You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Guatemala Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in Guatemala. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Dengue in the Americas April 18, 2024 Dengue is a risk in many parts of Central and South America, Mexico, and the Caribbean. Some countries are reporting increased numbers of cases of the disease. Travelers to the Americas can protect themselves by preventing mosquito bites. Destination List: Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, including the Galápagos Islands, French Guiana (France), Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Martinique (France), Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Turks and Caicos Islands (U.K.), Uruguay
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Guatemala.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Guatemala. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Guatemala.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Guatemala take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Guatemala.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Guatemala. If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Guatemala, there may be limited or no rabies treatment available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Guatemala.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥1 year old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites, chagas disease (american trypanosomiasis).
- Accidentally rub feces (poop) of the triatomine bug into the bug bite, other breaks in the skin, your eyes, or mouth
- From pregnant woman to her baby, contaminated blood products (transfusions), or contaminated food or drink.
- Avoid Bug Bites
Chagas disease
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Guatemala, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Guatemala. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Guatemala include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Guatemala. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Guatemala’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Guatemala. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Guatemala may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Guatemala, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Guatemala, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Guatemala .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Guatemala for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.

Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Places the U.S. Government Warns Not to Travel Right Now
You may want to reconsider traveling to these countries right now.
Do Not Travel to These Countries

Getty Images
Crime, civil unrest and terrorism are common risk factors for countries that end up on the State Department's "Do Not Travel" advisory list.
In 2024, tourism across the globe is “well on track” to return to pre-pandemic levels, according to projections by UN Tourism.
Global conflicts and natural disasters , ranging from a series of coups across Africa to catastrophic earthquakes in the Middle East affected international travel patterns throughout 2023. Still, international tourist arrivals reached 87% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023, according to estimates by UN Tourism .
In January 2024 alone, about 4.6 million U.S. citizens left the country for international destinations, 17% higher than the same month in 2019, according to the International Trade Administration . But some destinations warrant more caution than others.
On Oct. 19, 2023, following the outbreak of war between Israel and Gaza and flaring tensions in the region, the U.S. State Department issued a worldwide caution advisory due to “increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests.” Prior to this update, the most recent worldwide caution advisory was issued in 2022 after a U.S. strike killed Ayman al-Zawahiri, Osama bin Laden’s successor as leader of Al Qaeda, causing “a higher potential for anti-American violence.” The worldwide caution advisory remains in effect.
The U.S. State Department also issues individual travel advisory levels for more than 200 countries globally, continually updating them based on a variety of risk indicators such as health, terrorism and civil unrest. Travel advisory levels range from Level 1, which means exercise normal precautions, to Level 4, which means do not travel there.
About 10% of countries – 19 total – have a Level 4: “Do Not Travel” advisory as of Mar. 4. In Level 4 countries, the U.S. government may have “very limited ability” to step in should travelers’ safety or security be at risk, according to the State Department. Crime, civil unrest, kidnapping and terrorism are common risk factors associated with Level 4 countries.
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list.
Places With a Level 4 Travel Advisory
These are the primary areas the U.S. government says not to travel to right now, in alphabetical order:
Jump to Place: Afghanistan Belarus Burkina Faso Central African Republic Myanmar (formerly Burma) Gaza Haiti Iran Iraq Libya Mali Mexico North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) Russia Somalia South Sudan Sudan Syria Ukraine Venezuela Yemen
Afghanistan: The Central Asian country is wrestling with “terrorism, risk of wrongful detention, kidnapping and crime,” according to the State Department. U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for wrongful detention and kidnapping. In 2022, the government reinstituted public floggings and executions, and women’s rights are disappearing under Taliban control. The U.S. Embassy in Kabul halted operations in August 2021. Since the Taliban took control , many forms of international aid have been halted . Meanwhile, in 2023, some of the year’s deadliest earthquakes killed more than 2,400 in Afghanistan while the country continues to face a years-long extreme drought.
Belarus: Belarus, which shares a western border with Russia and a southern border with Ukraine, has been flagged for “Belarusian authorities’ continued facilitation of Russia’s war against Ukraine, the buildup of Russian military forces in Belarus, the arbitrary enforcement of local laws, the potential of civil unrest, the risk of detention, and the Embassy’s limited ability to assist U.S. citizens residing in or traveling to Belarus.” The U.S. Embassy in Minsk halted operations in February 2022.
Burkina Faso: Terrorism, crime and kidnapping are plaguing this West African nation. Terrorist attacks may target hotels, restaurants and schools with little to no warning, and the East and Sahel regions of the country are under a state of emergency. In late November 2023, hundreds died in clashes between state security forces and rebels near the country’s border with Mali. In June, more than 2 million people in Burkina Faso were displaced due to “violence linked to al-Qaida and the Islamic State group.”
Central African Republic: While there have not been specific incidents of U.S. citizens targeted with violence or crime, violent crime and sudden closure of roads and borders is common. The advisory states that “Embassy Bangui’s limited capacity to provide support to U.S. citizens, crime, civil unrest, and kidnapping” is a factor in its assessment. Recent data from UNICEF suggests the country has the worst drinking water accessibility of all countries in 2022.
Myanmar (Formerly Burma): Armed conflict and civil unrest are the primary reasons to not travel to this Southeast Asian country, which experienced a military coup in early 2021. Limited health care resources, wrongful detentions and “areas with land mines and unexploded ordnance” are also listed as risk factors. After Ukraine and Israel, Myanmar had the highest conflict-related death toll in 2023.
Gaza : Hamas, a foreign terrorist organization as designated by the State Department, controls much of the Gaza Strip, which shares borders with both Israel and Egypt. On Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas fighters broke across the border into Israel, killing hundreds of civilians and soldiers in a brazen attack that stunned Israelis. On Oct. 10, Israel hit the Gaza Strip with “the fiercest air strikes in its 75-year conflict” according to Reuters . The conflict has since escalated into war between Israel and Hamas, with regular Israeli airstrikes leading to extensive civilian casualties in Gaza. As of mid-December, nearly 85% of Gaza’s population were displaced from their homes, according to UN estimates . The region continues to face shortages of food , water, electricity and medical supplies , with conditions deemed “far beyond a humanitarian crisis.” The State Department warns of terrorism and armed conflict within Gaza’s borders.
Haiti: In July 2023, the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Port-au-Prince in response to the increased risk of kidnapping and violent crime in the country , as well as armed conflict between gangs and police. The travel advisory states that cases of kidnapping “often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings.” The travel advisory also states that “U.S. citizens in Haiti should depart Haiti as soon as possible” given “the current security situation and infrastructure challenges.” A series of gang attacks in late September 2023 caused thousands to flee their homes, and many aid groups have been forced to cut or suspend operations amid escalating violence in recent months.
Iran: Terrorism, kidnapping and civil unrest are risk factors for all travelers to Iran, while U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for “arbitrary arrest.” U.S.-Iranian nationals such as students, journalists and business travelers have been arrested on charges of espionage and threatening national security. Executions in Iran rose sharply between 2021 and 2022, bringing the country’s total to nearly 580 people over the year, according to a report by Amnesty International released in May 2023.
Iraq: The State Department cites “terrorism, kidnapping, armed conflict [and] civil unrest” as cause for the country’s Level 4 distinction. Iraq’s northern borders, and its border with Syria, are especially dangerous. Since the escalation of conflict in neighboring Israel in October, there has been an increase in attacks against Iraqi military bases, which host U.S. troops and other international forces. In October 2023, non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members were ordered to leave the U.S. embassy in Baghdad.
Libya: Following the end of its dictatorship over a decade ago, Libya has been wrought with internal conflict between armed groups in the East and West. Armed conflict, civil unrest, crime, kidnapping and terrorism are all risk factors. U.S. citizens have been targets of kidnapping for ransom, with terrorists targeting hotels and airports frequented by Westerners. The U.S. Embassy in Tripoli halted operations in 2014. In mid-September 2023, floods, which some say were intensified by climate change , killed thousands in eastern Libya. Clashes between armed factions escalated across the country in the latter half of 2023, including in the capital city of Tripoli and in Benghazi.
Mali: After experiencing military coups in 2020 and 2021, crime, terrorism and kidnapping are all prevalent threats in this West African landlocked nation. In July 2022, non-emergency U.S. government employees and their families were ordered to leave the country due to higher risk of terrorist activity. A U.N. report in August 2023 said that military groups in the country, including both Mali security forces and possibly Russian Wagner mercenaries, were spreading terror through the use of violence against women and human rights abuses. Democratic elections were supposed to occur in February 2024, but Mali’s military junta postponed the plans indefinitely. In December, the U.N. officially ended a decade-long peacekeeping presence in the country, which had been among the agency’s deadliest missions, with hundreds of the mission personnel killed since 2013.
Mexico: Each state in Mexico is assessed separately for travel advisory levels. Six of the 32 states in Mexico are designated as Level 4: Colima, Guerrero, Michoacan, Sinaloa, Tamaulipas and Zacatecas. Crime and kidnapping are listed as the primary risk factors throughout the country. Nearly 112,000 people were missing across the country as of October, a number the U.N. has called “alarming.”
North Korea (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea): U.S. passports are not valid for travel “to, in, or through” this country, home to one of the world's longest-running dynastic dictatorships. The travel advisory states that the Level 4 distinction is due to “the continuing serious risk of arrest and long-term detention of U.S. nationals.” In July 2023, a U.S. soldier fled across the border into North Korea, where he is believed to be in North Korean custody, the first American detained in the North in nearly five years. He was returned to U.S. custody in September 2023.
Russia: The travel advisory for Russia cites its invasion of Ukraine , harassment of U.S. citizens by Russian government officials and arbitrary law enforcement as a few of the reasons for the Level 4 designation. Chechnya and Mount Elbrus are specifically listed as Level 4 regions. Terrorism, civil unrest, health, kidnapping and wrongful detention are all noted as risks.
Russia Invades Ukraine: A Timeline

Somalia: A severe drought resulting from five failed rainy seasons in a row killed 43,000 people in 2022, and caused a famine amid conflict with Islamist insurgents . Violent crime is common throughout Somalia , pirates frequent its coast off the Horn of Africa, and medical facilities, where they exist, have limited capacity. Crime, terrorism, civil unrest, health and kidnapping are all risk factors. In January 2024, some passengers aboard a U.N.-contracted helicopter were taken hostage by al-Shabaab militants after the vehicle crashed in central Somalia.
South Sudan: Crime, kidnapping and armed conflict are the primary risk factors for South Sudan, which separated from Sudan in 2011, making it the world’s newest country . Weapons are readily available, and travelers have been victims of sexual assault and armed robbery.
Sudan: The U.S. evacuated its embassy in Khartoum in April 2023, and the country closed its airspace due to the ongoing conflict in the country, only permitting humanitarian aid and evacuation efforts. Fighting has escalated in the region between two warring generals seeking to gain control after a military coup in 2021 ousted the country’s prime minister. Civil unrest is the primary risk factor for Africa’s third largest country by area. Crime, terrorism, kidnapping and armed conflict are also noted. The International Criminal Court began investigating alleged war crimes and violence against African ethnic groups in the country in 2023. Millions have fled their homes due to conflict, and the U.N. has said its efforts to provide aid have been hindered by a lack of support, safety and resources. As recently as December 2023, the United Nations warned of catastrophic famine , with millions of children at-risk for malnutrition .
Syria: The advisory states that “No part of Syria is safe from violence,” with terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, armed conflict and risk of unjust detention all potential risk factors. U.S. citizens are often a target for kidnappings and detention. The U.S. Embassy in Damascus halted operations in 2012. Fighting in neighboring Israel has escalated since October, and the conflict has spilled over into Syria, where the U.S. has carried out air strikes following drone and rocket attacks against American troops in Syria and Iraq, triggered by the Israel-Hamas war.
Ukraine: Russian setbacks in their invasion of Ukraine buoyed hopes in Ukraine in 2023. However, Ukraine is a Level 4 country due to Russia’s invasion, with crime and civil unrest also noted as risk factors. The country’s forces shot down two Russian fighter jets on Christmas Eve 2023, in a move Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said “sets the right mood for the entire year ahead.”
Venezuela: Human rights abuses and lack of health care plague this South American nation, which has been in a political crisis since 2014. In 2019, diplomatic personnel were withdrawn from the U.S. Embassy in Caracas. Threats in the country include crime, civil unrest, kidnapping, wrongful detention and poor health infrastructure.
Yemen: Six of the nine risk factors defined by the State Department – terrorism, civil unrest, health risks, kidnapping, armed conflict and landmines – are all present in Yemen. Despite private companies offering tourist visits to the Yemeni island of Socotra, the U.S. government argues those arranging such visits “are putting tourists in danger.” Civil war and cholera are also both present throughout the country. The U.S. Embassy in Sanaa halted operations in 2015. The country has experienced a relative lull in the civil war fighting, but as peace negotiations have gotten traction, flare ups in the fighting have jeopardized progress. Most recently, the U.S. and U.K. have carried out a series of airstrikes in the country, targeting Iran-backed Houthi sites.
Other Countries to Watch
Since Jan. 1, the State Department has updated travel advisories for 17 different countries as well as for the West Bank and Gaza, adding information about specific regions or risk factors, or simply renewing an existing advisory. Travel advisory levels can change based on several factors in a nation, such as increased civil unrest, policies that affect human rights or higher risks of unlawful detention.
The State Department has given about 25 countries an assessment of Level 3, meaning it recommends people “reconsider travel” to those destinations.
On Oct. 14, one week after the deadly Hamas attack on Israel, Israel and the West Bank were both moved from Level 2 to Level 3, while Gaza remains at Level 4. The region’s travel advisory was updated in November to reflect travel restrictions for certain government employees who have not already left the area, and it was updated again on Jan. 3.
Following the outbreak of the Israel-Hamas war in early October, the U.S. State Department raised Lebanon ’s travel advisory level from a Level 3 to a Level 4 level due to “the unpredictable security situation related to rocket, missile, and artillery exchanges” between Israel and Hezbollah or other militant groups. In December, the U.S. Embassy in Beirut returned to normal staffing and presence, and on Jan. 29, the country was moved back to Level 3. Crime, terrorism, armed conflict, civil unrest, kidnapping and unexploded landmines are listed as the country’s primary risk factors. However, the country’s borders with Syria and with Israel, as well as refugee settlements within Lebanon, are specifically noted as Level 4 regions.
China became a Level 3 country in late 2020, with an update in December 2022 citing “the surge in COVID-19 cases, arbitrary enforcement of local laws, and COVID-19-related restrictions” as the reason for the advisory. In June 2023, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR) was moved from the Level 3 to the Level 2 list, but travelers are still advised to be cautious in the area due to “arbitrary enforcement of local laws.” Meanwhile, Macau remains at Level 3.
Following an attempted coup in August 2023, Niger was elevated to Level 4 in August and the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Niamey. In early January 2024, the overall risk level for the country was lowered back to Level 3. Despite the new classification, the State Department still asks non-emergency government personnel and eligible family members to depart the country.
In mid-December 2023 there was an explosion at Guinea’s main fuel depot which has since affected access to health care and basic goods and services. The country was subsequently designated a Level 3 nation after having previously been Level 2. Concerns about civil unrest, health, crime and fuel shortages impacting local infrastructure were listed as the primary risk factors contributing to the change.
Several Level 3 countries are among the worst countries for human trafficking, as designated by the State Department’s annual Trafficking in Persons Report . Level 3 countries on this list include Papua New Guinea, Guinea Bissau, China and Chad. There are also nine Level 4 countries designated as among the worst for human trafficking: Afghanistan, Belarus, Iran, Myanmar, North Korea, Russia, Syria, South Sudan and Venezuela.
Over 70 countries are currently at Level 2, meaning the State Department recommends travelers “exercise increased caution” when traveling to those destinations.
Botswana became the newest Level 2 country on Feb. 26 after having previously been Level 1, with crime noted as the primary risk factor.
France, which saw nationwide protests throughout 2023, has civil unrest and terrorism noted as risk factors for its Level 2 status, and Sweden’s Level 2 status is associated with risks of terrorism.
The Level 2 travel advisory for the Bahamas was updated in January to reflect water safety concerns. The advisory warns that “activities involving commercial recreational watercraft, including water tours, are not consistently regulated” and notes that government personnel are “not permitted to use independently operated jet-ski rentals on New Providence and Paradise Islands.” It also warns visitors to be mindful of sharks, weather and water conditions. The advisory also says that crime is a primary risk factor with gang-on-gang violence contributing to high homicide rates in some areas. Visitors are asked to “be vigilant” and to not physically resist robbery attempts.
Bangladesh 's Level 2 travel advisory was updated in October 2023 to add a note about the country’s general election , which took place Jan. 7, 2024. The advisory states “demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence.” The U.S. has since claimed the country’s election was not free nor fair.
In November 2023, several Level 2 travel advisories were updated with new cautionary information. The advisory for Ghana was updated to reflect threats against LGBTQI+ travelers specifically, noting “anti-LGBTQI+ rhetoric and violence have increased in recent years.” Meanwhile, the advisory for South Africa was updated in February to note that routes recommended by GPS may be unsafe with higher risk for crime.
Turkmenistan was moved off of the Level 2 list to become the newest addition to the Level 1 list on Jan. 22, meaning normal precautions are recommended but there are no risk factors causing travelers to practice increased caution.
The State Department asks travelers to pay attention to travel advisory levels and alerts , review country information pages for their destinations and read related country security reports before going abroad.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Russia , Ukraine , Travel , Coronavirus , Travel Tips , Israel , Gaza , violence , Civil War , crime , kidnapping
Recent Articles
Best countries.

Education News

Best Countries Rankings
- # 1 Switzerland
- # 5 Australia
- # 5 United States
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
Switzerland is world's best country.
Julia Haines Sept. 6, 2023

Photos: Best Countries Around the World
Sept. 6, 2023

The 25 Best Countries in the World
Elliott Davis Jr. Sept. 6, 2023

Ecuador Says It Has Sued Mexico Over Granting of Asylum to Former VP
Reuters April 29, 2024

Lawmakers Scuffle Again in Georgia Over 'Foreign Agent' Bill

We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Guatemala Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 17, 2023, guatemala - level 3: reconsider travel.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Reconsider travel to Guatemala due to crime . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do not travel to:
- San Marcos Department (except the city of San Marcos) due to crime .
- Huehuetenango Department (except the city of Huehuetenango) due to crime .
- Zone 18 and the city of Villa Nueva in Guatemala City due to crime .
Country Summary: Violent crime such as extortion, murder, armed robbery, carjacking, narcotics trafficking and gang activity are common in Guatemala. Local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to criminal incidents resulting in a low arrest and conviction rate. Guatemala’s National Tourist Assistance Program ( PROATUR ) provides 24-hour emergency assistance and routine guidance to tourists. PROATUR also provide additional security in locations frequented by tourists. The call center is staffed with Spanish and English speakers and can be reached 24/7 by calling 1500 or +502-2290-2800.
U.S. government personnel and family members are prohibited from traveling to/throughout the above-mentioned areas for personal travel but are permitted to travel throughout the rest of Guatemala, including tourist destinations such as Tikal, Antigua, Lake Atitlán, and Pacific coast areas in the Santa Rosa and Escuintla Departments.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Guatemala.
If you decide to travel to Guatemala:
- When traveling to Lake Atitlán, use certified tourist providers and travel between villages on the lakeshore by chartered boat, as perimeter paths pose a serious crime risk and are not easily accessible by emergency services. Hiking in the area, while popular, is best undertaken with the assistance of a local guide to ensure safety, as criminals are known to target some routes.
- When visiting Pacific coast beaches and resorts in the Santa Rosa and Escuintla Departments, arrange travel through hotel, resort, or charter agents. We recommend traveling to and from hotels, resorts, and fishing charters via road from Guatemala City during daylight hours only.
- Visitors are strongly advised to avoid swimming in the Pacific Ocean, since currents and undertows are strong, and beaches lack adequate lifeguards or emergency response.
- Visitors should not leave drinks unattended in bars and restaurants and are advised to decline invitations from strangers to private parties or gatherings.
- Consider staying in hotels or other lodging facilities that offer secure parking, doormen, and a dedicated and professional security staff.
- Request security escorts, which are available for tourist groups, from the Guatemalan Tourism Institute ( INGUAT ).
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid walking or driving at night.
- Do take radio-dispatched taxis (Taxi Amarillo), INGUAT-approved taxis from the “SAFE” stand at the airport, hotel taxis, vetted private drivers, and/or Uber.
- Do not take public transportation, including white car taxis. U.S. government personnel and their family members are prohibited from using these forms of transportation.
- Do not attempt to hike walking trails or volcanoes without the services of a qualified local guide. Robberies are commonplace, and emergency response is lacking.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Do not use public ATMs.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry, and avoid using mobile devices in public.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts while in Guatemala and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Guatemala.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
San Marcos Department – Level 4: Do Not Travel
All U.S. government personnel and family members are prohibited from traveling to San Marcos Department for personal travel, except for the city of San Marcos. Narcotics trafficking is widespread, and large portions of the department are under the influence of drug trafficking organizations. Several municipalities lack police presence, and local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Avoid areas outside of major roads and highways. Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Huehuetenango Department – Level 4: Do Not Travel
All U.S. government personnel and family members are prohibited from traveling to Huehuetenango Department for personal travel, except for the city of Huehuetenango. Narcotics trafficking is widespread, and large portions of the department are under the influence of drug trafficking organizations. Several municipalities lack police presence, and local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Avoid areas outside of major roads and highways.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Zone 18 and Villa Nueva within the Guatemala Department – Level 4: Do Not Travel
U.S. government personnel and family members are free to travel within Guatemala City except for zone 18 and the municipality of Villa Nueva. The following zones in Guatemala City are of elevated concern due to crime: 5, 6, 7, 12, 13, 17, 19, 21, and 24. U.S. citizens should take appropriate security measures when traveling to and from the airport such as only using vetted transportation services, not displaying valuables or other signs of wealth, refraining from using mobile devices in public, and not lingering outside the airport. U.S. citizens are advised not to hail white-car taxis on the street in Guatemala City. Use radio-dispatched taxis (Taxi Amarillo), INGUAT-approved taxis from the “SAFE” stand at the airport, hotel taxis, vetted private drivers, or Uber.
Travel Advisory Levels
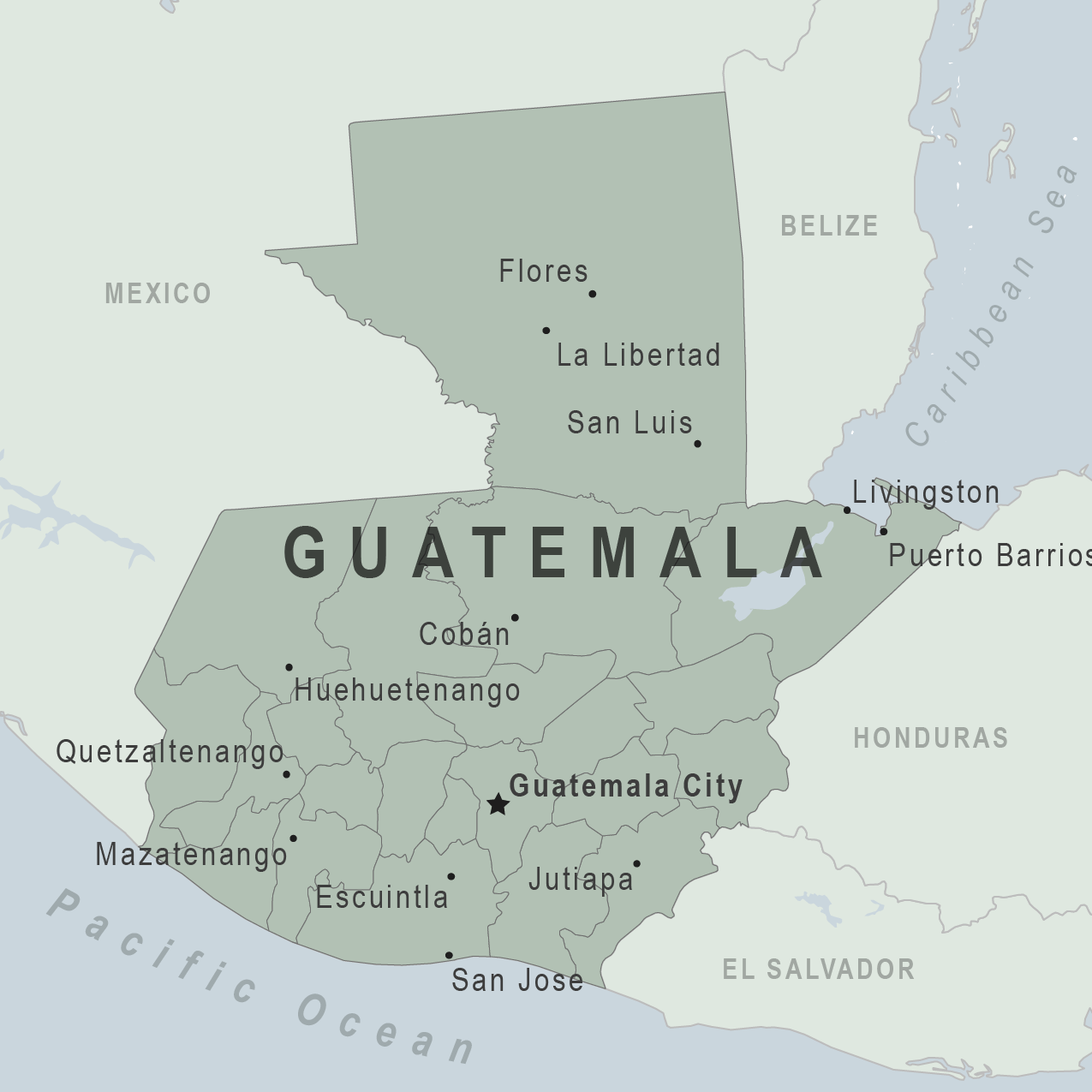
Assistance for u.s. citizens, guatemala map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 17, 2023
Guatemala - level 3: reconsider travel.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Reconsider travel to Guatemala due to crime . Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do not travel to:
- San Marcos Department (except the city of San Marcos) due to crime .
- Huehuetenango Department (except the city of Huehuetenango) due to crime .
- Zone 18 and the city of Villa Nueva in Guatemala City due to crime .
Country Summary: Violent crime such as extortion, murder, armed robbery, carjacking, narcotics trafficking and gang activity are common in Guatemala. Local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to criminal incidents resulting in a low arrest and conviction rate. Guatemala’s National Tourist Assistance Program ( PROATUR ) provides 24-hour emergency assistance and routine guidance to tourists. PROATUR also provide additional security in locations frequented by tourists. The call center is staffed with Spanish and English speakers and can be reached 24/7 by calling 1500 or +502-2290-2800.
U.S. government personnel and family members are prohibited from traveling to/throughout the above-mentioned areas for personal travel but are permitted to travel throughout the rest of Guatemala, including tourist destinations such as Tikal, Antigua, Lake Atitlán, and Pacific coast areas in the Santa Rosa and Escuintla Departments.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Guatemala.
If you decide to travel to Guatemala:
- When traveling to Lake Atitlán, use certified tourist providers and travel between villages on the lakeshore by chartered boat, as perimeter paths pose a serious crime risk and are not easily accessible by emergency services. Hiking in the area, while popular, is best undertaken with the assistance of a local guide to ensure safety, as criminals are known to target some routes.
- When visiting Pacific coast beaches and resorts in the Santa Rosa and Escuintla Departments, arrange travel through hotel, resort, or charter agents. We recommend traveling to and from hotels, resorts, and fishing charters via road from Guatemala City during daylight hours only.
- Visitors are strongly advised to avoid swimming in the Pacific Ocean, since currents and undertows are strong, and beaches lack adequate lifeguards or emergency response.
- Visitors should not leave drinks unattended in bars and restaurants and are advised to decline invitations from strangers to private parties or gatherings.
- Consider staying in hotels or other lodging facilities that offer secure parking, doormen, and a dedicated and professional security staff.
- Request security escorts, which are available for tourist groups, from the Guatemalan Tourism Institute ( INGUAT ).
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid walking or driving at night.
- Do take radio-dispatched taxis (Taxi Amarillo), INGUAT-approved taxis from the “SAFE” stand at the airport, hotel taxis, vetted private drivers, and/or Uber.
- Do not take public transportation, including white car taxis. U.S. government personnel and their family members are prohibited from using these forms of transportation.
- Do not attempt to hike walking trails or volcanoes without the services of a qualified local guide. Robberies are commonplace, and emergency response is lacking.
- Do not physically resist any robbery attempt.
- Do not use public ATMs.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive watches or jewelry, and avoid using mobile devices in public.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts while in Guatemala and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Guatemala.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
San Marcos Department – Level 4: Do Not Travel
All U.S. government personnel and family members are prohibited from traveling to San Marcos Department for personal travel, except for the city of San Marcos. Narcotics trafficking is widespread, and large portions of the department are under the influence of drug trafficking organizations. Several municipalities lack police presence, and local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Avoid areas outside of major roads and highways. Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Huehuetenango Department – Level 4: Do Not Travel
All U.S. government personnel and family members are prohibited from traveling to Huehuetenango Department for personal travel, except for the city of Huehuetenango. Narcotics trafficking is widespread, and large portions of the department are under the influence of drug trafficking organizations. Several municipalities lack police presence, and local police may lack the resources to respond effectively to serious criminal incidents. Avoid areas outside of major roads and highways.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Zone 18 and Villa Nueva within the Guatemala Department – Level 4: Do Not Travel
U.S. government personnel and family members are free to travel within Guatemala City except for zone 18 and the municipality of Villa Nueva. The following zones in Guatemala City are of elevated concern due to crime: 5, 6, 7, 12, 13, 17, 19, 21, and 24. U.S. citizens should take appropriate security measures when traveling to and from the airport such as only using vetted transportation services, not displaying valuables or other signs of wealth, refraining from using mobile devices in public, and not lingering outside the airport. U.S. citizens are advised not to hail white-car taxis on the street in Guatemala City. Use radio-dispatched taxis (Taxi Amarillo), INGUAT-approved taxis from the “SAFE” stand at the airport, hotel taxis, vetted private drivers, or Uber.
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Passport must be valid at the time of entry.
One page per stamp.
A visa is not required.
There are no restrictions, but if the passenger is carrying $10,000 or more, s/he will need to justify the income and the purpose
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Guatemala City
Boulevard Austriaco 11-51, Zone 16 Guatemala City, Guatemala Telephone: +(502) 2354-0000 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(502) 2354-0000 [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
To enter Guatemala, you will need a U.S. passport that is valid at the time of entry. There is no minimum validity period for a U.S. passport. U.S. citizens do not need a visa and are admitted to Guatemala for 90 days. Some airlines require that passengers complete the electronic Guatemalan immigration form prior to check-in Although you may select to fill out the form in English, in drop down menus, United States is listed as “Estados Unidos.”
If your passport is lost or stolen while you are in Guatemala, please obtain a new passport at the U.S. Embassy as soon as possible. In order to be permitted to depart Guatemala, you will present the new passport together with a police or Ministerio Publico report regarding the loss/theft to the Guatemalan Immigration Agency ( Dirección de Migración ).
Visit the Ministry of Foreign Affairs website (Spanish only) or contact the Guatemalan Embassy for the most current visa information. If a U.S. citizen exceeds the period of authorized stay, a fine of 15 Guatemalan quetzals (GTQ) per day is imposed, and this fine must be paid to be permitted to depart Guatemala.
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Guatemala.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction , and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Guatemala has a dedicated tourism assistance program (called PROATUR ) whose sole mission is to assist and protect foreign tourists in Guatemala. Their emergency assistance call center – staffed with Spanish and English speakers – may be contacted 24/7 by calling 1500 or +502-2290-2810. You may also contact PROATUR by WhatsApp at +502-5188-1819.
Crime: Theft, armed robbery, and carjacking are the most common crimes against U.S. citizens.
Travelers have experienced carjackings and armed robberies upon leaving the airport. Victims have been violently assaulted when they resisted an attack or refused to give up money or valuables. Pickpockets and purse-snatchers are prevalent in major cities and tourist sites, especially the central market and other parts of Zone 1 in Guatemala City. In a common scenario, an accomplice distracts the victim while an assailant slashes a bag or backpack or simply steals it.
Reports of sexual assault remain high. Support for victims of sexual assault is lacking.
The Guatemalan border with Mexico, in particular the northwestern corner of Petén, is a high-risk area due to large scale drug and alien smuggling. There have been instances of narco-related homicides in this area, especially along CA-13. Visitors are encouraged to fly to nearby Flores when visiting Tikal. Travelers should remain in groups, stay on principal trails leading to the Central Plaza and the Temple IV complex, and avoid remote areas of the park.
Due to heightened risk of crime, U.S. Embassy personnel are not permitted to go to Zone 18 in Guatemala City, Huehuetenango Department (except the city of Huehuetenango), and San Marcos Department (except the city of San Marcos). For more detailed information, please see the Guatemala Travel Advisory .
To decrease the likelihood of becoming a victim:
- Be aware of your surroundings. Report any crime incidents promptly to the police.
- Carry a photocopy of your passport in case you lose your passport.
- Do not use public ATMs. Only use ATMs inside secure bank lobbies or hotels. Scams involving attempts to acquire a victim’s ATM card and personal identification number (PIN) are common. U.S. citizens have been victims of credit card scams where the card is copied and used improperly.
- Do not display signs of wealth, such as wearing expensive jewelry or watches. Refrain from using a cell phone on the street. A common crime against foreign citizens in Guatemala is robbery of cell phones.
- Do not use local public buses . U.S. Embassy personnel are not permitted to use any local buses. Avoid low-priced public inter-city buses (often recognizable as recycled and repainted U.S. school buses). Travelers also have been attacked on first-class buses on highway CA-2 near the border areas with both Mexico and El Salvador, on highways CA-1 and CA-9 near the border with El Salvador, and in the highlands between Quetzaltenango and Sololá. Public buses are subject to frequent attacks by armed robbers, and often are poorly maintained and dangerously driven.
- Do not hail taxis on the street in Guatemala City, instead use radio-dispatched taxis (Taxi Amarillo), INGUAT-approved taxis from the “SAFE” stand at the Guatemala City airport, or hotel taxis. Uber is also considered safe to use in Guatemala City and Antigua.
Tourist groups are advised to request security escorts. Security escorts for tourist groups are available from INGUAT and may be requested by calling 1500 or +502-2290-2800.
- Requests should be directed to the attention of the Coordinator of the National Tourist Assistance Program , and should provide the itinerary, names of travelers, and model and color of the vehicle in which they will be traveling.
- The request should be submitted by mail, fax, or e-mail , and should arrive at INGUAT at least three business days in advance of the proposed travel.
- INGUAT may not be able to accommodate all requests.
- Visit INGUAT’s web site .
Demonstrations occur frequently. They may take place in response to political or economic issues, on politically significant holidays, and during international events.
- Demonstrations can be unpredictable. Avoid areas around protests and demonstrations
- Past demonstrations have turned violent.
- Check local media for updates and traffic advisories.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Internet romance and financial scams are prevalent in Guatemala. Scams are often initiated through Internet postings/profiles or by unsolicited emails and letters. Scammers almost always pose as U.S. citizens who have no one else to turn to for help. Common scams include:
- Romance/Online dating
- Money transfers
- Lucrative sales
- Contracts with promises of large commissions
- Grandparent/Relative targeting
- Free Trip/Luggage
- Inheritance notices
- Work permits/job offers
- Bank overpayments
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy for assistance. Report crimes to the police through the tourist assistance program ( PROATUR ) at 1500 or +502-2290-2800 and contact the U.S. Embassy at+502-2354-0000. Remember that local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
The U.S. Embassy can:
- help you find appropriate medical care.
- assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion.
- provide a list of local attorneys
- provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the United States.
- provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution.
- help you find accommodations and arrange flights home.
- replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence may contact the U.S. Embassy for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate basic medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders may encounter obstacles to accessing areas outside of major cities, and/or be unable to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Water Safety: Basic safety measures and precautions for swimming, boating, and other outdoor activities may not be observed in Guatemala.
- Beware of strong currents, riptides, and undertows along Guatemala's Pacific coast beaches, as well as at Lake Atitlan. Lifeguards are rarely present.
- Signs that warn of treacherous surf are rare and confined mostly to private beaches owned by hotels.
Potential for Natural Disasters:
- There are four active volcanoes in Guatemala: Fuego, Pacaya, Tacaná, and Santiaguito. Volcanic activity has forced evacuations of nearby villages. U.S. Embassy personnel are not permitted to visit the Agua volcano due to the high incidence of robberies on the volcano.
- Be aware of the possibility of earthquakes at any time and make contingency plans. Consult Guatemala’s National Seismic Institute ( INSIVUMEH ) for updates on earthquakes and seismic activity.
- Both the Caribbean and Pacific coasts of Guatemala are vulnerable to hurricanes and tropical storms from mid-May through November.
- Mudslides and flooding during the May to November rainy season often kill dozens of people and close roads.
- Consult Guatemala’s National Disaster Reduction Coordination Office (CONRED) for updates on natural disasters or tropical storms and hurricanes.
Indigenous Areas: Be mindful of local traditional practices when visiting indigenous Maya communities as tensions can rise quickly and locals occasionally take the law into their own hands.
- Particularly in small villages, residents are often wary and suspicious of outsiders.
- Avoid activities that might unintentionally violate a cultural or religious belief.
- In the past, Guatemalan citizens have been lynched for suspicion of child abduction. Maintain distance from local children and refrain from actions that could fuel such suspicions.
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some violations of law that occur in Guatemala are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our websites on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or have to give them up if you bring them back to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTQI+ events in Guatemala. While there is no legal recognition of same-sex partnerships or marriages, private same-sex sexual activity between consenting adults is legal.
- Antidiscrimination laws exist, but do not include specific protections based on sexual orientation or gender identity.
- There is general societal discrimination against LGBTI persons in relation to their access to education, health care, employment, and housing.
- According to LGBTI rights groups, gay and transgender individuals often experience police abuse. LGBTI rights groups allege that police officers regularly engage in extortion by waiting outside clubs and bars frequented by LGBTI persons to demand protection money or payment to avoid jail.
- A lack of trust in the judicial system and a fear of further harassment or social recrimination discourages victims from filing complaints.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers with Disabilities: The law in Guatemala prohibits discrimination against persons with physical, , intellectual or mental disabilities, and the law is enforced. Social acceptance of persons with disabilities in public is not as prevalent as in the United States. The most common types of accessibility may include accessible facilities, information, and communication. Expect accessibility to be limited in public transportation, information, and general infrastructure, and common in lodging and communication. There is a significant difference between Guatemala City and the rest of the country.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Customs: Guatemalan customs authorities may enforce strict regulations concerning temporary importation into or export from Guatemala of items such as antiquities and other cultural property.
When traveling to Guatemala for temporary work related to your profession, if you bring in any technical equipment or tools, you must declare this equipment/these tools upon entry. The equipment/tools must be of a personal, not commercial, quantity. You must take the equipment/tools with you when you depart. If, upon entry, you intend to leave any equipment/tools in Guatemala, you are required to report that to customs authorities and pay import taxes.
Contact the Embassy of Guatemala in Washington, D.C . ion. (phone: 202-745-4953) or one of Guatemala’s consulates in the United States for specific information.
The full range of medical care is available in Guatemala City, but medical care outside of the city is limited. Guatemala’s public hospitals frequently experience serious shortages of even the most basic medicines and equipment. Care in private hospitals is generally adequate for most common illnesses and injuries, and many of the medical specialists working in them are U.S.-trained and -certified. The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of medical providers and hospitals on our website. We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Many hospitals in Guatemala require payment prior to treating patients, even if personal insurance will cover the treatment. They do not typically enter into payment plan agreements, and they may decline to discharge you from the hospital if you owe money for treatment.
For emergency services in Guatemala, dial 110.
Ambulance services are not present throughout the country or are unreliable in most areas except urbanized areas.
We do not pay medical bills . Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription. Check with the Guatemalan Public Health Ministry to ensure the medication is legal in Guatemala.
Vaccinations: Be up to date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Road hazards are common. Secondary and rural roads have little to no illumination. U.S. Embassy employees are prohibited from traveling outside the capital city at night. Be vigilant of motorcyclists who weave unexpectedly across lanes of traffic and pedestrians who unexpectedly dart across roads due to the lack of defined crosswalks.
Robberies of occupied vehicles are common in Guatemala City, often by two assailants on motorcycles who pull up alongside a car stopped at a traffic light. There have also been numerous reports of violent criminal activity along Guatemala’s main highways, including the Carretera a El Salvador (Inter-American Highway CA-2).
Armed attacks have occurred in various places in Guatemala, including:
- On roads between Guatemala City and the Petén region;
Between Tikal and the Belize border; and
- On tThe Inter-American Highway (CA-1) and the road from Guatemala City to the Caribbean coast (CA-9), due to heavy traffic, including large trucks and trailers.
U.S. Embassy employees are prohibited from driving from or through Mexico to Guatemala.
Stay on main roads when traveling to and from Antigua and Lake Atitlan. Secondary roads in those areas are poorly maintained and have experienced higher incidents of robbery, rape, and armed assault.
PROVIAL, a roadside assistance force, patrols most of the major highways in the country. PROVIAL can be contacted by calling +502-2422-7800. Travelers may also call the police for roadside assistance by dialing 110 or 120, or the fire department by dialing 122 or 123; however, patrols are sporadic.
Traffic Laws: Valid U.S. driver’s licenses are accepted for the first 30 days of a visit, and international driving permits are accepted for extended stays. Laws and speed limits are often ignored, turn signals are rarely used, and passing on dangerous stretches of highway is common.
It is against the law for drivers to operate cellular phones while driving.
People found driving under the influence of alcohol or other drugs will be arrested and may serve jail time.
All drivers involved in accidents resulting in injury may be detained and held in protective custody pending investigation and/or payment of alleged damages.
Public Transportation: The most common form of public transportation is the system of brightly-painted recycled school buses. Criminal activity and frequent fatal accidents, however, make these low-priced local and inter-city buses particularly dangerous. U.S. Embassy employees are not permitted to use these public buses.
Use of radio-dispatched taxis or Uber is far safer than hailing taxis on the street. In Guatemala City, there are several radio taxi companies in operation:
- Taxi Seguro can be reached at +502-2312-4243.
- Taxi Amarillo Express (yellow taxis) is a radio-dispatch taxi service reached by dialing 1766.
- A Green Cab radio dispatch service operates in the suburbs near zone 15 and the Cayalá entertainment and shopping destination.
- To use Uber, download their app or go to https://www.uber.com .
U.S. Embassy employees are prohibited from using the white taxis. The Guatemalan Tourist Assistance Program, PROATUR , may be able to provide additional information and can be reached by dialing 1500 or +502-2290-2800.
See our Road Safety page for more information. Visit the website of Guatemala’s national tourist office and national authority responsible for road safety, or contact them via e-mail .
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the Government of Guatemala’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Guatemala’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Guatemala should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Guatemala . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.”
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, guatemala map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Check passport expiration dates carefully for all travelers! Children’s passports are issued for 5 years, adult passports for 10 years.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

COMMENTS
Read the entire Travel Advisory. Do not travel to: San Marcos Department (except the city of San Marcos) due to crime. Huehuetenango Department (except the city of Huehuetenango) due to crime. Zone 18 and the city of Villa Nueva in Guatemala City due to crime. Country Summary: Violent crime such as extortion, murder, armed robbery, carjacking ...
The Department of State published a new Travel Advisory for Guatemala on January 24, 2022, upgrading the COVID-19 information from Level 2 (Exercise Increased Caution) to Level 3 (Reconsider Travel) following The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)'s release of a Level 3 Travel Health Notice for Guatemala. The overall Travel ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
Guatemala Travel Advisory : Level 3: Reconsider Travel: July 17, 2023: Guyana Travel Advisory : Level 3: Reconsider Travel: July 17, 2023: Haiti Travel Advisory : Level 4: Do Not Travel: ... Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Office of the Spokesperson. April 19, 2021. State Department Travel Advisory Updates. In order to provide U.S. travelers detailed and actionable information to make informed travel decisions, the Department of State regularly assesses and updates our Travel Advisories, based primarily on the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC ...
Assistance: U.S. Embassy Guatemala City https://gt.usembassy.gov/ Tel. (502) 2326-4000 [email protected]. State Department - Consular Affairs 888-407-4747 or 202-501-4444. Guatemala Country Information and Travel Advisory Page. Enroll in Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security updates
Since July, 2021 the United States has donated 8,500,060 safe and effective COVID-19 vaccine doses with the people of Guatemala. This includes 8,500,060 Moderna doses. Of the 8,500,060 vaccine doses,100% were donated through bilateral agreements. The United States is committed to leading an international and coordinated effort to accelerate ...
Please enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive alerts and be located in an emergency. Please call 1 (888) 407-4747 (U.S. and Canada) or 1 (202) 501-4444 (overseas) or contact the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate. As a first step in planning any trip abroad, check the Travel Advisories for your intended destination.
US State Dept Travel Advisory The US Department of State currently recommends US citizens Reconsider Travel to Guatemala due to crime. Some areas have increased risk. ... [502] 2326-4000; US Embassy in Guatemala City, Avenida Reforma 7-01, Zona 10, Guatemala Ciudad, Guatemala; https://gt.usembassy.gov/
Travel.State.Gov > Travel Advisories > Mexico Travel Advisory. Congressional Liaison; Special Issuance Agency; Legal Resources; U.S. Passports ... U.S. government employees must travel directly from the United States and observe a curfew from midnight to 6:00 a.m. in ... U.S. Embassy Mexico City . Paseo de la Reforma 305 Colonia Cuauhtemoc ...
Visit the U.S. Embassy Guatemala webpage on COVID-19 for information on conditions in Guatemala. Assistance: U.S. Embassy Guatemala City, Guatemala. Website: https://gt.usembassy.gov/ Phone: (502) 2326-4000. Email: [email protected]. State Department - Consular Affairs. 888-407-4747 or 202-501-4444 Guatemala Country Information and ...
US Embassy/Consulate [502] 2326-4000; US Embassy in Guatemala City, Avenida Reforma 7-01, Zona 10, Guatemala Ciudad, Guatemala; LGBTQIA+ Travelers. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, intersex, and asexual (LGBTQIA+) travelers can face unique challenges when traveling abroad. Laws and attitudes in some countries may affect safety and ...
Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP). Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home. Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace. While at your ...
Places With a Level 4 Travel Advisory. These are the primary areas the U.S. government says not to travel to right now, in alphabetical order: Jump to Place: Afghanistan: The Central Asian country ...
The U.S. Embassy in Pretoria is requesting quotes for iPhone 15 Pro Max, Blue Titanium and Accessories: 18 x iPhone 15 Pro Max, Blue Titanium (must have SIM card slot) 25 x Apple EarPods (USB-C) MTJY3ZM/A
Ambassador. Tobin Bradley arrived as U.S. Ambassador to Guatemala in February 2024. Previously, he served as Deputy Assistant Secretary in the Bureau of International Narcotics and Law Enforcement Affairs (INL) from 2020 to 2024, overseeing the Africa and Middle East and Knowledge Management offices, and serving as the INL Senior. Complete Bio.
However, if the CDC raises a country's COVID-19 THN to a Level 4, the State Department's Travel Advisory for that country will also be raised to a Level 4: Do Not Travel due to COVID-19. This update will leave approximately 10% of all Travel Advisories at Level 4: Do Not Travel. This 10% includes Level 4 Travel Advisories for all risk ...
Secretary of State Antony J. Blinken traveled to Shanghai and Beijing, the People's Republic of China, for meetings with President Xi Jinping, Director of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) Central Foreign Affairs Commission and Foreign Minister Wang Yi, Minister of Public Security Wang Xiaohong, and Shanghai Party Secretary Chen Jining from ...
Ask the Consul. Sometimes medical results for residency visa cases are not ready before the appointment date. Currently, applicants must attend their appointment anyway if the panel of physicians instructs this. After the interview, it is recommended that the Immigrant visa applicant follows up on their exams through the panel of physicians ...
Product Request Number: RFQ-PR12491520. The US Embassy Yaounde is seeking for the services of a qualified contractor with excellent knowledge in metal works to install razor wires on US Embassy residential perimeter fence walls. A. SCOPE OF WORK. The US Embassy is seeking the services of a qualified technician, with excellent knowledge in metal ...
US State Dept Travel Advisory. The US Department of State currently recommends US citizens Reconsider Travel to Guatemala due to crime. Some areas have increased risk. ... [502] 2326-4000; US Embassy in Guatemala City, Avenida Reforma 7-01, Zona 10, Guatemala Ciudad, Guatemala; Telephone Code. 502. Local Emergency Phone.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to El Salvador. If you decide to travel to El Salvador: Read the Department of State's COVID-19 page before planning any international travel, and read the Embassy COVID-19 page for country-specific COVID-19 information. Be aware of your surroundings.
Please call: 45 3341 7100 Outside of Office Hours, contact: 45 3341 7100 Outside of Denmark: 45 3341 7100 Emergency Contact - All Locations Get Travel Alerts International Parental Child Abduction Arrest of a U.S. Citizen Death of a U.S. Citizen Victims of Crime Emergency Financial Assistance Get Travel Alerts International Parental Child Abduction Arrest of
U.S. Embassy Guatemala City Website: https://gt.usembassy.gov/ Phone: +502 2326-4000 Email: [email protected] State Department - Consular Affairs 888-407-4747 or 202-501-4444 Guatemala Country Information and Travel Advisory Page
U.S. DEPARTMENT of STATE — BUREAU of CONSULAR AFFAIRS. Travel.State.Gov > Travel Advisories > Guatemala Travel Advisory . Congressional Liaison; Special Issuance Agency; Legal Resources
U.S. DEPARTMENT of STATE — BUREAU of CONSULAR AFFAIRS. Travel.State.Gov > International Travel > Learn About Your Destination > Guatemala International Travel Information
Visas for U.S. citizens hoping to travel, study or work in Japan are controlled by the Japanese government. While the Japanese Government is the ultimate authority on visa matters, we would like to present some general information on visas for U.S. citizens to aid in your planning. U.S. citizens without a work visa cannot work in Japan.
Review your personal security plans. Assistance: U.S. Embassy Nassau, The Bahamas. #42 Queen Street, Nassau. 1-242-322-1181. [email protected]. U.S. Embassy Nassau webpage: Services for U.S. and Local Citizens - U.S. Citizen Services - U.S. Embassy in The Bahamas (usembassy.gov) For U.S. Citizens in an Emergency: Call State Department ...
U.S. Embassy Guatemala City, Guatemala. Website: https://gt.usembassy.gov/ Phone: (502) 2326-4000. Email: [email protected]. State Department - Consular Affairs. 888-407-4747 or 202-501-4444. Guatemala Country Information and Travel Advisory Page. Enroll in Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security updates. Follow ...
ALERT - Doctors Strike May Affect Local Healthcare Access. LOCATION: Republic of Korea, Country-wide The Embassy has been monitoring the ongoing doctors strike occurring across the Republic of Korea (ROK).