We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

Travel Vaccinations for Vietnam
Are you planning to travel to Vietnam soon? It’s a beautiful destination in Southeast Asia full of vibrant and welcoming people, scenic beaches and historic sites, and enticing cuisine with French, Chinese and Cambodian influences.. There are a range of vaccinations for Vietnam that should be considered before your next adventure. It’s crucial to get in contact with a medical provider specialising in vaccinations for Vietnam so that you have plenty of time to get the ones you need.
Remember that many vaccines do not provide lifetime immunity. Even if you have been vaccinated in the past, booster vaccinations which boost your immunity are often required for a range of serious illnesses that are prevalent in Vietnam.
If you plan to travel to Vietnam or also nearby Southeast Asian countries like Cambodia and Thailand, this brief guide will help you learn about the vaccinations for Vietnam and Cambodia and how to reduce other potential health risks during your journey.
Pre-travel Preparation Will Help Protect Your Health While You Are Away
The life and lights of Vietnam can place well-meaning travellers at risk of exposure to diseases and illness. Consult a travel doctor prior to departure to assess your risks in relation to your medical history and travel plans as diseases like Japanese encephalitis may be of risk depending on the time of year and places you visit in your Vietnam travel.
Safe Eating and Drinking Practices
One of the great pleasures of Vietnam travel is sampling the local cuisine. However, contaminated food and beverages are a common cause of traveller’s diarrhoea and other gastrointestinal illnesses. Safe eating and drinking practices are essential in minimising your risk of contracting traveller’s diarrhoea.
Insect Avoidance
There are a number of viruses and illnesses that are contracted through insects such as fleas, ticks and flies. Mosquitoes however are the biggest culprit of spreading insect borne diseases such as Zika Virus and Malaria which are a risk when you travel Vietnam. Ensure you a prepared and read up on our insect avoidance tips.
What vaccinations do I need for Vietnam?
These routine vaccinations for Vietnam should be up to date prior to your departure date. You will need to be vaccinated if you did not receive these in childhood or if they are past the date in which a booster vaccine should have been received.
- Tetanus-Diphtheria-Pertussis Your medical provider will ensure that you are up to date on your routine vaccines including your tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (whooping cough vaccinations). You may need a tetanus-diphtheria-pertussis (Tdap) vaccination booster if it has been 10 years since your last vaccination.
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR) These are easily spread viral illnesses that are found in Vietnam and many other countries. Outbreaks have occurred recently in Vietnam. They are easily preventable through vaccinations. If you do not have evidence of immunity, or if you have not received two previous vaccines in your lifetime, a booster dose will be recommended. In some states this is provides as part of a free program.
Additional potential vaccinations for Vietnam
These additional vaccinations for Vietnam may be recommended by your medical provider depending on where you will travel, your prior vaccinations and other factors:
- Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is a viral disease that affects the liver and can be spread through contaminated food and water no matter where you end up visiting. This vaccination is recommended for most travellers to Vietnam. Once you complete the vaccine course it is lifelong.
- Hepatitis B This viral illness also affects the liver and other organs and is spread through sexual contact, blood products or contaminated needles. This vaccine has been part of the standard vaccine schedule for over 20 years now so many will already be vaccinated. This vaccine is often recommended for those who may be travelling in more remote areas or who are frequent travellers to at risk countries. It would also be recommended in those who may have sexual contact with a new partner, who may have medical procedures or receive a tattoo or piercing. These activities would cautioned against in a country such as Vietnam due to this risk. Once the course is completed vaccination is lifelong.
- Typhoid Fever Typhoid can be transmitted through contaminated food or water and it is common in developing countries like Vietnam, therefore this vaccine is often recommended, particularly for travel to smaller cities or for those who plan to be more adventurous with eating and drinking.
- Yellow Fever There is no of yellow fever in Vietnam, however if you have visited a country with a yellow fever risk, the government may require proof of vaccination prior to your travel to Vietnam.
- Japanese Encephalitis This is a serious viral illness transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. Because this illness is endemic throughout the country, this vaccine may be recommended, especially for those visiting rural areas, rice farms or irrigation areas.
- Rabies Rabies is a deadly viral illness transmitted through the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Depending on where you travel and the nature of your activities, you may be recommended to receive a course of rabies vaccination. Once vaccinated it is gives lifelong cover and reduces necessary treatment if bitten significantly.
Other potential health risks for Vietnam travel
There are a range of other health risks to take into account before you travel to Vietnam. Most of these risks can be reduced by ensuring you receive vaccinations for Vietnam before you travel and by following simple precautionary hygiene habits like frequent hand washing, practicing social distancing, and taking caution with food and drink consumption.
- Cholera Cholera risk is minimal in Vietnam. Following basic sanitary practices like hand washing and only drinking treated water will significantly reduce your cholera risk.
- Insect Borne Diseases Japanese encephalitis, malaria, zika virus, dengue fever, chikungunya, and other insect borne diseases can be prevented by taking steps to avoid mosquito bites. Malaria risk in Vietnam is present in parts of the country, including rural areas, and as a result anti-malarial tablets may be prescribed depending on where you travel. A vaccine is available for Japanese Encephalitis as above.
- Traveller’s Diarrhoea This can affect anywhere from 20%-50% of travellers to Vietnam and can vary from mild to very severe dysentery It can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and other symptoms. Prevention involves frequent hand washing, only drinking treated water, botted or boiled water, and taking precautions with food and beverage choices. Medications can be provided in a kit to take with you for your trip to self-treat yourself for travellers’ diarrhoea if required.
- Other health risks This is not an exhaustive list of illnesses that you may encounter in Vietnam, you may also need to receive vaccinations for diseases such as chickenpox, pneumonia, influenza, shingles, and meningitis. Your medical provider will inform you about additional these and other potential vaccinations that you may need to receive.
Do you need vaccinations for Vietnam?
Although there are no specific vaccinations required for Vietnam travel by Vietnamese law other than potentially yellow fever in some instances, you are strongly recommended to meet with a medical provider to determine the vaccinations needed for Vietnam.
Even if you have received many of these vaccinations in the past, you will very likely need some of the above-mentioned vaccinations for Vietnam or boosters before you travel.
Your medical provider will give you specifics on which vaccinations for Vietnam that you are recommended to have based on where you plan on travelling, your prior vaccinations and other health factors.
Travel to Vietnam from Australia can be an exciting and rewarding experience, but it is important to contact a medical provider specializing in vaccinations for Vietnam as soon as you know you will be travelling to the country.
Speak to a medical provider no later than 6-8 weeks before you travel to Vietnam. This is because it takes time for your immunity to build after receiving a vaccine and you may need to space your vaccinations required for Vietnam apart.
Even if your trip to Vietnam is occurring sooner than this, you should still schedule a consultation because you can receive your required vaccinations on a more urgent schedule.
Health Risks
How can we help.
Travel Doctor-TMVC provides specific health recommendations tailored to your individual holiday plans. Our medical and nursing staff at Travel Doctor-TMVC have extensive knowledge of international health issues, immunisation and preventative medicine. Travellers should have individual risk assessments by one of our doctors whether they are holiday makers, businesspeople, or long-term expatriates.
Travel Doctor-TMVC has clinics throughout Australia. We are always available to assist you before you travel, on your holiday, or when you return. You can book an appointment online at any time of the day or night by visiting our locations pages, or you can talk to one of our friendly team members during business hours on 1300 658 844.
Health Alerts
South asian cities worst for air pollution, china reports three more h9n2 avian flu infections, polio reported in pakistan.
- Search Our Website
To get started select your state or territory.
Now select one of the available clinics listed below.
- South Australia
Suite 1, Ground Floor 55-67 Hindmarsh Square Adelaide SA 5000
Level 5, West Tower 410 Ann Street Brisbane QLD 4000
Coolangatta Medical Centre 4/91 Griffith Street Coolangatta QLD 4225
- Australian Capital Territory
Suite 14, Lena Karmel Lodge 1 Childers Lane Canberra ACT 2601
Northern Territory
22 Smith Street Darwin NT 800
215 Spring Street Melbourne VIC 3000
Albury Wodonga
Wodonga West Medical Clinic 60-62 Waratah Way Wodonga VIC 3690
Mornington Peninsula
28 Cranbourne Road (PO Box 889) Frankston VIC 3199
M15 Southgate Arts and Leisure Precinct 3 Southgate Avenue Southbank VIC 3006
- Western Australia
Level 1 847 Hay Street Perth WA 6000
- New South Wales
Level 16, 60 Margaret St, Sydney NSW 2000
Campbelltown
241 Queen St Campbelltown NSW 2560
Artarmon Medical Centre 134-136 Hampden Road Artarmon NSW 2064
Enter your search in the box below and click enter.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Dial 115 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance company quickly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccine recommendations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
- the latest vaccine recommendations for Vietnam in TravelHealthPro’s Vietnam guide
- where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
See what health risks you’ll face in Vietnam , including:
- mosquito-borne diseases like Zika virus, dengue, malaria and Japanese encephalitis
- air pollution – see information on air quality on TravelHealthPro
Altitude sickness is a risk in parts of Vietnam. Read more about altitude sickness on TravelHealthPro .
Some medicines can be hard to find in Vietnam and many are fake.
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro .
Vietnam has restrictions on medicines it classifies as ‘addictive’ or ‘psychotropic’. These include medicine used to treat of addiction, anxiety, depression, insomnia and other conditions.
It is illegal to have more than the amount prescribed by a doctor for 7 days (addictive medicine) or 10 days (psychotropic medicine). You should carry the prescription with your medication and a letter from your doctor stating how much of the medication you need during your trip.
The letter can be in English and should:
- include your name and age
- list the medicine name, volume and dosage
- include the doctor’s signature and address
If you’re unsure if your medication falls within these categories or you need to bring more medication than is usually allowed, contact the Vietnamese Embassy in the UK before travelling.
Healthcare in Vietnam
FCDO has a list of medical facilities in Vietnam where some staff will speak English.
There is also guidance on healthcare if you’re living in Vietnam .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 24, 2023
Vietnam - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed. Exercise normal precautions in Vietnam.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Vietnam.
If you decide to travel to Vietnam:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Vietnam.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
Must have six months’ validity remaining.
One visa page required for entry stamp.
Not required.
None. However, Vietnamese Dong in excess of VND 15,000,000 or foreign currency in excess of 5,000 U.S. dollars or equivalent must be declared.
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Hanoi - Consular Annex 170 Ngoc Khanh Ba Dinh District Hanoi, Vietnam Telephone: From outside Vietnam: +84-24-3850-5000 From the U.S.: 011-84-24-3850-5000 From landline within Hanoi: 3850-5000 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 024-3850-5000
Emergency: From outside Vietnam: +84-24-3850-5000 or +84-24-3850-5105 From the U.S.: 011-84-24-3850-5000 From landline within Hanoi: 3850-5000 or 3850-5105 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 024-3850-5000 or 024-3850-5105 Fax: (+84-24) 3850-5010 Email: [email protected] Facebook
U.S. Consulate General Ho Chi Minh City 4 Le Duan, District 1 Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Telephone: From outside Vietnam: +84-28-3520-4200 From the U.S.: 011-84-28-3520-4200 From landline within Ho Chi Minh City: 3520-4200 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 028-3520-4200
Emergency: From outside Vietnam: +84-28-3520-4200 From the U.S.: 011-84-28-3520-4200 From landline within Ho Chi Minh City: 3520-4200 From mobile or landline within Vietnam: 028-3520-4200 Fax: (+84-8) 3520-4244 Email: Contact Us Here
EMERGENCY TELEPHONE NUMBERS WITHIN VIETNAM
Police: 113 Fire brigade: 114 Ambulance: 115
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Entry Requirements: You must have a valid passport and a visa (or pre-approval for a visa on arrival) to enter Vietnam. Your passport must be valid for six months beyond your planned stay, and you must have at least one blank visa page (not including the endorsement page). Visit Mission Vietnam’s website for the most current information. If you arrive in Vietnam without an appropriate visa (which could be an e-visa) or pre-approval for a visa on arrival, you will be denied entry . The U.S. Mission to Vietnam cannot assist U.S. citizens who arrive in Vietnam without required visas. U.S.-Vietnam dual nationals should consult the Department of State’s information page for Travelers with Dual Nationality and the Embassy of Vietnam for travel requirements. You must enter and exit Vietnam on the same passport. If using a Vietnamese passport to enter and exit the country, your passport must have at least six months’ validity from your return date to the United States.
Visas: The Government of Vietnam requires a “visa sponsor” for all visa categories, except for E-visa. A visa sponsor is a local business or travel agent to apply for a pre-approval letter with a Vietnamese Immigration Office in Vietnam on behalf of the traveler. Only on receipt of the pre-approval letter can a foreigner apply for an appropriate visa at a Vietnamese Embassy or Consulate abroad, or for a visa on arrival. For more information about this process, please visit the website of the Vietnamese Embassy here . When you apply for a visa to enter Vietnam, be sure to request the visa category that corresponds to your purpose of travel. Please refer to Vietnam’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs website for information detailing visa categories. If you plan to work in Vietnam, you must obtain a work permit before applying for your visa. If you change the purpose of your visit after you have received your visa, you must obtain a new visa outside of Vietnam appropriate for your new activities before beginning those activities. Under local immigration law, employment-based visas are based on a petition from a specific employer, and workers may be unable to switch jobs without securing a new visa. In addition, employers may prevent the departure of contracted employees from Vietnam if they violate contract terms. Before accepting employment in Vietnam, make sure you understand the conditions of contracts and employment-based visas.
Note that travelers with a U.S. APEC Business Travel Card will still need a valid visa to enter Vietnam. The United States is a transitional member of APEC and does not reciprocate with other economies regarding full pre-clearance benefits to applicants. As such, no countries are listed on the back of U.S. APEC Business Travel Cards and card holders are required to present any travel or identity documentation, such as a passport and visa (where applicable), required by Vietnam. If a U.S. APEC Business Travel Card holder does not conform to Vietnam’s entry requirements, the card holder may be refused entry.
Please consult Mission Vietnam’s website for more information.
Please note that Vietnam requires a valid visa, residence card, or approval from the Immigration Department to leave the country. Immigration officials will apply a fee to replace lost/stolen visas or will assess a fine for any visa overstays. The Government of Vietnam has recently increased the penalties for visa overstays, and fines can be substantial. In addition, the processing of exit visas for cases involving visa overstays can take one to two weeks, and longer for more complex cases.
If your U.S. passport is lost or stolen in Vietnam, you will need both a replacement passport and a replacement Vietnamese visa to legally remain in or depart Vietnam. The U.S. Embassy in Hanoi and the Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City can usually issue you a limited validity replacement passport in as little as one business day for emergency purposes; however, the Vietnamese government requires three to five working days to issue a replacement visa. For lost and stolen passports, immigration officials will also request a police report. You must file a report of a lost or stolen passport with the police in the location where the loss or theft of your passport occurred, or authorities may refuse to accept the report. The U.S. Embassy and the Consulate General cannot expedite the replacement of your Vietnamese visa.
If you plan to travel from Vietnam to Laos by land, you should request that an adhesive visa be affixed to your passport instead of a detachable one. Lao immigration officials require proof that travelers have departed Vietnam, something that can only be shown with an adhesive visa. Vietnamese officials remove detachable visas from passports when travelers depart Vietnam, leaving travelers with no proof of their Vietnam departure. This situation can result in Lao officials requiring travelers to return to Vietnam.
Pre-approval for Visa on Arrival: The Government of Vietnam has authorized some businesses and travel agencies to arrange for pre-approval for a “visa on arrival” at the airport. On a receipt of a pre-approval letter, travelers may then travel to Vietnam and apply for a visa upon landing to Vietnam. Please be advised that you should not travel to Vietnam without having been issued a pre-approval letter as it may result in a denial of entry by immigration authorities. To avoid having to rearrange your travel date, please do not make travel arrangement before you receive your pre-approval letter.
E-visa: U.S. citizens can apply online for an E-visa on the Vietnam Immigration website . The E-visa is valid for a maximum of 90 days, single or multiple entry, and does not allow for renewal or extension from within the country. The E-visa is valid for a maximum of 90 days, single or multiple entry, and does not allow for renewal or extension from within the country. An E-visa is usually processed within three to five working days after the Vietnam Immigration Department receives the completed application and E-visa fee. E-visa holders must present the printed E-visa and valid passport at the port of entry. Prior to your travel with an E-visa to Vietnam, we recommend travelers to carefully check their E-visa to make sure all information is correct, and that you will enter/exit Vietnam through a port of entry that you had selected at the time of application. An error on E-visa, including minor differences between the information on the application and the biographical information on the passport, may result in a denial of entry by immigration authorities. The U.S. Embassy and Consulate General are unable to change the information on your E-visa or help expedite the process as Vietnamese E-visa is under the sole jurisdiction of the Vietnamese government.
Certificate of Visa Exemption: Vietnamese nationals residing abroad indefinitely, their spouses, and their children may apply for a Certificate of Visa Exemption. The certificate has a maximum validity of five years, during which time the holder can enter Vietnam and stay for up to six months without applying for a visa. More information can be found on the Vietnam Embassy website .
The U.S. Department of State is unaware of any HIV/AIDS entry restrictions for visitors to or foreign residents of Vietnam.
Immunization information for travelers can be found on the Centers for Disease and Control’s website .
Information about dual nationality or the prevention of international child abduction can be found on our website. For further information about customs regulations, please read our Customs Information page .
Safety and Security
The Department of State recommends that U.S. citizens overseas always maintain a high level of vigilance and take appropriate steps to increase their security awareness while traveling internationally. Please visit www.travel.state.gov for up-to-date information.
Messages regarding weather-related events are posted here and on the Embassy/Consulate General website .
While in Vietnam you are subject to Vietnamese laws. U.S. citizenship will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be arrested, expelled, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Vietnamese authorities routinely do not provide timely notification of the arrest of a U.S. citizen to the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General or approval for consular officials to visit U.S. citizens. The delays for both – particularly for access – can take several weeks. Note that if you enter Vietnam with a non-U.S. passport, the Government of Vietnam has different notification and access responsibilities for the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General. See our webpage for further information.
Small-scale, peaceful protests occasionally occur in Vietnam’s major cities, but large-scale demonstrations are rare. As in any country, you should avoid large protests, as they can become violent with little or no warning.
The Government of Vietnam may not allow or authorize travel to certain areas of the country that are deemed sensitive. Check with local authorities before visiting border areas to see if you need to obtain a travel permit issued by local authorities. U.S. citizens have been detained after traveling in areas close to the Vietnamese borders with the People’s Republic of China, Cambodia, and Laos. These areas are not always marked, and there are no warnings about prohibited travel.
Safety standards in Vietnam are not at the same level as those in the United States and vary greatly from company to company and province to province. This is especially true for fire safety codes. Travelers should be aware that many buildings, including hotels, shops, and restaurants, have limited or no fire safety equipment or emergency exits. Ground and water transportation also lack safety regulations.
Travelers to Vietnam should have no expectation of privacy and should safeguard all personal documents and electronic devices. Exercise caution when discussing sensitive or proprietary information.
Crime: Crime in Vietnam is rated high. Exercise vigilance and the same commonsense security precautions you would in any major metropolitan city in the United States.
Violent crime against foreigners is rare; however, petty crimes, such as theft, bag grabs, and pickpocketing occur regularly, especially in crowded areas and tourist locations. Typically, there is a rise in petty crime during the Christmas and Tet (Lunar New Year) holiday seasons, including during the day and in well-lit areas. Motorcyclists are known to snatch bags, cameras, cell phones, and other valuables from individuals riding or walking on the street. If you are targeted by thieves, do not resist, and report the incident immediately to local police and to the U.S. Embassy in Hanoi or the U.S. Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City. Keep a tight hold on bags as you enter and exit vehicles and as you walk around. Hold tightly to cell phones when using them outside and lock and stow phones until you actually need to use them.
Some U.S. citizens have reported threats of death or physical injury connected to business-related disputes. You should report such threats to local authorities and if you feel unsafe, you should depart the country.
Keep your passport and other important valuables in your hotel in a safe or another secured location at all times and carry both photo and digital copies of your passport. You should immediately report the loss or theft of your U.S. passport to the local police and the U.S. Embassy or the U.S. Consulate General. See section on “Visas” for information on what to do if your passport/visa are lost or stolen.
Sexual Assault: Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault, harassment and rape do occur. To minimize the risk avoid travelling alone, especially at night; remain particularly vigilant in less populous areas; and be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances. Local authorities may not always respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General. Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum, or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
Male violence against women and sexual harassment is often ignored by the police. In areas foreigners frequent, women have reported harassment and assault such as men exposing themselves, asking for sexual favors, and groping.
Drugs: Recreational drugs available in Vietnam can be extremely dangerous and can result in death. Drugs sold in Vietnam may be fake, synthetic, or laced with toxic ingredients undetectable to the buyer. This includes nitrous oxide balloons widely available in nightlife establishments. You should also avoid purchasing liquor or cigarettes from street vendors or strangers, as the authenticity of the contents cannot be assured.
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of sexual assault are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General for assistance. Vietnam’s local equivalent of an emergency line is 113. Local police will issue a report of a crime, but generally will only initiate investigations for crimes they determine serious, which do not always equate with U.S. standards. Investigations can take several months or even years to complete.
In the event you are a victim of a crime, local police will issue a crime report in Vietnamese, but generally will only initiate investigations for crimes they determine serious. While the overall situation is improving, some police have asked for bribes, ostensibly to support local police efforts or to facilitate investigation of a crime. If you are involved in a situation where a police officer is soliciting money, contact American Citizen Services at the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
We can:
- Help you find appropriate medical care.
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police.
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent.
- Provide general information regarding the victim’s role during the local investigation and following its conclusion.
- Provide a list of local attorneys.
- Provide information on victim’s compensation programs in the United States.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited support in cases of destitution.
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home.
- Replace a stolen or lost passport.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the Embassy or Consulate General for assistance . Note that local authorities take a different attitude towards domestic violence cases and are hesitant to get involved in cases involving foreigners. Vietnam has very limited infrastructure to support victims of domestic violence.
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to Vietnamese laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Vietnam are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines, or even the death penalty. Police periodically raid nightlife establishments suspected of engaging in the drug trade and during these raids will subject all patrons present to drug testing at the police station. A positive result, regardless of whether drugs were consumed in Vietnam or before entry, may result in criminal charges.
In Vietnam, you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have proper ID, such as a passport or a copy of your visa. Driving under the influence of alcohol resulting in a fatal accident could lead to immediate imprisonment. If you break local laws in Vietnam, your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution. Note that the Vietnamese legal system allows for lengthy criminal investigation periods that can lead to prolonged pre-trial detention; some investigations can last years without any explanation.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. You can be prosecuted in the United States for engaging in sexual conduct with children or for using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country regardless of the legality of these activities under the host country’s laws.
Arrest Notification in Vietnam: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General immediately. There are often delays in notification by the Vietnamese authorities to the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General and officials have been known to delay consular access to prisoners for several weeks.
Counterfeit and Pirated Goods: Although counterfeit and pirated goods are prevalent in many countries, they may still be illegal according to local laws. You may also pay fines or forfeit them upon return to the United States. See the U.S. Department of Justice website for more information.
Gambling: Gambling is highly regulated by the government and persons or businesses running games or gambling halls are required to be licensed. The Government of Vietnam pursues cases of running or playing in unlicensed games aggressively. There are currently U.S. citizens serving jail sentences of three to five years because of illegal gambling.
Dual Nationality: Dual nationality is accepted by the Vietnamese government in some, but not all, circumstances. However, dual nationals should be aware that Vietnam recognizes their Vietnamese citizenship as primary before others. In such cases, the U.S. Embassy and Consulate General may be limited in the consular services we are able to provide. U.S. citizens who also hold Vietnamese citizenship and are currently residing in Vietnam may wish to contact local authorities and/or seek competent legal advice on how local laws may affect their status. For detailed information on Vietnamese nationality law and other legal issues visit the Embassy of Vietnam website .
Work Authorization: The Government of Vietnam maintains strict laws with respect to foreign workers. U.S. citizens planning to work in Vietnam should make sure that they are in full compliance with Vietnamese regulations. Penalties can be severe and include deportation, fines, or detention. Vietnam immigration law allows for companies sponsoring foreign employees to exercise control over their employees’ visas, including prohibiting their exit from the country if they have any outstanding debts.
Teaching English: We advise those considering accepting an English teaching job in Vietnam to carefully review the terms of the contract regarding working and living conditions and to ask for multiple references from persons familiar with the institution, especially former U.S. citizen employees, before committing to contracts. Some U.S. citizens have reported their employers have reneged on contract terms, including offering significantly lower salaries than agreed or seizing their passports, and employers have caused complications with the exit visa process for employees who quit, complicating the exit visas required to depart the country.
Hotels: Hotels in Vietnam require you to present your passport (and visas, if issued separately) upon check-in so that your stay can be registered with local police. Every guest in a hotel room or private residence must be registered, regardless of nationality. If you stay at a private residence (i.e., at the residence of family or friends), you must comply with registration requirements by visiting the local police station and registering your stay within 24 hours. Some provinces allow registration online.
Exports: Vietnamese law prohibits the export of antiques. However, these laws are vague and unevenly enforced. Customs authorities may inspect and seize your antiques without compensating you, and the determination of what is an “antique” can be arbitrary. If you purchase non-antique items of value, you should retain receipts and confirmation from shop owners and/or the Ministry of Culture and the Customs Department to prevent seizure when you leave the country.
Imports: Vietnamese authorities have seized documents, audio and video tapes, compact discs, literature, and personal letters they deem to be pornographic or political in nature or intended for religious or political proselytizing. It is illegal to import weapons, ammunition, explosives, military equipment and tools (including uniforms), narcotics, drugs, toxic chemicals, pornographic and subversive materials, firecrackers, or children's toys that have "negative effects on personality development, social order, and security." For up-to-date information on Vietnam Customs information, please visit the Vietnam Customs website .
Freedom of Expression: The Government of Vietnam maintains strict control over all forms of political speech, particularly dissent or speech it deems as critical of the government and/or party. U.S. citizens have been detained, tried, and convicted for political activities (including criticizing the government or its domestic/foreign policies or advocating alternatives to Communist Party rule), possession of political material, and non-sanctioned religious activities (including proselytizing). Authorities have also detained U.S. citizens for posting messages on blogs or online chatrooms that are perceived to be political or critical of the government. U.S. citizens of Vietnamese descent should be especially careful with their online postings. Review the latest version of the Vietnam Human Rights Report for the latest information on Freedom of Expression in Vietnam.
Association with Groups: Persons whom the Government of Vietnam perceives to be associated with dissident or political groups may be denied entry to Vietnam, prevented from departing, detained, interrogated, placed under surveillance, or even tried and convicted. Note that if arrested, you could be subject to lengthy detention without access to an attorney or family members. U.S. citizens of Vietnamese descent should be especially careful about associating with dissident groups. U.S. citizen travelers have been summoned by immigration or local security officials for reasons that are unclear or not explicitly related to any suspected or alleged violation of law. We recommend that U.S. citizens finding themselves in this situation contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate General immediately for further information and/or assistance.
Photography: Taking photographs of anything that could be perceived as being of military Taking photographs of anything that could be perceived as being of military or security interest may result in questioning by authorities, fines, or delayed travel. You should be cautious when traveling near military bases and avoid photography in these areas. Disputes: The Vietnamese government has occasionally seized the passports and blocked the departure of foreigners involved in commercial disputes. U.S. citizens whose passports have been seized by Vietnamese authorities should contact the Embassy or Consulate General for assistance .
Civil Procedures: Civil procedures in Vietnam, such as marriage, divorce, documenting the birth of a child, and issuance of death certificates, are highly bureaucratic and can be slow. Local authorities may refuse a request to include a non-Vietnamese name on a birth certificate. In addition, for those wishing to get married in Vietnam, you will need a notarized affidavit of single status. Please contact the Vietnamese Embassy in Washington, D.C. , or the Vietnamese Consulate General in San Francisco or Houston concerning documentary requirements for these services. Enforcement of civil orders is frequently difficult or non-existent.
Women Travelers: See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
LGBTQI+ Rights: There are no legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or in attending LGBTIQ+ events in Vietnam. See our LGBTQI+ Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Accessibility: Most public places and public transportation are not accessible to persons with disabilities. Sidewalks, curb ramps, restrooms, road crossings, and tourist areas are not equipped to assist such individuals. New, modern buildings and facilities in larger urban cities are regularly built with ramps and accessible entryways.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Medical facilities in Vietnam, including emergency response services, frequently do not meet international standards and may lack medicine and supplies. We strongly recommend travelers purchase medical evacuation insurance before visiting Vietnam.
- Medical personnel generally speak little or no English. Doctors and hospitals expect immediate cash payment for health services. You may obtain lists of local English-speaking physicians from the U.S. Embassy in Hanoi or the U.S. Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City from our website .
- International health clinics in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City can treat minor illnesses and injuries, but more serious problems often require medical evacuation to other cities in the region.
- Although you can purchase many prescription and non-prescription medications at pharmacies, some common U.S. medications may not be available. You should bring adequate supplies of medications for the duration of your stay in Vietnam and ensure with the Ministry of Health that the medicine you need is allowed to enter Vietnam. You should carry a copy of your prescription if carrying medicine in a travel case or container.
- We strongly recommend travelers purchase medical evacuation insurance before visiting Vietnam.
- Travelers to Vietnam are at risk of the following diseases: Tuberculosis, Dengue Fever, Zika, Avian Influenza (H5N1), and HIV. You can find detailed information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the CDC website .
We do not pay medical bills. The U.S. government cannot pay medical bills and does not provide medical assistance. Also, be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept upfront payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage . Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas. If covered by TriCare, check the TriCare website ( https://www.tricare.mil/ ) for additional information about overseas coverage.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation as it can cost many thousands of dollars. Always carry your prescription medication in original packaging, along with your doctor’s prescription.
It is extremely important that travelers have sufficient funds and/or insurance to cover any potential medical costs. Frequently hospitals will hold onto a patient’s passport as collateral for payment, and patients may have difficulty getting their passport back without paying their medical bills in full. Patients who do not pay their medical bills in full also run the risk of being barred from departing the country.
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Air quality: Air pollution is a significant problem in Vietnam’s major cities, and you should consult your doctor prior to travel and consider the impact that seasonal smog and heavy particulate pollution may have on you. To obtain information on the air quality in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City, please follow the link to the Environmental Protection Agency’s AirNow website . Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City’s Air Quality Index (AQI) can be observed either by clicking on the Vietnam location on the map, or by selecting Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City in the “Select a City” option on the upper right part of the page. The page provides AQI over the last 24-hour period as well as pollutant concentration and a downloadable historical document.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety: Traffic in Vietnam is dangerous, chaotic, and undisciplined. Road conditions are poor; traffic accidents are the leading cause of death, severe injury, and emergency evacuation of foreigners in Vietnam. Long-distance buses and trains do not meet U.S. safety standards. Buses and trucks are often overloaded and travel at high speeds with little regard to other modes of road transportation.
Traffic Laws: Driving in Vietnam is not comparable to driving in other countries. Vietnamese drivers routinely ignore traffic laws, causing traffic fatalities on a daily basis. We strongly discourage you from operating a motorcycle or scooter in Vietnam. Vietnamese drivers and pedestrians may not behave in a manner to which Americans are accustomed. If you do choose to operate a motorcycle or scooter in Vietnam, wear a helmet and always yield to larger vehicles. Motor bike fatalities are a leading cause of death or serious injury among foreign nationals visiting or living in Vietnam, with several fatalities having occurred on major roads and rural routes within the past year. If you are the victim of a serious motor bike accident in Vietnam, the prognosis for full recovery and survival is low due to Vietnam’s poor medical infrastructure. A motorbike license is required to operate a motorcycle or scooter in Vietnam. Motor scooter drivers without a license can be held criminally liable for injuries to or death of a victim in an accident, and you may be held in custody for an extended period of time without the ability to speak to family or a lawyer during the investigation.
Pedestrians should always look carefully in both directions before crossing streets, even when using a marked crosswalk with a green “walk” light illuminated or when crossing what is believed to be a one-way street. When walking on sidewalks, be mindful of scooters that may be behind you. Vietnamese commonly drive their scooters against traffic and on sidewalks.
Because the United States is not a party to the Convention on Road Traffic, international driving permits and U.S. drivers’ licenses are not valid in Vietnam. Foreigners renting vehicles risk fines, prosecution, and/or imprisonment for driving without a Vietnamese license endorsed for the appropriate vehicle. If you wish to drive in Vietnam, contact the Provincial Public Transportation Service of the Vietnamese Department of Communications and Transport to obtain a Vietnamese driver’s license. Note that you may be required to take a medical examination as part of the driver license application process.
For more information, please refer to Vietnam’s national tourism office website.
Public Transportation:
Bus System: While Vietnam does have an extensive bus system, buses can be overcrowded and are often driven with little or no regard for passenger safety.
For-hire vehicles: Major taxi companies tend to be reliable. Occasionally boutique taxi companies have rigged meters, particularly on routes to and from the international airports. Exercise caution in choosing ground transportation upon arrival at the airport in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City. Some travelers have reported being robbed by drivers who greeted them upon arrival with a placard showing the traveler's name. If you are expecting to be picked up, ask the company for the driver’s name, phone number, and license plate number before you travel. Areas outside of large cities typically have only rudimentary public transportation and often do not have metered taxis. Travelers are advised to use caution in these situations.
We strongly discourage the use of motorcycle taxis (known as “xe om”). Motorcycle taxis are unregulated and unsafe, and the helmets provided to riders offer little to no protection against injury in the case of an accident.
Smartphone-based for-hire vehicle services: GrabTaxi and local taxi companies are readily available, accessible via Smartphone apps, and routinely utilized by foreigners and locals.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Vietnam’s Civil Aviation Authority as being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Vietnam’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Vietnam should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) broadcast warnings website portal.
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Vietnam . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, vietnam map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Check passport expiration dates carefully for all travelers! Children’s passports are issued for 5 years, adult passports for 10 years.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Quick Links
- Make An Appointment
- Our Services
- Price Estimate
- Price Transparency
- Pay Your Bill
- Patient Experience
- Careers at UH
Schedule an appointment today

Vietnam Travel Requirements & Vaccinations
Vietnam is a country in southern Asia on the Indochina Peninsula that, in recent years, has become one of the fastest growing tourist destinations. Officially known as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, it is bordered by China to the north and Thailand to the southwest. Vietnamese is the official language of Vietnam with French being the most commonly spoken second language. English is gaining popularity but is not yet widely used.
Due to marked variety in the terrain of Vietnam, the climate can vary greatly based on location. Temperatures tend to be higher in the plains and cooler in the mountainous regions and plateaus. During the winter season – November through April – monsoon winds usually blow from the northeast, picking up considerable moisture. The country is also affected by tropical depressions, tropical storms and typhoons. Vietnam has a uniquely high level of biological diversity and is home to approximately 840 different species of birds and 310 species of mammals.
Some popular tourist destinations include:
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Hanoi, the capital city
- Ha Long Bay
- Nha Trang, a popular beach destination with a tropical climate
Recommended Vaccinations for Vietnam Travel
- Hepatitis A
- Japanese encephalitis
*Rabies vaccination is typically only recommended for very high risk travelers given that it is completely preventable if medical attention is received within 7 – 10 days of an animal bite.
Travelers may also be advised to ensure they have received the routine vaccinations listed below. Some adults may need to receive a booster for some of these diseases:
- Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR)
- Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis)
Older adults or those with certain medical conditions may also want to ask about being vaccinated for shingles and/or pneumonia.
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a travel medicine professional. Not all of the vaccines listed here will be necessary for every individual.
Talk to the experts at UH Roe Green Center for Travel Medicine & Global Health to determine how each member of your family can obtain maximum protection against illness, disease and injury while traveling, based on age, health, medical history and travel itinerary.
Make an Appointment
To schedule a pre-travel consultation call, 440-482-7416 .
Please note: You must be physically located in Ohio for a virtual consultation
What Can You Do to Help?
Make a gift to support urgent patient care at University Hospitals.
- Company History
- Mission Statement
- Philippines
- South Africa
- Afghanistan
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
- Canary Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Cote d'Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
- Easter Island
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liechtenstein
- Madeira Islands
- Marshall Islands
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Pitcairn Islands
- Puerto Rico
- Republic of the Congo
- Saint Barthelemy
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Sint Eustatius
- Solomon Islands
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Switzerland
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- U.S. Virgin Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Wake Island
- Western Sahara
- Travel Vaccines
- Travel Health Consultations
- Travellers’ Diarrhea Kits
- Dengue Fever Prevention
- Malaria Prevention
- Chikungunya Prevention
- Zika Prevention
- Ebola Virus
- Yellow Fever
- Hepatitis A
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Hepatitis B
- Tickborne Encephalitis (TBE)
- Tetanus-Diphtheria-Pertussis
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella
- Influenza (Flu)
- Blood Tests
- Vitamin Injections
- Physician Referral Program
- London – Euston Travel Clinic

Travel Vaccines and Advice for Vietnam

Vietnam has become a popular tourist destination.
Visitors looking to be swept away by gorgeous landscape will be can see jungles, caves, grottoes, and immence limestone pillars. Those looking to explore new flavours and foods will be thrilled with the delicious, on the cheap street food.
Even those looking to experience a new culture will be able to indulge in Vietnam’s peculiar blend of Confucianism, Buddhism, Hinduism, Southern Chinese, and French influences.
Do I Need Vaccines for Vietnam?
Yes, some vaccines are recommended or required for Vietnam. The National Travel Health Network and Centre and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Vietnam: hepatitis A , hepatitis B , typhoid , Japanese encephalitis , rabies , cholera and tetanus .
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunisations:
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travellers to the region, especially if unvaccinated.
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Recommended for travellers to most regions.
- Tetanus – Wounds or Breaks in Skin – Recommended for travellers to most regions, especially if not previously vaccinated.
- Typhoid – Food & Water – Jab lasts 3 years. Oral vaccine lasts 5 years, must be able to swallow pills. Oral doses must be kept in refrigerator.
- Japanese Encephalitis – Mosquito – Recommended depending on itinerary and activities. Recommended for extended travel, recurrent travellers and travel to rural areas. Present throughout country, especially northern regions. Most cases from May to October.
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-stay travellers and those who may come in contact with animals.
- Cholera – Food & Water – Recommended for travel to most regions.
See the tables below for more information:
Travellers should also take steps to avoid mosquito bites. Share your itinerary with a travel medicine specialist to see if there are other steps you can take to prevent malaria , including taking prescription medicine. Antimalarials are highly recommended when visiting rural areas.
Japanese encephalitis vaccination is recommended for many travellers going to Vietnam. The mosquito-borne virus is potentially deadly and poses a risk to all travellers.
See our vaccinations page to learn more about these infections and vaccines. Ready to protect yourself? Book your travel health appointment today by calling or schedule online now .
Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Vietnam?
UK citizens may enter Vietnam for up to 15 days without a visa. Longer stays require an eVisa. Passports must be valid for at least six months. Proof of yellow fever vaccination may be required if you are travelling from a region where yellow fever is present.
Sources: Embassy of Vietnam and GOV.UK
What is the Climate Like in Vietnam?
There are various climate zones within Vietnam. The far north experiences a dry season from October to March and a wet season from April to September. It can get particularly cold during December and January, but is otherwise pleasant.
In north Vietnam there are four distinct seasons: winter, where temperatures reach below 20.
In central Vietnam the weather is hot and dry from mid-January to late August. During the winter there is significant rainfall, occasionally typhoons, and much cooler temperatures.
In South Vietnam the temperatures are constant all year. There is a dry season from November to April and a wet season from May to November.
How Safe is Vietnam?
Crime does occur in Vietnam and the Overseas Security Advisory Council ranks Hanoi as medium in Overall Crime and Safety Situation.
Petty crime, such as pick-pocketing and theft occurs often. Travelling alone after dark is not recommended. Violent crime has been growing, mostly in urban areas.
Scams are common. Foreign travellers should be very careful, particularly when entering motor-bike taxis, as there are many fake ones.
Visiting the Củ Chi Tunnels
The Củ Chi tunnels are a huge network of underground tunnels located in Ho Chi Minh City. They are a small part of a network of tunnels that exist under most of Vietnam. The tunnels played a great importance during many wars and battles. The government of Vietnam has turned the Củ Chi tunnels into a war memorial park.
Visitors can crawl into the tunnels and see the various traps that soldiers rigged to protect themselves. One can even visit underground conference rooms where various military campaigns were planned. Above ground, visitors can see monkeys or visit a shooting range.
What Should I Take To Vietnam?
Here are some essential items to consider for your trip to Indonesia:
- Money Belt – These are a great way to avoid pickpocketing whilst in Vietnam.
- Mosquito Repellent – Mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases are common in many parts of Vietnam. Ensure you’re protected from these insects whilst travelling.
- Walking Shoes – Visitors can walk the streets to explore the street vendors or beautiful wildlife, making good shoes a must.
Embassy of the United Kingdom in Vietnam
If you are in Vietnam and have an emergency (for example, been attacked, arrested or someone has died) contact the nearest consular services. Contact the embassy before arrival if you have additional questions on entry requirements, safety concerns or are in need of assistance.
British Embassy Hanoi 25 Le Duan Street, District 1 Ho Chi Minh Vietnam Telephone: +84 (0)24 3936 0500 Emergency Phone: +84 (0) 24 3936 0500 Fax: +84 (0)24 3936 0561 Contact Form: Click Here
If you have any questions about travelling to Vietnam or are wondering which jabs you may need for your trip, schedule an appointment by calling or book online today .
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Vietnam? Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Vietnam? What is the Climate Like in Vietnam? How Safe is Vietnam? Visiting the Củ Chi Tunnels What Should I Take To Vietnam? Embassy of the United Kingdom in Vietnam

- Privacy Policy
- Automatic Data Collection Statement
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more

Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
- Destinations
- Asia (East)
- Asia (Central)
- Australasia & Pacific
- Central America
- Europe & Russia
- Middle East
- North America
- South America & Antarctica
Vietnam (Asia)
Advice for all destinations.
Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Vaccinations and malaria risk
Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
If you think you require vaccines and/or malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional:
- How to make an appointment with a travel health professional
A travel health risk assessment is also advisable for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets are not required.
- Do I need a travel health risk assessment?
Risk prevention advice
Many of the health risks experienced by travellers cannot be prevented by vaccines and other measures need to be taken.
Always make sure you understand the wider risks at your destination and take precautions, including:
- food and water safety
- accident prevention
- avoiding insect bites
- preventing and treating animal bites
- respiratory hygiene
- hand hygiene
Our advice section gives detailed information on minimising specific health risks abroad:
- Travel Health Advice A-Z
Other health considerations
Make sure you have travel insurance before travel to cover healthcare abroad.
Find out if there are any restrictions you need to consider if you are travelling with medicines .
Know how to access healthcare at your destination: see the GOV.UK English speaking doctors and medical facilities: worldwide list
If you feel unwell on your return home from travelling abroad, always seek advice from a healthcare professional and let them know your travel history.
Vaccinations
- Confirm primary courses and boosters are up to date as recommended for life in Britain - including for example, seasonal flu vaccine (if indicated), MMR , vaccines required for occupational risk of exposure, lifestyle risks and underlying medical conditions.
- Courses or boosters usually advised: Diphtheria; Tetanus.
- Other vaccines to consider: Hepatitis A; Hepatitis B; Rabies; Typhoid.
- Selectively advised vaccines - only for those individuals at highest risk: Japanese Encephalitis.
No yellow fever vaccination certificate required for this country
Notes on the diseases mentioned above
- Diphtheria : spread person to person through respiratory droplets. Risk is higher if mixing with locals in poor, overcrowded living conditions.
Risk is higher where personal hygiene and sanitation is poor.
Risk is higher for long stays, frequent travel and for children (exposed through cuts and scratches), those who may require medical treatment during travel.
- Japanese Encephalitis : spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. This mosquito breeds in rice paddies and mainly bites between dusk and dawn. Risk is highest for long stay travellers to rural areas, particularly if unable to avoid mosquito bites.
- Tetanus : spread through contamination of cuts, burns and wounds with tetanus spores. Spores are found in soil worldwide. A total of 5 doses of tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK. Boosters are usually recommended in a country or situation where the correct treatment of an injury may not be readily available.
- Typhoid : spread mainly through consumption of contaminated food and drink. Risk is higher where access to adequate sanitation and safe water is limited.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes.You cannot be vaccinated against malaria.
Malaria precautions
- Malaria risk is low throughout the year in Kon Tum, Gia Lai, Dak Lak, Dak Nong, Binh Phuoc and western parts of Phu Yen, Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan, Binh Thuan and north west Lai Chau. In these areas, malaria tablets are not recommended, however, they may be considered for certain travellers who may be at higher risk (see below under Low risk areas with additional advice)
- Low to no risk in other areas including Ho Chi Min City and Hanoi, the Red River and Mekong deltas, Phu Quoc Island and coastal plains.
- Malaria precautions are essential. Avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers especially after sunset, using insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleeping under a mosquito net.
- Check with your doctor or nurse if antimalarial tablets may be required.
- See malaria map – additional information can be found by clicking on the Regional Information icon below the map.
- Low risk with additional advice: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised, however, they can be considered for certain travellers who may be at higher risk e.g. longer stay in rural areas, visiting friends or relatives, those with medical conditions, immunosuppression or those without a spleen. Atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline OR mefloquine is advised for those at risk.
- Low to no risk: antimalarial tablets are not usually advised.
- If you have been travelling in a malarious area and develop a fever seek medical attention promptly. Remember malaria can develop even up to one year after exposure.
- If travelling to an area remote from medical facilities, carrying standby emergency treatment for malaria may be considered.
Other Health Risks
Altitude and travel, dengue fever.
There is a risk of exposure to coronavirus (COVID-19) in this country.
Please be aware that the risk of COVID-19 in this country may change at short notice and also consider your risk of exposure in any transit countries and from travelling itself.
- The 'News' section on this page will advise if significant case increases or outbreaks have occurred in this country.
Prior to travel, you should:
- Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return.
- Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination.
- You can check this in the FAQ's.
- If you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 you should carefully consider your travel plans and consider seeking medical advice prior to making any decisions.
For further information, see Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel pages.
Zika Virus Infection
This country has been categorised as having a risk of Zika (ZIKV) virus transmission.
ZIKV is mainly spread through mosquito bites. The mosquito responsible most commonly bites during daylight hours and is common in towns and cities.
The illness is usually mild but infection during pregnancy may lead to babies being born with birth defects. There is no vaccine currently available against ZIKV.
Advice for All Travellers
You should practice strict mosquito bite avoidance at all times. Do not travel without adequate travel insurance . Seek pre-travel health advice from a travel health professional 6 to 8 weeks in advance of travel.
Additional recommendations for pregnant travellers or those planning pregnancy
If you are planning pregnancy in the very near future you should consider whether you should avoid travel to this country.
- contact your GP, obstetrician or midwife for further advice, even if you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- use barrier methods of contraception during and after travel and for the duration of your pregnancy, even in you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- If you develop symptoms of ZIKV infection, it is recommended that you avoid becoming pregnant for a further 2 months following your recovery
- 2 months afterwards if you are female
- 3 months afterwards if you are male or if both partners travelled
These measures reduce the chance of sexual transmission of ZIKV and/or the risk of ZIKV infection in pregnancy.
For further information, see Zika virus infection page.
- 74 additional items in the news archive for this country
back to top
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Routine Vaccines
It’s important to be up to date on recommended routine vaccines prior to travel, including Flu, RSV and COVID-19.

Find a Clinic
Advice for Travelers
Personalized Health Information Tool for Global Travel
Disease Directory
Frequently Asked Questions
CDC Yellow Book
Pre-travel Rapid Evaluation Portal for Patients
Clinician Resources
Research and Surveillance
- Medical Tourism
- Cholera Information for Health Care Professionals
- COVID-19 Travel Information
- Travel Industry Resources
Learn about CDC’s Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country.
Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips.
See the full list of Travel Health Notices , including:
Level 2 - Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Updated Global Polio April 26, 2024
- Diphtheria in Guinea April 23, 2024
- Chikungunya in Timor-Leste April 05, 2024
Level 1 - Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Measles April 26, 2024
- Updated Oropouche Fever in South America April 24, 2024
- Dengue in Asia and the Pacific Islands April 18, 2024
There are no Warning , Alert, Watch, COVID-19 Very High, COVID-19 High, COVID-19 Moderate, COVID-19 Low, COVID-19 Unknown, Level 4, or Level 3 notices currently in effect.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

- Vaccinations for Mexico
- Vaccinations for Brazil
- Vaccinations for Argentina
- Vaccinations for Peru
- Vaccinations for Ecuador
- Vaccinations for Panama
- Vaccinations for South Africa
- Vaccinations for Kenya
- Vaccinations for Tanzania
- Vaccinations for Botswana
- Vaccinations for Uganda
- Vaccinations for Bali and Indonesia
- Vaccinations for Thailand
- Vaccinations for Myanmar (Burma)
Vaccinations for Vietnam
- Vaccinations for Cambodia
- Vaccinations for Laos
- Vaccinations for Philippines
- Vaccinations for China
- Vaccinations for Hong Kong
- Vaccinations for India
- Vaccinations for Sri Lanka
- Vaccinations for Nepal
- Vaccinations for Fiji
- Vaccinations for Vanuatu
- Vaccinations for Papua New Guinea
Yellow Fever
- Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
- Corporate Vaccinations

If you are planning on travelling to Vietnam in the near future, there are some diseases you should be aware of and you may be recommended to have additional vaccinations beyond the childhood immunization schedule before travelling.
If you are travelling from Australia you should ensure that you are fully up to date with your childhood immunization schedule, which will protect you against common preventable diseases. If you are unsure whether you are sufficiently up to date, or require a booster shot the doctor can assist you and ensure you are up to date before travelling. You should speak to the doctor about:
- Your vaccination history
- Travel plans while in Vietnam and beyond if visiting other countries
- What style of accommodation and transport you will use
- Your general health and wellbeing
- Any plans for adventurous or outdoors activities
Commonly occurring preventable diseases, which you should consider getting vaccinated for, are discussed below. The advice contained is general advice only and does not substitute medical advice by a professional Travel Vaccination Clinic doctor or your own doctor. You can use the advice to start a conversation with the doctor.
What vaccinations do I need for travelling to Vietnam?
You should discuss the following vaccines during your appointment:
Hepatitis A and Typhoid
Both Hepatitis A and Typhoid are present in Vietnam, and a dual vaccine where one shot protects against both is available. The vaccine can protect you for a number of years once administered.
Hepatitis A: Hepatitis A can be passed on through contaminated food or water and is preventable via vaccination before you travel to Vietnam. Symptoms may be flu-like such as fever, tired, vomiting or nausea and loss of appetite, but may also include jaundice (yellowing of the eyes). Symptoms can last up to six months.
Typhoid: Typhoid is also passed on through contaminated food or water, and is also preventable when the vaccine is administered. This disease also has flu like symptoms.
Hepatitis B may occur through sexual contact, needle use or sharing of needles or medical procedures involving needles such as tattoos, piercings or cosmetic procedures. If you might consider any activities that would increase risk of exposure to Hepatitis B you should talk to the doctor and get vaccinated. This would include having sex with a new partner or getting a tattoo or piercing.
Japanese Encephalitis and vaccinations for Vietnam
Japanese Encephalitis is a mosquito borne disease and may be present, particularly in rural areas in Vietnam. This vaccine may be recommended if you are travelling to Vietnam for more than one month, and/or are highly likely to spend time in rural and undeveloped areas. If you will be spending a lot of time in rural areas and your trip is less than one month you should definitely speak to the doctor about getting this vaccine as it may be recommended for you.
Seasonal peaks in outbreaks of Japanese Encephalitis can occur between May and October and the largest number of cases is reported from Hanoi and Northern provinces bordering China.
Depending where you are going in Vietnam and what you will be doing you may be recommended anti malarial drugs, as malaria, which is transmitted through mosquito bites , is present in Vietnam and avoiding mosquito bites can be difficult.
All travellers to Vietnam should take precautions against mosquito bites, including wearing long loose clothing, using repellent and mosquito nets and not sleeping outdoors. If your activities might involve sleeping outdoors or spending a lot of time where mosquitos are present you should ask the doctor what precautions to take or whether you need to take anti malaria medication with you.
Malaria risk is generally low enough that avoiding mosquitos can be enough in Vietnam, and there is no reported malaria in Da Nang, Haiphong, Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City (Saigon), Nha Trang, and Qui Nhon. If you will be visiting other parts of Vietnam you should check the risk with the doctor.
Rabies is present in Vietnam, and all travellers should avoid contact with dogs, bats and other mammals that may carry the rabies virus. Those who are more likely to come into contact with animals while in Vietnam, such as wildlife workers, vets, researchers etc will usually be advised to take precautions and have a preventative vaccine. Those spending an extended period in Vietnam or moving to Vietnam may be at increased risk of exposure to rabies.
If you are planning on doing adventure activities such as caving, hiking or camping the vaccine may be recommended for you, so let the doctor know what you plan on doing while in Vietnam and what areas you will visit. Children may also be more likely to come into contact or experience an unprovoked animal attack or not report animal contact at all.
There is no considered risk of yellow fever in Vietnam, and the authorities may require proof you have been vaccinated against yellow fever depending where you will arrive from. Generally airport transit is not considered risky, but you should speak to the doctor if you have concerns about leaving an area with a risk of yellow fever infection , as you may need to be vaccinated. The doctor can advise you which areas carry a high risk of yellow fever infection and what to do about it.
Other important health information about travel to Vietnam
Vietnam is a country where outbreaks of watery diarrhea or cholera can occur, and water borne illnesses may be present. You should be careful and pay attention to food safety and hygiene while in Vietnam, and seek medical attention if any symptoms persist.
Outbreaks of Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) can occur in Vietnam between March and May, and can continue until October each year. Fever and blisters on the hands, feet and buttocks can indicate HFMD. The disease is transmitted through contacted with bodily fluids from someone infected (nose, mouth and faeces).
Outbreaks of ‘pink eye’ or conjunctivitis can also occur in Vietnam, and you should avoid contact with anyone who displays symptoms. Red/itchy eyes and discharge can occur with conjunctivitis. Diligent hand washing may also help reduce the risk of infection.
It is recommended to boil water or drink bottled water in Vietnam, and avoid uncooked and unpeeled vegetables and unpasteurized dairy products.
Book your appointment now at our Sydney CBD clinic, get instant confirmation.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Vietnam travel advice
Latest updates: The Health section was updated - travel health information (Public Health Agency of Canada)
Last updated: April 18, 2024 07:54 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, vietnam - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Vietnam due to high rate of petty crime.
Back to top
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs frequently. It’s most prevalent in larger cities and may increase during major public holidays, such as Tet (Lunar New Year).
Criminals work alone or in groups and may use various techniques to distract you and steal your belongings. They may try to grab your bag and other valuables while passing on a motorbike or slash your bag in crowded streets and markets.
Theft is frequent:
- in popular tourist areas
- in markets, shopping centres and commercial streets
- on public transportation including sleeper trains
- in transportation hubs such as airports and train stations
- in restaurants, including patios and outdoor cafés
- at beaches and seaside destinations
While travelling:
- ensure that your belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- keep a digital copy of your identity and travel documents
- avoid showing signs of affluence or wearing expensive jewellery
- avoid carrying large sums of cash
- avoid isolated areas, especially at night
- pay attention to your surroundings, particularly in crowded and tourist areas
- be extra cautious when withdrawing cash from ATMs
Violent crime
Although violent crimes targeting foreigners are rarer, they may occur. In some cases, criminals have used weapons such as knives and razors. Threats of physical injury related to personal disputes also occasionally occur.
- If you are involved in a dispute, contact the police as soon as possible
- If you are threatened by robbers, don’t resist
Residential break-ins
Residential break-ins occur, especially in large cities and may increase before and during the Tet holiday (Lunar New Year). Burglars may target houses or apartments rented or owned by tourists and foreigners.
- Stay in accommodations with adequate security measures
- Make sure you lock doors and windows at night and when you’re away
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assault and harassment do occur, including:
- in beach destinations
- in bars, nightclubs and entertainment districts
- on taxis and public transportation
Local authorities may not always respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are a victim of sexual assault:
- seek immediate medical assistance, whether or not you appear to have been physically harmed
- contact the local police and ensure they file a report
- inform consular officials at the nearest Canadian embassy or consulate
Advice for women travellers
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit and debit card as well as ATM fraud occurs frequently.
- Avoid using your credit card in small establishments
- Consider using a card with a small credit limit
- Cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- Pay careful attention when others are handling your cards
- Avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- Use ATMs located in public areas or inside a bank or business
- Check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Cybercrime occurs. Perpetrators may compromise public Wi-Fi networks to steal credit card or personal information.
- Avoid using unsecured public Wi-Fi networks
- Avoid making purchases on unencrypted websites
- Be cautious when posting information on social media
- Be especially vigilant if you decide to meet someone you met online
- Don’t click a suspicious link in an email or text message asking for your credit card details
At the airport
Criminals posing as taxi drivers have targeted foreign visitors at Nội Bài International Airport in Hanoi and robbed them by forcing them to withdraw money from ATMs.
Travellers have also been robbed by drivers who greeted them upon arrival with a placard showing their name.
- Arrange your pickup with your hotel before arrival, or use authorized airport taxis
- Confirm the driver’s identity and the licence plate before getting in the car
Gambling scams
Tourists have been victims of gambling scams in Hanoi, as well as in Ho Chi Minh City, particularly in the Pham Ngu Lao neighbourhood.
The scam consists of a friendly invitation sent to the victim to go to someone’s home in order to meet a relative interested in visiting Canada. While waiting for the relative, the scammers suggest a casual game of cards involving an initial small wager. Some victims have lost thousands of dollars over the course of an evening.
Be wary of unsolicited proposals from strangers.
If you’ve been scammed:
- get to a safe location immediately
- take note, as soon as possible, of the name and address of the facility where you were held
- notify the police and obtain a report
- if a bank card was involved, report the scam to your banking company, which will likely request a copy of the police report to cancel the transaction
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Snacks, beverages, gum and cigarettes may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
- Be wary of accepting these items from new acquaintances
- Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers
Unregulated alcohol
Some people died after consuming unregulated and adulterated rice wine due to high levels of methanol.
- Be cautious if you choose to drink alcohol
- Only consume reputable alcohol brands
- Avoid buying alcohol from individuals or street vendors
- Seek medical assistance if you begin to feel sick
Alcohol, drugs and travel
Demonstrations
Current situation in dak lak.
An increased police presence in Dak Lak continues, after organized attacks on a police station in June 2023.
If you are in the area, do not photograph security forces.
Public demonstrations are rare since local authorities don’t usually authorize them. Demonstrating without authorization can lead to heavy consequences, including lengthy prison sentences.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Don’t photograph demonstrations
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Internet censorship and surveillance
Within the Vietnamese territory, local authorities block access to several:
- social media
- search engines
- online services
You shouldn’t expect internet privacy.
Local authorities may monitor your communications at any time. They may review the content stored or consulted on your electronic devices. They may also place certain foreigners under electronic surveillance. They can search your home or hotel room without your knowledge or consent.
Cyber security while travelling
Foreign journalists and other media workers in Vietnam may face considerable restrictions in the context of their work. The Vietnamese government may employ measures such as:
- physical and electronic surveillance
- delaying or refusing renewals of press cards and visas
- intimidation and harassment
Be particularly vigilant if researching or reporting on subjects critical of or sensitive to the government.
Landmines and war remnants
Landmines and unexploded ordnance still pose a serious risk in several areas, particularly:
- in the province of Quảng Trị
- along the border with Laos
- in North and Central Vietnam
Unmarked minefields are common. If you plan travelling outside of major tourist destinations:
- pay attention to signs indicating the possible presence of landmines
- remain on paved roads
- avoid open fields, roadside ditches, shoulders and unmarked trails
- report any suspicious items to local authorities
Adventure tourism
Outdoor activities, such as trekking, zip-lining, rock climbing, speleology, or parasailing and other adventure activities can be dangerous if unprepared. Trails are not always marked, and weather conditions can change rapidly, especially during the rainy season.
Tour operators may not always adhere to international safety standards.
If you intend to practice adventure tourism:
- never do so alone, and do not part with your expedition companions
- consider hiring an experienced guide from a reputable company
- obtain detailed information on your activity and on the environment in which you will be setting out
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- avoid venturing off marked trails
- ensure that you’re adequately equipped and bring sufficient water
- stay informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- refrain from using facilities or equipment if you have doubts on their safety
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary
Water activities
Tidal changes and strong winds can cause hazardous currents and riptides.
Swimming and diving
Beaches are not always supervised.
Corals, sea urchins, jellyfish and other aquatic life found along reefs may be poisonous. A sting to the touch can cause poisoning or infection.
If you plan to dive:
- choose a reputable company
- always respect warning flags advising of dangerous conditions
- ask about the presence of dangerous species
- seek immediate medical attention in case of injury
- wear swimming shoes to protect yourself from reefs, rocks, corals or sea urchins
- keep a safe distance from boats and restricted areas
- avoid beaches or coastal areas during periods of severe weather warnings
- avoid diving into unknown waters, as hidden rocks or shallow depths can cause serious injury or death
- follow the advice of the local authorities
Boat accidents have occurred due to the overloading and poor maintenance of some vessels, including in Ha Long Bay.
- Choose a reputable boating company
- Ensure that your tour operator follows up-to-date safety regulations
- Don’t board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy
Water safety abroad
Although rare in Vietnam, pirates commit attacks and armed robbery against ships in coastal waters.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau
Road safety
Road safety is poor throughout the country.
Fatal accidents are frequent. They frequently involve motorcycle and pedestrians are commonly victims.
Always use elevated walkways or pedestrian bridges when available.
Road conditions
Road conditions are poor throughout the country.
Driving can be dangerous due to:
- poorly maintained roads and vehicles
- traffic jams and heavy traffic, especially in urban areas
- potholes
- slippery roads during the rainy season
Driving habits
Drivers don’t always respect traffic laws.
Some vehicles, especially motorcycles, drive against the flow of traffic and on the sidewalks.
If you plan to travel by car in Vietnam, you should consider hiring a driver.
If you choose to drive:
- always drive defensively
- avoid travelling after dark or during adverse weather conditions
- avoid driving a motorcycle
- Make sure you have proper insurance and a valid licence
Public transportation
Official taxis are generally safe.
Motorcycle taxis (known as “xe oms”) are not safe.
- Avoid motorcycle taxis
- Use only official taxis or a trusted ridesharing app
- Negotiate the fare in advance, or insist that the driver use the meter
- Never share a taxi with a stranger
- Be familiar with your hotel’s address and the neighbourhood to avoid being brought to a wrong location
Bus and coach accidents are common.
Trains are generally reliable.
Thefts have been reported on certain train lines, including sleeper trains.
Ticket stub is required to exit the train station. Passengers without a ticket stub will be required to pay the fare again.
Retain your ticket stub when travelling by train.
Ferry accidents have occurred due to the overloading and poor maintenance of some vessels, particularly on the line connecting Ho Chi Minh City to Vung Tau.
Don’t board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy.
Transport within Vietnam - Vietnam Tourism
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Vietnamese authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Vietnam.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required Work visa: required
E-visa authorization
If you have a valid Canadian passport, you may be eligible to apply online for an e-visa. This can be a single-entry or multiple-entry electronic tourist visa, valid for a maximum of 90 days. It allows you to enter Vietnam via the port of entry indicated in the visa approval notice only. Some restrictions apply.
For visits longer than 90 days, you must get a visa from the nearest Vietnamese embassy before departure.
Apply for an e-visa - Immigration Department of Vietnam
Visa exemptions
Canadian spouses or children of Vietnamese citizens may be eligible for a visa exemption certificate.
Contact the Embassy of Vietnam in Canada for more information on this process.
Visa extension
You must have a visa to enter Vietnam.
If required, you can request a visa extension at:
- the Vietnam Immigration Department in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City
- certain local travel agencies and tour companies
Vietnamese visas in expired Canadian passports are not valid. The visa needs to be transferred to the new passport.
Overstaying your Vietnamese visa or having the wrong type of visa is a serious matter. You may be delayed from onward travel until a fine is paid.
Check the visa validity and conditions carefully.
Registration
You must report your presence to local authorities upon arrival.
Commercial accommodations will generally file the declaration on your behalf. If you're staying in a non-commercial accommodation, you must do so with the nearest police station.
Make sure you request the return of your passport once it has been registered by hotel staff.
The hotel staff may ask to see your passport at check-in. They may make copies of it. They may also insist on holding your passport until you leave. There is no legal reason for this.
- Never leave your passport or any other ID document with anyone
- Ask for your documents to be returned to you as soon as check-in is complete
Travel restrictions
Travel near military facilities is restricted:
- in some parts of the central highlands
- in some border area
If you wish to visit a village, commune or ward that is close to the border, you must obtain permission from the provincial police department.
Contact the relevant local authority to confirm these requirements.
Health screening
Upon entry, you may be subject to a body temperature check.
Vietnamese authorities may place an exit ban on certain individuals to prevent them from leaving the country.
An exit ban can relate to investigations into:
- an individual, their family or an employer
- criminal and civil matters, such as business disputes or motor vehicle accidents
- employment without a valid work permit
- unpaid financial debts
It is difficult to obtain information on bans from Vietnamese authorities. An exit ban can be requested by people involved in any of these circumstances. You may not be aware that authorities have placed an exit ban on you until you try to leave the country. Your passport may be seized until the case is fully investigated and settled.
If you're unable to leave the country because of an exit ban, consult a lawyer and contact the closest office of the Government of Canada.
Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is not required to enter this country.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
* It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. Rabies treatment is often available in this destination.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Human cases of avian influenza have been reported in this destination. Avian influenza is a viral infection that can spread quickly and easily among birds and in rare cases it can infect mammals, including people. The risk is low for most travellers.
Avoid contact with birds, including wild, farm, and backyard birds (alive or dead) and surfaces that may have bird droppings on them. Ensure all poultry dishes, including eggs and wild game, are properly cooked.
Travellers with a higher risk of exposure include those:
- visiting live bird/animal markets or poultry farms
- working with poultry (such as chickens, turkeys, domestic ducks)
- hunting, de-feathering, field dressing and butchering wild birds and wild mammals
- working with wild birds for activities such as research, conservation, or rehabilitation
- working with wild mammals, especially those that eat wild birds (e.g., foxes)
All eligible people are encouraged to get the seasonal influenza shot, which will protect them against human influenza viruses. While the seasonal influenza shot does not prevent infection with avian influenza, it can reduce the chance of getting sick with human and avian influenza viruses at the same time.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
Good health care is limited. The quality of care varies greatly throughout the country.
Both medical facilities and supplies are limited outside of Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
Private clinics and hospitals are usually better equipped. Services can be expensive, but they usually have qualified medical staff who speak English or French well. Emergency and ambulance services response times may be slow du to traffic congestion. In case of emergency, you may consider taking a taxi or private vehicle to go to the hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
Medical evacuation is very expensive. You may need it to neighbouring countries in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
If you take prescription medication, you’re responsible for determining their legality in Vietnam.
- Bring sufficient quantities of your medication with you
- Always keep your medication in the original container
- Pack your medication in your carry-on luggage
- Carry a copy of your prescriptions
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
No transfer of offenders treaty exists between Canada and Vietnam. If you’re convicted of a serious crime, you must serve your jail sentence in Vietnam. You may also have to remain in Vietnam for a parole period after your release.
Penalties for possession, use, production or trafficking of drugs, including cannabis, are severe. Convicted offenders can expect heavy fines, jail sentences or the death penalty.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Identification
Local authorities may request to see your ID at any time.
- Carry valid identification or a photocopy of it at all times
- Keep a photocopy of your passport in a safe place in case it’s lost or seized
- Keep a digital copy of your ID and travel documents
Gambling outside of licensed casinos is illegal in Vietnam.
You must hold of a foreign passport to gamble in these licensed establishments.
Political activities
There are severe restrictions on political activities, including:
- participating in public protests
- publishing messages critical of the government on social media
If you engage in political activities you may face detention, deportation and travel ban to Vietnam in the future.
Photography
Photography of sensitive installations is prohibited. This includes:
- military sites
- border crossings
These sensitive areas are not always identified.
- Refrain from photographing military installations or personnel even if no sign is posted
- Comply with all requests from local authorities
Religious activities
There are restrictions on certain religious activities, such as preaching, distributing literature and associating with unapproved religious groups.
Sexual and intimate activities
As a foreigner, you are not allowed to invite Vietnamese nationals of the opposite sex into your hotel room to stay overnight unless you are married.
You are allowed to stay with a Vietnamese family only if you have obtained permission from local authorities.
Importation, possession and distribution of pornographic material is illegal.
Exportation of antiques
Vietnamese law restricts the export of antiques, but these laws are vague and unevenly enforced. If you purchase items that may be considered as antiques:
- keep receipts and all paperwork provided by the seller
- ensure you have the proper exportation permits from the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism and the Vietnam General Department of Customs
If you can't present the required paperwork, the items may be confiscated.
Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism of Vietnam (in Vietnamese)
Dress and behaviour
The Vietnamese society is conservative.
When visiting religious and culturally places to avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
- seek permission from locals before photographing them
Tet celebrations
The lunar new year is celebrated between the end of January and the end of February. Theses celebrations usually last several days and can have an impact on the availability and provision of essential services such as:
- banking services
- public services including healthcare
- food distribution
Plan your trip accordingly if you travel to Vietnam during this period.
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in Vietnam.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Vietnam, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
Mandatory military service
Canadians with Vietnamese citizenship may be subject to mandatory military service and other national obligations.
Confirm this requirement before travelling to Vietnam.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Vietnam.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Vietnam by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Vietnam to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Travelling with children
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
Doing business in Vietnam
Disputes related to business agreements or arrangements are costly and take time to resolve. You may be subject to a travel ban restricting you from leaving the country until matters are resolved.
If you plan on doing business in Vietnam:
- seek legal advice in Canada and in Vietnam before making commitments
- choose your own lawyer
- ensure that all documents are translated so that conditions, terms and limitations are well understood
There are many teaching opportunities in Vietnam. However, make sure you are well informed before signing a contract.
- Consult a local lawyer or professional
- Ensure that the contract specifies the maximum number of classroom hours per day and per week, maximum workdays per week, and vacation periods
- Confirm the living arrangements if any are included
- Ensure that you possess the right visa for the activities you will perform
- Ensure you understand any liabilities linked to early termination of a contract
You must hold a valid Vietnamese driver's licence to drive a vehicle with an engine of 50CC or more. This includes most motorcycles. Motorcycle drivers and passengers must wear a helmet.
The country has a zero-tolerance policy for drinking and driving or cycling. Penalties for drinking and driving or cycling include:
- licence suspension
- heavy fines
If you are involved in a traffic accident as a driver, you may:
- face criminal charges as a driver
- have to pay compensation to the victims
- face a travel ban preventing you from leaving the country until compensation is paid
There are restrictions on vehicles crossing from and into neighbouring countries.
Contact the Department of Transport in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City for information on for licences or restrictions.
Department of Transport in Ho Chi Minh City (in Vietnamese)
The currency of Vietnam is the Vietnamese dong (VND).
Cash declarations
Upon arrival, you must declare if you have:
- more than 15 million Vietnamese dong, more than US$5,000, or the equivalent in any other currency, in cash
- more than 300 grams of gold, including jewellery, gold bar and raw gold
Upon departure, you must:
- declare if you have more than 15 million Vietnamese dong, more than US$5,000, or the equivalent in any other currency, in cash
- present a written approval to carry foreign currency or Vietnamese dong in cash abroad, issued by an authorized Vietnamese credit institution in accordance with the laws on foreign exchange control or the State Bank of Vietnam
Rainy season
The rainy season extends:
- from June to September in the north and south
- from October to December in central Vietnam
Seasonal flooding occurs in October and November in central Vietnam. It’s also common:
- in and around Hanoi, particularly along the Red River
- in the Mekong River Delta regions in the south
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable due to mudslides and landslides. Bridges, buildings, and infrastructure may be damaged.
- Remain vigilant, especially in areas around major rivers
- Stay away from flooded areas
- Monitor weather reports
- Monitor local media for the latest updates, including those on road conditions
- Follow the instructions of local authorities, including evacuation orders
- Mekong Flood and Drought Forecasting - Mekong River Commission
- Forecasting - National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting
Typhoons usually occur from June and December. During this period, even small tropical storms can quickly develop into major typhoons.
These severe storms can put you at risk and hamper the provision of essential services.
If you decide to travel to Vietnam during this period:
- know that you may expose yourself to serious safety risks
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
- Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
- Large-scale emergencies abroad
Humidity and heat may be severe, particularly during the rainy season.
Know the symptoms of dehydration and heatstroke, which can both be fatal.
Forest fires may occur.
The air quality in areas near active fires may deteriorate due to heavy smoke.
In case of a major fire:
- stay away from affected areas, particularly if you suffer from respiratory ailments
- follow the instructions of local emergency services personnel
- monitor local media to stay informed on the evolving situation
Air pollution
Smog and other types of air pollution can be hazardous in urban areas. Air quality can also be affected in rural areas due to agricultural burning.
Air pollution levels can change quickly.
During periods of high pollution:
- limit your outdoor activities, especially if you suffer from respiratory ailments or have pre-existing medical conditions
- monitor local media
- follow the instructions of local authorities
- Air pollution in Hanoi - World Air Quality Index
- Air pollution in Ho Chi Minh City - World Air Quality Index
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 113
- medical assistance: 115
- firefighters: 114
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Vietnam, in Hanoi, or the Consulate General of Canada to Vietnam, in Ho Chi Minh City, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
Featured on

- What is a visa?
- Electronic Visa (eVisa)
- Visa on Arrival
- Appointment Required Visa
- Invitation Letter
- Arrival Card
- Passport Renewal
- Project Kosmos: Meet the man with the world's most challenging travel schedule
- Australia Visa and ETA requirements for US citizens explained
- Brazil eVisa for US citizens
- India Tourist Visa for UK citizens
- Possible B1/B2 Visa questions during the interview
Select Your Language
- Nederlandse
- 中文 (Zhōngwén), 汉语, 漢語
Select Your Currency
- AED United Arab Emirates Dirham
- AFN Afghan Afghani
- ALL Albanian Lek
- AMD Armenian Dram
- ANG Netherlands Antillean Guilder
- AOA Angolan Kwanza
- ARS Argentine Peso
- AUD Australian Dollar
- AWG Aruban Florin
- AZN Azerbaijani Manat
- BAM Bosnia-Herzegovina Convertible Mark
- BBD Barbadian Dollar
- BDT Bangladeshi Taka
- BGN Bulgarian Lev
- BIF Burundian Franc
- BMD Bermudan Dollar
- BND Brunei Dollar
- BOB Bolivian Boliviano
- BRL Brazilian Real
- BSD Bahamian Dollar
- BWP Botswanan Pula
- BZD Belize Dollar
- CAD Canadian Dollar
- CDF Congolese Franc
- CHF Swiss Franc
- CLP Chilean Peso
- CNY Chinese Yuan
- COP Colombian Peso
- CRC Costa Rican Colón
- CVE Cape Verdean Escudo
- CZK Czech Republic Koruna
- DJF Djiboutian Franc
- DKK Danish Krone
- DOP Dominican Peso
- DZD Algerian Dinar
- EGP Egyptian Pound
- ETB Ethiopian Birr
- FJD Fijian Dollar
- FKP Falkland Islands Pound
- GBP British Pound Sterling
- GEL Georgian Lari
- GIP Gibraltar Pound
- GMD Gambian Dalasi
- GNF Guinean Franc
- GTQ Guatemalan Quetzal
- GYD Guyanaese Dollar
- HKD Hong Kong Dollar
- HNL Honduran Lempira
- HTG Haitian Gourde
- HUF Hungarian Forint
- IDR Indonesian Rupiah
- ILS Israeli New Sheqel
- INR Indian Rupee
- ISK Icelandic Króna
- JMD Jamaican Dollar
- JPY Japanese Yen
- KES Kenyan Shilling
- KGS Kyrgystani Som
- KHR Cambodian Riel
- KMF Comorian Franc
- KRW South Korean Won
- KYD Cayman Islands Dollar
- KZT Kazakhstani Tenge
- LAK Laotian Kip
- LBP Lebanese Pound
- LKR Sri Lankan Rupee
- LRD Liberian Dollar
- LSL Lesotho Loti
- MAD Moroccan Dirham
- MDL Moldovan Leu
- MGA Malagasy Ariary
- MKD Macedonian Denar
- MNT Mongolian Tugrik
- MOP Macanese Pataca
- MUR Mauritian Rupee
- MVR Maldivian Rufiyaa
- MWK Malawian Kwacha
- MXN Mexican Peso
- MYR Malaysian Ringgit
- MZN Mozambican Metical
- NAD Namibian Dollar
- NGN Nigerian Naira
- NIO Nicaraguan Córdoba
- NOK Norwegian Krone
- NPR Nepalese Rupee
- NZD New Zealand Dollar
- OMR Omani Rial
- PAB Panamanian Balboa
- PEN Peruvian Nuevo Sol
- PGK Papua New Guinean Kina
- PHP Philippine Peso
- PKR Pakistani Rupee
- PLN Polish Zloty
- PYG Paraguayan Guarani
- QAR Qatari Rial
- RON Romanian Leu
- RSD Serbian Dinar
- RUB Russian Ruble
- RWF Rwandan Franc
- SAR Saudi Riyal
- SBD Solomon Islands Dollar
- SCR Seychellois Rupee
- SEK Swedish Krona
- SGD Singapore Dollar
- SHP Saint Helena Pound
- SLL Sierra Leonean Leone
- SOS Somali Shilling
- SRD Surinamese Dollar
- SVC Salvadoran Colón
- SZL Swazi Lilangeni
- THB Thai Baht
- TJS Tajikistani Somoni
- TOP Tongan Pa anga
- TRY Turkish Lira
- TTD Trinidad and Tobago Dollar
- TWD New Taiwan Dollar
- TZS Tanzanian Shilling
- UAH Ukrainian Hryvnia
- UGX Ugandan Shilling
- USD United States Dollar
- UYU Uruguayan Peso
- UZS Uzbekistan Som
- VND Vietnamese Dong
- VUV Vanuatu Vatu
- WST Samoan Tala
- XAF CFA Franc BEAC
- XCD East Caribbean Dollar
- XOF CFA Franc BCEAO
- XPF CFP Franc
- YER Yemeni Rial
- ZAR South African Rand
- ZMW Zambian Kwacha
We've updated our app!
Download it now
Vietnam vaccination requirements: do I need a vaccine to travel to Vietnam?
If you have travel plans for Vietnam , you should know the requirements and recommendations to enter the country. Local authorities suggest vaccinations for Vietnam entry as there are health risks, especially visiting rural areas. It’s also important to be up to date on the current COVID-19 protocols visiting Vietnam. Most travelers will need a visa to travel to Vietnam.
This may seem like a lot, but don’t worry. iVisa is here to make travel easy for you , and we will help you with all the information you need about routine vaccinations, health risks, and Vietnamese authorities' entry and exit requirements.

You can count on our services for a hassle-free eVisa application and get the documents to enter the country easily and quickly. The entire process is online, so you don’t need to visit an embassy or consulate, and the document will arrive in your email. Remember that without a visa, you will be denied entry.
Read below for more information about disease control protocols, vaccinations for Vietnam, and the steps to get the travel documents you need.

Vietnam vaccine requirements
Vaccinations for vietnam: do i need a vaccine to travel to vietnam.
The Vietnamese Government's local laws don’t require specific vaccinations to travel to Vietnam. However, some vaccines are strongly recommended to visit the country as there is a higher risk of some diseases, especially in rural areas.
You should avoid mosquito bites and be vaccinated against yellow fever, malaria, and Japanese Encephalitis. These are all insect-borne diseases.
Other health risks include infected animals, which is why the rabies vaccination is among the recommended vaccines. Check the vaccines you should have up to date:
Routine vaccines : Chickenpox (Varicella), Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis, Flu (influenza), Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR), Polio, and Shingles.
Hepatitis A ,
Hepatitis B ,
Japanese Encephalitis ,
They aren’t vaccinations needed to enter the country, but the government can request them if you come from other countries that have a Malaria risk or if you will visit rural areas, for example.
Click here to read all the CDC website recommendations. And remember to take simple measures to avoid mosquito bites, such as using insect repellent and avoiding exposed skin in areas with an increased risk of infected mosquitos.
DO I NEED A COVID VACCINE OR VACCINATION CERTIFICATE TO ENTER VIETNAM?
No, you don’t. Currently, COVID-19 vaccination passports or certificates are not mandatory to enter Vietnam. Since information may change quickly, we advise you to contact your local embassy before departure to check the latest medical care protocols.
COVID-19 restrictions
Does the vietnamese government request a covid-19 test to enter vietnam.
No, travelers no longer need to take a COVID-19 test before traveling to Vietnam.
ARE THERE ANY QUARANTINE REQUIREMENTS FOR TRAVELERS TO VIETNAM?
Like the other COVID-19 requirements, the government does not have any quarantine restrictions. There is no quarantine requirement on arrival .
Vietnam Visa
Many travelers can apply for a Vietnam e-Visa to visit the country. This electronic visa was introduced by the Vietnamese immigration department in 2017, intending to facilitate travel for tourists. The Vietnam visa policy enables travelers needing visas to obtain one online without going to a Vietnam embassy.
The Vietnamese e-Visa is now available for citizens of over 80 countries who wish to stay in Vietnam for up to 90 days Per Entry . Travelers must get a Vietnam tourist visa, even for short stays.
Regular passport holders of 25 countries don’t need a visa for Vietnam . The length of stay varies between 14-90 days for each nationality. Those passengers can simply show their passports at border control to get a visa on arrival.
Vietnamese citizens with a Permanent US Resident Card can apply for a Visa Exemption Certificate instead of a visa. Visit Vietnam’s government site for further information.
Some countries may not be eligible for a visa on arrival or the eVisa to travel to Vietnam. In that case, you can use our Visa Checker tool to determine if your nationality qualifies and apply online . Contact your nearest Vietnam embassy if you are in doubt or need another type of visa.
WHAT IS THE VALIDITY OF THE VIETNAM TOURIST E-VISA?
The Vietnam e-Visa is valid for 30 days after arrival in Total from the entry date. It is a Multiple Entry . Visitors wishing to stay longer than the duration of a standard tourist visa or e-visa will need a visa extension. They can request this document at the nearest Vietnam embassy.
WHAT ARE THE ENTRY REQUIREMENTS AND DOCUMENTS TO APPLY FOR THE VIETNAM E-VISA?
Below is a list of the current requirements for your application form and entry into Vietnam:
Passport : You must have a passport that is valid for at least six months from the date of arrival in Vietnam. The passport must have at least two blank pages for an entry and exit stamp (one on each page).
Recent passport photo : If you don't have one, no problem! Simply use the iVisa Passport Photo Service .
Health insurance : You will need to show proof of medical or travel insurance with coverage for COVID-19 medical treatment in Vietnam, with a minimum cover of USD 10,000 for medical services.
Method of payment : Credit or debit card to pay the e-visa fees.
Valid email address : To receive your e-visa receipt and confirmation.
DO I NEED A VIETNAM VISA IF I AM TRANSITING?
The Vietnam visa requirement is not applicable to air travelers transiting the country, provided they remain in the transit area at the airport and do not stay more than 24 hours. If you plan to leave the airport anytime, you must apply for the eVisa online before departure.
HOW TO APPLY FOR YOUR VIETNAM VISA ONLINE
It is recommended that you apply for your visa at least a few weeks prior to your trip to Vietnam, but if you're in a rush, we have you covered. The whole process is very simple:
First , read all of the information and provide your details. Then, choose the preferred processing time for the Vietnam e-visa.
Second , double-check and confirm your information and pay the iVisa service fee (see below for information about visa fees).
Third , attach any required documents and click on the ‘submit’ button to apply for your Vietnam visa. Once you have successfully applied for your Vietnam visa, you will receive a receipt and confirmation of the final e-Visa.
Make sure to save a copy in a safe place on your electronic device, and print your Vietnam e-visa confirmation to carry with you while you travel. Upon arrival, the Vietnam immigration department may ask you to present it.
WHAT ARE THE PRICES AND PROCESSING TIMES OF THE VIETNAM VISA?
If you apply through iVisa, the processing time and charges will depend upon how fast you need your visa:
Standard processing time : Get your Vietnam visa in 10 days for a fee of USD $112.99 .
Rush processing service : This option is slightly faster and takes 8 days for a fee of USD $159.99 .
Super Rush processing time : For those urgently needing a Vietnam visa, we offer this option, which takes just 6 days for a fee of USD $174.99 .
VIETNAM E-VISA SAMPLE

Is it safe to apply through iVisa?
Applying for your visa with iVisa couldn’t be more reliable. Although we are not affiliated with Vietnam’s government, we are a certified travel agency with a competent review team that will thoroughly handle your application in the most effective way . You may also view what our customers have to say about us and our whole set of services here .
Where can I find more information about the visa application?
You can contact iVisa’s customer care portal to find more information about the application process and the vaccination rules to travel to Vietnam and gather all of the needed information from there. If you prefer, you can email your questions to [email protected] .
iVisa recommends
Vietnam is a country in Asia that has a lot to offer. Tourists can explore its beaches, cities, and rivers. With French-colonial architecture Vietnam is culturally rich but has endured challenging historical moments, such as the infamous Vietnam War. In addition to the culture and beautiful landscapes, gastronomy is another excellent reason to visit the country: there are many lip-smacking dishes to try.
Vietnam also has cities full of features that will leave the tourists awe-struck. Ho Chi Minh City (formerly Saigon) has French colonial sites, Vietnam War history museums, and the Củ Chi tunnels used by Viet Cong soldiers. On the other hand, the capital Hanoi pays tribute to the nation’s iconic communist-era leader Ho Chi Minh with a massive marble mausoleum.
For those looking for paradisaic natural places, Ha Long Bay is worth visiting. It’s in northeast Vietnam and is known for its emerald waters and thousands of towering limestone islands. You can enjoy boat tours and sea kayak expeditions to explore the area.
Count on iVisa services to be ready for this fantastic trip!
Where can I contact you?
If you still have any concerns about vaccination requirements to visit Vietnam, you can chat with our experts from customer service , or you can send an email to [email protected] . They will be happy to assist you with anything you need 24/7.
Related Articles

Vietnam eVisa for Brazilian citizens

Vietnam eVisa for Polish citizens

Vietnam eVisa for Dutch citizens
- iVisa is NOT affiliated with any government agency. This site does not provide legal advice and we are not a law firm. None of our customer service representatives are lawyers and they also do not provide legal advice. We are a private, internet-based travel and immigration consultancy provider dedicated to helping individuals travel around the world. You may apply by yourself directly on the various government websites. The source of information: https://www.vietnam.gov.vn
- COUNTRY INFORMATION
- LATEST NEWS
- OUTBREAK SURVEILLANCE
- TOPICS IN BRIEF
- FACTSHEETS & RESOURCES
- WORLD OVERVIEW

Capital City: Hanoi
Official Languages: Vietnamese
Monetary Unit: dong (VND)
- General Information
- Vaccine Recommendations
- Other Risks
TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS ARE IN PLACE FOR THIS COUNTRY
There are entry requirements for anyone who plans to travel to England from this country. Please check here for further information. Advice may vary in Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
The information on these pages should be used to research health risks and to inform the pre-travel consultation.
Due to COVID-19, travel advice is subject to rapid change. Countries may change entry requirements and close their borders at very short notice. Travellers must ensure they check current Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) travel advice in addition to the FCDO specific country page (where available) which provides additional information on travel restrictions and entry requirements in addition to safety and security advice.
Travellers should ideally arrange an appointment with their health professional at least four to six weeks before travel. However, even if time is short, an appointment is still worthwhile. This appointment provides an opportunity to assess health risks taking into account a number of factors including destination, medical history, and planned activities. For those with pre-existing health problems, an earlier appointment is recommended.
All travellers should ensure they have adequate travel health insurance .
A list of useful resources including advice on how to reduce the risk of certain health problems is available below.
- Food and water hygiene
- Insect and tick bite avoidance
- Personal safety
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Sun protection
Details of vaccination recommendations and requirements are provided below.
All travellers
Travellers should be up to date with routine vaccination courses and boosters as recommended in the UK . These vaccinations include for example measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine and diphtheria-tetanus-polio vaccine.
Country-specific diphtheria recommendations are not provided here. Diphtheria tetanus and polio are combined in a single vaccine in the UK. Therefore, when a tetanus booster is recommended for travellers, diphtheria vaccine is also given. Should there be an outbreak of diphtheria in a country, diphtheria vaccination guidance will be provided.
Those who may be at increased risk of an infectious disease due to their work, lifestyle choice, or certain underlying health problems should be up to date with additional recommended vaccines. See the individual chapters of the 'Green Book' Immunisation against infectious disease for further details.
Certificate requirements
There are no certificate requirements under International Health Regulations.
Most travellers
The vaccines in this section are recommended for most travellers visiting this country. Information on these vaccines can be found by clicking on the blue arrow. Vaccines are listed alphabetically.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral infection transmitted through contaminated food and water or by direct contact with an infectious person. Symptoms are often mild or absent in young children, but the disease can be more serious with advancing age. Recovery can vary from weeks to months. Following hepatitis A infection immunity is lifelong.
All travellers should take care with personal, food and water hygiene.
Hepatitis A vaccination
As hepatitis A vaccine is well tolerated and affords long-lasting protection, it is recommended for all previously unvaccinated travellers.
Hepatitis A in brief
Tetanus is caused by a toxin released from Clostridium tetani bacteria and occurs worldwide. Tetanus bacteria are present in soil and manure and may be introduced through open wounds such as a puncture wound, burn or scratch.
Travellers should thoroughly clean all wounds and seek medical attention for injuries such as animal bites/scratches, burns or wounds contaminated with soil.
Tetanus vaccination
- Travellers should have completed a tetanus vaccination course according to the UK schedule.
- If travelling to a country or area where medical facilities may be limited, a booster dose of a tetanus-containing vaccine is recommended if the last dose was more than ten years ago even if five doses of vaccine have been given previously.
Country-specific information on medical facilities may be found in the 'health' section of the FCDO foreign travel advice pages.
Tetanus in brief
Typhoid is a bacterial infection transmitted through contaminated food and water. Previous typhoid illness may only partially protect against re-infection.
Vaccination is recommended for most travellers, particularly travellers visiting friends and relatives, those in contact with an infected person, young children, frequent or long-stay travellers visiting areas where sanitation and food hygiene are likely to be poor, and laboratory personnel who may handle the bacteria for their work.
Typhoid vaccination
- Oral and injectable typhoid vaccinations are available.
Typhoid in brief
Some travellers.
The vaccines in this section are recommended for some travellers visiting this country. Information on when these vaccines should be considered can be found by clicking on the arrow. Vaccines are listed alphabetically.
Cholera is a bacterial infection transmitted by contaminated food and water. Cholera can cause severe watery diarrhoea although mild infections are common. Most travellers are at low risk.
Cholera vaccination
This oral vaccine is recommended for those whose activities or medical history put them at increased risk. This includes:
- aid workers.
- those going to areas of cholera outbreaks who have limited access to safe water and medical care.
- those for whom vaccination is considered potentially beneficial.
Cholera in brief
Hepatitis b.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection; it is transmitted by exposure to infected blood or body fluids. This mostly occurs during sexual contact or as a result of blood-to-blood contact (for example from contaminated equipment during medical and dental procedures, tattooing or body piercing procedures, and sharing of intravenous needles). Mothers with the virus can also transmit the infection to their baby during childbirth.
Hepatitis B in Vietnam
2% or more of the population are known or thought to be persistently infected with the hepatitis B virus (intermediate/high prevalence).
Travellers should avoid contact with blood or body fluids. This includes:
- avoiding unprotected sexual intercourse.
- avoiding tattooing, piercing, public shaving, and acupuncture (unless sterile equipment is used).
- not sharing needles or other injection equipment.
- following universal precautions if working in a medical/dental/high risk setting.
A sterile medical equipment kit may be helpful when travelling to resource poor areas.
Hepatitis B vaccination
Vaccination could be considered for all travellers, and is recommended for those whose activities or medical history put them at increased risk including:
- those who may have unprotected sex.
- those who may be exposed to contaminated needles through injecting drug use.
- those who may be exposed to blood or body fluids through their work (e.g. health workers).
- those who may be exposed to contaminated needles as a result of having medical or dental care e.g. those with pre-existing medical conditions and those travelling for medical care abroad including those intending to receive renal dialysis overseas.
- long-stay travellers.
- those who are participating in contact sports.
- families adopting children from this country.
Hepatitis B in brief
Japanese encephalitis.
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is a viral infection transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected mosquito. These mosquitoes usually bite between dusk and dawn, mainly in rural areas; especially where there are rice fields, swamps and marshes. Mosquitoes become infected by biting JE infected animals (particularly pigs) or birds.
Travellers are at increased risk of infection when visiting rural areas. Short trips (usually less than a month) especially if only travelling to urban areas, are considered lower risk.
Japanese encephalitis in Vietnam
JE occurs in this country, with year-round transmission in the south and from May to October in the north. Cases may be reported outside these months in the north of the country.
All travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly between dusk and dawn.
Japanese encephalitis vaccination
- Vaccination is recommended for those whose activities put them at increased risk (see above).
- Vaccination could be considered for those on shorter trips if the risk is considered to be sufficient e.g. those spending time in areas where the mosquito breeds such as rice fields, marshlands, or pig farming areas.
Japanese encephalitis in brief
Rabies is a viral infection which is usually transmitted following contact with the saliva of an infected animal most often via a bite, scratch or lick to an open wound or mucous membrane (such as on the eye, nose or mouth). Although many different animals can transmit the virus, most cases follow a bite or scratch from an infected dog. In some parts of the world, bats are an important source of infection.
Rabies symptoms can take some time to develop, but when they do, the condition is almost always fatal.
The risk of exposure is increased by certain activities and length of stay (see below). Children are at increased risk as they are less likely to avoid contact with animals and to report a bite, scratch or lick.
Rabies in Vietnam
Rabies is considered a risk and has been reported in domestic animals in this country. Bats may also carry rabies-like viruses.
- Travellers should avoid contact with all animals. Rabies is preventable with prompt post-exposure treatment.
- Following a possible exposure, wounds should be thoroughly cleansed and an urgent local medical assessment sought, even if the wound appears trivial.
- Post-exposure treatment and advice should be in accordance with national guidelines.
Rabies vaccination
A full course of pre-exposure vaccines simplifies and shortens the course of post-exposure treatment and removes the need for rabies immunoglobulin which is in short supply world-wide.
Pre-exposure vaccinations are recommended for travellers whose activities put them at increased risk including:
- those at risk due to their work (e.g. laboratory staff working with the virus, those working with animals or health workers who may be caring for infected patients).
- those travelling to areas where access to post-exposure treatment and medical care is limited.
- those planning higher risk activities such as running or cycling.
- long-stay travellers (more than one month).
Rabies in brief
Tuberculosis.
TB is a bacterial infection most commonly affecting the lungs but can affect any part of the body. When a person with TB in their lungs or throat coughs or sneezes they could pass TB on to other people. TB is curable but can be serious if not treated.
The BCG vaccination helps to protect some people, particularly babies and young children who are at increased risk from TB.
Tuberculosis in Vietnam
This country has reported an annual TB incidence of greater than or equal to 40 cases per 100,000 population at least once in the last five years ( further details ).
Travellers should avoid close contact with individuals known to have infectious pulmonary (lung) or laryngeal (throat) TB.
Those at risk during their work (such as healthcare workers) should take appropriate infection control and prevention precautions.
Tuberculosis (BCG) vaccination
BCG vaccine is recommended for those at increased risk of developing severe disease and/or of exposure to TB infection. See UK Health Security Agency Immunisation against infectious disease, the 'Green Book '.
For travellers, BCG vaccine is recommended for:
- unvaccinated, children under 16 years of age, who are going to live for more than 3 months in this country. A tuberculin skin test is required prior to vaccination for all children from 6 years of age and may be recommended for some younger children.
- unvaccinated, tuberculin skin test-negative individuals at risk due to their work such as healthcare or laboratory workers who have direct contact with TB patients or potentially infectious clinical material and vets and abattoir workers who handle animal material, which could be infected with TB.
There are specific contraindications to BCG vaccine. Health professionals must be trained and assessed as competent to administer this vaccine intradermally.
Following administration, no further vaccines should be administered in the same limb for 3 months.
The BCG vaccine is given once only, booster doses are not recommended.
Tuberculosis in brief
Malaria is a serious illness caused by infection of red blood cells with a parasite called Plasmodium. The disease is transmitted by mosquitoes which predominantly feed between dusk and dawn.
Symptoms usually begin with a fever (high temperature) of 38°C (100°F) or more. Other symptoms may include feeling cold and shivery, headache, nausea, vomiting and aching muscles. Symptoms may appear between eight days and one year after the infected mosquito bite.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment is required as people with malaria can deteriorate quickly. Those at higher risk of malaria, or of severe complications from malaria, include pregnant women, infants and young children, the elderly, travellers who do not have a functioning spleen and those visiting friends and relatives.
Travellers should follow an ABCD guide to preventing malaria:
A wareness of the risk – Risk depends on the specific location, season of travel, length of stay, activities and type of accommodation.
B ite prevention – Travellers should take mosquito bite avoidance measures.
C hemoprophylaxis – Travellers should take antimalarials (malaria prevention tablets) if appropriate for the area (see below). No antimalarials are 100% effective but taking them in combination with mosquito bite avoidance measures will give substantial protection against malaria.
D iagnosis – Travellers who develop a fever of 38°C [100°F] or higher more than one week after being in a malaria risk area, or who develop any symptoms suggestive of malaria within a year of return should seek immediate medical care. Emergency standby treatment may be considered for those going to remote areas with limited access to medical attention.
- There is a low risk of malaria in the southern part of the country in the provinces of Tay Ninh, Lam Dong, Dak Lak, Gia Lai, and Kon Tum, and other rural areas of Vietnam: awareness of risk and bite avoidance recommended.
- There is no risk in large cities, including Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh (Saigon), the Red River delta, coastal areas north of Nha Trang and Phu Quoc Island: bite avoidance recommended.
Special risk groups
In low risk areas, antimalarials may be considered in exceptional circumstances for travellers who are at higher risk of malaria (such as long term travellers visiting friends and relatives), or of severe complications from malaria (such as the elderly [over 70 years], the immunosuppressed, those with complex co-morbidities, pregnant women, infants and young children). The final decision whether or not to advise antimalarials rests with the travel health advisor and the traveller after individual risk assessment.
Travellers with an absent or poorly functioning spleen should be dissuaded from travel to any area with risk of malaria. Where travel is essential awareness, rigorous bite avoidance and antimalarials should be advise, even for the low risk areaa.
For special risk groups, you may wish to seek specialist advice. For the low risk areas in this country/area atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline would be suitable options.
Antimalarial recommendations map

- Click on map to open in a new window
- Malaria in brief
- Malaria factsheet
- Children's antimalarial dose table
- Malaria prevention guidelines for travellers from the UK
There are some risks that are relevant to all travellers regardless of destination. These may for example include road traffic and other accidents, diseases transmitted by contaminated food and water, sexually transmitted infections, or health issues related to the heat or cold.
Some additional risks (which may be present in all or part of this country) are mentioned below and are presented alphabetically. Select risk to expand information.
There is a risk of altitude illness when travelling to destinations of 2,500 metres (8,200 feet) or higher. Important risk factors are the altitude gained, rate of ascent and sleeping altitude. Rapid ascent without a period of acclimatisation puts a traveller at higher risk.
There are three syndromes; acute mountain sickness (AMS), high-altitude cerebral oedema (HACE) and high-altitude pulmonary oedema (HAPE). HACE and HAPE require immediate descent and medical treatment.
Altitude illness in Vietnam
There is a point of elevation in this country higher than 2,500 metres. An example place of interest: Mt Fansipan 3,143m.
- Travellers should spend a few days at an altitude below 3,000m.
- Where possible travellers should avoid travel from altitudes less than 1,200m to altitudes greater than 3,500m in a single day.
- Ascent above 3,000m should be gradual. Travellers should avoid increasing sleeping elevation by more than 500m per day and ensure a rest day (at the same altitude) every three or four days.
- Acetazolamide can be used to assist with acclimatisation, but should not replace gradual ascent.
- Travellers who develop symptoms of AMS (headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea and sleep disturbance) should avoid further ascent. In the absence of improvement or with progression of symptoms the first response should be to descend.
- Development of HACE or HAPE symptoms requires immediate descent and emergency medical treatment.
Altitude illness in brief
Biting insects or ticks.
Insect or tick bites can cause irritation and infections of the skin at the site of a bite. They can also spread certain diseases.
Diseases in South-eastern Asia
There is a risk of insect or tick-borne diseases in some areas of South-eastern Asia. This includes diseases such as chikungunya , leishmaniasis and scrub typhus .
- All travellers should avoid insect and tick bites day and night.
- There are no vaccinations (or medications) to prevent these diseases.
Further information about specific insect or tick-borne diseases for this country can be found, if appropriate on this page, in other sections of the country information pages and the insect and tick bite avoidance factsheet .
Dengue is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes which mainly feed during daytime hours. It causes a flu-like illness, which can occasionally develop into a more serious life-threatening illness. Severe dengue is rare in travellers.
The mosquitoes that spread dengue are more common in towns, cities and surrounding areas.
Dengue in Vietnam
There is a risk of dengue in this country.
- Travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly during daytime hours.
- A dengue vaccine is licensed in the UK for the prevention of dengue disease in individuals from 4 years of age. The Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) and World Health Organization are in the process of reviewing the product information. Recommendations on the use of this vaccine will be published in due course.
Dengue in brief
Seasonal influenza is a viral infection of the respiratory tract and spreads easily from person to person via respiratory droplets when coughing and sneezing. Symptoms appear rapidly and include fever, muscle aches, headache, malaise (feeling unwell), cough, sore throat and a runny nose. In healthy individuals, symptoms improve without treatment within two to seven days. Severe illness is more common in those aged 65 years or over, those under 2 years of age, or those who have underlying medical conditions that increase their risk for complications of influenza.
Seasonal influenza in Vietnam
Seasonal influenza occurs throughout the world. In the northern hemisphere (including the UK), most influenza occurs from as early as October through to March. In the southern hemisphere, influenza mostly occurs between April and September. In the tropics, influenza can occur throughout the year.
All travellers should:
- Avoid close contact with symptomatic individuals
- Avoid crowded conditions where possible
- Wash their hands frequently
- Practise ‘cough hygiene’: sneezing or coughing into a tissue and promptly discarding it safely, and washing their hands
- Avoid travel if unwell with influenza-like symptoms
- A vaccine is available in certain circumstances (see below)*
*In the UK, seasonal influenza vaccine is offered routinely each year to those at higher risk of developing of severe disease following influenza infection, and certain additional groups such as healthcare workers and children as part of the UK national schedule (see information on vaccination ). For those who do not fall into these groups, vaccination may be available privately.
If individuals at higher risk of severe disease following influenza infection are travelling to a country when influenza is likely to be circulating they should ensure they received a flu vaccination in the previous 12 months.
The vaccine used in the UK protects against the strains predicted to occur during the winter months of the northern hemisphere. It is not possible to obtain vaccine for the southern hemisphere in the UK, but the vaccine used during the UK influenza season should still provide important protection against strains likely to occur during the southern hemisphere influenza season, and in the tropics.
Avian influenza
Avian influenza viruses can rarely infect and cause disease in humans. Such cases are usually associated with close exposure to infected bird or animal populations. Where appropriate, information on these will be available in the outbreaks and news sections of the relevant country pages. Seasonal influenza vaccines will not provide protection against avian influenza.
Avian influenza in brief
Outdoor air quality.
Poor air quality is a significant public health problem in many parts of the world. Exposure to high levels of air pollution over short time periods (e.g. minutes/hours/days) and longer time periods (e.g. years) is linked to many different acute and chronic health problems. These effects are mainly on the respiratory (lungs and airways) and cardiovascular (heart function and blood circulation) systems.
Current information on world air quality is available from the world air quality index project .
Travellers with health problems that might make them more vulnerable to the effects of air pollution who are travelling to areas of high pollution should:
- discuss their travel plans with their doctor, and carry adequate supplies of their regular medication.
- take sensible precautions to minimise their exposure to high levels of air pollution.
- check local air quality data and amend their activities accordingly.
- take notice of any health advisories published by the local Ministry of Health and Department for Environment, and follow the guidance provided.
It is unclear if face masks are beneficial at reducing exposure and may make breathing more difficult for those with pre-existing lung conditions. Those who choose to use one should make sure that the mask fits well and know how to wear it properly.
Outdoor air quality in brief
Zika virus (ZIKV) is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes which predominantly feed during daytime hours. A small number of cases of sexual transmission of ZIKV have also been reported. Most people infected with ZIKV have no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they are usually mild and short-lived. Serious complications and deaths are not common. However, ZIKV is a cause of Congenital Zika Syndrome (microcephaly and other congenital anomalies) and neurological complications such as Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Zika virus in Vietnam
There is a risk of Zika virus in this country. Details of specific affected areas within this country are not available, but information on current outbreaks where available will be reported on our outbreak surveillance database.
Pregnant women should discuss the suitability of travel and the potential risk that Zika virus may present with their health care provider.
- All travellers should avoid mosquito bites particularly during daytime hours.
- There is no vaccination or medication to prevent Zika virus infection.
- Women should avoid becoming pregnant while travelling in this country, and for 2 months (8 weeks) after their last possible Zika virus exposure* (see below if male partner has travelled).
- If a woman develops symptoms compatible with Zika virus infection, it is recommended she avoids becoming pregnant for a further 2 months following recovery.
- Women who visited this country while pregnant, or who become pregnant within 2 months after their last possible Zika virus exposure*, should contact their GP, obstetrician or midwife for further advice, even if they have not been unwell.
Please note screening of returning travellers without Zika virus symptoms is not available on the NHS. Couples planning pregnancy in the very near future should consider whether they should avoid travel to a country or area with risk of Zika virus, rather than delay conception for the recommended period (see below) after travel. This particularly includes couples in assisted fertility programmes.
Prevention of sexual transmission
Couples should follow guidance on prevention of sexual transmission of Zika virus and avoid conception as follows:
- If both partners travelled, for 3 months after last possible Zika virus exposure*
- Male traveller only, for 3 months after last possible Zika virus exposure*
- Female traveller only, for 2 months after last possible Zika virus exposure*
See further information for pregnant women, their partners and couples planning pregnancy .
*Last possible Zika virus exposure is defined as the later of either the date of leaving a country or area with risk for Zika virus transmission, or the date on which unprotected sexual contact with a potentially infectious partner took place.
See detailed guidance on factors to consider when assessing the risk of Zika virus.
Zika virus in brief
COVID-19 disease is caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV2. The main symptoms of COVID-19 are a new continuous cough, a high temperature, and a loss of, or change in, normal sense of taste or smell. Symptoms range from mild to life-threatening. Older people and those with underlying health problems are more likely to develop severe disease.
COVID-19 is spread through close contact with people who have the virus. It is mainly transmitted from person to person by breathing in droplets produced when someone infected with the virus breathes, speaks, coughs or sneezes. It is also spread by touching the infected droplets on surfaces, then touching the eyes, nose or mouth.
COVID-19 vaccines provide high levels of protection against severe illness, hospitalisation, or dying from the virus. Vaccination against COVID-19 reduces, but does not eliminate the risk of infection, so social distancing and personal and respiratory hygiene remain important interventions, particularly during overseas travel.
Travellers should always check the UK Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO) travel advice and their country-specific pages for the latest COVID-19 travel advisories which may include information on travel restrictions, quarantine, COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements. This includes considering the recommendations and requirements for any transit countries.
Travellers should be aware that COVID-19 case numbers in individual countries/areas can increase rapidly, and healthcare capacity and country requirements can change at short notice.
COVID-19 in Vietnam
Most countries worldwide present a risk of exposure to COVID-19. The risk of COVID-19, public health policy, and travel advice or restrictions may change quickly, therefore travellers should ensure they have access to up to date information on COVID-19 and be prepared for rapid changes in guidance both before and during travel.
All travellers should check the FCDO travel advice and carefully consider their personal situation and risks of COVID-19 before travel to this country. This is particularly important in those at higher risk from COVID-19 who may wish to seek medical advice before travel.
Individuals entering or returning to the UK may be required to follow additional UK border measures .
If travelling to this country, travellers should:
- Consider the risk at all destinations including any transit countries, and the risk during travel itself.
- Check with the airline/tour operator about preventive measures in place to reduce risk during travel.
- Follow the latest guidance on social distancing and face coverings, including any local requirements and maintain good hand, respiratory, and personal hygiene at all times. This may be particularly important if staying with friends and family.
- Ensure they are up to date with their COVID-19 vaccination courses and boosters as recommended in the UK vaccination programme.
See guidance on factors to consider when assessing the risk of COVID-19 for travellers .
If travellers develop COVID-19 symptoms while abroad, they should:
- Follow local guidelines on self-isolation, testing and avoiding travel.
- Contact their travel insurance provider.
- Seek medical advice if needed.
COVID-19 in brief

Lunar New Year: Travel advice
Celebrating the Lunar New Year abroad? Lunar New Year is a public holiday celebrated across several days in many countries worldwide

Changes to the Country Information pages: Zika
UK Health Security Agency and NaTHNaC have reviewed and updated country-specific Zika information and prevention advice

Malaria: a reminder for travellers over the winter holiday season
Advice for travellers and health professionals about malaria
Using information collated from a variety of sources, we regularly review and update information on overseas disease outbreaks and other health issues that may affect the UK traveller.
Please note that not all cases of disease or outbreaks are reported ; some diseases may only be reported if they occur outside of the usual recognised risk area or season, or they have been reported in greater than usual numbers.
Further information on the Outbreak Surveillance section.
Influenza A(H9N2) in Vietnam
As of 7 April 2024, the Vietnam Department of Information and Communications reported a confirmed human case of avian influenza A(H9N2) infection. This is the first confirmed human case of avian influenza A(H9N2) reported in Vietnam. To date, no further cases have been detected among close contacts.

Foreign travel advice

FEEDBACK SURVEY
Personal information:, successfully submitted .
UK Health Security Agency
Hospital for Tropical Diseases
Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine
London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Bank Holiday
There will be changes to delivery and our customer service hours over the Early May Bank Holiday. Stay up to date here .
- Vietnam Tourism
- Vietnam Hotels
- Vietnam Bed and Breakfast
- Vietnam Vacation Rentals
- Flights to Vietnam
- Vietnam Restaurants
- Things to Do in Vietnam
- Vietnam Travel Forum
- Vietnam Photos
- All Vietnam Hotels
- Vietnam Hotel Deals
- Last Minute Hotels in Vietnam
- Things to Do
- Restaurants
- Vacation Rentals
- Travel Stories
- Rental Cars
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travelers' Choice
- Help Center
Does Typhoid vaccine prevent travelers stomach bugs? - Vietnam Forum
- Asia
- Vietnam
Does Typhoid vaccine prevent travelers stomach bugs?
- United States Forums
- Europe Forums
- Canada Forums
- Asia Forums
- Central America Forums
- Africa Forums
- Caribbean Forums
- Mexico Forums
- South Pacific Forums
- South America Forums
- Middle East Forums
- Honeymoons and Romance
- Business Travel
- Train Travel
- Traveling With Disabilities
- Tripadvisor Support
- Solo Travel
- Bargain Travel
- Timeshares / Vacation Rentals
- Asia forums
- Vietnam forum

11 replies to this topic

Hope the above helps. Getting vaccinated won’t be a waste of money in my opinion.
- Mosquito Repellant - what seems effective in South Vietnam 6:37 am
- Halong Bay seaplane trip from Hanoi 6:20 am
- New routeplans, suggestions for Hanoi,Cao Bang area. 6:14 am
- Itinerary August 6:02 am
- Any Reliable Driver/Guide from DaNang to Hue to Phong Nha 5:59 am
- Best e-SIM for Vietnam? 3:48 am
- What to do instead of the ha giang loop 3:43 am
- Hai Phong 3:20 am
- Itinerary suggestion for 7-8 days in Ho Chi Minh 11:56 pm
- Day trip to Halong Bay or 2 days 1 night 11:10 pm
- Guitar yesterday
- Mozzies? yesterday
- Hanoi Airport - eSim yesterday
- Evisa express yesterday
- When Best To Visit Vietnam? Weather? 4 replies
- Beach near Ho Chi Minh 6 replies
- visa on arrival 124 replies
- Beach resort near Ho Chi Minh City - any suggestions? 4 replies
- power plug adapters 7 replies
- Paradise Resort Doc let beach 7 replies
- SaiGon to Rach Gia by bus 4 replies
- Top 5 Places to Visit in Vietnam 11 replies
- Mekong Express Limousine Bus Contact Details?? 9 replies
- Phuong Trang bus from Da lat to Ho Chi Minh ? 22 replies
Vietnam Hotels and Places to Stay
- FAQ - E-Visa information Aug2023
- Best ATM to use
- Sim Card info
- Halong Junks Official Website???
- Do I have to give the hotel reception my passport?


Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise normal safety precautions in Vietnam.
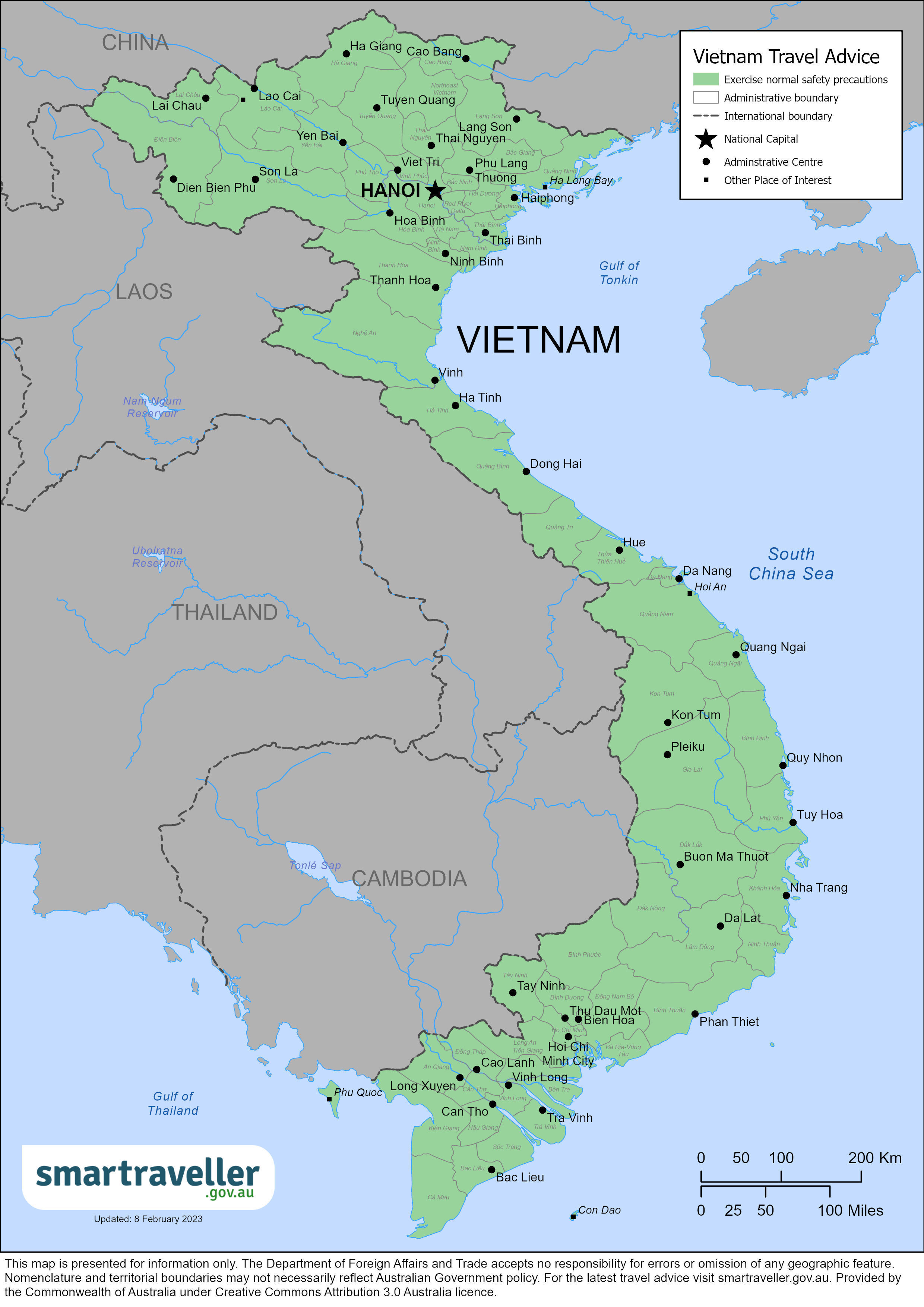
Vietnam (PDF 920.32 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies, advice levels.
Exercise normal safety precautions in Vietnam.
- Road accidents are a major cause of injury. Be alert at all times on the roads.
- Petty theft, including bag slashing, is common in tourist areas and crowded places, especially during holiday times. Snatch-and-grab theft by thieves on motorcycles is also common. Hold bags and backpacks in front of you or on the opposite side to the traffic to make them harder to steal. Be aware of motorbikes approaching as you walk. Carry the minimum amount of valuables. Be prepared to surrender your valuables rather than risk being injured in a struggle.
- Aggravated theft, sexual assault and assault happen. Travellers have been assaulted after having their food or drinks spiked. Pay attention when your drinks are being mixed. Get urgent medical help if you suspect drink spiking.
- Personal or commercial disputes sometimes lead to threats of physical violence or death. Have a clear agreement on the expected level of service. Report any threats to police.
- Travellers have been robbed withdrawing money from ATMs. Credit and debit card fraud and card skimming happen across Vietnam. Taxi and gambling scams are also common. Only use ATMs in banks and shopping centres. Always keep your credit card in sight. Use metered or prearranged taxis, especially at airports. Report gambling scams to police.
- During the rainy season (June to November), floods, typhoons and severe weather can disrupt essential services. Follow the advice of local officials.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Air pollution levels can be high in Vietnam, particularly in large cities.
- Insect-borne diseases such as dengue, Japanese encephalitis, malaria and zika virus are a risk. If you’re pregnant, discuss your travel plans with your doctor. Use insect repellent. Get vaccinated before you travel. Consider taking anti-malarial medication.
- Rabies occurs in Vietnam, especially in the north. It’s fatal without treatment. If you’re bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help immediately.
- HIV/AIDS is a risk. Take precautions if you’re taking part in high-risk activities.
- Diphtheria is a risk. Ensure your vaccinations are up-to-date.
- Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is common. It mainly affects children and young adults. Foodborne, waterborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases include cholera, hepatitis and typhoid. Wash your hands well and often. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don’t use or carry illegal drugs, including marijuana. Penalties for drug offences include the death penalty and life imprisonment. Never carry parcels or luggage for others.
- Get professional legal advice before signing any contract. If you're in a business or civil dispute, officials could stop you leaving Vietnam until it’s resolved.
- It's illegal to gamble in a non-government licensed casino or possess pornography. Non-state sanctioned political or religious activity or material, or involvement with groups perceived by the Government of Vietnam to be associated with dissident groups, is also illegal.
- It’s illegal to export antiques without a permit. Get a permit from the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (Vietnamese) . It’s illegal to photograph border areas or military sites. Be careful when taking photos.
- Possessing or distributing images or objects linked to the former Republic of Vietnam, including commemorative or Vietnam War service-related items, is an offence that could attract harsh penalties.
- Vietnam recognises dual nationality in limited situations. If you're a dual national, travel on your Australian passport. You may need to do compulsory military service. Contact your nearest Vietnamese embassy or consulate for details.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You must have an appropriate visa before travelling to Vietnam. You can apply online for an eVisa for tourism or business purposes. If approved, the eVisa allows for a stay of up to 90 days and is valid for multiple entries. Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for the latest details.
- You must check your details are correct when applying for a visa. The visa details must match exactly the information on your passport's biodata page, such as your full name and date of birth. Any errors or name omissions may result in you being refused entry. You may be charged a significant fee at check-in or on arrival to correct the visa error.
- If you're travelling with prescription medication, check the value and quantity restrictions on the import and export of prescription medication with the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam .
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can’t do to help you overseas.
- For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Hanoi , or the Australian Consulate-General in Ho Chi Minh City .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy’s social media accounts
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Petty crime.
Petty crime, street crime and harassment happen, especially in larger cities.
Bag slashing is common in tourist areas, at markets, on crowded trains and buses, and at supermarkets. It increases in the lead up to and during Vietnamese and Western holiday periods.
Thieves on motorcycles commit snatch-and-grab crimes against pedestrians. This happens often and sometimes results in injury.
Thieves steal valuables, such as jewellery, handbags, mobile phones and cameras.
To protect your belongings:
- take care crossing the street or walking along footpaths
- be aware of motorcycles approaching from behind as you walk on the footpath
- hold bags and backpacks in front of you or in ways that make them harder to snatch
- carry only what you need and leave other valuables in a secure location
- be prepared to surrender your valuables rather than risk being injured in a struggle
Violent crime
Aggravated theft, sexual assault and assault happen. Hot spots include:
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Sapa, especially on the train to and from Lao Cai
- Cat Ba Island, near Ha Long Bay
Reports of groping and other sexual assault are rising.
Drink spiking occurs. Foreigners have been robbed and sexually assaulted after having spiked food and drinks. This happens at late-night establishments in major cities.
To protect yourself from drink spiking:
- only drink alcohol at reputable places
- pay attention when your alcoholic drinks are being mixed
- stay with people you trust in bars and at nightclubs
If you think your drink or a friend's drink has been spiked, get urgent medical attention.
If you're a victim of a violent crime, especially sexual assault, get medical attention. There is a risk of contracting HIV/AIDS, hepatitis and other sexually transmitted diseases in Vietnam.
Although gun violence is uncommon in Vietnam, there have been isolated incidents in recent years.
Travellers have been robbed after withdrawing money from ATMs.
Break-ins to hotels and private homes are reported. This happens even while guests are in their rooms.
To protect yourself from robbery :
- only use ATMs in banks and shopping centres
- make sure your hotel room is locked at all times, including when you're inside
- pay close attention to your personal belongings, especially in crowded areas
- be alert on overnight trains and buses and on quiet stretches of road
Report thefts straight away to the local police and hotel management.
Personal or commercial arguments sometimes lead to threats of physical violence or death.
If you're threatened with violence, report it to local police.
To avoid commercial disputes, have a clear agreement on what the expected level of service is.
Many travellers have become victims of credit and debit card, taxi and gambling scams .
Credit and debit card skimming is where card data is taken for use in fraudulent transactions. This happens throughout Vietnam.
Some Australians have lost thousands of dollars after accepting invitations to private homes from friendly locals. Beware of rigged card games and other confidence tricks organised by criminals.
Gambling may break local laws, which also apply to travellers. See Laws .
To avoid credit and debit card scams:
- keep your credit card in sight at all times
- don't share or show your PIN to others, especially when using ATMs
- check your transaction statements
At airports, use airport taxis, prearranged hotel transfer services, taxis from clearly marked taxi ranks with staff, or one reserved through a car booking app.
Check that any person holding a placard with your name on it knows where you are going.
Be careful of people who are overly friendly and invite you to their home.
If you're a victim of a gambling scam, report it to local police.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at low risk.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
More information:
Civil unrest and political tension
Although rare, protests sometimes happen.
Don't take photos of demonstrations, the military or the police. Authorities may not tolerate this.
Some localised violent clashes between protesters and police have resulted in casualties. The most recent incident occurred in Đắk Lắk Province in June 2023, when several police were killed in organised attacks on police stations.
Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can turn violent.
Demonstrations and civil unrest
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators' safety and maintenance standards may not meet your expectations. This can include adventure activities, such as mountain climbing and boat trips.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Climate and natural disasters
Vietnam experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- flash floods
Severe weather events can disrupt air, sea, road and rail transport, electricity and communications.
If there's a natural disaster:
- always carry your passport in a waterproof bag
- keep in regular touch with family and friends
- check the media and other local sources for information
- follow the advice of local authorities
Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Flooding and typhoons
Floods , flash floods, typhoons and severe weather are common during the rainy season, from June to November.
Flooding can lead to landslides including in built up and residential areas of towns and villages.
Typhoons mostly affect the coastal areas of the north and central regions. Though less common, typhoons also happen in the south.
Monitor the media, and weather and flood level reports during the rainy season.
The Mekong River Commission gives information on flood levels for the Mekong River region.
If there's a flood, typhoon or severe weather:
- don't enter the affected areas without getting advice from local authorities
- check with tour operators before travelling to affected areas
- if in doubt about the safety of any location, change your travel plans.
Large, frequent earthquakes in the region make destructive tsunamis more likely.
Be alert to warnings. A tsunami can arrive within minutes of a nearby tremor or earthquake.
To receive tsunami alerts, register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System .
Move immediately to high ground if advised by local authorities or if you:
- feel a strong earthquake that makes it hard to stand up
- feel a weak, rolling earthquake that lasts a minute or more
- see a sudden rise or fall in sea level
- hear loud and unusual noises from the sea
Do not wait for official warnings. Once on high ground, monitor local media.
If there's a tsunami or if a tsunami warning is current, check the US Tsunami Warning System .
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won’t pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you’ll be away
Physical and mental health
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare, or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some addictive and psychotropic medications are controlled.
If you plan to take medication, check if it's legal in Vietnam. Take enough legal medicine for your trip and always carry it in its original packaging.
If you are travelling with prescription medication, check the value and quantity restrictions on the import and export of prescription medication with the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam .
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Localised outbreaks of diphtheria can occur in Vietnam.
Seek medical advice to en sure your vaccinations are up-to-date.
- Diphtheria (HealthDirect)
Insect-borne illnesses
Zika virus continues to be a risk. There's no vaccination for it.
If you're pregnant, the Australian Department of Health recommends you:
discuss any travel plans with your doctor
consider deferring non-essential travel to affected areas
Dengue is found, especially in the south. There's no vaccine or treatment.
Japanese encephalitis is also found. To protect yourself, consider getting vaccinated. A vaccine is available in Australia.
Malaria is a risk in some remote mountainous areas.
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
Discuss your travel plans and other vaccination needs with your doctor before you travel.
Infectious diseases
Rabies is potentially fatal if you don't get vaccinated or receive quick treatment.
Rabies is found in infected dogs, monkeys, bats and other mammals.
Most reported cases are in the mountain areas of northern Vietnam. It's most commonly passed on through dog bites.
To reduce your risk of rabies, don't go near dogs and other mammals.
If you're bitten or scratched, seek medical help immediately.
HIV/AIDS is a risk.
Take precautions if you engage in activities that expose you to risk of infection.
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is common. Sometimes more serious outbreaks happen.
Outbreaks usually peak from March to May and from September to December.
HFMD mostly affects children under the age of 10 years. Adult cases, especially young adults, are not unusual.
The illness appears as a fever, blisters and rashes on the hands, feet and buttocks.
HFMD is spread by direct contact with nose and throat discharges and faeces of infected people.
To reduce the risk of getting or passing on HFMD, pay close attention to hygiene. Wash your hands well and often.
Bird flu (avian influenza)
Human cases of avian influenza or 'bird flu' are reported in Vietnam.
Cholera and other health risks
Acute watery diarrhoea and cholera occur.
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases occur. These include:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid uncooked and undercooked food, such as salads
Get urgent medical attention if you have a fever or diarrhoea or you suspect food poisoning.
Air pollution
There can be high levels of air pollution, up to and including hazardous levels, in major cities, especially during January to March. Pollution can increase the risk of breathing problems. People with pre-existing medical conditions, particularly heart and lung conditions, may be affected.
If you're concerned about the levels of air pollution:
- seek medical advice
- follow advice from local authorities about methods to reduce exposure
- monitor an air quality index
- reduce your exposure
World Air Quality
Drug use has been reported to cause psychotic episodes and hospitalisation.
If you use drugs in Vietnam, you face possible health and legal risks. See Local laws
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities and care varies, is generally below Australian standards, and may lack medicine and supplies.
Foreign private medical clinics are available in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang. They may not meet Australian standards.
Medical facilities and care at most public hospitals are poor. This is especially true outside Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
You may need medical evacuation to a major centre, even for minor operations.
Doctors and hospitals expect payment before providing medical services, including for emergency care.
Some hospitals may talk with your travel insurance company to secure payment. Others may need up-front payment before they will start treating you.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you may need to be evacuated to Bangkok or Singapore. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
You may need to show a legalised birth certificate to be recognised as next of kin for medical consent purposes.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Vietnamese authorities have broad powers to implement various measures to contain COVID-19. These include movement restrictions and mandatory isolation for positive cases. These can vary from province to province. Follow the advice of local authorities.
There are strict security and investigative measures to stop drug trafficking.
Penalties for all types of drug offences, including those with small amounts of drugs, are severe. Many drug offences attract the death penalty or life in jail.
Marijuana in any form is illegal.
More than 20 Australians are serving sentences for drug offences in Vietnam. More have been arrested and are waiting for further investigation or trials.
Never carry parcels or luggage for others.
For information about carrying prescription medications into Vietnam, see Travel .
Carrying or using drugs
Marriage laws
Foreigners who want to marry a Vietnamese citizen in Vietnam must get formal approval from the Department of Justice. This must be done in the province where the Vietnamese citizen is registered.
You also need a Certificate of No Impediment to Marriage (CNI) if you plan to marry in Vietnam.
Apply for a CNI through the:
- Australian Embassy in Hanoi
- Australian Consulate-General in Ho Chi Minh City
You can also apply for the CNI from DFAT in Australia. Fees apply. The embassy or consulate of Vietnam in Australia needs to authenticate it. Only then will the Department of Justice in Vietnam recognise it.
Getting married
Business laws
Increased Australian business activity has resulted in a higher number of commercial disputes in recent years.
If you're thinking about entering into a contract, get professional legal advice.
If you're involved in a business or civil dispute, authorities could stop you from leaving Vietnam until you resolve the matter.
- Doing business
- Doing business in Vietnam
- Living or working overseas
Disputes over alleged misrepresentation of working and living conditions for Australians working in Vietnam often happen. This is especially the case for people teaching English.
Before signing an employment contract or travelling to Vietnam for work, verify the true nature of the work you're offered.
Check for unacceptable employment conditions. For example, conditions for early termination may state that you surrender your right to a return air ticket. Your potential employer may also withhold your pay.
To safeguard your stay, also:
- check the living arrangements your potential employer has offered
- make sure you have the correct visa before arriving — ask an embassy or consulate of Vietnam
- get professional legal advice before signing any contract
- get all the work permits you need
The Australian embassy or consulate-general can provide a limited range of notarial services for some documents needed for a work permit.
Never hand over your passport to your employer, even for safekeeping. Reputable businesses won't ask you to hand over your passport.
Make sure you keep a valid visa and work permit. If you don't, authorities will fine you and could detain you.
Going overseas to live or work
Penalties for serious crime, such as rape, espionage and hijacking, may include the death penalty.
It's illegal to:
- take photos at border crossings or military installations
- go too close to the border with China, Cambodia or Laos without prior written permission from the local authorities
- gamble, except in government-licensed casinos where foreign passport holders can gamble
- possess pornography
- possess non-state sanctioned political or religious material
These activities may result in arrest and imprisonment.
Taking part in unsanctioned religious activities, including online, is against the law. Any involvement with non-state sanctioned political organisations, or groups perceived by the Government of Vietnam to be associated with dissident groups is also illegal. If authorities suspect you of involvement in these activities, they could stop you from entering the country, detain or deport you. Authorities could also stop you from leaving, place you under surveillance or subject you to interrogation until an investigation has been completed.
It's illegal to export antiques without a permit. The Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (Vietnamese) offers advice and necessary permits.
Possessing or distributing images or objects linked to the former Republic of Vietnam, including commemorative or Vietnam War service-related items, is an offence that could attract harsh penalties.
Embassy or consulate of Vietnam
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you’re overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law
Local customs
Same-sex relationships are legal. However, social and cultural attitudes towards same-sex relationships can be conservative, especially in rural areas.
Avoid public displays of affection.
Same-sex partners aren't legally protected or recognised.
Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Dual citizenship
Vietnam recognises dual nationality in limited situations.
If you're a dual citizen and you enter Vietnam on a Vietnamese passport, this limits the consular services we can give if you're arrested or detained. Vietnamese authorities may not tell us of your situation.
Always travel on your Australian passport .
Australian citizens must re-enter Australia on an Australian passport.
If you're a dual national, you may need to do compulsory military service in Vietnam.
Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam in Australia before you travel.
Advice for dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
To enter Vietnam, you must have either a:
- visa exemption certificate
Australian passport holders are not able to obtain visas on arrival in Vietnam.
Learn more about visa requirements.
You can now apply for an eVisa for tourism or business purposes. It allows eligible travellers to stay up to 90 days in Vietnam if granted. The eVisa is valid for single or multiple entries.
You can complete the visa application form online. As there have been reports of difficulties in accessing eVisas during airport check-in, once granted, you should consider printing a hard copy of the visa approval document.
Make sure you enter your details correctly when applying for a visa. The visa details must match exactly the information on your passport's biodata page, such as your full name and date of birth details. When you're issued a visa to enter Vietnam, check that all your Vietnam visa details are correct, match the information in your passport, that your full name is listed, and that there are no spelling or other errors. Any errors or name omissions may result in you being refused entry, or you could be charged a significant fee at check-in or on arrival to correct the visa error.
For stays longer than 90 days, please contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam.
If your visa expires or is no longer valid, you may be detained and/or fined when leaving.
The Australian Government cannot sponsor your visa application or extension.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
You must register your place of residence with local police within 24 hours of arrival. Check that your hotel does this as part of the check-in process. Register at the local police station if you're staying in private accommodation.
Travellers have been scammed by private online visa services and travel agents.
Only apply for your visa through the Government of Vietnam’s official website or offices.
Vietnamese spouse or parent visas
If your spouse or parent is a Vietnamese national, you can apply for a visa exemption certificate.
Changes to visa status and visa extensions
You can't change the status of your entry visa to any other visa type in Vietnam. For example, you can't change a tourist or a spouse visa to a working visa.
Vietnam does not issue automatic visa extensions. If your visa has expired, contact the Vietnamese immigration authorities to make arrangements to exit Vietnam. Visa extensions are only possible before your visa expiry date.
To get a visa extension from the Vietnamese immigration authorities, your passport must have at least 6 months validity left at the time of application.
This requirement is subject to change.
Check with the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for details.
Border measures
Travel and entry requirements may change rapidly. Contact your nearest Vietnamese Embassy or Consulate for details on entry and exit requirements.
Other formalities
Import and export of prescription medication .
Medication and medical equipment
Register place of residence
All foreigners must register their place of residence with the local police within 24 hours of arrival.
The Australian embassy and consulate can't provide translation services to help with registration.
If you stay at a hotel, check that you'll be registered as part of the normal check-in process. They'll need your passport details.
Many hotels ask foreigners to leave their passport with hotel staff for registration purposes. It isn't a legal requirement for hotels to keep your passport for the time you stay there.
If you stay with family, friends or in another private residence, you need to register at the local police station. Use a translator if needed.
Local hosts need to pre-register foreign guests. If you stay in a private residence, make sure your host has followed this legal requirement.
Some countries won’t let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you’re just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport’s expiry date before you travel. If you’re not sure it’ll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost and stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
Keep a photocopy (or photograph) of your passport bio page and visa somewhere separately in case you lose your passport.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with 'X' gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The currency of Vietnam is the Vietnamese Dong (VND).
When you arrive or exit Vietnam, declare:
- foreign currency in excess of $US5,000, including cash and traveller's cheques
- more than 15 million Vietnamese dong
If you carry more currency or gold than you declared, authorities could confiscate it. They could arrest or fine you.
These requirements may be subject to change. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for details.
Credit cards are widely accepted throughout major cities in Vietnam.
ATMs are widespread in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang.
Check with your bank to confirm if your ATM (eftpos) card will work in Vietnam.
Card skimming happens throughout Vietnam. See Safety .
You may have trouble getting replacement ATM cards.
Many Australian banks don't have local or regional branches with English-speaking staff.
The Vietnamese postal services are generally unreliable. If you need a new card, consider using an international courier service. The Australian embassy or consulate can't help you with money while you wait for a new card. It can't act as a personal mail-holding service.
Local travel
Travel is restricted:
- in some parts of the central Highlands
- around some border areas
- near military installations
Long Tan Cross site
The Vietnamese Government won't permit official Long Tan commemorations at the Long Tan Cross site in Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province.
Access to the site will remain open to small groups of people for private visits without media coverage. This may change at short notice.
Visitors to the site may not:
- wear medals or uniforms
- carry banners or flags
You must behave in a solemn manner, respecting the wishes of local communities.
Landmines and explosive remnants of war
Unexploded ordinance and landmines are a danger in former battlefields, especially in central Vietnam and along the Laos border.
Mine-free roads and paths are well-marked.
If you visit former battlefields, stay on marked pathways.
Driving permit
You must have a valid Vietnamese driver's licence to drive or ride in Vietnam. This includes for motorcycles of 50cc or more.
An International Driving Permit (IDP) issued in Australia is not recognised in Vietnam.
Authorities may fine you for driving without a valid licence.
Your travel insurer will likely deny any claims you make if:
- You're unlicensed and/or
- You don't hold the correct class of licence.
Australian embassy, Hanoi
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Vietnam than in Australia.
Hazards include:
- crowded streets in major cities
- drivers ignoring road rules
- poor vehicle and road maintenance
Traffic accidents often happen and attract large crowds.
If you're involved in an accident, you could face criminal charges. This is regardless of who's at fault. You may need to pay a large sum to the injured person or their family.
If you're not familiar with local conditions, avoid driving or riding a motorcycle.
Whether driving, riding or walking, be very careful when crossing busy streets. Traffic can appear from any direction.
Road Safety
Motorcycles
The number of travellers involved in serious motorcycle accidents is increasing.
Check your travel insurance policy covers you when travelling by motorcycle.
Always wear a helmet that meets Australian safety standards.
Only ride motorcycles if you're:
- properly licensed (Australian driver licences or International Driver Licences issued in Australia are not accepted in Vietnam; you must hold a Vietnamese driving licence to ride a motorbike 50cc or above); and
- familiar with and comfortable in local driving conditions
Be careful using taxis hailed on the street.
Major metered taxis are generally reliable. Ensure the taxi driver knows how to get to where you're going before you get in.
Check the meter is used. Leave the taxi if the driver tries to pick other passengers up.
If you book a taxi online or through an app, make sure the details of the vehicle and driver match those the company gives you.
Unless using an Australian safety standard-approved helmet, we discourage using motorcycle taxis as they provide riders with helmets that offer little to no protection against injury in the case of an accident.
Be careful of taxi scams. See Safety
Public transport
Inter-city buses have a high accident rate.
Petty theft often happens on buses. See Safety .
When travelling by rail, keep the ticket stub as you need it when leaving the train station.
Getting around
Boats, hydrofoils and ferries may not meet Australian safety standards.
Accidents on waterways happen. Vessels have sunk and people have died. This includes in Ha Long Bay.
Whenever you plan to travel by boat :
- ask tour operators about the safety record and emergency procedures
- make sure there is enough safety equipment such as life jackets on board
- if proper equipment is not available, use another provider
Piracy happens in coastal areas of Vietnam.
- Reducing the risk of piracy
- International Maritime Bureau piracy reports
You may need to show your luggage tags when leaving a Vietnamese airport. Keep your luggage receipt from your airline on you at all times.
By law, children under 14 years travelling alone on domestic flights must:
- bring a birth certificate
- have an authorisation letter between the legal guardian of the child and the airline confirming the child can travel alone
Contact the airline in advance to check what is needed for unaccompanied minors.
DFAT doesn’t provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Vietnam's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Travelling by air
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Emergency numbers in Vietnam are operated in Vietnamese only and may be unreliable. You may have a long wait before emergency services arrive.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Take a translator with you to report a crime to the local police. Cases reported by foreigners may be accepted at the discretion of local police.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can’t do to help you overseas.
For consular assistance, contact the nearest embassy or consulate.
Australian Embassy, Hanoi
8 Dao Tan Street
Ba Dinh District, Hanoi, Vietnam
Phone: (+84 24) 3774 0100
Website: vietnam.embassy.gov.au
Facebook: Australia in Vietnam
X: @AusAmbVN
Australian Consulate-General, Ho Chi Minh City
20th Floor, Vincom Centre
47 Ly Tu Trong Street
Ben Nghe Ward, District 1
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Phone: (+84 28) 3521 8100
Website: hcmc.vietnam.embassy.gov.au
Check the relevant website for details about opening hours, and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Vietnam?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
- Cover Letters
- Jobs I've Applied To
- Saved Searches
- Subscriptions
Marine Corps
Coast guard.
- Space Force
- Military Podcasts
- Benefits Home
- Military Pay and Money
- Veteran Health Care
- VA eBenefits
- Veteran Job Search
- Military Skills Translator
- Upload Your Resume
- Veteran Employment Project
- Vet Friendly Employers
- Career Advice
- Military Life Home
- Military Trivia Game
- Veterans Day
- Spouse & Family
- Military History
- Discounts Home
- Featured Discounts
- Veterans Day Restaurant Discounts
- Electronics
- Join the Military Home
- Contact a Recruiter
- Military Fitness
Supreme Court Rejects Military Chaplains' Lawsuit Claiming Refusal of COVID-19 Vaccine Hurt Their Careers
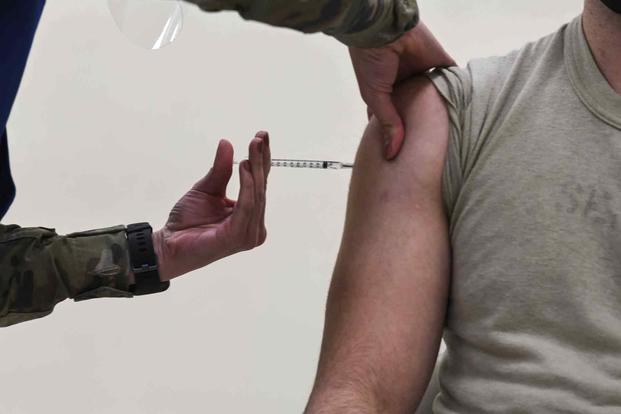
The U.S. Supreme Court has decided not to hear a case involving 39 military chaplains who say they continue to face recrimination for refusing to get the COVID-19 vaccine for religious reasons.
In an announcement Monday of the cases the court has selected to hear next year, the justices denied the chaplains' petition to review last year's dismissal of the case by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit.
The appellate court ruled that the Defense Department's decision in January 2023 to rescind the vaccine mandate rendered the chaplains' case moot.
Read Next: Proposed Transfer of Guard Units to Space Force Sparks Opposition from 48 Governors, 5 US Territories
In their petition, the chaplains said they needed the court to consider the case to protect them and their First Amendment rights. They argued that many continue to have bad marks in their fitness reports that influence assignments and promotions.
"These chaplains' careers are dead men walking, direct consequences of filing [religious accommodation requests]," the petition stated.
According to court documents, the chaplains filed the lawsuit "when it became obvious" that the Defense Department was denying religious accommodation requests. They claimed that since the mandate was dropped, the Defense Department has made false claims that all adverse actions have been removed from the personnel files of those who had asked for a religious exemption.
With the Supreme Court's decision not to hear the case, the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling stands, an affirmation of the lower court's finding that renders the case, Israel Alvarado et. al. v. Austin, moot.
At least 50 service members previously sued the Defense Department over its vaccine mandate, alleging that the services and the Pentagon had violated their right to religious freedom for "categorically denying" their request for religious exemptions from the COVID-19 vaccine.
In one case involving several Navy SEALs , a district court judge quashed the Navy's ability to punish the sailors for refusing the vaccine order, a ruling which was upheld by the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals but later rejected by the U.S. Supreme Court .
The Defense Department was later ordered to pay $1.8 million in legal fees as settlement for two lawsuits over the mandate.
The Defense Department began requiring service members to get the COVID-19 vaccine in August 2021. More than 2 million troops and nearly 350,000 Defense Department civilian employees received the vaccines, two of which used emerging technology -- messenger RNA -- to teach a recipient's immune system to replicate the spike protein found on the COVID-19 virus and destroy it.
More than 17,000 service members refused to take the vaccine, with some citing concerns over the new technology and others saying they objected on religious grounds, noting that the widely available vaccines from Moderna, Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson were tested using cell lines derived from fetal tissue obtained from abortions decades ago.
Roughly 8,400 troops were discharged, including 3,717 Marines, 2,041 Navy sailors, 1,841 Army soldiers, and 834 Air Force and Space Force members, and more than 1,000 service members received religious exemptions before the mandate was dropped.
A total of 690 service members, dependents and civilian Defense Department employees died from COVID-19 between the start of the pandemic in early 2020 and Dec. 8, 2022, the date the DoD stopped publishing updates of its COVID-related deaths.
Nearly 1.2 million Americans have died and more than 7 million deaths have occurred worldwide as a result of the virus, first detected in China in late 2019.
Related: CDC Now Watching for Cases of Heart Inflammation Following COVID-19 Vaccine
Patricia Kime

You May Also Like

U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken was meeting with Israeli leaders in his push for a cease-fire deal between Israel and...

A U.S. Navy ship and several Army vessels involved in an American-led effort to bring more aid into the besieged Gaza Strip...

Ralph Puckett Jr. was awarded the Medal of Honor in 2021, the nation's highest military honor, seven decades after his...

Israel is determined to launch an offensive against Hamas in Rafah, Gaza’s southernmost town, a plan that has raised global...
Military News
- Investigations and Features
- Military Opinion
Select Service
- National Guard
Most Popular Military News

The aircraft carrier USS George Washington is finally underway to its new homeport in Japan, following six arduous years in a...

A prominent Democratic senator is demanding the Department of Veterans Affairs review the quality of its privatized...

The VH-92's lawn-scorching problems were first discovered in 2018 during the Trump administration.

The billet, which is called the dual-military coordinator, will act as a liaison between couples and their career monitors in...

The Defense Department has publicly acknowledged that during the Vietnam War era it stored Agent Orange at the Naval...
Latest Benefits Info
- 4 Tips for Flying Space-A
- The Mental Burden of Using Military Benefits
- Fertility Benefits for Active-Duty Service Members
- Military Child Care Fees
- Military Tuition Assistance (TA) Overview
More Military Headlines
The justices rejected a petition from 39 military chaplains who said they continue to face consequences for refusing the...

The change in coverage comes as people younger than 50 are getting colon cancer more often, according to the American Cancer...

Cooper became a reservist in 1970 and served in a variety of capacities and rising to the rank of major general in 1988, when...

Former Capt. Aaron Dimmock, who now is a business consultant, filed paperwork last week to challenge Gaetz in the heavily...
- 'Lack of Respect': Army National Guard Criticized by Lawmakers for Bungling Enlistment Bonus Payments
- US Military Ships Are Working to Build a Pier for Gaza Aid. It's Going to Cost at Least $320 Million
- Congress Honors Deceased Korean War Hero With Lying in Honor Ceremony
- Proposed Transfer of Guard Units to Space Force Sparks Opposition from 48 Governors, 5 US Territories
- Air Force Urged to Put Electronic Warfare Wing at Massachusetts' Hanscom Air Force Base
- Air Force MQ-9 Crashed in Africa Last Year Due to Engine Failure, Report Details
- A Former Naval Officer Will Challenge Florida Congressman Matt Gaetz in Upcoming GOP Primary
- Retired Captain of First US Nuclear Submarine Celebrates Turning 100 in Spokane
Military Benefits Updates
- J. Gary Cooper, Military and Governmental Trailblazer from Alabama, Dead at 87
- Marine Corps Says It Wants Counter-Drone Capabilities 'Yesterday' as It Rushes to Roll Out New Systems
- A Group Aims to Rebuild Tun Tavern, Birthplace of the Marines, as a Tavern and Restaurant
- Chaplain of the Coast Guard Fired for 'Loss of Confidence' After Not Acting on Case of Sexual Misconduct
- New Coast Guard Unit Commissioned at Fort Drum
- Several Dozen Ships Lost Propulsion in Maryland Waters Before Key Bridge Collapse: 'You're Basically Just Drifting'
Entertainment
- 9 Games You Can Fit in Your Ruck and Play in the Field
- World War II Veteran and Director John Ford Is the Next Subject of TCM's 'Plot Thickens' Podcast
- 9 Lyrics from Taylor Swift's 'The Tortured Poets Department' That Perfectly Describe Life as a Military Spouse
- Travel Insurance
The journalists on the editorial team at Forbes Advisor Australia base their research and opinions on objective, independent information-gathering.
When covering investment and personal finance stories, we aim to inform our readers rather than recommend specific financial product or asset classes. While we may highlight certain positives of a financial product or asset class, there is no guarantee that readers will benefit from the product or investment approach and may, in fact, make a loss if they acquire the product or adopt the approach.
To the extent any recommendations or statements of opinion or fact made in a story may constitute financial advice, they constitute general information and not personal financial advice in any form. As such, any recommendations or statements do not take into account the financial circumstances, investment objectives, tax implications, or any specific requirements of readers.
Readers of our stories should not act on any recommendation without first taking appropriate steps to verify the information in the stories consulting their independent financial adviser in order to ascertain whether the recommendation (if any) is appropriate, having regard to their investment objectives, financial situation and particular needs. Providing access to our stories should not be construed as investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell any security or product, or to engage in or refrain from engaging in any transaction by Forbes Advisor Australia. In comparing various financial products and services, we are unable to compare every provider in the market so our rankings do not constitute a comprehensive review of a particular sector. While we do go to great lengths to ensure our ranking criteria matches the concerns of consumers, we cannot guarantee that every relevant feature of a financial product will be reviewed. We make every effort to provide accurate and up-to-date information. However, Forbes Advisor Australia cannot guarantee the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of this website. Forbes Advisor Australia accepts no responsibility to update any person regarding any inaccuracy, omission or change in information in our stories or any other information made available to a person, nor any obligation to furnish the person with any further information.
Travel Insurance For South Africa: Everything You Need To Know
Updated: Apr 30, 2024, 1:13pm
Table of Contents
Featured Partners
Do I Need Travel Insurance for South Africa?
What does travel insurance for south africa cover, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Tourism is on the rise in South Africa according to the local government , with more than four million tourists visiting the nation in the first half of 2023 alone. Australians form a sizable chunk of those numbers, with an estimated 125,000 Australians touring the country each year pre-pandemic.
With travel still high on the agenda for many Australians, that figure is expected to rise in the coming years.
If you’re considering a trip to South Africa, you’ll want to purchase travel insurance. Our guide explains everything you need to know.
Fast Cover Travel Insurance
On Fast Cover’s Secure Website
Medical cover
Unlimited, 24/7 Emergency Assistance
Cancellations
Unlimited, (Trip Disruption $50,000)
Key Features
25-Day Cooling Off Period, Australian Based Call Centre, 4.6 Star Product Review Rating
Cover-More Travel Insurance

On Cover-more’s secure website
Unlimited, with a $2000 limit to dental
Yes, amount chosen by customer
Southern Cross Travel Insurance

Medical Cover
Including medical treatment, doctors’ visits, prescribed medication, specialist treatment & medical transport costs
$2,500 with option to increase to unlimited
Yes, Australians should purchase travel insurance for South Africa. While not a legal requirement to enter the country, it is highly recommended from the Australian government—especially for medical care.
The standard of medical facilities in South Africa can vary by region, but medical facilities are generally of a much lower standard than Australia. In fact, many regional hospitals only provide basic facilities, meaning you may have to be relocated in order to receive the right medical attention.
There is no shared healthcare agreement between Australia and South Africa, which makes travel insurance even more essential. If you need to be transferred by air evacuation to a major city in order to receive treatment, and you don’t have travel insurance, you’ll likely face a hefty bill out of your own pocket.
As Smartraveller advises all Australians, if you can’t afford travel insurance, you can’t afford to travel.
Vaccinations to Consider for Your Trip to South Africa
There is a high risk of certain diseases in South Africa, so it is worth making sure your vaccinations are up to date before you travel and taking any preventative measures with you, such as medications.
This can help reduce your chances of needing to seek medical attention.
There is a risk of Hepatitis A and B throughout South Africa, so vaccinations for Australian travellers are recommended. There is also a moderate risk for most travellers of typhoid, so a vaccination is also recommended if you are travelling to smaller cities, villages and rural areas.
Malaria is present throughout the country, so it could be a good idea to equip yourself with malaria tablets before you travel.
It is essential that you consult a medical practitioner regarding your need for vaccinations before you travel to South Africa, especially as some medical conditions can predispose travellers to certain infections.
When purchasing a travel insurance policy for South Africa, you will have the option to choose a basic policy or a comprehensive policy. A basic policy is cheaper , but may turn out to be more expensive in the long run if you aren’t covered for the things you need.
While a basic policy will usually cover medical needs, it may not provide cover for things such as lost luggage and cancellations (or, if it does, will provide it at a much lower claim level).
That’s why a comprehensive policy is highly recommended for travel to South Africa, as you will receive cover for stolen items, lost luggage, delays and more, in addition to medical and emergency dental care.
Smartraveller asks Australians to exercise a high degree of caution due to the threat of violent crime in South Africa, which includes robbery and carjacking.
The government website warns that opportunistic criminals will target travellers at the approaches to tourist-hotspot Kruger National Park, at well-known resorts, and on public transport.
Additionally, as ATM and credit card fraud are common crimes in South Africa, a comprehensive policy can be the more financially sound choice to give you peace of mind.
Going on a Safari?
South Africa is a popular tourist region for many reasons, including wildlife safaris. If you wish to partake in a safari or a game walk—walking with wild animals and a professional guide—you will need to ensure that these activities are covered in your policy’s list of included sports and activities.
If they are not, you will not receive cover for anything that occurs during the safari.
However, your policy may offer the option for you to choose an ‘adventure pack’ at an additional cost, which can include many activities that aren’t covered in the standard offering.
This can also include hiking or trekking to certain altitudes.
It’s important to consider which activities you may be participating in during your trip to South Africa in order to ensure you have the appropriate coverage, and purchase an additional add-on if necessary.
What Travel Insurance Won’t Cover
Your travel insurance policy won’t cover anything that is set out in its exclusions, as per the product disclosure statement (PDS). This could include certain sports and activities (such as a safari), or travel to certain regions in South Africa due to safety.
While each travel insurance policy differs on the fine-print, it is standard for most policies not to cover:
- Cancellations due to ‘disinclination to travel’, being if you change your mind about your holiday;
- Accidents or injuries that occur when not following the appropriate safety guidance or official guidelines;
- Intoxicated behaviour, including recreational drugs;
- Any illegal activity.
Be sure to carefully read the PDS of your policy so you know exactly what you can and cannot claim on your trip to South Africa.
Is it safe to travel to South Africa?
Smartraveller recommends that Australians exercise a high degree of caution when travelling to South Africa, due to the threat of violent crime. This includes armed robbery, mugging, carjacking, credit card theft, and more.
There is a higher risk of violent crime in major cities after dark, or during “rolling blackout” periods.
For these reasons (and more), Smartraveller urges Australians to take out a travel insurance policy before travelling to South Africa.
Do Australians need a visa for South Africa?
No, Australians do not need a visa for South Africa if they are visiting for tourism for stays of up to 90 days.
Where can I buy travel insurance for South Africa?
Most Australian travel insurance providers will cover Aussies wanting to head abroad to South Africa. When shopping around for a policy, you will be able to choose your destination when you request a quote. If there is no option to choose South Africa, this would be a clear indicator that the insurance provider does not provide policies to this region.
At the time of writing, a few of our top picks for comprehensive travel insurance cover South Africa, including Allianz and Cover-More .
Travel insurance providers can revoke the issuing of new policies to certain destinations at any time, especially if Smartraveller changes the alert warning for a country to ‘Do Not Travel’.
- Best Comprehensive Travel Insurance
- Best Seniors Travel Insurance
- Best Domestic Travel Insurance
- Best Cruise Travel Insurance
- Best Family Travel Insurance
- Travel Insurance Cost
- Pregnancy Travel Insurance Guide
- Travel Insurance Cancellation Cover
- Travel Insurance For Bali
- Travel Insurance For Fiji
- Travel Insurance For The USA
- Travel Insurance For Thailand
- Travel Insurance For New Zealand
- Travel Insurance For Japan
- Travel Insurance For Europe
- Travel Insurance For Singapore
- Travel Insurance For Indonesia
- Travel Insurance For Vietnam
- Travel Insurance For Canada
- Cover-More Travel Insurance Review
- Fast Cover Travel Insurance Review
- Travel Insurance Saver Review
- Allianz Comprehensive Travel Insurance Review
- 1Cover Comprehensive Travel Insurance Review
- Australia Post Comprehensive Travel Insurance Review
- Tick Travel Insurance Review
More from
Do frequent flyer points expire, travel insurance for canada: what you need to know before you go, travel insurance for vietnam: everything you need to know, tick travel insurance top cover review: features, pros and cons, was discovery travel insurance review: features, pros and cons, fast cover comprehensive travel insurance review: pros and cons.
Sophie Venz is an experienced editor and features reporter, and has previously worked in the small business and start-up reporting space. Previously the Associate Editor of SmartCompany, Sophie has worked closely with finance experts and columnists around Australia and internationally.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information. COVID-19 vaccine. Hepatitis A: Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Vietnam. Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A.
Advice. Travelers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Vietnam has become a popular tourist destination. Visitors looking to be swept away by gorgeous landscape will be can see jungles, caves, grottoes, and immense limestone pillars. Those looking to explore new flavors and foods will be thrilled with the cheap and delicious street food.
The travel notice can be viewed here. The following is the CDC's key information: Make sure you are fully vaccinated before travelling to Vietnam. Unvaccinated travelers should avoid nonessential travel to Vietnam. Because of the current situation in Vietnam, all travelers may be at risk for getting and spreading COVID-19 variants.
Recommended Travel Vaccinations for Vietnam: VACCINE HOW DISEASE SPREADS DETAILS; Hepatitis A: Food & Water: Recommended for most travellers: Hepatitis B: Blood & Body Fluids: Accelerated schedule available: Typhoid: Food & Water: Shot lasts 2 years. Oral vaccine lasts 5 years, must be able to swallow pills. Oral doses must be kept in refrigerator.
Step 2: Click this link or access https://immigration.gov.vn/ and go to 'E-visa Issuance' then click on the link for 'Outside Vietnam foreigners'. Step 3: Upload your .jpg images (passport data page and passport photo) and fill out the required fields on the form completely. Submit your form. Step 4: Pay the e-Visa fee of 25 USD.
The Ministry of Health's most recent guidance on COVID-19 prevention and control allows travelers to enter Vietnam without being isolated, and exempts children under 2 years of age from arrival testing. ... Vietnam maintained a high vaccination rate (in fact, Vietnam was among the countries having the highest vaccine rate) and the number of ...
Travel to Vietnam from Australia can be an exciting and rewarding experience, but it is important to contact a medical provider specializing in vaccinations for Vietnam as soon as you know you will be travelling to the country. Speak to a medical provider no later than 6-8 weeks before you travel to Vietnam.
where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page. See what health risks you'll face in Vietnam, including: mosquito-borne diseases like Zika virus, dengue ...
We strongly recommend travelers purchase medical evacuation insurance before visiting Vietnam. Travelers to Vietnam are at risk of the following diseases: Tuberculosis, Dengue Fever, Zika, Avian Influenza (H5N1), and HIV. You can find detailed information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the CDC website. We do not pay medical bills.
Vietnam Travel Requirements & Vaccinations . Vietnam is a country in southern Asia on the Indochina Peninsula that, in recent years, has become one of the fastest growing tourist destinations. Officially known as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, it is bordered by China to the north and Thailand to the southwest. ...
Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhoea Kits. Available. Vietnam has become a popular tourist destination. Visitors looking to be swept away by gorgeous landscape will be can see jungles, caves, grottoes, and immence limestone pillars. Those looking to explore new flavours and foods will be thrilled with the delicious, on the cheap street food.
Advice for All Destinations COVID-19. Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.. Vaccinations and malaria risk. Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
Hepatitis A and Typhoid. Both Hepatitis A and Typhoid are present in Vietnam, and a dual vaccine where one shot protects against both is available. The vaccine can protect you for a number of years once administered. Hepatitis A: Hepatitis A can be passed on through contaminated food or water and is preventable via vaccination before you travel ...
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals). ... If you decide to travel to Vietnam ...
Local authorities suggest vaccinations for Vietnam entry as there are health risks, especially visiting rural areas. It's also important to be up to date on the current COVID-19 protocols visiting Vietnam. Most travelers will need a visa to travel to Vietnam. This may seem like a lot, but don't worry.
COVID-19 vaccines provide high levels of protection against severe illness, hospitalisation, or dying from the virus. Vaccination against COVID-19 reduces, but does not eliminate the risk of infection, so social distancing and personal and respiratory hygiene remain important interventions, particularly during overseas travel.
The four vaccines which most travellers to Vietnam are recommended are diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis A and typhoid. Depending upon where you will be travelling to and what activities you will be undertaking, you may also require the vaccines for cholera hepatitis B, Japanese encephalitis and rabies. Although these vaccinations are recommended ...
Vaccinations are not compulsory to travel to Vietnam and your it is 100% your choice. Heiatitis a and b are commonsense for majority of countries. We always got the typhoid vaccine for the whole family every 2-3 years when our kids were little when we travelled to Vietnam.
Rabies occurs in Vietnam, especially in the north. It's fatal without treatment. If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help immediately. HIV/AIDS is a risk. Take precautions if you're taking part in high-risk activities. Diphtheria is a risk. Ensure your vaccinations are up-to-date. Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is ...
Airman receives his first shot of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, Jan. 21, 2021. (U.S. Air Force photo by Airman 1st Class Kiaundra Miller)
Tourism is on the rise in South Africa according to the local government, with more than four million tourists visiting the nation in the first half of 2023 alone.Australians form a sizable chunk ...
Worldwide, more than 99% of the burden of measles infections and deaths affects populations in low-income and middle-income countries.1 Measles accounts for 3% of the global mortality of children younger than five years, constituting 90% of deaths from measles,2 and rubella is the main vaccine-preventable cause of birth defects.3 Vaccine coverage, both through routine immunisation and ...