We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked


Search Smartraveller
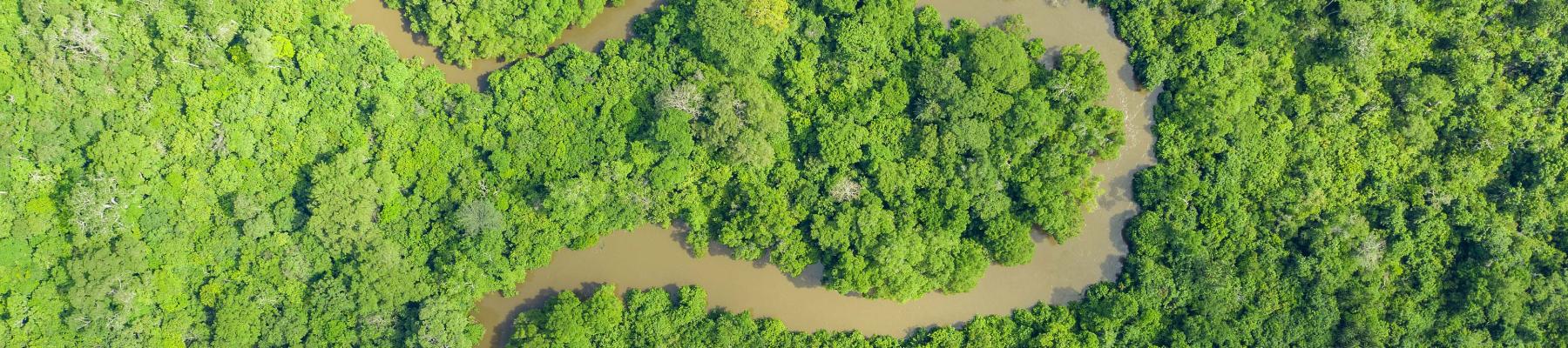

Democratic Republic of the Congo
Latest update.
Reconsider your need to travel to the Democratic Republic of the Congo overall due to the volatile security situation and the threat of terrorism and kidnapping.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
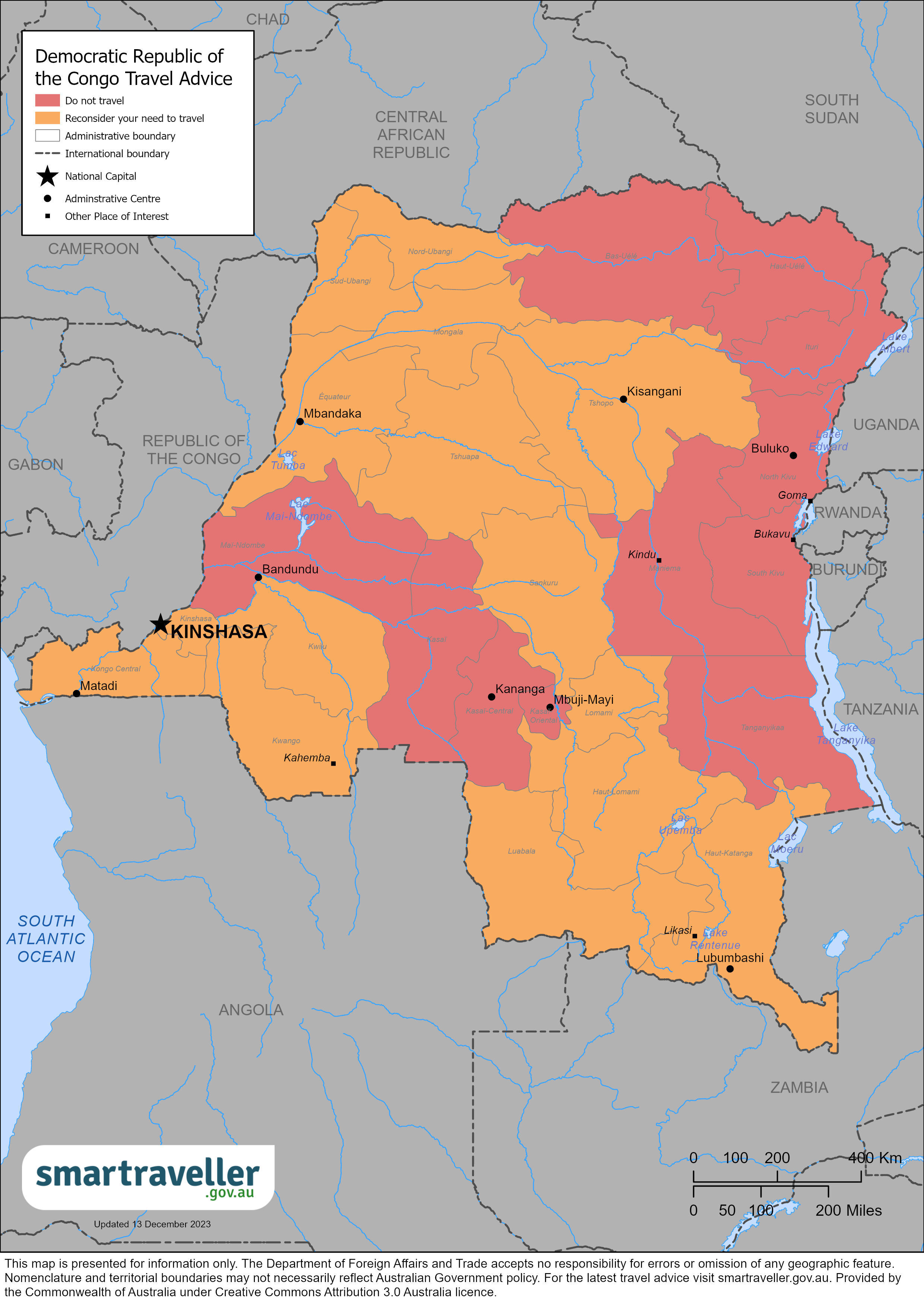
DRC map December 2023 (PDF 1023.33 KB)
Africa (PDF 1.68 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
There's no national emergency number in the DRC.
Advice levels
Reconsider your need to travel to the Democratic Republic of the Congo overall due to the volatile security situation and the threat of terrorism and kidnapping.
Do not travel to Kasai, Kasai Central, Kasai Oriental, Mai Ndombe, South Kivu, North Kivu, Ituri, Maniema, Tanganyika, Bas-Uélé and Haut-Uélé provinces.
Do not travel to:
- Kasai Central,
- Kasai Oriental,
- Mai Ndombe,
- South Kivu,
- North Kivu,
- Tanganyika,
- Bas-Uélé, and
- Haut-Uélé provinces
due to the significant threat of armed conflict and violence.
- Since 5 February, protests have been occurring outside some foreign embassies and UN offices in Kinshasa. Avoid areas where protests are occurring. Monitor the media for potential demonstrations or protests and follow the advice of local authorities. The US Embassy in Kinshasa issued a security alert on 11 February advising that protests throughout Kinshasa are likely to continue.
- Kidnappers often target foreigners. The risk is highest in the eastern and northeast regions. Express kidnappings in parts of Kinshasa have increased. If you're travelling to these areas, seek professional security advice. Be alert to possible threats.
- The security situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is volatile. Conflict between government forces and armed groups in the east is ongoing. If it's safe to do so, leave affected areas.
There's an ongoing threat of terrorist attacks in the DRC, particularly in eastern DRC. An attack is possible at any time. Always be alert to possible threats, especially in public places.
Intercommunal violence in Mai Ndombe province, particularly in the territory of Kwamouth, has escalated. Intercommunal violence may continue to increase and lead to further deaths and displacement.
- On 6 May 2021, the DRC Government declared a 'State of Siege' in the eastern provinces of Ituri and North Kivu. Military administrations have replaced civilian administrations in these provinces until further notice. The new military administrations have been granted extended security powers, and there is potential for increased armed conflict in the region during this time.
- Crime rates are very high, especially in Kinshasa and the country's east. Risks increase after dark. Ensure your accommodation is secure. Don't walk alone in Kinshasa, even during the day.
- The DRC has active volcanoes. If there's an eruption, avoid contact with ash. Seek medical help if you have breathing problems. In the rainy season, landslides and flooding can disrupt transport networks. Be prepared to change your travel plans.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Several outbreaks of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) have occurred in DRC. There is an ongoing risk of EVD transmission in the DRC. EVD is often fatal. Avoid contact with EVD patients as the disease is spread through bodily fluids.
- Ensure you've been vaccinated against yellow fever and polio before you travel. Carry proof of vaccination with you.
- HIV/AIDS is widespread. Take precautions if you're taking part in high-risk activities.
- Some insect-borne disease such as yellow fever and malaria are widespread. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof and use insect repellent.
- Foodborne, waterborne and other infectious diseases include cholera, typhoid, hepatitis and monkeypox. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food. Don't swim in fresh water.
Full travel advice: Health
- The death penalty applies to a number of offences.
- Always carry your passport and visa or immigration permit. It's illegal not to show them if officials ask.
- Be careful when taking photos. It's illegal to photograph presidential or official motorcades. It's also illegal to take photos near government buildings or other infrastructure, including airports.
- If you're walking or driving, stop for motorcades and flag ceremonies. Failing to stop is illegal.
- The DRC doesn't recognise dual nationality. If you're a dual national, make sure you enter and exit the country on the same passport.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You need to obtain a visa before you enter the DRC. You can't get one on arrival. Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest high commission/embassy or consulate of the DRC for the latest details.
- Carry your yellow fever vaccination certificate. You'll need it to enter the country.
- Military and police roadblocks are common. If you have them, always carry your government-issued identification, insurance card (carte rose), registration (carte grise) and driver's licence.
Don't use public transport. Bus and rail services are unsafe due to poor safety standards and crime.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- Australia doesn't have an embassy or consulate in the DRC. Our ability to provide consular assistance may be limited.
The Canadian Embassy in Kinshasa provides consular assistance to Australians in the DRC. It can issue Australian provisional travel documents . Its services are limited outside Kinshasa.
- For full consular help, contact the Australian Embassy in Zimbabwe .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy’s social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Civil unrest and political tension.
The security situation in DRC is volatile.
There are over 130 active armed groups in eastern DRC. Armed conflict has caused widespread civilian displacement and deaths. Conflict between local armed groups and government forces is ongoing. It's a more serious threat in eastern and northern provinces. This includes:
- Kasai, Kasai Central and Kasai Oriental provinces.
- South Kivu, North Kivu, Ituri, Maniema, Tanganyika, Bas-Uélé and Haut-Uélé provinces where fighting has displaced hundreds of thousands of people.
- Mai Ndombe province
On 6 May 2021, the DRC Government declared a 'State of Siege' in the eastern provinces of Ituri and North Kivu. Military administrations have replaced civilian administrations in these provinces until further notice. The military administrations have been granted extended security powers, and there is potential for increased armed conflict in the region during this time.
A large UN military presence and several aid organisations operate in the DRC. This includes the United Nations Organisation Stabilisation Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO). On 25 July 2022, large protests began in the cities of Beni, Betembo, Goma and Rutshuru targeting MONUSCO. MONUSCO sites have been looted and the demonstrations have resulted in deaths. Avoid crowds, demonstrations and sites associated with MONUSCO in eastern DRC.
Some local non-government organisations have suspended operations in North and South Kivu due to the security situation.
To protect yourself during periods of unrest:
- monitor local media for updates
- take into account the information provided by Congolese authorities and MONUSCO
- follow advice from local authorities
- avoid affected areas
- arrange effective personal safety measures
- keep adequate supplies of water, food, fuel, cash and medications
Keep your passport and other travel documents (e.g. visas, flights) up to date.
Regularly review your contingency plans in light of local developments. Be ready to leave the DRC at short notice if the situation worsens.
If, despite our advice, you decide to go to 'do not travel' areas, get professional security advice.
Demonstrations and protests
Since 5 February, civil unrest and political violence have been occurring outside some foreign embassies and UN offices in Kinshasa. Protesters have started fires and thrown rocks at foreign vehicles. Further protests are expected and may also spread to other parts of DRC. Foreigners may be randomly targeted.
Public protests and events that draw large groups can quickly turn violent.
To protect yourself from violence:
- avoid demonstrations and protests
- limit your movements
- monitor local media and other information sources for updates
- follow the advice of local authorities
Security incidents can occur in Kinshasa, including:
- demonstrations
- attacks on vehicles
Roads may be closed with little or no notice.
The only road to the N'Djili Airport in Kinshasa may be blocked. Flight schedules may be disrupted. Confirm flight schedules with your airline or travel provider.
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Kidnappers often target foreigners.
Kidnapping is most common in the eastern and north-eastern regions.
Areas with a high risk of kidnapping include:
- Virunga National Park in North Kivu
- Kasai, Kasai Central and Kasai Oriental provinces
- South Kivu, North Kivu, Ituri, Maniema, Tanganyika, Bas-Uélé and Haut-Uélé provinces
Express kidnappings
Express kidnappings targeting foreigners have increased. The threat is particularly high in the Limete area of Kinshasa.
These attacks usually occur in broad daylight and victims can be abducted for a few hours and stripped of their possessions or taken to an ATM to withdraw money.
These attacks are often perpetrated by small groups of individuals dressed in police uniforms.
To protect yourself from kidnapping:
- seek professional security advice
- be alert to possible threats
- change your routes and patterns of travel
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
There's a very high level of crime. Risks increase after dark.
Criminals may use roadblocks and pose as police or military personnel to rob travellers at night.
Security authorities may target travellers to ask for bribes or make random arrests, such as at roadblocks.
Violent crime has increased in the east because of the unstable security situation.
Crimes that commonly affect travellers, especially in Kinshasa, include:
- violent robbery
- vehicle thefts
To protect yourself from crime and express kidnappings :
- keep vehicle doors locked and windows up
- secure your accommodation against intruders
- avoid travelling after dark
- don't walk alone in Kinshasa
- avoid sensitive areas, such as military facilities
- don't permit soldiers or police officers to enter your vehicle, and avoid getting into vehicles with strangers, even if they identify themselves as police officers
- avoid using taxis. If you must take one, do not hail off the street, use a privately booked taxi
- be extra vigilant when withdrawing cash from ATMs, even in hotels.
Carry colour photocopies of your passport and identity documents. Hand these to officials, not the originals.
Cyber Security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Areas prone to terrorist attacks include:
- in the region of Beni-Butembo and Goma in North Kivu
- in the vicinity of Boga in Ituri
- the border with Uganda
Possible targets for terror attacks include:
- government buildings and sites associated with the DRC armed forces (FARDC)
- areas frequented by foreigners, such as hotels, clubs, restaurants and bars and markets
- airports, other transportation hubs and vehicle convoys
- schools and places of worship
To reduce your risks:
- take official warnings seriously and follow the instructions of local authorities
- consider the level of security at venues you are visiting
- be alert in crowded places and monitor the media
- pay close attention to your personal security
If there's a terrorist attack:
- leave the affected area immediately if it's safe to do so
- avoid the area afterwards in case of more attacks
Don't gather in groups after an attack. This also applies if you're evacuated from a building for security reasons, such as a bomb threat.
Natural disasters
The DRC experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- earthquakes
- volcanic eruptions
To protect yourself if a natural disaster occurs:
- keep your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- monitor local media and other sources
- keep in touch with family and friends
- contact your tour operator or airline to confirm bookings
Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
The DRC experiences earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Mount Nyiragongo, near Goma, is one of the world's most active volcanoes and last erupted in May 2021.
Exposure to volcanic ash, dust and toxic fumes is a major health risk.
Seek medical help if you have existing respiratory problems.
To protect yourself if there's a volcanic eruption:
- stay inside with the windows and doors shut
- place damp towels at doors and other draft sources
- protect your skin with long-sleeved clothing and long pants
- wear a disposable face mask outside and change it frequently
- protect your eyes with goggles
- avoid contact with ash
Floods and landslides
Landslides and flooding may occur in the rainy season. This can affect transport infrastructure.
The rainy season is April to October in the north and November to March in the south.
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave. Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
You'll probably need a special insurance policy for any 'do not travel' destinations. Some Australian policies may not cover you for these areas.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may be illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in the DRC. Take enough legal medication for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Ebola virus disease (evd).
Several outbreaks of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) have occurred in DRC. There is an ongoing risk of EVD transmission in the DRC.
EVD is often fatal with a mortality rate of around 50 per cent.
Symptoms of EVD can include:
- muscle pain and weakness
- sore throat
- vomiting and diarrhoea
- internal and external bleeding
Approved vaccines are currently only administered during a confirmed outbreak to those considered at highest risk of contracting the virus. They are not available to the general public as a preventative measure at this point in time. T here's no proven safe and effective treatment but prompt and high-quality care can be life-saving.
EVD spreads through direct contact with body fluids, even after an infected person has died. EVD can also be transmitted through direct contact with bodily fluids of those who have survived and recovered from infection.
Maintain strict hygiene standards. Avoid direct contact with EVD patients.
See a doctor if you feel unwell and separate yourself from others if you develop any EVD symptoms.
Call ahead and tell the doctor about your recent travel and symptoms. Advance notice will help the doctor treat you and protect others.
See the Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care for more information on how to protect yourself against catching EVD, and what to do if you’re in an area where EVD is known to happen.
- Ebola virus disease, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Infectious diseases
Outbreaks of polio have occurred.
Stay up-to-date with polio vaccinations and booster doses. Speak to your doctor if you're unsure if you're vaccinated for polio.
If you're staying longer than 4 weeks, you'll need to show proof on exit that you've had the polio vaccine or a booster within the past 12 months. If you don't, you may need to be vaccinated before leaving the DRC.
Australian Immunisation Handbook
Insect-borne diseases
Yellow fever is widespread in the DRC.
Malaria occurs widely throughout the year.
Other insect-borne diseases can also occur, including:
- African sleeping sickness
To protect yourself from disease:
- check your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Get vaccinated against yellow fever before you travel.
Consider taking medicine to prevent malaria.
Seek medical advice if you have a fever, muscle pain, rash or severe headache.
HIV/AIDS is widespread. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
Other health risks
Monkeypox is transmitted to humans from animals, usually monkeys, rodents, and squirrels.
In areas where monkeypox occurs, avoid:
- contact with rodents and primates
- contact with people infected with monkeypox
- items that may have come in contact with an infected person.
Waterborne, foodborne and other infectious diseases are widespread. These include:
- Tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
- avoid swimming in fresh water
- avoid contact with dogs, monkeys, rodents and other animals
If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help straight away.
Get medical advice if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Medical care
Public medical facilities are basic in Kinshasa and inadequate outside the capital. Private medical facilities are of higher quality but may not meet Australian standards.
Doctors and hospitals will generally ask for payment before treatment. Evidence of travel insurance may not be accepted as a guarantee of payment at some hospitals.
If you're seriously ill or injured, you'll likely need to be evacuated to a place with better facilities. Medical evacuation can be expensive.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Penalties for possessing illegal drugs include harsh prison sentences and fines.
Carrying or using drugs
A number of offences carry the death penalty.
Always carry a copy of your passport and visa or immigration permit. Police and immigration officials can ask to see your travel documents at any time.
Same-sex relationships are not illegal in the DRC. Homosexuality remains a cultural taboo and same-sex couples who engage in public displays of affection may be subject to harassment. Same-sex relationships are not recognised in the DRC.
Curfews can be imposed with little or no warning.
Pedestrians and motorists must stop for motorcades. Warnings include security personnel and sirens.
You must also stop when passing a government installation during the raising and lowering of the national flag. This happens at about 7:30am and 6pm every day.
In the DRC it's illegal to:
- take photos of or near government buildings or other infrastructure, including airports
- take photos of a presidential or other official motorcade
- fail to produce your passport and visa or immigration permit on request
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
The DRC doesn't recognise dual nationality.
If you're a dual citizen, this limits the consular services we can give if you're arrested or detained.
You need to enter and exit the DRC using the same passport or you may be stopped from departing.
Always travel on your Australian passport .
Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Visa conditions
You'll need a visa before you enter the DRC. You can't get one on arrival.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You can contact the nearest embassy or consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
The closest embassy of the DRC is in Tokyo.
Border measures
Border openings and other restrictions may change at short notice. Due to the ongoing insecurity in these areas, you should avoid the border entry points from Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, South Sudan and the Central African Republic.
Contact your airline directly for the latest update and register with the Canadian Embassy in Kinshasa for advice on departure options.
Yellow fever vaccination
You'll need a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate to enter DRC. You may be asked to show your vaccination certificate before boarding, on arrival and at departure.
Find out about returning to Australia after exposure to yellow fever .
Countries with a risk of yellow fever
Other entry requirements
Declare satellite phones and GPS equipment on arrival.
A departure tax applies if you leave the DRC by air. The tax includes a $50 airport exit fee and a $5 boarding fee, which is subject to change with no notice. Get an official receipt and copies for each fee. You should hand the originals on request to immigration officials and at boarding and keep the copies.
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
The Canadian Embassy in Kinshasa can issue Australian provisional travel documents (PTDs). You can't travel to or through South Africa on a PTD.
Passport with 'X' gender identifer
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTI travellers
The local currency is the Congolese Franc (CDF).
Declare local and foreign currency in excess of USD10,000 on arrival and departure. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
US dollars are widely accepted. Counterfeit currency is common. Check USD banknotes before accepting them.
Change currency at licensed commercial banks and exchange bureaus. Money transfer agencies operate in major towns.
Traveller's cheques aren't accepted. Some major hotels accept credit cards.
ATMs are available in Kinshasa and major centres. It may be difficult to withdraw cash from international accounts, even at major hotels.
Check that your cards will work in the DRC before you travel.
Local travel
Mining districts.
You'll need official clearance from the relevant DRC ministry or government department before visiting a mining district.
Ministry of Mining (French)
Driving permit
To drive in the DRC, you'll need both:
- a valid international driving permit (IDP)
- your current Australian driver's licence
You must get your IDP before you leave Australia.
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in the DRC than in Australia. Dangers include:
- aggressive driving
- low driving standards
- a lack of street signage and lighting
Military and police roadblocks are common.
Following large-scale prison breaks in Kinshasa, Béni and Kasangu, local authorities increased the number of checkpoints at night. Checkpoints include Gombe, Limete, Ngaba, Kintambo, Ngaliema, Ndjili, Mont Ngafula and around Camp Kokolo.
Criminals may use roadblocks to pose as police or military personnel and rob you. See Safety
To protect yourself while travelling on DRC roads:
- familiarise yourself with local traffic laws and practices
- be alert to possible hazards, especially at night
- check road conditions and risks before travel outside Kinshasa
Carry government-issued identification, carte rose, carte grise and driver's licence at all times.
Ask for credentials if approached by an officer.
If you travel outside Kinshasa, have contingency plans and take emergency equipment such as a satellite phone.
Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check with your travel insurer whether your policy covers you when riding a motorbike.
Always wear a helmet.
Use registered taxis and limousines, preferably arranged through your hotel.
Avoid unofficial taxis or taxis hailed on the street. Robberies can occur.
Public transport
Boat travel.
Many boats and ferries are overloaded, lack lifesaving equipment and aren't seaworthy.
Kinshasa's main ferry terminal is congested and can close at short notice. Pay attention to your personal security in and around the terminal.
Civil unrest may cause flight cancellations to and from Kinshasa at short notice.
Local immigration and customs procedures at Kinshasa Airport are difficult. You may need help from people familiar with the process. If travelling by air, arrange for them to meet you when you arrive.
Pay attention to your personal security in and around the airport.
Avoid local airlines with poor maintenance and safety standards.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check the DRC's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Remember to get a police report when reporting a crime.
Your travel insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australia doesn't have an embassy or consulate in the DRC. Our ability to provide consular assistance may be limited.
Embassy of Canada, Kinshasa
17 Avenue Pumbu Commune de Gombe, Kinshasa
Phone: (+243) 996 021 500 Fax: (+243) 996 021 510 or (+243) 996 021 511 Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.international.gc.ca/country-pays/democratic_republic_congo-republique_democratique_congo/kinshasa.aspx?lang=eng
You can also get consular assistance from the Australian Embassy in Harare, Zimbabwe.
Australian Embassy, Harare
1 Green Close Borrowdale Harare, Zimbabwe
Phone: +263 24 2853 235 55, +263 24 2852 471-6 Fax: +263 24 2870 566 Email: [email protected] Website: zimbabwe.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australian Embassy, Zimbabwe X (Twitter): @AusEmbZim
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Democratic Republic of the Congo?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.

Democratic Republic of Congo
Carpeted by huge swaths of rainforest and punctuated by gushing rivers and smoking volcanoes, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC, formerly Zaire) is the ultimate African adventure. As much a geographical concept as a fully fledged nation, DRC has experienced one of the saddest chapters in modern history, suffering a brutal 20th century of colonial exploitation, authoritarian madness and what has been dubbed Africa's first 'world war', which finally ended in 2003 with the rise of the Kabila political dynasty.
Attractions
Must-see attractions.
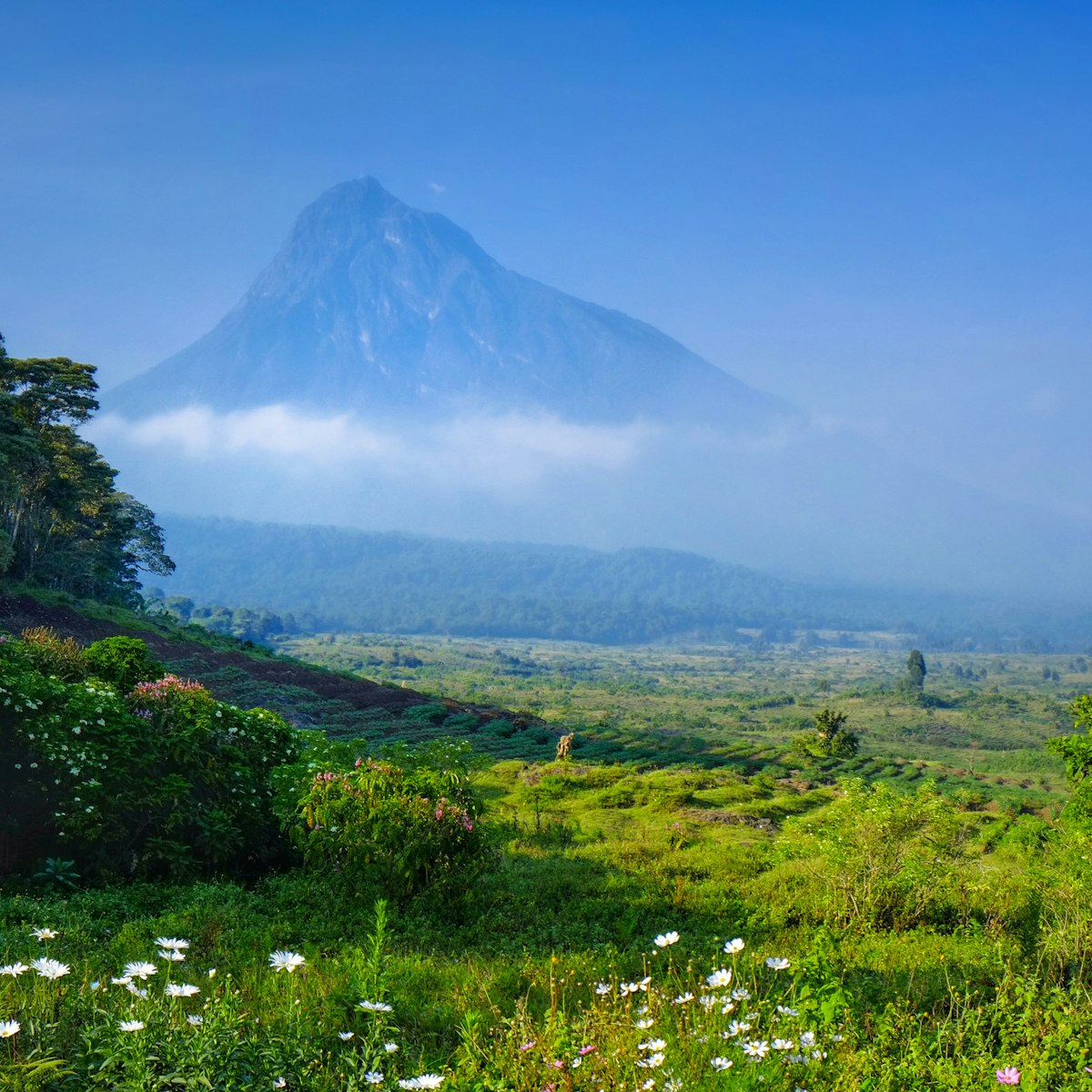

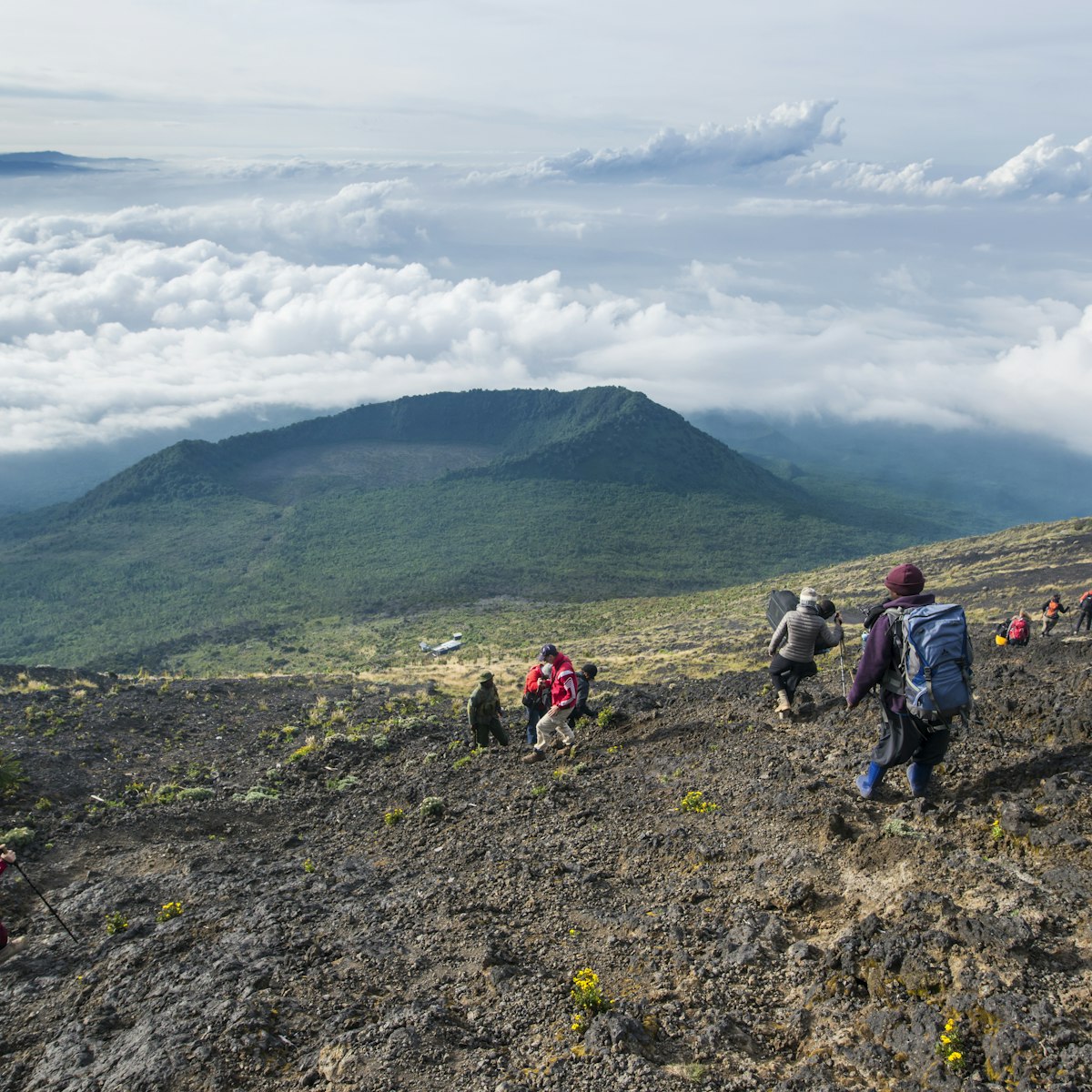
Parc National des Virunga
Eastern DRC
DRC's magnificent calling card is Virunga, Africa's oldest national park and home to mountain gorillas, chimpanzees and the incredible, active Nyiragongo…

Perhaps DRC's most magnificent single sight, active volcano Nyiragongo soars above the city of Goma and the surrounding Virunga National Park and sends…
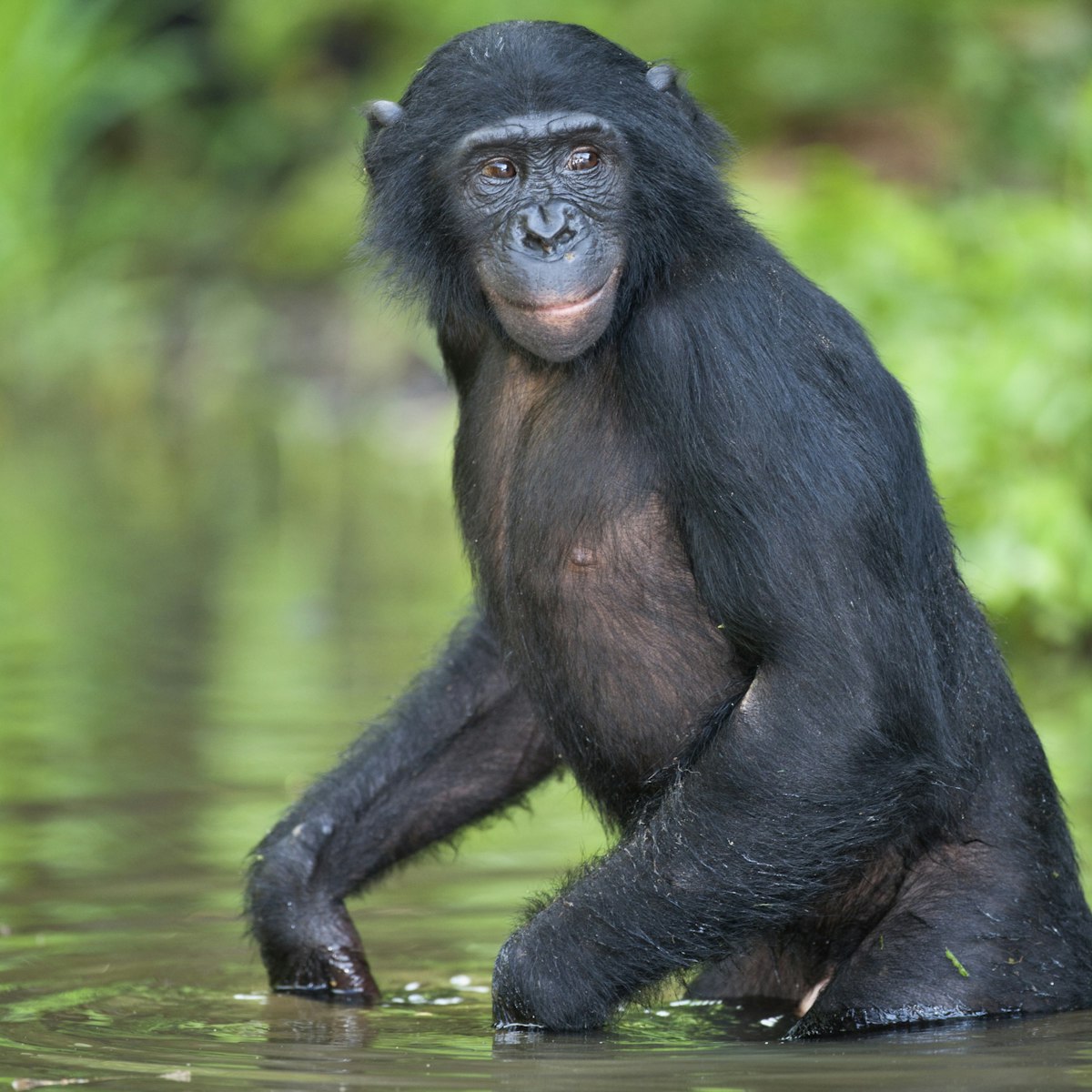

Lola Ya Bonobo Sanctuary
Ninety minutes west of Kinshasa, just beyond the city's sprawl, this excellent project provides a home for orphaned bonobos. Long thought to be…
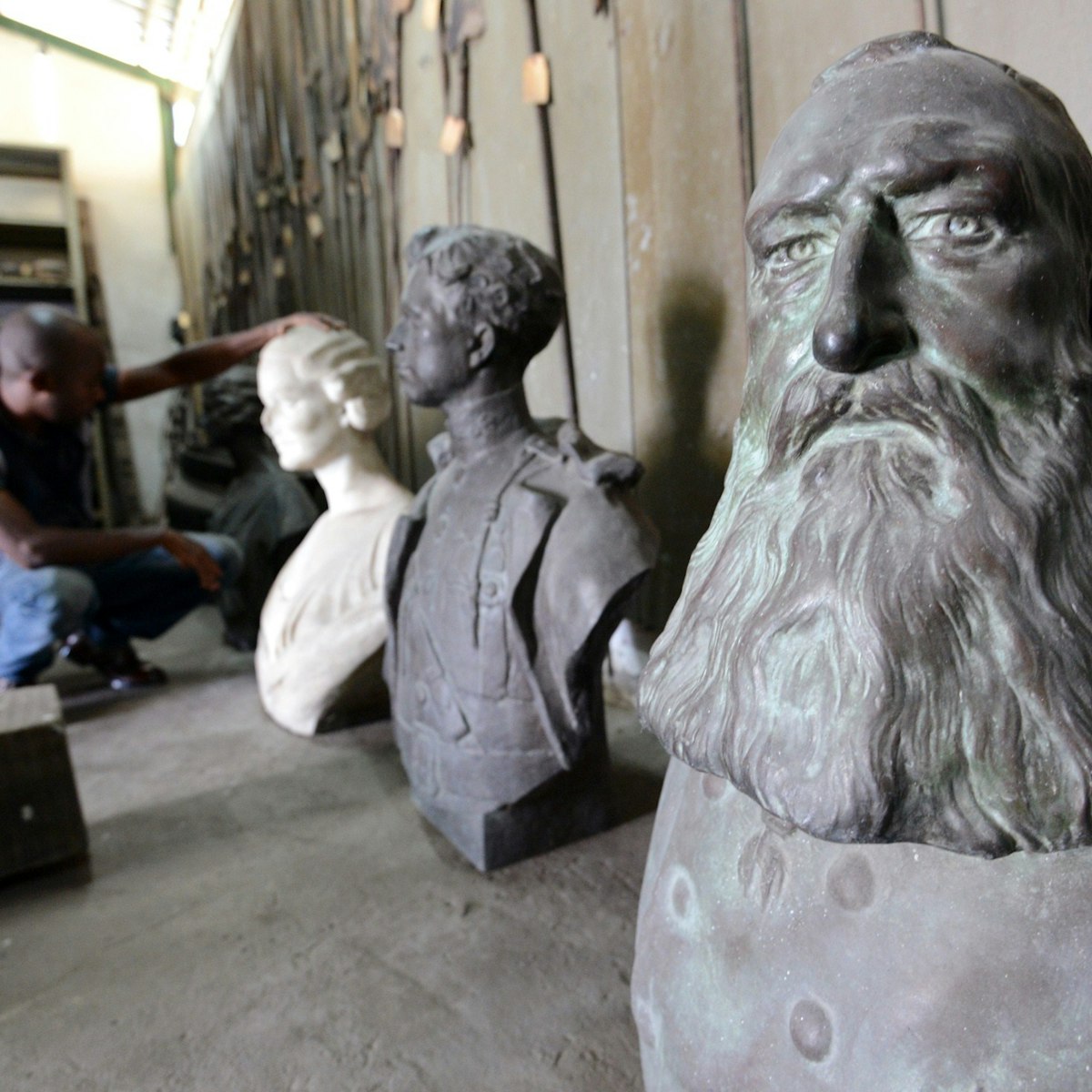

Musée National de Kinshasa
This amazing ethnographic archive comprising some 45,000 objects has been waiting patiently for its new home, a US$10 million prestige investment from…

Parc National de Kahuzi-Biéga
South Kivu's star attraction is this national park, where you can track habituated eastern lowland gorillas (Grauer’s gorillas) for just US$400 per person…

Chutes du Zongo
A popular day trip from Kinshasa despite the expensive 4WD hire (US$200) necessary to get here, the gorgeous 65m-high Zongo Falls are one of DRC's most…

Serpents du Congo
This excellent snake farm is located 28km from downtown Kinshasa and makes for a great day out. Owner Franck will gladly show you the poisonous and…

Senkwekwe Gorilla Orphanage
Provided you make it back from your gorilla track in a timely fashion, it should be possible to visit the world’s only mountain gorilla orphanage, which…
Latest stories from Democratic Republic of Congo
Filter by interest:
- All Interests
- Adventure Travel
- Art & Culture
- Beaches, Coasts & Islands
- Food & Drink

Jun 4, 2020 • 10 min read
Traveler, Abongi Gael Bokongo, shares how fleeing a civil war with his family shaped how he travels the world.

Dec 20, 2019 • 2 min read

Nov 17, 2017 • 2 min read

Dec 12, 2011 • 3 min read
Purchase our award-winning guidebooks
Get to the heart of Democratic Republic of Congo with one of our in-depth, award-winning guidebooks, covering maps, itineraries, and expert guidance.
Democratic Republic of Congo and beyond

Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Travel Advisory July 31, 2023
Democratic republic of the congo - level 3: reconsider travel.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Reconsider travel to the Democratic Republic of Congo due to crime and civil unrest . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do Not Travel To :
- North Kivu province due to crime , civil unrest , terrorism , armed conflict , and kidnapping .
- Ituri province due to crime , civil unrest , terrorism , armed conflict , and kidnapping .
- The eastern DRC region and the three Kasai provinces (Kasai, Kasai-Oriental, Kasai-Central) due to crime , civil unrest , armed conflict and kidnapping .
Country Summary: Violent crime, such as armed robbery, armed home invasion, and assault, is common and local police lack resources to respond effectively to serious crime. Assailants may pose as police or security agents.
Demonstrations are common in many cities and some have turned violent. Police have at times responded with heavy-handed tactics that resulted in civilian casualties and arrests.
The U.S. government has extremely limited ability to provide emergency consular services to U.S. citizens outside of Kinshasa due to poor infrastructure and security conditions.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
If you decide to travel to the Democratic Republic of the Congo:
- Avoid demonstrations.
- Use caution when walking or driving.
- Always have a copy of your U.S. passport and DRC visa. Keep originals in a secure location. Carry your U.S. passport and DRC visa when crossing provincial borders or flying domestically.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for the DRC.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
North Kivu Province – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Violent crime, such as murder, rape, kidnapping, and pillaging, continue throughout North Kivu province. Road travelers are frequently targeted for ambush, armed robbery, and kidnapping.
Demonstrations and large gatherings can occur throughout these regions, especially in urban areas, and escalate to violence. Extrajudicial mobs can form rapidly and turn violent, posing a threat to humanitarian aid workers and other personnel operating in the area.
Terrorist and armed groups operating in North Kivu province have attacked military and civilian targets and represent an ongoing threat to humanitarian aid workers and other NGO personnel operating in the area.
Armed groups, individuals, and military forces routinely clash with each other. Civilians are frequently targeted in attacks.
The U.S. government is unable to provide emergency consular services to U.S. citizens in North Kivu province as U.S. government travel to these areas is restricted.
Visit our website for Travel to High- Risk Areas.
Ituri Province – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Violent crime, such as murder, rape, kidnapping, and pillaging, continue throughout Ituri province. Road travelers are frequently targeted for ambush, armed robbery, and kidnapping.
Terrorist and armed groups operating in Ituri province have attacked military and civilian targets and represent an ongoing threat to humanitarian aid workers and other NGO personnel operating in the area.
The U.S. government is unable to provide emergency consular services to U.S. citizens in Ituri province as U.S. government travel to these areas is restricted.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Eastern DRC Region and the Three Kasai Provinces – Level 4: Do Not Travel
Violent crime, such as murder, rape, kidnapping, and pillaging, continue throughout South Kivu, Tanganyika, Haut Lomami, Bas-Uele, and Haut-Uele and three Kasai provinces of Kasai Oriental, Kasai Central, and Kasai. Road travelers are frequently targeted for ambush, armed robbery, and kidnapping.
The U.S. government is unable to provide emergency consular services to U.S. citizens in eastern DRC and these provinces, as U.S. government travel to these regions is restricted.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Yes, obtain in advance.
Yellow fever.
5 million CDF ($5,400).
Illegal to export CDF.
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. embassy kinshasa.
310 Avenue des Aviateurs Kinshasa/Gombe Telephone: +(243) 081-556-0151 (Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m.) Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(243) 081-556-0151 Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Requirements for Entry:
- Passport: Must be valid for six months after entry into country
- Visa: Obtain your visa before traveling.
- Immunizations: World Health Organization (WHO) card with yellow fever vaccination.
Visit the Embassy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo website for the most current visa information. Overseas inquiries may be made at the nearest Congolese Embassy or Consulate. However; U.S. citizens are generally required to apply for visas from the DRC Embassy in Washington, D.C. Allow at least two to three weeks for visa processing.
The DRC does not recognize dual nationality. U.S. citizens should always present themselves as U.S. citizens to Congolese authorities. Otherwise, it may impede our ability to provide consular services.
Airport Fees: All departing international travelers must pay these official fees when checking in:
- $50 airport exit fee
- $5 boarding fee
- Passengers on domestic flights pay $10.
If you experience harassment at any port of entry, such as detention, passport confiscation or demands by immigration and security personnel for unofficial “fees,” ask to contact the U.S. Embassy immediately.
Intending Residents: If you plan to reside in the DRC, register at the office of the Direction General of Migration (DGM) in your commune of residence.
Journalists: Journalists working in the DRC must:
- enter the DRC through Kinshasa
- obtain a permit from the Ministry of Communication and Media (a $250 permit is valid for one month)
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of the DRC.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
See the Department of State Travel Advisory and Alerts for the DRC.
The security situation in most parts of eastern DRC remains unstable due to the activities of rebel and other armed groups and ongoing military operations. Armed groups, individuals, and military forces routinely clash with each other. Civilians are frequently targeted in attacks and other illegal activities, such as kidnapping, forced taxation, and forced labor.
Terrorist and armed groups operating in North Kivu and Ituri provinces have regularly attacked military and civilian targets and represent an ongoing threat to humanitarian aid workers and other NGO personnel operating in the area. Armed group violence has increased in parts of South Kivu.
Sporadic but severe outbreaks of violence targeting civilians, including killing, rape, kidnapping, and pillaging, continue throughout North Kivu, South Kivu, Ituri, Tanganyika, Haut Lomami, Bas-Uele, and Haut-Uele and three Kasai provinces of Kasai Oriental, Kasai Central, and Kasai Provinces.
Travelers in remote area of the country, especially in the eastern DRC, should travel with a minimum of two vehicles equipped with global positioning systems (GPS) and satellite phones. Road travelers are frequently targeted for ambush, armed robbery, and kidnapping.
Terrorism: Terrorist groups and those inspired by such organizations are intent on attacking U.S. citizens abroad. Terrorists are increasingly using less sophisticated methods of attack – including knives, firearms, and vehicles – to more effectively target crowds. Frequently, their aim is unprotected or vulnerable targets, such as:
- High-profile public events (sporting contests, political rallies, demonstrations, holiday events, celebratory gatherings, etc.)
- Hotels, clubs, and restaurants frequented by tourists
- Places of worship
- Shopping malls and markets
- Public transportation systems (including subways, buses, trains, and scheduled commercial flights)
For more information, see our Terrorism page.
Crime: Crimes of opportunity (mainly for financial gain) are the most reported incidents of crime against U.S. citizens in Kinshasa and throughout the DRC. Most incidents involve theft such as pickpocketing, burglary, and robbery. Petty crime may be more likely in public places and areas of congregation. Criminal elements do not typically single out U.S. citizens, but may view them as targets of opportunity based on perceived affluence or vulnerability.
Roadblocks: Security forces set up spontaneous roadblocks, especially after dark, to conduct vehicle searches and check identity papers. They may also solicit bribes. Remain inside your vehicle with doors locked and open the window slightly to communicate. Remain calm and, if threatened, do not resist.
Demonstrations: Demonstrations and gatherings occur with increasing frequency and with little notice. They may take place in response to political or economic issues, on significant holidays, and during international events. Police have at times responded to demonstrations with heavy-handed tactics that resulted in civilian casualties and arrests. In the eastern DRC, demonstrations can rapidly become extrajudicial mobs and turn violent, posing a threat to humanitarian aid workers and other personnel operating in the area.
- Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and become violent.
- Avoid areas around protests and demonstrations.
- Monitor consular Alerts and messages and local and international news from reliable sources. English-language news can be found on BBC at 92.6 FM. Radio Okapi broadcasts in French on 103.5 FM at 7:00 a.m., 8:00 a.m., 12:00 noon, and 6:00 p.m., and provides updates throughout the day.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Kidnapping for Ransom: The risk of kidnapping for ransom exists throughout the country, but is more common in eastern DRC. International humanitarian workers have been targeted. Reports of kidnapping of a U.S. citizen should be passed to the U.S. Embassy immediately.
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault should first contact the U.S. Embassy for assistance. Report crimes to the local police at +243 81-555-5944 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +243 97 261- 6145. Dial 112 to contact the police in an emergency in Kinshasa.
Remember local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion.
- Provide a list of local attorneys
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence may contact the Embassy for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are limited and are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance, especially given the current COVID-19 pandemic.
See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
You may have difficulties at immigration if you are traveling with satellite phones, GPS receivers or military clothing.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the U.S., regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
International Adoption: Intercountry adoption of Congolese children is illegal in the DRC and there are no legal means for an adopted child to depart the country. U.S. adoptive families of Congolese children are cautioned that attempting to circumvent the law could have severe consequences.
Photography : It is illegal to take pictures of government buildings, military installations, and along border areas. You could be fined, have your photographic equipment confiscated, or be detained or arrested. Do not take photos of Congolese without permission.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Phone Service: Cellular phones are the norm, as other telephone service is unreliable, and landlines are nearly non-existent. It may be possible to purchase a SIM card locally and use a U.S.-compatible cell phone.
Currency: The Congolese Franc is the currency of the DRC (CDF) but U.S. dollars are widely accepted in urban areas. Most vendors and banking institutions will accept only bills printed from 2010 or later. Bills must be crisp and in good condition; even those with minor stains or small tears may be rejected. One-dollar bills are rarely accepted. Counterfeit currency is widely circulated. Examine U.S. bills before accepting them to ensure they are legitimate. Exchange currency only at reputable banks.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in the DRC. However, individuals engaging in public displays of same-sex sexual conduct can be subject to prosecution under public indecency provisions. Homosexuality remains a cultural taboo, and harassment by the state security forces occurs.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance: Persons with disabilities face limited access to transportation, communication, accommodations, and public buildings. There are few sidewalks and no curb-cuts, and most buildings lack functioning elevators.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Sexual assault is widespread and occurs largely in the conflict zones in North Kivu province, but also throughout the country by security forces, rebel and militia groups, and civilians, often during attacks on villages and sometimes as a tactic of war to punish civilians. Domestic violence is common. Although the law considers assault a crime there is no specific penalty for spousal abuse. Intervention by police or action by judicial authorities is rare.
See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Medical facilities, medicine severely limited.
For emergency services in DRC, dial 112 for the police and call a local private hospital for medical assistance. A list of medical providers is available on the U.S. Embassy website.
Ambulance services are:
- not present throughout the country except by private medical providers in major cities.
- not equipped with state-of-the-art medical equipment.
- not staffed with trained paramedics and often have little or no medical equipment.
- Injured or seriously ill travelers may prefer to take a taxi or private vehicle to the nearest major hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance. All care providers expect payment in U.S. dollars before treatment.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance covers you overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental medical insurance with medical evacuation coverage.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription. Check with the government of DRC to ensure the medication is legal in DRC.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
Air pollution is a significant problem in several major cities in DRC. Consider the impact seasonal smog and heavy particulate pollution may have on you, and consult your doctor before traveling if necessary.
The air quality varies considerably and fluctuates with the seasons. It is typically at its worst in the dry season from May to October. People at the greatest risk from particle pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema
- People with heart disease or diabetes
- People who work or are active outdoors
Health facilities in general:
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
- Public medical clinics lack basic resources and supplies.
- Hospitals and doctors require payment “up front” prior to service or admission. Credit card payment is not always available. Hospitals and medical professionals may require cash payment.
- Medical staff may speak little or no English.
- Generally, in public hospitals only minimal staff is available overnight and food services and supplies are the responsibility of the patient. Consider hiring a private nurse or having family spend the night with the patient, especially a minor child.
- Patients bear all costs for transfer to or between hospitals.
- Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities.
Pharmaceuticals:
- Exercise caution when purchasing medication overseas. Pharmaceuticals, both over the counter and requiring prescription in the United States, are often readily available for purchase with little controls. Counterfeit medication is common and may prove to be ineffective, the wrong strength, or contain dangerous ingredients. Medication should be purchased in consultation with a medical professional and from reputable establishments.
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
- Travelers should carry medical prescriptions for medicine they take to the DRC.
- DRC does not allow the importation of Dipyrone (Metamizole, Noramidopyrine) and Apha Beta-Arteether. Travelers should avoid carrying these medications.
Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy:
- If you are considering traveling to the DRC to have a child through use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) or surrogacy, please see our ART and Surrogacy Abroad page .
- There is no legal framework for foreigners or same-sex couples to pursue surrogacy in DRC. As a result, surrogacy agreements between foreign or same-sex intending parents and gestational mothers are not enforced by DRC courts.
- If you decide to pursue parenthood in DRC via assisted reproductive technology (ART) with a gestational mother, be prepared for long and unexpected delays in documenting your child’s citizenship.
Water Quality:
- In many areas, tap water is not potable. Bottled water and beverages are generally safe, although you should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Be aware that ice for drinks may be made using tap water.
Adventure Travel:
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
The following diseases ae prevalent:
- African trypanosomiasis
- Chikungunya
- Diarrheal diseases
- Hepatitis A
- Meningococcal meningitis
- Schistosomiasis
- Tuberculosis
- Yellow fever
Use the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended mosquito repellents and sleep under insecticide-impregnated mosquito nets. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended for all travelers even for short stays.
HIV/AIDS: In 2018, HIV was noted as the 10 th leading cause of death in the DRC. The disease is still prevalent and standard precautions should be taken, including safe sex practices.
There are shortages of medicine and medical supplies throughout the rural areas of DRC and some areas suffer clean water shortages.
Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Resources for Travelers regarding specific issues in DRC.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Outside of main cities, most roads are not drivable, even with an off-road vehicle. Road conditions are poor and deteriorate significantly during the rainy season from October to May. Traffic is hazardous due to lack of infrastructure, poorly trained drivers, poor maintenance, and indifference toward pedestrians and cyclists. Outside of Goma and Bukavu, travel in a convoy and avoid all travel after dark.
Traffic Laws: An international driving permit is necessary to drive in the DRC. Use of cell phones while driving is prohibited.
Accidents: In the event of an automobile accident, remain inside the vehicle and wait for police. If in danger, leave the scene and proceed directly to the nearest police station. Do not stop at the scene of an accident, as mobs can develop quickly.
Official motorcades pose serious risks to drivers and pedestrians in Kinshasa.
- Pull to the side of the road as far as possible and extinguish the vehicle’s headlights when sirens or security forces announce their presence.
- Do not take photographs of motorcades.
- Do not attempt to move until the entire motorcade has passed and proceed only when security forces permit it.
Drivers should stop their cars and pedestrians should stand still when passing a government installation during the raising and lowering of the Congolese flag. This ceremony occurs daily at roughly 7:30 a.m. and 6:00 p.m.
Public Transportation: Avoid all travel by public transportation, and hire private transport from a reliable source. Any form of public transportation is unregulated, unreliable, and generally unsafe.
- Few taxis meet U.S. safety standards.
- Reputable car rental firms will include the services of a driver.
Ferry: Ferry accidents are commonplace and often fatal. Ferry service between Brazzaville and Kinshasa may close completely with minimal notice. The ferry stops running in late afternoon, and there is no service on Sundays. A visa for the destination country (Republic of Congo or DRC) is required to cross the Congo River between Brazzaville and Kinshasa.
See our Road Safety page for more information. See also the national authority responsible for road safety.
Aviation Safety Oversight: As there is no direct commercial air service to the United States by carriers registered in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has not assessed the government of the Democratic Republic of Congo’s Civil Aviation Authority for compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to DRC should also check for U.S.maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Democratic Republic of the Congo . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, democratic republic of the congo (d.r.c.) map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:

Introducing Democratic Republic of Congo
About democratic republic of congo.
- Images of Democratic Republic of Congo
- History, language & culture
- Weather & geography
- Doing business & staying in touch
Plan your trip
- Travel to Democratic Republic of Congo
- Where to stay
While you’re there
- Things to see & do
- Shopping & nightlife
- Food & drink
- Getting around
Before you go
- Passport & visa
- Public Holidays
- Money & duty free
Book your flights
Democratic Republic of Congo travel guide
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is one of the largest and most enigmatic countries in Africa. It has many beautiful landscapes, mainly comprising dense and undulating rainforest interspersed with waterfalls and teeming with fascinating wildlife.
The great body of the Congo River runs across the northern reaches of the country and has long been a site of considerable historic importance, made famous by the explorer Henry Morton Stanley and later used as the backdrop for Joseph Conrad’s Heart of Darkness.
In many ways, much of the DRC remains as wild and impenetrable today as it would have been in Conrad’s time. The transport infrastructure built by the brutal Belgian colonial regime has largely been reclaimed by the jungle and there are few links between the country’s vast interior and the urban areas dotted around its fringes.
Kinshasa, the capital, is situated in the far west of the country and, though largely impoverished and crumbling, it is a veritable hub for colourful African music and culture.
DRC’s tourist capital, if such a thing exists, is Goma, which sits on the banks of Lake Kivu in the far east of the country. It is presided over by the imposing Nyiragongo volcano, which sits at the heart of Virunga National Park, the oldest national park in Africa and one of just a handful of places where you can still see mountain gorillas in their natural habitat.
Goma and the mineral-rich Kivu region were hit particularly hard by a civil war from 1998 to 2003 that resulted in the deaths of at least three million people; sporadic bouts of violence since the war officially ended have continued to burden the region’s considerable tourist potential.
However, peace and a semblance of stability have returned to Goma for the time being and small handfuls of adventurous tourists are beginning to trickle across the border once again. Visitors are advised to check the latest travel advice before visiting.
2,345,410 sq km (905,563 sq miles).
79,722,624 (UN estimate 2016).
33.8 per sq km.
President Félix Tshisekedi since 2019.
Prime Minister Judith Suminwa Tuluka since 2024.
Travel Advice
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Areas where FCDO advises against travel
Your travel insurance could be invalidated if you travel against FCDO advice.
Republic of Congo-Central African Republic border area in Likouala Region
FCDO advises against all travel to within 50km of the Republic of Congo-Central African Republic border in Likouala Region.
Some districts in Pool Region
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to the Pool Region districts of:
Mouyondzi District in Bouenza Region
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to Mouyondzi District in Bouenza Region.
Find out more about why FCDO advises against travel .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide and any specific travel advice that applies to you:
- disabled people
- LGBT+ people
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK, for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in the Republic of Congo set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Republic of Congo Embassy in the UK.
Telephone: 0203 691 5979
Email: [email protected]
Address: 83 Victoria Street, London, SW1H OHW
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering the Republic of Congo.
Passport validity requirements
Your passport must be valid for the duration of your stay. No additional period of validity is needed.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Visa requirements
You must have a visa to enter the Republic of Congo.
Applying for a visa
Apply for a visa before you travel. Contact the Republic of Congo Embassy in the UK for more information.
Vaccine requirements
To pass border control in the Republic of Congo, you must have certificates to prove you’ve had:
- a yellow fever vaccination, due to a risk of yellow fever transmission
- a polio vaccine, due to the risk of polio transmission
For more details about health entry requirements and recommended vaccinations, see TravelHealthPro’s Republic of Congo guide .
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of the Republic of Congo. You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
This guide also has safety advice for regions of the Republic of Congo .
There is a high threat of terrorist attack globally affecting UK interests and British nationals, including from groups and individuals who view the UK and British nationals as targets. Stay aware of your surroundings at all times.
UK Counter Terrorism Policing has information and advice on staying safe abroad and what to do in the event of a terrorist attack. Find out how to reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad .
Terrorism in the Republic of Congo
Although there’s no recent history of terrorism in the Republic of Congo, attacks cannot be ruled out.
Political situation
Demonstrations happen occasionally. In the past, demonstrations have become violent. Even when they are peaceful there is a risk of violence. Avoid any areas with demonstrations.
Reports of crime, particularly opportunistic crime such as pickpocketing, have increased in Brazzaville and Pointe Noire, and criminals target foreigners. You’re at greater risk of crime at night, and also in rural areas.
Protecting yourself and your belongings
Take care of your belongings, particularly in Brazzaville and Pointe Noire. To reduce your personal risk:
- avoid walking in the streets after dark
- do not carry large amounts of cash or valuables
- avoid isolated areas, including beaches
Vehicle crime
Armed gangs may target your car. Take security advice if you intend to travel any distance. Reduce the risk of carjacking and break-ins by:
- locking doors and keeping windows closed
- not driving away from main routes
- always parking in a secure location
Laws and cultural differences
Personal id.
Police may ask you for ID. Always carry a colour copy of your passport, including your visa entry stamp. If you live in Congo, also always carry a colour copy of your residency card.
Transport risks
Road travel.
If you are planning to drive in the Republic of Congo, see information on driving abroad .
You can use a UK photocard driving licence to drive in the Republic of Congo. If you still have a paper driving licence, you may need to update it to a photocard licence or get the correct version of the international driving permit ( IDP ) as well.
Hire car companies often have stricter requirements for their customers, such as a year of driving experience, a higher minimum age and holding an IDP .
Road conditions are generally poor and deteriorate during the wet season from November to May. If you travel overland off the main roads, you’ll need a 4-wheel-drive vehicle.
Checkpoints
There are frequent vehicle checkpoints in the Republic of Congo, which can be poorly marked. If you’re asked for documents at a checkpoint, stay in your vehicle and show them through a closed window.
The UK Air Safety List (ASL) lists all known airlines in the Republic of Congo that do not meet international safety standards and are banned from operating commercial air services to, from, and within the UK. Check the UK Air Safety List when considering which airlines to fly with. The list is maintained by the Department for Transport, based on advice from the UK Civil Aviation Authority .
Rail travel
There are currently no rail services between Brazzaville and Pointe Noire. When rail services were running, there were several instances of criminal gangs targeting trains on this route.
Boat travel
The river border crossing between Brazzaville and Kinshasa can close without warning. The ferry stops running in late afternoon, and there is no service on Sundays. Check before travelling.
This section has safety advice for regions of the Republic of Congo. It only covers regions where FCDO has specific advice.
You should also read FCDO ’s overall travel advice and safety and security advice .
FCDO advises against all travel within 50km of the Republic of Congo-Central African Republic ( CAR ) border in Likouala Region.
There is a risk of violence, crime and insecurity in this area due to instability in CAR .
In the Pool Region there continue to be reports of:
- sporadic fighting between rebel groups and the military
- large numbers of displaced people
- crime and armed banditry
The authorities may stop you travelling at night. To travel by day, you may need a permit from the Congolese army and a military escort.
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to Mouyondzi District in Bouenza Region. There is a risk of violent crime including carjackings and targeted attacks.
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
There’s no central number for emergency services. Check for local medical facilities and carry contact details with you.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Health risks and recommended vaccines
Check TravelHealthPro’s current advice on the Republic of Congo to find out how to reduce the health risks you’ll face there.
TravelHealthPro also lists the recommended vaccines that could apply to you. At least 8 weeks before you travel, check how to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
If you take medication, bring enough for your time in the Republic of Congo and make sure it is clearly labelled. Bring a copy of any prescription.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad .
Healthcare facilities in the Republic of Congo
Medical facilities in the country are limited, particularly in rural areas. Medical evacuation is likely to be necessary for all but the most basic treatments. If you become ill while in the Republic of Congo or straight after leaving the country, get immediate medical advice.
Make sure you have adequate travel and medical insurance to cover the cost of any medical treatment abroad and repatriation; this should specifically include the very high costs of evacuation by air ambulance.
FCDO has a list of medical providers in the Republic of Congo where some staff will speak English.
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) cannot provide tailored advice for individual trips. Read this travel advice and carry out your own research before deciding whether to travel.
Emergency services in the Republic of Congo
There’s no central number for emergency services in the Republic of Congo. You can report crimes to local police on 06 665 4804. Few police will speak English.
Check for local medical facilities and carry contact details with you.
Telephone numbers can be unreliable.
Contact your travel provider and insurer
Contact your travel provider and your insurer if you are involved in a serious incident or emergency abroad. They will tell you if they can help and what you need to do.
Refunds and changes to travel
For refunds or changes to travel, contact your travel provider. You may also be able to make a claim through insurance. However, insurers usually require you to talk to your travel provider first.
Find out more about changing or cancelling travel plans , including:
- where to get advice if you are in a dispute with a provider
- how to access previous versions of travel advice to support a claim
Support from FCDO
FCDO has guidance on staying safe and what to do if you need help or support abroad, including:
- finding English-speaking lawyers , funeral directors and translators and interpreters in the Republic of Congo
- dealing with a death in the Republic of Congo
- being arrested or imprisoned in the Republic of Congo
- getting help if you’re a victim of crime
- what to do if you’re in hospital
- if you’re affected by a crisis , such as a terrorist attack
Contacting FCDO
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this travel advice is updated.
You can also contact FCDO online .
Help abroad in an emergency
If you are in the Republic of Congo and you need emergency help from the UK government, contact the British Embassy in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo , who provide consular assistance for the Republic of Congo.
FCDO in London
You can call FCDO in London if you need urgent help because something has happened to a friend or relative abroad.
Telephone: 020 7008 5000 (24 hours)
Find out about call charges

Book a Hotel
© Columbus Travel Media Ltd. All rights reserved 2024
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Democratic Republic of Congo (Kinshasa) travel advice
Latest updates: The Health section was updated - travel health information (Public Health Agency of Canada)
Last updated: April 19, 2024 08:42 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, democratic republic of congo (kinshasa) - avoid non-essential travel.
Avoid non-essential travel to to the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) due to high crime rates, civil unrest and the risk of kidnapping.
Eastern and northeastern areas of DRC - Avoid all travel
- Bas-Uélé, Haut-Uélé and Ituri
- Haut-Lomami
- points of entry to Burundi, Uganda and Rwanda
- areas bordering South Sudan (including the Garamba National Park), the Central African Republic and Uganda (including Virunga National Park).
If you decide to travel to these areas despite this advisory, you should regularly review the situation to determine whether your continued presence in the area is warranted.
The security situation around Goma, in North Kivu, is unstable. If you are in the region, be ready to leave on short notice should the situation further deteriorate.
Kasaï provinces - Avoid all travel
- Kasaï-Central
- Kasaï-Oriental
Mai-Ndombe province - Avoid all travel
Avoid all travel to the province of Mai-Ndombe due to intercommunal violence.
Back to top
Security situation in eastern DRC
Since the beginning of February, 2024, the security situation in eastern DRC has become more unstable and unpredictable.
Fighting has intensified between security forces and the M23 rebel group in North Kivu. The conflict has caused hundreds of casualties and displaced thousands of people.
Avoid all travel to eastern DRC, including to North Kivu. If you decide to travel despite this advisory, continually reassess the situation to determine whether your presence in the area is warranted.
Demonstrations in Kinshasa
Starting February 10, 2024, violent demonstrations are taking place in Kinshasa, near Boulevard du 30 Juin.
Foreign embassies have also been targeted by demonstrators, including those of:
- the United States
- the United Kingdom
Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
If you are in Kinshasa:
- avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- follow the instructions of local authorities
- be prepared to modify your plans in case of disturbances
- expect enhanced security measures and an increased police presence
The security situation in DRC is unpredictable and could deteriorate suddenly.
Demonstrations
Demonstrations occur frequently, especially in Kinshasa. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent suddenly. They can also cause major disruption to traffic and public transport.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Eastern DRC
The situation remains volatile in the east of the country due to the persistent presence of and regular clashes between over 120 armed groups.
The affected provinces are:
- Bas-Uélé
- Haut-Uélé
Crime is endemic throughout these areas, and there are many reports of human rights violations.
State of siege
Since 2021, the provinces of North Kivu and Ituri have been under a state of military siege. These provinces are under military administration until further notice.
Provinces of North Kivu and South Kivu
Clashes between the Congolese army and the M23 rebel group continue around Goma in North Kivu.
Despite the signing of peace agreements and the presence of UN forces, armed conflict persists in certain regions outside the provincial capitals. Members of various armed groups continue to perpetrate acts of pillage and violent crimes against the civilian population, including murder, kidnapping, armed assault and rape. The ensuing humanitarian crisis has led to major displacements.
Military operations are still underway in some areas, including near:
- Virunga National Park
- the tri-border area with Uganda and Rwanda
Military operations could lead to a deterioration in the security situation in various locations outside the two capitals, Goma and Bukavu. Some places are particularly dangerous, including:
North Kivu
Avoid all travel to the provinces of North and South Kivu. If you decide to travel despite this advisory:
- continually reassess the situation to determine whether your presence in the area is warranted
- take into account the information provided by Congolese authorities and MONUSCO, to help avoid dangerous situations
- avoid public transportation
- expect disruptions to local businesses and services, including airports
Tanganyika Province
The province of Tanganyika, and especially Manono Territory, is the theatre of an ethnic conflict between the Pygmies and the Luba. The Mai-Mai militia periodically re-engage.
Ituri Province
Armed clashes persist in the province of Ituri. There is a terrorist threat in the Beni and Irumu territories.
Haut-Lomami Province
Violent crime continues in Haut Lomami Province. Travellers have been ambushed, robbed and kidnapped.
Border regions of South Sudan, Central African Republic, and Uganda, including Garamba National Park
Despite intensified operations by the Ugandan, Congolese and South Sudanese armed forces and the United Nations, the Lord's Resistance Army continues to commit acts of violence against the civilian population. Numerous casualties have been reported, and thousands of people have fled the region.

Points of entry from Burundi, Rwanda and Uganda
Entry points at the Burundi, Uganda and Rwanda borders should be avoided at all times due to the prevailing insecurity and disorder. The borders separating the DRC from Burundi and Rwanda may be closed at any time.
Kasaï provinces
Although the situation is currently calm in the Kasaï provinces, armed clashes have previously claimed thousands of victims in the provinces of Kasaï, Kasaï-Central and Kasaï-Oriental. Kidnappings have also taken place.
Intercommunal violence in Mai-Ndombe
Inter-community violence has been a regular occurrence in Mai-Ndombé Province since June 2022, particularly in the Kwamouth territory where thousands of residents have been displaced. The violence has claimed hundreds of victims. Attacks have also occurred in neighboring provinces, including the commune of Maluku in northern Kinshasa Province.
In the capital, choose a hotel in the commune of Gombe, which is both the administrative headquarters and a commercial zone.
- Exercise extreme caution outside the commune of Gombe
- Avoid all travel after dark
There is a threat of terrorism in the Democratic Republic of Congo, particularly:
- in the region of Beni-Butembo and Goma in North Kivu
- in the vicinity of Boga in Ituri
- towards the border with Uganda
Terrorist groups clash over control of good-trafficking routes, mining sites, and agricultural areas.
Attacks on civilians and government targets occur frequently. Further attacks are likely.
Targets could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as restaurants, bars, coffee shops, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
Large-scale events could be targeted.
- Always be aware of your surroundings when in public places
- Monitor local media
- Follow the instructions of the local authorities
Crime rates are high in the DRC due to extreme poverty and the lack of enforcement.
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs regularly throughout the country, including in Kinshasa. Theft is frequent:
- on public transportation
- in crowded areas
- at and around ATMs
During your trip to the DRC:
- ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and your other travel documents are secure at all times
- avoid showing signs of affluence or wearing expensive jewellery
- always leave your car doors locked and windows up
- avoid carrying large sums of cash or unnecessary valuables
- avoid travelling alone
- be especially cautious of your surroundings when withdrawing cash from ATMs, even in a hotel
Violent crime
Violent crime occurs in both urban and rural areas, especially after dark. Incidents include:
- armed robbery
- sexual assaults
- armed home burglaries
- car and motorcycle hijackings
During your stay:
- be aware of your surroundings at all times
- avoid walking alone
- don't leave major highways, and don't park in unsupervised areas
- if you are attacked, don't resist
Kidnappings
Kidnappings occur regularly in the eastern and northeastern provinces. Foreigners are often targeted. Incidents occur mainly in the following areas:
- Virunga Park in North Kivu
- North Kivu, South Kivu, Ituri, Maniema, Tanganika, Bas-Uélé and Haut-Uélé provinces
Express kidnappings
Express kidnappings targeting foreigners occur. Victims are usually abducted for a few hours in broad daylight and stripped of their possessions.
These attacks are often perpetrated by small groups of individuals dressed in police uniforms. The threat is particularly high in the Gombe district in Kinshasa.
If you plan to travel to the DRC despite the risks:
- be vigilant at all times
- avoid walking in areas accessible to the public
- use varied and unpredictable routes and schedules
- travel only in a convoy of at least two vehicles for long trips
- if you are threatened, don’t resist
Curfews can be imposed without notice.
Always comply with the directives issued by local authorities.
Road safety
Road safety is poor throughout the country. Fatal accidents are frequent.
Road conditions
Roads are generally poorly maintained and badly lit throughout the country.
Some roads can become impassable during the rainy season and require a four-wheel drive vehicle, including in some parts of the capital, Kinshasa.
The road between Kinshasa and Matadi is paved, but the risk of accidents is very high due to:
- vehicles that are poorly maintained, overloaded and often abandoned on the road
- insufficient lighting
- lack of road signs
Driving habits
Drivers don't always respect traffic laws, and police rarely enforce it. Drivers can be aggressive and reckless.
If you drive in the DRC:
- always drive defensively
- plan your trip in advance, especially if you are visiting a rural area
- only travel in convoys of at least two vehicles on long journeys
- avoid traveling after dark
- check with local authorities to see if you need authorization to travel within the country
Official motorcades
Motorists should pull over to the shoulder of the road when sirens or police announce the approach of presidential or other official motorcades.
- Avoid taking photos of processions
- Only proceed when the police signal for you to do so
Local authorities may increase the number of roadblocks during the night, especially at the following locations:
- in Limete, Ngaba, Kintambo, Ngaliema, Ndjili and Mont Ngafula
- around Camp Kokolo
Carry official identification at all times.
Don't cross any roadblock without stopping, even if it seems unguarded.
Representatives of local authorities may try to confiscate your identification in hopes of receiving a bribe to return them. To reduce this risk in the event of an identification check, try as much as possible to show your identification without lowering your car window.
Law enforcement impersonation
Criminals may impersonate law enforcement officers to extort money from you.
- If you are stopped by an officer, ask to see proof identity
- Don't get into a car with strangers, even if they claim to be police officers
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment or verbal abuse.
Advice for women travellers
Tourist infrastructure
Tourist facilities are very limited in Kinshasa and virtually non-existent outside the capital.
- Plan your trip accordingly
- Keep a supply of water, food and fuel on hand
- Bring a cell phone, charger and local emergency numbers
Power outages
Power outages can occur on a nationwide scale.
Local authorities may impose electricity rationing measures.
Power outages sometimes disrupt essential services, such as:
- public transport, including flights
- medical services
- public water supply
- telecommunications
- purchase of essential goods
Not all buildings have generators.
- Plan accordingly
- Make sure you always have a complete emergency kit on hand
Telecommunications
The telecommunications network is not always reliable. Fixed telephone lines are virtually non-existent, and cell phone coverage can be intermittent.
Internet access may be limited during periods of civil unrest.
- Don't rely on your cell phone in an emergency, especially outside major cities
- Avoid traveling alone
- Inform someone close to you of your itinerary
Public transportation
Public transport in the DRC is neither reliable nor safe.
You can rent a car with or without a driver from rental companies or travel agencies.
If you're going to Kinshasa, make sure someone meets you at the airport.
Avoid using public transport, including cabs, especially after dark.
Bus routes are not well displayed, and bus stops are poorly located. Vehicles are often overloaded and in very poor condition. Accidents are frequent.
Only use tour operators offering direct routes from your point of departure.
Taxis and ride-sharing apps
Not all taxis are officially marked, and they generally do not meet safety or mechanical reliability standards. Some ride-sharing apps are available in Kinshasa.
If you need to take a taxi:
- use an officially marked, reliable cab company recommended by your hotel
- never share a cab with strangers
- use a recommended car apps in Kinshasa
Rail service is limited and unsafe. Accidents occur regularly. Poor track conditions and mechanical breakdowns often cause delays. Trains are crowded and often frequented by thieves.
Ferries are available in many parts of the country, but most are unsafe. Ferry accidents occur regularly.
If you decide to take a ferry:
- only use the services of a reliable company
- always confirm the departure time before arriving at the port
- make sure the appropriate safety equipment is available
- don't board a boat that looks overloaded or unseaworthy
Pirate attacks and armed robbery against ships occur in coastal waters. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from Congolese authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave from DRC.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required - students must obtain a tourist visa Transit visa: required
To enter DRC, Canadians must obtain a visa from the DRC embassy in Ottawa before leaving Canada.
You cannot obtain a visa at a port of entry or at a DRC embassy other than that of your country of residence.
Foreign diplomatic missions and consulates in Canada
Difficulties at ports of entry
Travellers going to DRC commonly encounter difficulties at the airport and other ports of entry.
Arrival at N’Djili International Airport in Kinshasa can be chaotic. Travellers can sometimes be temporarily detained and asked by security and immigration officers to pay unofficial “special fees.”
Departure tax
All air passengers leaving DRC must pay an airport infrastructure development tax (IDEF) in the amount of US$58 (subject to change without notice). You must obtain proof of payment of the IDEF (called a Go Pass) to be permitted to board your flight. This document is available at special counters in banks or designated institutions, and at airports.
Crossing to Brazzaville
To cross the Congo River from Kinshasa to Brazzaville, you must have an entry visa issued by the Embassy of the Republic of Congo (Brazzaville).
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Polio: Advice for travellers - 17 April, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Mpox (monkeypox): Advice for travellers - 16 April, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is a risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of yellow fever vaccination for travellers from all countries.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is recommended.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of their trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites .
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
This destination is in the African Meningitis Belt, an area which has the highest rates of meningococcal disease in the world. Meningococcal disease is a serious and sometimes fatal infection.
Travellers who are at higher risk should discuss vaccination with a health care provider. High-risk travellers include those living or working with the local population (e.g., health care workers) or those travelling to crowded areas or taking part in large gatherings.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes.
Malaria is a risk to travellers to this destination. Antimalarial medication is recommended for most travellers to this destination and should be taken as recommended. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times:
- Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin.
- Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows.
- Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area.
- Wear permethrin-treated clothing.
If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Polio (poliomyelitis) is an infectious disease that can be prevented by vaccination. It is caused by poliovirus type 1, 2 or 3. Wild poliovirus (WPV1) and/or circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV1 or cVDPV3)) is/are present in this destination.
This destination is subject to Temporary Recommendations under the World Health Organization’s polio Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) .
Polio is spread from person to person and through contaminated food and water. Infection with the polio virus can cause paralysis and death in individuals of any age who are not immune.
Recommendations:
- Be sure that your polio vaccinations are up to date before travelling. Polio is part of the routine vaccine schedule for children in Canada.
- One booster dose of the polio vaccine is recommended as an adult .
- Make sure that the polio vaccinations are documented on the International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis. This is the only document accepted as proof of vaccination. It is provided at Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres .
- Carry the certificate as proof of vaccination.
Proof of vaccination:
- Travellers who are visiting for longer than 4 weeks may be required to receive a dose of polio vaccine 1 to 12 months before they leave this destination. This may be required even if you have previously received all the recommended polio vaccine doses as part of the routine vaccine schedule in Canada.
- Make sure that the polio vaccination is documented on the International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
There is a risk of schistosomiasis in this destination. Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by tiny worms (blood flukes) which can be found in freshwater (lakes, rivers, ponds, and wetlands). The worms can break the skin, and their eggs can cause stomach pain, diarrhea, flu-like symptoms, or urinary problems. Schistosomiasis mostly affects underdeveloped and r ural communities, particularly agricultural and fishing communities.
Most travellers are at low risk. Travellers should avoid contact with untreated freshwater such as lakes, rivers, and ponds (e.g., swimming, bathing, wading, ingesting). There is no vaccine or medication available to prevent infection.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a tsetse fly. Tsetse flies usually bite during the day and the bites are usually painful. If untreated, the disease is eventually fatal. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from bites especially in game parks and rural areas. Avoid wearing bright or dark-coloured clothing as these colours attract tsetse flies. There is no vaccine available for this disease.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Onchocerciasis (river blindness) is an eye and skin disease caused by a parasite spread through the bite of an infected female blackfly. Onchocerciasis often leads to blindness if left untreated. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from blackfly bites, which are most common close to fast-flowing rivers and streams. There is no vaccine available for onchocerciasis although drug treatments exist.
Lymphatic filariasis , also known as elephantiasis, is caused by filariae (tiny worms) spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause a range of illnesses. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from mosquito bites. There is no vaccine available for lymphatic filariasis although drug treatments exist.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
There is a risk of plague in this country. Plague is a bacterial disease that can cause serious illness, and if left untreated, death.
The occurrence of cases in areas where the plague bacteria are known to circulate can be influenced by weather and environmental conditions. In some countries, this results in seasonal outbreaks. Travellers to areas where plague routinely occurs may be at risk if they are camping, hunting, or in contact with rodents.
Plague is spread by:
- bites from fleas infected with the plague
- direct contact with body fluids or tissues from an animal or person who is sick with or has died from plague
Overall risk to travellers is low. Protect yourself by reducing contact with fleas and potentially infected rodents and other wildlife.
Mpox (monkeypox) is a risk in this country. It is a viral disease that can cause serious illness in some circumstances. Risk is generally low for most travellers.
Mpox spreads in 3 ways:
- from animals to humans through direct contact or by eating or preparing undercooked meat of infected animals or coming into contact with an infected animal's body fluids
- from person to person through close contact, including direct contact with the skin lesions, blood, body fluids, or mucosal surfaces (such as eyes, mouth, throat, genitalia, anus, or rectum) of an infected person
- through direct contact with contaminated objects such as bedding and towels, or by sharing personal objects used by an infected person
Follow recommended public health measures and avoid contact with animals such as rodents and primates to help prevent getting or spreading the infection.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks and impairs the immune system, resulting in a chronic, progressive illness known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
High risk activities include anything which puts you in contact with blood or body fluids, such as unprotected sex and exposure to unsterilized needles for medications or other substances (for example, steroids and drugs), tattooing, body-piercing or acupuncture.
Sporadic outbreaks of Ebola disease occur in this country.
Ebola disease can be caused by 6 different viruses, including Sudan virus and Ebola virus, which spread through contact with infected bodily fluids (from people or animals). It is very serious and often fatal.
Practise good hygiene (frequent and proper hand washing) and avoid contact with the body fluids of people with Ebola disease or unknown illnesses. Avoid contact with wild animals.
Of the different viruses that cause Ebola disease, there is only a vaccine to prevent disease caused by Ebola virus. It is available under certain circumstances; however, it is not authorized for sale in Canada. There are currently no approved vaccines or effective treatments for Ebola disease caused by the other viruses, including Sudan virus.
Medical services and facilities
Health care is adequate in Kinshasa and Lubumbashi. Public facilities may lack medical supplies and equipment.
Doctors and hospitals generally require immediate payment.
Medical evacuation is often very costly and may be necessary in the event of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Some prescription medications may not be available in the DRC.
If you take prescription medications, you’re responsible for determining their legality in the DRC.
- Bring sufficient quantities of your medication with you
- Always keep your medication in the original container
- Pack them in your carry-on luggage
- Carry a copy of your prescriptions
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Persons convicted of the possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs can expect prison terms and heavy fines.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Identification
Local authorities may ask you to present your passport and visa at any time. In such situations, you should remain calm and cooperative. Failure to comply could result in expulsion.
- Always carry a certified copy of your passport and visa with you
- Always keep your original passport in a secure place
Photographs
It is forbidden to take photographs, under penalty of arrest or detention, of the following places:
- government buildings
- military installations
Dress and behavior
The DRC is a conservative society. Public displays of affection, including holding hands or kissing, are not socially acceptable.
To avoid offending local residents:
- dress conservatively
- behave with discretion
- respect social and religious traditions
- ask permission before taking their photos
Lèse-majesté
The law forbids disrespecting the head of state, as well as making remarks alleged to threaten national security and malicious comments in public.
Local authorities have sometimes intimidated, harassed, and arrested journalists, activists, and politicians when they have publicly criticized the government, president or state security forces.
Penalties can be severe, including imprisonment.
You should carry an International Driving Permit.
International Driving Permit
Other traffic laws
Motorists and pedestrians are required to stop for the raising and the lowering of the national flag at approximately 7:30 a.m. and 6 p.m. every day. Failure to do so may result in a fine.
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in the DRC.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of the DRC, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and the DRC.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in the DRC by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in the DRC to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
The currency is the Congolese franc (CDF).
The DRC is a cash-based economy. The US dollar is widely accepted. Shopkeepers and foreign exchange dealers require banknotes to be in good condition (without tears and of recent issue, i.e. US dollars printed after 2009).
Credit cards are generally not accepted, except in certain hotels, restaurants and department stores.
Large hotels have ATMs where cash advances can be made using certain credit cards, but these are not always in operation.
Currency declaration
You must declare:
- any sum equivalent to more than US$10,000 upon arrival in the country
- any foreign currency upon exit from the country
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from April to October in the north and from November to March in the south. Flash flooding and landslides may occur during these periods and could severely disrupt essential services.
If you are in the affected areas:
- exercise caution
- monitor local news and weather reports
Seismic activity
The DRC is located in an active seismic area. Earthquakes may occur.
Earthquakes - What to Do?
Volcanic eruptions are common in some parts of the country. Mount Nyiragongo, situated on the edge of Goma, is one of the world’s most active volcanoes. The latest eruption in May 2021 forced the evacuation of hundreds of thousands of people, caused significant damage to infrastructure and resulted in many casualties.
If you are travelling near an active volcano:
- take official warnings seriously and respect exclusion zones
- monitor local media to stay up-to-date on latest developments and volcanic activity levels
- follow the advice of local authorities
Forest fires and bush fires
Forest and bush fires are frequent from June to August. Fire risk ratings and high alert levels may be issued in affected areas. Air quality in an area affected by a forest fire may deteriorate due to thick smoke.
In the event of a major fire:
- stay away from affected areas, especially if you suffer from respiratory problems
- prepare to modify your itinerary or even evacuate the area quickly
- follow the instructions of local emergency services personnel
- check local media regularly for updates
Local services
There is no centralized number to reach emergency services. Research and carry contact information for local police and medical facilities.
Consular assistance
Republic of Congo
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada in Kinshasa and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Travel advice for Democratic Republic of Congo

Switzerland and the Democratic Republic of Congo
Eda.base.components.templates.base.accesskeys.
- Travel advice
Start of page Last update 27.11.2017
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
There’s no central number for emergency services. Check for local medical facilities and carry contact details with you.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Health risks and recommended vaccines
Check TravelHealthPro’s current advice on the Republic of Congo to find out how to reduce the health risks you’ll face there.
TravelHealthPro also lists the recommended vaccines that could apply to you. At least 8 weeks before you travel, check how to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
If you take medication, bring enough for your time in the Republic of Congo and make sure it is clearly labelled. Bring a copy of any prescription.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad .
Healthcare facilities in the Republic of Congo
Medical facilities in the country are limited, particularly in rural areas. Medical evacuation is likely to be necessary for all but the most basic treatments. If you become ill while in the Republic of Congo or straight after leaving the country, get immediate medical advice.
Make sure you have adequate travel and medical insurance to cover the cost of any medical treatment abroad and repatriation; this should specifically include the very high costs of evacuation by air ambulance.
FCDO has a list of medical providers in the Republic of Congo where some staff will speak English.
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

Crisis in the DRC: What you need to know and how to help
Four reasons why the IRC’s Emergency Watchlist identifies the Democratic Republic of Congo as one of the countries most at risk of experiencing a worsening crisis in 2024.
Intense conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has displaced millions and is driving humanitarian needs across the country while regional tensions remain high, especially with neighboring Rwanda. Meanwhile, flooding, food insecurity, the outbreak of disease and severe barriers to humanitarian action threaten to exacerbate the situation.
These factors have pushed the DRC into the top 10 of the 2024 Emergency Watchlist—a report that analyzes and ranks the countries most likely to experience a worsening humanitarian crisis.
These are the risks that the DRC faces in 2024.
Donate today
Escalating conflict in eastern drc is worsening humanitarian conditions.
Intense conflict persists in Eastern DRC, even after the government's ceasefire with the M23 nonstate armed group in March 2023, leading to a significant increase in internal displacement. The DRC is currently facing one of the most substantial displacement crises globally, with approximately 6.9 million people displaced throughout the country. Among the internally displaced, 5.6 million individuals are located in the country's eastern regions, highlighting a pronounced regional demand for aid.
Weak governance in the DRC has paved the way for more than 120 armed groups to operate in Eastern DRC. This includes the M23 group and the Islamic State-affiliated Allied Democratic Forces (ADF) which has escalated attacks throughout 2023, with reports of an increase in civilian killings and sexual violence.
An increasing number of displaced individuals are seeking refuge in camps, where resident communities already endure unstable living conditions and limited service access. Security is a pressing issue in these settings, especially for women and girls.

Political tensions could spark renewed regional violence
The run-up to the DRC’s December 2023 elections sparked political tensions across the country and came amid escalating regional tensions, especially with neighboring Rwanda. The Congolese and Rwandan governments have exchanged accusations of supporting armed groups in the border regions, posing a risk of wider conflict in 2024.
The U.N. has voiced concerns about the possibility of a confrontation between the two countries. Meanwhile, the U.N. is winding down its peacekeeping mission in the DRC, amidst pressure from the government and persistent protests stemming from the perception that the U.N. has failed to improve security conditions.

El Niño could lead to flooding, food insecurity and disease
The DRC is highly vulnerable to flooding, partly due to deforestation and rising water levels in Lake Albert—which caused flooding in the country’s eastern Ituri province in May 2023. The looming El Niño season of 2024 is expected to bring above-average rainfall to the DRC, particularly in it’s northern and central regions.
The impending El Niño season is anticipated to usher in above-average rainfall in the DRC, heightening the potential for nationwide flooding. This surge in rainfall may lead to significant displacement and worsen the transmission of communicable diseases, further escalating the already dire cholera crisis in the DRC .
A lack of access to water and sanitation services in overcrowded camps for internally displaced persons is contributing to the spread of disease at a time when the country’s health system is on the brink of collapse . Those affected include the DRC’s food-insecure populations—one of the largest in the world—who are likely to experience worsening outcomes amid the combined impacts of conflict and flooding.

Constraints on humanitarian access impede service delivery
Despite immense needs in the country, the DRC’s 2023 humanitarian response plan received just 40% of its necessary funding, causing shortfalls in critical service provision and aid delivery. Meanwhile, ACAPS rated constraints on humanitarian access to be “very high” (4 of 5), particularly in conflict-affected regions, and cites a deterioration in conditions since 2022.
Bureaucratic constraints, such as visa restrictions, have grown while protests against the U.N.’s peacekeeping mission in the country indicate growing local suspicion of international actors, including humanitarians.
How is the IRC responding to the crisis in the DRC?
Since 1996, the IRC has been responding to crises in the Democratic Republic of Congo by providing emergency assistance to individuals and fostering communal social cohesion in partnership with local organizations. We also provide essential health services, including primary health, infection prevention and control, as well as water, sanitation and hygiene .
We reinforce violence prevention and support survivors of gender-based violence through comprehensive interventions, including providing psychosocial support, facilitating economic recovery, and ensuring access to essential services (such as legal and medical assistance), particularly in eastern DRC where there is a severe protection crisis. Our approach involves collaboration with communities and their institutions to promote social cohesion aimed at reducing conflict and supporting primary and secondary schools.
Learn more about the IRC’s work in the DRC .

How can I help the Democratic Republic of the Congo?
The IRC is working with partners to deliver critical emergency aid to families in the Democratic Republic of Congo and conflict zones around the world. Donate now to support our critical work . We are on the frontlines providing critical aid to crisis-affected people in more than 50 countries, including places on the 2024 Emergency Watchlist.
Read more about the top 10 crises the world can’t ignore in 2024 and download the full 2024 Emergency Watchlist report for profiles of all 20 crisis countries on the IRC's list.
*Last name excluded for privacy
Explore related topics:
- 2024 Watchlist
Related news & features

- Where We Work
- How To Help
- Code of Conduct
- Ethics Hotline
- 87% Program services
- 8% Management and general
- 5% Fundraising
Get the latest news about the IRC's innovative programs, compelling stories about our clients and how you can make a difference. Subscribe
- U.S./Global
- Phone Opt Out
- Respecting Your Privacy
- Terms and Conditions
- Fraud Prevention
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Republic of the Congo Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in the Congo. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 2 Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Updated Global Polio April 26, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines. Destination List: Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Guinea, Indonesia, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Republic of the Congo, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, including Zanzibar, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Measles April 26, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Timor-Leste (East Timor), Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Active cholera transmission is localized to Niari (last case reported 6–9 months ago) and Pool (last case reported 6–9 months ago) in the Republic of the Congo. Cholera is rare in travelers. Certain factors may increase the risk of getting cholera or having severe disease ( more information ). Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera.
Vaccination may be considered for children and adults who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to the Congo.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to the Congo. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to the Congo.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to the Congo take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for the Congo.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in the Congo. If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in the Congo, there may be limited or no rabies treatment available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to the Congo.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for all arriving travelers ≥9 months old.
Recommended for all travelers ≥9 months old.
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
African sleeping sickness (african trypanosomiasis).
- Tsetse fly bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
African Trypanosomiasis
African Tick-Bite Fever
African Tick-bite fever
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Mosquito bite
Avoid animals
- Touching infected animals (including bats and primates) or their body fluids
- Touching body fluids (blood or sweat) from an infected person
- Touching objects contaminated with the body fluids of a person infected with Ebola or Marburg virus
- Avoid sick people
- Avoid animals and areas where they live
Ebola virus
- Scratched or bitten by an infected animal such as a rodent or primate
- Touching an infected animal or touching animal products, including skins and meat
- Being near an infected person who is coughing or sneezing
- Touching the body fluids or rash of a person with monkeypox
- Avoid animals and animal products
- Avoid people who are sick
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in the Congo, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in the Congo. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in the Congo include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis, a parasitic infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in the Congo. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call the Congo’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in the Congo. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of the Congo may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in the Congo, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Congo, Republic of the for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

28 Facts About the Democratic Republic of Congo
From diverse flora and fauna to a tragic history, these are the most interesting facts about the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Official name: Democratic Republic of the Congo
Capital city: Kinshasa
Population: 111.8 million
Area: 2,344,858 sq km
Major languages: French, Lingala, Kingwana, Kikongo, Tshiluba
Time zone: UTC+1 (West / Central African Time)
Interesting facts about the Democratic Republic of Congo
1. The Democratic Republic of Congo in Central Africa is often referred to as DRC, DR Congo and sometimes Congo (Kinshasa) to distinguish it from the Republic of the Congo which is often referred to as Congo (Brazzaville).
Note: we refer to the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) as DR Congo below.
2. Harpoon tips discovered on the banks of the Semliki River in DR Congo are more than 90,000 years old and some of the earliest instruments ever shaped by modern humans using a material other than stone or wood.
3. The Kingdom of Kongo ruled much of the region from the 14th to 19th centuries.
4. In 1482, Portuguese navigator Diogo Cao became the first European to visit the Congo setting up ties with the king of Kongo.
5. Belgium’s King Léopold II set up a private venture to colonise Kongo from the 1870s onwards. The colony was the largest private estate ever acquired by a single man and possibly led to the deaths of 10 million people.
6. DR Congo’s flag consists of a blue background with a yellow-bordered red diagonal stripe running across it and a yellow star in the top left corner. The flag dates from 1877 and was initially blue with a gold star symbolizing a shining light in the “Dark Continent.”
7. In 1960, DR Congo finally gained independence from Belgium.
8. DR Congo’s recent history has been plagued by civil war, conflict and political upheaval. It has been at the centre of what has been called “Africa’s world war”, which directly or indirectly killed up to six million people.
9. In 1971, the country was renamed Zaire and the River Congo became the River Zaire following a military takeover. The country reverted to the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1997.
10. At 2,900mi (4,700 km), the Congo River, which runs through DR Congo, is Africa’s second-longest river after the Nile. It is also the world’s deepest river.
11. From 1874-77, famed British explorer Henry Stanley became the first to navigate the Congo River to the Atlantic Ocean. The city of Kisangani (Stanleyville) and the Boyoma Falls (Stanley Falls) were named after him. The Boyoma Falls are a 100km (60mi) stretch of seven cataracts that are the last point ships can travel upriver from Kinshasa.
12. DR Congo’s capital city, Kinshasa, is located on the Congo River opposite Brazzaville, the capital of Congo (Republic of Congo). The two cities are 2.96 mi (4.76 km) apart, making them the closest capital cities in the world. Rome and Vatican City are closer, but Vatican City is not a UN member and as it’s a city-state, it technically doesn’t have a capital.
13. From 1881, Kinshasa was called Léopoldville after King Léopold II of Belgium. In 1966, the city was renamed Kinshasa, after a village that once stood near the site.
14. DR Congo’s capital city Kinshasa, with a population of more than 12 million, is the world’s largest French-speaking city.
15. The world’s second-largest rainforest, the Congolese Rainforest, is part-located in DR Congo. The Congolese Rainforest spans six countries: Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon.
16. The Congo Basin spans six countries including DR Congo. The Congo Basin makes up one of the most important wilderness areas on Earth and is home to approximately 10,000 plant species, 400 mammal species, 1,000 bird species and 700 fish species.
17. As such, DR Congo is one of 17 megadiverse countries in the world. Megadiverse countries are the world’s most biodiversity-rich countries.
18. There are more than 200 African ethnic groups in DR Congo. The majority are Bantu with the four largest tribes – Mongo, Luba, Kongo (all Bantu) and the Mangbetu-Azande (Hamitic) – making up around 45% of the population.
19. DR Congo and the Congo Basin countries are home to the ethnic group of Pygmy people, known for their short stature – typically under five feet tall. The word “Pygmy” comes from the Greek for “dwarfish”, although pygmies are conventionally proportioned.
20. In 1904, Pygmy Ota Benga was kidnapped from what is now DR Congo and taken to the US, where he was exhibited with monkeys in a zoo. More than a century later, the Bronx Zoo in New York finally issued an apology.
21. DR Congo has five UNESCO World Heritage Sites. All are natural heritage sites and include four national parks and one wildlife reserve.
22. The UNESCO-listed Virunga National Park is Africa’s oldest national park and home to an array of wildlife and natural landscapes including mountain gorillas and chimpanzees as well as the active volcano Nyiragongo.
23. The DR Congo is home to the endangered okapi , a unique creature often referred to as the “forest giraffe” due to its appearance resembling a blend of a deer and a zebra. The okapi is found exclusively in the wild within the Ituri Rainforest of the DR Congo.
24. DR Congo is the world’s 11th-largest and Africa’s second-largest country after Algeria.
25. DR Congo would be landlocked if it weren’t for a 25-mile (40-km) coastline on the Atlantic Ocean.
26. Mount Nyiragongo is one of the world’s most dangerous volcanoes and is known locally as “General Nyiragongo”. In 2002, lava from the volcano destroyed part of the nearby city of Goma.
27. DR Congo is potentially one of the world’s richest countries with vast natural resources including cobalt, copper, niobium, tantalum, petroleum, industrial and gem diamonds, gold, silver, zinc, manganese, tin, uranium, coal, hydropower and timber.
28. However, DR Congo is the world’s fourth poorest country when measured by GDP per capita based on purchasing power parity (PPP).
Every effort has been made to verify these facts about the Democratic Republic of Congo. However, if you find an error or have any questions, please contact us .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Travel Advisory. July 31, 2023. Democratic Republic of the Congo - Level 3: Reconsider Travel. O K U T C. Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed. Reconsider travel to the Democratic Republic of Congo due to crime and civil unrest. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Review the Traveler's Checklist. Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel. +242 06 612 2000. +242 06 612 2010. No Fax. [email protected]. https://cg.usembassy.gov/. Republic of the Congo Map. View Larger Map.
FCDO travel advice for the Republic of Congo. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers should carefully consider the risks of travelling to the Republic of Congo. Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics. Money. The currency in the Republic of Congo is the CFA franc (XAF). The economy is primarily cash-based.
FCDO advises against all travel to the provinces of: Haut-Uélé and Ituri, including the entire DRC-South Sudan border. North Kivu, including all travel by air into and out of Goma airport, but ...
Mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo February 16, 2024 There is an outbreak of mpox in 22 out of 26 provinces, including urban areas, in the DRC. Global Polio January 05, 2024 Some international destinations have circulating poliovirus. Before any international travel, make sure you are up to date on your polio vaccines.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Reconsider travel to Democratic Republic of the Congo due to COVID-19, crime, civil unrest and Ebola. ... Consult a doctor for preventive medical advice. Many diseases present in the DRC have symptoms similar to Ebola. If suspected to have Ebola, you could face travel delays, quarantine, and extremely expensive medical costs. ...
FCDO travel advice for the Republic of Congo. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Be alert to possible threats. The security situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is volatile. Conflict between government forces and armed groups in the east is ongoing. If it's safe to do so, leave affected areas. There's an ongoing threat of terrorist attacks in the DRC, particularly in eastern DRC.
Safe transport in The Republic of the Congo. Roads in Brazzaville are relatively well maintained. If you want to travel south from the capital, you should consider flying, as road and train travel from Brazzaville to Pointe Noire is not recommended for safety concerns. There is a well-paved highway to go north towards the city of Ouesso.
Republic of Congo. Africa. A land of steamy jungles hiding half the world's lowland gorillas, masses of forest elephants, and hooting, swinging troops of chimpanzees, the Republic of Congo is on the cusp of becoming one of the finest ecotourism destinations in Africa. 01 / Attractions.
To cross the Congo River from Kinshasa to Brazzaville, you must have an entry visa issued by the Embassy of the Republic of Congo (Brazzaville). Children and travel. Learn more about travelling with children. Yellow fever. Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Democratic Republic of Congo. Carpeted by huge swaths of rainforest and punctuated by gushing rivers and smoking volcanoes, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC, formerly Zaire) is the ultimate African adventure. As much a geographical concept as a fully fledged nation, DRC has experienced one of the saddest chapters in modern history ...
For additional travel information. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency. Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern ...
If you become ill while in the Republic of Congo or straight after leaving the country, get immediate medical advice. Make sure you have adequate travel and medical insurance to cover the cost of any medical treatment abroad and repatriation; this should specifically include the very high costs of evacuation by air ambulance.
FCDO travel advice for the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
If you are planning international travel at this time, please read our COVID-19 related travel advice here, alongside our destination specific travel advice below. Do not travel. Do not travel to eastern and north-eastern regions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), including the provinces of Bas-Uélé, Haut-Uélé, Haut Lomami ...
Travel Advice and Advisories from the Government of Canada for Democratic Republic of Congo (Kinshasa) Skip to main content; ... Democratic Republic of Congo (Kinshasa) travel advice. Avoid non-essential travel (with regional advisories) Latest updates: Editoral change. Last updated: April 6, 2023 09:47 ET. On this page.
Earthquakes occasionally take place in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The most recent one occurred in 2015 and measured approximately 5.6 on the Richter scale. If travelling to or living in the Democratic Republic of Congo, make sure you know what to do in the event of an earthquake. Volcanos
All consular services and visa support for people resident in Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of Congo and Gabon are provided by the Embassy of Switzerland in Democratic Republic of the Congo. Information can be found on the websites concerned: Services - Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of Congo and Gabon
FCDO travel advice for the Republic of Congo. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Intense conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has displaced millions and is driving humanitarian needs across the country while regional tensions remain high, especially with neighboring Rwanda. Meanwhile, flooding, food insecurity, the outbreak of disease and severe barriers to humanitarian action threaten to exacerbate the situation.
Active cholera transmission is localized to Niari (last case reported 6-9 months ago) and Pool (last case reported 6-9 months ago) in the Republic of the Congo. Cholera is rare in travelers. Certain factors may increase the risk of getting cholera or having severe disease (more information).Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera.
DR Congo's capital city, Kinshasa, is located on the Congo River opposite Brazzaville, the capital of Congo (Republic of Congo). The two cities are 2.96 mi (4.76 km) apart, making them the ...