- April 14, 2024

24-hour emergency consular support
If you’re an Australian citizen and you have serious concerns about your welfare or that of another Australian overseas, contact your local Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate, or call our 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on
- 1300 555 135 within Australia
- +61 2 6261 3305 from anywhere in the world.
Read more about getting help overseas on Smartraveller.
Travel advice
We maintain travel advisories on Smartraveller for over 175 destinations, assigning an overall advice level to each. The advice levels reflect the risks for Australian travellers in each destination. We also provide general advice on a range of travel topics.
Visit Smartraveller to explore our travel advice for all destinations .
We continually review and update our travel advice based on credible information. Stay up to date with any changes by subscribing for updates .
The Australian Passport Office and its agents are committed to providing a secure, efficient and responsive passport service for Australia.
Visit the Australian Passport Office for more about passports.
The Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade does not issue visas for overseas travel or visiting Australia and can’t provide specific information on visas.
Read about visas for Australians travelling overseas .
Find out about visas to visit Australia .
© 2003,www.australiangovernment.org/. All rights reserved/ Homepage / privacy-policy / Sitemap
- Skip to navigation
- Skip to main content

Popular searches
Your previous searches.
Reopening to tourists and other international travellers to secure our economic recovery
Joint media release with the hon. scott morrison mp, the hon. greg hunt mp and the hon. dan tehan mp.
Australia will reopen to all fully vaccinated visa holders, welcoming the return of tourists, business travellers, and other visitors from 21 February.
These changes will ensure we protect the health of Australians, while we continue to secure our economic recovery.
Australia’s health system has demonstrated its resilience throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, including though the recent Omicron wave. With improving health conditions, including a recent 23 per cent decline in hospitalisations due to COVID, the National Security Committee of Cabinet today agreed Australia is ready to further progress the staged reopening of our international border.
Visa holders who are not fully vaccinated will still require a valid travel exemption to enter Australia, and will be subject to state and territory quarantine requirements.
Today’s announcement will give certainty to our vital tourism industry, and allow them to start planning, hiring and preparing for our reopening. In 2018-19, tourism generated more than $60 billion for the Australian economy, with more than 660,000 jobs dependent on the industry.
Since the Morrison Government commenced Australia’s staged international border reopening on 1 November 2021 we have seen almost 580,000 arrivals come to Australia including to reunite with loved ones, work or study.
The Commonwealth continues to work with States and Territories on the safe resumption of the cruise industry and looks forward to further announcements on this in due course.
Need a hand?
- Minister for Foreign Affairs
- Minister for Women
Senator the Hon Marise Payne
- Media Releases
- Transcripts
This content has been archived.
Further steps to support australians to travel abroad.
- Media release
Australians can now prepare for safe overseas travel when borders progressively re-open from 1 November, with the Australian Government reinstating country-specific travel advice levels for 177 destinations.
The updated country-specific travel advice will allow Australians planning to travel overseas to assess risks, understand requirements, and prepare to travel safely. It will also help Australians to access travel insurance more readily.
While fully vaccinated Australians will be able to depart Australia without an exemption from 1 November, all travellers will need to be aware of risks and take care, regardless of where they travel, while COVID-19 remains an ongoing global health risk.
Smartraveller’s ‘Do not travel’ global advisory has been removed. This advisory was put in place for all destinations in March 2020 due to the COVID-19 health risks and significant disruption to global travel.
Under the travel advice framework announced today, no destination will be set lower than level 2 ‘Exercise a high degree of caution’, given the ongoing COVID-19 health risks and the continuing complexities of international travel.
Border settings and quarantine requirements in other countries continue to change. We strongly encourage Australians to closely monitor the Australian Government’s travel advice available on smartraveller.gov.au .
Australians will also need to consider the requirements of airlines, transit and destination countries, as well as return arrangements to Australia in making decisions on when and where to travel abroad. Many of these requirements are subject to change at short notice given COVID-19 situations.
Fully vaccinated Australians who want to travel overseas can download the International COVID Vaccine Certificate via MyGov to provide internationally recognised proof of their COVID-19 vaccinations.
We know it has been a difficult 18 months for Australians overseas trying to return, and for Australians with family and friends overseas.
The changes announced today are a vital next step in re-uniting Australian families and safely re-opening Australia to the world.
Media enquiries
- Skip to navigation
- Skip to main content

- ImmiAccount
- Visa Entitlement Verification Online (VEVO)
- Select language Language Unavailable English
TravelSECURE
TravelSECURE provides a range of advice and tips to help you prepare for your journey and clear security checks quickly and easily.
Security screening measures are there to keep travellers secure and safe. Every passenger and bag boarding a flight is screened to reduce the risk of a security incident occurring. Security checks may sometimes seem inconvenient, but they are in place to protect us. We encourage you to gain an understanding of the screening processes at an airport. This will help make your passage through security screening as fast and efficient as possible.

See who to contact if you have any travel enquiry or provide feedback.
Need a hand?
Popular searches, your previous searches.
Situation in Haiti April 13, 2024
U.s. citizens in haiti, update april 12, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory September 8, 2023
Australia - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with removal of major event information.
Exercise normal precautions in Australia.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Australia.
If you decide to travel to Australia:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Australia.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Must be valid at time of entry
One page required for entry stamp
Amounts over AUD 10,000, or equivalent, must be declared
Embassies and Consulates
U.s. consulate general sydney.
Suite 2, 50 Miller Street North Sydney, NSW 2060 Australia Telephone: +(61) (2) 2 8219-2100 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (2) 4422-2201 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Embassy Canberra (The Embassy does not provide consular services.) Moonah Place Yarralumla, ACT 2600 Australia Telephone: +(61) (2) 6214-5600 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (2) 411-424-608 Fax: +(61) (2) 6214-5970
U.S. Consulate General Melbourne 553 St. Kilda Road Melbourne, VIC 3004 Australia Telephone: +(61) (3) 9526-5900 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (3) 9389-3601 Fax: +(61) (3) 9526-5968 Email: [email protected]
U.S. Consulate General Perth 4th Floor 16 St. George's Terrace Perth, WA 6000 Australia Telephone: +(61) (8) 6144-5100 Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(61) (8) 9476-0081 Fax: +(61) (8) 9325-5914 Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
You must have a valid U.S. passport and a visa or an approved Electronic Travel Authority (ETA) to enter Australia. Most U.S. passport holders traveling to Australia for tourism or business purposes for less than 90 days can obtain an ETA. The ETA is an electronic label-free visa and can be obtained at the ETA website for a small service fee. Airlines and many travel agents in the United States are also able to apply for ETAs on behalf of travelers.
If you overstay your ETA or any other visa, even for short periods, you may be subject to exclusion, detention, and removal by the Australian Department of Home Affairs.
If you are travelling on a valid U.S. ePassport (a passport that contains an electronic chip) and are 16 years of age or older, you are eligible to use Australia’s automated border processing system, SmartGate, upon arrival in Australia (SmartGate kiosks are available only at participating airports). There is no additional enrollment process or fee to use SmartGate. Visit the SmartGate website for more information and for a list of participating airports in Australia.
Visit the Embassy of Australia website for the most current visa information.
HIV/AIDS restrictions. Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors and foreigners seeking permanent residence in Australia. Depending on the type of visa you apply for, the length of your stay, and your intended activities in Australia, you may be required to undergo a medical examination before the Australian Department of Home Affairs will issue you a visa.
If you are in the application process, and are found to be HIV positive, a decision on the application will be considered on the same grounds as any other pre-existing medical condition (such as tuberculosis or cancer), with the focus on the cost to Australia’s health care and community services.
Additional information about Australian immigration health requirements can be found here.
Please verify this information with the Embassy of Australia in Washington D.C. before you travel.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorists have targeted, and could continue to target, Australia.
- Australia has an alert system for possible terrorist attacks. The threat levels range from “not expected” to “certain.” The Australian National Security website has up-to-date information regarding the current terrorism threat level. You may also contact the Australian National Security Hotline at 61-1-800-123-400.
- U.S. citizens in Australia should remain vigilant toward their personal security and exercise caution.
- Australian law protects the right of individuals and groups to engage in peaceful protest and to publicly express their views. Demonstrations and political rallies are generally approved by local authorities and well publicized. However, please be cautious of any possible confrontation that could escalate into violence. You should attempt to avoid the areas of demonstrations and be careful within the vicinity of any demonstrations. You should stay current with media coverage of local events and always be aware of your surroundings.
- You should be aware that robberies, burglaries, assault, and auto theft are common in Australia’s larger cities.
- Foreign visitors in popular tourist areas are targets for pickpockets, purse-snatchers, and petty thieves. Most petty crime can be avoided if basic security precautions are taken.
- Be careful when visiting bars or clubs in the entertainment areas of major cities, as “bar brawls” and other assaults sometimes occur. You should watch out for drink spiking when consuming alcohol with unfamiliar people.
See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information on scams.
Victims of Crime:
- Report crimes to the local police at 000 and contact the U.S. Consulate in your district.
- The local authorities are responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes.
- See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- Help you find appropriate medical care.
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms.
- Provide a list of local attorneys.
- Provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide information about Australian Victim Assistance programs.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution.
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home.
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence may contact the U.S. consulate in your district for assistance.
Tourism: The tourism industry is generally regulated, and rules and safety inspections are regularly enforced. Hazardous areas/activities are identified with appropriate signage, and professional staff is typically on hand in support of organized activities. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is widely available throughout the country. Outside of a major metropolitan center, it may take more time for first responders and medical professionals to stabilize a patient and provide life-saving assistance. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, imprisoned or deported.
- It is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings, such as inside certain areas of Australian airports, near prisons, and at military bases.
- Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Alcohol and Drugs:
- Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of drugs are strict. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy sentences and fines. Please see Australia’s Department of Health webpage for further information.
- Driving under the influence of alcohol can result in jail time.
- Random breath testing of a driver's blood alcohol level is a common occurrence.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Potential Health Screening: Australian authorities have broad powers to prevent the entry of diseases and other materials into Australia that might pose a threat to its welfare. In the event of a public health emergency involving a communicable disease, passengers arriving in Australia may be subject to strict health screening measures, including testing, monitoring, and assessment for possible quarantine.
Customs: Australian customs authorities enforce very strict regulations concerning the importation from all countries of items such as agricultural goods, including plants and food products, and wood products, as well as very strict quarantine standards for animals and pets. Can you bring it in?
Contact the Embassy of Australia in Washington, D.C., or one of Australia's consulates in the United States for specific information regarding customs requirements, and visit the Australian Government’s Department of Agriculture website for additional information.
Natural Disasters:
Australia experiences a range of natural disasters, including bushfires, floods, and severe storms. These events are difficult to predict and can result in loss of life. You should be aware of conditions around you and monitor local weather and safety reports so you can take appropriate action when needed.
See our webpage for information on storm preparedness and response.
Safety Concerns:
Outdoor Recreation/Adventure
- Be aware that Australian fauna can be dangerous. From jellyfish to crocodiles, sharks, poisonous insects, and snakes, the continent and its waters host wildlife that merit awe and respect in equal doses.
- Visit the Wet Tropics Management Authority visitor information guide for information on Australian wildlife and marine life.
- Take important safety precautions when swimming, such as swimming only between the flags where a lifeguard is present, and never swimming alone.
- Further information on beach safety can be found on the Surf Life Saving website.
Follow recommended precautions when snorkeling and scuba diving and never dive alone. Over the past few years, there have been numerous deaths related to snorkeling and scuba diving incidents.
Faith-Based Travelers : See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in Australia. Australian federal law prohibits discrimination based on sexual orientation.
As of December 9, 2017 Australia defines marriage as “the union between two people.” Australia grants temporary and permanent visas to same-sex partners of Australian citizens.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance
- Australia enforces laws prohibiting discrimination against access to premises, facilities, and accommodation.
- Many of the downtown areas of Australian cities were built in the 1800s. These areas often have narrow sidewalks crowded with pedestrians and tourists.
- Most public transit, parking, streets, and buildings are accessible for disabled travelers.
- Tourist spots at the beach or in the Australian outback can have varying degrees of accessibility.
- Many accommodations and venues provide accessibility information on their websites.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
For emergency services in Australia, dial 000.
Ambulance services are widely available.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
- Excellent medical care is available in Australia.
- Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services.
- Serious medical problems requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to the United States can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on overseas insurance coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
Prescriptions:
- If traveling with prescription medication, check with the government of Australia to ensure the medication is legal in Australia .
- Always, carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of hospitals and a link to the Australian National Health Services Directory at Medical Assistance - U.S. Embassy & Consulates in Australia (usembassy.gov) . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for information on Medical Tourism, the risks of medical tourism, and what you can do to prepare before traveling to Australia.
Pharmaceuticals:
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Adventure Travel
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
Air Quality
Air pollution is a significant problem during certain months in Australia due to bush fires. Consider the impact seasonal bush fire season pollution may have on your health and consult your doctor before traveling.
The air quality varies considerably and changes with the season. It is typically at its worst in the bush fire season. People at the greatest risk from particle pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema;
- People with heart disease or diabetes
- People who work or are active outdoors
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety:
- Traffic operates on the left side of the road, and all vehicles use right-hand drive.
- Use caution when crossing streets and when driving.
- When crossing roads on foot, make sure you look carefully in all directions.
- Seat belt use by drivers and all passengers is mandatory, and fines apply for not wearing them.
- Motorcyclists must wear helmets.
- Speed limits and laws are rigorously enforced. Speed limits vary throughout Australia and are measured in kilometers, not miles. Be aware that speed cameras are everywhere and you will be ticketed for driving over the speed limit.
- Roads and streets are frequently narrower and less graded than U.S. highways.
- Outside major metropolitan areas, most highways are two-lane roads with significant distances between destinations.
- When driving in Australia, exercise caution while passing or merging with adjacent traffic.
- If driving in rural areas, be alert to free-roaming animals, such as kangaroos, and "road-trains" (several semi-truck trailers connected together).
- Passing road-trains is dangerous, and you should pull over to allow on-coming road-trains to pass to avoid being sideswiped.
- If you have no experience with a 4-wheel drive vehicle, you should exercise common-sense when driving in the Australian outback.
Traffic Laws:
- Each state/territory has different rules about using a foreign driver’s license and the conditions under which a visitor might have to get an international driver’s license. More information about driving rules and regulations is available by state .
- Texting or holding your phone while driving is against the law in Australia, but you can use a hands-free system to communicate while driving.
- For specific information concerning Australian driving permits, vehicle inspection, road tax, mandatory insurance, and the rental and operation of motor vehicles in Australia, visit the Australian Tourist Commission website.
Public Transportation: Australia has an extensive and safe public transportation network consisting of buses, streetcars, ferries, trains, and subways. Metered taxis and ride sharing services are also prevalent. Use common sense safety practices, such as guarding valuables and remaining aware of your surroundings, on all public transportation.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Australia’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Australia’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Australia should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings website portal select “broadcast warnings”.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Australia . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, australia map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Advertisement
Supported by
‘Fortress Australia’ Has a New Message: Come Back
For nearly two years, the country projected a harsh message of rigidity and “rules are rules.” Will long-haul travelers bet on the easygoing, inviting image it is sending out now?
- Share full article

By Tacey Rychter and Isabella Kwai
Moments after the Australian government announced that it would reopen the country’s borders to international travelers later this month, Emily Barrett locked in a fare for a flight to Sydney. The 32-year-old nanny from Palo Alto, Calif., spent three days researching and talking to Australian friends before she decided to book her trip to the island continent, which for two years had some of the world’s strictest border controls and longest lockdowns aimed at controlling the spread of the coronavirus.
“They all said, ‘if we go back into a lockdown now, people will go into the streets,’” she said. Her two-week trip is scheduled to start a few days after the border opens on Feb. 21.
Potential travelers and tourism operators alike are cautiously optimistic about the reopening of “Fortress Australia,” but many wonder if the isolated nation’s ongoing Covid restrictions — such as vaccine and testing requirements, as well as mask mandates — will make the return of international travel more of a trickle than a splash. Australia’s reputation for rigidity and reclusiveness during the pandemic — at odds with the inviting, easygoing nature portrayed by the country’s tourism boards — may also be a hurdle to overcome.
“There is no doubt that a full recovery will take time, but we are confident that the demand for Australia is strong,” said Phillipa Harrison, the managing director of Tourism Australia, the country’s tourism board.
Tourism was one of the fastest growing sectors in Australia’s economy before the pandemic, contributing 45 billion Australian dollars in 2019, or $32 billion.
Australia is among the world’s most immunized countries for Covid-19, with 94 percent of people over 16 fully vaccinated. Through 2020 and 2021, the country pursued a tough “zero Covid” strategy that closed national and state borders; restricted Australians from returning home and even leaving; enforced monthslong lockdowns and required its few visitors to undergo expensive hotel quarantines . Surging cases of the Omicron variant of the coronavirus in January, which persist, but have since declined , tipped most of the country into a new ‘living with the virus’ phase .
“It’s about coming back so the virus is under our control, whereas we felt that the virus was controlling us,” said Catherine Bennett, an epidemiologist at Deakin University in Melbourne, adding that opening the borders represented a turning point. “This is saying: We’re ready for this.”
Australia’s walls come down
Australia’s grand reopening comes with a few ground rules. Travelers entering the country must be fully vaccinated to avoid a costly hotel quarantine, and must test before arrival — somewhat common requirements for travel now.
But it will take a little more time for Australia’s welcome mat to roll out all the way. The entire state of Western Australia — a third of Australia’s vast land mass, but home to just 10 percent of the population — has essentially been closed to both international travelers and even vaccinated Australian citizens for most of the pandemic. It plans to reopen to vaccinated travelers on March 3, with testing rules on arrival. The state, which has reported about 2,900 total cases and 10 deaths since the pandemic began, is home to Perth — one of the world’s most remote major cities — more than 7,000 miles of coastline, the Kimberley region’s dramatic sandstone gorges and wine destinations like Margaret River. While the federal government can open the nation’s borders, the states can still set their own Covid restrictions, including entry rules.
“We desperately want people to come back,” said Graeme Skeggs, a general manager at Adam’s Pinnacle Tours , one of Western Australia’s larger tour companies, which, until the pandemic, operated luxury tours of the state’s renowned coastlines and landscapes. Much of their business evaporated after Covid struck, and some smaller operators the company worked with have closed. “Two years is a lot longer than any of us thought,” Mr. Skeggs said.
While many operators who rely on foreign tourists are hopeful, it’s clear that there is no simple return to prepandemic times.
China overtook New Zealand as Australia’s largest foreign tourist market for the first time in 2017, and 1.3 million visitors from mainland China spent more than $12 billion Australian dollars , or nearly $9 billion, in 2019, about 27 percent of the year’s international visitor spend.
With China still severely limiting outbound travel, that leaves a gaping hole in Australia’s tourism economy.
Michelle Chen opened the Apollo Surfcoast Chinese Restaurant in 2012 along Victoria’s Great Ocean Road — one of the state’s major scenic attractions, about a 2.5-hour drive from Melbourne — to cater to the hundreds of Chinese day-trippers who would stream off buses each day on their way to view the Twelve Apostles, a limestone rock formation farther down the coast.
When Australia closed to Chinese travelers on Feb. 1, 2020, she lost “nearly a hundred percent” of her business. In another stroke of misfortune, the restaurant burned down in April of last year. She reopened in December a few doors down. But Ms. Chen is not expecting her core customers to return for a long time.
She’s even revamped her menu, which used to feature dishes like Sichuan chile chicken that appealed to mainland Chinese visitors. Now the menu is “80 percent Australian-Chinese,” Ms. Chen said, with milder offerings like Mongolian beef. “I find I can’t sell the Chinese-Chinese dishes.”
Another thing desperately she’s looking forward to with the return of international travel: more workers. “Everywhere is shortage of labor,” she said.
The Djokovic drama
In January, the Australian Open — one of the country’s biggest sporting events, which draws hundreds of millions of viewers annually — became a media circus when Novak Djokovic, the world’s number one men’s tennis player, who is not vaccinated, was detained and finally deported from Melbourne because of his risk for “civil unrest.” The drama, which stretched on for 10 days, triggered protests in Australia from groups who believed the battle was the latest example of Covid-related mandates trampling public freedoms.
“Strong borders are fundamental to the Australian way of life,” the country’s prime minister, Scott Morrison, said after the decision to cancel the tennis star’s visa.
Australia’s fixation with border security is highly contentious within the country, particularly its harsh treatment of asylum seekers , but ultimately plays well with voters. But how would Mr. Djokovic’s unceremonious booting fit into Australia’s new “come on in” narrative?
“From our view, it really highlights the strength of Australia’s border policies,” said Chris Allison, Tourism Australia’s acting manager of the Americas. While Mr. Djokovic’s treatment was divisive, he said, it showed that “Australia has zero tolerance in terms of requiring vaccinations to come into the country,” and affirms the message of “how we’re trying to reopen our borders safely and protect the health of the nation.”
But time — and bookings — will tell if long-haul travelers are willing to bet on Australia’s reopening.
Some prefer to wait and see. Australia was where “everyone wanted to go” before the pandemic, said Samantha Carranza, a manager at Sky Tours , a travel agency in downtown Los Angeles. But “there isn’t much demand right now,” she said, adding that Australia’s protectiveness has made her clients cautious to travel there. “No one’s sure if it’s really open or not. Will it close again, will they get stuck there?”
The data shows that interest in travel to Australia is already on the rise: Flight bookings were up 200 percent following the border-opening announcement compared to the week before, according to Forward Keys, a travel analytics company.
“While the immediate jump in bookings is encouraging, the overall booking volume compared to the equivalent week in 2019 is modest,” said Olivier Ponti, the firm’s vice president of insights.
“I imagine there will be more and more confidence over the course of the year,” said Christie Hudson, a senior public relations manager at Expedia, the major online travel agency. “People are really ready to start thinking about these bucket-list trips again. I think for a lot of Americans, Australia is a bucket-list-type trip.”
Opening Aboriginal Australia to the world, cautiously
Cultural experiences led by Australia’s diverse Indigenous groups will be a focus of marketing to overseas travelers, according to Tourism Australia. But in the Northern Territory, the region with the highest proportion of Indigenous people, many remote communities are barred to outsiders until at least March 3 in an effort to protect the residents there from infection.
International visitors are key for the region’s Indigenous tourism sector: Before the pandemic, nearly 70 percent of overseas visitors to the Northern Territory engaged in Aboriginal tourism activities, compared to 16 percent of Australian tourists.
Victor Cooper, who owns and operates Ayal Aboriginal Tours in Kakadu National Park, said he used to welcome visitors from Europe and the United States to his “grandmother’s country,” where he taught them about bush tucker (native foods) and told traditional stories of the land.
“I had a really, really good thing in the overseas market, it took a long time to get that,” Mr. Cooper said. He has not had any overseas bookings since the reopening announcement, and worries things may be “complicated” for a while yet. “I don’t think I’m going to get the clients I used to have back in 2019.”
Other tourism operators are already seeing signs of recovery, which gives them hope for a better year ahead.
“It’s good to see people again,” said Dave Gordon, an employee at Wake Up Bondi , a hostel on Sydney’s famous beach, of the limited number of travelers who have been filtering back in recent months. “It’s exciting.”
Since the news of the border reopening, booking numbers for later in the year have risen, he said.
The first year of the pandemic was “quite a struggle,” he said. To survive, the hostel, which is on Bondi Beach’s main thoroughfare, slashed its rates and accepted longer-term lodgers, and even closed for a period.
But the border opening removes a major hurdle for him and other operators across the country, who want to convey a clear message for would-be tourists thinking of Australia: “Come!” he said. “This is the time to travel.”
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram , Twitter and Facebook . And sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to receive expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places for a Changed World for 2022.
Tacey Rychter is the social editor for the Travel section. More about Tacey Rychter
Isabella Kwai is a breaking news reporter in the London bureau. She joined The Times in 2017 as part of the Australia bureau. More about Isabella Kwai

© Department of Finance This content is only accurate as at the date of printing or download. Refer to Home | Department of Finance to ensure you are viewing the latest version.
Australian Government Travel Guide
The Australian Government Travel Guide provides an overview of the Arrangements including:
- a summary of the fare conditions that apply to negotiated domestic and international airfares
- value adds for tier 1 international airfares.
- tips on how to make bookings and reduce travel costs
Due to the sensitive content of this document, it is not possible to post to the website. Please contact WoAG Travel if you require a copy of the Guide, noting that is only available to Participating Entities.

Search Finance.gov.au
Please note: Search is currently being indexed on the new site, Friday 8 November.
Search will be available later today.
Thank you for your patience.
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care
Immunisation for travel
It’s important to protect your health when travelling overseas. You can avoid diseases and other health conditions by planning ahead for any vaccinations you may need.
If you are looking for information COVID-19 vaccines, please visit the COVID-19 digital certificate page.
Vaccines needed for travel
If you travel outside Australia, you may get sick from a number of diseases that vaccination can prevent. Travellers can bring these diseases into Australia when they return and cause disease outbreaks.
You should always ask your doctor or travel health clinic about vaccinations before you travel.
Your immunity to some diseases may have changed or reduced with time – you may need a booster.
Different countries have different vaccination requirements. The recommended vaccines for travelling depend on a number of factors, including:
- pregnancy or planning pregnancy
- underlying medical conditions
- vaccination history
- season of travel.
When to get vaccinated
You should consult your doctor or visit a travel health clinic 6 to 12 weeks before you leave Australia.
It is important to see your doctor early. If you do need vaccinations:
- your body needs time to develop full immunity
- you may need several doses of a vaccine to achieve full immunity.
How to check your vaccination record
You may have already received recommended vaccines from previous travel or routine vaccinations. These may be recorded in the Australian Immunisation Register.
The Australian Immunisation Register (AIR) is a national register that records vaccines given to all people in Australia.
The AIR includes vaccines given:
- Under the National Immunisation Program
- through school programs
- privately, such as for flu or travel.
You can check your immunisation record :
- online on MyGov through Medicare
- via the Express Plus Medicare mobile app
- by calling 1800 653 809 (Monday to Friday 8 am to 5 pm).
Cost of vaccines
The vaccines you need for travel may not be covered by the National Immunisation Program. In this case, you will need to buy them. This may involve:
- getting a prescription for the vaccine
- buying it from a pharmacy
- returning to your doctor to give you the vaccination.
The cost of vaccines varies depending on the type, the formula and where you buy them.
Some doctors might have these vaccines available in their clinics. Some pharmacies also offer vaccination services.
Check with your provider when you book your appointment.
How to stay safe overseas
The vaccine information you find on various websites is only a guide. You should not rely on such information. Talk to your doctor or travel health clinic for advice on travel vaccines and how to stay safe while you are overseas.
Find more information:
- Travel Health Information for things to consider before you leave, while you are away and when you return.
- Smartraveller (Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade)
- Travellers’ health (US Center for Disease Control & Prevention)
Keep routine vaccinations up to date
Travel is an important time to check whether you and your children are up to date with your vaccinations. This includes routine childhood vaccinations and boosters. Some of these include:
- measles-mumps-rubella (MMR)
- diphtheria-tetanus-whooping cough (pertussis)
- chickenpox (varicella)
Influenza is the most common vaccine-preventable disease caught by travellers.
The chance of getting these diseases may be greater while travelling overseas. Travellers can bring these diseases into Australia. This can lead to disease outbreaks.
Get more about information about routine vaccinations:
- National Immunisation Program Schedule
- When to get vaccinated
Diseases to be aware of
Some countries require proof of immunisation for certain infectious diseases before you can legally enter that country. Ask your doctor or travel health clinic if you need proof of immunisation before you travel.
Read about some of the common vaccine-preventable diseases found in other areas of the world.
Cholera is found in places with poor water and waste facilities. It spreads through contaminated food and water and causes severe diarrhoea and dehydration.
Humanitarian disaster workers should get vaccinated for cholera because they are more likely to get infected. Most travellers do not need a cholera vaccination because the risk of getting cholera is very low.
Your doctor may recommend the cholera vaccine if you have a condition that puts you at greater risk of travellers’ diarrhoea.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is one of the most common vaccine-preventable diseases caught by travellers. It is a liver disease spread by contaminated food and water. It is common in parts of India, Africa, Asia, South and Central America and the Middle East where there is poor sanitation and limited access to clean water.
You and your children over 1 year of age should get a Hepatitis A vaccination if you are travelling to an area where Hepatitis A is common.
Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis is a serious disease spread by mosquitoes in Asia and the Torres Strait region of Australia. We recommend vaccination against this disease if you are travelling to these parts and will be:
- travelling in rural areas
- undertaking certain activities with increased risk of exposure
- spending a month or more in the region.
You should avoid mosquito bites when you are in these areas.
Meningococcal
Meningococcal disease is a serious disease spread by close contact with an infected person. It is commonly found in sub-Saharan Africa.
Rabies is common to Central and South America, Eastern Europe, Africa and Asia. It is spread from infected animals to humans through bites, scratches and licks to open wounds. It is fatal when left untreated. The animal does not have to appear ill to have rabies. Infected animals can include dogs, monkeys, cats, rats, bats, foxes and chipmunks.
Ask your doctor if you need the rabies vaccine before you travel.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease spread by close contact with an infected person. It is common in developing countries.
We recommend the TB vaccine called BCG for children aged 5 years or under who are:
- travelling a lot
- spending a long time in countries where TB is common .
Typhoid is a disease spread through contaminated food and water. It causes diarrhoea and other symptoms. It is common in parts of India, Africa, Asia, South and Central America and the Middle East where there is poor sanitation and limited access to clean water.
Yellow fever
Yellow fever can be a serious disease. It causes fever, yellowing of the skin (jaundice) and damages the liver and kidneys. Mosquitoes spread yellow fever. It is found in Africa, the Caribbean and Central and South America.
You must be immunised for yellow fever before you can legally enter some countries. Only authorised yellow fever vaccination centres can give yellow fever vaccinations and certification. Ask your doctor about this.
Find more information: Yellow fever fact sheet
- Immunisation
- Travel health
Is there anything wrong with this page?
Help us improve health.gov.au
If you would like a response please use the enquiries form instead.

- About the Handbook
Vaccination for international travellers
Ensure that travellers are up to date with routine vaccines. Also consider other vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and risk of disease exposure.
Recently added
This page was added on 09 June 2018 .
Updates made
This page was updated on 23 October 2023 . View history of updates
Millions of Australians travel overseas every year. More than half of these trips are to destinations other than New Zealand, North America and Europe. 1
This page helps with making decisions about travel vaccines. Also check the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for details about specific vaccines.
See also Infographic. Vaccination for international travellers .
Health risks of overseas travel
Health risks associated with international travel include exposure to:
- infective agents
- altitude and temperature extremes
- other physical, psychological and environmental hazards
- poor-quality or limited access to clean water, shelter, hygiene and sanitation facilities, and health and medical care
The level of health risks depends on factors such as:
- the traveller’s underlying physical and mental health and physiological state
- the itinerary and activities undertaken
- the duration of exposure to various hazards during travel
Travellers at increased risk of serious travel-associated infections include:
- young children and infants
- pregnant women
- people with underlying medical conditions, especially immunocompromising conditions due to disease or medical treatment
- people spending extended periods in multiple regions with poor resources or in remote areas
- people participating in events where large numbers of people will gather, such as major sporting, cultural, social or religious events
- migrant families travelling back to their region of origin to visit friends and relatives
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are more likely to: 2
- have closer contact with local populations
- stay in remote or rural areas
- consume higher-risk food and beverages
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are less likely to: 2,3
- recognise the health risks associated with travelling
- seek pre-travel health advice
- obtain the recommended vaccines or prophylaxis
Common infections acquired by travellers
Exposure to infectious diseases is one of the many health hazards of international travel. Some of these diseases are vaccine preventable. Although some of these diseases are present in Australia, the risk of acquiring them overseas may be higher because of:
- higher disease incidence in other countries
- increased risk of exposure from participating in certain activities while travelling
Foodborne and waterborne infections
It is common for travellers to ingest contaminated food or beverages, resulting in an illness. 4-6 Practicing safe eating and drinking habits is essential to minimise the risk of contracting food and waterborne diseases while travelling. These include treating water or only drinking bottled water, avoiding undercooked meat, and avoiding raw fruit and vegetables (unless they can be peeled or washed in safe water prior to eating). Most infections are diarrhoeal diseases due to enteric pathogens, but some are due to extra-intestinal microorganisms, such as hepatitis A virus and Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (causing typhoid).
Vaccines are available against hepatitis A, typhoid and cholera.
Vector-borne infections
Insect-borne — especially mosquito-borne — infections, such as malaria and dengue, are important causes of fever in Australian travellers returning from endemic areas, particularly Southeast Asia and Oceania. 4,6
A dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is available for the prevention of secondary dengue infections (not primary prevention of initial dengue infection ) in select individuals. See Clinical advice: ATAGI statement on use of Dengvaxia® for Australians .
Japanese encephalitis occurs throughout much of Asia and the Western Pacific region, including eastern Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. 7 Yellow fever occurs only in parts of Africa and South America, 8 and tick-borne encephalitis occurs in parts of Europe and Asia. 9
Vaccines are available against Japanese encephalitis , yellow fever and tick-borne encephalitis .
Some other vector-borne diseases and parasitic (including protozoal and helminthic) diseases are also important for international travellers. Some are preventable through appropriate barrier precautions and chemoprophylaxis (for example, malaria). 9
Aerosol-borne infections
Vaccine-preventable infections transmitted by aerosols and/or droplets include: 9
- influenza (the most common vaccine-preventable infection among travellers) 10
- meningococcal disease
- varicella (chickenpox)
The incidence of measles and mumps is higher in many overseas countries, including some developed countries, than in Australia.
Tuberculosis is a rare infection in travellers. 11 Expatriates who live in endemic areas for a long time are more likely to acquire tuberculosis than short-term visitors. 12
Vaccines are available against all of these diseases.
Bloodborne and sexually transmitted infections
Some Australian travellers may be at risk from bloodborne and sexually transmissible infections, such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV. In some areas, healthcare workers using non-sterile medical equipment or other poor infection control practices may transmit these viruses and other bloodborne agents.
Vaccines are available against hepatitis B.
Exotic infectious agents
Travellers may be exposed to a variety of other exotic infections, such as:
- rabies from bites or scratches from rabid dogs, bats and other mammals in many countries
- schistosomiasis from exposure to water infested with the parasites, especially in Africa
- leptospirosis through activities such as rafting or wading in contaminated streams
Of these diseases, vaccines are available only against rabies.
Recommending travel vaccines
Although recommending appropriate vaccines is important, it is not the only part of a pre-travel medical consultation. Travel vaccines — those relevant for travelling — include all relevant vaccines, not just the ones that prevent diseases that most commonly occur overseas.
Do not recommend a vaccine based only on the destination country, because there is no single ‘correct’ list of vaccines for travel to any particular country.
There are 3 categories of travel vaccines:
- routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
- selected vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
- vaccines required by the International Health Regulations 2005 (IHR) or for entry into specific countries
Questions for a pre-travel medical consultation
During a pre-travel medical consultation, ask questions about the traveller’s:
- personal information, including age and whether they are pregnant or planning pregnancy
- underlying medical conditions, particularly immunocompromising conditions, and current medicines
- vaccination history (including adverse events following immunisation) and allergy history
- purpose of travel and intended activities, especially those associated with various environmental risks and hazards
- plans for travel insurance
Also ask about their itinerary in detail, including:
- date of departure and time available for vaccinations
- specific localities and routes
- rural versus urban stay
- duration of stay
- likely access to health care and other services
- likelihood of changing the planned itinerary
This information helps to tailor recommendations about preventive vaccination or chemoprophylaxis for exposure risks during the proposed trip. It also allows the clinician to advise about other appropriate preventive health measures (for example, food and water precautions, avoiding bites from mosquitoes or other arthropods) and about managing possible health conditions during travel.
Organisational requirements for vaccination
Some overseas organisations, such as schools, colleges and universities, require evidence of vaccination or immunity against some vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles and meningococcal disease. Consider these requirements when planning and scheduling vaccines before departure.
Routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
Vaccinate all prospective travellers according to the recommended vaccination schedule appropriate for their age, underlying health conditions, occupation and lifestyle. Vaccines might include, for example, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for an older person, or hepatitis B vaccine for a first aid officer.
Also ensure that all children are vaccinated according to the National Immunisation Program schedule. In exceptional circumstances, give the National Immunisation Program vaccines at the minimum age rather than the recommended age (see Table. Minimum acceptable age for the 1st dose of scheduled vaccines in infants in special circumstances ). Children vaccinated using the minimum age rather than the recommended age may need extra vaccine doses to ensure adequate protection. Observe the minimum interval requirements between doses (see Table. Minimum acceptable dose intervals for children <10 years of age ). The chances of being exposed to some diseases, such as measles and mumps, may be greater during overseas travel, even to other developed countries.
For some itineraries, it may be appropriate for the traveller to receive some booster doses earlier than the routine recommended time. An example may be diphtheria-tetanus booster.
Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis
Vaccinate adult travellers against tetanus before departure, particularly if:
- their risk of sustaining a tetanus-prone wound is high
- there could be delays in accessing health services where they can receive tetanus toxoid boosters safely, if required
Offer dTpa vaccine during a pre-travel consultation if the traveller has never received a dose of dTpa . This provides protection against pertussis (see Pertussis ).
For high-risk travel, consider giving a booster dose of either dTpa or dT vaccine if more than 5 years have passed (see Tetanus ).
Hepatitis B
Most Australian children born since 2000 have been vaccinated against hepatitis B under the National Immunisation Program or state and territory school-based vaccination programs.
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for long-term or frequent travellers to regions of intermediate or high endemicity of hepatitis B, including:
- Central and South America
This is because travellers may be exposed to hepatitis B virus through bloodborne routes (including during emergency medical or dental procedures) or sexual routes. According to 1 survey, about half of Australian travellers who spent at least 3 nights in Southeast or East Asia participated in at least 1 activity that had a risk of hepatitis B transmission. 13
See also Hepatitis B .
Influenza and pneumococcal disease
Older travellers and those with any relevant underlying medical or behavioural risk factors should receive pneumococcal vaccine. See Pneumococcal disease for more details.
Consider influenza vaccine for all travellers, especially if they are travelling to a region during its influenza season. Influenza vaccine is particularly relevant if:
- there is an influenza epidemic at the traveller’s destination
- the person is travelling in a large tourist group, especially one that includes older people
- the person is travelling on cruises, where people are relatively confined for days to weeks
See also Influenza.
Measles, mumps and rubella
Inadequately vaccinated young adult travellers are responsible for most current measles outbreaks in Australia. This occurs when they acquire the infection overseas and bring it back to Australia. Some countries, regions or communities — including developed countries — have a higher incidence of measles and mumps than Australia. 9
Australians born during or since 1966 who have not received the recommended 2 doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella)–containing vaccines are recommended to receive MMR vaccine before travelling. This also applies to infants 6–12 months old travelling to areas with measles outbreaks or where measles is endemic . The exception is for pregnant women, because MMR is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
People born before 1966 do not need to receive measles-containing vaccine (unless serological evidence indicates that they are not immune). This is because circulating measles virus and disease were prevalent before 1966, so most people would have acquired immunity from natural infection .
However, confirmed cases of measles have occurred in people born before 1966. 14 If in doubt about a person’s immunity, it may be faster and easier to vaccinate the person than conduct serological testing . See Serological testing for immunity to measles .
See also Measles .
Unvaccinated travellers are recommended to receive varicella vaccine if they either:
- have not had clinical disease, or
- have an uncertain history of clinical disease and serology shows a lack of immunity
The exception is for pregnant women, because varicella vaccine is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
See also Varicella .
Meningococcal disease
Vaccination against meningococcal serogroups A, C, W-135, Y and B is recommended for certain age and population groups who are at increased risk of meningococcal disease.
In addition, MenACWY (quadrivalent meningococcal) vaccine is recommended for people who are:
- planning travel to, or living in, parts of the world where epidemics of serogroup A, C, W-135 or Y meningococcal disease occur, particularly the ‘meningitis belt’ of sub-Saharan Africa 15
- planning travel to mass gatherings, such as pilgrims travelling to the Hajj in Saudi Arabia
Seek up-to-date epidemiological information to determine whether a traveller needs meningococcal vaccination. See Accessing up-to-date travel information.
The Saudi Arabian authorities require that all pilgrims travelling to Mecca (for the Hajj or Umra) have evidence of recent vaccination with the quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine. 16 See Requirements for travellers to Mecca and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
See also Meningococcal disease .
Poliomyelitis
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against polio (see Poliomyelitis ).
If the person is travelling to a country where wild poliovirus is still circulating, they should receive inactivated poliovirus ( IPV ) vaccine if they have not completed a 3-dose primary course of any polio vaccine. Travellers who have completed the primary course should receive a single booster dose.
The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Polio Eradication Initiative website website has an up-to-date list of polio-affected countries.
Documented evidence of polio vaccination is not routinely required for travellers under the International Health Regulations. However, documented evidence of vaccination may be temporarily required according to WHO recommendations in response to new evidence of the spread of wild poliovirus (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries and Documentation and certificates ).
International polio epidemiology and associated travel requirements can change. Check the Australian Government Department of Health website for current recommendations for Australian travellers .
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against COVID-19. Foreign governments may require evidence of COVID-19 vaccination before a traveller is allowed to enter. The Australian-issued International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate is a secure way to prove COVID-19 vaccination history that has been developed to meet agreed international travel standards. Parents and carers of children <14 years of age, adolescents ≥14 years of age and adults can get a copy of their COVID-19 vaccination certificate at any time:
- using their Medicare online account through myGov
- through the Medicare Express Plus mobile app
- by calling 1800 653 809 (free call)
See also COVID-19 .
Vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
Use a risk assessment approach when recommending travel vaccines. Weigh the potential risks of disease exposure and protective benefits from vaccination against potential adverse effects, and the non-financial and financial costs of vaccination.
Prioritise vaccines for diseases that are:
- common and of significant impact, such as influenza and hepatitis A
- less common, but have severe potential adverse outcomes, such as Japanese encephalitis and rabies
Consider booster doses, where appropriate (see disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations). If the person is departing for travel soon, consider an accelerated schedule, if appropriate, such as for hepatitis B vaccine or the combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccine (see Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B ). Although immunity may be established sooner with the accelerated schedule, people who receive an accelerated schedule need another dose about a year later to complete the course and ensure long-term protection.
Most travellers do not need cholera vaccine. 16,17 The risk of a traveller acquiring cholera is very low if they avoid contaminated food and water.
No country requires travellers to have certification of cholera vaccination. No country has official entry requirements for cholera vaccination
See also Cholera .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for all travellers ≥1 year of age travelling to moderately or highly endemic countries (including all developing countries). The exceptions are people who have evidence of natural immunity after previous infection .
Normal human immunoglobulin is no longer used to protect travellers against hepatitis A.
See also Hepatitis A .
Japanese encephalitis
While now considered an emerging disease in Australia, Japanese Encephalitis is more likely in travellers to endemic regions overseas. 18 Japanese encephalitis ( JE ) vaccine is recommended for travellers spending a month or more in endemic areas in Asia, Papua New Guinea or the outer islands of Torres Strait during the JE virus transmission season.
Consider JE vaccination for shorter-term travellers, particularly if:
- travel is during the wet season
- travel may be repeated
- the person will spend a lot of time outdoors
- the person’s accommodation has no air-conditioning, screens or bed nets
Check a reputable source before travel for information about JE virus activity — for example, Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’) . 19
A traveller’s overall risk of acquiring JE in these JE - endemic countries is likely to be low (<1 case per 1 million travellers). Determine the specific risk according to the: 17
- season of travel
- regions visited
- duration of travel
- extent of outdoor activity
- extent to which the person avoids mosquito bites
See also Japanese encephalitis .
Before travel to rabies- endemic regions, advise people about:
- the risk of rabies infection
- avoiding close contact with wild, stray and domestic animals — especially dogs, cats, monkeys and bats
- the importance of appropriate immediate wound care of all animal bites and scratches
See also Rabies and other lyssaviruses, including Australian bat lyssavirus .
Recommendations for rabies vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
When deciding whether to give a pre-travel prophylactic rabies vaccination, assess the:
- likelihood of exposure to potentially rabid animals
- access to appropriate health care and availability of post-exposure prophylaxis , including rabies immunoglobulin , should there be an at-risk exposure
- timeliness of access to health care after exposure
Use a lower threshold for recommending rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis for children travelling to endemic areas.
Benefits of vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
Pre-travel rabies vaccination:
- ensures that the traveller has received a safe and efficacious vaccine
- simplifies the management of a subsequent exposure because the person will need fewer doses of vaccine
- means that rabies immunoglobulin — which is often extremely expensive, and difficult or even impossible to obtain in many developing countries — is not needed
- reduces the urgency of post-exposure prophylaxis
Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is caused by a tick-borne RNA flavivirus. The disease may involve the central nervous system. TBE is prevalent in parts of central and northern European temperate regions, and across northern Asia. Travellers are at risk when hiking or camping in forested areas in endemic regions during the summer months.
Safe and effective vaccines are available. Vaccination is recommended only for people with a high risk of exposure.
TBE vaccine is not registered in Australia, but a small stock of vaccine may be available for use under the Special Access Scheme .
Tuberculosis
Vaccination with BCG (bacille Calmette–Guérin) vaccine is generally recommended for tuberculin-negative children <5 years of age who will be staying in high-risk countries for an extended period (3 months or longer).
Vaccinating older children and adults appears to be less beneficial. However, consider vaccinating tuberculin-negative children aged ≥5 years but <16 years who may be living or travelling for long periods in high-risk countries.
A high-risk country is one that has a tuberculosis incidence of >40 per 100,000 population.
For travellers who need BCG vaccine, consider the following precautions when scheduling their vaccination visits:
- If possible, give BCG vaccine at least 3 months before the person will arrive in an endemic area.
- Give other live viral vaccines (for example, MMR , varicella, yellow fever) at the same time or with a minimum 4-week interval after BCG vaccination.
- A tuberculin skin test (TST; Mantoux), performed by trained and accredited healthcare practitioners, is recommended before receiving BCG vaccine for all individuals (except infants aged <6 months).
- People may suppress reactions to tuberculin for 4–6 weeks after viral infections or live viral vaccines, particularly measles infection and measles-containing vaccines.
State and territory tuberculosis services can provide tuberculin skin tests and BCG vaccine.
See also Tuberculosis .
Typhoid vaccine may be recommended for travellers ≥2 years of age travelling to endemic regions, including:
- the Indian subcontinent
- most Southeast Asian countries
- several South Pacific nations, including Papua New Guinea
This advice is also relevant for those travelling to endemic regions to visit friends and relatives.
Inactivated parenteral and live oral typhoid vaccine formulations are available.
See also Typhoid fever .
Yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccine is recommended for all people ≥9 months of age travelling to, or living in, an area with a risk of yellow fever virus transmission. 20
To minimise the risk of introducing yellow fever, some countries require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination for entry, in line with the International Health Regulations (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries ).
When assessing the need for yellow fever vaccination, consider:
- the risk of the person being infected with yellow fever virus
- country entry requirements
- individual factors such as age, pregnancy and underlying medical conditions
Vaccination is generally not recommended for travel to areas with a low probability of yellow fever virus exposure — that is:
- where human yellow fever cases have never been reported
- where evidence suggests only low levels of yellow fever virus transmission in the past
However, consider vaccination for a small subset of travellers to lower-risk areas who are at increased risk of exposure to mosquitoes or who are unable to avoid mosquito bites. 20
People aged ≥60 years are at increased risk of severe adverse events after primary yellow fever vaccination. Weigh the adverse effects of vaccinating people in this age group against the potential for yellow fever virus exposure and, in turn, the benefits of vaccination. 17
See also Yellow fever .
Booster doses
Most people do not need a booster dose of yellow fever vaccine. A single dose induces protective antibody levels that last for many decades. However, certain people are recommended to receive a booster if their last dose was more than 10 years ago and they are at ongoing risk of yellow fever virus infection . See Yellow fever .
Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries
Yellow fever requirements.
The International Health Regulations require yellow fever vaccination for travelling in certain circumstances. This is to:
- protect travellers who are likely to be exposed to yellow fever
- stop importation of the virus into countries that have the relevant vectors (see Yellow fever ).
Some countries may require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination as a condition of entry or exit (see Planning and documenting vaccines ). This includes countries that do not currently have yellow fever circulating.
Australia’s yellow fever travel requirements are detailed in the Australian Government Department of Health’s yellow fever fact sheet .
Contact the relevant embassies or consulates in Australia to confirm the entry requirements for yellow fever vaccination for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through.
Requirements for travellers to Mecca
Each year, Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Health publishes the requirements and recommendations for entry visas for travellers on pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj and Umra). 16
For pilgrims travelling directly from Australia, only evidence of MenACWY vaccination is currently mandatory. However, check the current requirements when advising prospective Hajj and Umra pilgrims (see Meningococcal disease and Accessing up-to-date travel information ).
Temporary requirements
The International Health Regulations may temporarily introduce requirements for other vaccine-preventable diseases in response to changes in disease epidemiology that are of international health concern. An example is for polio vaccination.
Because country vaccination requirements are subject to change at any time, confirm all current vaccination requirements for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through before travel. See Poliomyelitis and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Planning and documenting vaccines
Ideally, start vaccination courses early enough before departure to allow:
- monitoring of any possible adverse events
- time for adequate immunity to develop
Requirements for multiple vaccines
A traveller may need multiple vaccines before they depart. Apply the standard recommendations and precautions when giving multiple vaccines (see Administration of vaccines ).
A traveller may need more than 1 clinic visit if they need multiple vaccines or doses (for example, rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis or hepatitis B vaccine). Pay special attention to scheduling of these visits, and consider:
- dose interval precautions (for example, for multiple live vaccines)
- requirements for pre-vaccination tests (for example, tuberculin skin test)
- potential interference by some antimalarials, if relevant (for example, rabies vaccine)
Documentation and certificates
It is important to document travel vaccines:
- in the clinic’s record
- in the traveller’s record that they can carry with them
- on the Australian Immunisation Register
The record should also include all the other routinely recommended vaccines that the traveller has ever received.
For yellow fever vaccination, a traveller needs to have an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), which only Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres can provide under the International Health Regulations (see Yellow fever ).
Travellers may also need an ICVP for other vaccine-preventable diseases, such as polio, based on temporary recommendations.
See also Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Vaccinating travellers with special risk factors
See Vaccination for women who are planning pregnancy, pregnant or breastfeeding , Vaccination for people who are immunocompromised and the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations for travellers who are pregnant or immunocompromised.
Accessing up-to-date travel information
International travellers’ health risks constantly change. Up-to-date information, and knowledge of the changing epidemiology and current outbreaks of infectious and emerging diseases are essential. Reliable online information sources include:
- World Health Organization (WHO) for disease outbreak news, and its Travel and health section for specific advice on travel and health, including travel vaccination recommendations
- Travelers’ health , United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Travel health information , Australian Government Department of Health
- Smartraveller , the Australian Government’s travel advisory and consular information service, which provides up-to-date advice about health, safety and other risks of specific destinations for Australian travellers
The following resources have comprehensive technical advice on international travel and health, including vaccination:
- the latest edition of WHO’s International travel and health
- the CDC’s Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’)
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 3401.0 – Overseas arrivals and departures, Australia, Mar 2018 (accessed May 2018).
- Paudel P, Raina C, Zwar N, et al. Risk activities and pre-travel health seeking practices of notified cases of imported infectious diseases in Australia. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24(5):tax044.
- Heywood AE, Watkins RE, Iamsirithaworn S, Nilvarangkul K, MacIntyre CR. A cross-sectional study of pre-travel health-seeking practices among travelers departing Sydney and Bangkok airports. BMC Public Health 2012;12:321.
- Chen LH, Leder K, Barbre KA, et al. Business travel-associated illness: a GeoSentinel analysis. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Angelo KM, Kozarsky PE, Ryan ET, Chen LH, Sotir MJ. What proportion of international travellers acquire a travel-related illness? A review of the literature. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24.
- Freedman DO, Weld LH, Kozarsky PE, et al. Spectrum of disease and relation to place of exposure among ill returned travelers. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354:119-30.
- Halstead SB, Hills SL, Dubischar K. Japanese encephalitis vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- Staples JE , Monath TP, Gershman MD, Barrett AD. Yellow fever vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Chapter 6: Vaccine-preventable diseases and vaccines . In: International travel and health. Geneva: WHO; 2017.
- Steffen R. Travel vaccine preventable diseases-updated logarithmic scale with monthly incidence rates. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Denholm JT, Thevarajan I. Tuberculosis and the traveller: evaluating and reducing risk through travel consultation. Journal of Travel Medicine 2016;23.
- Lachish T, Tenenboim S, Schwartz E. 35 - Humanitarian Aid Workers. In: Keystone JS, Kozarsky PE, Connor BA, et al., eds. Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). London: Elsevier; 2019. (Accessed 6 July 2023). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323546966000355
- Leggat PA, Zwar NA, Hudson BJ. Hepatitis B risks and immunisation coverage amongst Australians travelling to Southeast Asia and East Asia. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 2009;7:344-9.
- Winkler NE, Dey A, Quinn HE, et al. Australian vaccine preventable disease epidemiological review series: measles, 2012-2019. Commun Dis Intell (2018) 2022;46.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Epidemic meningitis control in countries of the African meningitis belt, 2017. Weekly Epidemiological Record 2018;93:173-84.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health: health conditions for travellers to Saudi Arabia for the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) . 2017 (accessed May 2018).
- Freedman DO, Chen LH. Vaccines for International Travel. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2019;94:2314-39.
- Furuya-Kanamori L, Gyawali N, Mills DJ, et al. The Emergence of Japanese Encephalitis in Australia and the Implications for a Vaccination Strategy. Trop Med Infect Dis 2022;7.
- Hills SL, Rabe IB, Fischer M. Infectious diseases related to travel: Japanese encephalitis . In: CDC yellow book 2018: health information for international travel. New York: Oxford University Press; 2017.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health (accessed Apr 2018).
Page history
Minor updates to clinical guidance around routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas), including the addition of advice regarding COVID-19.
Editorial update to reflect changes to pneumococcal vaccine recommendations for older adults and people with medical risk factors.
Guidance on vaccination of travellers against measles, mumps and rubella updated to reflect advice in the Measles chapter.
Help us improve the Australian Immunisation Handbook
Printed content may be out of date. For up to date information, always refer to the digital version:
Subscribe to receive notifications regarding updates to the Australian Immunisation Handbook and changes to immunisation policy.
Help us improve
We are always looking for ways to improve our website, the NICC and mobile app.
Provide feedback
Acknowledgement
The Department of Health and Aged Care acknowledges First Nations peoples as the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia, and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to them and their cultures, and to all Elders both past and present.
© Commonwealth of Australia | Department of Health and Aged Care
Link , share or bookmark directly to this section of the page.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Warnings and insurance
The Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office ( FCDO ) provides advice about risks of travel to help British nationals make informed decisions. Find out more about FCDO travel advice .
Before you travel
No travel can be guaranteed safe. Read all the advice in this guide as well as support for British nationals abroad which includes:
- advice on preparing for travel abroad and reducing risks
- information for women, LGBT+ and disabled travellers
Follow and contact FCDO travel on Twitter , Facebook and Instagram . You can also sign up to get email notifications when this advice is updated.
Travel insurance
If you choose to travel, research your destinations and get appropriate travel insurance . Insurance should cover your itinerary, planned activities and expenses in an emergency.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Fares fall as Australian air travel returns to pre-Covid capacity, Flight Centre says
Higher seat availability has resulted in lower airfares, group says, but cost-of-living pressures continue their impact on holiday plans
- Get our morning and afternoon news emails , free app or daily news podcast
Airlines have finally shaken off the lingering effects of Covid, with capacity back to pre-pandemic levels for the first time, according to data from Flight Centre.
Global seat availability climbed back over 100% of 2019 levels in April, with travellers enjoying lower air fares as a result.
“An analysis of key international routes for Australian travellers found fares on some international routes out of Australia dropped by up to 25%,” said Flight Centre Corporate’s managing director, Melissa Elf. “With more and more capacity and competition being introduced to the market, it’s a trend we’ll continue to see throughout the rest of the year.”
Australia’s international capacity is expected to tick up from 95% to 98% next month, while domestic capacity has been hovering between 98 and 100% for the last few months.
Elf said there are promising signs that air fares will continue to fall beyond the short term, with major carriers – including Delta, Singapore Airlines and China Southern – recently announcing new routes to Australia.
In the first quarter of 2024, flights to Australia’s most popular travel destination Indonesia were down 21% from the previous year at $798 return on average. Available seats to the holiday spot were at 115% of pre-pandemic capacity.
Sign up for Guardian Australia’s free morning and afternoon email newsletters for your daily news roundup
Capacity to Japan, Qatar and Papua New Guinea are also above pre-Covid levels, while the UK is back even. Routes to Hong Kong and the US have the biggest room for recovery, at just 63% and 70% of pre-pandemic capacity respectively.
International and domestic seat capacity across Qantas and Jetstar recovered to 90% of pre-pandemic levels in the second half of 2023, an increase of 25% on the previous year, the group said.
Despite falling air fares, rising cost-of-living pressures elsewhere are forcing more Australians to holiday within their own state or cancel travel plans altogether.
In a survey of 1,500 Australians conducted by Pure Profile for the travel industry’s peak body, 70% planned to go away for a holiday during the autumn school break, including 41% within their own state, up from 36% during summer.
after newsletter promotion
A further 21% will holiday interstate and 8% were planning to go overseas.
The Tourism and Transport Forum’s chief executive, Margy Osmond, said it was pleasing to see Australians supporting the local economy and tourism operators.
“But we’re concerned the sector is still feeling the impact of cost-of-living pressures with many families taking shorter holidays than originally planned, staying with friends or relatives to save money or recently cancelling their travel plans altogether,” she said.
Just over half of respondents said cost-of-living pressures had affected their decision to travel, with a quarter saying they would go away for shorter than originally planned as a result.
- Airline industry
Most viewed

Countries, economies and regions
Select a country, economy or region to find embassies, country briefs, economic fact sheets, trade agreements, aid programs, information on sanctions and more.
International relations
Global security.
- Australia and sanctions
- Australian Safeguards and Non-proliferation Office (ASNO)
- Counter-terrorism
- Non-proliferation, disarmament and arms control
- Peacekeeping and peacebuilding
Regional architecture
- Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- East Asia Summit (EAS)
- Australia and the Indian Ocean region
- Pacific Islands regional organisations
Global themes
- Child protection
- Climate change
- Cyber affairs and critical technology
- Disability Equity and Rights
- Gender equality
- Human rights
- Indigenous peoples
- People Smuggling, Human Trafficking and Modern Slavery
- Preventing Sexual Exploitation, Abuse and Harassment
- Australia’s treaty-making process
International organisations
- The Commonwealth of Nations
- United Nations (UN)
- World Trade Organization
Foreign Arrangements Scheme
Trade and investment, about free trade agreements (ftas).
- The benefits of FTAs
- How to get free trade agreement tariff cuts
- Look up FTA tariffs and services market access - DFAT FTA Portal
- Discussion paper on potential modernisation – DFAT FTA Portal
About foreign investment
- The benefits of foreign investment
- Investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS)
- Australia's bilateral investment treaties
- Australia's foreign investment policy
For Australian business
- Addressing non-tariff trade barriers
Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai
Stakeholder engagement.
- Ministerial Council on Trade and Investment
- Trade 2040 Taskforce
- First Nations trade
Australia's free trade agreements (FTAs)
- ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand (AANZFTA)
- Chile (ACLFTA)
- China (ChAFTA)
- Hong Kong ( A-HKFTA & IA)
- India (AI-ECTA)
- Indonesia (IA-CEPA)
- Japan (JAEPA)
- Korea (KAFTA)
- Malaysia (MAFTA)
- New Zealand (ANZCERTA)
- Peru (PAFTA)
- Singapore (SAFTA)
- Thailand (TAFTA)
- United Kingdom (A-UKFTA)
- USA (AUSFTA)
- Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)
- European Union (A-EUFTA)
- India (AI-CECA)
- Australia-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement
- Australia-Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Trade and investment data, information and publications
- Fact sheets for countries and regions
- Australia's trade balance
- Trade statistics
- Foreign investment statistics
- Trade and investment publications
- Australia's Trade through Time
WTO, G20, OECD, APEC and IPEF and ITAG
Services and digital trade.
- Service trade policy
- Australia-Singapore Digital Economy Agreement
- Digital trade & the digital economy
Development
Australia’s development program, performance assessment.
- Development evaluation
- Budget and statistical information
Who we work with
- Multilateral organisations
- Non-government organisations (NGOs)
- List of Australian accredited non-government organisations (NGOs)
Development topics
- Development issues
- Development sectors
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Sustainable Development Goals

Where we deliver our Development Program
Humanitarian action.
Where and how Australia provides emergency assistance.
People-to-people
Australia awards.
- Australia Awards Scholarships
- Australia Awards Fellowships
New Colombo Plan
- Scholarship program
- Mobility program
Public diplomacy
- Australian Cultural Diplomacy Grants Program
- Australia now
- UK/Australia Season 2021-22
Foundations, councils and institutes
- Australia-ASEAN Council
- Australia-India Council
- Australia-Indonesia Institute
- Australia-Japan Foundation
- Australia-Korea Foundation
- Council for Australian-Arab Relations (CAAR)
- Council on Australia Latin America Relations (COALAR)
International Labour Mobility
- Pacific Labour Mobility Scheme
- Agriculture Visa
Australian Volunteers Program
Supporting organisations in developing countries by matching them with skilled Australians.
Sports diplomacy
Australia is a successful global leader and innovator in sport.
A global platform for achievement, innovation, collaboration, and cooperation
- About Australia
Australia is a stable, democratic and culturally diverse nation with a highly skilled workforce and one of the strongest performing economies in the world.
Australia in Brief publication
This is the 52nd edition of Australia in Brief, revised and updated in February 2021
Travel advice
To help Australians avoid difficulties overseas, we maintain travel advisories for more than 170 destinations.
- Smartraveller – travel advice
International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate
Prove your COVID-19 vaccinations when you travel overseas.
- Services Australia
The Australian Passport Office and its agents are committed to providing a secure, efficient and responsive passport service for Australia.
- Australian Passport Office
24-hour consular emergency helpline
- Within Australia: 1300 555 135
- Outside Australia: +61 2 6261 3305
- Getting help overseas
- Visas for Australians travelling overseas
Visas to visit Australia
Whether you are visiting Australia for less than 72 hours or planning on a stay of several years you must have a valid Australian visa.
A visa is a form of permission for a non-citizen to enter, transit or remain in a particular country.
Information on visas to Australia can be found at the Department of Home Affairs .
Related links
- Visiting Australia
- Australia.com - official Australian tourism website
Brazil Again Extends Visa Exemptions for US, Canada and Australia, This Time Until 2025
Brazil’s government has extended exemptions to tourist visa requirements for citizens of the U.S., Australia and Canada until April 2025, extending a program aimed at boosting tourism that had been scheduled to end Wednesday

Bruna Prado
FILE - A tourist takes a selfie with the Christ the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Nov. 25, 2017. Brazil’s government has postponed until April 2025 tourist visa exemptions for citizens of the U.S., Australia, and Canada that had been scheduled to end on Wednesday, according to a decree published in the nation's official gazette. (AP Photo/Bruna Prado, File)
RIO DE JANEIRO (AP) — Brazil’s government extended exemptions to tourist visa requirements for citizens of the U.S., Australia and Canada until April 2025, extending a program aimed at boosting tourism that had been scheduled to end Wednesday.
The decision, issued by Brazilian presidency and the Ministry of Foreign Relations late Tuesday, marks the third time Brazil has delayed the visa requirement since President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva took office in 2023.
His predecessor, Jair Bolsonaro, exempted the countries from visas as a means to boost tourism — although all three countries continued to demand visas from Brazilians.
That went against the South American country’s tradition of requiring visas from travelers based on the principle of reciprocity and equal treatment, and prompted Lula’s Foreign Ministry to say it would scrap the exemptions.
“Brazil does not grant unilateral exemption from visiting visas, without reciprocity, to other countries,” the ministry said at the time, while noting that the government stood ready to negotiate visa waiver agreements on a reciprocal basis. It did reach a deal with Japan to ease travel provisions.
The decision to maintain exemptions for the three countries is important for boosting tourism in Brazil, notably from the U.S., Brazil’s official tourism board Embratur said in a statement Tuesday.
Photos You Should See - April 2024

Official data shows that nearly 670,000 Americans visited Brazil in 2023, making the U.S. the second largest country of origin after neighboring Argentina.
The government initially postponed the reinstatement of the visa requirement in October, then again in January. At the time, the government said it was still finalizing a new visa system and wanted to avoid implementing it close to the high season, mainly during the New Year’s celebrations and Carnival festivities in February, which attract tens of thousands of tourists.
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , politics , business , world news
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

Trump Gives Johnson Vote of Confidence
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton April 12, 2024

U.S.: Threat From Iran ‘Very Credible’
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder April 12, 2024

Inflation Up, Consumer Sentiment Steady
Tim Smart April 12, 2024

House GOP Hands Johnson a Win

A Watershed Moment for America
Lauren Camera April 12, 2024

The Politically Charged Issue of EVs

Queensland premier defends BPIC agreement that delivers union tradies pay rises of more than $10 per hour
Queensland's premier has defended a deal brokered with construction unions that includes pay rises of more than $10 an hour over the next four years and an extra $1,000 a week to work away from home.
Union workers will receive a 5 per cent pay rise on the first of July, which will continue every year until the end of the agreement in 2027.
Carpenters and other qualified tradespeople will be paid nearly $1,948 a week.
By 2027, the same carpenters will be paid $2,351 a week, jumping from $54.12 an hour to $65.78.
Skilled labourers will also see their wages increase by $10 an hour over the agreement, increasing from $47.63 to $57.89. By 2027, they'll be paid $2,084 a week.
The deal comes at a time when Queensland is looking at huge array of projects across the next decade, ranging from Olympic infrastructure to green energy projects.
"These are all prevailing conditions in the industry," Premier Steven Miles said.
"I think it's appropriate that on government jobs, workers aren't competing with each other on wages.
"These conditions have been in place for some time."
Travel allowances and leave loading
The living away from home allowance section of the BPIC states that a "distant construction sites allowance of $1,000 per week or $200 per day for part weeks" will be paid when an employee is directed to work on a project "located 50 kilometres or more from the address of the employer".
A travel allowance will be paid to workers on government projects worth more than $50 million, while all workers will receive a $50 dollar travel allowance each day.
Starting in July that will jump to $55, and workers who travel more than 50 kilometres will be paid up to $95 dollars a day.
This too will go up over the next four years, reaching $106 per day in 2027.
Workers conducting emergency work or pouring concrete will be paid double time to work in the rain.
A site allowance will be paid per hour to workers on large projects, starting at $1.70 for projects worth $50 million to $80 million, reaching $10 an hour on projects worth $900 million to $1 billion.
All workers will accrue a rostered day off (RDO) every 10 working days, with RDO's still accumulating while workers are on leave.
"The purpose of this calendar is to ensure workers and site management manage their fatigue levels, thereby encouraging safer and more productive projects," the contract says.
Workers on leave will receive 17.5 per cent leave loading on top of their usual pay packet.
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Construction and Real Estate Industry
- State and Territory Government

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall due to security risks.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
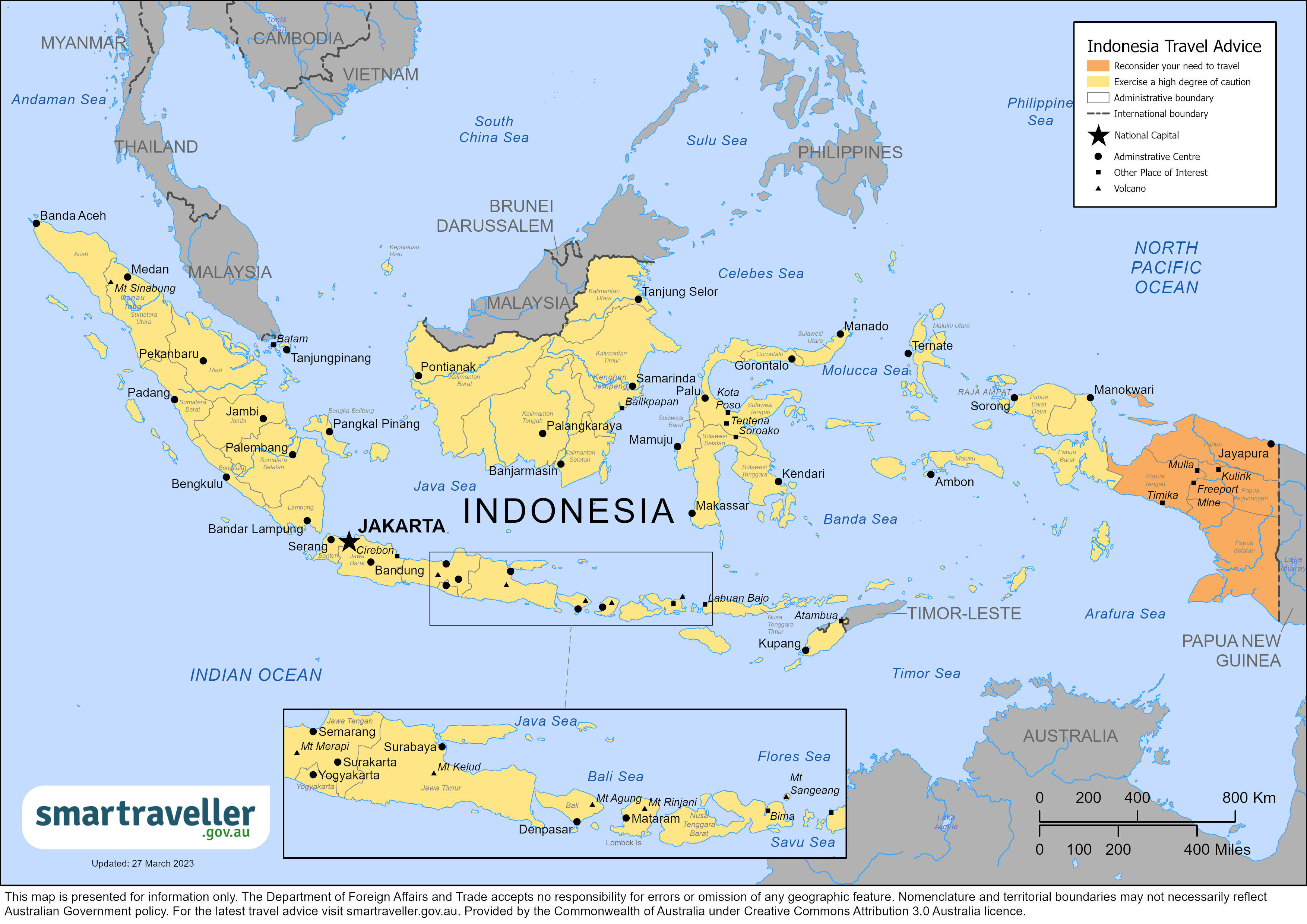
Indonesia (PDF 699.19 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire services, ambulance and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 110 or 112.
Tourist Police, Bali
Call (+0361) 759 687.
Tourist Police, Jakarta
Call (+201) 526 4073.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Indonesia overall.
Reconsider your need to travel to the provinces of Papua (Papua), Papua Highlands (Papua Pegunungan), Central Papua (Papua Tengah) and South Papua (Papua Selatan).
Reconsider your need to travel to the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan due to the risk of serious security incidents or demonstrations that may turn violent.
- There's an ongoing risk of terrorist attack in Indonesia. Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities. Popular tourist areas may be the target of terrorist attacks.
- Public protests and events that draw large groups of people occur regularly and can turn violent with little notice. Expect traffic delays and restricted access to locations if there are protests. Avoid protests and demonstrations and monitor local media for the latest updates.
- Many of Indonesia's volcanoes are active and can erupt without warning. Adhere to exclusion zones around volcanoes, which can change at short notice, and follow the advice of local authorities. Domestic and international flights can be disrupted. Monitor Indonesia's Volcano Observatory Notice for the latest volcanic activity (Bahasa Indonesia and English), Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System and the Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre for updates.
- There's been tension, including demonstrations and violence, in certain towns in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan in recent years. Armed groups have stated that they're targeting foreigners, including Australians. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited. Armed groups have shot at aircraft, including commercial planes, in remote airports in Papua Pegunungan and Papua Tengah provinces.
- Petty and violent crime occurs in Indonesia. Opportunistic crime, such as pickpocketing occurs. Drinks may be spiked or mixed with toxic substances. Crimes involving taxis and taxi drivers occur. Solo women are at higher risk. Be alert in taxis, public transport, crowds, bars and nightclubs.
- Legal disputes over real estate are common, including in Bali. Before entering into an agreement or providing financial details, do your research and get legal advice.
- Natural disasters such as severe weather, floods, landslides, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and tsunamis occur regularly. Weather conditions can change quickly during the wet season (October – April). Regularly check weather reports, monitor media and speak to your travel provider before continuing with planned activities. Follow the advice of local authorities.
- When undertaking adventure activities, ensure that functioning safety equipment is available, that you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for these activities.
Full travel advice: Safety
- The standard of medical facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than in Australia. Many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities.
- Some medications, including prescription medications, drugs for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), all cannabis-based products including medicinal cannabis, cannabis-based oils and creams, hemp-based products, CBD, THC, hash and edibles, are illegal in Indonesia. Harsh penalties, such as arrest and jail time, can apply even if you have a prescription. Make sure your medication is legal in Indonesia .
- Purchasing prescription medication online or over the counter in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller before your purchase.
Full travel advice: Health
- Indonesia has revised its criminal code, which includes penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions will not come into force until January 2026.
- Penalties for drug offences include heavy fines, long prison sentences and the death penalty. Police target tourist destinations.
- Some medications are illegal in Indonesia. Harsh penalties can apply even if you have a prescription. It is also illegal to purchase prescription medications online or over the counter without an Indonesian prescription. Ensure you have a valid Indonesian prescription. See ' Health '.
The death penalty exists for some crimes in Indonesia.
- Standards of dress and behaviour are conservative in many parts of Indonesia. Learn about local customs. Take care not to offend.
- Aceh province upholds aspects of sharia law. Sharia law applies to everyone, including travellers. Inform yourself about the laws, and be careful not to offend or break local laws. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- The Idul Fitri holiday period will take place from 10 April. Many people will travel across Indonesia until 22 April, with many expected to move in and out of the greater Jakarta area. This may impact traffic and public transport, including airports, seaports, highways, toll roads, train and bus stations across Indonesia. Airports are expected to be busy. Plan your travel carefully and prepare for significant delays. Contact your travel provider for up-to-date details.
- The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the e-Visa on Arrival or the Visa on Arrival. Cashless payments can be made online prior to travel or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali's airport and seaport. See the Bali Provincial Government's official website and FAQs for further information.
- If you're travelling to Indonesia for tourism, official government duties or business meetings, you can apply for an e-Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) online at least 48 hours before your travel to Indonesia. This also applies if you're transiting through Indonesia at international airports, seaports and land crossings. You can get a Visa on Arrival (VOA) at some international airports, seaports or land crossings.
- To apply for the e-VOA or VOA, you must have an ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter (we also recommend having at least 6 months of passport validity from the date you plan to leave Indonesia, to avoid any issues for your departure or onward travel) and a return or onward flight booking to another country.
- You may need to apply for a visa in advance to enter Indonesia for purposes not covered by the e-VOA or VOA. Check the latest entry requirements with your travel provider or an Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before travel. Entry, exit and transit conditions can change at short notice. Monitor media for the latest updates.
- You'll be required to complete an e-customs declaration for arrival. You can complete this within 3 days of departure to Indonesia.
- Travel requirements may change at short notice, including travel to Bali and Jakarta by air, land or sea. Contact your travel provider and monitor media for up-to-date details.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter tells you what the Australian Government can and can't do to help when you're overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy, Jakarta , the Australian Consulate-General, Bali , the Australian Consulate-General, Makassar or the Australian Consulate-General, Surabaya .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
The terrorist threat in Indonesia is ongoing. Attacks could happen anywhere and anytime. This includes places that foreigners visit.
Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities. Remain respectful of religious and local customs.
Indonesian authorities continue to investigate and disrupt terrorist groups in Indonesia, including Bali.
Terrorist attacks are motivated by extreme beliefs. Both local grievances as well as events in other parts of the world could motivate extremists in Indonesia towards violence.
Recent terrorist attacks
In December 2022, an explosion occurred at a police station in Bandung, Jawa Barat, killing 2 and injuring 11.
In March 2021, 2 suicide bombers attacked a church in Makassar, injuring dozens.
In the past, police have said that terrorist suspects remain at large and may seek Western targets.
Indonesian security agencies continue to conduct operations against terrorist groups.
Terrorists in Indonesia may carry out small-scale violent attacks with little or no warning.
Be alert in places of worship, especially during periods of religious significance.
Terrorists have targeted places of worship in:
As well as places of worship, other possible targets by terrorists include:
- Indonesian government facilities, premises and symbols associated with the Indonesian Government
- police stations and checkpoints
- bars, nightclubs, cafes and restaurants
- cinemas and theatres
- shopping centres, public transport and transport hubs
- airports and airlines
- clubs, including sporting clubs
- tourist areas and attractions, tour buses and tour groups
- outdoor recreation events
Supporters have committed additional acts of violence in response to high-profile extremists being detained or killed.
To protect yourself during a terrorist attack:
- leave the area as soon as it's safe
- follow the advice of local authorities
- don't gather in a group after an attack
- don't gather in a group if you're evacuated from a building
Security remains at a high level at:
- the Australian Embassy in Jakarta
- the Consulates-General in Bali, Makassar and Surabaya
More information:
Civil unrest and political tension
Most events are announced before they happen; however, protests may occur with little or no notice.
Protests and events are often held near major government buildings and embassies in Jakarta, including the Australian Embassy.
Protests may also occur at any of Australia's Consulates-General in Surabaya, Bali and Makassar, at government buildings, or the offices of international organisations in Indonesia.
You can expect traffic delays and restricted access to locations if there are protests.
Phone or email ahead for an appointment before going to the Embassy or the Consulates-General (see Local contacts ).
Demonstrations and acts of violence can happen when courts try and sentence extremists.
Conflict between different communities can sometimes occur, including in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited.
Local violence can also be directed at minority groups in other parts of Indonesia, including in Java.
If you're found to endanger security or public order, you may be prosecuted under Indonesia's Immigration laws, which may result in imprisonment or deportation.
To protect yourself from possible violence:
- avoid protests and demonstrations
- monitor local media for the latest security updates
- plan your activities to avoid potential unrest on significant dates
- be prepared to change your travel plans
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Armed conflict
The provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan experience regular violent clashes involving armed groups, civilians, Indonesian police, and the military. Armed groups have stated that they are targeting foreigners, including Australians. Our ability to provide consular support in these provinces is limited.
Many people have been killed and injured in clashes. This includes members of security forces, armed groups and civilians. Violent attacks have occurred in several areas of these provinces, including in and around Jayapura. There's a risk of more attacks.
On 23 February 2023, a riot broke out in Wamena, Papua Pegunungan, when a crowd attacked Indonesian security personnel following the arrest of two people accused of child kidnapping. 12 civilians and rioters were killed.
Violent attacks have occurred around the Freeport Mine in Papua Tengah.
Armed groups have:
- taken a New Zealand pilot hostage in Paro, Papua Pegunungan
- shot at aircraft, including commercial planes, at Beoga airport in Pupua Tengah province and Nop Goliat Dekai airport in Papua Pegunungan province.
- killed people in attacks, including one Australian
- attacked vehicles using the road between Grasberg and Timika
- killed people in violent attacks in Puncak Jaya District, Papua Tengah
- more attacks are possible and could target infrastructure and national institutions.
A range of crimes, including violent crime, occur in Indonesia. Crimes can happen in popular tourist locations in Bali.
To protect yourself from crime:
- be aware of your surroundings
- be alert in crowds
- understand the potential crime risks
Theft, robbery and bag and phone snatching have occurred. These crimes can sometimes involve violence. Opportunistic crime such as pickpocketing occurs.
Be careful of thieves:
- on motorcycles targeting pedestrians
- in upmarket shopping malls
- in crowded public transport
- at traffic lights targeting people in stopped cars
- at bars and nightclubs
- when entering accommodation, including villas in Bali
Keep bags and valuables out of sight in vehicles.
If you're travelling on foot, walk:
- on footpaths
- away from the curb
- with your bag held away from traffic
Sexual assault
If you're a victim of sexual assault :
- get immediate medical assistance. If you have any doubts about seeking medical assistance after a sexual assault, contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate in Indonesia (see Local contacts ) as quickly as possible.
- make a full statement to local police, in person, so they can conduct a criminal investigation. You may wish to seek consular help before you visit the police station. Contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate (see Local contacts ).
Local police can only investigate a crime after you've left Indonesia if you've reported it.
Your sworn statement, or statements by witnesses, can be used as evidence in criminal court proceedings.
You don't always need to be in Indonesia for trial. Neither do witnesses who live outside of Indonesia.
Counselling support
Should you wish to speak to a counsellor, you can call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy or Consulate (see Local contacts ). They can connect you to counselling hotlines and services.
- Reducing the risk of sexual assault
Bars and nightclubs
Be alert in bars and nightclubs. Drink-spiking and snatching of valuables may occur if you're not alert.
Drinks may be contaminated with drugs or toxic substances. See Health .
Don't leave your food or drinks unattended.
Never accept drinks, food, gum, cigarettes, vapes or e-cigarettes from people you've just met.
- Partying safely
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card, online banking and ATM fraud occurs in Indonesia.
Check your bank statements.
Make sure your bank doesn't block your cards. Tell your bank you'll be visiting Indonesia.
Never let your card out of your sight. This includes when you pay in restaurants.
Shield your PIN from sight.
Some vendors install hidden cameras and use card skimmers.
Don’t click on unknown links in WhatsApp or mobile phone text messages, particularly if your phone is linked to mobile banking.
Use ATMs at controlled and secure places, such as:
- shopping centres
Scams and confidence tricks
Beware of scams and confidence tricks.
Only exchange money at authorised money changers. Authorised money changers can also be found on the Bali Foreign Exchange website . Unauthorised money changers have been known to scam foreign tourists in Bali and elsewhere.
All types of gambling are illegal in Indonesia.
Australians have lost large sums of money in card game scams run by organised gambling gangs, particularly in Bali. See Local laws
Some tourists have been robbed or planted with drugs after taking new acquaintances back to their hotel rooms. In some cases, their drinks were spiked.
Legal disputes over the purchase of real estate are common, including in Bali, involving:
- holiday clubs and resorts
- timeshare schemes
Before entering into an agreement or providing financial details:
- thoroughly research the proposal
- get legal advice and know your rights, especially before you sign any documents
Using taxis
Only use licensed official metered taxis. Crimes involving unregistered taxis include:
- taxis departing before the passenger can take their baggage from the vehicle
- taxi drivers robbing or temporarily holding passengers, including in urban areas
- taxi drivers forcing passengers to withdraw money at ATMs before releasing them
Lone female travellers are at higher risk of crime.
If you're in an incident involving a taxi, leave the taxi and the immediate area if it's safe to do so.
To protect yourself from overcharging and scams:
- only travel in licensed taxis with signage, a "taxi" roof sign and meters working
- ensure the driver's identification card is visible
- book via your phone, on an official taxi company mobile app, from inside an airport, or at stands at major hotels
See Travel .
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas while travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including destinations that are typically at lower risk.
On 7 February 2023, a New Zealand pilot was taken hostage by an armed group in Paro, Papua Pegunungan.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Adventure activities
Many businesses don't follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes transport and tour operators, water sports providers, hotels, restaurants and shops.
It may affect adventure activities, such as:
- bungee jumping
- scuba diving and snorkelling
- chairlift or gondola rides
In the past, Australians have been seriously injured or died while participating in adventure activities. If you require intensive care medical treatment, emergency surgery or medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about safety, search and rescue procedures
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
- check with your travel provider on vessel capacity limits before embarking on sea, land or air travel
- check weather and ocean conditions, and whether the vessel has had any mechanical issues, on the day and before continuing with water activities or sea travel
- check where the nearest medical facilities are
If proper safety equipment isn't available or you're unsure of the provider's safety or maintenance procedures, use another provider.
Trekking and climbing
Some mountain treks suit only experienced climbers. Travel with a guide and check the level of difficulty beforehand.
Many trekking options may be on or around an active volcano. Many of Indonesia's volcanoes are active and can erupt without warning. Volcanic and seismic activity may continue for some time. Adhere to exclusion zones around volcanoes, which can change at short notice, and follow the advice of local authorities. If you're planning to travel to an area near an active volcano, check with local authorities before climbing and check:
- Bureau of Meteorology Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre
- MAGMA Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia) for daily updates on status and alert levels
- National Disaster Management Authority (BNPB) (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Swimming safety
People have drowned in coastal areas, including in Bali, due to rough seas, strong currents, or from swimming, snorkelling or scuba diving in areas where there is frequent passage of boats, resulting in collisions.
Local beach rescue services may not be of the same standard as in Australia.
Saltwater crocodiles are in rivers throughout Indonesia. Avoid swimming around river estuaries and seek local advice in other locations.
If you plan to spend time in or on the water:
- regularly check weather reports as sea conditions can change rapidly
- take warnings seriously
- check media and local sources for information about potential dangers
- speak to your travel provider about safety equipment and weather conditions before continuing with planned activities
- take a friend or family member with you when you undertake swimming or water activities
- be careful when swimming, snorkelling or scuba diving near motor-powered boats or where there is frequent passage of boats
- ensure you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for planned activities
Ensure you have travel insurance and that your policy covers you for planned activities.
Climate and natural disasters
Indonesia experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- landslides and mudslides
- volcanic eruptions
- earthquakes
- storms resulting in turbulent sea conditions
- tsunamis and high wave events
If there's a natural disaster or severe weather:
- always carry your passport in a waterproof bag
- keep in contact with family and friends
- check the media and local sources for information
- don't undertake sea, land or air travel if it's not safe to do so
- Indonesian Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency (BMKG) (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
Floods and mudslides
Floods , landslides and mudslides occur regularly during the wet season from October to April, with some severe events resulting in injury, displacement, death or damaged infrastructure.
Heavy rains can cause significant flooding in urban areas, including the greater Jakarta region, causing disruption to transportation. Monitor the local media for updates.
Walking and driving in flooded areas can be dangerous. Flood waters may hide uncovered drainage ditches.
Volcanic activity may escalate with little or no notice, leading to flight disruptions and airport closures, including in surrounding provinces. Contact your airline for the latest flight information.
There are 147 volcanoes in Indonesia. 76 of them are active volcanoes and could erupt at any time.
Volcanic alert levels and exclusion zones may rise quickly. You may be ordered to evacuate at short notice. Volcanic activity can disrupt domestic and international flights. There are 4 volcano alert levels in Indonesia; 1 - normal, 2 - advisory, 3 - watch, 4 - warning.
Before you travel to areas that are prone to volcanic activity, monitor media and ensure you read the Indonesian Government's latest advice on current volcanic activity, including:
- Volcanic Activity Report by Indonesia's Multiplatform Application for Geohazard Mitigation and Assessment (MAGMA) (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Volcano Activity and Observatory Notices (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- MAGMA Indonesia Map of Latest Volcano Levels and Climate Information (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Bureau of Meteorology's Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre
If there's volcanic activity:
- avoid the area
- take official warnings seriously and adhere to exclusion zones
- follow the instructions and advice of local authorities
- follow evacuation orders
- read our advice on Volcanic eruptions while travelling
Volcanic ash can cause breathing difficulties. The risk is higher for people with chronic respiratory illnesses, including:
Recent and frequent volcanic activity has included:
- Mount Ile Lewetolok in East Nusa Tenggara (Nusa Tenggara Timur)
- Mount Lewotobi Laki Laki in East Flores Regency, Nusa Tenggara Timur
- Mount Marapi in West Sumatra
- Mount Anak Krakatau, to the south of Sumatra
- Mount Merapi, near Yogyakarta
- Mt Dukono in North Sulawesi
- Mount Semeru, near Malang, East Java
- Mount Agung in Bali
- Mount Sinabung in North Sumatra
Some trekking routes are on or near active volcanoes, including Mount Agung and Mount Batur in Bali, Mount Marapi in West Sumatra, Mount Merapi near Yogyakarta, Mount Rinjani in Lombok, Mount Bromo and Mount Ijen in East Java. See 'Trekking and climbing'.
If you're planning to travel to an area near an active volcano, make sure you have comprehensive travel insurance and check if any restrictions apply.
If a volcanic eruption occurs:
- make a backup plan in case you're affected
- contact your airline or travel insurer to confirm flight schedules and get help
- keep in touch with family and friends
- Learn more about volcanic eruptions (Geoscience Australia)
- See practical advice and information about volcanic eruptions (US CDC)
- See worldwide volcanic activity reports in real-time (GDACS)
Earthquakes
Indonesia is in an active earthquake region. It has a high level of earthquake activity, that sometimes triggers tsunamis.
There are approximately 4,000 earthquakes across Indonesia every year. Around 70 to 100 of these are over 5.5 magnitude.
Earthquakes can cause death, injury and significant damage to infrastructure.
Strong earthquakes can occur anywhere in Indonesia. They are less common in Kalimantan and south-west Sulawesi.
To stay safe during an earthquake:
- know the emergency plans at your accommodation
- take precautions to avoid exposure to debris and hazardous materials, including asbestos
- MAGMA Indonesia (Bahasa Indonesia)
- Indonesia's Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency (Bahasa Indonesia) or BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Indonesia)
- Indonesia's Centre for Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation (Bahasa Indonesia)
- US Federal Emergency Management Agency advice on what to do before, during and after an earthquake (English)
Forest fires and smoke haze
During the dry season in April to November, widespread forest fires can cause smoke haze resulting in poor air quality across parts of Indonesia, particularly the Riau Islands, central Sumatra and Kalimantan.
Smoke haze could affect your health and travel plans.
Keep up to date with local information and seek medical advice on appropriate precautions.
- ASEAN Regional Haze Situation
- Smartraveller advice on Bushfires
Tsunamis and high wave events
The Indian and Pacific Oceans experience more frequent, large and destructive tsunamis than other parts of the world.
There are many large earthquakes along major tectonic plate boundaries and ocean trenches.
High wave events can happen throughout coastal regions and between islands. They're caused by strong weather conditions and storms.
If you plan to surf, undertake water activities or travel by sea, check local conditions regularly.
If there’s a tsunami or high wave event:
- don't travel by sea if it's not safe to do so
- Indonesia Tsunami Early Warning Centre issues warnings when a potential tsunami with significant impact is expected
- Indonesia's Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics Agency with the latest list of earthquakes with a magnitude greater than 5.0 on the Richter scale (Bahasa Indonesia) or BMKG Multi-Hazard Early Warning System app (English and Bahasa Indonesia)
- US Federal Emergency Management Agency page on what to do before, during and after an earthquake
Piracy occurs in the coastal areas of Indonesia.
The International Maritime Bureau (IMB) issues weekly piracy reports.
If you decide to travel by boat in these regions:
- check IMB piracy reports
- get local advice
- arrange security measures
- Travelling by boat
- Going on a cruise
- International Maritime Bureau
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including emergency treatment and medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
Before you travel, confirm:
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away, including on all forms of transport you plan to take
- whether it covers medical evacuation in the event of hospitalisation or injury
- any exclusions to your policy
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some drugs used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are illegal in Indonesia.
If you plan to bring over-the-counter or prescription medication, check if it's legal in Indonesia by contacting the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra well in advance of your planned travel. Take enough legal medicine for your trip and carry it in its original packaging. Purchasing prescription medication online in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller prior to your purchase.
Carry a copy of your prescription and a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medicine is
- your required dosage
- that it's for medical treatment or use
If you're caught with illegal medicine, you could face detention, fines or harsher penalties. You could face charges even if an Australian doctor prescribed the medication.
Ask the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra for advice before you travel.
Medicinal cannabis and cannabis-based products
Cannabis-based products such as cannabis oil and creams, hemp, CBD, THC, hash and edibles remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation or the death penalty.
- Medications
Health Risks
Critical care for Australians who become seriously ill, including in Bali, is significantly below the standard available in Australia. Medical evacuation may not be possible.
The Australian Government cannot guarantee your access to hospitals and other health services in Indonesia.
Medical evacuation to Australia for medical conditions, is possible but is very expensive and may not be covered by travel insurance. Check your policy before you travel.
Ban on sale of liquid/syrup medication
The Indonesian Ministry of Health (MoH) has advised local health workers and pharmacists to stop selling liquid/syrup medication, including commonly used medications containing paracetamol and cough syrups. MoH and the Indonesian Paediatrician Association (IDAI) received reports of a sharp increase in cases of Atypical Progressive Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in children , especially under the age of 5 years.
Insect-borne illnesses
Insect-borne illnesses are common throughout the year.
To protect yourself from disease:
- research your destination
- ask locals for advice
- make sure your accommodation is mosquito-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Dengue occurs throughout Indonesia, including Bali, Jakarta and other major cities.
Dengue is common during the rainy season.
Australian health authorities have reported an increase in dengue infections in people returning from Bali in recent years.
There are now two dengue vaccines, but they are not currently available in Australia. For further information, contact your doctor.
Zika virus can occur in Indonesia.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites.
The Australian Department of Health and Aged Care advises pregnant women to:
- discuss any travel plans with their doctor
- consider deferring non-essential travel to affected areas
Malaria , including chloroquine-resistant strains, is widespread in rural areas, particularly in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah, Papua Selatan, Papua Barat Daya, Papua Barat, Maluku and Nusa Tenggara Timur. There is no malaria transmission in Jakarta.
- Consider taking medicine to prevent malaria.
Japanese encephalitis and filariasis
Japanese encephalitis and filariasis occur in Indonesia, especially in rural agricultural areas.
Japanese encephalitis has been present in Australian travellers returning from Indonesia, including Bali.
Vaccination is recommended for certain groups of travellers.
- Infectious diseases
Drink poisoning
People have been poisoned by alcoholic drinks contaminated with harmful substances, including methanol and arak (a traditional rice-based spirit). Locals and foreigners, including Australians, have died or become seriously ill from poisoned drinks.
Cases of drink poisoning have been reported in Bali and Lombok.
Contaminated drinks have included:
- local spirits
- spirit-based drinks, such as cocktails
- brand name alcohol
To protect yourself from drink poisoning:
- consider the risks when drinking alcoholic beverages
- be careful drinking cocktails and drinks made with spirits
- drink only at reputable licensed premises
- avoid home-made alcoholic drinks
Labels on bottles aren't always accurate.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning can be similar to drinking too much. However, they are usually stronger.
Symptoms of methanol poisoning include:
- vision problems
Vision problems may include:
- blindness, blurred or snowfield vision
- changes in colour perception
- difficulty looking at bright lights
- dilated pupils
- flashes of light
- tunnel vision
If you suspect that you or someone you're travelling with may have been poisoned, act quickly. Urgent medical attention could save your life or save you from permanent disability.
Report suspected cases of methanol poisoning to the Indonesian police.
Magic mushrooms
Don't consume magic mushrooms. They're illegal.
Australians have become sick or injured after taking magic mushrooms.
Australians have been in trouble with local police after taking magic mushrooms, particularly in Bali.
Magic mushrooms can cause major health problems, including:
- erratic behaviour
- severe hallucinations
Rabies is a risk throughout Indonesia, especially in:
- Nusa Tenggara Timur, including Labuan Bajo
- South Sulawesi
- West Kalimantan
- Nias, off the west coast of Sumatra
To protect yourself from rabies:
- avoid direct contact with dogs
- don't feed or pat animals
- avoid contact with other animals, including bats and monkeys.
Talk to your doctor about getting a pre-exposure rabies vaccination.
If bitten or scratched by an animal:
- immediately use soap and water to wash the wound thoroughly for 15 minutes
- seek urgent medical attention.
Rabies treatment in Indonesia may be limited, including the rabies vaccine and immunoglobulin availability. If you're bitten, you may need to return to Australia or travel to another country for immediate treatment.
You're at risk of contracting rabies if you visit a market where live animals and fresh food are sold because:
- live rabies-positive dogs may be present
- rabies-positive dog meat may be sold as food
Selling dog meat for human consumption is a breach of government disease control regulations.
Avoid contact with monkeys, even in places where you're encouraged to interact with them. This includes:
- popular markets
- tourist destinations
- sanctuaries
Legionnaires' disease
Cases of Legionnaires' disease have been reported in people who have travelled to Bali. Travellers who are unwell with flu-like symptoms within 10 days of returning from Bali are advised to consult their GPs.
- Legionnaires' disease warning for Bali travellers (Western Australian Government Department of Health)
- Legionnaires’ disease (Better Health Channel, Victorian Government Department of Health)
- Legionnaires' disease (World Health Organization)
Cases of poliovirus (type 1) have been reported in the provinces of Papua, Papua Pegunungan, Papua Tengah and Papua Selatan. Poliovirus (type 2) cases have been reported in the provinces of Aceh, East, West and Central Java. There may be unreported cases in other provinces in Indonesia.
Ensure that you're vaccinated against polio.
- Factsheet on poliovirus types (World Health Organization)
- Health emergencies information for Indonesia (World Health Organization)
Periodic outbreaks of measles continue to be reported in Indonesia, including Bali.
You need 2 doses of vaccine 4 weeks apart to be fully vaccinated against measles.
If you have symptoms of measles, seek medical attention.
Measles is highly infectious. Call before attending a healthcare facility.
Nipah Virus and Yellow Fever
There are no cases of Nipah virus or Yellow Fever in Indonesia. You may be temperature checked on arrival at international and domestic airports. If you have fever symptoms, you may be referred to the airport clinic for further tests and asked to seek medical treatment. See your doctor or travel clinic before you travel to plan any vaccinations you need.
HIV/AIDS is a risk for travellers. Take steps to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are widespread. These include:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- boil drinking water or drink bottled water
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw food, such as salads
To minimise the risk of food poisoning, only eat meat from reputable suppliers.
Seek urgent medical attention if you suspect food poisoning or have a fever or diarrhoea.
Seafood toxins
You can become sick from naturally occurring seafood toxins, including:
- ciguatera fish poisoning
- scombroid (histamine fish poisoning)
- toxins in shellfish
Avoid temporary black henna tattoos. The dye often causes serious skin reactions.
Before you get any tattoo, check the hygiene and safety of your tattoo provider.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities in Indonesia is generally lower than Australia. Many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities.
Hospitals expect families to provide support to patients, including all financial support.
Psychiatric and psychological services are limited in Indonesia. Hospital staff may use physical restraints on patients.
When diving in Indonesia, there is a risk that you may experience decompression illness. An illness may occur when a diver ascends to the water surface too quickly and may have severe consequences. Understand the risks before you dive.
Decompression chambers are available in various areas, including the following locations:
- Bali's Sanglah General Hospital
- Siloam Hospital in Labuan Bajo
- Hospitals in Jakarta, Balikpapan, Bintan, Medan, Makassar, Raja Ampat (Waisai), Maluku, Tual and Manado near popular dive sites
Before admitting patients, hospitals usually need:
- guarantee of payment from the patient or their next of kin (family or friend)
- confirmation of medical insurance
- deposit payment
There's no reciprocal healthcare agreement between Australia and Indonesia.
The Australian Government cannot provide guarantee of payment, confirmation of medical insurance or a deposit payment for services.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you may need to be evacuated to a place with better care. Medical evacuation can be very expensive. Check your insurance policy before you travel. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs. It's best to check with your travel provider on the location and functionality of decompression chambers and other medical facilities available in the area before undertaking remote travel.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
Indonesian Parliament has passed revisions to its criminal code, which includes penalties for cohabitation and sex outside of marriage. These revisions will not come into force until January 2026.
Indonesia has signed into law revisions to the Electronic and Information Transactions Law (ITE Law). Tough penalties apply for defamation, hate speech, spreading hoaxes and uploading immoral content to the Internet. The law applies both within and outside Indonesia.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
- Arrested or jailed
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
You may face heavy fines or jail for consuming or possessing even small amounts of drugs, including marijuana. Cannabis-based products such as cannabis oil and cream, hemp, CBD, THC, hash and edibles remain illegal in Indonesia, including for medicinal purposes. A medical prescription does not make it legal. If you take such products to Indonesia or purchase or use them in Indonesia, you can be arrested and face imprisonment, fines, deportation or the death penalty.
Some prescription medications that are available in Australia are illegal in Indonesia. Purchasing prescription medication online or over the counter in Indonesia without an Indonesian prescription is illegal. Ensure you provide a valid prescription from an Indonesian doctor before purchasing prescription medication and confirm that it's accepted by the seller before your purchase.
Magic mushrooms are illegal. Indonesian police work to prevent their distribution.
Police target illegal drug use and possession across Indonesia. Police often target popular places and venues in Bali, Lombok and Jakarta.
- Carrying or using drugs
Local labour laws can change at short notice. This can affect expatriate workers.
Under Indonesian law, you must always carry identification. For example, your:
- Australian passport; and
- Resident's Stay Permit (if applicable)
Gambling is illegal.
Property laws are strict, seek legal advice before acquiring property in Indonesia.
It's sometimes illegal to take photographs in Indonesia. Obey signs banning photography. If in doubt, get advice from local officials. See Safety .
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Local customs
Standards of dress and behaviour are conservative in many parts of Indonesia. Take care not to offend.
Find out what customs apply at your destination.
If in doubt, seek local advice.
LGBTI information
Same-sex relationships are legal in Indonesia, except in the province of Aceh. Same-sex relationships in Aceh may attract corporal punishment. Visible displays of same sex relationships could draw unwanted attention.
Some laws and regulations can be applied in a way that discriminates against the LGBTI community, including for pornography and prostitution.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
The Islamic holiday month of Ramadan is observed in Indonesia. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws at this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking and smoking may be illegal in public during this time. If you're not fasting, avoid these activities around people who are. Seek local advice to avoid offence and follow the advice of local authorities.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Aceh is governed as a special territory, not a province, and has a degree of special autonomy.
Some aspects of sharia law are upheld. This includes regulations and punishments that don't apply in other parts of Indonesia.
Local sharia police enforce sharia law.
Sharia law applies to anyone in Aceh, including:
- foreigners (expats and travellers)
- non-Muslims
Sharia law doesn't allow:
- drinking alcohol
- prostitution
- same-sex relationships
- extra-marital sex
- co-habitation before marriage
It also requires a conservative standard of dress.
Learn about the laws in Aceh. If in doubt, seek local advice.
Dual citizenship
Indonesia doesn't allow dual nationality for adults, and you may be prosecuted by Immigration authorities should you be found to hold valid passports of two nationalities. If you entered Indonesia on your non-Australian citizenship passport, Indonesian Immigration will require you to exit Indonesia on that nationality's passport.
A child of Indonesian and Australian parents can maintain citizenship of both countries until the age of 18 years. Before a dual Australian-Indonesian citizen minor travels from Indonesia, additional identity documentation may be required from Indonesian Immigration. Check with Indonesian Immigration or the Indonesian Embassy in Canberra well in advance of your planned travel.
- Embassy and Consulate of Indonesia
- Information on limited dual citizenship
- Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Bali Tourism Levy
The Bali Provincial Government has introduced a new tourist levy of IDR 150,000 per person to foreign tourists entering Bali. The tourist levy is separate from the e-Visa on Arrival or the Visa on Arrival. Cashless payments can be made online prior to travel or on arrival at designated payment counters at Bali's airport and seaport. Exemption from payment of the levy applies to transit passengers and certain visa holders. See the Bali Provincial Government's official website and FAQs for further information.
e-Visa on Arrival and Visa on Arrival
You can apply for an e-Visa on Arrival (e-VOA) no later than 48 hours prior to travelling to Indonesia if you are travelling for tourism, business meetings, purchasing goods or transiting only. Check the e-VOA requirements from Indonesian Immigration before applying.
You can still apply for a regular Visa on Arrival (VOA) at certain international airports, seaports and land crossings, including Jakarta, Bali, Surabaya, Makassar, Lombok, Batam, Medan, Manado, Aceh, Padang, Tanjung Pinang and Yogyakarta, if you do not apply for an e-VOA at least 48 hours in advance of your travel to Indonesia.
The e-VOA or VOA can be used for tourism, official government duties, business meetings, or to transit through Indonesia. You cannot transit in Indonesia without an e-VOA or VOA.
Additional requirements apply if you are travelling on government duties.
For the latest list of entry points for the e-VOA or VOA, refer to the Directorate General of Immigration's list of land border crossings, international airports, and international seaports .
The e-VOA and VOA cost IDR 500,000 (approximately $A 50), with the e-VOA charging a small online processing fee.
For the VOA, some airports, including Jakarta's international airport, are only accepting cash payment. Card payment facilities are available at Bali's international airport. ATM facilities may be in high demand. Be prepared to pay in cash if required.
The visa is valid for a 30 day stay and can be extended once (for a maximum of 30 days) by applying at an immigration office within Indonesia. Ensure you extend your visa within the initial 30 days to avoid an overstay fine and deportation.
To apply for a regular VOA, you must show:
- your ordinary (non-emergency) passport with at least 6 months of validity from the date you plan to enter (we also recommend having at least 6 months passport validity from the date you plan to leave Indonesia, to avoid any issues for your departure or onward travel)
- a return flight booking to Australia or onward flight booking to another country
Contact your travel agent, airline, or your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia for details.
Other visas
If you're entering Indonesia from a port or airport that does not issue a visa on arrival, or you're visiting Indonesia for a purpose not allowed under the e-VOA or VOA conditions, you must apply for a visa in advance of travel. Check the Indonesian Immigration website for further information, or contact your nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia .
Overstaying your permit may result in fines, detention and/or deportation.
- check your visa and permit, and contact the Directorate General of Immigration (DGI) for advice specific to your needs
- if you use an agent to extend your visa or stay permit, use only reputable companies
- if you have specific enquiries on visas or stay permits, contact DGI's Customer Service team via WhatsApp on +62 821 1295 3298
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest Embassy or Consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and entry rules.
You can't work or conduct research in Indonesia unless you have the appropriate visa. Fines of IDR1,000,000 (approx. $A 100) per day apply for the maximum 60 day overstay period.
If you breach Indonesian immigration regulations, you may face:
- deportation
- re-entry bans
You may not be allowed to enter Indonesia if you have a criminal record. This is regardless of how long ago the offence took place. If you're concerned, contact an Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before you travel.
Indonesian Immigration and visa decisions are final. The Australian Government can't help you.
- Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia
Border measures
You'll be required to complete an e-customs declaration for arrival . You can complete this within 3 days of departure to Indonesia.
Check entry requirements with your travel provider or the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia before you travel.
You may be temperature checked on arrival at international and domestic airports. If you have fever symptoms, you may be referred to the airport clinic for further tests and asked to seek medical treatment. See your doctor or travel clinic before you travel to plan any vaccinations you need.
Departure from Indonesia
Indonesia, including Bali, currently has an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease affecting animals. In preparing to travel to Australia, read Smartraveller's advice on biosecurity and border controls . Measures include cleaning dirty shoes, clothing or equipment before boarding your flight to Australia and not packing meat or dairy products. On your Incoming Passenger Declaration, you must declare any meat, dairy or animal products and any of your travel in rural areas or near animals (e.g., farms, zoos, markets).
Other formalities
If you're staying in a private residence, not a hotel, register when you arrive with both:
- the local Rukun Tetangga Office
- local police
If you plan to be in Indonesia for more than 30 days:
- register with the local immigration office
- make sure you have the right visa
- Embassy of Indonesia in Canberra
Indonesia won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave Indonesia. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over. You can end up stranded or returned back to your previous port overseas at your own cost, if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months from the date you enter and the date you plan to leave Indonesia.
Indonesia does not accept entry with an emergency passport, even if it is valid for more than 6 months. Ensure you enter Indonesia on a valid ordinary, official, or diplomatic passport.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply these rules inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian Embassy, Consulate or High Commission.
Damaged Passports
Indonesian authorities have strict standards for damaged passports, and travellers have been refused entry into Indonesia with a damaged passport. Normal wear and tear, including water damage, minor tears or rips to the pages, can be considered damaged.
It's important that:
- there are no tears or cuts in the passport pages, especially the photo page
- everything on the photo page is legible and clear
- there are no marks across your photo or in the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) on the photo page
- no pages have been removed
- there is no alteration or tampering
If you're not sure about the condition of your passport, call the Australian Passport Office on 131 232 or contact your nearest Australian embassy or consulate overseas . We may need to see your passport to assess it.
- Passport Services
- Damaged and faulty passports
- Using and protecting your passport
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
The local currency is the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR).
Declare cash in excess of IDR100,000,000 or equivalent when you arrive and leave. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
IDR100,000,000 is worth about $A10,000.
Local travel
Idul fitri 2024.
The Idul Fitri holiday period will take place from 10 April. Many people will travel across Indonesia until 22 April, with many expected to move in and out of the greater Jakarta area. This may impact traffic and public transport, including airports, seaports, highways, toll roads, train and bus stations across Indonesia. Airports are expected to be busy. Plan your travel carefully and prepare for significant delays. Contact your travel provider for up-to-date details.
Travel Permits
You may need a travel permit or Surat Keterangan Jalan to travel to some areas of the Papua provinces.
Check if you need a permit with the nearest Embassy or Consulate of Indonesia or with your travel provider.
Mobile Phone Reception and Wi-Fi
Mobile phone reception and Wi-Fi are not always available, including in remote areas and some resort islands.
If you plan to stay in Indonesia for more than 90 days and would like to use your mobile phone purchased overseas, you'll need to register your mobile phone IMEI number with Indonesian Customs within the first 60 days of your stay.
If you plan to stay in Indonesia for less than 90 days, you can visit the local cellular operator/provider booth at the airport to get an access period to use the Indonesian cellular network, which is only valid for 90 days and includes data roaming.
A customs payment may be required, or a tourist SIM card can be purchased for short-term stays. You can use Wi-Fi networks without registration.
To stay in communication and avoid mobile service interruptions:
- check mobile coverage with your service provider
- register your mobile device with Indonesian Customs on arrival if you plan to connect to the mobile network
Driving permit
To drive in Indonesia, you need either:
- an Indonesian licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Check that your licence or permit is appropriate for the type of vehicle you're driving.
Your Australian licence isn't enough.
Your travel insurer will deny any claims you make if:
- you're unlicensed
- you don't hold the correct class of licence
Road travel
Traffic can be extremely congested.
Road users are often unpredictable or undisciplined.
You're more likely to be killed in a motor vehicle accident in Indonesia than in Australia. Drive defensively. Some traffic incidents can escalate into violent disputes quickly.
Consider hiring a taxi or a driver who is familiar with local roads and traffic conditions.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Motorcycle accidents have killed and injured foreigners, including Australians. This includes in tourist areas, particularly Bali, Lombok and the Gili Islands.
If you're riding a motorbike and there's an accident, you'll often be assumed to be at fault. You may be expected to compensate all parties.
If you hire a motorbike:
- make sure your insurance policy covers you
- check if any policy restrictions apply, for example if you're not licensed to ride a motorcycle in Australia
Always wear a helmet.
Public transport
Buses, trains and the metro rail can be crowded, particularly:
- around public holidays
- during peak commute times
Safety standards may not be observed.
- Transport and getting around safely
Only use licensed official metered taxis.
- only travel in licensed taxis with signage, a "taxi" roof sign and meters
- book via phone or an official taxi company mobile app
You can book licensed official metered taxis
- on the taxi company's official mobile app
- from inside airports
- at stands at major hotels
Unofficial operators can have taxis that look similar to those run by reputable companies. Make sure the taxi meter is working before you get into the taxi.
See Safety .
Rail travel
Inter-city rail networks operate on the islands of Java, Sumatra and Sulawesi.
Commuter trains operate in Java, including Jakarta.
Trains can be crowded, particularly:
- during peak commuter times
Travel between islands
Travel by ferry or boat can be dangerous.
Passenger and luggage limits aren't always observed.
Equipment may not be properly maintained, and they may not have GPS or emergency communications equipment.
There may not be enough life jackets. It's unlikely that the crew will have life jackets for children.
In March 2024, a ferry sank in the Thousand Islands off the coast of Jakarta, resulting in one death, and a liveaboard boat caught fire and sank in Raja Ampat, Papua Barat Daya, requiring several passengers to be rescued.
In August 2023, two crew died after a boat carrying passengers sank in the Banyak Islands, Aceh, and three people went missing after a ship sank in the Thousand Islands off the coast of Jakarta.
In July 2023, 15 people died after a ferry sank off Sulawesi Island.
In January 2023, 23 passengers and 6 crew were rescued after an inter-island ferry sank while returning from Nusa Penida to Sanur Beach, Bali.
In May 2022, 19 people died after a ferry sank in the Makassar Strait.
In June 2018, a ferry sank on Lake Toba in Sumatra and 100s of people died.
If you plan to travel by sea between islands:
- make sure any ferry or boat you board has appropriate safety equipment, GPS and communication equipment, and life jackets
- wear a life jacket at all times
- take enough life jackets for all children travelling with you
- ask your tour operator or crew about safety standards before you travel
- check sea, weather conditions and forecasts before embarking on boat or ferry travel, and delay travel if conditions are not safe
If appropriate safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Avoid travelling by water after dark unless the vessel is properly equipped. Avoid travel during wet weather or storms.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Indonesia's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
The European Union (EU) has published a list of airlines that have operating bans or restrictions within the EU. See the EU list of banned airlines .
Australian travellers should make their own decisions on which airlines to travel with.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Search and rescue services
Medical emergencies and ambulance.
SMS 1717 for Jakarta Police
Police Stations in Bali
Refer to the Bali Tourism Board’s list of police stations in Bali
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australian Embassy, Jakarta
Jalan Patra Kuningan Raya Kav. 1-4 Jakarta Selatan 12950
Phone: (+62 21) 2550 5555 Email: [email protected] Website: indonesia.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australian Embassy Jakarta, Indonesia X: @DubesAustralia Instagram: @KeDubesAustralia
Make an appointment online or call (+62 21) 2550 5500 or (+62 21) 2550 5555.
Australian Consulate-General, Bali
Jalan Tantular 32 Renon Denpasar Bali 80234
Phone: (+62 361) 2000 100 Email: [email protected] Website: bali.indonesia.embassy.gov.au X: @KonJenBali Instagram: @konjenbali
Australian Consulate-General, Makassar
Wisma Kalla Lt. 7 Jalan Dr Sam Ratulangi No. 8 Makassar South Sulawesi 90125
Phone: (+62 411) 366 4100 Email: [email protected] Website: makassar.consulate.gov.au Facebook: Australian Consulate-General, Makassar, Sulawesi X: @KonJenMakassar Instagram: @konjenmakassar
Australian Consulate-General, Surabaya
Level 3 ESA Sampoerna Center Jl. Dokter.Ir. H. Soekarno No. 198 Klampis Ngasem, Sukolilo, Surabaya
Phone: (+62 31) 9920 3200 Email: [email protected] Website: surabaya.consulate.gov.au Instagram: @KonJenSurabaya
Check the websites for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Indonesia?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Expat reveals one thing she wishes she had known about Australia: ‘Relentless’
Share this article
A traveller from the UK has posted a hilarious video documenting the reality of working in the Australian outback, quipping that if she knew what was in store, she would have never visited the land down under.
Most tourists are warned about the spiders, snakes and crocodiles that inhabit Australia.
However, one woman has vented about the fact that no one cautioned her about the excessive amount of flies in a TikTok that has garnered more than 2.4 million views in only a few days.
The British woman is currently visiting Western Australia on a working visa. She filmed herself at Karijini National Park , which is a massive wilderness area in the Hamersley Range, with loads of flies swarming around her head.
“So everyone says ‘do a working holiday visa, go and travel there, it’s the best thing you’ll ever do’,” she complained in the clip.
“When I said I was going to do it, everyone was like, ‘Oh, you know, be careful of the spiders, the snakes, the crocodiles, the sharks, oh the kangaroos, they’ll be nice, the koalas, isn’t that cute’.

“Do you know what nobody f*****g talks about? The f*****g flies.”
She went on to reveal that if she had been told about the annoying insects, she probably wouldn’t have ventured to the outback.
“Nobody warned me about this, did they?”
While put off by the flies, the English tourist did take a moment to gush about how beautiful the Karijini National Park was.
“But this (flies) is a reality,” she joked.
She went on to tell her followers that she had to wear a net over her hat because the flies were so unbearable.

“These flies are relentless, they’re not like English flies. I’ve said that before and I’m saying it again, they f*****g won’t give you a break and this is a reality.
“Think about that before you come to Australia, guys. Anyway, I’m having a great time.”
Her hilarious TikTok has been flooded with comments from Aussies chiming in with her fly complaints, dubbing the flies in rural parts of Australia “horrendous”.
“I’m working right next door to Karajini and yes the flies are crazy at the moment. They do disappear when the sun goes down,” one TikTok user wrote.
“Yeah but what I wanna know is where do they go at night ahaha,” she replied, to which the TikToker said: “That is one of life’s greatest questions.”
Another person wrote: “It’s only really bad in the outback”, while another told her “it’s not like that everywhere in Australia”.
“I would go mad. the flies would drive me mad,” wrote another social media user.
One Western Australia local said: “Lived here all my life and will never get use to the flies.”

Latest from Travel

You're wrong about Dargaville, there's more here than just Kai Iwi Lakes
There's so much more to do here than the obvious.

What one expat wishes she had known before visiting Australia

Copenhagen remains one of Europe's most criminally overlooked cities

Government warns against travel to Gaza, Israel border regions

‘Dark delights’ of Great Barrier Island

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Australian Government provides 24-hour consular emergency assistance. +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas. 1300 555 135 from within Australia. For how we can help you overseas see the Consular Services Charter.
If you're an Australian citizen and you have serious concerns about your welfare or that of another Australian overseas, contact your local Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate, or call our 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on. 1300 555 135 within Australia. +61 2 6261 3305 from anywhere in the world.
Since the start of the pandemic, the Australian Government has implemented stricter border measures to protect the Australian community from COVID-19. You may need to abide by additional departure and re-entry measures when you travel. ... Australian citizens who travel without an Australian passport might have their entry delayed until their ...
Travel 24-hour emergency consular support If you're an Australian citizen and you have serious concerns about your welfare or that of another Australian overseas, contact your local Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate, or call our 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on 1300 555 135 within Australia +61 2 6261 3305 from anywhere in the world. Read more […]
In 2018-19, tourism generated more than $60 billion for the Australian economy, with more than 660,000 jobs dependent on the industry. Since the Morrison Government commenced Australia's staged international border reopening on 1 November 2021 we have seen almost 580,000 arrivals come to Australia including to reunite with loved ones, work or ...
The Australian Government does not currently have any COVID-19 requirements in place for travellers entering and departing Australia. COVID-19 however continues to pose a health risk in Australia and overseas. We strongly encourage wearing masks and being vaccinated while travelling internationally.
The updated country-specific travel advice will allow Australians planning to travel overseas to assess risks, understand requirements, and prepare to travel safely. It will also help Australians to access travel insurance more readily. While fully vaccinated Australians will be able to depart Australia without an exemption from.
TravelSECURE. TravelSECURE provides a range of advice and tips to help you prepare for your journey and clear security checks quickly and easily. Security screening measures are there to keep travellers secure and safe. Every passenger and bag boarding a flight is screened to reduce the risk of a security incident occurring.
For additional travel information. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency. Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern ...
Follow the tips below to help you apply for a visitor visa to come to Australia. . Submit your application well in advance of your travel. Attach all required d ocuments. You must submit all the documents we ask for with your application, including a clear copy of the personal details page of your passport.
What we're doing about travel health. We provide information for travellers to help them avoid infectious diseases and other health-related issues. Our work to support vaccination services helps to keep travellers safe. We also work to reduce the risk of diseases entering Australia through international travel.
Published Feb. 18, 2022 Updated Feb. 28, 2022. Moments after the Australian government announced that it would reopen the country's borders to international travelers later this month, Emily ...
The Australian Government Travel Guide provides an overview of the Arrangements including: a summary of the fare conditions that apply to negotiated domestic and international airfares. value adds for tier 1 international airfares. tips on how to make bookings and reduce travel costs. Due to the sensitive content of this document, it is not ...
The Australian Immunisation Register (AIR) is a national register that records vaccines given to all people in Australia. The AIR includes vaccines given: privately, such as for flu or travel. You can check your immunisation record: by calling 1800 653 809 (Monday to Friday 8 am to 5 pm).
tasking of the Australian Government's fleet of Special Purpose Aircraft (SPA). Under the SPA Guidelines, the Prime Minister may choose to approve the use of a SPA by Ministers (as entitled persons) for official travel where commercial airline options are not available or appropriate for the proposed travel.
Today the Australian Government's official travel and cultural advice service, Smartraveller, released its latest advertising campaign. With more than 1 million monthly departures from Australia, the Smartraveller campaign aims to help all Australians travelling overseas to be as prepared as possible by visiting the website and subscribing to updates.
Smartraveller, the Australian Government's travel advisory and consular information service, which provides up-to-date advice about health, safety and other risks of specific destinations for Australian travellers; The following resources have comprehensive technical advice on international travel and health, including vaccination:
Latest FCDO travel advice for Australia including on entry requirements, ... Government activity Departments. Departments, agencies and public bodies. News. News stories, speeches, letters and ...
In the first quarter of 2024, flights to Australia's most popular travel destination Indonesia were down 21% from the previous year at $798 return on average. Available seats to the holiday spot ...
Failure to meet the requirements may result in problems gaining certificate endorsement or difficulties upon arrival in the destination country. Health certificates must be legible, accurate, and complete. NOTE: For dogs and cats traveling from other countries via the United States to Australia, please read this guidance (108.46 KB) first.
Visas to visit Australia. Whether you are visiting Australia for less than 72 hours or planning on a stay of several years you must have a valid Australian visa. A visa is a form of permission for a non-citizen to enter, transit or remain in a particular country. Information on visas to Australia can be found at the Department of Home Affairs.
RIO DE JANEIRO (AP) — Brazil's government extended exemptions to tourist visa requirements for citizens of the U.S., Australia and Canada until April 2025, extending a program aimed at ...
A travel allowance will be paid to workers on government projects worth more than $50 million, while all workers will receive a $50 dollar travel allowance each day.
Defence Minister Richard Marles is preparing to travel to Ukraine in a show of support aimed at combating claims of faltering Australian support for Ukraine's war against Russia. Marles is ...
Emergency consular assistance. The Australian Government provides 24-hour consular emergency assistance. +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas. 1300 555 135 from within Australia. For how we can help you overseas see the Consular Services Charter.
Apr 12, 2024, updated Apr 12, 2024. Horizontal Falls will soon phase out boat rides. Photo: AAP. Sir David Attenborough once called Western Australia's Horizontal Falls "one of the greatest ...
The Australian Government cannot provide guarantee of payment, confirmation of medical insurance or a deposit payment for services. If you become seriously ill or injured, you may need to be evacuated to a place with better care. Medical evacuation can be very expensive. Check your insurance policy before you travel.
The British woman is currently visiting Western Australia on a working visa. She filmed herself at Karijini National Park , which is a massive wilderness area in the Hamersley Range, with loads of ...