You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.


All about Reverse Power Relay and Preferential Trips on Ship Electrical System
Reverse Power Relay is a directional protective relay that prevents/protect the generator from motoring effect (going to reverse direction). It is used where generator runs in parallel with other utility or generator. The relay monitors the power supply from the generator and in case the generator output falls below a preset value, it quickly activates the trip and disconnects the generator .
Construction of ship Reverse Power Relay

The relay is made up of lightweight non-magnetic Aluminium disc between two soft laminated iron core electromagnets. The upper magnet is wound with Voltage Coil (PT) which is supplied from one phase & artificial neutral of generator output. The other output magnet is wound with Current Coil (CT) connected to the same phase as the voltage in the upper electromagnet.
Working of ship Reverse Power Relay
Since Voltage Coil has more number of turns, so it has move inductive value and more induced current that lag in the coil by an angle of 90°. The current coil has less number of turns so less number of turns, so it has less inductive valve & less induced current that lag less.
As we all know that current carrying conductor produces the magnetic field. So both upper and lower section produces magnetic fields. But Induced current in PT lags more than CT so magnetic field produced in upper section will be weaker than lower section & both magnetic fields will have a difference of 90°
When both fields pass through the Aluminium disc, it produces eddy current. As a result of the formation of eddy current torque is generated that tries to rotate the disc. Under normal power flow, the trip contact on the disc are open and rotation is restricted by stoppers but if a reverse power starts to flow the disc is rotated in opposite direction, moves away from the stoppers in the direction of trip contact that activates the trip.
Why is Reverse Power Relay required?
When two or more power units are running in parallel and if reverse power flow occurs, the same unit will start drawing power from the main bus bar. it can cause overloading of the other power supply unit and hence leads for the preferential trip or may lead to total power failure(Blackout). At the same time the faulty unit will draw power from main bus bar and go for motoring effect and RPM will soot up which leads to over speed trip or in worst case some mechanical failure to the prime mover.
When does reverse power flow…..?
When the prime mover of a generator is not supplying sufficient torque to keep the generator rotor spinning at the same frequency as the bus goes to which the generator is supposed to be connected, the generator will start behaving like a motor and instead of supplying power it will draw power from bus bar. During synchronization, it might be possible to have the synchroscope rotates slow (anticlockwise direction) and then close the breakup. under this condition. The generator would then be drawing current from the bus for instead of supplying current through the bus (which occurs when the breaker is closed with the synchroscope rotates in the fast anticlockwise direction). Faulty Governer of the prime mover. Loss of excitation in the alternator. How do you test reverse power trip? Reverse power trip can be tested by load shifting with the help of Governor control. when the Load has shifted sufficiently from the generator to be offloaded (Nearly 10% of the max rated ), reverse power relay will open the ACB of the same generator. this relay can be tested by simulation using boost test push button on the relay to see if it gives a trip signal.
PREFERENTIAL TRIPPING ON SHIP ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
What is the use of preferential trip.
The preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement on the ship which is designed to disconnect the non-essential circuit .i.e non-essential load from the main bus-bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply.
The non-essential circuit or loads on the ship are air conditioning unit, exhaust ventilation fans, & galley equipment which can be disconnected momentarily . The main advantage of the preferential trip is to supply uninterrupted power for propulsion and safe navigation under overloading condition of the power unit.
Construction of preferential trip on ship system

The preferential trip circuit consists of an Electromagnetic coil and a dashpot arrangement to provide some delay to disconnect the non-essential circuits. Along with this, there is also an alarm system provided, which function as soon as overload is detected and trips start operating. There are some mechanical linkages provided in the circuit which instantaneously operates the circuit for preferential trips.
The dashpot arrangement consists of a small Piston with the small orifice and which is placed inside a small cylinder assembly. The Piston moves up against the viscous fluid silicon and the time delay is governed by the orifice in the Piston
Working of ship safety preferential trip
The current passes through the electromagnetic coil and the linkage are kept from the contacting using a spring arrangement. As soon as the current value increases the limit, the electromagnetic coil pulls the linkage up against the spring force and operates the instantaneous circuit and the alarm system. The lower linkage completes the circuit for the preferential trip circuit.
The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit which pulls the piston in the dash pot arrangement. The movement of the piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same. The preferential trip operates at 5,10, & 15 seconds and the load is isolated accordingly. If the overload still persists, then blackout will occur.
Shop for mariners

© The Electro Technical Officer (ETO) | Disclaimer | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | FAQ
Privacy Overview
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
Chief Engineer's Log
"your guide to maritime engineering education".

What you need to know about electrical preferential tripping and sequential restarting
Onboard vessels, modern power management systems make it less likely for power to go out for no reason, but engineers must be familiar with the specific procedures, where to find the instructions and procedures, and ready to act in case of automation failure.

Example of Power Management System
In case of a problem with power main diesel generators or in case of overcurrent, non-essential loads are interrupted automatically, in order to prevent the ship’s power failure. Preferential tripping has been fitted to reduce the possibility of the loss of essential vessel supplies if an event as described above will occur. It has been arranged that load reduction will be achieved by an ordered disconnection of non-essential supplies to prevent a blackout that may put the vessel’s safety at risk.

Example of preferential trip alarm
Depending on the vessel electrical layout and design, there are different stages (two or three) of preferential tripping. For example:
- if the current on a running generator exceeds 100% of the generator rating for a period exceeding 5 seconds, the PMS will initiate the release of the 1st stage preferential tripping (PT1), thereby providing protection against the overcurrent which would otherwise trip the circuit-breaker – non critical ship systems.
- if the current on a running generator exceeds 100% of the generator rating for a further 5 seconds, the PMS will initiate the release of the 2nd stage preferential tripping (PT2) – cargo hold vent fans and packaged air conditioning units.
- in some vessels if the current on a running generator exceeds 100% of the generator rating for a further 5 seconds, the PMS will initiate the release of the 3rd stage preferential tripping (PT3).

Example of 1st and 2nd stage preferential trips alarm
on some other systems the preferential trips can be triggered in three ways regardless of the generator being under PMS or manual control:
- an overcurrent condition in a main generator for a preset time will initiate first stage trips – if the current on a running generator reaches 120 % of the rated full load current for a period of 10 s, the breaker overcurrent protection circuit will initiate the release of the first stage of preferential tripping. If the 120% overload condition should continue for 40 seconds the generator VCB itself would trip, initiating the 2nd stage trip.

Example of DG overcurrent alarm leading to preferential trip alarms
When normal conditions resume, the tripped breakers must be manually reset.
- low lubricating oil pressure
- high fresh water cooling temperature
- overspeed of generator engine
- short-circuit current
- nuisance trip
Should such trip occur then the remaining preferential trips will operate simultaneously.
- manual tripping – the bus tie panel carries emergency stop contacts and preferential trips.
To trip the specific consumers, their circuit breakers are fitted with undervoltage (UV) trips. The supply to these UV trips is interrupted by the preferential tripping relays.

Example of UVT trip device
The identifications labels of the consumers configured for preferential tripping are coloured yellow with either PT1, PT2 or PT3 engraved into them.
Preferential tripping stages are accompanied by alarms into the alarm and monitoring system.
The vessel’s automatic control system will automatically restart the required machinery to restore power to the vessel, but to fulfil this requirement, at least one diesel generator must be left in the automatic standby mode. The essential machinery is started automatically according to the example sequence shown below.

Example of sequential restart list
The sequence is started when power is restored to the 440V main switchboard. The restart sequence is usually left enabled, however, the operator may disable the sequence, and if the sequence is disabled, an ‘auto start sequence disabled’ alarm is raised. The sequence is automatically halted in the case of another blackout.
When normal power is restored after a blackout, all essential service machinery in service before the blackout will be started automatically when the main switchboard has regained power. Motors that were selected for duty before the blackout will be automatically returned to duty when power is restored. Similarly, motors selected for standby will automatically return to standby. If the machinery designated for duty does not restore normal system conditions, such as pressure, within a preset time, the standby motor will cut in automatically. If power is only restored to the emergency switchboard, motors whose supply is from the emergency switchboard will start irrespective of any previous selection. In the event of a blackout all transformers in the HVS will switch off. After the first main generator is connected to the HV busbar the transformer outlets will automatically switch in sequentially in two steps, depending upon the part of the switchboard concerned.
If you have any questions regarding above, please feel free to use our existing forum Seafarer’s World and will try to answer to all your queries.
If you like my posts, please don’t forget to press Like and Share. You can also Subscribe to this blog and you will be informed every time when a new article is published. Also you can buy me a coffee by donating to this website, so I will have the fuel I need to keep producing great content! Thank you!
Partajează asta:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Please feel free to leave a reply! Cancel reply
Discover more from chief engineer's log.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Project Management – Dry Docking and Repairs
- Ship Services
- Marine CAD Services
- Marine IT Services
- Academic services
- MEO Class 1
- MEO Class 2
- MEO Class 4
- ASM / Masters
- Class IV Level
- Academic Papers
- Year/Month Sets
- Shirts & Trousers
- Deck Officers
- Engineer Officers
- Coveralls / Boiler Suits
- Marine Uniform Shirts & Trousers
- Epaulettes for Marine Deck Officers
- Epaulettes for Marine Engineer Officers
- Marine Belts | Peak cap | Accessories
- Marine Accessories
- Marine Engineering – General
- Marine Engineering – Motor
- Marine Electro Technology
- Ship Safety & Naval Architecture
- MMD Procedures
- Merchant Navy Courses
Preferential tripping in a marine electrical distribution system
- 21 May 2016
Preferential tripping in a marine electrical distribution system are designed to disconnect non-essential circuits (e.g. breakers controlling air conditioning, galley power, blowers, refrigeration etc.) in the event of partial overload or partial failure of the supply, with the aim of preventing operation of the main breaker trip and loss of power on essential services.
- A method for operating all the overload type trips from one load current carrying coil uses two instantaneous trip levers.
- The top lever is arranged as an instantaneous short circuit trip and opens the breaker directly through mechanical linkages.
- The bottom lever closes instantly at the lower overload current setting and by doing so, completes the circuit through two (or more) non essential circuit trips and a main breaker trip, all incorporating dashpot time delay.
- These relays will trip out non essentials at 5 and 10 second intervals based on their priority and finally, if the over load persists, the main breaker after 15 sees.
- Warning of overload is given by the alarm. Overload protection is provided on both poles.
Working of preferential trip
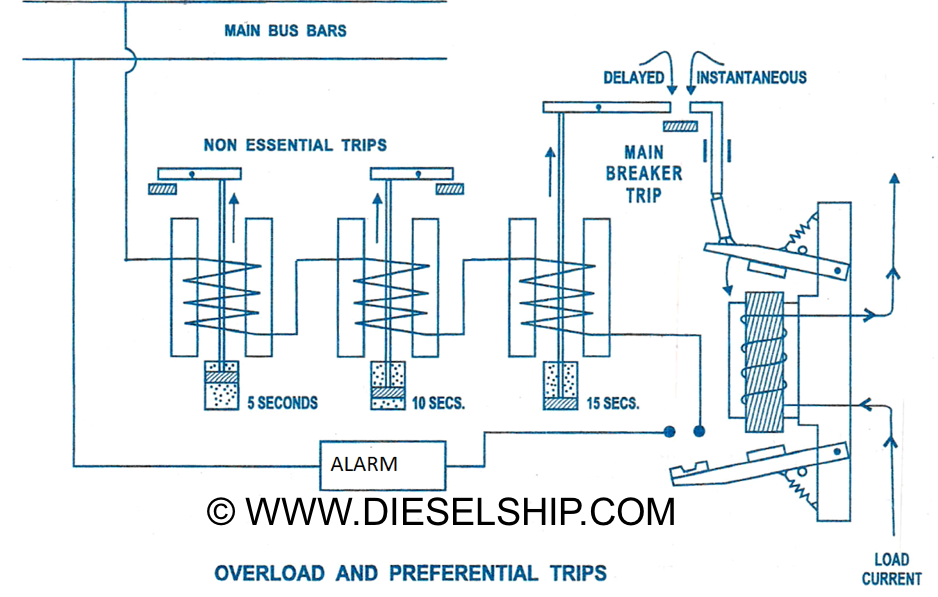
- The current passes through the electromagnetic coil and the linkages are kept from contacting using a spring arrangement. As soon as the current value increases the limit, the electromagnetic coil pulls the linkage up against the spring force and operates the instantaneous circuit and the alarm system. The lower linkage completes the circuit for the preferential trip circuit.
- The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit which pulls the piston in the dashpot arrangement. The movement of this piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same.
- The preferential trip operates at 5, 10 and 15 seconds and the load is removed accordingly. If the overload still persists, then an audible and visual alarm is sounded.
One thought on “ Preferential tripping in a marine electrical distribution system ”
sir, how to test the preferential trip ?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow us on Social Media
Username or email address *
Password *
Note: Entering wrong username in the login form will ban your IP address immediately. Entering wrong password multiple times will also ban your IP address temporarily.
Lost your password? Remember me
No account yet?

Preferential Trip
- Preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement on ship which is designed to disconnect the non essential circuit that is non essential load from the main bus bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply the non essential circuit all loads on ship are air conditioning, exhaust and ventilation fans, and galley equipments which can be disconnected mementarily and can be connected again after fault finding.
- The main advantage of preferential trip is that it helps in preventing the operation of main circuit breaker trip and loss of power on essential services and prevents blackout and overloading of generator.
No comments
Adertisement, buy at amazon, maritime news, contact form, blog archive.
- RECREATIONAL ITEMS
- MEO Class 4 preparation Notes by Nithin
- IMPORTANT REFERENCE BOOKS FOR GME (GRADUATE MARINE...
- ELECTRICAL ORAL NOTES PREPARED BY SAMUDRA INSTITUTE
- Complete List Of courses for Indian seafarers , an...
- Function : 6 - MEO Class 4 Orals : MEP or MROL [Maintenance and Repairs at Operational Level]
- Function : 4b - MEO Class 4 Orals : MOTOR or MEOL[Marine Engineering at Operational Level]
- Function : 3 - MEO Class 4 Orals : SAFETY or COSCOPOOL
- Function : 5 - MEO Class 4 Orals: Electrical or( EECEOL)
- MEK (Motor) - written
- Marine Electro Technology - written
- MEP - written
- NAVAL ARCH NUMERICAL.
- Ship Construction and Stability (Naval Arch) -written
- Ship Safety and Environmental Protection - written
- MEK (General) - written
- MEO Class 4 Orals questions asked mostly by surveyors in all MMD orals.
Copyright (c) 2020 marineengineersknowledge All Right Reseved

WHAT IS PREFERENTIAL TRIP AND REVERSE POWER TRIP ?
Preferential trip:.
Preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement on ship which is designed to disconnect the non-essential circuit i.e. non-essential load from the main bus bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply The non-essential circuits or loads on ships are air conditioning, exhaust and ventilation fans,and galley equipment’s which can be disconnected momentarily and can be connected again after fault finding. The main advantage of preferential trip is that it helps in preventing the operation of main circuit breaker trip and loss of power on essential services and thus prevents blackout and overloading of generator.
Reverse power trip:
There is not much difference between an alternator and electric motors from the engineer’s perspective. They are both based on similar principles. So just imagine what would happen if an alternator suddenly would act as a motor. This is only possible in systems where two or more generators are running in parallel. Hence this type of protection system is used only if there is more than one alternator on board a ship. The system is designed in such a way that it will release the breaker and prevent motoring of alternator if a reversal of power occurs. This protection device is also used to prevent damage to the prime mover, which might be stopped due to some fault. Though it is extremely difficult to detect reverse current with an alternating current system, reverse power can be detected and protection can be provided by reverse power relay
Sanjeev Kumar
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts
Gimlet tool : definition, uses, image, drawing, meaning, functions, parts, constrained motion – definition, types, examples, images, temperature class, what is process planning | process planning steps, types, advantages, marine diesel engine shipping company interview questions, how ship engine work , pinch point in exhaust gas boiler, why discharge valve closed during starting of centrifugal pump .
Marine Engineering Study Materials
Information for marine engineers, browsed by tag: preferential trip.
MEO Orals on Marine Electro Technology Function 5- Part 2
November 2, 2015 Jaz Comments 0 Comment
What is essential load .
- Essential services are those required for the safety of personal and for the safe navigation and propulsion of the ship.
- They include certain supplies to navigation aids, machinery spaces, control stations and steering gear.
What is non-essential load ?
- It is a load that has no effects on the safe navigation and main propulsion unit when they are cut off.
- They are a ir conditioning system, some blower fan except E/R blowers, galley power, r efrigerated cargo plant, d eck equipment, purifier, air compressor, cabin power source except lighting
What is dash pot, where fitted ?
- It is a mechanical device which makes time lag of trip with different viscosity of oil.
- It is fitted in overload trip, p referential trip, u nder voltage release / trip
What is dash pot ?
- Dashpots are fitted for overload trip to get time delay action, so that breaker will not be opened, due to momentary current surge
- When load current is in excess, it attracts plunger of the solenoid
- Plunger or piston moves up against the displacement of viscose oil or silicone fluid, through a small hole on the piston
- Time lag depends upon hole size, and viscosity of oil
- Load current setting for trip is about 25% above maximum, but should not exceed 50%
What is preferential trip ?
- It is a generator protection device which is designed to disconnect nonessential load from the main switchboard in the event of generator over load or partial failure of the supply.
- Operate after a fixed time delay, causing non-essential loads to be shed
- Usual setting for overload trip is 150% load (50% overload)
- When generator load reaches 110%, preferential Trip comes into operation as follows
First tripping at 5 sec
- Shut down non-essential loads (air-condition, entertainment, accommodation fans, cargo hold fans, amplifiers, etc.) to reduce the generator load
Second tripping at 10 sec
- Shut down essential loads (service required for running the ship properly, leaving the loads of top priority services to maintain propulsion and navigation) if generator load is still high
Third tripping at 15 sec
- Shut down the main generator as last action, if the load is still too high, it may be due to short circuit or insulation breaking.
What is the purpose of reverse power relay ?
- If prime mover failure occurred, the generator would act as a motor; the reverse power relay detects this fault and acts to trip the generator circuit breaker.
What is fuse ?
- Fuse is a protecting device in the circuit against damage from excessive current.
- It is fitted in a circuit to protect the circuit from short circuit and over load.
- Once a fuse is blown, it must be replaced.
Difference between Circuit Breaker and Fuse ?
Circuit breaker
- Has switching actions to close the circuit or to open the circuit, and has a trip circuit if load current exceeds the set value
- After tripping, circuit breaker can be reused without replacing any part
- Have only breaking function, and fitted in the circuit to protect the circuit from damaging effect of high current flow
- It breaks the circuit by melting the fuse metal itself
- After breaking, the blown fuse must be renewed
What is an intrinsically safe circuit or equipment ?
- An electrical circuit or part of a circuit is intrinsically safe, if any spark or thermal effect produced normally (e.g. by breaking or closing the circuit) or accidentally (e.g. by short circuit or earth fault), is incapable of igniting a prescribed gas mixture, under prescribed test condition.
- An equipment, which cannot released sufficient electrical or thermal energy, under any condition to ignite a particular flammable vapour in its vicinity.
What is primary cell ?
- It is a chemical cell in which it is possible to transform chemical energy into electrical energy.
- It cannot be recharged.
- The internal resistance of a primary cell is usually high
- Capacity of cell low
- Voltage per cell is also low
- Simple cell consists of copper plate (positive plate) and zinc plate ( negative electrode) and dilute H2 SO4 acid.
What is secondary cell ?
- It is a chemical cell (accumulator) which store up electric energy converting chemical substance into another form while charging.
- The stored electric charge in chemical form transforms back electrical energy.
- It has two types [lead acid and alkaline (Nickel Cadmium battery) type].
- It has low internal resistance
- Capacity and voltage per cell is high.
Oral Guide by – MIN ZAR TAR
- MEO Class 4
- _Epareeksha MCQ
- Machineries
- _Main Engine
- _Aux Engine (D/G)
- _Air Compressor
- _Freshwater Generator
- _Hydrophore
- _Refrigeration
- Naval Arch.
- Electricity
Preferential Trips Generators
Post a comment.
>> Your Comments are always appreciated... >> Discussion is an exchange of knowledge It Make the Mariner Perfect.... Please Discuss below...
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. Learn more
Contact Form
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A Guide to Ship's Electro-Technology

Related Papers
Prabir Datta
Eberechukwu Okoagha
CALIFA7SEAS MARITIME ACADEMIA HANDBOOK - PART 7: QUALIFICATION AND COMPETENCE
Engr. Khairulmuzammil YUZRI
konstantinos triantafillou
Miran Stefan
Ahmed Ghowel
Marine Electrical Knowledge
Chetna Goyal
HANNAH LEESE
win htun aung
Zaheer Are-Qkim
RELATED PAPERS
Debby Debby
Abdullah al Mamun
Christian Villa
Raphael Onyiaorah
Nguyen Van Phu
SYED MUDASSIR NAZAR
Daniel Charles
Federico Sanchez
ประดิษฐ์ โคตวงษ์
Evenso Ndlovu
Minhlongevn BD
Charles Conconi
Francisco Almonacid
nino slosar
Vinit Kant Majumdar
bagus istiyawan
Salman Farizy
Debebe Tsedeke
Sudipta Chatterjee
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Marine generator protection in reverse power & under voltage situations
- Categories : Marine machinery, engines & controls
- Tags : Marine engineering
Introduction
In the previous article we learnt about the importance of alternator on a ship and a method for alternator protection - Over current protection and about preferential trips . In this article we will learn about two more methods for protecting alternators on ship - reverse power protection system and under voltage protection.
Reverse Power Protection
There is not much difference between an alternator and electric motors from the engineer’s perspective. They are both based on similar principles. So just imagine what would happen if an alternator suddenly would act as a motor. This is only possible in systems where two or more generators are running in parallel .
Hence this type of protection system is used only if there is more than one alternator on board a ship. The system is designed in such a way that it will release the breaker and prevent motoring of alternator if a reversal of power occurs. This protection device is also used to prevent damage to the prime mover, which might be stopped due to some fault. Though it is extremely difficult to detect reverse current with an alternating current system, reverse power can be detected and protection can be provided by reverse power relay.
Construction and Working
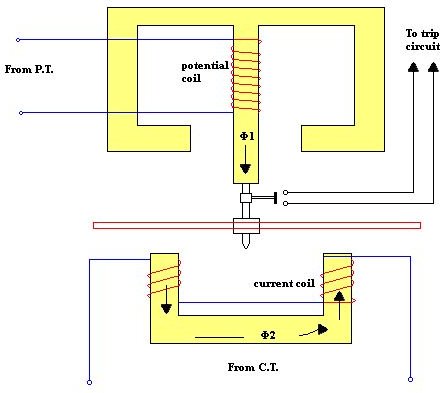
The system consists of a lightweight non magnetic aluminium disc, which is mounted on a spindle having low friction bearings. This disc is placed between two electromagnets made up of soft laminated iron core. The upper electromagnet contains a voltage coil which is connected through a transformer between one phase and an artificial neutral of alternator output. The lower electromagnet also contains a current coil which is supplied from the same phase with the help of a transformer.
The voltage coil is particularly designed with a high inductance so that it can lag current in the coil by an angle approaching 90 degrees. Due to this lag, the magnetic field produced by the current also lags the magnetic field in lower electromagnet. When both these field passes through the aluminium disc, production of eddy currents take place, which results in a torque that tries to rotate the disc.
Under normal power flow, the trip contacts on the disc spindle are open and the disc bears against a stop.When reverse power occurs , the disc rotates in other direction and moves away from the stop and moves towards the trip relay. A time delay of 5 seconds is also provided so as to prevent tripping during synchronizing process. The general reverse power settings are 2 to 6% for turbine power movers and 8 to 15% for diesel engines .
Under Voltage Protection
This method is used to prevent closure of the breaker by mistake, or the generator that is coming on load during parallel operation. It also provides protection against loss of voltage while machinery is connected to the switchboard .
In this system tripping is generally delayed for discrimination purposes. This is done so that the voltage drop is caused by fault and time is allowed for the appropriate fuse or breaker to operate and the voltage to be recovered without the loss of power supply
Image References
Marine electrical equipment and practice - H.D Mc George

Skip to content
- Board index The forum area of www.dieselduck.net The Workshop
Preferential Trip testing
Post by mann84 » Thu Jul 06, 2017 8:10 pm
Re: Preferential Trip testing
Post by JollyJack » Fri Jul 07, 2017 5:57 am
Post by Big Pete » Fri Jul 07, 2017 3:32 pm
Return to “The Workshop”
- The forum area of www.dieselduck.net
- ↳ Crew Mess
- ↳ The Workshop
- ↳ Training Room
- ↳ Events and Anouncements
- ↳ F.W.E
- ↳ Trading Post
- ↳ Website Area
- Marine Engineering Job Board and forum at www.dieselduck.net
- ↳ General Job topics
- ↳ Project Tango Charlie
- ↳ Available Positions
- ↳ Available Marine Engineers
- ↳ Available Marine Engineers looking for shore base work
- ↳ Available Marine Engineering Cadets / Apprentices, and experienced ER professionals
- Board index
- All times are UTC
Powered by phpBB ® Forum Software © phpBB Limited
Privacy | Terms

Understanding Power Management System: How To Reduce Power Consumption On Ships
Power conservation and management is an integral part of operations on board ships. Nowadays, ship engineers are specifically advised to inculcate best power saving practices while carrying out on various on board operations.
Power management on ships comprises of two main aspects:
a. Automatic Power Management Systems: Using automation to conserve power.
b. Using best practices and management guidelines to reduce power consumption.
Most modern day ships today are built with provisions for periodically unattended machinery spaces (PUMS). On such vessels, automatic power management system (PMS) plays a role, which is of utmost vitality. Not only does the PMS does away with manual synchronisation of generators, it efficiently regulates the number of generators on the busbar according to the changing load.
Some of the major functions performed by the PMS are as follows:
- Cutting in and out of the generators according to increase and decrease of load.
- Gradually loading and unloading of generator alternator sets, so as to minimise thermal and frictional stresses.
- Performing load sharing operations among the generators symmetrically or asymmetrically (depending on auto/manually set parameters).
Diesel generators are the primary components of the PMS. All generators have a maker’s specific minimum, maximum load criteria, and optimum load criteria. When the generators are synced with the ship’s PMS, engineers have the option of changing the minimum and maximum point beyond which, the generator cannot be loaded. This is to prevent various stresses on the physical components of the generator.
The loading and unloading of power from the alternator of the generator is driven by time lag functions, which often means, that a sudden spike in the load cannot be compensated by the PMS. A hardwired preferential trip, then, becomes, an essential requirement of the system in order to prevent sudden blackout.

Some ships are also fitted with a shaft motor, which not only compensates for a sudden drop in load, but also, minimises shaft torque on engines with a long propulsion shaft. Another advancement in technology has been in the form of a combined Shaft Motor/Generator set which is regulated by the PMS.
When generator sets are run in parallel, including, shaft generators , diesel generators and/or steam driven turbine generator, the PMS almost completely regulates the load on each component. Generally, in case of generators with equal load capacity, the load on the bus bar is distributed symmetrically on the alternators. However, different kinds of power generating machines, having different maximum an optimum load, the PMS distributes asymmetrically.
For efficient fuel consumption, it is always desirable to run the minimum number of generators, each at a load that is optimum. For instance, one generator running at 30% load may be more fuel efficient than 2 running at 15% and, conversely, one generator running at 70% may consume more fuel than 2 running at 35% load each. Thus, performance evaluation of generators according to their maximum and optimum rated capacity must be carried out regularly.
At the start of each voyage, marine engineers must discuss the power management plan and consider various factors like, number of reefers onboard, use of stabilisers during the voyage, maintenance to be carried out on any generator during the voyage to determine which and how many generators to run. An unexpected breakdown in the generators may require cutting down on the power consumption. Let’s take a look at a few factors which would help in smart reduction of consumption of power.
1. Reefers – Container ships, also, designed to carry reefers , will, of course consume a higher power with the increase in the number of live reefers onboard. Stowage plans must be checked so that reefers requiring ventilation would be carried on open decks. Where placed in cargo holds, efficient usage of reefer cooling water system is a much more economic way than using heavy inlet and exhaust fans for cargo hold ventilation. Thus, it is imperative the fresh water cooling system for reefers, which includes fresh water and sea water pumps, expansion tank and pipelines are kept in good working condition.
2. Ballast pumps – Most ballast pumps are heavy duty pumps which consume a lot of power. Ballast plans should be formulated with the aim of using ballast pumps only when required. Filling of tanks, where practical, must be carried out by gravity. Similarly, use of ejectors only while final stripping of tanks and not continuously while deballasting , reduces usage of pumps and eventually power.
3. Fuel Transfer pumps- Usage of service steam effectively to heat the fuel in storage tanks is an important power reduction factor. Fuel to be transferred must be kept at the temperature mentioned in the fuel specification document. Low temperatures of fuel result in frequent tripping of the pumps, not to mention, prolonged running of the pumps to transfer the same amount of fuel.
Related Read:
- 10 Practical Tips To Handle Engine Room Pumps
- 7 Common Problems Found in Pumps On board Ships
4. Air compressors- Any air leaks in the start air or service and working air must be repaired as soon as detected to prevent continuous running of compressors and to prevent frequent loading/unloading of compressors. Running hours of the compressors must be looked at closely and planned maintenance on the compressors must be carried out according to maker’s specification.
5. Fresh water- Most ships today use hydrophore tanks to pump fresh water for domestic and other purposes. These tanks must be topped up frequently with air, so as to minimise frequent running of hydrophore pumps to achieve the set pressure in the tank.
6. Central Cooling water system- Care must be taken when establishing the number of sea water, high temperature and low temperature pumps which are running. Sometimes, additional pumps may start resulting in higher power consumption.
7. Engine room ventilation- Ventilation fans are also large consumers. Engine room pressure and temperature must be carefully evaluated so as to run only the required number of fans. Where fan motors are dual speed or of a variable frequency type, selection of lower speeds, where practical, go a long way in reducing power consumption.
8. Lights – A simple, yet largely unpractised factor is switching off lights which are not in use. Cargo hold lights, steering gear room lights, deck lights should be switched on only when in use. This practice will go a long way in curtailing power consumption.
The above clearly shows how important planning a voyage is in order to minimise consumption of power. Considering the number of ship operations carried out on board ships, close coordination among deck and engine departments is absolutely essential, perhaps more important than the PMS itself.
Over to you..
What according to you are the most important points for an efficient power management on board ships.
Let’s know in the comments below.
Image credits: © Carabay – Fotolia.com
You may also like to read:
Important Points To Comply With Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan
Disclaimer : The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Related Articles
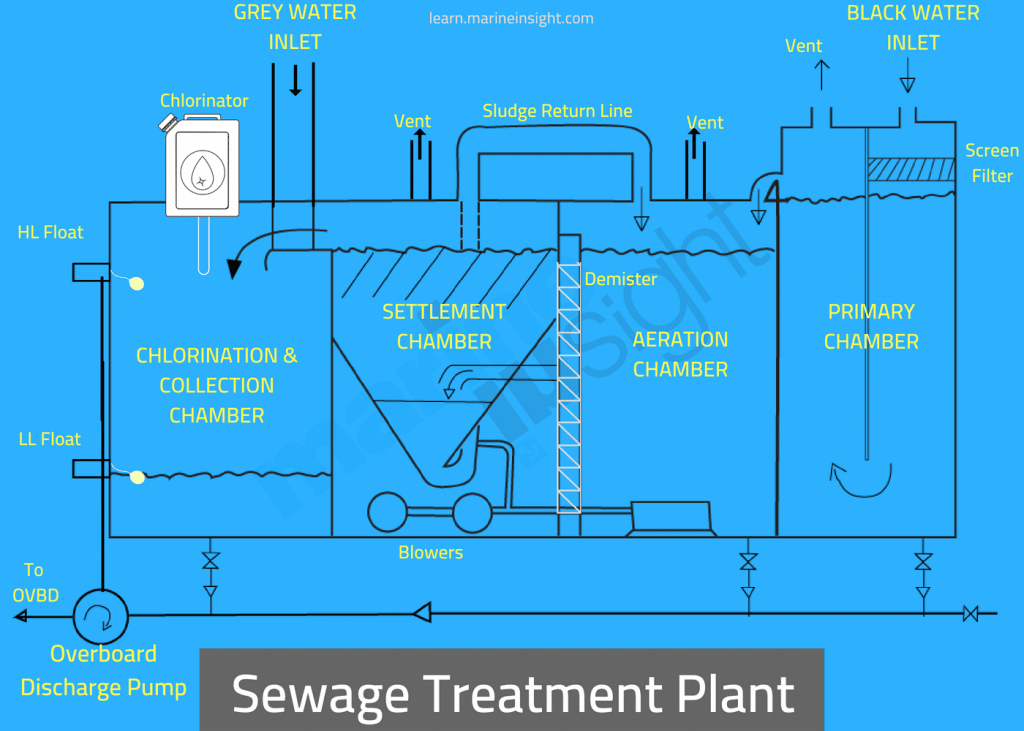
Sewage Treatment Plant on Ships Explained
20 Important Tips to Maintain Nuts and Bolts of 2 Stroke Marine Engine

Different Types of Mechanical Measuring Tools and Gauges Used on Ships
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction

About Author
Vibhor Kashyap is a marine engineer. He is presently sailing as third engineer with A.P.Moller -Maersk.
Read More Articles By This Author >
Daily Maritime News, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get Daily Newsletters
Join over 60k+ people who read our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
BE THE FIRST TO COMMENT
I have a objection at one point, we can simply not switch off the lights of cargo holds or steering gear room or simply we can say any area of engine room, lights from accommodation can be switched off whenever those are not required or else lights doesn’t make a much difference at all.
good marine insight, nevertheless let me share some few points here, there some vessels that as well has the sea water hydrophore systems they should as well be managed, they should be used when very necessary. as well putting of the cabin light is a good suggestion, but dont you think it can either make the room or cabin either more hotter or colder, thereby after the crew onboard, considering the fact that every before the vessel was commissioned to sail, each vessel cabin had a cooling load estimation calculated and determined as well. so that even the light point functions in a two way traffic, it helps to light up the cabin and as well helps to balance the cooling load estimation.
please help me with more light in marine because i am a engine cadet in a ship.
hi all nice to see your discussions i am doing my ph.d in electrical i am currently working in war ship building industry ,can u someone tell me how to choose research topic in electrical war ships
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to Marine Insight Daily Newsletter
" * " indicates required fields
Marine Engineering
Marine Engine Air Compressor Marine Boiler Oily Water Separator Marine Electrical Ship Generator Ship Stabilizer
Nautical Science
Mooring Bridge Watchkeeping Ship Manoeuvring Nautical Charts Anchoring Nautical Equipment Shipboard Guidelines
Explore
Free Maritime eBooks Premium Maritime eBooks Marine Safety Financial Planning Marine Careers Maritime Law Ship Dry Dock
Shipping News Maritime Reports Videos Maritime Piracy Offshore Safety Of Life At Sea (SOLAS) MARPOL

WAIT! Did You Download 13 FREE Maritime eBooks?
Sign-up and download instantly!
We respect your privacy and take protecting it very seriously. No spam!
WAIT! Did You Download 12 FREE Maritime eBooks?
- Get custom product tools and services
- Access training
- Manage support cases
- Create and manage your orders (authorised partners only)
Welcome to the Schneider Electric Website
Search FAQs
What is the procedure for primary current injection testing procedure for mccb with tmd trip unit, released for: schneider electric india, attachment(s).
Articles that might be helpful
Discuss this topic with experts
Start here!
Find answers now. Search for a solution on your own, or connect with one of our experts.
Contact Support
Reach out to our customer care team to receive more information, technical support, assistance with complaints and more.
Where to buy?
Easily find the nearest Schneider Electric distributor in your location.
Search topic-related frequently asked questions to find answers you need.
Contact Sales
Start your sales enquiry online and an expert will connect with you.

- REGULATIONS
- _ELECTRICAL
- _ELECTRONICS
Marine alternator oral questions and answers |ETO| Marine Electrical

What will happen if we overexcite the alternator? OR If we overexcite what will happen to the power factor?
What is the effect in pf of the bus bar when overexcitation, two generators are running parallel with different kw (200,800kw) with unequal kw sharing what is your action., what causes the generator under a voltage problem, how to check the air gap and purpose of the air gap, what is the result of an uneven air gap between rotor and stator of the generator, why there are two tie breakers in the circuit diagram of emergency gen auto start.
- One tie-breaker is in the MSB Where we can manually isolate the ESB if we want to do any maintenance or repair work.
- And the other one is interlocked with the main breaker of EM. Gen
- The tie-breaker is an ESB it will not allow the power from ESB to MSB
- It will give the power from only one direction from MSB to ESB
- It will not allow the power from ESB to MSB
- If the main and emergency generator is running this breaker will not switch on
- If it is in MSB it divides MSB into two parts for maintenance purpose or any fire hazard purpose.
What is the role of a Voltage sensing relay in a generator panel?
Why alternator is connected in star, what will happen if the generator voltage is not the same while paralleling, what will happen if air gap reduces.
- Air gap reduced means pedestal bearing is damaged.
- For alternator, the rotor will touch the stator and damage it.
- Alternator characteristics and efficiency will be reduced drastically.
- Motor same thing bearing is damage or shaft is bend. The consequence will be the same.
Why is Reverse Power Relay required?
- Prevent the motor effect
- Prevent the mechanical failure of the prime mover.
- Prevent total power failure.
When does reverse power flow?
- Faulty Governor of the prime mover.
- Loss of excitation in the alternator.
- Faulty synchroscope.
What is sequential starting?
What are the reason for the loss of residual magnetism in the generator, what happens if we increase the excitation of one alternator, when two alternators are in parallel condition, can we use a 50hz supply for a 60hz system and if we use it then what are the effects on voltage, torque and speed and current on the machinery, what is the importance of power factor in paralleling two generators, if we increase the excitation of one generator, will the impedance of both generators be equal or different, is there any time delay for under-voltage, over-voltage, under frequency and over frequency, in which all condition reverse power can happen.
- Mechanical failure
- Improper synchronising
- ACB not opening after the load shifted.
What is magnetic resistance?
Can we parallel emergency generator and main generator, consequences of difference in power factor during the parallel running of generators., what are the function of reactor coils and capacitors in static excitation, what is the form factor, what is the reason to fail auto start of emergency generator.
- Switch in manual mode
- Fuel valve is closed
- The battery is fully discharged
- Fuel is empty in the tank
- Auto circuit problem.
There is blackout for 10 hours; how you will prepare the ship (for cleaning) for maintenance of MSB?
- Carry out a risk assessment and follow the company procedures
- Inform to dry dock ship repair manager (SRM)
- Inform chief cook to prepare the food.
- General-purpose battery should be fully charged.
- Will make sure that emergency lights are working.
- Make an arrangement to switch off the unwanted load in dry dock.
- Portable torches should be fully charged and ready for use.
- Make sure shore connection is disconnected and lockout
- Make sure MSB is death condition and Earthing has to be done prior to work.
Why we don't parallel with the unknown generating station?
If two generators are running in parallel and kw is showing same but current is lower than the other what may be the problem and how to rectify, why generator rpm slightly drops instantaneously when a heavy load cuts in, what will happen if the load is not reduced after the preferential trip, why we use a short time delay in acb, why synchroscope pointer moves clockwise when incoming generator speed higher and vice versa, generator output voltage is ok at 50 % load but when you increase beyond 50 % then the voltage drops, what was the reason, two generators running one generator lube oil attached pump stuck what will happen which alarm come first directly trip or before any alarm came and what happened in other generator.
- Lub oil low-pressure alarm will come first
- L.O low-pressure trip activate
- So generator breaker trip
- When the load increases up to 80-85% of total capacity than a standby generator will come to load in case it fails then at 90-95% of total load capacity preferential trip will activate.
Why are generator and motor bearings insulated?
How did the surge resistor protect the diodes in the brushless generator, what will happen if any of the diodes get open in running condition, what will happen if diode gets short in running condition, generator started but no voltage producing.
- Voltmeter may be faulty-Replace it
- Residual magnetism may be lost-flash the alternator
- Diode may be a shorted-replace whole bank
- Surge suppressor resistor may be shorted-replace the whole bank
- AVR malfunctioning-change it
- Circuit may open-make the connection according to drawings.
- Very low insulation resistance to earth (ground), on exciter stator or main stator.
- Winding fault. Open circuit or short circuit on any winding in the machine.
How to restore residual magnetism?
- Do the flashing
- Please follow the maker procedure
- Stop the generator.
- Then bring the 12v DC battery.
- Remove terminal F1 & F2 (J and K) from AVR (if you not disconnect may damage the AVR)
- Check the resistance between F1 and F2 it should show some value (Please refer the maker manual). If it is zero means field winding shorted. And have to check the resistance with respect to the ground also.
- Touch the terminals of batteries with F1 & F2 terminals. With same
- Polarity (positive to positive and negative to negative), for a very short time (5-6 seconds).
What will happen if the generator is immersed in seawater?
After starting generator, it is producing less voltage than rated voltage.
- Any of the diodes may be open.
- AVR may be malfunctioning.
- Excitation trimmer is disturbed.
- Somebody touched accidentally.
- With vibration, it disturbed.
After starting generator, it produces more voltage than rated Voltage
The generator started but the breaker is not closing (or) individual generator is not coming on load..
- The generator may not be developing voltage.
- UV coil may be malfunctioning.
- Control supply may not be available.
- Charging motor may be malfunctioning.
- Charging spring defective.
- There may be mechanical damage in ACB.
- Racking handle is still inside/inserted.
- During dry clock, shore supply is available.
- Any of the interlocks are active.
- You were trying to close the wrong breaker.
Generator started but not paralleling
- Paralleling condition is not met.
- Synchronous relay malfunctioning.
During parallel the operation, one generator is showing less voltage, what the reason is and what action Will you take?
- AVR trimmer may be disturbed
- Rectifier diode may be open circuit
- AVR may be a malfunction
- Faulty voltmeter.
Difference between shunt coil and trip coil?
Governor motor control for auxiliary engine.

About The Author: B MANIKANDAN ETO
You may like these posts, post a comment.
1xbet korean sports betting,online casino,online poker games 1xbet korean sports betting,online 메리트카지노총판 casino,online poker games,online poker games,online 1xbet poker games,online poker games,online poker หารายได้เสริม games,online poker games,online poker games,online poker games
Thanks a lot sir. It is very helpful for the preparation..
Nandri anna
This is very interesting and helpful, thanks awfully. Could you please treat same on DP 2 system?
Thank you sir. By the way, the video you uploaded is not playing.

Totoodo the Apple iPhone service center in Bangalore, Chennai and Hyderabad are the leading mobile Repair services. dell service center bangalore
We love to hear your comments on this article, so that we may better serve you in the future.
Join Our Group
Social Plugin
Total pageviews, popular posts.

Frequently asked questions and answers-steering gear systems of ships

Isolated and Earthed neutral systems on ships | Neutral Earthing Resistor

SOLAS Regulations | Chapter II-1 | Part D - Electrical installations

Fully explained-Marine batteries | How to order a battery on ship?

How will you check AVR? (AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE CONTROLLER)

ETO COC Syllabus | Preparation for ETO COC Oral examination

ETO COC NUMERICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS - SOLVED I

ETO COC NUMERICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS - SOLVED II

Short notes of MGPS | ETO ORAL
Featured post.
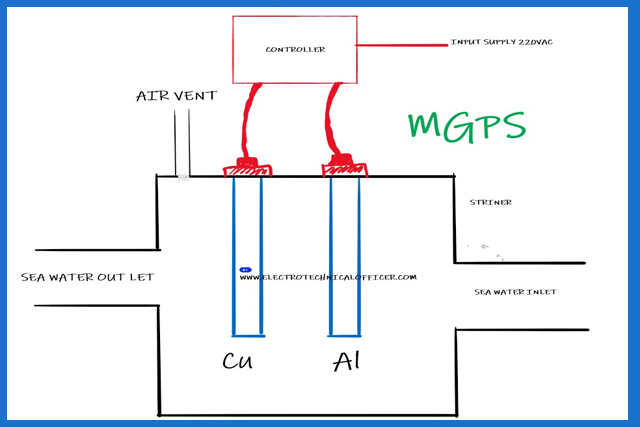
Contents MGPS – Marine Growth Prevention System The seawater system…
- AUXILIARY MACHINERY
- BIO FOULING
- CONTROL SYSTEMS
- NAVIGATIONAL SYSTEMS
- POWER ELECTRONICS
- SHORE POWER
- STEERING GEAR
- TRANSFORMER
Menu Footer Widget

MARINE ELECTRO TECHNICAL OFFICER

BEST TIPS TO AWE INSPIRING CAREER AS ETO

ELECTRICAL SAFETY TRAINING – LOTO (LOCKOUT/TAGOUT)

JOBS ASHORE FOR ETO AFTER QUITTING FROM MERCHANT NAVY

EGCS – DETAILED OVERVIEW
ULTIMATE BEARING GUIDE & FACTS FOR ETO

SUEZ CANAL TRANSIT CHECKS ETO MUST KNOW

VFD (VARIABLE FREQUENCY DRIVE) COMPLETE GUIDE

LIST OF SOLAS REGULATION EVERY ETO MUST KNOW

MARINE ALTERNATOR MAINTENANCE GUIDE

SHIP ETO & ETR MAJOR DIFFERENCE?

PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS COMPLETE GUIDE

OVERVIEW OF NAVIGATION EQUIPMENTS USED IN SHIP
ME ENGINE ELECTRONICS FULL GUIDE

ME ENGINE MPC (MULTI-PURPOSE CONTROLLER)

QnA: MSBD (MAIN SWITCHBOARD)
Q. What is the IP(Ingress Protection) degree provided for MSBD ?
Q. What are the safeties protection provided by ACB?
A. In above list, Some are optional It may have or may not
- Adjustable Long Time Delay Trip -LTD (Normally 105 to 120% of Full Load Current, Trip time from 20 to 120 seconds)
- Adjustable Short Time Delay Trip -STD (Normally 200 to 600% of Full Load Current, Trip time from 0.1 to 1 seconds)
- Adjustable Instantaneous Trip -INST (1000% of Full Load Current, Instant Trip)
- Adjustable Pre Trip Alarm -PTA
- Adjustable Ground Fault Trip -GFT
- Under Voltage Trip -UVT (set at 50% of rated voltage)
- Arc Contacts, Arc Runner, Arc Chutes
Q. What are the safeties provided for MSBD?
A. Following safeties are provided
- Overload protection
- Under frequency protection(58Hz trip,59Hz alarm)
- Over frequency(62Hz trip,61Hz alarm)
- Under Voltage protection(80% of rated voltage,120% of rated voltage)
- Over Voltage Protection
- Reverse Power protection
- Preferential trip protection.
- Continuos Insulation Monitoring is also provided.
- No liquid line over MSB
- Ebonite Handrail
- Approved insulation rubber and Gloves ( It should sustain 15KVA for at least 1 minutes)
- 0.6 meter clearance area all around MSB(For High Voltage its 1 meter)
- Danger, High Voltage, Precaution against electric shock, Burn Playcards
- Circuit diagram of MSB should be near MSB
- MSB is installed in less vibration area of ship
- 1 portable CO2 extinguisher near MSB
Q. How the reverse power is detected?
A. It is difficult to determine the direction of AC to make tripping of generator during motoring. For this purpose the reverse power relay utilizes technique of monitoring current lagging direction to voltage. During sourcing (Generating)the current will lag the voltage by some angle positive way. During motoring of generator this positive lagging to voltage will change to negative lagging to voltage. This change in phasor angle will cause the aluminium disc inside the relay to rotate in opposite direction causing to trip the ACB
Q. What are setting values for reverse power relay?
A. 15% of KW for 4 stroke engine, 25% for 2 stroke engine at synchronous speed. For steam turbine 3% of KW.
Q. What is preferential tripping?
A. When Generator load reaches 110% trip operates after a fixed time delay causing non-essential loads to be shed in order to avoid overload on generators. The tripping sequence is as follows:
First tripping at 5 sec: Shut down non-essential loads [air condition, entertainment, accommodation fans, cargo hold fans, amplifiers, etc.] to reduce the generator load. Second tripping at 10 sec: Shut down essential loads [services required for running the ship properly, leaving the loads of top priority services to maintain Propulsion and Navigation. if generator load is still high. Third tripping at 15 sec: Shut down the main generator as last action, if the load is still too high, it may be due to short circuit or insulation breaking.
Q. What is mechanism of Preferential tripping?
A. Now PLC or Embedded system based PMS(Power Management System). Earlier Dashpot & Timers was used.
Q. What are the methods of synchronization?
A. Synchroscope, Bright Lamp Method, Dark lamp method, Voltmeter method.
SYNCHROSCOPE METHOD: When the incoming generator frequency is same as bus bar frequency say 60Hz and indicator in synchroscope rotates slowly clockwise(about 5 to 7 seconds per revolution). The incoming generator breaker is closed when indicater indicates 12 o clock position in Synchroscope Usually at 11 o clock closing action is taken by personnel because of human response time.
DARK LAMP METHOD: Two lamps are connected to same phase of incoming generator and busbar. Flickering of lamps are monitored. Flickering must be slow and when both lamps are dark ACB is closed.
BRIGHT LAMP METHOD: Two lamps are connected to different phase of incoming generator and bus bar. In phase condition is shown when both lamps are equally bright.
VOLTMETER METHOD: Connect Analog voltmeter(except up to 500V on a 440V system). This procedure is done safely behind synchroscope terminals. Check circuit diagram of synchroscope before doing it. Adjust generator speed until voltmeter move very slowly from zero to maximum and close the breaker when the voltmeter indication passes through zero.
Q. What is Dead-Front Switchboard & Dead Switchboard?
A. Dead-Front switchboard is one with insulated switches and no exposed terminals on front.
Dead-SwitchBoard is one in which there is no supply available
Q. What is Sequential starting?
A. The Automatic starting of Essential machineries after power is restored from Blackout condition. Following is the general sequence starting of machineries.
Immediate starting machineries after power restored without any delay: 1)Steering gear 2)Fuel Oil Feed & Booster pump 3)Radio & Navigation Equipment 4)Engine Room & Accommodation Lighting 05 Secs after main power is restored: 1) Stern Tube Lube oil pump 2) Main LO Pump 10 Secs after main power is restored: 1) MCSW P/P 2) LT CW P/P 3) M/E JCW p/p 15 Secs after main power is restored: 1) Deck seal water p/p 2) Aux.Boiler & Comp.Boiler Feed p/p 20 Secs after main power is restored: 1) All E/R fans 2) Fire & GS Pump
LIKE POST? PLEASE SHARE
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Watchkeeping
- Maersk Bear
Select Page
The use of maritime prefferential tripping
Posted by Ryan Oneill | Aug 3, 2023 | Electrical , Engine Room , Latest Articles | 0 |

This content is restricted to site members. If you are an existing user, please log in. New users may register below.
About The Author
Ryan Oneill
Ryan O'Neill is a well-known maritime enthusiast and writer who has dedicated his life to studying and writing about ships and the maritime industry. With a deep passion for the sea and all things nautical, Ryan has spent years exploring the world's oceans and studying the history and culture of seafaring.
Related Posts

Understanding of the International Medical Guide for Ships
6 July 2024

Marine Powerplants
7 July 2024

Battery Systems Used Onboard Ships

Princess Cruise Lines “Magic Pipe”
Recent posts.

Our Authors
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
MEO CLASS 4 KOCHI MMD & CLASS 2 EXAM PREPARATIONS
Recently asked questions in kochi mmd and class 2 numerical solutions.
- FUNCTION 4B & 6
- CLASS 2 NAVAL
- CLASS 2 MET
- Class 4 Written
29 September 2018
What is preferential trips and how it works.

- The current passes through the electromagnetic coil and the linkages are kept from contacting using a spring arrangement. As soon as the current value increases the limit, the electromagnetic coil pulls the linkage up against the spring force and operates the instantaneous circuit and the alarm system. The lower linkage completes the circuit for the preferential trip circuit.
- The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit which pulls the piston in the dashpot arrangement. The movement of this piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same.
0 comments:
Post a comment.

COMMENTS
A preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement on the ship which is designed to disconnect the non-essential circuit i.e. non-essential load from the main bus bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply ... how to test the preferential trip and overload trip while generator running in parrellel. ananthan says ...
Preferential trip is a part of the ship's generator protection system. The tripping system is designed in such a way that it removes all non essential loads ...
The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit which pulls the piston in the dash pot arrangement. The movement of the piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same. The preferential trip operates at 5,10, & 15 seconds and the load is isolated accordingly.
Depending on the vessel electrical layout and design, there are different stages (two or three) of preferential tripping. For example: if the current on a running generator exceeds 100% of the generator rating for a period exceeding 5 seconds, the PMS will initiate the release of the 1st stage preferential tripping (PT1), thereby providing protection against the overcurrent which would ...
Overload trip is set at 150% current with 20 second time delay and preferential trip is set at 110% current with instantaneous operation. If the generator gets overloaded, then preferential trip gets activated and operate time delay, which will disconnect non essential services in specific order at specific interval according to priority.
There are two very important safety system on our Main Switchboard and these are the Preferrential trip and Revere Power Trip.here is the step by step guide ...
The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit which pulls the piston in the dashpot arrangement. The movement of this piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same. The preferential trip operates at 5, 10 and 15 seconds and the load is removed accordingly.
Preferential Trip. Preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement on ship which is designed to disconnect the non essential circuit that is non essential load from the main bus bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply the non essential circuit all loads on ship are air conditioning, exhaust and ventilation fans, and ...
Preferential trip: Preferential trip is a kind of electrical arrangement on ship which is designed to disconnect the non-essential circuit i.e. non-essential load from the main bus bar in case of partial failure or overload of the main supply The non-essential circuits or loads on ships are air conditioning, exhaust and ventilation fans,and ...
Preferential trip is a part of the ship's generator protection system. The tripping system is designed in such a way that it removes all non essential loads from the generator in case of overload or partial failure of supply, thus preventing main power loss on the bus-bar. In order to learn about the working of preferential trip, it is ...
Usual setting for overload trip is 150% load (50% overload) When generator load reaches 110%, preferential Trip comes into operation as follows. First tripping at 5 sec. Shut down non-essential loads (air-condition, entertainment, accommodation fans, cargo hold fans, amplifiers, etc.) to reduce the generator load. Second tripping at 10 sec.
0. Preferential trip on ship. Preferential tripping in ships is to avoid total black out in the ship. >Operate after a fixed time delay, causing non-essential loads to be shed. >Usual setting for overload trip is 150% load [50% overload]. >When generator load reaches 110%, Preferential Trip comes into operation as follows. First tripping at 5 ...
Reverse Power Trip. When two or more generators are running in parallel and if one of the units starts drawing power from the main bus bar, it can lead to reverse power flow. It can cause overloading of the other power supply unit and hence leads to the preferential trip or may lead to total power failure (Blackout). The faulty unit may ...
The preferential trip operates at 5, 10 and 15 seconds and the load is removed accordingly. If the overload still persists, then an audible and visual alarm is sounded. The preferential trip is one of those important electrical circuits, which help in removing the excessive load from the main bus bar, thus preventing situation like blackout ...
Introduction. In the previous article we learnt about the importance of alternator on a ship and a method for alternator protection - Over current protection and about preferential trips.In this article we will learn about two more methods for protecting alternators on ship - reverse power protection system and under voltage protection.
Re: Preferential Trip testing. by Big Pete » Fri Jul 07, 2017 3:32 pm. Used to be easy on Old Time ships but there is usually a much bigger reserve of power available from generators now. You might have to get an Electrician in with Current Injection Kit, to test the trip just like you do for testing main Breakers. It is always better to ask a ...
A hardwired preferential trip, then, becomes, an essential requirement of the system in order to prevent sudden blackout. Some ships are also fitted with a shaft motor, which not only compensates for a sudden drop in load, but also, minimises shaft torque on engines with a long propulsion shaft. Another advancement in technology has been in the ...
Single phase test results might not be the same as three phase testing together.. Note: TMD has its co-efficiency when test on ambient temperature different than 40 degree, and also when test is done on one pole For all the TMD curves, You may know that the catalogue tripping curves are given for an ambient temperature of 40°C in cold start ...
Action: perform the megger test. Cause 4: Loose connections on the control circuit. Action: Check the connections as per the manufacturer guide. ... (early days where 3 trips are given in preferential trip, 3rd one i.e. 15-second one will cause the main breaker to trip and it lead to a blackout. But in new ships, we don't have the third trip).
30 June 2016, 07:41 PM. There are a few things which will trip the prefs such as a reverse power trip on a generator, an overcurrent on a breaker or certain alarms or signals from the power management system. These can either by properly tested, e.g. by reverse powering the generator, simulated by current injection or simulated in other ways.
Adjustable Long Time Delay Trip -LTD (Normally 105 to 120% of Full Load Current, Trip time from 20 to 120 seconds) ... Preferential trip protection. Continuos Insulation Monitoring is also provided. No liquid line over MSB; Ebonite Handrail; Approved insulation rubber and Gloves ( It should sustain 15KVA for at least 1 minutes) ...
About The Author. Ryan O'Neill is a well-known maritime enthusiast and writer who has dedicated his life to studying and writing about ships and the maritime industry. With a deep passion for the sea and all things nautical, Ryan has spent years exploring the world's oceans and studying the history and culture of seafaring.
The current passes through the coil in the preferential trip circuit which pulls the piston in the dashpot arrangement. The movement of this piston is governed by the diameter of the orifice and the time delay made by the same. The preferential trip operates at 5, 10 and 15 seconds and the load is removed accordingly. If the overload still ...