & Francis: London and New York
Spaargaren G (2000) Ecological modernization theory and the changing discourse on environment and modernity. In: Spaargaren G, Mol APJ, Buttel FH (eds) Environment and global modernity. Studies in International Sociology 50. SAGE, New Delhi, India, pp 41–72
Stewart E (2013) No ethical way to keep elephants in captivity. A voice for elephants (May 3, 2013). National Geographic. Retrieved from, http://voices.nationalgeographic.com/tag/ed-stewart/ . Accessed 10 Dec 2016
Stoddart MCJ (2012) Making meaning out of mountains: the political ecology of skiing. UBC Press, Vancouver
Szarycz G (2011) The representation of animal actors: theorizing performance and performativity in the animal kingdom. In: Taylor N, Signal T (eds) Theorizing animals: re-thinking humanimal relations. Brill, Leiden & Boston, pp 149–174
Taylor AB, Goldsmith ML (eds) (2003) Gorilla biology: a multidisciplinary perspective. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tribe A (2001) Captive wildlife tourism in Australia. Wildlife Tourism Research Report Series n. 14. Cooperative Research Centre for Sustainable Tourism—CRC, Queensland, Australia
Tyler T (2009) Introduction; the case of the camel. In: Tyler T, Rossini MS (eds) Animal encounters. Brill, Leiden and Boston
Usher MB (ed) (1986) Wildlife conservation evaluation. Chapman and Hall, London
UNTWO (2016) World Tourism Organization - UNTWO Highlights 2016 Edition. Available online, http://www.e-unwto.org/doi/pdf/10.18111/9789284418145 , accessed on November 2016
Vaccaro I, Smith EA, Aswani S (2010) Environmental social sciences: methods and research design. Cambridge University Press, New York
Vidal J (2016) Tiger temple scandal exposes the shadowy billion-dollar Asian trade. The Guardian online (4th June 2016). Online content. Retrieved from, https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2016/jun/04/tiger-temple-scandal-billion-dollar-trade-china-thailand . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
WPSI (2016) Wildlife protection society of India. Tiger Reserves. Sundarbans. Online content. Retrieved from, http://www.wpsi-india.org/tiger/sundarban.php . Accessed on 08 Dec 2016
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Business and Tourism, Southern Cross University, Gold Coast, Australia
Ismar Borges de Lima
MultiAmazon lab, Recinatur Intl Foundation, and UNIFESSPA, Roraima State University, UERR, Boa Vista, Brazil
Environmental Futures Research Institute, Griffith University, Nathan, Australia
Ronda J. Green
Wildlife Tourism Australia Inc., Rathdowney, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ismar Borges de Lima .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Business and Tourism, Southern Cross University, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia
Wildlife Tourism Australia (WTA) , Rathdowney, Queensland, Australia
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Borges de Lima, I., Green, R.J. (2017). Introduction: Wildlife Tourism Management and Phenomena: A Web of Complex Conceptual, Theoretical and Practical Issues. In: Borges de Lima, I., Green, R. (eds) Wildlife Tourism, Environmental Learning and Ethical Encounters. Geoheritage, Geoparks and Geotourism. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55574-4_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55574-4_1
Published : 16 June 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-55573-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-55574-4
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

At Elephant Valley Thailand, in Chiang Rai, tourists are instructed to observe the animals from a safe distance.
What I learned investigating the wildlife tourism industry
I traveled the world documenting unseen suffering. Here’s what you can do to respect animals during your travels.
Right away, Elephant Valley Thailand felt different. The property, nestled in the forest on the outskirts of Chiang Rai, a small city in northern Thailand, was the fifth elephant attraction I’d visited in a week. I’d seen shows where elephants kicked soccer balls and twirled hula hoops. I’d watched people ride on their backs and swing from their trunks. I’d peeked into the stalls to which elephants returned after working, where they’re chained by their ankles to posts.
But Elephant Valley was quiet. It was the first time all week that I’d seen elephants from a distance. One was bathing in a pond, alone. Another two were eating in the middle of a field. Wooden fences surrounded most of the fields—to keep us out, not them in, John Lee, a manager at Elephant Valley, told me. That’s what struck me most: No one was allowed to touch the animals. These were elephants being elephants. ( Here's why we're shining a light on wildlife tourism. )

Elephant Valley Thailand ”was the most responsible elephant sanctuary that we visited,” says author Natasha Daly.
Elephant Valley Thailand, home to five elephants that previously worked in trekking camps and the logging industry, is unlike most other elephant attractions in Thailand. Many of the country’s 3,800 captive elephants live in camps that offer up-close, interactive experiences that allow visitors to ride or bathe the animals or watch them perform in shows. The activities are a massive draw for travelers from around the world, part of a lucrative global industry that puts people together with exotic animals for once-in-a-lifetime encounters.
It’s what brought me to Thailand , a monthlong stop on a reporting trip for National Geographic magazine that took photographer Kirsten Luce and me to four continents over a year and a half. Our goal was simple: to look at the animals that entertain us and the people who seek them out. Those people are you and they’re me. I have a photo of myself at two years old, perched on an elephant’s back at a zoo in my hometown of Toronto , Canada. Eight years ago, on my honeymoon, I went swimming with captive manta rays in Mexico . But seven years later, while reporting the story, I found myself watching a group of tourists pass around a tiger cub after paying a couple of dollars to feed him a bottle of milk—and wondering if anyone else was questioning why he wasn’t with his mom.
It’s complicated. People love animals and naturally want to get close to them—and genuinely want to learn more about them too. It’s a desire that’s increasingly fueled by social media, where travelers share their experiences instantaneously. The reality that many tourists don’t see is that to stay in business, elephant interactions—and photo ops with tigers and swimming with manta rays—rely on a steady stream of working wild animals, all of which have been caught or bred or trained into submission.
Related: 10 animals to see on a Botswana safari

And it’s all too easy to misread signs of suffering. Captive elephants sway their trunks back and forth—almost as if they’re dancing. In reality, it’s a sign of psychological distress. Sloths seem to love cuddling, but their hug is really just an attempt to cling to what feels to them like a tree trunk. Dolphins appear to be smiling but that’s the natural set of their mouths.
Travelers are increasingly recognizing that many animal tourist attractions may not be ethical. More and more backpackers are shunning elephant riding. ( Follow these tips for ethical animal encounters. )
The industry knows it. Dozens of properties in Thailand now call themselves “sanctuaries.” Many look a lot like Elephant Valley and boast five-star ratings on travel sites such as TripAdvisor . But Kirsten and I found that, unlike Elephant Valley, almost every one offers elephant bathing for visitors who wish to splash with an elephant in a river or mud pit. Often the bathing is repeated all day long. And only trained elephants will submit to baths.
Jack Highwood opened Elephant Valley in 2016. The 40-acre property is his second elephant sanctuary, following a much bigger one he established in Cambodia. He chose to go small with the Thai sanctuary, installing inexpensive wooden fencing and minimal infrastructure because he wanted to make the model as easy as possible for others to copy. It felt peaceful, several visitors at Elephant Valley told me. As if the elephants didn’t even know they were there.
While traveling the world, I spoke to tourists everywhere. In restaurants and hostels. At aquariums and monkey shows. I would often ask people if they prefer to have an up-close experience with an animal in captivity or observe it from afar in the wild. More often than not, they told me the latter. Yet captive encounters remain extremely popular. Maybe because an animal sighting is assured. Maybe because the animals seem happy, and it seems that your admission fee is going to contribute to someone’s paycheck. Maybe, perhaps most compelling of all, because it gives you a photograph—you, together with an exotic animal—that can go straight to your social media feed, where likes and comments are guaranteed.
Across the Pacific, on the North Shore of Oahu, in Hawaii , there’s a beach called Laniakea. People more commonly call it Turtle Beach, because sea turtles regularly come ashore. They’ll pick a spot and sleep in the sun, sometimes for hours at a time. Volunteers are there every day to keep people away from the animals. When a turtle emerges from the sea, the volunteers block off space for it with rope, giving the turtle ample room to relax in peace.
One weekday in September, I sat with dozens of tourists behind the rope and watched them watching a turtle. For the most part, people were respectful. A few asked why they couldn’t touch. It’s illegal to touch sea turtles in Hawaii, the volunteers explained. And it’s important to respect their space, they added. This is their beach too, after all.
It can be hard for most people to tell the difference between ethical and problematic wildlife experiences. There are many shades of gray. But you might follow a few simple guidelines :
Keep your distance. Seek experiences that offer observation of animals engaging in natural behaviors in natural environments.
Do your research. A highly rated place may not necessarily be humane. Read those one- and two-star reviews. It’s often in the pans that visitors chronicle animal welfare concerns.
Beware of buzzwords. A facility may use phrases on their website or promotional materials such as “gives back to conservation,” “rescue,” and “sanctuary,” but if it still offers extensive interaction, that may be a red flag.
- Nat Geo Expeditions
Related Topics
You may also like.

Inside the newest park in Argentine Patagonia

See Kenya’s wildlife in a different light: on horseback
Free bonus issue.
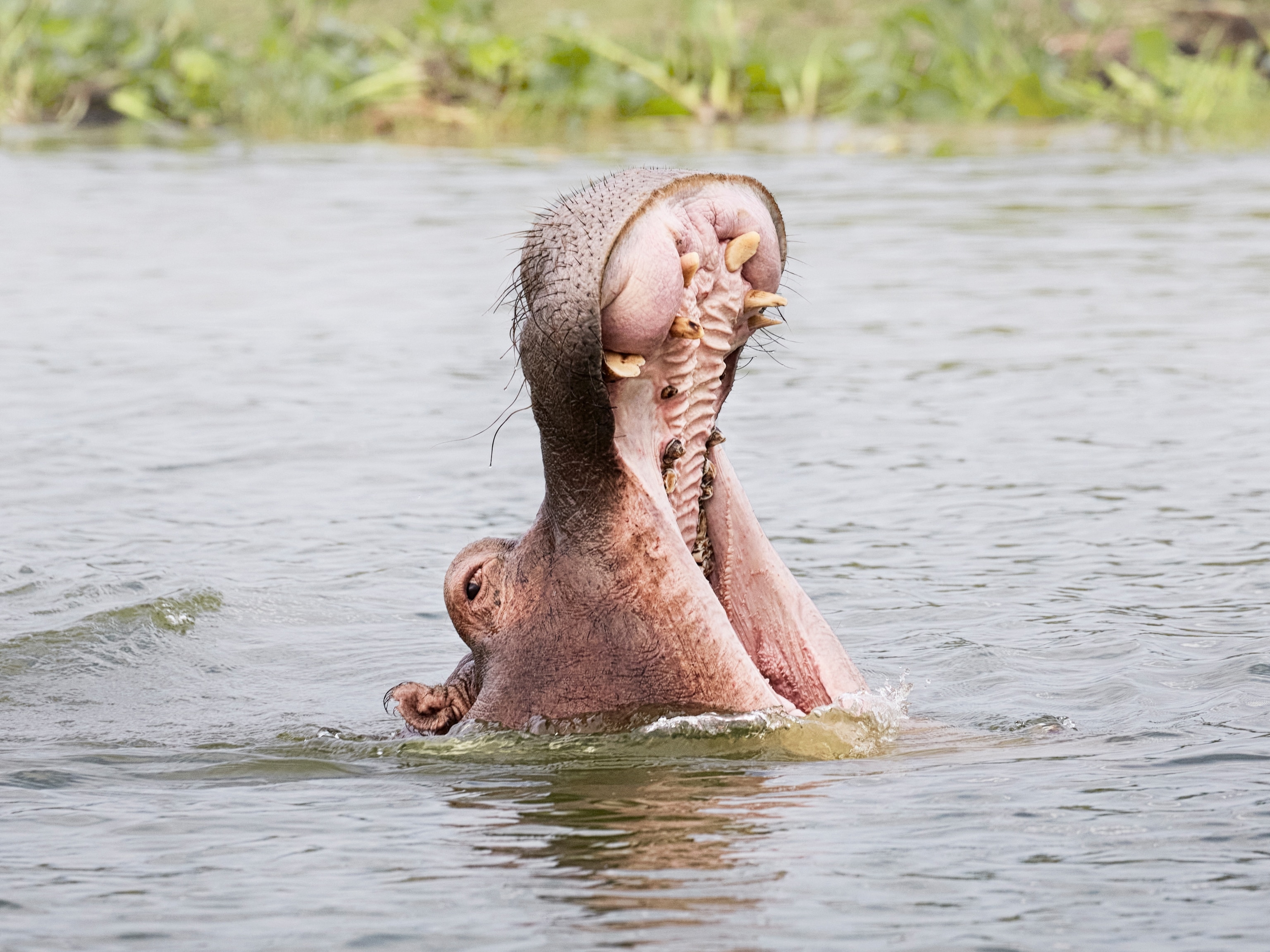

How I got the shot: Jonathan Gregson on witnessing Uganda's wallowing hippos

Winter vacations don't have to be about snow—check out these perfect getaways

Bear Grylls reveals his top travel tips
5 of alaska’s ultimate wildlife adventures.

The Cool List 2024: the 30 most exciting destinations to visit in 2024
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

- All projects
- Endangered species
- Farming and Wildlife
- Fundamental biology
- Land use and biodiversity
- Wildlife as a resource
Associated Members
- Dr Tom Moorhouse
Wildlife tourism
In studying the impacts of wildlife tourism we examined 48 types of wildlife tourist attraction (representing thousands of individual institutions), ranging from poorly-attended street performances, like snake charming, bear dancing and macaque shows, to large, established attractions such as dolphinaria and tiger interactions, which have tens of thousands of visitors every year. We audited 24 of these types in detail, collectively visited by 3.6–6 million tourists per year. We found that up to 4 million tourists who visit non-zoo tourist attractions involving wildlife are likely to be contributing to large-scale animal welfare abuses and declines in species’ conservation status – and are typically unaware of their impacts.
Moorhouse, T. P., Dahlsjö, C. A., Baker, S. E., D’Cruze, N. C., & Macdonald, D. W. (2015). The customer isn’t always right—conservation and animal welfare implications of the increasing demand for wildlife tourism . PloS One , 10 (10), e0138939.
Examining the feedback left for wildlife tourist attractions on TripAdvisor we discovered that at least 80% of tourists left positive feedback for attractions they had visited – even for those attractions with the poorest welfare standards. In each case a minority (approximately 20%) of tourists left reviews that correlated with welfare standards (i.e. were positive for beneficial attractions and negative for detrimental attractions). This overwhelmingly positive feedback probably arises from a number of psychological mechanisms that make tourists unlikely to consider the ethical dimensions of their consumption, and also likely to retrospectively diminish the severity of their contribution if they suspect the conditions at a given wildlife venue were not what they would usually have wanted to be involved in.
Moorhouse, T., D’Cruze, N. C., & Macdonald, D. W. (2017). Unethical use of wildlife in tourism: what’s the problem, who is responsible, and what can be done?. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 25 (4), 505-516.
Our findings have led us to advise that any wildlife attraction reviewed on TripAdvisor with 80% positive reviews or less (four stars or fewer), may be more likely to have detrimental impacts on wildlife. We are also working directly with TripAdvisor to create an information platform to educate tourists on the consequences of attending wildlife tourist attractions, and to support them in choosing beneficial, rather than exploitative.
https://www.tripadvisor.com/blog/animal-welfare-education-portal/
https://www.tripadvisor.com/blog/impacts-wildlife-tourist-attractions/
Our current project examines whether making potential wildlife tourists aware of the ethical dimension of their decisions – at the time when they are deciding which tourist attractions to visit – might lead them to preferentially choose attractions that have beneficial (for animal welfare and species conservation) impacts.
Related pages
Examining our recreational use of wildlife Exotic pets and reducing demand


Exploring the World of Wildlife Tourism
All the tools, pointers, and inspiration you need to plan your next ethical animal adventure..
- Copy Link copied

Courtesy of Chobe Game Lodge
Oh, baby it’s a wild world.
People go to great lengths to see exotic animals on their travels
Braving the bitter cold of Antarctica to observe penguins, shelling out big to experience the great migrations of the Serengeti, and diving in shark-infested waters in Australia to swim with, well, sharks. But animal tourism isn’t always so cute and cuddly. Animals kept in captivity for tourism purposes, from “zoos” to elephant corrals, are frequently abused and mistreated.
However, there are still ways to ethically include animals into your vacation—by choosing wildlife outfitters, safari lodges, sanctuaries, and tour experiences that are committed to animal welfare and habitat preservation. And the search to find ethical organizations doesn’t need to be a wild goose chase! In this guide, you’ll find resources that will help you discern what makes an animal experience ethical, as well as pointers to plan your next trip, whether that be in the United States or abroad. And, to really get in the spirit, check out our stories from animal lovers across the world, from a burgeoning “craniac” to a self-proclaimed safari enthusiast.
- Mae Hamilton
_________________________________________________
The ABC’s of Animal Tourism

Photo by Daniel Diesenreither/Unsplash
Is There Such Thing as Ethical Animal Tourism?
I’ll never forget the first time I saw a bullhook. In the late 90s, I visited the Big Apple Circus in New York City. Performers and crew members preparing for the night’s show raced around in an atmosphere that smelled of caramelizing cotton candy, hot peanuts, and animal manure. I was standing near a staging area when I saw a young girl wearing a sparkly costume and walking with an elephant. She held a stout pole with a metal hook at its end and I asked her what it was for. She raised her arm, made a fierce face, and said, “To hit them when they don’t obey.” My face flushed with shame—I considered myself an animal lover. Yet, I hadn’t known the elephants suffered for my entertainment. I felt foolish and sad. And I vowed to learn more.
Read the full story.
Everything You Need to Know About Wildlife Corridors—and Where to See Them
Yeah, yeah, we all know why the chicken crossed the road. But figuring out how a chicken could cross the road—especially in the age of six-lane highways and railroad crossings—is a far more pressing question for conservation biologists. The answer to the riddle may be wildlife corridors, which provide a “bridge” between habitats that have been separated by human activity. From elephant underpasses to crab bridges, these animal-friendly pathways provide safe passage for all kinds of critters and score big points for communities interested in ecotourism.
Straight From the Horse’s Mouth

Photo by Beliphotos/Shutterstock
The Great Nebraska Migration of the Sandhill Cranes and the Birders Who Love Them
I roll into Kearney, Nebraska in the pitch dark and hop out of my rental Buick at the Best Western Plus. I’m greeted first by a smell on the wind: the striking, wild, pungent attestation of livestock farming. It’s fantastic. I’m here.
It’s spring, and the sandhill cranes are making their annual journey north along the Central Flyway from southern Texas up into the northern reaches of Canada. For a couple weeks, these three- to four-foot-tall wading birds will take an intermission along this 75-mile stretch of Nebraska’s Platte River to stock up on food—remnants of last year’s corn harvest—and roost by night in massive numbers in the river’s shallow waters.
Botswana’s Chobe Game Lodge Is Changing Safaris With All-Women Guide Teams
As guests arrive at Kasane International Airport in the northeastern corner of Botswana, a woman driver begins to load luggage onto an open-air jeep. Wearing a khaki uniform with a red and white scarf tied neatly around her neck, she helps the fresh arrivals into her vehicle and cruises through the city’s asphalt roads until she arrives at the entrance of Chobe National Park . As she navigates the park’s bumpy dirt path, she points out blossoming fever berry trees, starlings winging away overhead, and a savanna elephant plodding along as her passengers ooh and ahh. She pauses for a moment to breathe in the air of the plains, before continuing on to join her 19 other fellow safari guides at Chobe Game Lodge —all of them women.
This Lion Safari Gives Travelers a Deeper Look at Wildlife Conservation in Africa
I had barely landed at Phinda Airport when I caught my first glimpse of lions.
I peered through the window of the bush plane at andBeyond Phinda Private Game Reserve , located in a remote corner of South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province, and couldn’t believe my eyes. About a half dozen drowsy felines taking shade beneath an acacia tree near the tarmac began to rise from their nap. They stretched, then meandered away from the sound of our propellers. I’ve been on close to two dozen safaris in eastern and southern Africa, and lion sightings rarely come this easy. It’s as if these cats knew I was on a lion-themed safari and were here to greet me at the start of my journey.
Journalist Peter Martell on How Conservation Brought Kenyan Communities Together
Peter Martell is a British reporter who spent the past two decades as a correspondent for the BBC and Agence France-Presse, covering war, famine, and climate change across East Africa. His second book, Flowers for Elephants: How a Conservation Movement in Kenya Offers Lessons for Us All (March 2022, Hurst Publishers), includes many of these themes—but in a fresh and inspiring way. It tells the incredible story of how communities across northern Kenya worked together to create a network of protected lands across an area larger than Switzerland.
Wild Trip Inspiration

Photo by Ilona Froehlich/Unsplash
The 10 Best Places in the U.S. to See Wildlife
With nearly 3,000 different types of native animal species in the United States and 18,000 types of plants, this is one of the world’s most ecologically rich countries —in fact, it’s recognized by the World Conservation Monitoring Center as one of 17 mega-diverse nations. From Maine’s rocky shores to the green rain forests of Washington, there’s much to see and do right here at home—no long-haul plane ticket or safari lodge reservation required.
The Best International Trips for Wildlife Lovers
Encountering animals in their natural habitat is a sublime and unforgettable experience—and there are so many organizations angling to provide those moments for their guests. For every legitimate, ecofriendly operator, there are untold numbers whose practices are questionable, if not exploitive.
AFAR wants to help you find the best international trips to see wildlife in a responsible way. We have vetted a number of lodges and operators that embrace wildlife viewing practices that are ethical, sustainable, and socially responsible and offer close encounters—without getting too close.


- Press Releases
- Press Enquiries
- Travel Hub / Blog
- Brand Resources
- Newsletter Sign Up
- Global Summit
- Hosting a Summit
- Upcoming Events
- Previous Events
- Event Photography
- Event Enquiries
- Our Members
- Our Associates Community
- Membership Benefits
- Enquire About Membership
- Sponsors & Partners
- Insights & Publications
- WTTC Research Hub
- Economic Impact
- Knowledge Partners
- Data Enquiries
- Hotel Sustainability Basics
- Community Conscious Travel
- SafeTravels Stamp Application
- SafeTravels: Global Protocols & Stamp
- Security & Travel Facilitation
- Sustainable Growth
- Women Empowerment
- Destination Spotlight - SLO CAL
- Vision For Nature Positive Travel and Tourism
- Governments
- Consumer Travel Blog
- ONEin330Million Campaign
- Reunite Campaign
Global wildlife tourism generates five times more revenue than illegal wildlife trade annually

In 2018, wildlife tourism directly contributed $120.1bn to global GDP, versus the $23bn in revenue attributed to the illegal trade in wildlife, or 5.2 times more, according to new research from the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC). This includes viewing and experiencing animals in their natural habitat, which accounts for 4.4% of all direct tourism GDP last year and directly provided 9.1 million jobs worldwide.
Released on World Elephant Day, the research shows that the total economic contribution of wildlife tourism totals $343.6bn – equivalent to the entire economy of Hong Kong.
Asia-Pacific forms the largest regional market worth $53.3bn in direct GDP and responsible for 4.5 million jobs. In second place is Africa, where 3.6 million people are employed through wildlife tourism, which was worth $29.3bn last year.
Gloria Guevara, President & CEO, WTTC marked the release of this research, which falls on World Elephant Day, by saying, “Our message to tourism businesses, employees and visitors across the globe is that wildlife is worth far more alive than dead.
“Wildlife tourism is a rich segment of the industry, showing how our precious species can legitimately enrich tourism businesses without being harmed. In fact, the wildlife tourism market is so strong – worth five times more than the illegal trade – that it provides a strong incentive for communities to protect and display animals to the world rather than killing them for a one-off cash bonus. For years, we have professed the role and value of Travel & Tourism in alleviating poverty, and wildlife tourism is a key part of that.
“With more than 110 signatories to date, the WTTC’s Buenos Aires Declaration Against the Illegal Trade in Wildlife commits the travel industry to helping to eradicate the scourge of wildlife trafficking in the world, working together to responsibly inform the behaviour of one billion travellers across the world. This new research compounds the rationale behind our work, demonstrating the power and potential of travel to displace such illicit activity.”
Highlights from the report include: • Over one-third of all direct tourism GDP across Africa in 2018 attributed to wildlife (36.3%) • North America is the third largest wildlife tourism economy after Asia-Pacific and Africa, directly contributing $13.5 billion to GDP last year • 21.8 million jobs globally are supported by wildlife tourism – equivalent to the population of Sri Lanka • Case studies of wildlife tourism and its value in Brazil, Germany, China, India, Kenya, South Africa, Tanzania, Thailand, the UK and the USA.
This research is one piece in a series of comprehensive reports from WTTC analysing the impact of various travel segments, with the next focusing on medical tourism.

What Is Ecotourism? Definition, Examples, and Pros and Cons
- Chapman University
- Sustainable Fashion
- Art & Media
Ecotourism Definition and Principles
Pros and cons.
- Examples of Ecotourism
- Frequently Asked Questions
Ecotourism is about more than simply visiting natural attractions or natural places; it’s about doing so in a responsible and sustainable manner. The term itself refers to traveling to natural areas with a focus on environmental conservation. The goal is to educate tourists about conservation efforts while offering them the chance to explore nature.
Ecotourism has benefited destinations like Madagascar, Ecuador, Kenya, and Costa Rica, and has helped provide economic growth in some of the world’s most impoverished communities. The global ecotourism market produced $92.2 billion in 2019 and is forecasted to generate $103.8 billion by 2027.
A conservationist by the name of Hector Ceballos-Lascurain is often credited with the first definition of ecotourism in 1987, that is, “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, as well as any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas.”
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES), a non-profit organization dedicated to the development of ecotourism since 1990, defines ecotourism as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education [both in its staff and its guests].”
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) looks at ecotourism as a significant tool for conservation, though it shouldn’t be seen as a fix-all when it comes to conservation challenges:
“There may be some areas that are just not appropriate for ecotourism development and some businesses that just won’t work in the larger tourism market. That is why it is so important to understand the basics of developing and running a successful business, to ensure that your business idea is viable and will be profitable, allowing it to most effectively benefit the surrounding environment and communities.”
Marketing an ecosystem, species, or landscape towards ecotourists helps create value, and that value can help raise funds to protect and conserve those natural resources.
Sustainable ecotourism should be guided by three core principles: conservation, communities, and education.
Conservation
Conservation is arguably the most important component of ecotourism because it should offer long-term, sustainable solutions to enhancing and protecting biodiversity and nature. This is typically achieved through economic incentives paid by tourists seeking a nature-based experience, but can also come from the tourism organizations themselves, research, or direct environmental conservation efforts.
Communities
Ecotourism should increase employment opportunities and empower local communities, helping in the fight against global social issues like poverty and achieving sustainable development.
Interpretation
One of the most overlooked aspects of ecotourism is the education component. Yes, we all want to see these beautiful, natural places, but it also pays to learn about them. Increasing awareness about environmental issues and promoting a greater understanding and appreciation for nature is arguably just as important as conservation.
As one of the fastest growing sectors of the tourism industry, there are bound to be some downsides to ecotourism. Whenever humans interact with animals or even with the environment, it risks the chance of human-wildlife conflict or other negative effects; if done so with respect and responsibility in mind, however, ecotourism can reap enormous benefits to protected areas.
As an industry that relies heavily on the presentation of eco-friendly components to attract customers, ecotourism has the inevitable potential as a vessel for greenwashing. Part of planning a trip rooted in ecotourism is doing research to ensure that an organization is truly providing substantial benefits to the environment rather than exploiting it.
Ecotourism Can Provide Sustainable Income for Local Communities
Sustainably managed ecotourism can support poverty alleviation by providing employment for local communities, which can offer them alternative means of livelihood outside of unsustainable ones (such as poaching).
Research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that communities in regions surrounding conservation areas in Costa Rica had poverty rates that were 16% lower than in areas that weren’t near protected parks. These protected areas didn’t just benefit from conservation funds due to ecotourism, but also helped to reduce poverty as well.
It Protects Natural Ecosystems
Ecotourism offers unique travel experiences focusing on nature and education, with an emphasis on sustainability and highlighting threatened or endangered species. It combines conservation with local communities and sustainable travel , highlighting principles (and operations) that minimize negative impacts and expose visitors to unique ecosystems and natural areas. When managed correctly, ecotourism can benefit both the traveler and the environment, since the money that goes into ecotourism often goes directly towards protecting the natural areas they visit.
Each year, researchers release findings on how tourist presence affects wildlife, sometimes with varying results. A study measuring levels of the stress hormone cortisol in wild habituated Malaysian orangutans found that the animals were not chronically stressed by the presence of ecotourists. The orangutans lived in the Lower Kinabatangan Wildlife Sanctuary, where a local community-managed organization operates while maintaining strict guidelines to protect them.
Ecotourism May Also Hurt Those Same Natural Ecosystems
Somewhat ironically, sometimes ecotourism can hurt ecosystems just as much as it can help. Another study in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution found that ecotourism can alter animal behaviors in ways that put them at risk. If the presence of humans changes the way animals behave, those changes may make them more vulnerable by influencing their reaction to predators or poachers.
It's not just the animals who are at risk. As ecotourism activities become too popular, it can lead to the construction of new infrastructure to accommodate more visitors. Similarly, more crowds mean more pressure on local resources, increased pollution, and a higher chance of damaging the soil and plant quality through erosion. On the social side, these activities may displace Indigenous groups or local communities from their native lands, preventing them from benefiting from the economic opportunities of tourism.
Ecotourism Offers the Opportunity to Experience Nature
Renown conservationist Jane Goodall has a famous quote: “Only if we understand, will we care. Only if we care, will we help. Only if we help, shall all be saved.” It can be difficult to understand something that we haven’t seen with our own eyes, and ecotourism gives travelers the opportunity to gain new experiences in natural areas while learning about the issues they face.
Ecotourism also educates children about nature, potentially creating new generations of nature lovers that could someday become conservationists themselves. Even adult visitors may learn new ways to improve their ecological footprints .
EXAMPLES OF ECOTOURISM
The East African country has some competitive advantages over its neighbors thanks to its rich natural resources, paired with the fact that it has allocated over 25% of its total area to wildlife national parks and protected areas. Because of this, an estimated 90% of tourists visit to Tanzania seeking out ecotourism activities. Ecotourism, in turn, supports 400,000 jobs and accounts for 17.2% of the national GDP, earning about $1 billion each year as its leading economic sector.
Some of Tanzania’s biggest highlights include the Serengeti, Mount Kilimanjaro , and Zanzibar, though the country still often goes overlooked by American tourists. Visitors can take a walking safari tour in the famous Ngorongoro Conservation area, for example, with fees going to support the local Maasai community.
The country is also known for its chimpanzees , and there are several ecotourism opportunities in Gombe National Park that go directly towards protecting chimpanzee habitats.
Galapagos Islands
It comes as no surprise that the place first made famous by legendary naturalist Charles Darwin would go on to become one of the most sought-after ecotourism destinations on Earth, the Galapagos Islands .
The Directorate of the Galapagos National Park and the Ecuadorian Ministry of Tourism require tour providers to conserve water and energy, recycle waste, source locally produced goods, hire local employees with a fair wage, and offer employees additional training. A total of 97% of the land area on the Galapagos is part of the official national park, and all of its 330 islands have been divided into zones that are either completely free of human impact, protected restoration areas, or reduced impact zones adjacent to tourist-friendly areas.
Local authorities still have to be on their toes, however, since UNESCO lists increased tourism as one of the main threats facing the Galapagos today. The bulk of funding for the conservation and management of the archipelago comes from a combination of governmental institutions and entry fees paid by tourists.
Costa Rica is well-known throughout the world for its emphasis on nature-based tourism, from its numerous animal sanctuaries to its plethora of national parks and reserves. Programs like its “Ecological Blue Flag” program help inform tourists of beaches that have maintained a strict set of eco-friendly criteria.
The country’s forest cover went from 26% in 1983 to over 52% in 2021 thanks to the government’s decision to create more protected areas and promote ecotourism in the country . Now, over a quarter of its total land area is zoned as protected territory.
Costa Rica welcomes 1.7 million travelers per year, and most of them come to experience the country’s vibrant wildlife and diverse ecosystems. Its numerous biological reserves and protected parks hold some of the most extraordinary biodiversity on Earth, so the country takes special care to keep environmental conservation high on its list of priorities.
New Zealand
In 2019, tourism generated $16.2 billion, or 5.8% of the GDP, in New Zealand. That same year, 8.4% of its citizens were employed in the tourism industry, and tourists generated $3.8 billion in tax revenue.
The country offers a vast number of ecotourism experiences, from animal sanctuaries to natural wildlife on land, sea, and even natural caves. New Zealand’s South Pacific environment, full of sights like glaciers and volcanic landscapes, is actually quite fragile, so the government puts a lot of effort into keeping it safe.
Tongariro National Park, for example, is the oldest national park in the country, and has been named by UNESCO as one of only 28 mixed cultural and natural World Heritage Sites. Its diverse volcanic landscapes and the cultural heritage of the indigenous Maori tribes within the create the perfect combination of community, education, and conservation.
How to Be a Responsible Ecotourist
- Ensure that the organizations you hire provide financial contributions to benefit conservation and find out where your money is going.
- Ask about specific steps the organization takes to protect the environment where they operate, such as recycling or promoting sustainable policies.
- Find out if they include the local community in their activities, such as hiring local guides, giving back, or through initiatives to empower the community.
- Make sure there are educational elements to the program. Does the organization take steps to respect the destination’s culture as well as its biodiversity?
- See if your organization is connected to a non-profit or charity like the International Ecotourism Society .
- Understand that wildlife interactions should be non-invasive and avoid negative impacts on the animals.
Ecotourism activities typically involve visiting and enjoying a natural place without disturbing the landscape or its inhabitants. This might involve going for a hike on a forest trail, mountain biking, surfing, bird watching, camping, or forest bathing .
Traveling in a way that minimizes carbon emissions, like taking a train or bike instead of flying, may also be part of an ecotourism trip. Because these modes of travel tend to be slower, they may be appreciated as enjoyable and relaxing ecotourism activities.
The Wolf Conservation Center ’s programing in New York State is an example of ecotourism. This non-profit organization is dedicated to the preservation of endangered wolf species. It hosts educational sessions that allow visitors to observe wolves from a safe distance. These programs help to fund the nonprofit organization’s conservation and wildlife rehabilitation efforts.
Stonehouse, Bernard. " Ecotourism ." Environmental Geology: Encyclopedia of Earth Science , 1999, doi:10.1007/1-4020-4494-1_101
" What is Ecotourism? " The International Ecotourism Society .
" Tourism ." International Union for Conservation of Nature .
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307712111
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033357
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.010
https://doi.org/10.5897/JHMT2016.0207
" Galapagos Islands ." UNESCO .
" About Costa Rica ." Embassy of Costa Rica in Washington DC .
https://www.stats.govt.nz/information-releases/tourism-satellite-account-2019
- Costa Rica’s Keys to Success as a Sustainable Tourism Pioneer
- What Is Sustainable Tourism and Why Is It Important?
- What Is Community-Based Tourism? Definition and Popular Destinations
- How to Be a Sustainable Traveler: 18 Tips
- What Is Overtourism and Why Is It Such a Big Problem?
- Defeating Deforestation Through Rum, Chocolate, and Ecotourism
- Empowering Communities to Protect Their Ecosystems
- Best of Green Awards 2021: Sustainable Travel
- Why Bonobos Are Endangered and What We Can Do
- Why Are National Parks Important? Environmental, Social, and Economic Benefits
- IUCN President Tackles Biodiversity, Climate Change
- The World’s Smallest Tiger Is Inching Towards Extinction
- Ecuador Expands Protected Galapagos Marine Reserve by More Than 23,000 Square Miles
- What Is Voluntourism? Does It Help or Harm Communities?
- Regenerative Travel: What It Is and How It's Outperforming Sustainable Tourism
- New Zealand Aims to Become World's Largest 'Dark Sky Nation'
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, wildlife tourism and the education of children.
Children in Sustainable and Responsible Tourism
ISBN : 978-1-80117-657-6 , eISBN : 978-1-80117-656-9
Publication date: 7 March 2022
Learning about wildlife is an important part of childhood education, but it is yet to be capitalised upon in the context of educational tourism. This chapter considers the different types of wildlife tourism that are available to children, how wildlife tourism experiences might have educational value and what the benefits of this niche tourism type might be. By providing insight into the educational elements of wildlife tourism, this chapter provokes analytical thinking about how this can be implemented and managed in a sustainable and responsible manner.
- Wildlife tourism
- Animal tourism
- Responsible tourism
- Sustainable tourism
Stainton, H. (2022), "Wildlife Tourism and the Education of Children", Séraphin, H. (Ed.) Children in Sustainable and Responsible Tourism , Emerald Publishing Limited, Leeds, pp. 17-26. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-80117-656-920221002
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2022 by Emerald Publishing Limited
We’re listening — tell us what you think
Something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates

Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

TravelPulse
13 Ways Responsible Tourism Can Help Save Wildlife
Posted: April 19, 2023 | Last updated: June 7, 2023

Certifications
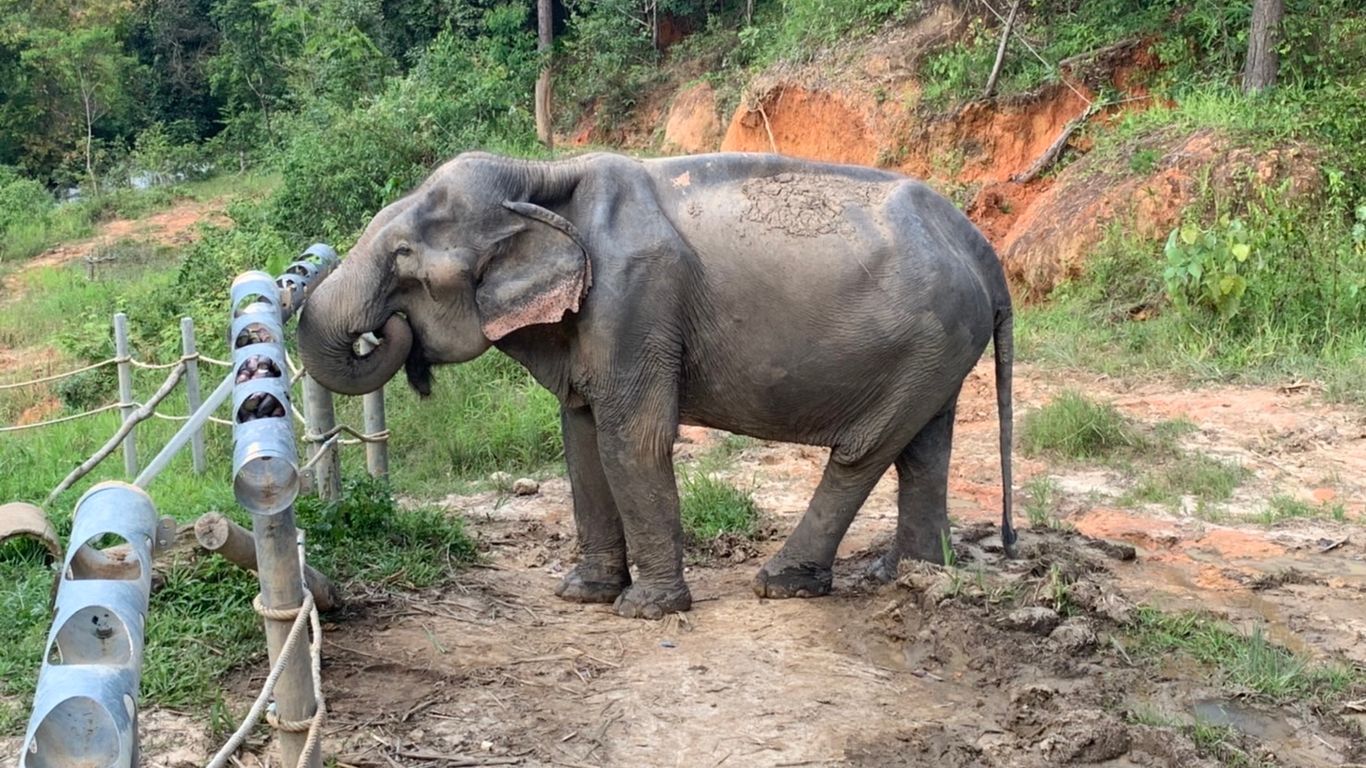

ChangChill Elephant Sanctuary, Thailand

Los Cabos whale watching

Two elephants enjoying their retirement at a sanctuary

Two lions (Panthera leo) resting high up in a tree

A monkey in a cage

A mother gorilla and her baby in the rainforest of the Congo Basin.
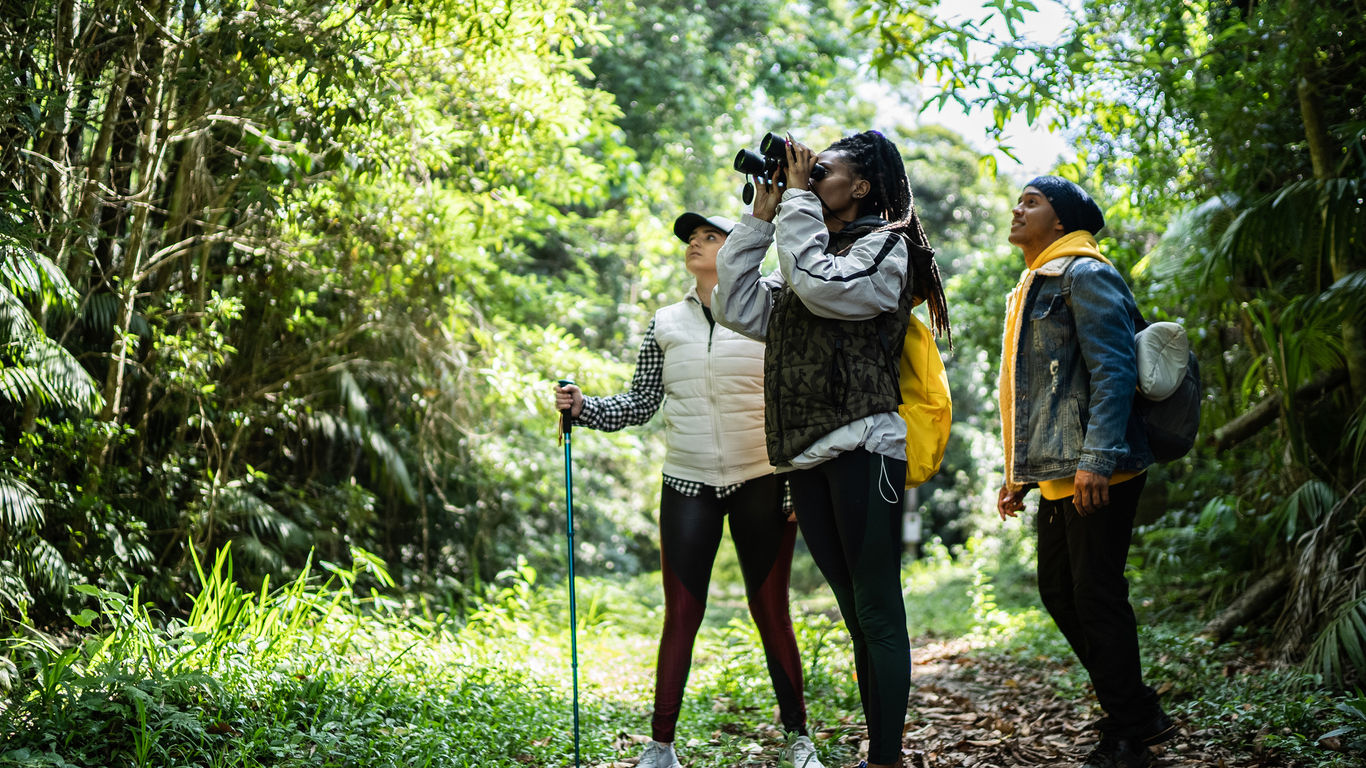

Travelers using binoculars in a forest

Hurtigruten Galapagos cruises

Visit Sumatra with Intrepid Travel

Intrepid Travel Plants Trees in Kenya

Travel planning on the computer

Exodus Travels
More for you.
Team USA Issues Statement Regarding Caitlin Clark's Olympic Status
Luke Grimes Supports Kevin Costner's Decision On ‘Yellowstone'
I'm abrosexual - it took me 30 years to realise
The most expensive state to live in isn't California or New York, based on data. Here are the top 10.
Marriage counsellor shares one sign your relationship is really over
Scientists claim people with this blood type more likely to have early stroke
John Jacob Astor IV was one of the richest men in the world when he died on the Titanic. Here's a look at his life.
'What's the point of earning this money?': Ramit Sethi says many Americans are reaching for a financial goal that means nothing. Is he right?
Don't Break The 6 Golden Rules Of Cooking Steak
The 'Dolomite Problem' Has Baffled Scientists for 2 Centuries—and Now They've Solved It
Netflix’s new movie trailer slammed as ‘AI propaganda’
The 26 Most Dangerous Cities in the U.S. Ranked
The seven new types of old age – and how to tell which one you are
Scientists say they have found a chapter of the Bible hidden under a section of text for more than a thousand years
Updated Preseason College Football Rankings Feature A New No. 1 Team
Super Bowl-winning quarterback explains why Falcons drafting Michael Penix Jr was 'brilliant'
This Social Security Spousal Rule Is Officially Finished in 2024 — But These 3 Strategies Remain
Map reveals best places to live in the US if nuclear war breaks out
Harvard professor who teaches a class on happiness: The happiest people balance and prioritize 3 things
Should you avoid living in a 55-plus community? Here are 5 big problems with adult retirement communities in America
- United Arab Emirates
- Switzerland
- The Netherlands
- Puerto Rico
- United States
- New Zealand
- ➨ Choose from World Map
- Budget Travel
- Family Travel
- Getting Around
- Visas & Passports
- Work with Us
Browsing Category
- Czech Republic
- Saint Martin
- Uncategorized

Moscow Travel Guide: Best Things to Do + More [2023]
· everything to know about visiting moscow, including the best things to do and how to get around. ·.

Moscow is Russia’s vibrant capital city, and it also happens to be the largest city in all of Europe. The city’s long and infamous history makes it one of the most unique places we have ever visited.
The architecture ranges from centuries-old palaces to uniform, gray concrete buildings. The people range from cold and private to warm and welcoming. Moscow is a city is strong juxtapositions, and we learned a lot during our time there.
This post will break down all you need to know about visiting Moscow, including the best things to do, how to get there, how to get around, and more.

The Best Things to Do in Moscow
1. explore the red square.
The Red Square is the heart of Moscow. Most of the city’s top attractions can be found here, including just about everything on this list. The Kremlin, St. Basil’s Cathedral, and Lenin’s Mausoleum are all located here, and the State Historical Museum and GUM are not far from here, either.
The Red Square is a common home for parades, protests, and seasonal celebrations. There are massive Christmas celebrations here, with food vendors and carnival rides set up in numbers.

2. Check Out the Ziferblat
The Ziferblat is a café in Moscow that is unlike any café we have ever been to. While most cafes charge you for your drinks and food, the Ziferblat charges you for your time.
Upon arrival, you are given a clock. When you leave, the barista calculates how much time you spent in the café and charges you accordingly. This concept was created to help visitors to be more intentional with their time, and the cafe itself is incredibly charming.
For a detailed look at everything you need to know before you visit, make sure you read my post about visiting the Ziferblat Cafe in Moscow .

3. Marvel at St. Basil’s Cathedral
St. Basil’s Cathedral is one of the most iconic churches in the world, and it was the single thing we were most excited to see while in Moscow. Built almost 500 years ago, St. Basil’s Cathedral is recognized by its colorful domes and whimsical style. The church is of the Russian Orthodox faith, and the inside is just as wondrous as the outside.
St. Basil’s Cathedral is located on the edge of the Red Square, making it incredibly convenient to visit. Entrance for non-worshippers costs 800 rubles, and tickets can be bought at the church

4. Explore the Kremlin
The Kremlin is the largest active fortress in Europe, and it is the site of most of Russia’s government affairs. In addition to government buildings, the Kremlin Complex is filled with courtyards, towers, and museums that are open to the public. If you have the time, you could spend a couple of days fully exploring all that there is to see in the Kremlin.

5. Walk Through Lenin’s Mausoleum
Vladimir Lenin is one of the most important figures in Russian history, and his body is located perfectly embalmed in a mausoleum in the Red Square. The Mausoleum is open to the public to visit, and as long as you are willing to go through a few security checks, it is easily one of the best things to do in Moscow. Its convenient location in the Red Square makes it a can’t miss attraction.
There is absolutely no photography allowed inside the Mausoleum. Do not test this rule.

6. Wander Along Arbat Street
The Arbat is a very popular street in Moscow that is lined with stores, cafes, and other touristy attractions. It is one of the oldest streets in the city, dating back to the 1400s. This street is both quaint and trendy, and there are many walking tours that introduce tourists to the neighborhood’s wonders and highlights.

7. Catch a Show at the Bolshoi Theatre
As a lover of the arts, it is hard to think of Moscow and not think of ballet. Russia has always been a top dog in the world of fine arts, and Bolshoi Theater is one of the best places to catch a performance. We were lucky enough to attend an Opera here, and it is a venue that you don’t want to miss out on if you enjoy opera, ballet, or orchestral performances.
8. Visit the State Historical Museum
The State Historical Museum is one of the most respected museums in Moscow. Despite its name, it is not really focused on the history of Russia as a nation. Rather, it contains a collection of artifacts from all throughout Russia’s history.
The museum’s collection is very broad in nature. It houses some items from indigenous tribes that used to occupy the region, pieces collected by the Romanov family, and more.
9. Wander Around GUM
GUM is an absolutely massive mall within walking distance of the Red Square. It isn’t just the size that draws visitors here; it’s the sense of luxury. The mall is so beautiful inside, much like the metro stations.
While visiting a mall might not sound like it belongs on a bucket list, this mall does. You will not want to miss out on visiting GUM while in Moscow.

10. Admire the Cathedral of Christ the Saviour
While St. Basil’s Cathedral is the most iconic church in Moscow, it isn’t the only one. The Cathedral of Christ the Saviour is absolutely stunning, with massive golden domes. It is the tallest Orthodox church in the world, and it is the seat of the Orthodox Patriarch of Moscow.
It is located just about a mile from the Red Square, just south of the Kremlin Complex. You can walk to it from the Red Square in about 20 minutes.
How to Get to Moscow
Flying to moscow.
Moscow has three major international airports: Sheremetyevo (SVO) , Domodedovo (DMO) , and Vnukovo (VKO) . All three of them are directly connected to downtown Moscow by the Aeroexpress trains, which leave every 30 minutes throughout the day. By Aeroexpress train, you can expect to get to the city center in 25-45 minutes depending on the airport that you fly into.
Sheremetyevo is the biggest and busiest of the three airports, and it is the one you are most likely to fly into – especially if you are coming from outside of Europe or the Caucus region. We flew into Sheremetyevo on a direct flight from New York City.
I usually provide backup airport options, because flying right into the city isn’t always the cheapest way to get where you’re going. Unfortunately, when it comes to Moscow, don’t really have a choice other than to fly right into Moscow. It is a very remote city, and it is usually the cheapest place to fly into in Russia as a whole.
Since Sheremetyevo is so busy, you will probably find a great flight option anyway. I wrote in my post about finding cheap flights that using hub airports will lead to more affordable airfare, and the same logic applies here. Even though Russia’s national airline, Aeroflot, is no longer a member of the SkyTeam Alliance, Moscow is still a major hub connecting passengers from all over the world.

READ OUR CHEAT SHEET
Train or Bus to Moscow
Trains and buses are one of the most popular ways to get around Europe. However, they’re of very little use when you’re trying to get to Moscow.
Moscow is hundreds of miles from the nearest major cities. The only major European city that can even be reached within 8 hours on the ground is St. Petersburg, and even the Baltic capitals of Riga, Vilnius, and Tallinn are over 12 hours away.
If you want to get to Moscow, the best option is almost always to fly. While the train routes to Moscow are scenic, they simply take forever.
How to Get Around Moscow
METRO | TROLLEYS | TRAMS | BUSES
Moscow has one of the most memorable metro systems in the world. Its metro lines are very deep underground, and the stations are absolutely stunning. Each station has its own unique style, but all of them contain escalators that seem to go on forever.

The system was built in an effort to showcase the power of the Soviet Union and its bright future. The plans were a form of propaganda, but they resulted in what is still one of the most visually appealing subway systems on earth.
Moscow’s metro system isn’t just pretty. It is also very useful and accessible. The system has 17 lines that connect the city and its surrounding area.
But wait; there’s more!
The Moscow metro system is also incredibly affordable, with each ride costing less than a dollar. The metro is by far the best way to get around Moscow, as it is almost impossible to beat the connection times and the low cost to ride.
Tickets can be bought at electronic, English-speaking kiosks in stations, or directly from ticket counters at certain larger stations. There are also day passes available, which are a very solid option if you plan on riding the metro several times per day.

The metro is by far the best way to get around Moscow.
In addition to the metro system, Moscow also has a network of buses, trams, and trolleys. This system is nowhere near as convenient or well-connected as the metro, though, and is likely of little use to you during your trip. There is no Uber in Moscow, but a similar app named Yandex is available if you need a ride in a pinch.
How Many Days Do You Need in Moscow?
Moscow is the biggest city in all of Europe, and it is absolutely loaded with things to do. You could spend weeks in Moscow and still find new things to do. Of course, most travelers don’t have that kind of time to spend in one place!
I recommend spending no less than three full days in Moscow, and ideally closer to five or seven.
Moscow is very spread out, and it can take some time to get from one major point to another. There are also so many places that are nice to just sit back and relax, which is hard to do when you’re in a hurry trying to cram activities into just a few days.
If you only have a week to visit Russia, I’d advise spending all of the time in one city. If you decide to split your time between Moscow and St. Petersburg, I recommend not trying to squeeze in any day trips beyond those two cities.

When Is the Best Time of the Year to Visit Moscow?
There are two different ways to approach this question. Personally, I think the best time to visit Moscow is around Christmas and New Year’s Day. While the weather will be absolutely freezing, Moscow is a surreal winter wonderland in December and January.
We were in Moscow right before Christmas. While it was very cold, you can always bundle up. Exploring the Christmas markets and pop-up ice skating rinks throughout Moscow is one of my favorite memories from anywhere I’ve traveled, and I dream of going back to do it again.
If you aren’t fond of the cold, Moscow is beautiful in the summer. It tends to get pretty cold in the shoulder seasons, so if you want warm weather, you should plan to visit in the summer. Moscow actually gets pretty warm in July and August, and there are a bunch of fantastic places to soak up the sun within the city.
The best time to visit Moscow is either around Christmas or from late May to August.

Is Moscow Safe to Visit?
While Moscow is a truly wonderful city, there’s no denying that visiting Russia comes with risks. As the country is run by an infamous communist dictator, concerns about visiting are valid. While we didn’t experience any sort of threat or negative treatment during our time in Moscow, we visited in a peaceful time.
In our experience, Russia doesn’t seem to detain normal Americans or Westerners to use as pawns. As a regular person, as long as you don’t commit any crimes, there is a slim chance you will run into any issues. However, Russia will not hesitate to enforce its laws against foreigners, and illegal behaviors will likely land you in a very compromising position.
Russia will not hesitate to enforce its laws against foreigners, and illegal behaviors will likely land you in a very compromising position.
To make matters worse, Russia has a bad reputation for gang violence. While the Russian mafia has very little interest in normal Western tourists, they won’t hesitate to pick a fight with anyone who ventures into their sphere of influence. If you seek out illegal substances or activities, you could be a target of the mafia.
If you seek out illegal substances or activities, you could be a target of the mafia.
Finally, since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, things are all very different. Russia is currently at war, and there are battles raging within 8 hours of Moscow. While it is still relatively safe to visit, that could change at any time as the war with Ukraine continues.
Is Moscow Worth Visiting?
Without a doubt, Moscow is worth visiting. It is one of the most unique major cities we have ever visited, and we hope to make it back one day. The Russian Orthodox churches are stunning, the city’s history is unlike any other, and the food is to die for.
While many visitors prefer St. Petersburg to Moscow, I think Moscow deserves a lot of hype of its own. Moscow is the beating heart of Russian culture and history, and it’s a place I highly recommend checking out if you have the chance.

That’s all we have for you about Moscow! I hope this post was helpful as you plan your trip to Russia’s capital.
Have you been to Moscow? Or is this your first time visiting? Comment below if you have anything to add to our travel guide!
Hi, I'm Greg. I'm an avid traveler who has traveled to over 50 countries all around the world with my wife and kids. I've lived in Italy, Mexico, China, and the United States, and I dream of moving abroad again in the future. With this blog, I provide my audience with detailed destination guides to my favorite places and pro-tips to make travel as stress-free as possible.
Leave a comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Meet The Author - Greg
Recent Post

How Much Does a Trip to Egypt Cost: Budget Breakdown
March 10, 2024

Best Time to Visit the India Gate in Delhi [2024]
March 1, 2024

Flying with a Sinus Infection: Tips to Avoid Pain
February 20, 2024

11 Best Things to Do in Breckenridge Besides Skiing
February 12, 2024

10 Best Beaches in Mexico for Families (We Lived Here)
February 3, 2024

The 50 best parks and gardens in Moscow
Navigate forward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.
Navigate backward to interact with the calendar and select a date. Press the question mark key to get the keyboard shortcuts for changing dates.

1 Gorky Central Park of Culture and Leisure
2 Kolomenskoye

3 Tsaritsyno Museum-Reserve
4 all-russian exhibition center, 5 sokolniki park.
Track your travel spending and split costs with friends
Plan your trip. Keep your budget organized. Split the cost between tripmates. Wanderlog does it all.

6 Zaryadye Park
7 moscow zoo, 8 izmailovsky park, 9 muzeon park of arts, 10 neskuchny garden, 11 bauman garden, 12 park krasnaya presnya, 13 moscow state university, 14 vorobyovy gory, 15 family park skazka..

Don’t forget to pack anything
Stay organized with a to-do list, packing list, shopping list, any kind of list.

16 Nebo Trampoline park
17 happylon, 18 the rink, 19 fishpoint, 20 vorob'yevy gory, 21 moscow-850, park attraktsionov i razvlecheniy, 22 gulliver, 23 le parterre, 24 vorob'yevy gory, 25 apothecary garden.
All travel reservations in 1 place
Never dig through your emails again — access all your flights, lodging, and any reservations in 1 place.

26 Alexander Garden
27 kuskovo estate museum, 28 patriarch's ponds, 29 hermitage garden, 30 main botanical garden of the russian academy of sciences, 31 nudistskiy plyazh v serebryanom boru, 32 yekaterininskiy park, 33 city farm, 34 pokrovskoye-streshnevo park, 35 park ostankino.

Perfect for road trips
See time and distance between places, and optimize your route to get the most of your day.
Collaborate with friends in real time
Plan along with your friends with live syncing and collaborative editing.

46 Mitino landscape park
47 park druzhby, 48 lefortovo park, 49 trubetskoy estate, 50 park sadovniki, top searches in moscow, popular road trips from moscow, what's the weather like in moscow.
It depends on when you visit! We've compiled data from NASA on what the weather is like in Moscow for each month of the year: see the links below for more information.
- Weather in Moscow in January
- Weather in Moscow in February
- Weather in Moscow in March
- Weather in Moscow in April
- Weather in Moscow in May
- Weather in Moscow in June
- Weather in Moscow in July
- Weather in Moscow in August
- Weather in Moscow in September
- Weather in Moscow in October
- Weather in Moscow in November
- Weather in Moscow in December
All road trips from Moscow
- Moscow to London drive
- Moscow to Paris drive
- Moscow to St. Petersburg drive
- Moscow to Berlin drive
- Moscow to Prague drive
- Moscow to Amsterdam drive
- Moscow to Budapest drive
- Moscow to Vienna drive
- Moscow to Istanbul drive
- Moscow to Florence drive
- Moscow to Venice drive
- Moscow to Stockholm drive
- Moscow to Milan drive
- Moscow to Krakow drive
- Moscow to Copenhagen drive
- Moscow to Warsaw drive
- Moscow to Helsinki drive
- Moscow to Munich drive
- Moscow to Brussels drive
- Moscow to Tallinn drive
- Moscow to Riga drive
- Moscow to Oslo drive
- Moscow to Turin drive
- Moscow to Hamburg drive
- Moscow to Vilnius drive
- Moscow to Yaroslavl drive
- Moscow to Nizhny Novgorod drive
- Moscow to Kyiv drive
- Moscow to Tula drive
- Moscow to Bruges drive
Explore nearby places
- Likino-Dulevo
- Ivanteyevka
- Orekhovo-Zuevo
- Semyonovskoye
- Ivanovskoye
- Rumyantsevo
- Dzerzhinsky
- Sovkhoz Imeni Lenina
- Dolgoprudny
All related maps of Moscow
- Map of Moscow
- Map of Danki
- Map of Shatura
- Map of Likino-Dulevo
- Map of Uspenskoye
- Map of Gorskoye
- Map of Ivanteyevka
- Map of Reutov
- Map of Domodedovo
- Map of Peresvet
- Map of Vorobyovo
- Map of Bronnitsy
- Map of Orekhovo-Zuevo
- Map of Moskovsky
- Map of Semyonovskoye
- Map of Izmaylovo
- Map of Nikolskoye
- Map of Ivanovskoye
- Map of Marfino
- Map of Govorovo
- Map of Nagornoye
- Map of Mosrentgen
- Map of Bratsevo
- Map of Rumyantsevo
- Map of Mytishchi
- Map of Putilkovo
- Map of Razvilka
- Map of Khimki
- Map of Dzerzhinsky
- Map of Sovkhoz Imeni Lenina
- Map of Dolgoprudny
Moscow throughout the year
- Moscow in January
- Moscow in February
- Moscow in March
- Moscow in April
- Moscow in May
- Moscow in June
- Moscow in July
- Moscow in August
- Moscow in September
- Moscow in October
- Moscow in November
- Moscow in December
Looking for day-by-day itineraries in Moscow?
Get inspired for your trip to Moscow with our curated itineraries that are jam-packed with popular attractions everyday! Check them out here:
- 1-Day Moscow Itinerary
- 2-Day Moscow Itinerary
- 3-Day Moscow Itinerary
- 4-Day Moscow Itinerary
- 5-Day Moscow Itinerary
Best attractions in nearby cities
- Top things to do and attractions in Khimki
Best restaurants in nearby cities
- Where to eat: the best restaurants in Mytishchi
- Where to eat: the best restaurants in Khimki

- Itinerary + map in one view
- Live collaboration
- Auto-import hotels and reservations
- Optimize your route
- Offline access on mobile
- See time and distance between all your places

Mission Moscow : A Conversation with Evgeny Kozlov
Mr. Evgeny Kozlov, Deputy Head Mayor of Moscow Government and Chairman of the Moscow City Tourism Committee, who has come to the city to attain BLTM, the annual prestigious travel event at the Leela Ambience Convention Centre, Delhi spoke with TW Editor Anirban Dasgupta on his vision and goal with the all-new tourism initiatives in Moscow.
The bond between India and Russia has a long history of culture, literature, love, and of course politics. But recently, there has also been a lot of talk about Gastronomical tourism. Any personal experience with this?
My personal take on the bond between India and Russia stems from my recent experience of trying authentic Indian cuisine in Moscow. I thoroughly enjoyed the spicy flavours of the Curry dish I tried and it left a lasting impression on me. This made me appreciate the cultural exchange between our two countries even more. I believe that Moscow, being a culinary hub, is a great place for people from all over the world, including Indian visitors, to immerse themselves in our rich history and culture. It’s a unique experience that brings people together and showcases the diversity of the gastronomic universe. Moscow has a thriving food scene with various international cuisines to explore, from Chinese to South African and Latin American. This culinary diversity reflects the open-mindedness and curiosity of the Russian people when it comes to trying new types of food. Moscow truly has something for everyone, and I encourage Indian tourists to come and indulge in this gastronomic journey.

How optimistic are the post-pandemic recovery figures?
After the Covid-19 pandemic, we have witnessed a remarkable recovery in tourism in Moscow. In fact, we have been able to restore 90% of the pre-pandemic tourist flow. In the first half of 2023, almost a million foreign tourists visited Moscow, with over 600,000 of them arriving during the summer season. Among the non-CIS countries, China has led the way in terms of tourist traffic, followed by Iran, the United Arab Emirates, Turkey, and India. Prior to the pandemic, India’s tourist flow was steadily growing at a rate of 12-15% annually. Although we faced challenges during the pandemic, we have now put in place all the necessary conditions for a successful recovery. Moscow is known for hosting numerous international exhibitions, forums, congresses, and conferences, attracting approximately 3.6 million business visitors in the past year alone. Among these visitors, India ranks third in terms of foreign business tourists in Moscow. To further promote tourism, we have initiated the MICE Ambassadors training program in India, which aims to assist Indian businesses in exploring opportunities and selecting relevant events in Moscow.
Can you please share your vision for future tourism development in Moscow?
Thank you for asking this question. I have a multi-faceted vision for the future tourism development in Moscow.
Firstly, I believe that tourism should provide a personal and authentic experience for each individual. Therefore, customization of experiences is crucial. For business tourists, we aim to offer special infrastructure facilities that cater to their specific needs and requirements. We are closely collaborating with infrastructure providers to ensure seamless experiences for those visiting Moscow for business purposes. On the other hand, when it comes to leisure or family tourists, we recognize the importance of providing a support system and guidelines for those traveling with their families, especially children. We are working with museums, theatres, and restaurants to customize their services and products to cater to tourists of all ages, including children. Furthermore, I envision rearranging tourism in Moscow to encourage visitors to delve into the history and heritage of our country. A significant part of my tourism goal is to motivate and inspire the youth and younger generations to travel to Russia. This involves providing affordable pricing for accommodations, entertainment, museums, and other attractions.
We are already constructing tailor-made infrastructure that specifically targets the young generation in Russia, and by next year, we plan to extend and promote these offerings to international young visitors as well. By rebranding the image of Moscow as a destination for longer stays, relaxation, and enjoying various facilities, we aim to change the perception that it is merely a transit or stop-over city. Lastly, the beautiful weather in Moscow during the summer months provides an opportunity to create delightful memories for tourists. I want every visitor to experience the sunshine, green landscapes, parks, cafes, restaurants, swimming pools, and sports facilities that Moscow has to offer during this time.
In summary, my vision for the future of tourism in Moscow revolves around creating customized travel experiences for every type of traveller.
How do you prioritize sustainability and responsible tourism practices in the development of business tourism?

How easy or difficult is it to get a Visa for an Indian Tourist at present?
Acquiring a Visa for Indian tourists has become easier with the introduction of the e-visa system. Since its launch in August 2023, more than 30,000 tourists have already utilized this system. The e-visa offers several advantages over traditional visas, such as avoiding the need to visit consulates or embassies. The application process only requires a digital photograph and a scan of the passport data page. The e-visa has a validity period of 60 days from the date of issuance, with a maximum stay of 16 days in Russia. This convenient and streamlined process is available to citizens of 55 countries, including India. Indian tourists are currently ranked third in terms of business travellers from outside the CIS countries visiting Moscow.
Author: Anirban
Share article, related news.

BLTM 2023 showcases top destinations for Bleisure and MICE Travel

École Ducasse Abu Dhabi Studio, in partnership with Erth Hospitality, to open this December
No comment be the first one., leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Wildlife tourism is an element of many nations' travel industry centered around observation and interaction with local animal and plant life in their natural habitats. While it can include eco- and animal-friendly tourism, safari hunting and similar high-intervention activities also fall under the umbrella of wildlife tourism.
Asia and the Pacific. Wildlife tourism refers to the observation and interaction with local animal and plant life in their natural habitats. It encompasses segments such as eco-tourism, safari tours and mountain tourism among others. Wildlife watching tourism occurs mainly in protected areas. Nature, national parks and wildlife are considered ...
Wildlife tourism is frequently characterized by four key components: the destination, the wildlife, the tourist and/or their expectations, and the interaction (species-specific, close encounters). The relationships among these components and their underlying drivers determine how wildlife tourism experiences are managed to achieve sustainable ...
Whilst there is great potential for wildlife tourism to do good, many businesses are poorly managed and demonstrate unethical practices. This most commonly includes; the mistreatment of animals, introduction of disease, dangerous behaviour, changes in the animal's behaviour and reduced breeding success.
In 2016, travel and tourism contributed $7.6 trillion, or 10.2%, to total GDP, and the industry provided jobs to one in 10 people, according to the World Travel & Tourism Council. While nature-based tourism, which includes wildlife tourism, has been expanding rapidly in the last decade or so due to increased demand and opportunities, wildlife ...
Wildlife tourism, as defined by Higginbottom (2004), is tourism based on encountering any non-domesticated (non-human) animals in the animal's natural environment or in captivity (Hill, 2002 ...
Wildlife tourism, with its emphasis on free-ranging wildlife (generally animals), is a subset of nature tourism; but it is also included in various discussions of ecotourism and adventure tourism.Conceptually wildlife tourism at any destination is a function of three primary components: the wildlife, the tourist, and the interaction (Newsome et al. 2005).
As 'wildlife tourism' has a plethora of definitions and approaches in the literature, and it is not the mission of this introductory chapter reviewing it all over again, thus wildlife tourism is defined as 'a nature-based tourism niche on interactions and viewing of wild animals in either their natural habitats, in semi-captivity or ...
Scan the space. Observe whether animals have an appropriate environment, including shelter, ample space, a comfortable resting area, and a secluded place away from crowds. Beware of buzzwords ...
What I learned investigating the wildlife tourism industry. At Elephant Valley Thailand, in Chiang Rai, tourists are instructed to observe the animals from a safe distance. Photograph by Kirsten ...
ABSTRACT. An online survey of the American public (n = 500) was used to explore perceptions of the effects of tourism on wildlife and definitions of key tourism terms.Results show that the public's assessment of the impacts of tourism are relatively nuanced and reflective of trade-offs discussed in the literature, and that there is broad recognition of the potential for wildlife to ...
Wildlife human interactions play a significant and growing role in the tourism industry. In its broadest terms, wildlife tourism can incorporate both fauna and flora. Yet, in most cases wildlife tourism refers to the watching and interacting with animals and can include both free-ranging and captive wildlife (Newsome et al. 2005; UNEP/CMS 2006 ...
Wildlife tourism (WT), defined as 'tourism based on encounters with non-domesticated (non-human) animals' (Higginbottom, 2004, p. 2), is an important sector in developed and developing countries. WT encounters can be non-consumptive and thus congruent with the tents of ecotourism, or consumptive based on activities such as hunting, fishing, and ...
Research Wildlife tourism. In studying the impacts of wildlife tourism we examined 48 types of wildlife tourist attraction (representing thousands of individual institutions), ranging from poorly-attended street performances, like snake charming, bear dancing and macaque shows, to large, established attractions such as dolphinaria and tiger interactions, which have tens of thousands of ...
AFAR wants to help you find the best international trips to see wildlife in a responsible way. We have vetted a number of lodges and operators that embrace wildlife viewing practices that are ethical, sustainable, and socially responsible and offer close encounters—without getting too close. Read the full story. Mae Hamilton.
"Wildlife tourism is a rich segment of the industry, showing how our precious species can legitimately enrich tourism businesses without being harmed. In fact, the wildlife tourism market is so strong - worth five times more than the illegal trade - that it provides a strong incentive for communities to protect and display animals to the ...
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES), a non-profit organization dedicated to the development of ecotourism since 1990, defines ecotourism as "responsible travel to natural areas that ...
Abstract. Learning about wildlife is an important part of childhood education, but it is yet to be capitalised upon in the context of educational tourism. This chapter considers the different types of wildlife tourism that are available to children, how wildlife tourism experiences might have educational value and what the benefits of this ...
Wildlife tourism is an important part of the tourism industries in many countries including many African and South American countries, Australia, India, Canada, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Malaysia, Sri Lanka and Maldives among many. It has experienced a dramatic and rapid growth in recent years worldwide and many elements are closely aligned to eco
The WAP report identified companies that are leaders in responsible wildlife tourism and those that are continuing to sell and profit off of venues that involve cruelty to animals. Concerned ...
3. Marvel at St. Basil's Cathedral. St. Basil's Cathedral is one of the most iconic churches in the world, and it was the single thing we were most excited to see while in Moscow. Built almost 500 years ago, St. Basil's Cathedral is recognized by its colorful domes and whimsical style.
But Carlson, who seems to be going through his foreign-exchange-student-likes-Barcelona-more-than-Paducah phase, misses a few finer details. If you are a journalist, life in Moscow means constant ...
Nature & Parks. The Hermitage Garden is a small, beautifully landscaped park in the heart of Moscow. It is popular with office workers and theatre-goers alike, and features a range of attractions including theaters New Opera, Hermitage and Sphera. We've collected the most-often-mentioned 50 places from other articles, including favorites like ...
Mr. Evgeny Kozlov, Deputy Head Mayor of Moscow Government and Chairman of the Moscow City Tourism Committee, who has come to the city to attain BLTM, the annual prestigious travel event at the Leela Ambience Convention Centre, Delhi spoke with TW Editor Anirban Dasgupta on his vision and goal with the all-new tourism initiatives in Moscow. The bond between India and Russia has a long history ...