Wait you forgot to try your Luck
Enter your email and get details on how you can win Prizes/ Shopping Vouchers

- Business Courses How to start a travel agency 4Ps of Tourism Marketing Interpersonal Skills Training Mastering in AIRBNB Travel Consultant Course Travel Photography Travel Agent Essentials Tourism Marketing Course International Tourism Course View All
- Destinations Alpines of Graubunden Lakshadweep Oman Andaman Manali Hampi Hawaii Hungary Saudi Arabia Ooty View All
- Hotels Centara Ras Fushi Resort Maldives Centara Grand Maldives Courtyard By Marriott Bangkok JW Marriott Bangkok FIVE Zurich Hyatt Ziva Los Cabos Hyatt Ziva Puerto Vallarta Sinner Paris Kandima Maldives View All
- Experiences ARTECHOUSE Kennedy Space Center An out of this world adventure SUMMIT One Vanderbilt Phillip Island Nature Park Trans Studio Bali Theme Park Zoos Victoria Vana Nava The Wheel at ICON Park View All

- Register with us
- Webinar Registration
- Destinations
- Experiences
- Business Courses
- TBO Portal Training
- Strategic Alliance

Existing Agents Login Here

Reset Password
Tourism planning: importance, benefits, types & levels.
Planning is to prepare a Road Map to achieve goals.
Faludi, in 1973, defined tourism planning as "Planning is a very important part of the process by which governments manage tourism at the national, local and organizational levels".
What is Tourism Planning?
The upkeep and expansion of the tourism sector in a particular area is referred to as tourism planning. Planning for tourism is, of course, a crucial component.
Creating strategies and plans to increase, develop, and stimulate tourism for/in a destination may be summed up as tourism planning. The primary motivation behind establishing and implementing strategies for the tourist industry is to generate money, which will eventually raise the GDP of a nation or region.
What is the need for Tourism Planning?
For the expansion of the sector important to plan tourism activities for the following reasons:
- It is necessary to plan tourism activities on different levels and in various manners to promote tourism and boost the economy.
- To provide quality to both tourists and residents.
- It involves making major decisions which cannot be taken spontaneously.
What are the components of Tourism Planning
- Exploration phase/ Preparatory
- Planning phase/Feasibility/
- Zoning phase/Formal planning
- Design and implementation phase
- Operational phase
Most nations that have successfully planned their tourism can be found online and are regarded as incredible holiday destinations. People go to these nations hoping their travel vlogs will increase their subscriber count on YouTube. That is an indication of success in the modern day.
Benefits of Tourism Planning
Tourism destination planning should be a vital component of every destination's tourism development plan to get the best outcomes and please all stakeholders. While some places do a great job of maintaining sustainable tourism, others (typically developing countries) need to recognize the significance of comprehensive tourism development planning.
Tourism planning can benefit various parties involved from the industry in the following ways:
- It boosts revenue and employment thanks to tourist spending.
- It safeguards cultural and natural assets so that visitors can enjoy them.
- It broadens the comprehension of cultural diversity
- It constructs new infrastructure, such as sewage systems, roads, etc., for the community.
Impacts of Tourism Planning
The impacts of tourism destination planning can be sorted into seven general categories:
- Environmental
- Social and cultural
- Crowding and congestion
- Community attitude
According to Inskeep, six "golden standards" should be followed when creating a strategy for tourist planning and policy (1991).
1. Goal Oriented: Tourism Planning should be oriented to achieve broad national and community goals.
2. Integrative: Integrating tourist policy and planning into the economy, land use and infrastructure, conservation, and environmental planning.
3. Market Driven: Planning for successful tourism growth in a cutthroat international market.
4. Resource Driven: Developing tourism that capitalizes on the location's inherent advantages while preserving and improving the features and experiences of existing tourism resources.
5. Consultative: Considering broader community attitudes, needs, and desires to determine what the population will accept.
6. Systematic: utilizing primary or secondary information to support planners conceptually or predictably, incorporating knowledge from other tourist locations
Levels of Tourism Planning
Planning and policy for the tourism industry occur at several levels. This can be done in a top-down approach, with international or national bodies, or a bottom-up approach from a local level.
1. International Tourism Planning: Tourism planning at the international level typically involves international transportation services, the movement and scheduling of tourist tours between different countries, the development of significant tourist attractions and facilities in neighboring countries, as well as the working strategies and promotional programs of many nations.
2. National Tourism Planning: Tourism policy, infrastructural facilities, and a physical structure plan, which includes significant tourist attractions, chosen tourism development regions, international entrance points, facilities, and services, are all addressed at the national level of tourism planning. Additionally, it is concerned with the quantity, types, and quality of lodging and other essential tourist facilities and services; the country's major travel routes and their regional connections; tourism organization
rights, laws, and investment policies; marketing and promotion strategies for the industry; education and training initiatives; and environmental, economic, and sociocultural analysis.
3. Regional Tourism Planning: Regional planning considers factors such as regional policy, regional entrance points, transportation facilities, and services; the types and locations of tourism attractions; the quantity, varieties, and places of lodging and other tourist facilities and services; and the sites of tourist development regions, such as resort areas.
They will also oversee sociocultural, environmental, economic, and impact analyses, regional education and training programmes, marketing strategies, investment policies, organizational structures, legal frameworks, and implementation strategies, including project plans and zoning ordinances.
4. Local Tourism Planning: Participants at the local level will think about the analyses, outputs, outcomes, and assessment of tourism planning at the ground level.
Types of Tourism Planning
Before creating a comprehensive plan to market the destination, the following types of tourism planning are taken into account:
Spatial Tourism Planning: Spatial tourism planning attempts to thoroughly process social, environmental, and economic change to bring about certain ends. Drawing plans, maps or diagrams are put together to decide where socio-spatial activities can occur.
Sectoral Tourism Planning: In this kind of planning, the regions are divided into sections, and each section is called a sector. It concentrates on a manageable area and takes into account the specific infrastructure, land use, transportation, and environmental requirements of that region. Depending on the nature of the products or services provided, economic, social, and administrative activities are grouped into sectors.
Complex Tourism Planning: When various regions are considered for the purpose of tourism planning, it is known as complex tourism planning. These regions are to be developed comprehensively because of the significant interest shown by international tourists. There is a possibility that these regions are located far away from one another.
Integrated Tourism Planning: Integrated tourism refers to making tourism the primary industry in a given area by systematically and comprehensively promoting all available economic, social, and tourism resources.
Sustainable Tourism Planning: Sustainable tourism planning involves striking the correct balance between the requirements of people and the environment. It entails stating the community's mission, vision, and unique selling point or identity in clear terms. With the help of this type of destination planning in our local communities, we are better equipped to plan for the long term, and respond to changing target markets, trends, and emergencies like the Covid-19 outbreak. Additionally, it guarantees that resources are allocated properly while ethically and sustainably establishing local communities. This method of tourism planning benefits people and places in positive ways on all fronts—socially, economically, culturally, and environmentally—puts sustainability at its core.
Centralized Tourism Planning: Centralized tourism planning is done by a single authority, usually the state or central government.
Decentralized Tourism Planning: Organizations are interested in developing tourist spots and planning the various activities visitors can enjoy. (Joint Venture).
They take assistance from government. Suggested Read: Sustainable Tourism
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. why is tourism planning important.
A1. Destination development plans should include tourism planning since it promotes a destination's long-term viability and encourages cooperation among important stakeholders..
Q2. What are the features of tourism planning?
A2. Three general principles of planning for tourism can be specified as anticipation, regulation and monitoring.
Q3. What are the barriers to tourism planning?
A3. A3. According to earlier research conducted in several nations, a common pattern of issues has emerged. For instance, financial constraints, a lack of knowledge, an insufficient amount of time, and other issues have prevented local governments from incorporating tourism into their development plans.
- Exploring Sigatoka Sand Dunes: The Crowned Jewel of Fiji
- 10 Most Beautiful Places to visit in Istanbul
- Things to do in Phillip Island: For an Incredible trip to Melbourne, Victoria
- Top 15 Things to Do in Victoria: Exploring Melbourne and Beyond
- Top 6 Places to Visit in Muscat: Top Attractions & Hidden Gems
- 10 Things to Do in Saudi Arabia Beyond a Spiritual Experience
- 8 Adventures in Oman: You shouldn’t be missing
- 8 Tourist Places to Visit in Lakshadweep: India’s Island Paradise
- 8 Best Things to do in Oman for a Holiday to Remember
- Full Proof Guide to 13 Top New Attractions in Dubai
- Top Things to Do at Katara Cultural Village, Doha, Qatar
- Exploring the Breathtaking Beaches of Tanzania: A Coastal Paradise
- Discovering Willy’s Rock: Boracay's Hidden Gem
- 10 Top Places to Visit in Oman, Tourist Places & Tourist Attractions
- Camping in Riyadh: A Recreational Escapade in the Desert

Tourism Planning
- Post last modified: 2 October 2021
- Reading time: 19 mins read
- Post category: Uncategorized
Tourism planning like any planning is purpose-oriented, determined to accomplish some of the objectives by corresponding to the accessible resources and programs with the necessities and desires of the people.
Tourism as a whole is an activity that is judged as part of physical, environmental, social and economic planning. It is seen as a business activity, in which the public or private and individual stakeholders have different perspectives to plan it. But, the role of government agencies in developing countries is central to tourism planning.
Table of Content
- 1 Importance of Tourism Planning
- 2 Constraints in Tourism Planning
- 3.1 Transport
- 3.2 Accommodation
- 3.3 Tourist Activities
- 3.4 Product Development
- 3.5 Tourism Zoning
- 3.6 Marketing and Promotion
- 3.7 Institutional Framework
- 3.8 Statistics and Research
- 3.9 Legislation and Regulation
- 3.10 Quality Standards of Tourism Services
- 4 Types of Tourism Planning
- 5 Levels of Tourism Planning
Planning in tourism is setting and achieving the goals, keeping constraints in mind such as time, money etc. there are many approaches involved in tourism planning such as bottom-up approach, collaborative, boosterism, interactive, integrated etc. If you talk about planning in tourism in developing countries, it is generally taken by consultancy firms. But it has only been in the 1990s that tourism has been thought as a serious planning activity (Gunn, 1990; WTO 1994).
Tourism planning occurs at all levels international, national, regional and for specific areas and sites. National and regional planning establishes the policies, physical and institutional structures, standards for developments, while the local bodies generally implement them.
In 1992, Gunn spotted out that tourism industry was the result of the tourist’s desire to visit a particular location and culminated when his desires got fulfilled. According to him, planning helps tourism by critically reviewing the various choices available & to choose the most appropriate plan, so that the destination achieves the desired results in terms of economic and social aspects.
Hence, wherever planning is involved in tourism, the various things important are- reviewing the ground position w.r.t resources available (capital, material, human); setting objectives; appraisal of the various plans, selection of the most appropriate plan in tandem with the local community support & approach and achieving the desired results.
Importance of Tourism Planning
At all levels of tourism in order to achieve success, planning is vital for managing and developing tourism. This has been exemplified by many tourism destinations throughout the globe that planning that also long term can only lead to economic, socio-cultural and ecological benefits to both local community and tourists.
Following are the importance of tourism planning:
- Development of linkages and co-ordination of tourism with other sectors through policy formulation.
- Ascertaining the objectives and tourism policy in order to realize the goals.
- Preserving & conserving the resources (natural/cultural/man-made) efficiently and effectively, so that they are also kept for coming generations also.
- Planning can be used to upgrade and revitalize existing outmoded or badly developed tourism areas. Through the planning process, new tourism areas.
- Integrating tourism policy at national, regional and local level.
- Helps in making a tourism framework for effectual execution of hard work done both by public & private sector. The public sector creates an environment conducive for tourism development, while the private sector pours financial assets for developing tourism.
- Helps in the harmonized growth of the various elements of the tourist sector through co-ordination and involvement.
- It helps to maximize the benefits (economic, socio-cultural and ecological) to local community; poor people etc and help in impartial distribution of the benefits to everyone.
- t helps to minimize the negative impacts of tourism, if any.
- Right type of planning can ensure that the natural and cultural resources for tourism are indefinitely maintained and not destroyed or degraded in the process of development.
- Developing specialized training facilities.
- Achieving controlled tourism development requires special organizational structures, marketing strategies and promotion programmes, legislation and regulations, and fiscal measures.
- Planning provides a rational basis for development staging and project programming. These are important for both the public and private sectors in their investment planning.
- It promotes rational thinking and development for tourism growth and expansion.
- It helps in formulation of a skeleton framework which directs the tourism development in terms of facilities, infrastructure, services and attractions.
- Helps in formulation of tourism policy, plans and effective management of tourism areas, facilities etc.
- Helps in creation of guidelines and standards which help in preparing detailed plans for developing tourism destinations and circuits.
- Helps in incessant monitoring of the developmental activities of tourism.
- Positioning tourism as a major engine of economic growth.
- Developing suitable marketing plans with realistic, practical and sustainable targets.
- Employing sustainable environmental practices.
- Review of tourism polices and their evaluation.
- Development of planning criterion and analysis of resources.
- Providing adequate recreation opportunities and facilities in the tourist destination and tourist circuits.
- Proper land- use and planning of the physical spaces.
- Allocating an adequate level of funding for tourism programmes
In order to develop tourism, planning is done at all levels of tourism through policy formulation and planning activities. Though the nature and type of planning vary from one country to another ranging from developed to least developed countries.
But, tourism planning should have a firm foundation for which good research and study of the grass-roots level is very essential. Also, the plans need to be revised again & again based on the study results and likely future trends but retaining the basic structure.
Constraints in Tourism Planning
The constraints in tourism planning are:
- Lack of community participation : The unwillingness of the people to participate in the tourism activity limits its future. The tourism planning and in fact tourism can only give positive results, if it receives people support at every stage of tourism process.
- Limited budgets: Usually, government provides low or limited budgets to the tourism a Industry. And this makes tourism a very limited process.
- Accuracy and reliability of market data: for planning and management is also a serious problem in tourism. If the market information is incomplete or hazy, then also the goals of the tourism planning would be affected.
- Low priority accorded to the tourism sector: No, doubt, there has been a positive mindset w.r.t tourism in the Indian economy. But, still this sector deserves much more, then it has received.
- The poor quality of infrastructure & facilities present at the attractions: also act as a constraint in tourism planning and development.
- Quality of transportation service: The quality and quantity of transportation service is not very good. And needs great improvement.
- Multiplicity and high level of taxation: also gives less inspiration to the tourism entrepreneurs and creates more & more obstacles for the tourism.
- Facilitation of entry of tourists at ports(Airport/seaport/land port): The lengthy procedures involved in immigration should be made reasonable without giving the visitors much botheration and anxiety, before they visit the country for tourist purpose.
- Poor communication & awareness: A sound plan without clear communication can lead to duplication of endeavors and create differences among the stakeholders of tourism. It can also lead to occurrence of feuds among the stakeholders and create complexity.
- Conflict of interest: At times, the tourism policies can lead to conflict of interest among the stakeholders and create questions at the very start of the tourism planning. Hence, whenever policies are framed the local community should be involved at all levels, so that tourism policies not lead to planning failures.
Management constraints
- Legislative constraints and adherence to rules/regulations/ executive orders: Touism planning will have to abide rules & regulation related to environment, wildlife, local resources. And at times, it also creates impediments for the overall tourism project or plan for a particular tourism area/destination or tourism project.
- Environmental constraints: The presence of wetland, certain wildlife species, sensitive habitat, steep slopes, unstable soil, hazardous geologic conditions, tectonic movement, seismicity, critical habitat, lack of land base are the limiting factors or constraints in tourism development. And their incidence can create problems for infrastructure development and tourism planning.
- Carrying capacity constraints: Carrying capacity is the ability of a place to accommodate fixed number of individuals without affecting the ecology of the place. But, if this threshold increases, then it affects the ecology and resource base of that place. Carrying capacity can be divided into four types i.e. (1) social, (2) physical, (3) environmental (or ecological), and (4) facility. So, all these carrying capacity are adversely affected, if the number of individuals increases. This is one of the biggest constraints in the tourism planning as it is often violated in tourism.
- Apt understanding of ground realities: The improper understanding of ground realities can also lead to creation of tourism polices and tourism planning, which leads to no results. Hence, the policies become rudimental often at its inception stage.
- Inactivity dilemma: For the tourism planning process, the nodal agency involved may have large infrastructure, bureaucracy, man power involved but may suffer from the fear of change. This mental state creates a lot of obstacles in the tourism planning.
Scope in Tourism Planning
Tourism planning has come a long way in the tourism development process. But still, there is ample scope for betterment. The scope of Tourism planning are briefly explained below:
Accommodation
Tourist activities, product development, tourism zoning, marketing and promotion, institutional framework, statistics and research, legislation and regulation, quality standards of tourism services.
Accessibility plays an important role in tourism planning. It provides mobility to not only the tourists, but also the tourism policy or plan. If the means of transport such as land, air and water are developed, it also makes ground for implementing the tourism plan at the grass-root level.
Accommodation is one of the important A’s of the tourism industry. It also increases the carrying capacity of a place by accommodating more tourists. But, currently in India, if we want to increase the flow of tourists, then we also need more hotels or accommodation facilities to accommodate them. Hence, the tourism plans should give a priority to develop them.
The tourist activities such as adventure activities, non-adventure activities, experiential activities in tourism such as in rural tourism, village tourism, Geotourism, ecotourism should be given more space in tourism development. And, these should be developed along with tourism concept as it gives more innovation to tourism, apart from enhancing the variety of experience to the tourists.
The diversity of the tourism product should be enhanced to give a variety of experiences to all tourists suiting their age, taste and culture. Also, emphasis should be laid down to develop the tourism product through quality gradation and innovation.
Also, importance should be given to developing a native product which is unique, indigenous to the land and helps in portraying the image of the land in terms of its culture, heritage, cuisine, festivals, folklores, traditions, dance forms, dresses etc.
Tourism zoning is an important aspect involved in tourism destination planning. It divides the tourist destination into various regions and segregates the tourist activity in those regions.
Marketing and Promotion are important elements in tourism planning and development. It needs more improvement in case of India. As, the tourism product of India is very diverse, indigenous and unique, still it lags in attracting the number of tourists. So, surely it is an area in tourism planning which needs great attention and careful planning.
Tourism development in India is institutionalized at a central level, state level and local level. But, still, there are large lacunas associated with it. The coordination of the institutions is delayed due to non-streamlined procedures, bureaucracy, nepotism, corruption etc and hampering the state of tourism in the country.
The tourism planning in India, still requires more research base and groundwork, prior to making the tourism policies. And, hence, if we want to improve our tourism planning and tourism policy, the research wings for the tourism industry have to be made sound and strong.
The existing legislation and regulations need to be revised to match up the current environment. Also, the legislation should be made keeping in mind the perspectives of all the stakeholders. They should not be made just by keeping the tourist in mind.
There has been great growth in the tourist infrastructure. But, in order to increase tourism competitiveness, importance have to be given on the quality of services and facilities. Also, the pricing of the tourism services is a big question. And, they should be made affordable keeping in consideration not only the foreign tourists, but also the domestic tourists whose role can also not be ignored.
Types of Tourism Planning
There are ‘n’ numbers of types of Tourism Planning. Some important ones are as follows:
- Spatial Tourism Planning: The space as well as the environment is scrutinized for creating good quality infrastructure e.g. Jim Corbett National Park.
- Sectorial Tourism Planning: Region to be developed is divided in to various broad sections called sectors e.g. South East Asia
- Integrated Tourism Planning: Parts of a tourist region are integrated so that the region becomes a hot destination.
- Complex Tourism Planning: When several regions are considered for planning which are far away e.g. Char Dham Yatra.
- Centralized Tourism Planning: Single authority, usually state or central Government, no private sector intervenes.
- Decentralized Tourism Planning: Parties who are keen to develop the spot, Government do not interfere. But it provides financial support.
- Urban – modern infrastructure
- Rural – culture, history, built from scratch
Levels of Tourism Planning
Tourism planning is implemented at different levels from the general level which may apply to an entire country or region down to the local level which may apply to detail planning for specific resort.
What is important to emphasize is the tourism planning and development must be integrated among all levels to take into account different levels of concern and to avoid duplication of efforts and policies.
Each level involves different considerations as follows:
- International level: Tourism planning at the international level involves more than one country and includes areas such as international transportation services, joint tourism marketing, regional tourism polices and standards, cooperation between sectors of member countries, and other cooperative concerns.
- National level: Tourism planning at the national level is concerned with national tourism policy, structure planning, transportation networks within the country, major tourism attractions, national level facility and service standards, investment policy, tourism education and training, and marketing of tourism.
- Regional level: Tourism planning at the regional level generally is done by provinces, states, or prefectures involving regional policy and infrastructure planning, regional access and transportation network, and other related functions at the regional level.
- Local or community level: Tourism planning at the local level involves sub regions, cities, towns, villages, resorts, rural areas and some tourist attractions. This level of planning may focus on tourism area plans, land use planning for resorts, and planning for other tourism facilities and attractions.
- Site planning level: Site planning refers to planning for specific location of buildings and structures, recreational facilities, conservation and landscape areas and other facilities carried out for specific development sites such as tourism Uttarakhand Open University 48 resorts and may also involve the design of buildings, structures, landscaping and engineering design based on the site plan.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window X
- Opens in a new window Facebook
- Opens in a new window Pinterest
- Opens in a new window LinkedIn
- Opens in a new window Reddit
- Opens in a new window WhatsApp
You Might Also Like
Indian hotel chain, customer retention: in marketing, measures of customer, recruitment, mice tourism, art galleries, what is beverages classification, advantages, communication skills in customer service, this post has one comment.
Your notes are up-to-date, thanks so much
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Why tourism planning is important
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Tourism planning should be an integral part of any destination’s tourism development plan in order to achieve the best results and satisfy all stakeholders. Tourism planning is key to maintaining sustainable tourism and whilst some destinations do this very well, others (often developing countries), fail the recognise the importance of effective tourism development planning.
In this post I will explain why tourism planning is so important and recommend some literature for further reading on this topic. This information on tourism planning should be helpful to a number of tourism stakeholders, including business entrepreneurs, Government bodies and tourism workers. It is also useful for those studying travel and tourism as well as those who have a general interest in the subject. For an introduction to the concept of tourism policy and planning visit this post- ‘ The different levels of tourism policy and planning ‘.
Wait! Before you read on, take a look at the short video that I created all about the importance of tourism planning!
What is tourism planning?
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, tourism planning is a very important part of this.
On a basic level, tourism development can be defined as creating strategies and plans to increase/develop/encourage tourism for a destination. The fundamental reason behind planning and implementing strategies for developing the tourism sector is primarily to make money and to subsequently increase the GDP of a country/area.
You might also be interested in my post- ‘ What is tourism? A definition of tourism ‘
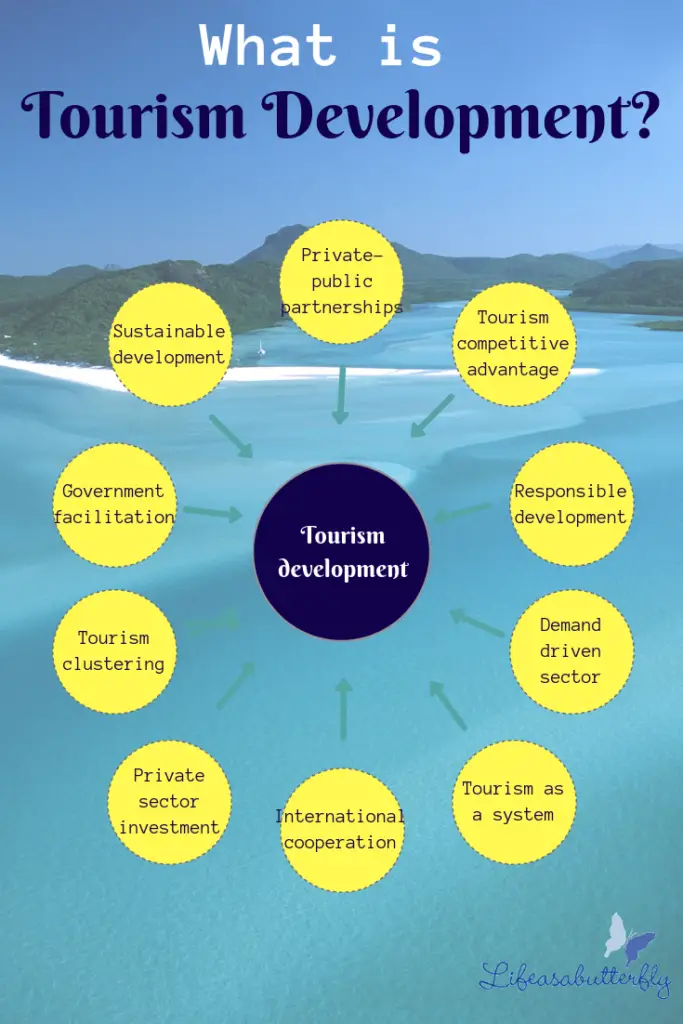
Tourism development consists of many elements including, but not limited to: developing and managing private-public partnerships, assessing the competitors to gain competitive advantage, ensuring responsible and sustainable development, viewing tourism as an interconnected system and a demand-driven sector, assessing private sector investment and international cooperation, tourism clustering and involvement by the Government.
According to Williams cited in Mason (2003);
‘The aim of modern planning is to seek optimal solutions to perceived problems and that it is designed to increase and, hopefully maximise development benefits, which will produce predictable outcomes’.
And Getz (1987) cited in Pearce (1989) defines tourism planning as;
“A process, based on research and evaluation, which seeks to optimise the potential contribution of tourism to human welfare and environmental quality”
Tourism development planning should be an integral part of any destination’s tourism plan in order to achieve the best results and satisfy all stakeholders. Tourism development planning is key to maintaining sustainable tourism and whilst some destinations do this very well, others (often developing countries), fail the recognise the importance of effective tourism development planning.
What is tourism development planning?
Tourism development refers to the growth and maintenance of the tourism industry in a given locality. And, of course, planning is a very important part of this.
Basic stages in tourism development planning
Tourism development planning is no simple task and there are many variables to consider. There are also different levels of tourism planning and policy . Fortunately , destinations can learn lessons from other areas which have been successful or otherwise. Take for example, over dependence on tourism in Egypt as I explain in this post- Why Unpaid Business is Better than No Business: The Case of the Egyptian Boatman. It is also worthwhile to look at the tourism policies of similar destinations. Some strong examples include Jamaica and Cape Town .
On a basic level, the main stages in tourism development planning include: the analysis of previous tourist development; evaluation of the position of tourism in the area including competition; formulation of relevant tourism policy by Government; the defining of a development strategy and the formation of a programme of action.

The benefits of tourism development
Tourism development planning enables a range of benefits to all stakeholders involved, for example:
- It increases income and jobs from tourist spending
- It helps preserve cultural and natural heritage for tourists
- It increases understanding of other cultures
- It builds new facilities such as sewage for whole communities or new roads
The costs of tourism development
There are also some costs which must be considered and planned for, which include:
- Costs of implementing tourist facilities can be costly
- The environment can be destructed to make room for hotels etc. to be built
- Social standards may be undermined e.g. topless women in Dubai
- The natural environment may be polluted
Formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning
There are six ‘golden rules’ that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism policy and planning, as outlined by Inskeep (1991).

- Goal oriented
Clear recognition of tourism’s role in achieving broad national and community goals
- Integrative
Incorporating tourism policy and planning into the mainstream of planning for the economy, land use and infrastructure, conservation and environment
- Market driven
Planning for tourism development that trades successfully in a competitive global marketplace
- Resource driven
Developing tourism which build on the destination’s inherent strengths whilst protecting and enhancing the attributes and experiences of current tourism assets
- Consultative
Incorporating the wider community attitudes, needs and wants to determine what is acceptable to the population
Drawing on primary or secondary research to provide conceptual or predictive support for planners including the experiences of other tourism destinations
Why tourism development planning is important
Tourism development planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community.
If done badly , tourism development can destroy the very environment or culture that it relies on. It can disrupt local economies, cause inflation and negative effects to local people and businesses. Unfortunately, developing countries tend to suffer the most from negative impacts such as these, largely as a result of limited education and experience in contrast with Western nations. For more on this topic, you can read this post.
If you wish to cite any of the content in the post please use reference ‘Stainton, Hayley. (2018) Lifeasabutterfly .’
§§cs§§
For more on what constitutes tourism planning I recommend that you refer to the texts Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow by Edgell and Swanson and Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing by Camilleri .
Tourism development planning is no simple task and there are many variables to consider. There are also different levels of tourism planning and policy. Fortunately, destinations can learn lessons from other areas which have been successful or otherwise. Take for example, over dependence on tourism in Egypt as I explain in this post- Why Unpaid Business is Better than No Business: The Case of the Egyptian Boatman. It is also worthwhile to look at the tourism policies of similar destinations. Some strong examples include Jamaica and Cape Town .

You might also be interested in my post- ‘ Best Universities In The UK To Study Travel and Tourism ‘
There are six ‘golden rules’ that should be applied when formulating an approach to tourism planning and policy, as outlined by Inskeep (1991).

You might also be interested in my post- ‘ What is ‘begpacking’ and why is it so bad ?’
Tourism planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community.
If done badly, tourism development can destroy the very environment or culture that it relies on. It can disrupt local economies, cause inflation and negative effects to local people and businesses. Unfortunately, developing countries tend to suffer the most from negative impacts such as these, largely as a result of limited education and experience in contrast with Western nations.
For more on this topic, I recommend the following texts:
Tourism Policy and Planning: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
Tourism Planning and Destination Marketing
Leisure, Sport and Tourism, Politics, Policy and Planning
Tourism Planning: Policies, Processes and Relationships
Liked this article? Click to share!
Tourism Development Planning
- First Online: 01 January 2015
Cite this chapter

- Anze Chen 4 ,
- Yunting Lu 5 &
- Young C. Y. Ng 6
Part of the book series: Springer Geography ((SPRINGERGEOGR))
1237 Accesses
2 Citations
Although tourism planning is a part of the general strategic planning system of the state, its complexity, hierarchy and scientific involvement are rarely found in other departmental planning, because, as a comprehensive undertaking, tourism have both its economic implications and its cultural contents. Economically, tourism involves industry, agriculture, traffic, trade and commerce; culturally, it involves many disciplines and fields. Therefore, tourism planning is a multi-level matrix planning involving many procedures, departments and disciplines. A series of theoretical and practical issues need to be addressed. These issues involve the nature, objective, characteristic, principle, content, category, step and method of tourism planning.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Chen, J. (1987). Study on evaluation and planning of tourism resources, tourism earth-science research and development of tourism resources (p. 53). Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press.
Google Scholar
Yu, Y., & Wang, L. (1989). Protection and development of tourism resources in Beijing, Beijing tourism development strategy (pp. 157–159). Beijing: Beijing Yanshan Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China
School of Geography, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
Association for Geoconservation, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Young C. Y. Ng
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Anze Chen .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg and Science Press Ltd.
About this chapter
Chen, A., Lu, Y., Ng, Y.C.Y. (2015). Tourism Development Planning. In: The Principles of Geotourism. Springer Geography. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46697-1_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46697-1_8
Published : 08 May 2015
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-662-46696-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-662-46697-1
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, a sustainable tourism planning model: components and relationships.
European Business Review
ISSN : 0955-534X
Article publication date: 12 October 2012
The purpose of the paper is to describe the concept of sustainable tourism planning, establishing the theoretical foundations, the components that make up the model, and the relationships that ensure the sustainability of a tourist destination.
Design/methodology/approach
Tourism planning is based on the principles of sustainability and is defined by three dimensions: environmental, economic and cultural tourism development.
The goal of comprehensive tourism planning is to achieve economic growth and efficiency, ensuring efficiency and social equity by solving the basic needs of the population and on the basis of stable and continuous environmental systems.
Research limitations/implications
The limitation of this paper is the need to validate the dynamic elements raised and test the robustness of the model in an application.
Practical implications
Finding the right balance between these three dimensions is necessary to ensure comprehensive long‐term sustainability, while finding ample references of theoretical and conceptual frameworks of sustainability are based on the triple bottom line, as referred to later in this paper.
Originality/value
The contribution of this paper is to propose, within the model itself, the mechanisms of connection between the three dimensions and the relationships among them, emphasizing the importance of the “stakeholders” in the process.
- Sustainable tourism
- Triple bottom line
- Tourism development
Padin, C. (2012), "A sustainable tourism planning model: components and relationships", European Business Review , Vol. 24 No. 6, pp. 510-518. https://doi.org/10.1108/09555341211270528
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2012, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Tourism Policy, Planning, and Development
General overview.
Tourism policy, planning, and development are all very connected and do not just occur when a geographic area decides to be a tourism destination. Policy, planning, and development are included in numerous aspects of communities.
continue but from different perspectives. An example would be the use of the destination/product lifecycle, discussed later. It is important to understand what tourism planning and development are individually as well as collectively. Planning is essential to effective development. Tourism is not always a beneficial industry for a geographical area, but without planning tourism can damage the area, including natural and cultural resources (Morrison et al., 2018). A destination might consider “Who, What, When, Where, Why” when working on a tourism plan. The same can be considered for tourism development, as well as other topics included in this alternative textbook (e.g., marketing and promotion).
Tourism Policy
A policy is essentially a course of action taken by some organization or institution (e.g., government, business, educational institution). A tourism policy as defined by Edgell et al. (2008) “is a progressive course of actions, guidelines, directives, principles, and procedures set in an ethical framework that is issues-focused and best represents the intent of a community (or nation) to effectively meet its planning, development, product, service, marketing, and sustainability goals and objectives for the future grown of tourism” (p. 7). Stated more simply, Hall and Jenkins (1995) suggest “tourism public policy is whatever governments choose to do nor not to do with respect to tourism” (p. 7-8). A tourism policy is essentially a framework including guidelines, goals, and initiatives to work toward achieving the goals. Where as an act by government, such as the Travel Promotion Act of 2009 establishing Brand USA, is a law or statute.
A policy for international travel is having a current passport and for many countries a Visa. The application for a Visa to visit a foreign country allows countries to approve who may visit the country and not allow individuals for a variety of reasons (e.g., security threat). The U.S also has the Visa Waiver Program, which is an agreement with 40 countries allowing citizens of those countries to visit the U.S. for business or leisure travel purposes for up to 90 days without a Visa, provided they meet other requirements (U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs, n.d.). The countries with the Visa Waiver Program also allows U.S. residents to travel to the respective countries with fairly similar criteria. The purpose of requiring a Visa is to regulate travel between countries. The Visa Waiver Program is an agreement to allow citizens of certain countries to visit without having to obtain a Visa if certain criteria are met. This essentially makes it easier to travel between the respective countries.
The International Trade Administration includes a Tourism Policy Council (TPC) to ensure national decision-making considers the national interests of travel and tourism (International Trade Administration, n.d.). The TPC provides resources to help with such issues or challenges as recovering from disaster, and links to Center for Disease Control (CDC), and many other potential issues or challenges for travel and tourism in the U.S.
At more local levels, Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism destinations can develop policies for development, marketing, tourist experiences, human resource issues, tourism organizations (e.g., structure), relationships throughout the community, quality assurance, and supporting services (e.g., safety and security).
Policy Setting Process
There are a series of recommended steps for the establishing policy (Morrison et al., 2018). First, identifying and assessing the circumstances related to the issue. This includes understanding contraints that you and/or will face. Constraints can be internal (e.g., locals’ awareness of tourism, training and education of employees in hospitality and tourism, budget) or external (e.g., economy, price of gas, natural disaster). The tourism organization/local industry has more control or ability to do something about internal constraints, while have little or no control over external constraints. For example, nothing can be done about bad weather or if a natural disaster occurs. However, if locals are not aware of tourism in the local community, education and information can be shared to make locals more aware. This step in the process can also make you aware of new opportunities (e.g., an attraction to develop, new target market).
The next step is typically to create a policy statement to provide guidelines, goals, and initiatives to help guide the organization, destination, etc. While not directly a policy statement, most CVB vision statements include something that provides a guideline with somewhat vague goals. For example, it might be to maintain and/or improve the quality of life for residents of the destination by promoting the destination for tourism and conventions, which would include an economic goal. A policy statement for this vision would be more specific with the goals and initiatives identified to fulfill the goals.
Consultation with government, local tourism businesses, and any other stakeholders is next. This step is to get feedback about the policy statement. Following the consultation and depending on the outcome, the policy statement might be rewritten or modified. Next would be another round of consultation and then rewriting until the the policy statement is approved.
Now is time to implement the policy statement. This will include identifying specific roles of individuals, committees, organizations, etc. This step also includes developing the budget and timeline for the initiative(s).
Finally, those involved evaluation the policy. Were the goals achieved? Why or why not? However, you do not wait until the end of the established timeline for the policy to evaluate. There should be constant assessment to identify if you are likely to achieve the goals. Remember there are numerous constraints that are external (e.g., weather, natural disaster) that might dictate the need to adjust the initiatives and other efforts related to the tourism policy.
Tourism Planning
Prior to tourism planning it is important to consider other types of planning for a community or geographic area. Planning is not new. Gunn and Var (2002) indicate physical planning goes back to early Greek and Roman times. Planning is done to manage visual appearance and land use. However, planning incorporates many disciplines and perspectives: “Planning is a multidimensional activity and seeks to be integrative. It embraces social, economic, political, psychological, anthropological, and technology factors. It is concerned with the past, present, and future” (Rose, 1984, p. 45).
Gunn and Var (2002) suggest when plans (not only tourism, but community, etc.) are created they often include very high or lofty goals and it is difficult to actually achieve such goals for numerous reasons. Planning is very vague and has no real theory behind it. For community plans the general goal is a better place to live. For tourism planning the goal might be to provide visitors with a good experience. As stated earlier, an effective tourism plan can also maintain or even improve the quality of life of residents, not just economically but the attractions provide activities for local residents as well as tourists.
Morrison et al. (2018) offer three primary reasons for tourism planning. The first two are related to impacts, to maximize the economic benefits and minimize damage to resources (i.e., natural, environmental, cultural). Another reason for a tourism plan is that tourism is constantly changing for many reasons (e.g., visitor expectations, needs, motives; politics; economy; technology). As a result, the plan needs to be adaptable.
Not all destinations have a tourism plan. Some reasons for not having a tourism plan include (Morrison et al., 2018):
- Objections – it should be taken care of by the private sector and there is no need for a formal plan.
- Cost – includes market research, consultations, and a lot of time.
- Complex – tourism is affected by numerous things, such as government policies, dynamic of the community and stakeholders.
- Diversity – various sectors involved directly or indirectly in tourism.
- Seasonality – in many destinations the jobs related to tourism can be seasonal (e.g., beach destinations, snow skiing destinations).
- Unpredictability – keep in mind the numerous things that affect and make tourism complex (e.g., natural disasters, crises, politics, economy).
Gunn and Var (2002) add the following tourism planning barriers:
- Lack of awareness of tourism impacts – which is ironic because it is a reason for a tourism plan.
- Do not understand tourism development – there needs to be a plan for developing tourism and then maintaining and even upgrading tourism (e.g., attractions, facilities, etc.).
- Inadequate infrastructure – might have deteriorated attractions, facilities, etc.
- Unorganized – no leadership to guide the process.
- Politics – usually various opinions among stakeholders (e.g., businesses, government, other stakeholders).
- Lack of hospitality training.
However, there can be serious consequences of unplanned tourism. In general, unplanned tourism is not likely to be sustainable tourism economically, environmentally, socially/culturally.
Tourism Planning Models or Approaches
Morrison et al. (2018) provide a seven step tourism destination planning model:
- Background analysis – including a SWOT analysis and assessments of government policies that affect tourism, inventory analysis (e.g., attractions, accommodations, restaurants, etc.), current demand for tourism at the destination.
- Research and analyses – identify/map locations of the inventory analysis, market survey of current visitors (e.g., motivations, what they like to do) and non-visitors (e.g., why have they not visited?, awareness of the destination, image/perception of the destination), competitive analysis (e.g., who are your competitors?, how can you differentiate your destination from competitors? what do and can you work to improve?).
- Where are we now? (position statement).
- Where would we like to be? (vision statement). Then, identify critical success factors or ways to measure and determine if you achieved your vision.
- Setting goals, establishing strategies, and setting objectives – develop a policy or (e.g., stimulate the economy). Set goals or achievable outcomes. Identify alternative strategies to achieve goals and select the most desired of the alternatives given environment or conditions (e.g., economy, resources, politics). Set objectives which are more short term goals to help monitor if you are going to achieve your longer term goals. If not, remember a tourism destination plan should be adaptable, which is the next step.
- Develop a plan – identify organizations and people to be involved and their roles, funding sources and budgets for different aspects of the plan, activities to implement your plan.
- Implement and monitor the plan – While the plan should be developed by input and participation by numerous stakeholders, it is generally implemented by a local tourism agency or organization (e.g., CVB). But, there should be committees derived of various stakeholders to which the agency is accountable. This helps monitor progress of implementing the tourism destination plan and adapt if needed.
- Evaluate the plan – measure performant of the various parts of the plan against the goals (e.g., did you achieve the goals? Why or why not?). Use the evaluation to see if and how you might adapt the plan moving forward.
Tourism Development
The tourism destination plan helps guide development of tourism. Destinations will be at various stages of development. So, it is not that the tourism plan is just for a destination just getting involved in tourism. As suggested by Mason (2003). development and change for destinations occurs as time progresses. The characteristics, motives, preferred activities and attractions, and many other things change over time and destinations redevelop to remain competitive. A fairly common way to view this is commonly referred to as “Butler’s Tourism Area Lifecycle”. There are five main stages to Butler’s Life Cycle (Butler, 1980):
- Exploration – at this stage there might be some tourism but not really an effort to provide traditional or common tourism attractions, facilities, etc. This stage mostly include tourists visiting facilities and local resources used by residents.
- Involvement – this is the beginning of the destination offering some facilities for tourists. The destination begins to more formally organize and provide or improve infrastructure, some attractions, and facilities for tourists at a local level.
- Development – the destination begins marketing and promoting the destination. This stage also begins development from outside organizations and/or businesses. The destination will begin to develop and look more like a noticeable tourist destination. More and more tourists will likely visit the destination as development progresses.
- Consolidation – at this stage the rate of increase in visitors will begin to decline. The rate of development will also begin to decline. Residents may become opposed to tourism with all of the non-locals who are in the community and there is more traffic and congestion. Some of the older attractions, facilities, etc. may also begin showing degradation.
- Decline – number of visitors will be begin to decrease as competitor destinations might have more appealing attractions, infrastructure, etc. The degradation of attractions, infrastructure, and other aspects of the destination will continue and possibly turn into what Butler (1980) refers to as a “veritable tourist slum” (p. 9).
- Rejuvenation – this outcome can occur by development of a new man-made attraction, which is likely to be followed by improvement of surrounding attractions, facilities, and other tourist needs. However, if competitor destinations also rejuvenate, the competition will remain and rejuvenation might be much less or possibly not rejuvenate and potentially decline. Another way Butler (1980) suggest rejuvenation can occur is to utilize natural resources that might not have been part tourism product throughout previous tourism development and marketing and promotion.
Butler (1980), as well as many other tourism scholars, suggest all of these efforts or stages of Tourism Area Life Cycle should be a collaborative effort within the community. For example, the government could offer incentives for private development of a new man-made attraction.
There are a number of potential ways to develop tourism. One way is to develop a “flagship” attraction, which are major attractions like a theme park (e.g., Disney Land, Disney World) and/or utilize natural attractions (e.g., ocean, lake, National Park). Gunn and Var (2002) offer recommendations for tourism destinations to develop destination zones. The zone would have clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) and a corridor connecting the clusters with some form of transportation. Clustering attractions provides tourists with more to do in a closer area so they spend more time at attractions and less traveling between attractions. The destination zone and clustering is a great example of planning and development and how integrated the two initiatives should be.
Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism involvement should be holistic. The holistic view would include consideration of the product (e.g., attractions, events, support facilities, transportation, infrastructure, etc.). Respective destinations could also ensure people (i.e., hosts, guests) are included to ensure there is community awareness and inclusion of local businesses, organizations, and residents. Morrison et al. (2018) also suggest visitor management (e.g., signage) and identifying the visitor mix of the destination. Packages (e.g., all inclusive, hotel and tickets to attraction) and programs (e.g., events, festivals, other activities) could also be developed to attract more tourists. However, destinations should approach tourism development and/or redevelopment from a sustainable approach to avoid overtourism (i.e., too many tourists).
Sustainable Tourism Development
Tourism development should also be sustainable and include the three impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural).
The United Nations (n.d.) proposes 17 goals to consider for economic development, which include economic (e.g., “No Poverty”, “Decent Work and Economic Growth”, environmental (e.g., “Clean Water and Sanitation”, “Affordable and Clean Energy”), and social/cultural (e.g., “Good Health and Well Being”, Quality Education”) goals. The 17th goal is “Partnerships For the Goals”, which are very important for tourism destinations, not only in tourism destination planning and development, but other aspects such as marketing and promotion.
Relating development back to the impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural). Sustainable development should include these impacts. Morrison et al. (2018) through applying the triple bottom line to tourism offers some examples of efforts for sustainable development in each of the three areas:
- Social – include residents, be sure development improves or at least maintains locals’ quality of life.
- Environmental – protect resources, educate visitors and residents of ways to protect resources.
- Economic – new employment opportunities, increase spending of visitors, find ways to have businesses purchase locally to minimize leakage.
Tourism Development Strategies
Various strategies exist to develop tourism. For example, flagship attractions (e.g., large amusement parks, National Parks) can provide something unique to market and promote. Development of clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) provide several attractions near each other so visitors do not have to drive long distances between attractions. Such districts could also include development of a circuit or trail for transportation via hiking or biking. Aside from man-made attractions, events can be developed by destinations to highlight such things as cultural or other unique aspects of a destination.
Considering all of the possible options of tourism development provides a holistic view. Not only the examples of attractions and events, but packages and programs can developed. Destinations need to also consider all of the elements of tourism in development (i.e., attractions, infrastructure, transportation, built/support facilities, service quality/hospitality). Again, not only businesses and organizations directly involved in tourism, but all stakeholders (e.g., residents, other local businesses) should be included and/or given the opportunity to provide feedback regarding the tourism development plan.
The general goals of tourism development should include improving visitors’ experiences, improving the local economy, not damaging natural resources, and integration throughout the destination so that tourism attractions and venues are not isolated from the rest of the community (Gunn & Var, 2002). Such goals of tourism development require all three sectors (i.e., private, non-profit, government) to be involved and collaborate.
Tourism Development Roles
The private sector, non-profit, government, and local community (e.g., residents) should be involved in tourism development. The private sector role is entrepreneurial and operations (Morrison et al., 2018). The entrepreneurial role is to identify investors to develop man-made attractions, accommodations, food and beverage, and other facilities for tourists. Once built their role becomes to hire workers, manage the operation and ensure it is successful. After all, they are taking a risk as entrepreneurs.
As discussed in the Tourism Organizations section, the non-profit organizations include CVBs to market and manage the destination, chambers of commerce, associations such as a local sports association to attract sporting events to the destination. The CVB typically works with all stakeholders and leads the marketing and sales (e.g., conventions, trade shows) for the destination. Chambers of commerce might be the tourism marketing and sales organization in smaller destinations. However, many of these non-profit types of organizations collaborate with each other, as well as with private or for-profit-sector (e.g., members of CVBs) and government (e.g., hotel tax dollars as a funding source). Non-profit organizations might also operate such things as museums and historical attractions, as well as festivals and events. Such organizations might be local cultural organizations.
The government really does not manage tourism attractions. However, there are exceptions, such as National Parks. Government roles are to stimulate development of tourism, as well as establish and enforce procedures, codes, such as zoning (e.g., business, residential). Government might also get involved for the following reasons: bankruptcy of an attraction where the government needs to help the business in some way, ensure cultural aspects of the community are conserved, encouraging private sector development, find ways to work with potential attractions and other elements of tourism provided through the private sector where businesses may have concerns about being profitable (Morrison et al., 2018).
Government might fulfill some of the above reasons for their role in tourism development by offering incentives (e.g., tax breaks) to entice development by the private sector. Government might also offer a piece of land for private sector development, which lowers the businesses cost to develop at attraction, supporting facilities, or other element of tourism.
While the sectors may have relatively unique roles in tourism development, it is also important the cooperate with each other for the good of the destination. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) offer a model whereby there are times each will work independently of the other two sectors, times when two sectors work together (e.g., private sector and government), and times when all three work together. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) call this “coopetition”. For example, while attractions compete within the destination for tourists to visit respective attractions, if all stakeholders cooperate the develop and manage tourism, the destination will do better overall.
Project Development Analyses
Prior to developing an attraction, hotel, or other element of tourism, there should be an assessment or analysis to determine the feasibility of being successful. Private sector developers who need be profitable will typically do feasibility studies. This may start with a pre-feasibility study, which is essentially to see if the project is even viable. For example, does the project make sense given what the destination already offers? Pre-feasibility studies might be conducted by whatever company or organization is interested in the project. If it does, the next step would be a more robust feasibility study to identify such things as potential sites for the product being considered, assess the market demand of the project, projected revenues and expenses, capital costs to develop the project, and will there be enough return on investment (ROI) if the project is developed. The full feasibility study is often conducted by an independent consulting company to minimize biases. The feasibility studies helps the company or organization identify if the project should move forward or not.
The market demand study within the full feasibility study would include secondary and primary research. Secondary research would include existing data, such as hotel metrics (e.g., supply, demand or rooms sold over a given period of time, occupancy, average daily rate (ADR), and revenue per available room (REVPAR) if the project is a hotel. Primary market analysis requires collection of data. This can include surveys (e.g., visitors of the destination to determine if the potential project is of interest), focus groups to get in-depth insight as to the interest of visitors. Surveys can also be conducted to potentially identify potential demand for the project.
If a project is not intended to be profitable, such as one being developed by the government or non-profit organization, a cost-benefit analysis can be conducted. Such a study essentially identifies the potential benefits to society are worth the cost of the investment.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area life cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer, XXIV (1), 5-12.
Draper, J., Woosnam, K. M., & Norman, W. C. (2011). Tourism use history: Exploring a new framework for understanding residents’ attitudes toward tourism. Journal of Travel Research, 50 (1), 64-77.
Edgell, D. L., Allen, M. D., Smith, G., & Swanson, L. E. (2008). Tourism policy and planning: Yesterday, today and tomorrow . Elsevier Inc.
Gunn, C. A., & Var, T. (2002). Tourism planning: Basics, concepts, cases (4th ed.). Routledge.
Hall, C. M., & Jenkins, J. M. (1995). Tourism and public policy . Routledge.
International Trade Administration. (n.d.). Tourism Policy Council (TPC). https://www.trade.gov/tourism-policy-council
Mason, P. (2003). Tourism impacts, planning and management . Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Morrison, A. M., Lehto, X. Y., & Day, J. G. (2018). The tourism system (8th ed.). Kendall Hunt.
Rose, E. A. (1984). Philosophy and purpose in planning. In M. J. Bruton (Ed.), The spirit and purpose of planning (2nd ed., pp. 31-65). Hutchinson.
United Nations. (n.d.). Department of Economic and Social Affairs: Sustainable Development. https://sdgs.un.org/goals
U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs. (n.d.) Visa Waiver Program. https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas/tourism-visit/visa-waiver-program.html
GHL 2365 - Tourism Copyright © 2024 by Jason Draper is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Tourism Planning
Tourism Planning: The written account of projected future course of action or scheme aimed at achieving or targeting specific goals or objectives within a specific time period is called a Plan. A Tourism plan explains in detail what needs to be done, when to be done, how to be done, and by whom to be done. It often includes best case, expected case, and worst case scenarios or situations.
A plan is usually a map or list of steps with timing and available resources, used to achieve an objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a temporary set of projected actions through which one believes that the goals or targets would be achieved.
Plans can be formal or informal:
Structured and formal plans, utilised by numerous people, are more likely to occur in projects, diplomacy, careers, economic development, military campaigns, combat, sports, games, agriculture, technology, tourism, IT, Telecommunication etc. or in the conduct of other businesses.
In most cases, the absence of a well-laid plan can have high effects: for example, a nonrobust project plan can cost the organization long time and high cost.
The persons to fulfill their various quests do informal or adhoc planning. But, what most importantly matters is the extensiveness, time interval, and preciousness of the plans. Though, all these planning categories are not self-governing and dependent on each other.
For example, there is an intimate connection between short-range and long-range plans and tactical (strategic) & functional (operational) planning classifications.
For businesses, sector planning’s (such as IT, telecommunication, services, banking, tourism, agriculture etc.) and military purposes formal plans used to a greater level. They are conceptualized, thought as abstract ideas, are likely to be written down, drawn up or otherwise stored in a form that is accessible to multiple people across time and space. This allows more reliable collaboration in the execution of the plan.
Tourism Planning and the Need for Tourism Planning
Planning is one of the most important project management and time management techniques or methods. It involves preparing or forming of a sequence of action steps to achieve some specific desired goals. If you do it effectively and efficiently, you can reduce much of the necessary time and effort used in achieving the goal.
A plan is like a map or a blueprint which would fetch you results slowly & steady according to a time frame. Whenever, you are following any plan, you are able to know how much you have neared to your assignment objectives or how much distant you are from your goals.
Why is planning important?
- To set direction and priorities for the workforce in the organisation:
The strategy is the chief requirement of the organization, in order to achieve the targets. The strategies give the route and primacies (priorities) for your organization. It describes your organization’s perspective and gives an order to the activities that will make the perspective into reality.
Read more on World Federation of Tourist Guide Associations (WFTGA)
The plan will assist the team in achieving goals and also give them familiarity about the tasks. The plainly defined and appropriate strategy will give priority initiatives that will drive the maximum success.
- To get everyone on the same room or the same box:
An organisation has different departments, but a single goal. That’s, why different departments work in a way that add to the goals of the organization.
Hence, a strategy is required, so that all actions move in one direction. Then only, the various departments such as marketing, administration, sales, operations etc. can move together to accomplish the anticipated goals of the organisation. Tourism Planning
- To simplify decision-making process within the organisation:
Whenever, there are targets, there are different solutions. The team also may have new philosophies or probable solutions. Therefore, you need a definite plan, so there are no inhibiting factors.
- To drive alignment:
Many a times, inspite of the best labour, you reach nowhere. The reason is that the efforts or labour is done in areas, which are of no use. Hence, the effort should coincide with the priorities or primacies. The plan serves as a vehicle for answering the enquiry, that “How well we can use all the resources such as material, man, machine etc. to upsurge our tactical (strategic) success?
- To communicate the message to everyone:
The countless managers in the top level management know how to make an effective plan/strategy, at which position their organisation is, what they need to do and where they need to be there Many a time, the strategies are not written down and the various aspects in the plan are not linked systematically.
Then, only few members of your team can work towards your goals. Therefore, it’s very important that your team, staff, customers, suppliers and other stakeholder’s know your plan of action and strategy base, this will lead to better probability of success and more efforts pouring in. Tourism Planning
Also read Contribution of Tour Guiding in Sustainability
Once, you ascertain your goal, you are in a good position to make a solid proof plan in which role of each team member is defined. There are very less managers, who have understanding of situations and actually comprehend to make the greatest use of their part in smoothing policy (Eagles, McCool, Haynes, Philips, & United Nations Environment Programme, 2002).
Techniques of Plan formulation
It involves a number of steps:
- Collection of information (data):
The most noteworthy phase of economic planning is the gathering of the economic data. The data not only contains economic defining variables, but also descriptive variables such as demographical, topographical, and political data. The economic planning also contains non-quantitative variables. And surely in order to collect appropriate data the planner should have intra-disciplinary as well as inter-disciplinary knowledge.
- Deciding the nature and duration of the plan:
After the collection of data in context to the economy. Now the next step is deciding the nature and period (time duration) of the plan. Now, the planner has to decide the planning levels i.e. micro or macro basis, functional (practical) or structural (operational),centralised (central) or decentralised (distributed), long or medium or short term etc. The medium term plan generally comprises 5 years and is enough time periods to apply its drivers, strategies and approaches.
Also read Goals and objective of sustainable tourism development
- Setting up of the objectives:
The third step after setting the nature and time period of the plan is setting the goals or objectives or aim of the plan. And, surely these objectives will have to be realized in a fixed time schedule. Generally, most of the objectives related to economy of the country are related to advanced progress rate of GNP, reduction in joblessness, eradication of local discrepancies, removal of illiteracy, growth of farming and manufacturing areas, etc.
After, the planner has analysed the ground situation and given the objectives. Now, the planner has to establish these objectives depending on the eminence/Significance to the individuals and the economy in totality.
- Determination of growth rate:
While framing the plan, the planner has to determine the growth rate i.e. at what rate the economy will grow through this time interval. Whatever plan, the planner and policy makers decide at least, it should maintain the per capita income level of the country. The plan should be such that the per capita income do not decreases or affect the progress of the country negatively.
And, such a thing is possible, if the growth rate of GNP or growth rate of the country and growth rate or progress of the population is same. But this growth rate is least recommended. Rather, the planner will choose for that growth rate which is better than the population rate. “For example, if India wants to maintain its present per capita income while population is growing at the rate of 8% p.a., then the obligatory GNP growth rate should not be less than 8%. If we want to grow GNP by 8%, NI should grow @ 16%.
If the capital output ratio (COR) is 1:3, then we will have to invest 16% of GNP. While defining the growth rate, the planner must keep in view the growth rate of other adjoining or developing countries like Pakistan, China, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Bangladesh, etc.” Tourism Planning
- Full utilisation of financial resources of the plan:
The utilization of resources including the fiscal resources should be in a way that the predetermined objectives are realized. The various resources used in a plan of a country are human resources, natural resources, technology, worthy governance, entrepreneurial skills, financial resources etc. Therefore, from these resources or sources advantages or profits can be achieved.
Read more Local Community Involvement in Tourism Development
Broadly it can be categorized into renewable or renewal resources. Advantages of resource application may be augmented prosperity or needs, appropriate operation of a system, or boosted welfare. With the resource allocation, resource management is also crucial in a plan. The various resources have three basic attributes- “utility, limited availability, and potential for depletion or consumption.”
In order to accomplish the planning requirements, outside (external) resources are also used, when internal (inside) resources fall short. The outside resources generally comprises of foreign relief and support, foreign grants, foreign direct investment, and foreign borrowings from various International Financial Institutions (IFI’s) and rich countries.
The role of government is important and cannot be ignored. They plan and take various roles depending upon the environment of the country. When, a country is developed, their role more becomes as a facilitator, while in case of developing or poor countries, they have to actively participate in it. They have to implement plans as well as pour on their resources.
Whenever, the plans have been made by the government, they are sent to the necessary departments with goals, necessary steps and outlays. Thereafter, the concerned ministries or departments see the feasibility of the sent projects and give recommendations about the feasibility (viability) of various schemes and projects of the plan. Here, the government organisations are asked of their keeping in mind the sectorial distribution and extent of the plan. There are also some projects where partnership occurs between governmental and private sectors. Here, the government may play role of a catalyst or facilitator and there may be some revenue sharing understandings.
- Formation of economic policies:
In planning, plans are fine. The role of planners is fine. But, most importantly the plans should be able to give the desired results. The results should have more positive effects than the negative effects. Here, economic programmes, policies or strategies play a substantial role. As, they act as a gasoline to the locomotive of economic development. Also, the plans implemented should be based on ground or current scenario, rather than being picked from other countries, environments or sectors.
- Plan execution:
The final phase of planning is plan operation. And, for actual implementation of plan, following conditions cannot be ignored:
- The regime should be steady, truthful, genuine and productive.
- The organisational (administrative) system should be well-organized,
- i.e. free of nepotism, dishonesty, enticement, red tapism.
- Upkeep of law and order inside the nation.
- There should be equivalent level of involvement of both private and public sectors in economic growth.
- Keep a check on convenience and electronic up keep of government records, monetary proclamations and cost statements. Tourism Planning
- The opposition should be Watchful and productive. (Wagner, Frick, & Schupp, 2007)
- Different countries use planning models/techniques dependent upon the nature of the economy.
- The availability of the data, the volume to use and manage such techniques and models.
Read more Tourism Policy formulation Bodies in India

You Might Also Like

Forms of Business Ownerships

Emergence of Thomas Cook

Retail Attractions: Small Specialist Shops
- English (CA)
- Deutsch (DE)
- Deutsch (CH)
8 types of tourism that you need to know
The three tourism categories, domestic tourism, inbound tourism, outbound tourism, the 8 types of tourism according to motivation, business tourism.
- Meet with business partners or prospects
- Attend an event, conference, or trade show
- Visit another office location of the same company
?)
See how to save money on business travel
Leisure tourism, shopping tourism, cultural tourism, sports tourism, rural tourism, mountain tourism, urban tourism, many people travel – but for completely different reasons.
?)
Make business travel simpler. Forever.
- See our platform in action . Trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, TravelPerk makes business travel simpler to manage with more flexibility, full control of spending with easy reporting, and options to offset your carbon footprint.
- Find hundreds of resources on all things business travel, from tips on traveling more sustainably, to advice on setting up a business travel policy, and managing your expenses. Our latest e-books and blog posts have you covered.
- Never miss another update. Stay in touch with us on social for the latest product releases, upcoming events, and articles fresh off the press.
?)
5 inefficient processes affecting your business and how to fix them
?)
Duty of care in the workplace: everything you need to know
?)

CEO Roles and Responsibilities: conquer your role as CEO
- Business Travel Management
- Offset Carbon Footprint
- Flexible travel
- Travelperk Sustainability Policy
- Corporate Travel Resources
- Corporate Travel Glossary
- For Travel Managers
- For Finance Teams
- For Travelers
- Thoughts from TravelPerk
- Careers Hiring
- User Reviews
- Integrations
- Privacy Center
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Modern Slavery Act | Statement
- Supplier Code of Conduct
Tourism Planning
University of oregon school of planning, public policy and management.

Types of Tourism
- aerotourism/aviation
- cryptozoology (i.e. Loch Ness monster, sasquatch, yeti)
- culinary/gastronomic/traditional cuisine
- Dizionario del Turismo Cinematografica (artistic costume movement)
- DNA/ancestry/genealogy
- ethnography
- Harry Potter London
- handicrafts
- intangible cultural heritage (ICH)
- pop-culture
- totaliltourism
- traditional music
- wine/enotourism
Educational
- professional development
- study abroad
- Burning Man
- FIFA World Cup
- Oktoberfest
- birth/maternity
- forest bathing (shinrin-yoku)
Religious/Spiritual
- sacred/faith
- cliff diving
- kiteboarding
- paddleboarding
- scuba diving
- submarine diving
- sun/sand/surf
- waterskiing
- windsurfing
- flightseeing (from sightseeing)
- hot air ballooning
- parachuting
- paragliding
- parasailing
- sailplaning
- bikesploring
- mountain biking
- bobsledding / bobsleighing
- cross-country skiing
- dogsledding
- downhill skiing
- ice skating
- luging / tobogganning
- ski mountaineering
- snowboarding
- snowmobiling
- snowshoeing
- boat sharing
- globetrotting
- self-guided
- urbex (urban exploration)
- backpacking
- eco-challenge
Alternative/Specific Interest Tourism (SIT)
- caving/spelunking
- mountain climbing
- wingsuit flying
- bliesure (from ‘business’ and ‘leisure’)
Experimental
- alphatourism / alphabet travel
- blind travel
- contretourism
- erotourism / find your other half travel
- flying by night
- monopolytourism
- sagittatourism
- slow-return travel
- twelve travel
- bungee jumping
- cliff jumping
- jailoo (from Kyrgztystan for “mountain pasture”)
- zorbing/globe riding/sphereing/orbing
Environmental
Agritourism
Ecotourism/Geotourism
- archeological digs
- birding/birdwatching
- sustainable
- whale watching
- urban decay
Technological
- astronomical
Immersion/Experiential
- exchange student
- Society of Creative Anachronism
- work exchange
- recession/staycation
- anniversary
- bachelor/stag/bachelorette party
- marriage/wedding
Universal/Accessible
Humanitarian
- justice/solidarity
- disaster response/relief
- international work camps
Volunteerism
Alcohol/Alcotourism
- booze cruise
- destination drinking
Dark/Black/Gloomy/Grief
- doom/last chance
- prison hotels
- slum/favela/ghetto/reality travel
- tombstone/cemetery
- tunnels (e.g. Shanghai Tunnels)
- illegal (i.e. Columbia, Mexico)
- legal/recreational (i.e. Amsterdam, legalized states)
- Legal/Quasi-legal
Travel With - The Holiday Story
18 Different Types of Tourism | Globally Accepted
Last few years, tourists and their demands have frequently been changing. Also, the tourism industry is changing based on needs. This article elaborates on different types of tourism, tourists, planning, activities, products, travel , etc. It helps your travel planning as well.
Along with recreation, tourism has become one of the growing industries, and it’s the source of income for many people.
“Life is all about adventure, so pack your bags and start the tour.”

Different Types of Tourism
What is tourism.

Tourism is a process of spending time away from daily routine or home to pursue recreation, relaxation, and pleasure while using the commercial provision of services.
Tourism in a country has many benefits: it creates employment, boosts revenue, develops infrastructure, helps in cultural exchange, etc. Travel duration under tourism must be less than 12 months (a consecutive year).
So, What comes first to mind when we hear the word Tourism?
The most common thought is to pack the rucksack and travel away from day-to-day life. That means the movement of people from their usual residence to another place.
Suppose your friend’s aim for the tour might differ from yours. For example, you may travel for recreation, but he may go for business.
Classification of Tourism
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism involves the movement of people in the country’s natural environment or outside the country for personal or other purposes. These different purposes classified the tourism industry in many ways.
This article lists the main tourism classifications: Domestic tourism, International tourism, Business tourism, Adventure tourism, Medical tourism, Educational tourism, etc.

Importance of Tourism – Why is tourism important?
Tourism has a direct impact on any country’s economy. The role of tourism in economic development is important. A vast amount of job possibilities can develop through public relations in tourism. Knowing another state/country’s taste culture is a great filling from a traveler’s perspective.
Mainly how many types of tourism are there
Mainly three types of tourism are found in any country. The classes are domestic tourism, International tourism, and outbound tourism. But nowadays, many types of tourism newly evolved.
18 Different Types of Tourism
The various types of tourism are developed nowadays and become popular; they are:-
- Domestic tourism
- International tourism
- Outbound tourism
- Business tourism
- Adventure tourism
- Wildlife tourism
- Medical tourism
- Wellness tourism
- Pilgrimage and spiritual tourism
- Cultural tourism
- Dark tourism
- Culinary tourism
- Celebrity tourism or Film tourism
- Educational tourism
- Cruise tourism
- Rural tourism
- Beach tourism
- Space tourism
Let’s discuss how many flavors and categories of tourism can be found in any country and accepted globally.
1. Domestic Tourism
Domestic tourism involves traveling in one’s own country, and tourists don’t cross international borders or entry points. Domestic tourism is used to minimize poverty, enhance infrastructure, and boost the economy’s growth and generation of employment.
2. International Tourism
Travel outside your country needs a visa and passport; called International tourism. For example, if you want to explore The UK from Sri Lanka, you need documents to enter another country.
Read How to Listen to Music on a Plane
3. Outbound Tourism
This tourism defines a tourist traveling for a holiday to a different country, like your residents in Bali and traveling to Barcelona . It is an example of outbound Tourism.
4. Business Tourism
This tourist travels to meetings, officially gets together for conferences, etc.
Business tourism plays a vital role in the tourism sector. Sometimes, people stay out of their typical environment for more than a year for business purposes and spend their vacations there.
General activities related to business tourism include attending meetings, officially getting together, conferences, seminars, visiting exhibitions and trade fairs, etc. This tourism levels up the purchasing power.

5. Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is a person’s travel from one place to another to seek fresh adventures and activities. This form of tourism is most famous among young tourists and people who like to explore remote areas. It encourages us to leave our comfort zone by undertaking activities like hiking , rafting, climbing, diving, etc.
Adventure tourism is increasing day by day. You could also try whitewater rafting, the Ladakh tour, the Kedarnath tour, Port Blair, and Andaman and Nicobar tour for the adventure.

6. Wildlife Tourism
Wildlife tourism is people’s travel to different places to observe and interact with wildlife, flora, and fauna in their natural habitat. Safaris, visiting the animal rescue center, swimming with dolphins, etc., are examples of wildlife tourism.
Because of exotic species of wildlife, this tourism became recognized. The Sariska Wildlife or Hyde Park Sanctuary , Keoladeo Gana National Park, and Corbett National Park are renowned for wildlife tourism. The Great Barrier Reef is also famous in Australia.

7. Medical Tourism
Many people travel for treatment, and several medical institutes cure foreign patients. Thailand has recorded 6000,000 new patients every year. Malaysia also treated over 100,00 tourists in 2005. 45% of foreign tourists come to Chennai for medical treatment.

8. Wellness Tourism
Wellness tourism has been a significant part of tourism since ancient times. This tourism mainly attracts those tourists who want to regain their health. Wellness tourism will help you to get rid of mental and health stress.
Tourists recover their health issues through physical, spiritual, or psychological activities. All around the world, plenty of destinations are popular for improving health.
Examples include Mexico Temazcal Beach Resort Spa, Caribbean wellness cruise, California weight loss and detox retreats, Colorado Hiking and Mountain Yoga retreat, and China Hot Spring Resorts TCM.
Ayurveda, Yoga , Meditation, Panchakarma, and Rejuvenation Therapy are the oldest Therapy of treatments to improve health and the best way to develop wellness tourism.

9. Pilgrimage and Spiritual Tourism
Pilgrimage or spiritual tourism is when a person journeys to other places for spiritual or religious reasons.
Spiritual tourism helps support local cultural activities and handicrafts, generating employment and revenue. Trips to Jerusalem, Bodh Gaya , Hajj, etc., are pilgrimage or spiritual tourism.
This tour has been famous for ages, but It’s popular among older people mainly. Vaishno Devi, Golden Temple, Char Dham, and Mathura Vrindavan are some places famous for Pilgrimage tours.
10. Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is a person’s journey to learn and participate in local festivals, rituals, and cultural activities of other places. It’s more than a commercial activity.
This form of tourism helps spread aboriginal communities’ culture, traditions, diversity, and richness to the rest of the world.
Visit the historical sites and the artistic features of that country too. Famous cultural tourism places are:-
- India – Durga puja in Kolkata , Temples at Banaras, Jaipur, known as the pink city Palace in Rajasthan. Forts and monuments in Delhi, Agra, UP.
- UK – Tower of London, The British Museum, Big Ben, London Durga puja , etc.
- Kenya – The main attraction is the dance of the Maasai tribe.
- Morocco – The main attractions are the Olive Festival and Honey Festival.
- Jordan – The main attraction- is Jerash, famous for Roman architecture Petra, the red-rose curved rock city and one of the seven world wonders, and Shoubak with its Montreal Crusader Castle.
- Greece – The main attraction- is the Lion Gate of Mycenae.
- Turkey – the main attraction- Sultan Ahmed. Mosque, House of the Virgin Mary.
- Vietnam – The main attraction- is Sapa Market.
- Ireland tour – Cliffs of Moher, Dublin, Killarney National Park, etc.

11. Dark Tourism
Dark tourism, Black tourism, or grief tourism are related to people’s travel to historical places involved with tragedy and death. Since 2016, dark tourism has significantly increased (over 1200%). Chornobyl, cemeteries, Ground Zero, historical museums, and Auschwitz are popular dark tourism destinations.
It is referred to as mourning tourism. Dark tourism involves visiting those places and sites that have witnessed the greatest tragedies in history. Besides this history of human suffering and bloodshed, these locations are famous for their historical value.
So, those sites that carry potent pesticides have become popular tourist destinations and attract many tourists yearly.
Like Famous sites In Japan, Hiroshima & Nagasaki bombing locations, Ground Zero, New York, USA . The War Remnants Museum, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz, Germany; Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, etc.

12. Culinary Tourism
Culinary or food tourism involves tasting and experiencing local and traditional food in a specific country, region, city/town/village.
It is significant that besides accommodation and infrastructure. Here, food is one of the prime components. Therefore, lots of tours are organized here to experience the culinary culture.
Today, with the overall growth of this sector, tourism has expanded and developed to the next level.
Every year, Different states of India organize food festivals at different times in different states. Thousands of people from abroad join this festival to enjoy traditional food.
Everyone knows India is called “The land of spices.” And every state has unique kinds of food culture. Today, it is a significant part of tourism.
Culinary Tourism includes where people visit certain regions like California, Napa Valley, Catalonia, USA, and Spain) to enjoy foreign wines.
Famous Destinations : London, France, Beijing, Mexico, Italy, etc.

13. Celebrity Tourism or Film Tourism
Celebrities are the primary source of attraction for celebrity or film tourism. In this form of tourism, tourists visit places where a celebrity currently lives or has lived. Management organizations use celebrity tourism to promote a place or attraction.
Although no celebrities are present, only you can see the entire studio. Many Destination Management organizations (DMOs) use celebrity tourism to promote destinations as an attraction.
Popular celebrity tourism destinations are – Hollywood, Harry Potter Studios, Ramoji Film City India, Cannes Film Festival, Hong Kong, and Madame Tussauds.

14. Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is a new pattern of tourism that comprises learning new things. It’s the journey a person takes to leave his hometown or country for educational or learning purposes. Educational tourism is famous in Japan, Australia, the UK, etc.
An educational tourist can be away from his hometown for many days. Education and learning are the key reasons for their travels, and it is learning knowledge from historical places, cultural and social events, and understanding a language.
It’s used as a tool to complement education by gathering travel experience. Many educational institutes combine these trends in primary schools and are compulsory in higher education.
15. Cruise Tourism
Holidays based partially or wholly on a cruise ship are considered cruise tourism. It provides tourists with a multi-centered holiday experience. Cruise ships (like small yachts, big ships, etc.) take people on a tour of oceans, fjords, or rivers.
Throughout their trip, tourists can enjoy time at various destinations. The Mediterranean, Caribbean, Arctic, Antarctica, etc., are famous destinations. It’s the newest and fastest-growing part of the world’s tourism industry.
The world’s famous coastline and inland waterways have the potential to develop cruise and houseboat tourism like Quark Expeditions, OZ Cruising, and A-ROSA River Cruises.
India has many types of tourist cruises. Soon, India will be including Ocean Cruise, River Cruises, and Lake Cruises.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by ⚓️ Iglu Cruise (@iglucruise)
16. Rural Tourism
There are many forms of tourism, and It’s divided into many parts. In this category, a tourist spends leisure time in rural areas or villages. Visitors can make a plan to visit the rural area for some days or a couple of months.
Especially Solo travelers can visit those places to enjoy their lonely time. They join all the local activities that happen in this village.
Rural tourism is included in a ‘country holiday’ where tourists spend much of their leisure time. Thus, they taste the recreational activities in the rural environment.
Like Farming in Rural Punjab, The Spiti Valley Rural Tourism, Sundarban and Jodhpur Village Life, Bhubandanga West Bengal, and Community Tourism in Kutch.

17. Beach Tourism
Beach tourism is how a beach plays a major element in the holiday, and it’s the most modern form and the staple of tourism.
In beach tourism, tourists travel to a beach for leisure, recreation, or business purposes. People who like the clear blue sight of a beach undertake this journey.
Popular Beach Destinations: The Maldives, Seychelles, Turks And Caicos, French Polynesia, Africa , Queensland, Australia, Philippines, Thailand, Bali In Indonesia, Lakshadweep, Goa, Puri, etc.
Why is Beach Tourism important?
- Beach tourism has brought about many economic benefits.
- It has led to the building of many attractions, resorts, etc.
- Beach resorts help in meeting the increase in intra-regional demand and domestic demand.
- This type of tourism creates numerous employment opportunities.

Negative Impacts of Beach Tourism
- It leads to the wastage of a lot of resources and space.
- Beach tourism pollutes water and environmental resources.
- Building new berths, marinas, etc., hurts coastal and marine life.
18. Space Tourism
We have seen significant changes in the aviation industry in the last 100 years. What was once used for warfare and cargo transport is now used for traveling.
Human development has now broken all bounds to take this journey to the vast emptiness of space.
Russia has been the pioneer in this field. Soyuz spacecraft conducted its first space trip with American businessman Dennis Tito in April 2001.
It was a government spacecraft that conducted seven space expeditions within the next six years. This surge in public interest led other organizations worldwide to dive into this area.

There are different types of space tourism
Orbital Space Tourism: These flights remain within an orbit around the Earth at a speed higher than suborbital space flights. These flights orbit the world constantly for their entire stay in outer space.
Sub-orbital Space Tourism : This was the beginning of space tourism. The spacecraft launches with a substantial initial velocity that pushes it out of the Earth’s atmosphere. But this doesn’t throw it entirely out of the gravitational sphere. The power is insufficient for orbiting, so it freezes once the engines are shut off.
SpaceX C.E.O. Elon Musk proposed the prospect of lunar tourism. In 2018, he announced the ‘Dear Moon Project,’ the highly anticipated first lunar space tourism mission. They will carry out this project in 2022 with Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa.
Space Tourism cost
The cost of each sub-orbital trip on the Soyuz spacecraft is reported to be 200,000-250,000 million U.S. dollars. Other trips carried out by different organizations were priced around the same margin.
Virgin Galactic recently announced that each ticket would cost 450,000 USD for the upcoming missions.
Space Tourism companies
Even though the industry is still up and coming, massive companies dominate the market. Space Adventures of Virginia, U.S.A, was the first successful space tourism company.
Elon Musk’s SpaceX, Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, and Amazon C.E.O. Jeff Bezos’s Blue Origin are all set to launch their space tourism business by 2022. Blue Origin recently conducted its debut flight with Jeff Bezos.
Oliver Daemen and Wally Funk were the world’s youngest and oldest men in space, respectively.
Space Tourism advantages
The universe and outer space have always been intriguing subjects for people on Earth. Yet, there were limited resources to satisfy their curiosity. The option of space tourism thus connects people with space in a unique way and solves its mystery. A more ecological advantage is the waste policy.
There is minimum pollution associated with these travels. Also, this allows a whole new sector of job opportunities for highly educated professionals and ambitious youth.
Top 13 list of space tourists
- Dennis Tito (American): April 28 – May 6, 2001
- Richard Branson
- Gennady Padalka
- Guy Laliberté
- Eytan Stibbe
- Sian Proctor
- Mark Shuttleworth (South African / British): April 25 – May 5, 2002
- Gregory Olsen (American): October 1 – October 11, 2005
- Anousheh Ansari (Iranian / American): September 18 – September 29, 2006
- Charles Simonyi (Hungarian): April 7 – April 21, 2007[8]
- Richard Garriott (American): October 12 – October 23, 2008[9]
- Sheikh Muszaphar Shukor (Malaysian): October 10 – October 23, 2007
Space Tourism in India
Space activities, in general, have been quite a staggering section in India. Last year, the government announced a policy that opens space exploration to private sectors, but hardly any company has taken action on it.
Entrepreneur Santhosh George Kulangara will be the first Indian space tourist as he booked his spot on a Virgin Galactic space flight in 2007. Hopefully, he will join Dennis Tito, Mark Shuttleworth, Gregory Olsen, and many more this year.
Forms of Tourism
- Atomic Tourism
- Beach Tourism
- Bicycle Tours
- Eco-Tourism
- Geo-Tourism
- Industrial Tourism
- Rural Tourism
- Space Tourism
- Sports Tourism
- Sustainable Tourism
- Virtual Tourism
- War Tourism
What is the main purpose of tourism?
- Economic Sustainability: It ensures the effectiveness and competitiveness of tourism destinations and enterprises. It helps continue improvement, which is beneficial in the long run.
- Local enrichment: Tourist destination prosperity is an enormous part of tourism. The tourism business continuously maximizes the economic growth of the host destination.
- Employment Standards: Tourism supported the level of wages, terms of service, and availability for all. It creates local jobs without discrimination based on gender, race, disability, or other means.
- Local management: Involve local communities and empower local people for planning and decision-making. The community and tourism management team helped to develop this.
- Community Welfare: Maintain and boost the local community’s lifestyle. They are part of social structures. But surely, this process should take place with no social humiliation or exploitation.
- Natural Integration : Maintain and improve the quality of both urban and rural landscapes. It avoids natural and visual degradation of the environment.
- Natural Integration: Maintain and improve the quality of both urban and rural landscapes. It avoids natural and visual degradation of the environment.
- Biodiversity: Another purpose of tourism is to assist in conserving wildlife and natural wildlife areas and reducing losses.
- Environmental cleanness: Besides the purpose of tourism, all tourists must reduce air, water, and land pollution and waste generation.
- Tourism is a significant part of national integration .
- Tourism always motivates tourists to understand their traditions, heritage, culture, and religion.
- Tourism’s most significant part is economic growth or the business part of the destination. It encourages local people to create handicraft items and prepares local food items, souvenirs, dresses, etc., for sale.
- Tourism is one such thing that constantly boosts the country economically.
Niche Tourism
This tourism focuses on a specific aspect of traveling. It also focuses on the consumer market segment’s interest. It makes the destination more exciting and marketable. Niche Tourism is one of the fastest-growing sectors. Niche tourism indicates a specific feature of travel.
For example, some tourists want a museum, some wish to visit old architectural monuments, buildings, palaces, etc., and some want to eat in a famous restaurant. Thus, niche Tourism shows a particular activity that is not the only focus of travel.

Types of Niche Tourism
- Macro-Niche
- Micro-Niche
What is Macro-Niche?
Macro-niche tourism can be explained as a niche with broad customer interest categories such as rural tourism, Business tourism, sports tourism, medical tourism, environmental travel, etc.
What is Micro-Niche?
It is a small group trip, such as gastronomy tourism, cycling tourism, and geo-tourism.
Niche tourism in South Africa
South Africa is an attractive destination because of the wide diversity of animal and bird species. As a result, tourism professionals found this country has considerable potential.
Advantages of Niche Tourism
- Even if niche tourism is smaller than mainstream markets, it spreads more.
- It has more potential to grow.
- It creates quality jobs that require specialized skills.
What are the different types of tourists?
When we visit a place, we find different kinds of travelers. The aim of each traveler is different. Let us discuss the types of visitors. Five types of tourists are found mostly :-
- Incentive tourists – These tourists did not plan for the tour earlier. Suppose you have been rewarded with two tickets from the office because of your performance. You and your colleagues came for the trip.
- Business tourist – This type of tourist travels for business. They will always prefer a hotel with a conference room. They don’t come to enjoy luxury, but they want the hotel to serve everything on time.
- Leisure tourist – This type of tourist comes to enjoy the vacation. They love those hotels that serve them something extra, like drinks. They choose hotels that give them comfort and luxury at their best.
- Special interest tourists – They often plan their tours very well. This tourist doesn’t need comfort but loves to do adventure.
- The Foodie tourist – This type is quite common. They wish to taste various foods in various places. The signature dishes of those areas and various kinds of foods.
Types of a Tourist Attraction
We have to keep in mind that attraction varies from person to person. For example, suppose Rahul and Sheela are traveling to Kashmir. Rahul is interested in climbing the mountains to see snowfall, whereas Sheela is excited to visit the temples in Kashmir.
Tourist attractions could be classified into the following two categories:-
- Natural attraction – If you are a nature lover, don’t miss The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand, Coorg, known as the ‘Scotland of India.’
- Events and heritage attractions – Goa is a place for heritage lovers. So pack your bag, take the camera, and start your journey towards Goa. I am sure you will have an unforgettable lesson in Goa’s history. Fort Aguada, Chandor, and some famous museums are places to visit.
What is Tourism Planning?
Perfect planning is always a matter of the success of any activity. Whenever we plan something and implement it, we get a better result. It’s the same with tourism. But it is neither guaranteed nor forever. It’s a process where the people’s needs are determined using the best resources, programs, and activities.
How do these tourism plans help us?
A tourism plan makes guidelines for the areas. Then, it helps the government and private sectors to develop those areas. Most importantly, we must remember a few steps involved in tourism planning.
Main types of tourism planning
- Financial planning
- To establish the objective
- Human resource planning
- Monitoring progress
- Human resource planning.
Types of Tourism Activities
There are various kinds of tourism activities. Like-
- Heritage trails
- Swimming with dolphins

Name of some international tourist organization-
- American Society of Travel Agents : Founded 1931, Headquarter- New York
- International Academy of Tourism : Founded-1951, Headquarter- Monge Carlo
- International Bureau of Social Tourism : Founded 1963, Headquarters- Brussels
- International Touring Alliance: Founded-1919, Headquarters- Europe
- World Tourism Organization : Founded 1975, Headquarter- Madrid.
Types of Tourism packages
For different categories of tourists, everybody needs a separate package. Let’s discuss the various types of Packages that are available.
1. Adventure Tourism Package
This tourism encourages people to come out of their comfort zone to feel the thrill of nature closely in life. It is found that people are taking adventure more often. It shows potential growth in recent years.
The most exotic and adventurous destinations are Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Jammu, and Kashmir.
2. Wildlife Tourism Package
In every country, wildlife tourism is famous. But, if you love wildlife, you must choose the right package. This package is exclusively for wildlife lovers who love taking their snaps.
3. Medical tourism package
It has been observed that medical tourism has grown rapidly in Asia-specific countries.
4. Pilgrimage tourism package
Many foreigners visit various temples in India, Sri Lanka, and Singapur. However, the major attraction is the traditional architecture, art forms, and rituals performed.
Famous pilgrimage areas are the Meenakshi Temple, Golden Temple, Jagannath Temple, Santa Cruz Cathedral Basilica, Atala Mosque, etc. Therefore, this type of package is chosen based on your religious beliefs.

5. Eco-tourism Package
This type of tourism has become one of the fascinating travel forms. Although eco-tourism is more of a travel philosophy, it attracts many tourists. Some eco-tourism destination areas are Kerala, Galgibaga Beach, Goa, and Coorg.
6. Cultural Tourism Package
The social richness of any country draws visitors from every corner of the world to witness sheer celebrations. The cultural tour package offers you a comprehensive exploration of the different shades. Moreover, this package will bring a tourist a closer view of traditions and architecture.
Along with these, we found tourism packages like-
7. Family Tourism Package
A family tour package is designed keeping in mind the family’s needs. It gives assurance of total relaxation and fun pastimes.
The package includes adults, kids, and the elderly. This package includes sightseeing trips, tours of historical places, and adventure trips.
8. Honeymoon Tourism Package
Couples, after their marriages, take a honeymoon tour package, and it provides newlyweds with all the perquisites to make their trip memorable.
The honeymoon tourism package includes lodgings, dining, food & drinks, etc. Famous destinations for a honeymoon tour package are Maldives, Bali, Mauritius, etc.
9. Wellness Tourism Package
Traveling to other places for health and well-being takes a wellness tourism package. Tourists take this package to visit sites that provide recuperation facilities. Wellness tourism has seen a significant boost in the modern years.
Popular destinations for a wellness tourism package are Ayurveda centers, Iceland (for its spas), Bali (for yoga), etc.
10. Cruise Tourism Package
A cruise tourism package provides tourists with a journey filled with fun and recreational activities onboard and excursions onshore.
Tourists get an all-planned ship or boat trip for a specific date to a particular location at a specific price. These packages are curated as per the needs of the tourists.
What are Tourism Products?
According to the market’s needs, the customer supplies anything in the market for use/consumption, called a product.
A product can be offered in the market observation, purchase, use, or any need or demand.
A tourism product is provided to the tourist during their traveling. It mainly focuses on facilities and services designed to meet the needs.
It includes physical objects, services, personalities, places, and ideas. The above components are provided by one company or any group of companies. Tourism products can be given to tourists in a tourist destination.
Products are needed for leisure, pleasure, religious, or business purposes. These products are provided in the market at a cost.
The main reason for choosing a tourist destination is a tourism product. It gives an economic boost to the destination. So it needs to be marketed and stored in a hassle manner.
Services are designed for the visitor to fulfill their needs. Therefore, it is a combination of products. Thus, the country’s total tourism and tourist satisfaction depend on the sum of its attractions, transportation, accommodation, entertainment, etc.
Individual service providers, such as hotels, airlines, travel agencies, etc, provide every element of a tourism product. Therefore, you can analyze these products’ attractiveness, accommodation, and accessibility.
Types of Tourism Products
Attractions: It is one of the main elements. Tourists will not be encouraged to visit certain places without attractions. Attractions are the ingredients. The product determines the choice of a particular tourist to visit a specific destination.
Attractions include archaeological, cultural, and historical buildings, monuments, beach resorts, mountains, flora and fauna, national parks, trade fairs, arts and music festivals, exhibitions, games, etc. Nowadays, tourists are susceptible to changes in fashion.
Accessibility: That means by which a visitor can reach the attraction place. Tourists visit the attraction destination by different transport modes. Visitors visit his predetermined location by car, motorcycle, train , ship or boat, airplane, or cycle.
The place becomes very cheap if any destinations do not have good transport systems. Tourist centers should be located near tourist-producing markets. It is connected to a network of efficient transportation to receive the largest number of tourists.
Accommodation: Another tourism product is accommodation. It is an essential part of tourism—the tourist destination location must-have hotels, guest houses, camping, and homestay. An alternate arrangement should exist if accommodation is not possible at the central location. At least some distance away.
Hospitality: It is a major factor for a tourist destination that will develop in the future. The location’s restaurants, pubs, cafes, foods, and beverage serving style increase location attractiveness.
Natural tourism products: Our nature is beautiful and precious to us. Nature has arranged amazing things in different parts of the world, such as – hills, mountains, caves, glaciers, sea, islands, beaches, waterfalls, rivers, lakes, wildlife, deserts, etc.
The tourism product utilizes those natural gifts as a Natural tourism product, such as snow-capped mountains in Kashmir, Dudhsagar Falls in Goa, palm-fringed beaches of Goa, the wildlife of Kaziranga National Park in Assam, the Thar Desert in Jaisalmer, etc.
Read Things to do in Bainbridge Island, Seattle Washington
Human-created tourism products
Artificial tourism products are those that humans create. Human-made tourism products’ primary purpose is to attract tourists, such as Temples, Forts, palaces, museums, theme parks, etc.
The destination’s tradition and culture play a vital role in tourism. Humans maintain it to attract tourists through- classical dance – music, folk dance, paintings, handicrafts, festivals, fairs, etc.

Examples: Machu Picchu World Heritage Site, Egyptian pyramids , Taj Mahal, Red Fort in Agra, Lothal in Gujarat, Mexican pyramids, or Mesoamerican pyramids are important archaeological sites.
The Bhangra dance form of Punjab, the Kolkata Book Fair, the Durga puja in Kolkata, the Brass work of Muradabad, etc., are also included in human-made tourism products.
Tour guides are another main aspect of traveling. It is also a parameter for tourism. National and international travelers need a travel guide to discover a new place. Sometimes, national travelers may visit any tourist destination on their own.
But an international traveler always wants a good tourist guide. How do you present the location, and how much information do you provide to understand the place? It depends on a guided tour and a travel guide. This parameter upgrades the tourist destination’s level.
What are the different types of tourist destinations?
Types of tourism and types of tourist destinations may sound synonymous. However, the two have slight conceptual differences. Tourism is a broader concept, including the aspects of tourism and hospitality.
At the same time, a tourist destination is a narrower concept applying to places of tourist attraction. Based on the type of place and the causes of interest, the tourist’s destinations are:
- Coastal Destinations – Preferred mostly for the ample sunshine and salty waters lining lands adjoining the sea. Be it domestic or international coastal locations, they are great for fun and relaxation. They are favored mostly by people living in inland areas away from the sea.
- Beaches – The meeting point of land with the ocean offers a great tourist attraction. Waves hitting the shores of sandy beaches are great for tourists. In addition, new beach activities like parasailing, beach biking, etc., also attract tourists immensely.
- Island – A land in the middle of the sea or ocean on all sides is an island. Tourists are taken mainly by boat from the mainland to explore these islands. Islands standing in between a river are called riverine islands.
- Mangroves – It offers a panoramic view amidst the confluence of a river with the sea/ocean. Example: Sundarbans of India.
- Inland Destinations – Travel away from the coast is an inland destination. A variety of sub-classifications can come in under like:
Based on the type of region:
- Hill stations – Offering a surreal view from an altitude, all mountains and hills are great tourist destinations.
- Jungles – Trekking/hiking/driving through the wild greenery are great tourist attractions. Protected areas like Reserve Forests and National Park serve the twin purpose of tourism and conservation.
Based on the population structure
- Rural – For a change, get away from the fast-paced urban life to taste village life. Touring rural locations is gaining popularity because of lower population density, greener areas, and a serene environment.
- Urban – Posh urban destinations offer a pull factor for tourists to experience ultra-modern and urban life. Examples: New York, Shanghai, etc.
- Offbeat – Previously undiscovered newer locations around famous tourist spots are offbeat destinations. With lower tourist popularity, the exclusiveness of these places is retained.
Based on the type of activity
- Hiking and Camping – Places, where tourists come mostly for hiking or camping (day/night), are fast gaining popularity. These places are primarily amidst nature and come under adventure tourism.
- Preserved sites – Sites like UNESCO World Heritage sites have become popular tourist destinations. The rich natural/cultural value owes them their status.
Based on historical/religious importance
- Historical Places & Monuments – Tourists flock to places holding remnants of the past. Areas having historic architecture and events give an insight into the past culture. Examples: Taj Mahal and Jalianwallah Bagh, etc.
- Pilgrimages & Holy Shrines: Religious tourism has flourished here, making it a spiritual destination. Example: Hajj of Mecca, Bethlehem for Christians.
- Museums and buildings: Places where artifacts and remnants of historical culture are well preserved. Famous among tourists of all ages.
Based on entertainment
- Luxury destinations: Locations that only promote high-end tourism are luxury destinations. Example: Bali.
- Carnival: Annually, countries host cultural events to celebrate any occasion for a short period. When tourists travel here to enjoy themselves, it becomes a popular destination. Example: Christmas Carnival in Toronto.
- Amusement Park and Zoo: Famous for the lot is Disney Land, a great tourist destination for children. Singapore Zoo, which ushers in global tourists.

Tourism Destinations
According to UNWTO in the “World’s Top Tourism Destination,” the first four places for International tourism are France, Spain, the USA, and China.
A tourism destination is the endpoint of the journey. But, of course, we all have some goals in every field, so it’s the same with tourism.
There are various types of tourist destinations. They are as follows:-
- Centered Destination
- Based Destination
- Multi-centre Destination
- Touring Destination
- Transit Destination
Types of Tourist Attractions
- Historial attractions
- Cultural attractions
- Political significance
- The natural or scenic beauty
- Leisure travel
- Fun and Amusement
How many Types of Tourism are there in India?
There are 16 Different kinds of tourism in India , but the list may increase.
Is there anything about tourism that I’ve missed?
Over the past 75 years, the travel industry has made great strides in harmoniously uniting strangers, travelers, and locals. As a result, visits and travel are more than adventure, learning new skills, rejuvenating, and achieving perfection.
Tourism has changed from providing services like rooms, flights, and meals that people were satisfied with ten years ago. Now, people want to experience whale watching or mountain biking.
In the luxury sector, wealthy people spend more money on an experience than objects. It is called experience economics, and there is an idea that the memories of tourist values are compared to some physical resources. The rate of global tourists is increasing daily, and every country is trying to make its tourism more developed and successful.
As you can see, the tourism industry is vast and diverse. There are different kinds of tourism here; some have been around for decades, and others are just emerging.
A tour to the Grand Canyon would fall under which type of tourism?
Grand Canyon tour would fall into natural adventure tourism. Here, you can enjoy – The floor Landing Helicopter Tour, ATV, Gold Mine Tour, White Water Adventure Tour, and Rim Airplane Tour.
Kindly Stay 5 Seconds More and Share this Article.
HI TRAVELLER …Myself Ruma Dey Baidya. I’ve been backpacking for the last 20+ years. Photography and travelling have been my passion since my childhood. Whenever I got an opportunity, I never missed it. I am not a solo backpacker, so I always try group travel. I prefer budget travel, and it also helps me to save expenses. We know that memories are not constant, so I decided to document them and created this travel diary. This website [ TheHolidayStory ] is dedicated to those who passionate about travel like me. Please feel free for any information related to my blog. I am always happy to reply. Mail id – ruma[@]theholidaystory.com

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Tourism Planning. Before creating a comprehensive plan to market the destination, the following types of tourism planning are taken into account: Spatial Tourism Planning: Spatial tourism planning attempts to thoroughly process social, environmental, and economic change to bring about certain ends. Drawing plans, maps or diagrams are ...
4 Types of Tourism Planning. 5 Levels of Tourism Planning. Planning in tourism is setting and achieving the goals, keeping constraints in mind such as time, money etc. there are many approaches involved in tourism planning such as bottom-up approach, collaborative, boosterism, interactive, integrated etc.
1- Wellness Tourism: With physical and psychological activities, this tourism planning type provides visitors with a critical step to support their health and well-being. Due to the modern ...
The national level of tourism planning is concerned with: tourism policy; infrastructure facilities and a physical structure plan which includes important tourist attractions, selected tourism development regions, international entry points, facilities, and services. It is also concerned with: the amount, kinds, and quality of accommodation and ...
Positive guidelines for better planning are in demand by developers and designers who need new understandings of the breadth of tourism's complexity for their own success. Long considered the seminal work on tourism development, Tourism Planning provides a comprehensive, integrated overview of all aspects of tourism and the planning functions ...
This publication lays the foundation for tourism development of a country and its regions. It establishes the principal guidelines for preparing tourism development plans at the national and regional levels with emphasis on the integrated approach, balancing economic, environmental, and socio-cultural factors achieving sustainable tourism.
Tourism Planning and Development (TPD) aims to explore and advance our theoretical and practical understandings of the intersections between tourism, planning and development studies. Each of these fields of study is characterised by rich scholarly and interdisciplinary traditions. ... Types of papers include: Theory, Methodology and ...
Why tourism planning is important. Tourism planning really can make or break a destination. If done well, it can ensure the longevity of the tourism industry in the area, take good care of the environment, have positive economic outcomes and a positive benefit to the community. If done badly, tourism development can destroy the very environment ...
Tourism planning has existed as a professional field for approximately 50 years. It started in countries such as Ireland and France where there was a strong belief in community long-term planning and especially in a regional context and rural areas. These earliest plans were done by government agencies and prepared by professionals with a background in regional and urban planning rather than ...
Types of tourism planning are very complex and can be divided from various perspectives. Generally speaking, by the planning content and nature, it can be divided into: tourism industry planning, planning of development and utilization of tourism resources, tourism city planning, scenic resort planning, tour route planning, tourist source ...
Tourism planning is based on the principles of sustainability and is defined by three dimensions: environmental, economic and cultural tourism development. Findings The goal of comprehensive tourism planning is to achieve economic growth and efficiency, ensuring efficiency and social equity by solving the basic needs of the population and on ...
Abstract. Tourism has become a major global activity, and the planning of tourism is emerging as a specialized type of development planning. Planners have accumulated considerable experience on methodological approaches to tourism planning and a number of techniques, principles, and models have evolved.
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
Tourism Planning. Prior to tourism planning it is important to consider other types of planning for a community or geographic area. Planning is not new. Gunn and Var (2002) indicate physical planning goes back to early Greek and Roman times. Planning is done to manage visual appearance and land use.
theory built on basic principles, models, and planning techniques was. weak up to the 1990's. At the turn of the century, Costa (2001) sug-. gested that that the growth of tourism planning had not ...
1. Introduction. Planning can be conceived as a set of ideas and principles that seek to control the spatial distribution of human activities over time (Gunn & Var, 2002; Hall, 2008; Inskeep, 1991).In the present work, attention is directed to the origin and ongoing development of tourism planning in relation to the broader field of planning theory.
Tourism Planning and Development (TPD) aims to explore and advance our theoretical and practical understandings of the intersections between tourism, planning and development studies. Each of these fields of study is characterised by rich scholarly and interdisciplinary traditions. ... Types of papers include: Theory, Methodology and ...
Learn what tourism planning is, why it is important, and how it is done. Explore the different techniques of plan formulation, such as collection of data, setting objectives, and determining growth rate, for tourism planning.
Beyond the ones we listed, there are plenty of other types of tourism, such as medical tourism, religious tourism, wellness tourism, dark tourism, and more. Broadly speaking, however, we could consider leisure and business tourism to be among the two main categories based on travelers' motivation. Categories.
6.2 LEVELS AND TYPES OF TOURISM PLANNING. Ideally, tourism should be planned as one element in a comprehensive manner. More commonly, however, tourism planning is done independently without recognising it as an integrated sector. Tourism plans are, thus, prepared at various levels. Each of these levels focusses on a different degree of specificity.
Tourism Planning University of Oregon School of Planning, Public Policy and Management
Famous cultural tourism places are:-. India - Durga puja in Kolkata, Temples at Banaras, Jaipur, known as the pink city Palace in Rajasthan. Forts and monuments in Delhi, Agra, UP. UK - Tower of London, The British Museum, Big Ben, London Durga puja, etc. Kenya - The main attraction is the dance of the Maasai tribe.