
Google, SEO & Metadata
Direct Hotel Bookings
Hotel Website
Review Management
Marketing Trends
Marketing Strategies
Hotel Visuals
Attract Different Types of Guests
Social Media Marketing
Hotel Distribution Channels
Up-selling Tips & Strategies
Hotel Guest Communications & Experience
Revenue Management Systems
Pricing Strategies
KPIs & Financial Metrics
Guides & Explainers
Revenue Management Trends
Staffing & Outsourcing
Hotel Positions
Front Office
Housekeeping
Restaurant & F&B
Smart Hotel
Tech Examples
Emerging Hotel Technology
- › Hotel Software
- › Hotel Guides & Explainers
- › Hotel Business & Finance
- › Hotel Jobs & Careers
Restaurant Management & Guides
Restaurant Marketing & Strategies
Restaurant Technology & Software
Hotel Software
Hotel Technology
Hotel Operations
Revenue Management
Hotel Marketing
Hotel Jobs & Careers
Hotel Business & Finance
Hospitality Marketing & Trends
F&B Marketing
Technology Trends & Examples
Emerging Tech
- › Hospitality Guides & Explainers
- › Hospitality Staffing & Careers
- › Airline & Aviation Industry
- › Cruise Industry
Technology & Software
Marketing Trends & Strategies
Travel Marketing & Trends
Hospitality Marketing
Restaurant Marketing
Emerging Technology
Hospitality Technology
Restaurant Technology
- › Sustainability
- › Travel Guides & Explainers
- › Business Travel
- › Travel Jobs & Careers
- Expert Panel
- Influencers
- Solution Partners

Tourism Management: All You Need to Know About Tourism

Tourism Management
Tourism management oversees operations and strategies in the tourism industry, including travel, accommodation, and attractions. It’s crucial for ensuring sustainable growth, enhancing tourist experiences, and contributing significantly to economic development. Effective management balances the needs of tourists, businesses, and local communities while focusing on environmental and cultural preservation.
Key Takeaways
- Tourism Management Scope: Encompasses a range of roles in hospitality and travel, offering opportunities for interaction with diverse people and travel experiences.
- Educational Requirements: A bachelor’s degree in tourism management is essential, providing knowledge in business, legal, economics, marketing, and finance specific to the tourism and hospitality sector.
- Career Opportunities: With a tourism management degree, one can pursue varied roles such as hotel manager, event manager, tourism marketing manager, or travel agency manager.
- Sustainable Tourism: Emphasizes the importance of sustainability in tourism, focusing on minimizing environmental impact and promoting local culture and economy.
- Global Trends Impact: Discusses how global trends and events, like economic shifts or health crises, can significantly affect the tourism industry.
Table of Contents:
- What is Tourism Management?
Which Degree Do You Need for Tourism Management?
Key skills gained with a tourism management degree, what jobs can you get with a tourism management degree, what does a tourism management job involve, service excellence, transport connectivity management, guest safety & security, cultural sensitivity, benefits of having a tourism management degree, tourism industry: an overview of all sectors, tourism trends: opportunities for the tourism industry, tourism marketing, tourism management and technology, the purpose of revenue management in tourism management, generate more bookings with these travel agencies, tourism jobs: job boards for finding tourism management positions, websites for finding tourism management jobs.
- Tourism Management of Description and Advice on Applying
Tips to Find Tourism Careers
An overview of tourism course options, find trends and tools with google travel insights, a guide to sustainable tourism.
- The Significant Damage Corona Virus has Caused Within Tourism Management
Tour Agencies That Help Hotels to Grow Their Revenue
Introduction
The tourism industry is rapidly growing, and jobs in tourism management are becoming highly sought after. Working in this sector will offer many interesting roles, such as meeting new people and the opportunity to travel. If you have a passion for all things travel-related and are a people person, this profession will be ideal for you.
What Is Tourism Management?
Tourism management refers to everything related to the hospitality and travel industries. It offers extensive training opportunities for travel, accommodations, and food management positions. Tourism management can also include working in associations or agencies directly involved with tourism services.
Video: Tourism Management Explained
A bachelor’s degree in tourism management is a precondition for acquiring in-depth practical and theoretical knowledge in administration and business management. The foundation course will also cover legal, economics, marketing, accounting, and finance and management principles in tourism, hotel, and hospitality.
Apart from the necessary qualifications, you must also set yourself apart from other candidates since tourism management is a fiercely competitive industry. Even if you don’t have the formal qualifications to work in this sector, you can still work up to the managerial position after gaining experience. You can also work in an entry-level job in the travel and tourism industry and study tourism management part-time to get qualified and earn a higher salary.
Tourism Management is a diverse field. Managers within the industry have to have an array of skills to deal with problems ranging from operational to conceptual. Below is a table, outlining some of the key skills within Tourism Management, with examples and implementations.
As a qualified tourism manager, you can work in various jobs related to the tourist industry. Some of these are:
- Front desk clerk/receptionist
- Events manager
- Hotel or resort manager
- Housekeeper
- Tour operator
- Tourism marketing manager
- Travel agency manager
- Tourist Information Centre manager
- Accountant or sales manager
- Guest relations manager
The duties associated with a tourism management job vary greatly from one business to another. In general, the main responsibilities are focused on:
- Monitoring accounts and managing budgets
- Overseeing the day-to-day functions of businesses
- Managing staff
- Interviewing and training new staff
- Promoting tourism
- Ensuring customer satisfaction
- Maximizing business revenue
- Taking part in financial planning
- Dealing with customer complaints or queries
- Marketing the business to attract tourists
- Keeping up-to-date with emerging industry trends through attending seminars or doing online research
- Seeking ways to improve the company’s tourism -related activities
Important Aspects for Guest Experience in Tourism Management
There are a number of components of tourism management that can be considered to be especially valuable to the guest experience. In the sections below, you can learn about some of these aspects of the role.
One of the most essential components of tourism management is providing excellent customer service so that tourists have a positive and memorable experience. Customers need to receive pleasant and helpful service, which requires knowledge of the area to make informed recommendations.
It is also important to reduce friction as much as possible. This means using technology to reduce response times, improve check-in processes, and provide a level of personalization. When the level of service is high, tourists are more likely to return in the future, recommend a destination to others, and leave positive reviews online.

Transport is another of the most vital tourist needs that must be catered for. Guests need to be able to get to the places they want to visit, and this means there is a clear connection between the quality of transport services, how easy transport is to access, and the overall level of satisfaction a tourist is likely to experience.
Good tourism management needs to include a transport connectivity management component. This could involve taking the time to understand the best options for guests looking to reach a particular destination, memorizing routes, monitoring and addressing guest feedback, or collaborating with transport providers to provide discounts.
Effective tourism management means you have to prioritize the safety and security of tourists. This applies not only to physical safety and security but also to digital safety and security. The provision of a safe and secure environment makes a destination more desirable and a tourism business more appealing.
This sense of safety and security can be provided through a number of means, ranging from physical security staff to consistently adhering to all safety and security regulations. Equipment and appliances should be inspected regularly, and you should invest in cyber security solutions to keep tourists’ personal and financial data safe.
Tourism has great potential to deliver major benefits for local communities, but without appropriate tourism management, it can also lead to harm, especially if tourism managers do not demonstrate sufficient cultural sensitivity. This means respecting local people and their ways of life, including their traditions, beliefs, and culture.
To succeed with this, you need to make sure your services and offerings are not at odds with what local people want. Success also means behaving in sustainable and environmentally conscious ways so that natural resources are not depleted, and the local area does not suffer other forms of unintentional damage.
A tourism management degree can be obtained from many academic institutions worldwide and can be especially valuable for long-term career prospects. The degree will be recognized globally and help you highlight your relevant skills and knowledge, opening up many possible career paths.
Tourism management degrees from respected universities have high post-graduation employment rates, meaning graduates will often return to full-time employment quickly. A typical tourism management degree will also cover many topics, from business management and hotel operations to marketing, event management, and even data analysis.
Ultimately, this will stand you in good stead for any tourism-related career you choose. However, the degree can be especially beneficial if you want to work in management or another senior position within a tourism company. Many companies will advertise these roles by specifying the need for a relevant degree.
On top of all this, a tourism management degree will teach various skills that can also be relevant for your entire professional career, regardless of which direction that eventually goes in. Your degree will likely help you build your communication, time management, problem-solving, teamwork, and much more.
The importance of tourism for every country in the world arises from the various benefits it offers to the host country. After all, tourism contributes to the country’s economic growth and development by bringing valuable benefits to the locals and businesses. According to the Market Size of the Tourism Sector Worldwide research report by Statista, the revenue of the tourism sector in 2023 was $2.29 trillion. It also helps create an attractive image of the country’s identity and value. There is no denying that the tourism industry goes far beyond attractive destinations and economic growth. ‘Tourism Industry; Everything You Need to Know About Tourism’ is an article that focuses on the benefits of the tourism industry and the sectors within it.

As tourism continues to evolve rapidly, modern business travelers rely more on technology to stay connected on their trips. For the business to remain relevant in this ever-changing sector, staying on top of the latest trends is important. From online booking portals to social media sites that engage with guests, the travel and tourism industry can use endless resources to their benefit to keep up with these trends. In the article ‘Tourism Trends: Opportunities for The Tourism Industry’ , you will get important insight into the latest tourism trends that can help your business.
A powerful marketing strategy is crucial in any industry, and tourism is no different. With new tourism-related businesses being launched everywhere, more companies are now becoming involved in the tourism industry than ever before. Tourism is one of the fastest-growing industries that help boost economies. As more destinations are attracting travelers, it’s no wonder that the industry has become so competitive. This is precisely why ensuring that your tourism marketing strategy is in tip-top condition is important. The article ‘Tourism Marketing,’ explains the upcoming marketing trends that define the tourism industry.
Video: What is Tourism Marketing?
Technology has changed how people travel, and the new developments promise an even more exciting experience. There is no doubt about the importance of technology and its role in the tourism sector. Today, technology has vastly influenced tourism and continues to do so for the future. From the destination you choose to travel to all the way to your accommodation needs, thanks to the convenience of the Internet, it’s possible to book your entire trip from the comfort of your home. ‘Key Technology Trends Emerging in the Travel Industry’ is an article that reveals the importance of emerging tech trends in the tourism industry.
Over the last few decades, revenue management has played a major role in the growth and development of the hospitality and tourism industry. Revenue management utilizes several inventories, such as pricing, marketing, and distribution systems, to increase profits. Having initially been developed to optimize pricing within the airline industry , the application of revenue management has expanded in hotels, cruise lines , airlines, railways, car rentals, and many other tourism sectors. You can find more information about revenue management in the article, ‘Revenue Management; clearly explained!’ .
As part of tourism management, a huge part of running a successful travel company involves optimizing demand. The distribution channels you use can be critical. In particular, travel agencies can provide incremental bookings, as they provide convenience and self-service while helping to guide customers who may require advice.
In our article, “Generate More Bookings With These Travel Agencies” , you can find a breakdown of some of the best-known and most widely utilized travel agencies to focus your efforts on.

Job boards are one of the best channels for finding online tourism management positions because they are used by a diverse range of employers across all tourism industry sectors. Of course, different job boards will advertise different vacancies, so it is best to use several different platforms during your search.
The article “Tourism Jobs: The Best Tourism Industry Job Boards for Your Career” , will provide more information, including a list of many of the best job boards to use, organized according to the sector they target most heavily.
When attempting to move into the field of tourism management, it is sensible to have a list of the numerous websites and online channels to use. After all, not all employers will turn to the same websites to advertise tourism management jobs. You may miss out on excellent opportunities if you narrow your search.
Our article, “Tourism Management Jobs: List of Websites to Find Your Next Job” , lists some of the most important websites you can use to find the management position you have always wanted.
Tourism Management Job Description and Advice on Applying
Tourism management jobs are rewarding but challenging, so before moving into a role of this kind, you must first understand what the job involves and what qualifications and skills you will require. Additionally, it is important to know who employs tourism managers and where you can go to apply.
Read the article, “Tourism Manager Job Description + Tips to Boost Your Career” , and you will find a detailed job description, along with some useful tips that can help you land the job you have always wanted.
You will likely run into substantial competition at various points during your tourism career, but this can be especially true when applying for tourism management positions. For this reason, you must take steps to improve your application, perfect your interview technique, and manage your own professional network.
In the article “Tourism Careers: Tips to Find a Job in the Tourism Industry” , you will come across nine individual tips that may be of assistance when applying for jobs within the tourism industry.
Tourism management positions are senior roles within the industry, so education and experience are both important. One of the ways you can equip yourself with the necessary skills and expertise is to take a tourism course, especially if it places an emphasis on managerial concepts and strategies.
To learn more about tourism course options, including those focused on management and how they can boost your career prospects, read our “Tourism Course: A Complete Overview of Courses & Tourism Educators” article.
Video: Travel and Tourism Management: Student Life
A major part of tourism management involves using data to identify and respond to those trends appropriately. With this in mind, the Google Travel Insights platform can be invaluable, as it provides access to information about hotel and flight searches, demand for specific destinations, and much more.
Take a look at “Google Travel Insights: Tools & Data Trends for The Travel Industry” for more details on the platform, its three main components, and its various uses for those involved with tourism management.
Those involved in tourism management need to understand the concept of sustainable tourism. Essentially, this refers to tourism where a conscious effort is made to lower the impact on local people, wildlife, land, and the environment to make tourism a more viable and less damaging long-term prospect. According to the Tourism Outlook Report by Economist Intelligence, tourism accounts for between 5% and 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions, so it is essential to include sustainable practices within the industry.
To explore sustainable tourism further, understand how it works, and read about some of the most significant real-world examples, check out “Sustainable Tourism Guide: What is, Why Important, Examples and More…” .
Are you considering a partnership with a tour agency but unsure where to start?
In “ Tour Agencies That Help Hotels To Grow Their Revenue “, you’ll discover everything you need to know about tour agencies and what they can bring to your hotel business. You’ll learn about the many different types of tour agencies and the kinds of markets they can connect you with. You’ll learn about partnerships’ possible benefits and drawbacks and what alternatives exist. You’ll also discover the most significant companies you might consider working with and why they might be a good fit for your hotel business.
Tourism Management FAQs
What are the functions of tourism management.
The functions of tourism management include planning and organizing tourism activities, developing tourism policies, marketing and promoting destinations, managing customer relations, ensuring sustainable practices, and coordinating between various service providers to enhance the tourist experience.
What is the difference between tourism and hospitality management?
Tourism management focuses on the broader aspect of travel and tourism, including destination marketing and visitor management, while hospitality management is more concerned with operational aspects of hospitality businesses like hotels, restaurants, and event planning.
Why study hospitality and tourism management?
Studying hospitality and tourism management provides knowledge and skills in business, customer service, and cultural awareness, preparing individuals for diverse careers in the global tourism industry, promoting professional growth, and understanding of the sector’s impact on economies and societies.
What can you learn from tourism?
From tourism, one can learn about different cultures, histories, and geographies, develop interpersonal and communication skills, understand global economic and environmental impacts, and gain insights into the operations and management of the travel industry.
Is tourism management a profession?
Yes, tourism management is a profession that encompasses a range of roles and responsibilities aimed at enhancing the tourist experience, promoting destinations, and contributing to the development and sustainability of the tourism industry. It requires specific knowledge, skills, and training.
Traveling to different destinations for business or pleasure is a growing field that offers many opportunities for those seeking to work in tourism management. As a tourism manager, you can meet people worldwide and even travel to other countries.
Want to Learn More About Management in Related Industries?
All hospitality, travel, and tourism-related industries have commonalities. However, specific, unique factors influence management in each industry. You can learn more about management within related industries in the following articles.
- Hotel Management: Everything You Need to Know About Managing a Hotel
- Hospitality Management: The Essentials About Hospitality
- Revenue Management; clearly explained!
- Restaurant Management: Everything You Need to Know
- What is Travel Management?
- Aviation Management: A Great Guide to Start Your Career in Aviation
- Destination Management: How Tourism Adds Value to Your Destination
More Tips to Grow Your Business
This article is written by:.

Martijn Barten
Related posts.

Tourism Meaning: Learn About the Definition of the Tourism Industry

Aviation Careers: An Overview of Different Aviation Positions

Travel and Tourism Industry; A Complete Overview of All Activities

Travel Industry: An Overview of One of the Largest Service Industries

Travel Trends: 21 Opportunities for the Travel Industry in 2024

Strategies to Optimize Your Holiday Park’s Revenue Next Summer
23 comments.
This is very good information about tourism management. Thank you for that.
I’m learning new things every week. Thanks for a this great website about tourism. I will visit this website again!
Very useful website. I’m doing research for a school report. I found the information on this website very interesting and useful, thank you.
Great article. Your blog contains professional content. Many thanks for that, this is exactly what I was looking for!
I have completed a BTTM (Bachelor in Travel and tourism management), I’m interested to work on cruises or international Airports. I’m searching for a new course for a study. Could anybody suggest me a good relevant course? Thank you for sharing the great information!
I have done a master’s in tourism and travel management. This article contains splendid information.
I really like your blog about Tourism Management, it’s very detailed and informative.
Thank you for providing the definition of tourism management and what it’s all about. It helped me choose to study tourism management. I am grateful for the provided info.
What nice information! Thank you for sharing the informative article about tourism management. I just completed my 12th year and I am exploring career options. After reading your article, I have a better understanding of tourism management.
Thank you for your kind words. The article “Tourism Course: A Complete Overview of Courses & Tourism Educators” might also help you to explore courses within the fils of Tourism :)
I’m working in tourism for more than 10 years and really find this information very informative. Thanks for sharing this information!
Good afternoon Sebastian. I’m a Tourism Management student at UCC, can I please get your contact for some discussions?
This information on tourism management is very useful. Thanks for such a piece of wonderful information. Sebastian can I please get your contact for some discussion?
I’m a small apartment owner, and Cov-19 has caused a huge gap in my small business. Many of us, decided to be vaccinated. Now the situation has improved and the tourists are coming fortunately back :) 60 % of our regular guests returned, who knows who we are, and they’re already familiar with our apartments, house and surroundings. So, take care of all your guests, and they might become regulars.
This article gave me a good idea about tourism management. l Learned a lot. Thank you!
Hi, I’m deciding to be a tour guide, but could anyone tell me if studying tourism and management will enable me to do so? Thanks, Sahan
What a nice blog about Tourism, I’m also a student at Machakos university pursuing Bachelor’s degree in Tourism Management and I found this blog important and I have learned a lot from it. Thank you!
Thank you Samwel, we are glad to hear that :)
I was searching for this kind of knowledge, and your blog provided it. Thank you for the comprehensive information about tourism management.
Who’s the author? I want to know who created such a good article about tourism.
Hi Achinthya, The article is written by the Revfine.com team and is continuously updated with the latest insights.
This information helped me so much!
Thank you a lot for this information about tourism management.
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
- Facebook Messenger

- Tourism Management Tutorial
- Tourism Management - Home
- Tourism Basics
Tourism Management - Introduction
- Tourism Management - Types
- Tourism Management - Terminology
- Tourism Management - Factors
- Tourism Management - Demand
- Tourism Mngmt - Motivation Factors
- Maslow's Pyramid of Motivation
- Consumer Behavior in Tourism
- Tourism Management - Plog's Model
- About Tourism Destinations
- Destination Awareness
- Tourism Management - Milieus
- Tourism Management Destination
- Tools for Destination Management
- Managing Tourism
- Tourism Management - Supply
- Tourism Functional Management
- Business Departments
- Market Segmentation
- Tourism Mngmt - Marketing Mix
- Tourism Mngmt - Products & Services
- Developing Product
- Product Development Phases
- Tourism Impacts, Trends, & Future
- Tourism Management - Impacts
- Tourism Mngmt - Trends & Future
- Tourism Management Resources
- Tourism Management - Quick Guide
- Tourism Management - Resources
- Tourism Management - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Tourism has turned out to be an economic booster contributing to the economic development of many countries over the last few decades. People see holidays as a necessity, and not as luxury in the present scenario. Tourism calls for coordination and cooperation between travel agents, tour operators, and tourists. Tourism has a few major elements − destinations, attractions, sites, accommodation, and all ancillary services.
What is Tourism?
Tourism involves the activities of people travelling and staying in a place away from their home environment for leisure, business or other purposes.
Mathieson and Wall (1982) define tourism as follows −
"The temporary movement of people to destinations outside their usual places of work and residence, the activities undertaken during their stay in those destinations, and the facilities created to cater to their needs."
Tourism was mainly been traditional in its early form. With the evolution of cultures, economies, and knowledge, tourism took a different form called sustainable tourism with the aspect of well-planned tour, well-studied destination, and conservation of destination.
Factors that Motivate People to Travel
The most common reasons for the people to travel away from home are −
- To spend holidays leisurely
- To visit friends and relatives
- To attend business and professional engagements
- To get health treatment
- To undertake religious pilgrimages
- Any other personal motives
Traditional and Niche Tourism
The following table lists down a few points that differentiate traditional tourism from niche tourism −
What is Tourism Management?
It involves the management of multitude of activities such as studying tour destination, planning the tour, making travel arrangements and providing accommodation. It also involves marketing efforts to attract tourists to travel to particular destinations.
There is a subtle difference between just travelling and tourism.
Travelling is going from the place of residence or work to another distant or a neighboring place by any means of transport. Routine commutation can be termed as travelling.
Tourism is travelling with an objective. All tourism necessarily include travel but all travel does not necessarily include tourism. We can say, travelling is a subset of tourism.
One similarity between travel and tourism is, they both are temporary movements.
Winter is here! Check out the winter wonderlands at these 5 amazing winter destinations in Montana
- Travel Tips
What Is Tourism Managment
Published: December 12, 2023
Modified: December 28, 2023
by Ashil Brookshire
- Plan Your Trip
- Sustainability
Introduction
Tourism is a flourishing industry that encompasses travel, accommodations, attractions, and activities for leisure, business, or educational purposes. As travel becomes more accessible and people’s desire to explore new places increases, the importance of effective tourism management becomes paramount. Tourism management plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation, sustainability, and profitability of tourism destinations and businesses.
Tourism management involves overseeing and coordinating various aspects of the tourism industry, including marketing, planning, development, operations, and customer service. It aims to provide a positive and enriching experience for tourists, while also benefiting the local communities and preserving the environment.
In this article, we will delve into the definition of tourism management, discuss its importance, explore the key elements and functions within tourism management, and highlight the challenges and emerging trends in the field.
By understanding the intricacies of tourism management, professionals in the industry can develop effective strategies to attract tourists, optimize the visitor experience, and contribute to the overall growth and sustainability of the tourism sector.
Definition of Tourism Management
Tourism management refers to the practice of planning, organizing, and coordinating all the activities and resources involved in the operation of tourism destinations, businesses, and services. It encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, including marketing, budgeting, development, operations, and customer service, with the ultimate goal of ensuring a positive and fulfilling experience for tourists.
Effective tourism management involves a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences, market trends, and destination dynamics. It requires a strategic approach to attract tourists, create memorable experiences, and maximize the economic and social benefits for the local communities. A successful tourism management plan takes into account factors such as infrastructure, transportation, accommodation, attractions, and local resources.
Tourism managers play a crucial role in coordinating the various stakeholders involved in the tourism industry, including government agencies, tourism boards, hospitality establishments, transportation companies, tour operators, and local communities. They work towards developing and implementing strategies that align with the objectives of all parties and ensure the sustainability of tourism destinations.
Furthermore, tourism management involves maintaining a delicate balance between preserving the natural and cultural heritage of a destination and providing quality experiences for tourists. It encompasses initiatives for environmental conservation, responsible tourism practices, and community engagement. By implementing sustainable measures, tourism managers can create long-term benefits and mitigate any negative impacts of tourism on the environment and local communities.
Ultimately, the goal of tourism management is to create a harmonious relationship between tourists, the destination, and the local community. By carefully examining and managing all aspects of the tourism experience, tourism managers strive to meet the demands of the modern traveler, while simultaneously promoting the social, economic, and environmental sustainability of the destination.
Importance of Tourism Management
The importance of effective tourism management cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in the sustainable development and success of tourism destinations and businesses. Here are several key reasons why tourism management is essential:
- Economic Impact: Tourism is a significant source of revenue and job creation worldwide. Tourism management helps maximize the economic benefits by attracting tourists, promoting local businesses, and ensuring the efficient utilization of resources. It stimulates economic growth, enhances employment opportunities, and generates income for the local community.
- Sustainable Development: By implementing sustainable tourism practices, tourism management aims to minimize negative impacts on the environment and culture of the destination. It fosters responsible tourism, encourages conservation efforts, and promotes the well-being of local communities. This ensures the long-term viability and preservation of the destination for future generations.
- Enhanced Visitor Experience: Tourism management focuses on providing exceptional experiences for tourists. It involves careful planning and coordination of attractions, accommodations, transportation, and activities to meet the needs and preferences of different types of travelers. By creating memorable and enjoyable experiences, tourism management fosters positive word-of-mouth recommendations and repeat visits.
- Destination Promotion: Effective tourism management plays a crucial role in destination promotion. It involves strategic marketing initiatives, digital campaigns, and partnerships to attract tourists from different regions. By showcasing the unique offerings of a destination, tourism management helps create a positive image and differentiate it from competitors in the global tourism market.
- Community Engagement: Tourism management actively engages with local communities to ensure their involvement and support in tourism activities. By promoting community participation, respect for local customs and traditions, and equitable distribution of benefits, tourism management fosters a positive relationship between tourists and the local community.
In summary, tourism management is vital for driving economic growth, environmental sustainability, and cultural preservation. It strives to enhance the visitor experience, promote responsible tourism practices, and foster positive relationships between tourists, the destination, and local communities. By prioritizing effective tourism management, destinations can thrive and maximize the benefits of tourism while mitigating potential negative impacts.
Elements of Tourism Management
Tourism management involves various elements that are essential for the successful operation and development of tourism destinations and businesses. These elements encompass the key components that contribute to the overall tourism experience. Here are the main elements of tourism management:
- Marketing and Promotion: This element focuses on creating awareness and attracting tourists to a destination or business. It involves market research, branding, advertising, digital marketing, public relations, and partnerships to effectively communicate the unique selling points of the destination or business.
- Planning and Development: This element involves strategic planning for the sustainable development of tourism destinations. It includes market analysis, infrastructure development, zoning regulations, carrying capacity assessment, and collaboration with stakeholders to ensure the optimal use of resources and development of tourism facilities.
- Operations and Logistics: This element deals with the day-to-day operations and logistical aspects of tourism businesses and destinations. It includes managing accommodations, transportation, attractions, tour operations, customer service, and ensuring smooth operations and seamless experiences for tourists.
- Customer Service and Experience: This element focuses on providing excellent customer service and creating memorable experiences for tourists. It includes training staff, implementing quality assurance measures, addressing customer feedback, and continuously improving the visitor experience to exceed customer expectations.
- Sustainability and Responsible Tourism: This element emphasizes the importance of preserving the natural and cultural heritage of a destination and promoting responsible tourism practices. It involves implementing sustainable measures, minimizing negative impacts of tourism, supporting local communities, and engaging in environmental conservation efforts.
- Economic Management: This element focuses on the financial aspect of tourism management. It involves budgeting, revenue management, pricing strategies, cost control, and financial analysis to ensure profitability and economic sustainability for tourism businesses and destinations.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: This element highlights the significance of collaboration with various stakeholders in the tourism industry. It includes establishing partnerships with government entities, tourism boards, local communities, businesses, and industry associations to foster cooperation, share resources, and work towards common goals.
By addressing and integrating these elements effectively, tourism management can create a well-rounded and holistic approach to the overall management and success of tourism destinations and businesses. It ensures a memorable and sustainable tourism experience for both tourists and the local community.
Functions of Tourism Management
Tourism management involves a range of functions that are essential for the efficient and effective operation of tourism destinations and businesses. These functions contribute to the overall success of the tourism industry and play a vital role in providing a positive experience for tourists. Here are the main functions of tourism management:
- Strategic Planning: This function involves setting goals, formulating strategies, and developing plans to achieve the desired outcomes. It includes analyzing market trends, identifying target markets, and determining the positioning and competitive advantage of the destination or business.
- Market Research: Market research is crucial for understanding customer preferences, market trends, and demand patterns. This function involves conducting surveys, collecting data, and analyzing market insights to develop marketing strategies, identify target audiences, and tailor tourism offerings accordingly.
- Product Development: This function focuses on creating tourism products and experiences that meet the needs and expectations of tourists. It involves identifying unique selling points, designing packages and itineraries, collaborating with local attractions and service providers, and ensuring product innovation to enhance the tourism experience.
- Marketing and Promotion: This function entails creating awareness, attracting tourists, and promoting tourism offerings. It includes advertising, digital marketing, public relations, social media management, content creation, and developing partnerships to effectively reach and engage with target audiences.
- Operations Management: This function deals with the day-to-day operations of tourism businesses and destinations. It includes managing accommodations, transportation, attractions, and activities, as well as ensuring efficient logistics and providing quality customer service to enhance the overall visitor experience.
- Financial Management: Financial management is crucial for the economic sustainability of tourism businesses and destinations. This function involves budgeting, revenue management, pricing strategies, cost control, and financial analysis to ensure profitability and optimize resource allocation.
- Sustainability and Responsible Tourism: This function focuses on environmental conservation, community engagement, and responsible tourism practices. It involves implementing sustainable measures, promoting cultural preservation, supporting local communities, and ensuring the long-term viability of tourism destinations.
- Customer Relationship Management: This function emphasizes building and maintaining strong relationships with customers. It includes managing customer inquiries, addressing feedback and complaints, providing personalized experiences, and fostering customer loyalty through effective communication and relationship building initiatives.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: Collaboration is crucial for the success of tourism management. This function involves establishing partnerships with government entities, tourism boards, local communities, businesses, and industry associations to collaborate, share resources, and work towards common goals for the development and growth of the tourism industry.
By fulfilling these functions, tourism management ensures the seamless operation, sustainable development, and memorable experiences for both tourists and the local community. It is a multifaceted discipline that requires a comprehensive approach to meet the ever-evolving demands of the tourism industry.
Challenges in Tourism Management
Tourism management faces various challenges that can impact the sustainability and success of tourism destinations and businesses. These challenges arise from both internal and external factors and require proactive strategies to overcome. Here are some common challenges in tourism management:
- Seasonality: Seasonality refers to the fluctuation in tourism demand based on the time of year. Many destinations experience peak tourist seasons followed by periods of low or off-peak seasons. Managing seasonality can be a challenge, as it requires finding ways to attract tourists during off-peak times and optimizing resources to accommodate peak season demands.
- Overtourism: Overtourism occurs when the number of tourists exceeds the carrying capacity of a destination, resulting in overcrowding, infrastructure strain, and negative environmental and sociocultural impacts. Managing overtourism involves implementing measures to distribute tourism flows, regulate visitor numbers, and promote sustainable tourism practices.
- Sustainability: Ensuring sustainable tourism is a challenge faced by tourism management. This involves balancing the economic, social, and environmental aspects of tourism to minimize negative impacts and maximize long-term benefits. It requires implementing sustainable practices, promoting responsible tourism, and engaging local communities in decision-making processes.
- Competition: The tourism industry is highly competitive, with destinations and businesses vying for the attention of tourists. Managing competition requires differentiating the destination or business through unique offerings, effective marketing strategies, and continuous innovation to attract and retain visitors.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Consumer behavior and travel preferences are constantly evolving. Tourism management needs to adapt to these changes by understanding emerging trends, catering to different market segments, and providing personalized experiences. This requires staying updated with technology advancements, digital marketing strategies, and consumer insights.
- Economic Volatility: Tourism can be impacted by economic factors such as recessions, exchange rate fluctuations, and political instability. These factors can influence travel decisions, tourist spending, and business operations. Tourism management needs to develop strategies to mitigate the effects of economic volatility and attract tourists during challenging times.
- Infrastructure and Resource Management: Adequate and well-maintained infrastructure is crucial for the smooth operation of tourism. However, managing limited resources, ensuring sustainability, and maintaining infrastructure can be challenging. Tourism management needs to prioritize infrastructure development, enhance resource management, and strike a balance between tourist needs and environmental conservation.
- Technology Disruptions: Rapid advancements in technology impact the tourism industry. Online platforms, social media, and mobile applications have changed the way tourists research, book, and experience travel. Tourism management needs to leverage technology to enhance marketing, distribution channels, customer service, and overall tourism experiences.
- Crisis Management: Tourism destinations are susceptible to natural disasters, political unrest, health crises, and other unforeseen events. Crisis management is crucial in ensuring safety, communication, and recovery. Tourism management should have contingency plans, crisis communication strategies, and cooperation with authorities to effectively manage crises.
Overcoming these challenges requires proactive and strategic approaches in tourism management. By addressing these issues, tourism destinations and businesses can thrive, deliver exceptional visitor experiences, and contribute to the sustainable development of the tourism industry.
Emerging Trends in Tourism Management
Tourism management is constantly evolving to adapt to changing market dynamics, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. Here are some emerging trends in tourism management that are shaping the future of the industry:
- Sustainable Tourism: The increasing emphasis on sustainability has led to a rise in sustainable tourism practices. Travelers are seeking eco-friendly and socially responsible experiences. Tourism management is embracing sustainable initiatives such as reducing carbon emissions, promoting local sourcing, and supporting community development.
- Authentic Experiences: Tourists are increasingly looking for unique and authentic experiences that provide a deeper connection with the destination and its culture. Tourism management is focusing on curating immersive activities, cultural interactions, and off-the-beaten-path experiences to meet these demands.
- Technology Integration: Technology continues to revolutionize the tourism industry. Tourism management is leveraging technologies like virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence to enhance the booking process, improve customer service, and create engaging marketing campaigns.
- Personalization: Personalization is gaining prominence as tourists seek customized experiences tailored to their preferences. Tourism management is utilizing data analytics and customer relationship management tools to segment markets, target specific demographics, and deliver personalized recommendations and offers to travelers.
- Wellness and Health Tourism: Wellness and health tourism have witnessed significant growth. As people prioritize their well-being, tourism management is incorporating wellness activities, spa treatments, yoga retreats, and healthy dining options into destination offerings.
- Community Engagement: Tourism management is recognizing the importance of involving local communities in tourism development. Engaging with local residents, empowering them economically, and showcasing their culture and traditions contribute to sustainable destination management.
- Multi-Generational Travel: With families traveling together, tourism management is focusing on catering to the diverse needs of multi-generational travelers. Destinations are offering a variety of activities and accommodations suitable for different age groups and interests.
- Sharing Economy: The sharing economy has disrupted the traditional tourism industry. Tourism management is adapting by collaborating with sharing economy platforms, integrating home-sharing options, and exploring new business models to meet the evolving demands of travelers.
- Destination Marketing through Influencers: Influencer marketing has become a powerful tool in tourism management. Collaborating with social media influencers to create authentic content and promote destinations has become an effective way to reach and engage with target audiences.
- Accessible Tourism: The focus on inclusivity and accessibility has led to the growth of accessible tourism. Tourism management is ensuring that destinations, accommodations, and attractions are accessible to people with disabilities, providing equal opportunities for all travelers.
These emerging trends are reshaping the tourism industry and presenting new opportunities and challenges for tourism management. By embracing these trends, tourism destinations and businesses can stay competitive, attract a wider range of visitors, and deliver exceptional experiences in the ever-changing landscape of travel and tourism.
Tourism management plays a crucial role in the successful operation, development, and sustainability of tourism destinations and businesses. It encompasses various elements and functions that aim to create exceptional experiences for tourists while considering the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism.
Throughout this article, we have explored the definition of tourism management, its importance, key elements, functions, challenges, and emerging trends. It is evident that effective tourism management is essential for driving economic growth, preserving natural and cultural heritage, promoting responsible tourism practices, and enhancing the overall visitor experience.
However, tourism management also faces challenges such as seasonality, overtourism, sustainability, competition, and changing consumer behavior. These challenges require proactive strategies and innovative approaches to ensure the long-term success and development of tourism destinations.
At the same time, emerging trends in tourism management, including sustainable tourism, personalization, technology integration, and wellness tourism, present new opportunities for growth and innovation within the industry.
In conclusion, tourism management is a dynamic and evolving field that plays a vital role in shaping the tourism industry. By effectively managing tourism destinations and businesses, tourism managers can create positive synergies between tourists, the destination, and local communities, fostering economic growth, environmental preservation, and cultural enrichment.
With the constantly evolving landscape of travel, it is imperative for tourism managers to stay updated with the latest trends, embrace sustainable practices, leverage technology, and engage with diverse stakeholders. By doing so, tourism management can contribute to the growth and sustainability of the tourism industry, creating unforgettable experiences for travelers while fostering a positive and responsible approach towards tourism.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
- Welcome Message
- Mission, Vision and Values
- Meet Our Team
- Why Study With Us
- Accreditations, Memberships & Affiliations
- Industry Partnerships
- Awards and Recognition
- Facts and Figures 2021
- Diploma in Business Administration Co-op
- Diploma in Business Management Co-op
- Diploma in Business Management
- Diploma in Digital Business Management Co-op
- Diploma in Digital Marketing Specialist Co-op
- Certificate in Business Essentials Co-op
- Certificate in General Business Management
- Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management Co-op
- Diploma in Fundamentals of Hospitality and Tourism Co-op
- Diploma in International Hospitality Operations Management Co-op
- Advanced Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management Co-op
- Advanced Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management
- Certificate in Customer Service Excellence Co-op
- Diploma in Data Analytics Co-op
- Preparatory Course for ACCA Examination
- ACCA Part-Time Courses
- Diploma in Cybersecurity Specialist Co-op
- English for Academic Purposes
- Our Study Guides
- Our Courses
- Individual Applications
- Partner Referred Applications
- Admission Requirements
- Better Jobs Ontario Program
- English Proficiency
- Start Dates
- International Students Fees
- Domestic Students Fees
- Scholarships
- Payment options
- Get ready for TSoM
- Convocation
- Internship and Job Fairs
- TSoM Calendar
- Special Events
- Toronto School of Management Reviews & Testimonials
- International Student Advisory (ISA)
- Graduation Requirements
- Chat with our Students and Staff
- Medical Insurance
- Alumni Community
- Career Services
- Our Hiring Process
- Our Co-op Partners
- Hire TSoM Co-Op Students
- Hire TSoM Graduates
- Meet our Students and Graduates
- FAQs for Students
- FAQs for Employers
- University Canada West
- Niagara College – Toronto
- Trebas Institute
- Arden University
- Yorkville University
Scope and future of tourism management

Tourism is considered to be an important aspect of economic growth and the development of a nation. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) , global tourism is expected to reach 1.6 billion (in terms of international arrivals) by the year 2020. Tourism management is generally considered a bright and potential employment sector as it offers a wide variety of career opportunities in both the private and public sector. This article covers the details of tourism management courses and the prospective job opportunities that it can offer you.
What are the different types of tourism?
Tourism is an evolving industry that provides tourists with various experiences that help promote the country, region, or whatever type of destination they are travelling to. There are many different kinds of tourism, and each one caters to a different set of interests. Here are the three main types of tourism:
Domestic Tourism: Domestic tourism refers to travel within your own country. It entails traveling to various regions, cities, or towns within the same country for business, pleasure, or other purposes. Domestic tourism is important for the growth of the tourism business in a country because it helps the economy and encourages other people enthusiastic about promoting local tourism.
Inbound Tourism: Inbound tourism refers to tourism by foreign visitors to a destination country. It involves international travel for pleasure, commerce, or other reasons. People who want to explore new cultures, experience various lifestyles, and visit historical and natural landmarks frequently engage in inbound tourism. Inbound tourism is essential to the growth of a country’s tourism industry because it contributes to the economy and helps promote the country as a travel destination.
Outbound Tourism: Outbound tourism refers to the practice of individuals traveling outside of their country of residence for tourism, business, or other purposes. Outbound tourism plays an essential role to the development of a country’s tourism industry because it adds significantly to the economy and promotes international travel.
What is tourism management?
Tourism management is a multidisciplinary field that includes all activities related to the tourism and hospitality industries. It prepares candidates with the experience and training required to hold managerial positions in food, accommodation and tourism industry. The three major areas of tourism management are:
- Business administration (finance, human resources and marketing activities);
- Management theories and principles;
- Tourism industry (travel accommodation, environmental factors and tourism organizations)
Tourism management implements marketing efforts in attracting tourists to travel to particular destinations. This involves the management of a variety of activities such as:
- Studying tour destination;
- Planning the tour;
- Making travel arrangements;
- Providing accommodation.
Who is eligible for a tourism management course?
- You should obtain an Ontario Secondary School Diploma certificate or equivalent;
- Your age should be 18 years or older;
- You should gain a minimum IELTS score of 5.5 (or its equivalent for non-native English speakers).
What is the course structure of tourism management?
- Front Office Operations – this includes an introduction about the systems and procedures required for Front Desk Office Operations. It helps students develop skills related to reception procedures.
- Customer Service – this module elaborates on the importance of effective communication skills while dealing with customers. It provides students with a better understanding of customer relations and services.
- Food and Beverage Management – focuses on the operations related to food and beverage management. It includes the following topics:
- Food and beverage operations;
- Standard product costs and pricing strategies;
- Productions;
- Controlling;
- Facility design, layout and equipment.
- Hospitality Accounting – this module can help a student enhance their decision making process in the field of management. It provides an in-depth knowledge about the processes and practices of hotel business.
- Human Resource Management – this module is structured to train students to build a strategic and coherent approach to their organizations assets. Students get an opportunity to learn about effective business practices of the hospitality industry.
Other modules covered by a tourism management course are as follows:
- Introduction to Hospitality and Tourism;
- Housekeeping;
- Food and Beverage Operations;
- Food Sanitation, Safety and Health;
- Organizational Behavior in the Hospitality Industry;
- Facilities and Maintenance Management;
- Marketing in Hospitality and Tourism;
- Meetings, Incentives, Conferences and Events;
- Issues in the Hospitality and Tourism Industry;
- Resort Management;
- Niche and Specialty Management.
How long is a tourism management course and how much does it cost?
The tourism management course is a full-time program lasting two years. It consists of 48 weeks of in-class academic sessions. The total length of the course exceeds up to 78 weeks, including scheduled breaks. The total course fee of the tourism management program is CAD 19,000.
What is the career scope of the tourism Industry?
Tour Manager (Average annual salary: $49,150 ) – they must possess language skills and knowledge about weather, customs and tourist attractions. Their main role is to ensure that the tour goes smoothly and tourists get to enjoy themselves during their holiday. Tour managers should have networking and customer service skills as well as a good grasp of the following subjects:
- Archaeology;
- Modern languages;
- Travel, tourism and leisure studies.
Let’s look at some of the responsibilities of a tour manager:
- Accompanying native and foreign groups travelling by bus, planes, boats and trains;
- Welcoming holidaymakers at the starting point and explaining travel arrangements (food, culture, itineraries and destinations) and stop-over points in detail;
- Resolving logistic issues and coordinating travel arrangements;
- Checking tickets or other relevant documents, as well as attending to special requirements such as seat allocations, passport or immigration issues;
- Making accommodation bookings on proposed dates and ensuring that the accommodation is satisfactory;
- Dealing with emergencies and responding to questions from tourists.
The career scope of the tourism industry does not only cover tours and other forms of travel; it also expands to the hospitality sector. Here’s an example of what a career as a Hotel Manager in Canada would look like:
Hotel Manager (Average annual salary: $42,967 ) – their function is to manage hotel employees and day-to-day operations of a hotel. This may include front-of-house reception, food and beverage operations, budgeting and financial management. They are expected to have an understanding of hotel management practices and relevant laws and guidelines. They execute the following tasks:
- Analysing and interpreting financial information;
- Implementing effective marketing strategies to promote the hotel’s services;
- Monitoring sales and profits;
- Supervising maintenance, supplies, renovations and furnishings;
- Dealing with suppliers, travel agencies and event planners;
- Inspecting services and property regularly by enforcing strict compliance with health and safety standards.
The scope of tourism is so diverse that you can also explore opportunities in properties and real estate! A career as a Property Manager would look like the following:
Property Manager (Average annual salary: $56,702 ) – property managers are assigned to work at a resort location to oversee the operations of a facility or assets. They are generally hired by property owners and real estate investors who are unable to manage their properties themselves. Commercial properties run by property managers include apartment complexes, retail malls and business offices. The basic responsibilities of a property manager are:
- Building an effective rental program;
- Providing customer services;
- Establishing positive relationships with long-term clients;
- Dealing with renovations;
- Coordinating group visits;
- Managing association-related business;
- Supervising and coordinating building maintenance;
- Resolving tenant concerns and complaints;
- Advertising, demonstrating and leasing vacant units;
- Collecting and depositing rent;
- Communicating with and sending updates to the property owner on the status of the property.
If you enjoy experiencing cultural exchanges, then you should opt for a tourism management career. Toronto School of Management (TSoM) offers an Advanced Diploma in Hospitality and Tourism Management course to help students enter the hospitality and tourism sector. This course can help you learn how to develop strategic plans for tourism and understand the needs of the target customers.
- What are some of the challenges facing the tourism industry? The tourism sector encounters various obstacles, including the effects of climate change, over-tourism in specific locations, geopolitical instability, evolving travel behaviours, and the emergence of accommodation alternatives.
- What are some of the opportunities for growth in the tourism industry? Despite the obstacles confronting the tourism industry, there are also numerous growth opportunities in this sector. These include the rise of responsible and sustainable tourism, the expansion of the digital economy, and potential for growth in niche markets such as adventure tourism, health and wellness tourism, and cultural tourism.
- How can individuals interested in pursuing a career in tourism management prepare for the future of the industry? Individuals pursuing a career in tourism management can prepare for a stable career by getting quality education in business management, marketing, and finance. It would also help you to have a solid grasp of the tourism industry, including its trends, challenges, and opportunities.

One Reply to “Scope and future of tourism management”
[…] is an important task of destination marketers and researchers in the field of tourism marketing as tourist experiences in destinations can correct and shape the preliminary destination image in their […]
Comments are closed.
Contact Us Today
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Competitiveness.
- Market Intelligence

Policy and Destination Management
- Product Development
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local.
The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance.
Governance has two specific dimensions:
- Directive capacity of government , determined by coordination and collaboration as well as by the participation of networks of stakeholders.
- Directive effectiveness, determined by institutional skills and resources that support the ways in which processes are conducted to define goals and search for solutions and opportunities for relevant stakeholders, and by the provision of tools and means for their joint execution.
In this sense, UN Tourism works to support its Members in their efforts to develop efficient governance models / structures and policies, focusing among others on:
- Tourism policy and strategic planning
- Governance and vertical cooperation, i.e. national-regional-local levels
- Public Private Partnership (PPP)
Destination Management
Destination management consists of the coordinated management of all the elements that make up a tourism destination. Destination management takes a strategic approach to link-up these sometimes very separate elements for the better management of the destination. Joined up management can help to avoid overlapping functions and duplication of effort with regards to promotion, visitor services, training, business support and identify any management gaps that are not being addressed.
Destination management calls for a coalition of many organizations and interests working towards a common goal, ultimately being the assurance of the competitiveness and sustainability of the tourism destination. The Destination Management Organization’s (DMO) role should be to lead and coordinate activities under a coherent strategy in pursuit of this common goal.
Though DMOs have typically undertaken marketing activities, their remit is becoming far broader, to become a strategic leader in destination development. This is a vital ingredient for success in every tourism destination and many destinations now have DMOs to lead the way.
From a traditionally marketing and promotion focus the trend is to become leading organizations with a broader mandate which includes strategic planning, coordination and management of activities within an adequate governance structure with the integration of different stakeholders operating in the destination under a common goal. Destinations wherein such an organization is not still in place are increasingly creating or plan to create a DMO as the organizational entity to lead the way.
UN Tourism has identified three areas of key performance in destination management at DMO level: Strategic Leadership, Effective Implementation and Efficient Governance.
UN Tourism supports its Members and Destination Management/Marketing Organizations through the UN Tourism.QUEST - a DMO Certification System. UN Tourism.QUEST promotes quality and excellence in DMOs planning, management and governance of tourism, by means of capacity building. UN Tourism.QUEST Certification evaluates the three areas of key performance in destination management at DMO level: Strategic Leadership, Effective Implementation and Efficient Governance. With a training and capacity building component, UN Tourism.QUEST is a strategic tool which allows the DMOs to implement an improvement plan to achieve the criteria and standards of the Certification with the aim of enhancing their management processes and thus contribute to the competitiveness and sustainability of the destinations they represent.
Events & Publications
- International Seminar on Destination Management
- 2nd Conference on Destination Management in the Mediterranean
- 6th International Conference on Destination Management
UN Tourism Guidelines for Institutional Strengthening of Destination Management Organizations (DMOs) – Preparing DMOs for new challenges
Many factors account for the increased focus on effective destination management, all of them urging destination management organizations (DMOs) to face and adapt to new challenges. From traditional marketing and promotion boards the trend is for these entities to increasingly enlarge their scope to become all embracing DMOs, aiming to enhance the competitiveness and sustainability of destinations within a harmonious relationship between the residents and visitors.
Competitiveness Committee (CTC)
The Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) is one of the technical committees of the UN Tourism and it is a subsidiary organ of the Executive Council . The Committee was established at the 95th session of the Executive Council in Belgrade, Serbia in May 2013 (CE/DEC/7(XCV). Its Rules of Procedure and the composition were approved by the Executive Council at its 96th session (Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe, August 2013) (CE/DEC/9(XCVI).
Since its establishment in 2013, CTC focused its work mainly on assessing the state of knowledge on the basic concept of “ tourism competitiveness ” and identifying its key factors . This process has also included identifying, developing and harmonizing concepts, models and operational definitions used in the tourism value chain .
Work priorities
(a) To support the Organization in fulfilling its normative role;
(b) To provide a dialogue mechanism between the public and private tourism stakeholders and academia to give guide in building and strengthening tourism competitiveness policies and strategies; and
(c) To build synergies and strategic alignments in the harmonization of the related activities of the Secretariat as well as other collaborating organizations/entities in order to ensure consistency and consensus in the delivery of the outputs and reinforce the official position of the Organization.
Provide UNWTO Members and other tourism stakeholders with a comprehensive and concise, operational, applicable and globally relevant conceptual framework to set the scene and contribute to establish a common ground for a clear harmonized understanding of:
i) concepts, models and operational definitions used in the tourism value chain;
ii) the quantitative and qualitative factors that explain competitiveness at the destination level which may be translated into technical guidelines facilitating a methodology for destinations to identify and evaluate their own factors of competitiveness.
As an outcome of the work of the CTC, the 22 nd Session of the General Assembly held in Chengdu, China (11-16 September 2017) adopted as Recommendations key definitions. Along with these definitions the Committee also focused on identifying the key quantitative and qualitative factors for “tourism competitiveness ” under two categories: i) governance, management and market dynamics, and ii) destination appeal, attractors, products and supply.
Full list of definitions adopted by the 22 nd Session of the General Assembly held in Chengdu, China (11-16 September 2017)
As part of the work of the UNWTO Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) in its mandate for the period 2015-2019 prepared a paper on " Tourism Policy and Strategic Planning " which delves into this factor for tourism competitiveness. This paper (available below in pdf) aims to:
- Provide UNWTO Members with a comprehensive understanding on national tourism policies and contribute to their successful formulation and implementation;
- Explore key areas which need to be addressed in tourism policy and strategic planning in order to ensure the competitiveness and sustainable development of tourism;
- Assess the key areas addressed by UNWTO Members in their tourism policies and provide case studies to illustrate key elements of a sound tourism policy; and
- Serve as a practical tool for UNWTO Members and tourism policymakers by including a set of recommendations.
Composition of the CTC (2019-2023)
Full Members
Bahamas Bahrain Brazil Fiji (Vice-chair) India Israel Kenya Republic of Moldova Senegal (Chair)
Representative of the Associate Members Macao, China (2019-2021) Puerto Rico (2021-2023)
Representative of the Affiliate Members FITUR, Spain (2019-2021) Asociación Empresarial hotelera de Madrid (AEHM), Spain (2021-2023)
Meetings of the CTC:
1st Meeting: 25 August, 2013, Victoria Falls, Zambia /Zimbabwe (during 20th UN Tourism General Assembly) 1st Virtual Meeting: 27 March, 2014 2nd Virtual Meeting: 3 July, 2014 3rd Virtual Meeting: 22 October, 2014 2nd Meeting: 28 January, 2015, Madrid, Spain 3rd Meeting: 13 September, 2015, Medellin, Colombia (during 21st UN Tourism General Assembly) 4th Meeting: 22 January, 2016, Madrid, Spain 4th Virtual Meeting: 21 April, 2016 5th Meeting: 20 January, 2017, Madrid, Spain 5th Virtual Meeting: 2 March, 2017 6th Meeting: 11 September, 2017, Chengdu, China (during 22nd UN Tourism General Assembly) 7th Meeting: 19 January, 2018, Madrid, Spain 8th Meeting: 10 September 2019, Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation (during 23rd UN Tourism General Assembly) 9th Meeting: 24 January, 2020, Madrid, Spain 10th Virtual Meeting: 30 July 2020 11th CTC Meeting: 30 November 2021, Madrid, Spain (during the 24th UN Tourism General Assembly) 12th Virtual Meeting: 12 September, 2022
11th CTC Meeting: 30 November 2021, Madrid, Spain
During the 24th un tourism general assembly.

Download PDF
- Position Paper on Tourism Policyand Strategic Planning
- UN Tourism Tourism Definitions
- Composition of the Committee on tourism and competitiveness

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
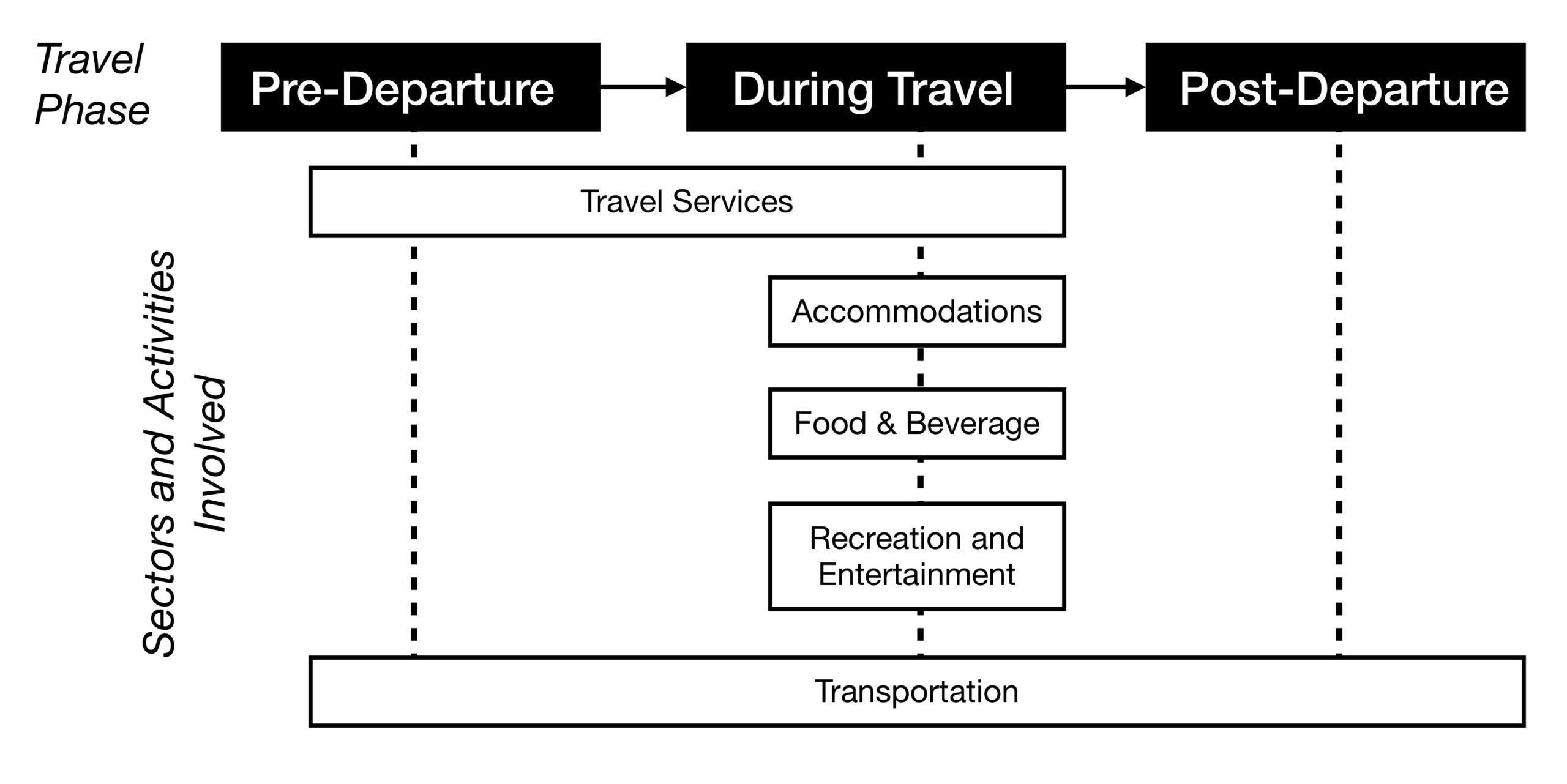
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
What does a Tourism Management do?
Published November 10, 2022 4 min read
A tourism management professional is responsible for the planning and execution of tourism-related activities. They may work in the travel and hospitality industry, or in a government or non-profit organization that promotes tourism. Tourism managers typically have a background in business, marketing, or tourism studies.
Tourism Management job duties include:
- Plan and direct all aspects of an organization's tourism management policies, objectives, and initiatives.
- Develop and implement marketing and advertising campaigns to promote tourism products and services.
- Conduct market research to identify new tourism opportunities and trends.
- Prepare feasibility studies for new tourism projects.
- Develop and oversee the implementation of new tourism products and services.
- Manage the operations of tourism facilities such as hotels, resorts, and tour operators.
- Coordinate the activities of various stakeholders involved in the tourism industry.
- Liaise with government agencies to formulate tourism policies and regulations.
- Represent the organization at international tourism forums and conferences.
Tourism Management Job Requirements
A career in tourism management may require a bachelor's degree in hospitality or tourism management, although some jobs may only require a high school diploma or equivalent. Many tourism management programs include internships or cooperative education experiences, which can give students the opportunity to gain practical experience in the field. Some tourism management positions may require certification from professional organizations such as the American Hotel & Lodging Association or the National Restaurant Association. In addition to formal education and certification, employers often seek candidates with prior experience working in the hospitality or tourism industry.
Tourism Management Skills
- Social Media
- Event Planning
- Fundraising
- Project Management
- Public Speaking
- Customer Service
Related : Top Tourism Management Skills: Definition and Examples
How to become a Tourism Management
A career in tourism management can be both exciting and rewarding. If you are interested in a career in this field, there are a few things you should know.
First, a degree in tourism management can open up many doors. With this degree, you will be able to work in a variety of settings, including hotels, resorts, cruise ships, and more. You will also have the opportunity to work with people from all over the world, which can be a great way to learn about different cultures.
Second, it is important to have strong communication skills when working in tourism management. You will be working with customers and clients from all over the world, so it is important that you are able to communicate effectively.
Third, it is also important to be organized and detail-oriented. This is necessary in order to keep track of all the different aspects of your job.
Fourth, it is helpful to have some knowledge of foreign languages. This can come in handy when working with clients or customers who do not speak English as their first language.
Finally, it is also important to be flexible. The tourism industry is constantly changing, so it is important that you are able to adapt to new situations.
If you are interested in a career in tourism management, keep these things in mind. With hard work and dedication, you can achieve success in this field.
Related : Tourism Management Resume Example
Related : Tourism Management Interview Questions (With Example Answers)
Editorial staff
Brenna Goyette
Brenna is a certified professional resume writer, career expert, and the content manager of the ResumeCat team. She has a background in corporate recruiting and human resources and has been writing resumes for over 10 years. Brenna has experience in recruiting for tech, finance, and marketing roles and has a passion for helping people find their dream jobs. She creates expert resources to help job seekers write the best resumes and cover letters, land the job, and succeed in the workplace.
Similar articles
- Top 17 Tourism Management Resume Objective Examples
- Top 11 Tourism Management Certifications
- What does a Management Analyst do?
- What does a Management Accountant do?
- What does a Management Assistant do?
- What does a Management Consultant do?
The magazine of Glion Institute of Higher Education
- What is tourism and hospitality?

Tourism and hospitality are thriving industries encompassing many sectors, including hotels, restaurants, travel, events, and entertainment.
It’s an exciting and dynamic area, constantly evolving and adapting to changing customer demands and trends.
The tourism and hospitality industry offers a diverse range of career opportunities that cater to various interests, skills, and qualifications, with positions available from entry-level to executive management.
The booming tourism and hospitality industry also offers job security and career growth potential in many hospitality-related occupations.
What is tourism?
Tourism is traveling for leisure, pleasure, or business purposes and visiting various destinations, such as cities, countries, natural attractions, historical sites, and cultural events, to experience new cultures, activities, and environments.
Tourism can take many forms, including domestic, or traveling within your country, and international tourism, or visiting foreign countries.
It can also involve sightseeing, adventure tourism , eco-tourism, cultural tourism, and business tourism, and it’s a huge contributor to the global economy, generating jobs and income in many countries.
It involves many businesses, including airlines, hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, tour operators, and transportation companies.
What is hospitality?
Hospitality includes a range of businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, bars, resorts, cruise ships, theme parks, and other service-oriented businesses that provide accommodations, food, and beverages.
Hospitality is all about creating a welcoming and comfortable environment for guests and meeting their needs.
Quality hospitality means providing excellent customer service, anticipating guests’ needs, and ensuring comfort and satisfaction. The hospitality industry is essential to tourism as both industries often work closely together.
What is the difference between tourism and hospitality?
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries.
Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including transportation, accommodation, and attractions.
Transform your outlook for a successful career as a leader in hospitality management
This inspiring Bachelor’s in hospitality management gives you the knowledge, skills, and practical experience to take charge and run a business

Is tourism and hospitality a good career choice?
So, why work in hospitality and tourism? The tourism and hospitality industry is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world, providing a colossal number of job opportunities.
Between 2021 and 2031, employment in the hospitality and tourism industry is projected to expand faster than any other job sector, creating about 1.3 million new positions .
A tourism and hospitality career can be a highly rewarding choice for anyone who enjoys working with people, has a strong service-oriented mindset, and is looking for a dynamic and exciting career with growth potential.
Growth and job opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Tourism and hospitality offers significant growth and job opportunities worldwide. The industry’s increasing demand for personnel contributes to economic and employment growth, particularly in developing countries.
The industry employs millions globally, from entry-level to high-level management positions, including hotel managers, chefs, tour operators, travel agents, and executives.
It provides diverse opportunities with great career progression and skill development potential.
Career paths in tourism and hospitality

There are many career opportunities in tourism management and hospitality. With a degree in hospitality management, as well as relevant experience, you can pursue satisfying and fulfilling hospitality and tourism careers in these fields.
Hotel manager
Hotel managers oversee hotel operations. They manage staff, supervise customer service, and ensure the facility runs smoothly.
Tour manager
Tour managers organize and lead group tours. They work for tour companies, travel agencies, or independently. Tour managers coordinate a group’s transportation, accommodations, and activities, ensuring the trip runs to schedule.
Restaurant manager
Restaurant managers supervise the daily operations of a restaurant. They manage staff, ensure the kitchen runs smoothly, and monitor customer service.
Resort manager
Resort managers supervise and manage the operations of a resort. From managing staff to overseeing customer service, they ensure the entire operation delivers excellence.
Entertainment manager
Entertainment managers organize and oversee entertainment at venues like hotels or resorts. They book performers, oversee sound and lighting, and ensure guests have a great experience.
Event planner
Event planners organize and coordinate events, such as weddings, conferences, and trade shows. They work for event planning companies, hotels, or independently.
vent planners coordinate all aspects of the event, from the venue to catering and decor.
Travel consultant
Travel consultants help customers plan and book travel arrangements, such as flights, hotels, and rental cars. They work for travel agencies or independently. Travel consultants must know travel destinations and provide superb customer service.
What skills and qualifications are needed for a career in tourism and hospitality?

Tourism and hospitality are rewarding industries with growing job opportunities. Necessary qualifications include excellent skills in communication, customer service, leadership, problem-solving, and organization along with relevant education and training.
Essential skills for success in tourism and hospitality
A career in the tourism and hospitality industry requires a combination of soft and technical skills and relevant qualifications. Here are some of the essential key skills needed for a successful career.
- Communication skills : Effective communication is necessary for the tourism and hospitality industry in dealing with all kinds of people.
- Customer service : Providing excellent customer service is critical to the success of any tourism or hospitality business . This requires patience, empathy, and the ability to meet customers’ needs.
- Flexibility and adaptability : The industry is constantly changing, and employees must be able to adapt to new situations, be flexible with their work schedules, and handle unexpected events.
- Time management : Time management is crucial to ensure guest satisfaction and smooth operations.
- Cultural awareness : Understanding and respecting cultural differences is essential in the tourism and hospitality industry, as you’ll interact with people from different cultures.
- Teamwork : Working collaboratively with colleagues is essential, as employees must work together to ensure guests have a positive experience.
- Problem-solving : Inevitably, problems will arise, and employees must be able to identify, analyze, and resolve them efficiently.
- Technical skills : With the increasing use of technology, employees must possess the necessary technical skills to operate systems, such as booking software, point-of-sale systems, and social media platforms.
Revenue management : Revenue management skills are crucial in effectively managing pricing, inventory, and data analysis to maximize revenue and profitability
Master fundamental hospitality and tourism secrets for a high-flying career at a world-leading hospitality brand
With this Master’s degree, you’ll discover the skills to manage a world-class hospitality and tourism business.

Education and training opportunities in tourism and hospitality
Education and training are vital for a hospitality and tourism career. You can ensure you are prepared for a career in the industry with a Bachelor’s in hospitality management and Master’s in hospitality programs from Glion.
These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of the guest experience, including service delivery and business operations, while developing essential skills such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving. You’ll gain the knowledge and qualifications you need for a successful, dynamic, and rewarding hospitality and tourism career.
Preparing for a career in tourism and hospitality
To prepare for a career in tourism and hospitality management, you should focus on researching the industry and gaining relevant education and training, such as a hospitality degree . For instance, Glion’s programs emphasize guest experience and hospitality management, providing students with an outstanding education that launches them into leading industry roles.
It would help if you also worked on building your communication, customer service, and problem-solving skills while gaining practical experience through internships or part-time jobs in the industry. Meanwhile, attending industry events, job fairs, and conferences, staying up-to-date on industry trends, and networking to establish professional connections will also be extremely valuable.
Finding jobs in tourism and hospitality
To find jobs in tourism and hospitality, candidates can search online job boards, and company career pages, attend career fairs, network with industry professionals, and utilize the services of recruitment agencies. Hospitality and tourism graduates can also leverage valuable alumni networks and industry connections made during internships or industry projects.
Networking and building connections in the industry
Networking and building connections in the hospitality and tourism industry provide opportunities to learn about job openings, meet potential employers, and gain industry insights. It can also help you expand your knowledge and skills, build your personal brand, and establish yourself as a valuable industry professional.
You can start networking by attending industry events, joining professional organizations, connecting with professionals on social media, and through career services at Glion.
Tips for success in tourism and hospitality

Here are tips for career success in the tourism and hospitality industry.
- Gain relevant education and training : Pursue a hospitality or tourism management degree from Glion to gain fundamental knowledge and practical skills.
- Build your network : Attend industry events, connect with colleagues and professionals on LinkedIn, and join relevant associations to build your network and increase your exposure to potential job opportunities.
- Gain practical experience : Look for internships, part-time jobs, or volunteering opportunities to gain practical experience and develop relevant skills.
- Develop your soft skills : Work on essential interpersonal skills like communication, empathy, and problem-solving.
- Stay up-to-date with industry trends : Follow industry news and trends and proactively learn new skills and technologies relevant to tourism and hospitality.
- Be flexible and adaptable : The tourism and hospitality industry constantly evolves, so be open to change and to adapting to new situations and challenges.
- Strive for excellent guest service : Focus on delivering exceptional guest experiences as guest satisfaction is critical for success.
Tourism and hospitality offer many fantastic opportunities to create memorable guest experiences , work in diverse and multicultural environments, and develop transferable skills.
If you’re ready to embark on your career in tourism and hospitality, Glion has world-leading bachelor’s and master’s programs to set you up for success.
Photo credits Main image: Maskot/Maskot via Getty Images

LISTENING TO LEADERS

BUSINESS OF LUXURY

HOSPITALITY UNCOVERED
WELCOME TO GLION.
This site uses cookies. Some are used for statistical purposes and others are set up by third party services. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you accept the use of cookies
Privacy Overview
Related Guides:
- North America
San Jose Tourist Information and Tourism
(san jose, california - ca, usa), more san jose information / fast facts and orientation.
- Country: United States of America (USA)
- Location: Santa Clara County, California (CA)
- Status: city, county seat
- Area: approximately 175 square miles / 453 square kilometers
- Population: approximately 899,000
- Language: American English
- Currency: US Dollar (USD)
- Time zone: GMT - 8 hours Pacific Standard Time (daylight saving time is observed)
- Country dialing code: +1
- Telephone area code: 408
- Religion: various religions
- Average daily January temperature: 17°C / 63°F
- Average daily July temperature: 23°C / 73°F
© Copyright TravelSmart Ltd
I'm looking for:
Hotel Search
- Travel Guide
- Information and Tourism
- Maps and Orientation
- Weather and Climate
- Transport and Car Rental
- SJC Airport Information
- History Facts
- Life and Travel Tips
- Accommodation
- Hotels and Accommodation
- Property and Real Estate
- Popular Attractions
- Tourist Attractions
- Landmarks and Monuments
- Art Galleries
- Attractions Nearby
- Parks and Gardens
- Golf Courses
- Things to Do
- Events and Festivals
- Restaurants and Dining
- Your Reviews of San Jose
- Travel Resources
- USA World Guide
- Guide Disclaimer
- Privacy Policy / Disclaimer
About Cal Pac SRM What's New - Meetings & Events Meet the Board Become a Member! Newsletters Publications & Resources Range Camp Awards Certified Rangeland Managers Contact Us Home
...the art and science of listening to the land.
California-pacific section of the society for range management, providing science, leadership, and information for california-pacific rangeland communities.

To see a map of the boundaries of the CalPac SRM section click here .
- Hosting the annual Range Camp for highschool students, where they discover the science and management of our natural resources from experienced professionals and university faculty, and are introduced to the rangelands careers.
- Managing California Certified Rangeland Manager Program , qualifying professionals to apply scientific principles to rangeland management in the context of the Professional Foresters law.
- Providing Range Manager of the Year and Excellence in Range Management Awards
• Offering leadership opportunities, professional development and continuing education to members by:
- providing and announcing other organizations' rangeland workshops and other training opportunities for members
- Publishing newsletter, Needlegrass Notes
- Offering collegiality at meetings and workshops
• Providing Technical Assistance to rangeland owners, practitioners and the general public by making presentations at educational and tour events.

Range Science integrates many disciplines in order to understand and predict the outcomes of management and ecosystem disturbance in the context of land management goals.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tourism management is the oversight of all activities related to the tourism and hospitality industries. It's a multidisciplinary field that prepares people with the interest, experience, and ...
Tourism management refers to everything related to the hospitality & travel industry. Here you find extensive knowledge about tourism.
Tourism Management - Introduction - Tourism has turned out to be an economic booster contributing to the economic development of many countries over the last few decades. ... Mathieson and Wall (1982) define tourism as follows − "The temporary movement of people to destinations outside their usual places of work and residence, the activities ...
Definition of Tourism Management. Tourism management refers to the practice of planning, organizing, and coordinating all the activities and resources involved in the operation of tourism destinations, businesses, and services. It encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, including marketing, budgeting, development, operations, and customer ...
Tourism is considered to be an important aspect of economic growth and the development of a nation. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), global tourism is expected to reach 1.6 billion (in terms of international arrivals) by the year 2020.Tourism management is generally considered a bright and potential employment sector as it offers a wide variety of career ...
A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. This publication represents a major contribution to developing professionalism in the field of destination management. It is intended as a practical guide, showing how concepts of destination management may be translated into practice. Besides it will be of considerable interest to academics ...
Tourism Management is the leading scholarly journal focuses on the management, including planning and policy, of travel and tourism. The journal takes an interdisciplinary approach in examining international, national and regional tourism as well as specific management …. View full aims & scope. $4550. Article publishing charge.
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. This publication represents a major contribution to developing professionalism in the field of destination management. It is intended as a practical guide, showing how concepts of destination management may be translated into practice. Besides it will be of considerable interest to academics ...
One of the leading texts in the field, Tourism Management is the ideal introduction to the fundamentals of tourism as you study for a degree, diploma or single module in the subject with a global focus. This 6 th edition has been revised and updated to include:. new content on: sports, festivals and event tourism including the impact of the Olympic Games, social media impacts on tourism and ...
International Tourism Management. International Tourism Management is a degree course, whose main focuses with regard to contents consist of business basics with a tourism covering, cross cultural and social competence as well as leadership- and professional competence.
A Practical Guide to Tourism Destination Management. Published: 2007 Pages: 163. eISBN: 978-92-844-1243-3. Abstract: This publication represents a major contribution to developing professionalism in the field of destination management. It is intended as a practical guide, showing how concepts of destination management may be translated into ...
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local. The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance. Governance has two specific dimensions:
Description. One of the leading texts in the field, Tourism Management is the ideal introduction to the fundamentals of tourism as you study for a degree, diploma or single module in the subject with a global focus. This 6 th edition has been revised and updated to include: new content on: sports, festivals and event tourism including the ...
12.7 Impact Factor. Research, Policies, Practice. Tourism Management is the leading scholarly journal focuses on the management, including planning and policy, of travel and tourism. The journal takes an interdisciplinary approach in examining international, national and regional tourism as well as specific management …. View full aims & scope.
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities ...
Tourism managers typically have a background in business, marketing, or tourism studies. Tourism Management job duties include: Plan and direct all aspects of an organization's tourism management policies, objectives, and initiatives. Develop and implement marketing and advertising campaigns to promote tourism products and services.
Hospitality and tourism are both related and separate industries. For instance, airline travel is considered as part of both the tourism and hospitality industries. Hospitality is a component of the tourism industry, as it provides services and amenities to tourists. However, tourism is a broader industry encompassing various sectors, including ...
An important part of the plan is to define the management tools for implementation, such as how to limit access or what regulations are needed to limit length of stay or group size. ... For example, there are PPPs for tourism management in PAs in Australia, and NGOs are involved in the management of some PAs within the 'Natura 2000' network ...
TripActions Travel Management Software TripActions is the only modern, all-in-one travel, corporate card, and expense solution, providing 5000+ customers around the globe unprecedented visibility ...
Average daily January temperature: 17°C / 63°F. Average daily July temperature: 23°C / 73°F. The city of San Jose stands in the state of California and is the capital of Silicon Valley, boasting some impressive statistics. San Jose is one of California's fastest-growing cities, the largest city in northern California, one of America's safest.
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that is a global center for high technology and innovation.Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical area of the Santa Clara Valley. The term "Silicon Valley" refers to the area in which high-tech business has proliferated in Northern California, and it also serves as a general ...
The Society for Range Management is a professional organization composed of individuals with a. common interest in the study, management, and rational use of rangelands and related ecosystems. Cal-Pac Section of SRM represents California and Pacific Islands. Cal-Pac promotes the art and science of sustainable rangeland management by: