Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The U.S. restricts travel from 8 countries as omicron variant spreads

Travelers exit the International Arrivals area at Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, on Monday. The Biden administration is banning travel for non-U.S. citizens from several African countries over concerns about the omicron variant. Jim Watson/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Travelers exit the International Arrivals area at Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, on Monday. The Biden administration is banning travel for non-U.S. citizens from several African countries over concerns about the omicron variant.
The U.S. is enacting travel bans in an effort to limit the spread of the new omicron variant of the coronavirus, which the World Health Organization warns poses a "very high" global risk .

Coronavirus Updates
As omicron spreads, studies suggest that travel bans alone don't do much good.
Starting Monday, President Biden has imposed travel restrictions for non-U.S. citizens from the following eight countries:
- South Africa

The Coronavirus Crisis
Biden says omicron variant is cause for concern but not panic.
The European Union , Canada, United Kingdom, and Israel have announced travel restrictions from southern African countries as well.
Some health officials and public health experts caution that travel restrictions alone may not be effective in controlling the spread of infectious disease , and could even have harmful effects, like exacerbating xenophobia and deterring countries from being transparent about the state of the virus in the future.
The variant was first reported last week in South Africa, where vaccination rates are about 24% .
Cases of the omicron variant have since been confirmed in Botswana, the United Kingdom, Italy, Germany, Belgium, Israel, the Netherlands, Australia and Hong Kong.
Biden is encouraging children and adults to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
"This pandemic will not end until we have global vaccinations," he said last week in a statement .
In an address on Monday, he said the variant is "a cause for concern — not a cause for panic."
Tien Le is an intern on NPR's News Desk.
This story originally appeared on the Morning Edition live blog .
- president biden
- coronavirus
- World Health Organization
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
A Proclamation on Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID- 19 Pandemic
The continued spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global threat to our health and safety. COVID-19 has resulted in more than 733,000 deaths in the United States and more than 4,932,000 deaths worldwide. New variants of SARS-CoV-2 have also emerged globally, and variants that are more transmissible or cause more severe disease than the original virus strain are identified by the United States Government SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group as variants of concern. Globally, as of October 20, 2021, 166 countries have reported cases of the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant, a variant of concern that spreads more easily than previously discovered variants of SARS-CoV-2. The potential emergence of a variant of high consequence — one that significantly reduces the effectiveness of prevention measures or medical countermeasures — is also a primary public health concern.
It is the policy of my Administration to implement science-based public health measures, across all areas of the Federal Government, to prevent further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States, including from international air travelers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the Department of Health and Human Services has determined that the best way to slow the spread of COVID-19, including preventing infection by the Delta variant, is for individuals to get vaccinated. According to the CDC, vaccinated individuals are 5 times less likely to be infected and 10 times less likely to experience hospitalization or death due to COVID-19 than unvaccinated individuals. Other mitigation measures are also critical to slowing the spread of COVID-19. These measures include testing and mask-wearing, which are particularly important strategies to limit the spread of COVID-19 from asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic individuals, as well as self-quarantining and self-isolating. But vaccination is the most important measure for reducing the risk of COVID-19 transmission and for avoiding severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
Substantial efforts are being made to increase vaccination rates across the globe. The availability of COVID-19 vaccines is rising, and over 6 billion doses have been administered globally. As of October 24, 2021, 29 countries have a COVID-19 vaccination rate higher than 70 percent, many countries are making efforts to encourage COVID-19 vaccination for their populations, and some countries are considering or adding proof of vaccination requirements as conditions for entry. Many low-income countries continue to have limited vaccine availability, but the United States is leading a global effort to donate hundreds of millions of vaccine doses where they are needed the most.
In light of these facts and circumstances, I have determined that it is in the interests of the United States to move away from the country-by-country restrictions previously applied during the COVID-19 pandemic and to adopt an air travel policy that relies primarily on vaccination to advance the safe resumption of international air travel to the United States. This proclamation governs the entry into the United States of noncitizen nonimmigrants — that is, noncitizens who are visiting the United States or otherwise being admitted temporarily — traveling to the United States by air. It suspends the entry of unvaccinated noncitizen nonimmigrants, except in limited circumstances, and it ensures that the entry of unvaccinated noncitizen nonimmigrants is consistent with applicable health and safety determinations made by the Director of the CDC, including a requirement that, where appropriate, such individuals agree and arrange to become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 upon their arrival. My Administration has also taken action, apart from this proclamation, to ensure that noncitizen immigrants are vaccinated prior to air travel to the United States. Together, these policies aim to limit the risk that COVID-19, including variants of the virus that causes COVID-19, is introduced, transmitted, and spread into and throughout the United States, potentially overwhelming United States healthcare and public health resources, endangering the health and safety of the American people, and threatening the security of our civil aviation system. Given the resumption of air travel as worldwide restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic begin to ease, these policies will, consistent with the measures required by Executive Order 13998 of January 21, 2021 (Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel), advance the safety and security of the air traveling public, the government personnel responsible for ensuring the security of air travel, and the millions of individuals employed by the United States air travel industry, as well as their families and communities, while also allowing the domestic and global economy to continue its recovery from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
NOW, THEREFORE, I, JOSEPH R. BIDEN JR., President of the United States, by the authority vested in me by the Constitution and the laws of the United States of America, including sections 1182(f) and 1185(a) of title 8, United States Code, and section 301 of title 3, United States Code, hereby find that it is in the interests of the United States to advance the resumption of international travel to the United States, provided necessary health and safety protocols are in place to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States. I further find that vaccination requirements are essential to advance the safe resumption of international travel to the United States and that the unrestricted entry of persons described in section 2 of this proclamation would, except as provided for in section 3(a) of this proclamation, be detrimental to the interests of the United States, and that their entry should be subject to certain restrictions, limitations, and exceptions. I therefore hereby proclaim the following:
Section 1. Revocation of Country-Specific Suspensions and Limitations on Entry. Proclamation 9984 of January 31, 2020 (Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus and Other Appropriate Measures To Address This Risk), Proclamation 9992 of February 29, 2020 (Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Certain Additional Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting 2019 Novel Coronavirus), Proclamation 10143 of January 25, 2021 (Suspension of Entry as Immigrants and Nonimmigrants of Certain Additional Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting Coronavirus Disease 2019), and Proclamation 10199 of April 30, 2021 (Suspension of Entry as Nonimmigrants of Certain Additional Persons Who Pose a Risk of Transmitting Coronavirus Disease 2019), are revoked.
Sec. 2. Global Suspension and Limitation on Entry of Certain Individuals Who Are Not Fully Vaccinated Against COVID-19. (a) The entry into the United States by air travel of noncitizens who are nonimmigrants and who are not fully vaccinated against COVID-19 is suspended and limited, except as provided in section 3 of this proclamation. This suspension and limitation on entry applies only to air travelers to the United States and does not affect visa issuance. (b) Any noncitizen who is a nonimmigrant, who is not fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and who, notwithstanding section 2(a) of this proclamation, is permitted to enter the United States by air travel pursuant to section 3(b) of this proclamation must agree to comply with applicable public health precautions established by the Director of the CDC to protect against the public health risk posed by travelers entering into the United States. Such precautions may be related to vaccination, testing, mask-wearing, self-quarantine, and self-isolation, as determined by the Director of the CDC, and may include requirements that individuals: (i) provide proof of pre-departure testing for COVID-19, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (ii) take precautions during air travel to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19, including by wearing a face mask, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (iii) provide proof of having arranged for post-arrival testing for COVID-19, as determined by the Director of the CDC; and (iv) provide proof of having arranged to self-quarantine or self-isolate after arriving in the United States, as determined by the Director of the CDC. (c) Any noncitizen who is a nonimmigrant, who is not fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and who, notwithstanding section 2(a) of this proclamation, is permitted to enter the United States by air travel pursuant to section 3(b) of this proclamation must agree to become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 within 60 days of arriving in the United States, within some other timeframe as determined by the Director of the CDC, or as soon as medically appropriate as determined by the Director of the CDC, and must provide proof of having arranged to become fully vaccinated against COVID-19 after arriving in the United States, unless: (i) the noncitizen’s intended stay is sufficiently brief, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (ii) the noncitizen is one for whom, given their age, requiring vaccination would be inappropriate, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (iii) the noncitizen has participated or is participating in certain clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccination, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (iv) COVID-19 vaccination is medically contraindicated for the noncitizen, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (v) the noncitizen is described in section 3(b)(i) or 3(b)(ii) of this proclamation and has previously received a COVID-19 vaccine that is authorized or approved by the noncitizen’s country of nationality, as determined by the Director of the CDC, in consultation with the Secretary of State; or (vi) the Director of the CDC otherwise determines that COVID-19 vaccination is not warranted for the noncitizen.
Sec. 3. Scope of Suspension and Limitation on Entry. (a) The suspension and limitations on entry in section 2 of this proclamation shall not apply to any noncitizen seeking entry as a crew member of an airline or other aircraft operator if such crew member or operator adheres to all industry standard protocols for the prevention of COVID-19, as set forth in relevant guidance for crew member health issued by the CDC or by the Federal Aviation Administration in coordination with the CDC. (b) The suspension and limitations on entry in section 2(a) of this proclamation shall not apply to: (i) any noncitizen seeking entry into or transiting the United States pursuant to one of the following nonimmigrant visa classifications: A-1, A-2, C-2, C-3 (as a foreign government official or immediate family member of an official), E-1 (as an employee of TECRO or TECO or the employee’s immediate family members), G-1, G-2, G-3, G-4, NATO-1 through NATO-4, or NATO-6 (or seeking to enter as a nonimmigrant in one of those NATO classifications); (ii) any noncitizen whose travel falls within the scope of section 11 of the United Nations Headquarters Agreement or who is traveling pursuant to United States legal obligation (as evidenced by a letter of invitation from the United Nations or other documentation showing the purpose of such travel); (iii) any noncitizen for whom, given their age, requiring vaccination would be inappropriate, as determined by the Director of the CDC, taking into account global vaccine availability for individuals in that age group; (iv) any noncitizen who has participated or is participating in certain clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccination, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (v) any noncitizen for whom accepted COVID-19 vaccination is medically contraindicated, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (vi) any noncitizen who has been granted an exception by the Director of the CDC for humanitarian or emergency reasons, as determined by the Director of the CDC; (vii) any noncitizen who is a citizen of a foreign country where the availability of COVID-19 vaccination is limited, as identified pursuant to section 4(a)(v) of this proclamation, and who seeks to enter the United States pursuant to a nonimmigrant visa, except for a B-1 or B-2 visa; (viii) any noncitizen who is a member of the United States Armed Forces or who is a spouse or child of a member of the United States Armed Forces; (xi) any noncitizen seeking entry as a sea crew member traveling pursuant to a C-1 and D nonimmigrant visa, if such crew member adheres to all industry standard protocols for the prevention of COVID-19, as set forth in relevant guidance for crew member health by the CDC; or(x) any noncitizen or group of noncitizens whose entry would be in the national interest, as determined by the Secretary of State, the Secretary of Transportation, the Secretary of Homeland Security, or their designees.
Sec. 4. Implementation and Enforcement. (a) The Secretary of Health and Human Services, through the Director of the CDC, shall implement this proclamation as it applies to the public health through such procedures as may be established, and consistent with the CDC’s independent public health judgment, including by: (i) defining and specifying accepted COVID-19 vaccines or combinations of accepted COVID-19 vaccines, and medical contraindications to accepted COVID-19 vaccines or combinations of accepted COVID-19 vaccines, for purposes of this proclamation; (ii) defining whether an individual is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, and specifying acceptable methods of proving that an individual is fully vaccinated against COVID-19, for purposes of this proclamation; (iii) specifying acceptable methods of proving that an individual has arranged to comply with applicable public health requirements and protocols to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States, including pre-departure testing, post-arrival testing, post-arrival self-quarantine or self-isolation, and post-arrival vaccination against COVID-19, for purposes of this proclamation; (iv) determining whether certain persons qualify as participants in certain clinical trials for COVID-19 vaccination, for purposes of this proclamation; (v) maintaining a list of countries where the availability of COVID-19 vaccination is limited, with such countries defined as those where less than 10 percent of the country’s total population has been fully vaccinated with any available COVID-19 vaccine or are otherwise determined by the Director of the CDC to qualify as countries where the availability of COVID-19 vaccination is limited; and (vi) establishing other public health measures consistent with this proclamation to protect against the further introduction, transmission, and spread of COVID-19 into and throughout the United States by persons described in section 2 of this proclamation. (b) The Secretary of Transportation and the Secretary of Homeland Security shall take steps to ensure that airlines do not permit noncitizens barred from entry pursuant to this proclamation to board an aircraft traveling to the United States, to the extent permitted by law. (c) Executive departments and agencies shall implement this proclamation, as appropriate and consistent with applicable law, in accordance with such procedures as they may establish. (d) The Secretary of State, the Secretary of Transportation, and the Secretary of Homeland Security shall review any regulations, orders, guidance documents, policies, and any other similar agency actions developed pursuant to Proclamations 9984, 9992, 10143, and 10199 and, as appropriate, shall consider revising or revoking these agency actions consistent with the policy set forth in this proclamation. (e) Nothing in this proclamation shall be construed to affect any individual’s eligibility for asylum, withholding of removal, or protection under the regulations issued pursuant to the legislation implementing the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment, consistent with the laws and regulations of the United States. (f) Nothing in this proclamation shall be construed to limit the CDC’s authority to impose public health requirements and protocols, including on individuals who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19, individuals covered by this proclamation, or individuals not covered by this proclamation, such as United States citizens, lawful permanent residents, or noncitizens traveling on immigrant visas.
Sec. 5. Termination. This proclamation shall remain in effect until terminated by the President. The Secretary of Health and Human Services shall, as circumstances warrant and no more than 60 days after the date of this proclamation and by the final day of each calendar month thereafter, recommend whether the President should continue, modify, or terminate this proclamation.
Sec. 6. Effective Date. This proclamation is effective at 12:01 a.m. eastern standard time on November 8, 2021. This proclamation does not apply to persons aboard a flight scheduled to arrive in the United States that departed prior to 12:01 a.m. eastern standard time on November 8, 2021.
Sec. 7. Severability. It is the policy of the United States to enforce this proclamation to the maximum extent possible to advance the national security, public safety, and foreign policy interests of the United States. Accordingly, if any provision of this proclamation, or the application of any provision to any person or circumstance, is held to be invalid, the remainder of this proclamation and the application of its provisions to any other persons or circumstances shall not be affected thereby.
Sec. 8. General Provisions. (a) Nothing in this proclamation shall be construed to impair or otherwise affect: (i) the authority granted by law to an executive department or agency, or the head thereof; or (ii) the functions of the Director of the Office of Management and Budget relating to budgetary, administrative, or legislative proposals. (b) This proclamation shall be implemented consistent with applicable law and subject to the availability of appropriations. (c) This proclamation is not intended to, and does not, create any right or benefit, substantive or procedural, enforceable at law or in equity by any party against the United States, its departments, agencies, or entities, its officers, employees, or agents, or any other person.
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, I have hereunto set my hand this twenty-fifth day of October, in the year of our Lord two thousand twenty-one, and of the Independence of the United States of America the two hundred and forty-sixth.
JOSEPH R. BIDEN JR.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
Travel Restrictions to Prevent the Spread of Disease
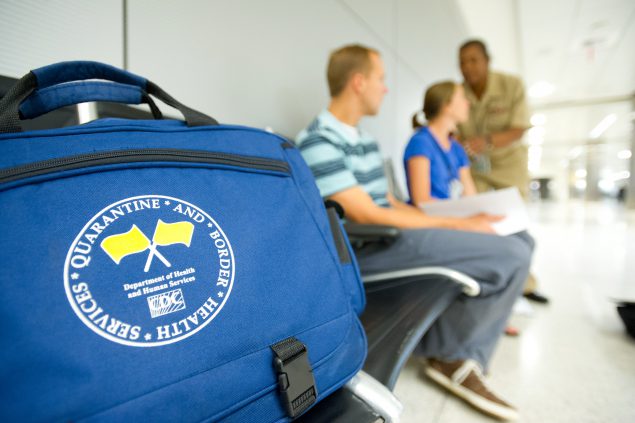

Credit: David Snyder
Disease is just a flight away. To protect America’s health, CDC partners with the Department of Homeland Security to prevent the spread of serious contagious diseases during travel. CDC uses a Do Not Board list to prevent travelers from boarding commercial airplanes if they are known or suspected to have a contagious disease that poses a threat to the public’s health. Sick travelers are also placed on a Lookout list so they will be detected if they attempt to enter the United States by land or sea. These tools can be used for anyone who poses a threat to the public’s health.
Local and state public health officials can request CDC’s assistance if a person who poses a public health threat intends to travel. CDC helps ensure these people do not travel while contagious.
Placing people on the lists
The criteria for adding people to the Do Not Board and Lookout lists are
- not aware of diagnosis or not following public health recommendations, or
- Likely to travel on a commercial flight involving the United States or travel internationally by any means; or
- Need to issue travel restriction to respond to a public health outbreak or to help enforce a public health order.
Criteria number one plus one of the three subsets must be met for a person to be placed on the Do Not Board and Lookout lists.
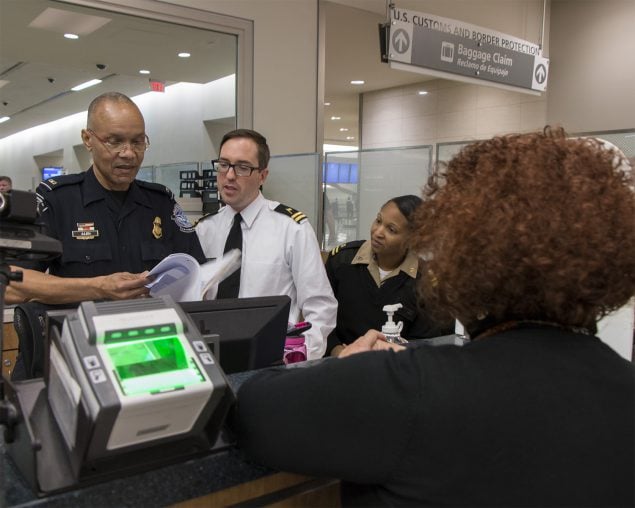

Credit: David Heaberlin
Once a person is placed on these lists, airlines will not issue a boarding pass to the person for any commercial flight within, arriving to, or departing from the United States.
The Do Not Board and Lookout lists have been used for people with suspected or confirmed infectious tuberculosis (TB), including multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and measles. During 2020-2022, CDC used these authorities to restrict travel of people with COVID-19 and close contacts who were recommended to quarantine. These authorities were also used for mpox during 2022. Travel restrictions can also be used for other suspected or confirmed contagious diseases that could pose a public health threat during travel, including viral hemorrhagic fevers such as Ebola.
Preventing people with contagious diseases from traveling also helps to make sure they get or continue medical treatment, such as for infectious tuberculosis.
Taking people off the lists
Once public health authorities confirm a person is no longer contagious, the person is removed from the lists (typically within 24 hours). Also, CDC reviews the records of all persons on the lists every two weeks to determine whether they are eligible for removal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Travel Restrictions to Prevent the Spread of Disease
- Importation
- Southern Border Health and Migration
- Travelers' Health
- Vessel Sanitation Program
- Funding and Guidance for State and Local Health Departments
- Emergency Preparedness and Response
- Division of Global Migration Health
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Advertisement
Supported by
With Scant Information on Omicron, Biden Turned to Travel Ban to Buy Time
“Here’s what it does: It gives us time,” President Biden said of the flight restrictions. He called the new variant a cause for concern, not panic.
- Share full article
Biden Urges Vaccinations Amid Omicron Variant Concerns
President biden called the new omicron coronavirus variant “a cause for concern, not a cause for panic,” and urged americans to get vaccinations and booster shots. the variant has not yet been detected in the united states..
The very day the World Health Organization identified the new variant, I took immediate steps to restrict travel from countries in Southern Africa. But while we have that travel restrictions can slow the speed of Omicron, it cannot prevent it. But here’s what it does. It gives us time, gives us time to take more actions, to move quicker, to make sure people understand you have to get your vaccine. You have to get the shot. You have to get the booster. The — sooner or later, we’re going to see cases of this new variant here in the United States. We’ll have to face this new threat just as we faced those that come before it. This variant is a cause for concern, not a cause for panic. We have the best vaccine in the world, the best medicines, the best scientists, and we’re learning more every single day. And we’ll fight this variant with scientific and knowledgeable actions and speed, not chaos and confusion. In the event — hopefully unlikely — that updated vaccinations or boosters are needed to respond to this new variant, we will accelerate their development and deployment with every available tool. I want to reiterate: Dr. Fauci believes that the current vaccines provide at least some protection against the new variant and the boosters strengthen that protection, significantly. We do not yet believe that additional measures will be needed, but so that we are prepared if needed, my team is already working with officials at Pfizer and Moderna and Johnson & Johnson to develop contingency plans for vaccines or boosters if needed.

By Michael D. Shear and Sheryl Stolberg
WASHINGTON — By the time President Biden was briefed on the emergence of a fast-moving new Covid variant on the morning after Thanksgiving, he had a choice to make — and little information to base it on.
In a secure conference call from a vacation compound overlooking Nantucket Harbor, the president listened as his health advisers told him that the highly mutated virus was far more concerning than other variants they had seen in recent months. It spread twice as fast as the dominant Delta variant and had the potential to evade treatments and vaccines .
Banning travel from southern Africa, where the variant was discovered last week, would not stop the coronavirus from finding its way to the United States, the officials told Mr. Biden, even though Britain and several other countries had announced similar restrictions. But the measures might slow the spread.
During the 30-minute briefing, Dr. Anthony S. Fauci, the president’s top medical adviser for the coronavirus, and other health officials acknowledged how little they knew about the threat, according to White House officials and others familiar with the discussion. But they concluded that even a potentially marginal benefit from a travel ban was worth the criticism that it was likely to generate from the affected countries, the officials said. Better to be criticized for something you do, rather than for something you don’t do.
A few hours later, as Mr. Biden ate lunch with his extended family at the Nantucket Tap Room, the White House issued a statement in his name announcing a ban on travel from eight countries in southern Africa , prompting outrage among leaders in that region — and from global health experts who questioned the benefits of the move, saying it was tantamount to punishing South Africa for being transparent about the virus.
“Here’s what it does: It gives us time. Gives us time to take more actions to move quicker,” Mr. Biden said at the White House on Monday morning as he called the new variant, named Omicron , “a cause for concern, not a cause for panic.”
The sudden arrival of Omicron represented a jarring, here-we-go-again moment for a weary and politically divided country after nearly two years of battling the pandemic. It also underscored the difficult position the president is in as he seeks to respond aggressively to yet another public health threat.
The scramble among White House and public health officials on Thursday night and Friday morning was a reminder that the United States remains vulnerable to a virus that is still spreading, unchecked through largely unvaccinated parts of the world — a problem that is well beyond the control of any global leader. And it once again highlighted the political dangers for Mr. Biden and his party if a new wave of infections derails the country’s economic recovery and return to some semblance of normalcy.
The president on Monday sought to reassure the public, ruling out a return to the kinds of nationwide “shutdowns and lockdowns” that ground economic and social life to a halt last year. Instead, he said, the administration would combat the new variant “with more widespread vaccinations, boosters, testing and more.”
Mr. Biden’s call for more vaccinations came as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Monday altered its guidance and urged all adults to get a booster shot when they are eligible, six months after their initial Pfizer or Moderna doses or two months after their initial Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The agency had previously urged eligible people over 50 and those living in long-term care facilities to get a booster shot, but stopped short of saying that everyone should do so.
In addition, Pfizer and BioNTech will ask federal regulators this week to authorize their booster shot for 16- and 17-year-olds , according to people familiar with the companies’ plan.
Scientists were working to make sure current tests could accurately detect the new variant, officials said; the administration was working with manufacturers to modify their vaccines and booster shots, should that prove necessary, Mr. Biden said.

White House officials said that the president would outline a detailed strategy for fighting the coronavirus this winter when he visits the National Institutes of Health on Thursday.
But significant risks remain, including to the nation’s economy.
Jerome H. Powell, the Federal Reserve chair, plans to tell lawmakers on Tuesday that Omicron creates more economic uncertainty and the possibility of further inflation, according to a copy of his prepared remarks.
“Greater concerns about the virus could reduce people’s willingness to work in person, which would slow progress in the labor market and intensify supply-chain disruptions ,” Mr. Powell plans to say.
In his remarks on Monday, Mr. Biden promised that he was “sparing no effort, removing all roadblocks to keep the American people safe.”
That pledge came as some Republicans seized on the existence of another variant to attack the president. The Republican National Committee issued a statement saying that “Biden failed to shut down the virus as he promised.” Representative Ronny Jackson of Texas, who served as President Donald J. Trump’s White House physician, suggested that Omicron was created by liberals eager to impose further Covid restrictions.
White House officials dismissed the political criticism. Natalie Quillian, the deputy Covid-19 response coordinator, said the potential dangers from the new variant were serious enough to prompt a flurry of meetings among officials from multiple agencies, calls with pharmaceutical companies and urgent messages to health officials in other countries.
“There was a sense of concern, a sense that this felt different from other variants,” Ms. Quillian said. “This had enough of the markers to differentiate itself in the level of concern we felt. We sort of kicked into action Thursday night and Friday.”
The new variant upended the Thanksgiving holiday for administration officials and top scientists, who had scattered across the country for celebrations.
The variant was identified by South African scientists on Thursday afternoon, as many U.S. officials were sitting down to dinner. Shortly before midnight, Dr. David A. Kessler, the chief science officer for the government’s coronavirus response, reached out to a South African partnership, which sent back a genomic sequencing report on the variant.
Dr. Fauci and Dr. Rochelle P. Walensky, the C.D.C. director, were in contact with their counterparts in South Africa late on Thanksgiving Day. Jeff Zients, the president’s Covid-19 response coordinator, and others spent most of the night making calls.
By Friday morning, it appeared that Mr. Zients was leaning toward travel restrictions, according to one person familiar with the deliberations. At 10:30, Mr. Zients, Dr. Fauci and other top scientists were briefed by the South Africans, including Tulio de Oliveira, a geneticist who helped identify the Omicron variant .
After Mr. Biden made the decision to impose the travel ban, State Department officials told diplomats in the affected countries, and administration officials began calling airlines to inform them of the change. From the beginning of the discussion late Thursday, it took about eight hours to issue the presidential directive.
“Even if we bought ourselves a little bit of time to understand this more, that was valuable,” Ms. Quillian said. “And this is an action that’s not permanent.”
For now, the travel restrictions are the president’s primary response.
Dr. Michael T. Osterholm, an infectious disease expert at the University of Minnesota who advised Mr. Biden during the presidential transition, said that while travel bans could help officials gain “situational awareness,” they offered only temporary benefits. He said he would not be surprised if the restrictions were soon lifted.
“It’s like in a crime scene,” Dr. Osterholm said. “When you go to a crime scene, what do the police do right away? They lock everything down so they can figure out what’s going on. But that doesn’t mean they are going to keep things locked down for the rest of the day or the rest of the week.”
But several public health experts expressed outrage at the bans, saying they punished South Africa for doing what the United States expected of other nations: tracking the coronavirus, identifying worrisome variants and making the information public.
“Travel restrictions are exactly the wrong incentive to give to countries when you want them to share data,” said Gregg Gonsalves, an activist and associate professor of epidemiology at Yale University. “You want them to be on the lookout for new variants, and you shut your borders?”
Mr. Oliveira warned on Twitter on Monday that because planes were no longer flying to South Africa, his lab might run out of some of the chemical components known as reagents that are needed to test for the variant.
“It will be ‘evil’ if we cannot answer the questions that the world needs about #Omicron due to the travel ban!” he wrote .
The new variant has again raised criticism that the Biden administration is not doing enough to vaccinate the rest of the world, though that effort is complicated by vaccine hesitancy in other nations.
South Africa has fully vaccinated only 24 percent of its population, according to the Our World in Data project at the University of Oxford. It has a better vaccination rate than most countries on the continent , but has asked vaccine makers to stop sending doses because of trouble getting shots into arms, in part because of distribution bottlenecks and hesitancy.
Elsewhere in Africa, the vaccination rate is much lower; in some countries, even health care workers have had trouble getting their shots. The W.H.O. reported last week that only 27 percent of health workers in Africa had been fully vaccinated.
The Biden administration has pledged to donate more than a billion doses to other nations; so far it has shipped 275 million doses to 110 countries.
“Now we need the rest of the world to step up as well,” the president said.
But activists and some global health experts said the administration needed to move faster, arguing that vaccine inequities were the reason for the emergence of the variant.
African officials on Monday criticized the global effort to provide vaccines to their countries, saying in a joint statement that their low vaccination rates were the result of a lack of consistent, reliable doses.
“The majority of the donations to date have been ad hoc, provided with little notice and short shelf lives,” they said in the statement. “This has made it extremely challenging for countries to plan vaccination campaigns and increase absorptive capacity.”
“This trend must change,” they added.
Michael D. Shear is a veteran White House correspondent and two-time Pulitzer Prize winner who was a member of team that won the Public Service Medal for Covid coverage in 2020. He is the co-author of “Border Wars: Inside Trump's Assault on Immigration.” More about Michael D. Shear

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Note: On April 12, 2024, President Biden revoked the 2021 executive order that had established the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force. As a result, the Safer Federal Workforce Task Force no longer exists and this website will no longer be updated. This website is preserved as it existed on April 12, 2024, for archival purposes only.

Official Travel
Federal employees should adhere strictly to CDC guidance for domestic and international travel before, during, and after official travel.
Q: Are there any restrictions on official travel approved by Federal agencies?
A: No. There are no Government-wide limits on official travel (i.e., travel conducted under an official travel authorization) for Federal employees, regardless of their vaccination status. Individuals should follow their agency’s travel policy.
In approving official travel for an individual, agencies should:
- Inform the traveling individual that CDC recommends that individuals make sure they are up to date with COVID-19 vaccines before travel;
- Recommend that the traveling individual consider being tested for current infection with a viral test as close to the time of departure as possible (no more than 3 days) before travel;
- Instruct the traveling individual to adhere strictly to CDC guidance for domestic and international travel before, during, and after official travel;
- Instruct the traveling individual to check their destination’s COVID-19 Community Level before traveling, and to wear a high-quality mask or respirator (such as an N95) while on-duty and around others indoors at their destination, if the COVID-19 Community Level in the county where their destination is located is HIGH;
- Instruct the traveling individual to make sure they understand and follow all travel restrictions put in place by State, Tribal, local, and territorial governments; and
- Advise the traveling individual to prepare to be flexible during their travel, as restrictions, policies, and circumstances may change during their travel.
Heads of agencies should issue specific travel guidance as needed to account for the specific requirements of their agency’s mission.
Q: Should Federal agencies recommend or require employees to complete CDC-recommended COVID-19 testing before and after official travel? Can the expenses associated with this testing be claimed on a travel voucher for employee reimbursement?
A: When CDC recommends that travelers consider COVID-19 testing for current SARS-CoV-2 infection with a viral test prior to or following travel, agencies should recommend to employees traveling on official business that they consider being tested consistent with such CDC guidance. When CDC otherwise recommends or requires COVID-19 testing prior to or following travel, agencies must require employees traveling on official business be tested consistent with such CDC guidance, pursuant to Executive Order 13991. Agencies should provide for any recommended testing and must provide for any required testing associated with official travel at no cost to the employee, such as through the agency’s screening testing program, the agency’s in-house capabilities for diagnostic testing at the worksite, or through an alternative process determined by the agency. The cost of such testing recommended or required for official travel, and not available through a Federal dispensary or not covered (or reimbursable) through travel insurance, can be claimed in a travel voucher as a Miscellaneous Expense under agency travel policies.
Q: Should agencies limit official travel for individuals who have had a known close contact with someone with COVID-19?
A: No. For asymptomatic individuals who have had a known exposure to someone with COVID-19 within the past 10 days, agencies may approve official travel, consistent with the agency’s travel policy. If the individual remains without COVID-19 symptoms before traveling, then pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance, the agency must instruct the individual to, in addition to other standard pre-travel instructions related to COVID-19:
- Wear a high-quality mask or respirator (such as an N95) the entire time they are on-duty and around others indoors for the full duration of their travel that falls within the 10 full days after their last known exposure;
- Not travel on public transportation such as airplanes, buses, and trains if they will not be able to wear a high-quality mask or respirator (such as an N95) when around others indoors for the full duration of their travel within the 10 full days after their last known exposure; and
- Follow other aspects of post-exposure protocols , including the requirement for individuals with a known exposure to be tested for COVID-19 after 5 full days following their last known exposure (ideally, on or after day 6)—note that this testing may need to occur while the individual is traveling, and that agencies do not need to require that employees wait for the results of this post-exposure diagnostic test to undertake official travel, including return travel.
If the individual develops COVID-19 symptoms after official travel has been approved, then pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance, the agency must instruct the individual to not undertake further official travel, including under that previously approved travel authorization, and to instead follow agency protocols consistent with Safer Federal Workforce Task Force guidance on travel for individuals with COVID-19 symptoms.
Q: What should agencies do regarding official travel for individuals who develop COVID-19 symptoms or have a positive viral test 10 full days or less prior to their intended departure date?
A: Pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance, agencies must not approve official travel (i.e., travel conducted under an official travel authorization) for individuals who have COVID-19 symptoms and are waiting for an initial diagnostic viral test result, and agencies must not approve official travel for individuals who have tested positive for COVID-19 for at least 5 full days after their first day of symptoms, or after the date of the initial positive diagnostic viral test for asymptomatic individuals.
If an individual who tested positive for COVID-19 has returned to working onsite at an agency workplace or interacting with members of the public as part of their official responsibilities (once they are fever-free for 24 hours without the use of fever-reducing medication and their other symptoms are improving), then the agency may approve official travel for the individual.
Pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance on isolation, the agency must instruct the individual to, in addition to other standard pre-travel instructions related to COVID-19:
- Wear a high-quality mask or respirator (such as an N95) the entire time they are on-duty and around others indoors for the full duration of their travel that falls within the period they are otherwise required to wear a high-quality mask or respirator after ending isolation , consistent with Safer Federal Workforce Task Force guidance;
- Not travel on public transportation such as airplanes, buses, and trains if they will not be able to wear a high-quality mask or respirator (such as an N95) when around others indoors for the full duration of their travel that falls within the period they are otherwise required to wear a high-quality mask or respirator after ending isolation , consistent with Safer Federal Workforce Task Force guidance; and
- Follow other aspects of post-isolation protocols .
If after official travel has been approved, the individual’s COVID-19 symptoms recur or worsen, then pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance on isolation, agencies must instruct the individual to not undertake further official travel, including under any previously approved travel authorization, and to again not enter a Federal facility or interact with members of the public as part of their official responsibilities, restarting at day 0 of isolation protocols.
Q: What should agencies do if an employee has probable or confirmed COVID-19 while on official travel?
A: If an employee has probable or confirmed COVID-19 while on official travel (i.e., travel conducted under an official travel authorization), then pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance, agencies must instruct the individual to follow agency isolation protocols and not undertake further official travel, including return travel, for at least 5 full days after their first day of symptoms, or after the date of the initial positive diagnostic viral test for asymptomatic individuals. The agency must cover all costs associated with travel and lodging expenses, as well as the cost of any diagnostic testing, in these circumstances, to the extent permitted by the Federal Travel Regulation.
After that point, once the individual is fever-free for 24 hours without the use of fever-reducing medication and their other symptoms are improving, then the agency may instruct the individual that they can proceed with undertaking further travel, including return travel. Pursuant to Executive Order 13991 and consistent with CDC guidance on isolation, the agency must then instruct the individual to, in addition to other standard pre-travel instructions related to COVID-19:
If at any point prior to their return travel the individual’s COVID-19 symptoms recur or worsen, agencies must instruct the individual to not undertake further official travel, including return travel, and to not enter a Federal facility or interact with members of the public as part of their official responsibilities, restarting at day 0 of isolation protocols, consistent with Executive Order 13991 and CDC recommendations on isolation and the protocols set forth by their agency.
The agency must cover all costs associated with travel and lodging expenses, as well as the cost of any diagnostic testing, in these circumstances, to the extent permitted by the Federal Travel Regulation.
Places the U.S. Government Warns Not to Travel Right Now
You may want to reconsider traveling to these countries right now.
Do Not Travel to These Countries

Getty Images
Crime, civil unrest and terrorism are common risk factors for countries that end up on the State Department's "Do Not Travel" advisory list.
In 2024, tourism across the globe is “well on track” to return to pre-pandemic levels, according to projections by UN Tourism.
Global conflicts and natural disasters , ranging from a series of coups across Africa to catastrophic earthquakes in the Middle East affected international travel patterns throughout 2023. Still, international tourist arrivals reached 87% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023, according to estimates by UN Tourism .
In January 2024 alone, about 4.6 million U.S. citizens left the country for international destinations, 17% higher than the same month in 2019, according to the International Trade Administration . But some destinations warrant more caution than others.
On Oct. 19, 2023, following the outbreak of war between Israel and Gaza and flaring tensions in the region, the U.S. State Department issued a worldwide caution advisory due to “increased tensions in various locations around the world, the potential for terrorist attacks, demonstrations or violent actions against U.S. citizens and interests.” Prior to this update, the most recent worldwide caution advisory was issued in 2022 after a U.S. strike killed Ayman al-Zawahiri, Osama bin Laden’s successor as leader of Al Qaeda, causing “a higher potential for anti-American violence.” The worldwide caution advisory remains in effect.
The U.S. State Department also issues individual travel advisory levels for more than 200 countries globally, continually updating them based on a variety of risk indicators such as health, terrorism and civil unrest. Travel advisory levels range from Level 1, which means exercise normal precautions, to Level 4, which means do not travel there.
About 10% of countries – 19 total – have a Level 4: “Do Not Travel” advisory as of Mar. 4. In Level 4 countries, the U.S. government may have “very limited ability” to step in should travelers’ safety or security be at risk, according to the State Department. Crime, civil unrest, kidnapping and terrorism are common risk factors associated with Level 4 countries.
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list.
Places With a Level 4 Travel Advisory
These are the primary areas the U.S. government says not to travel to right now, in alphabetical order:
Jump to Place: Afghanistan Belarus Burkina Faso Central African Republic Myanmar (formerly Burma) Gaza Haiti Iran Iraq Libya Mali Mexico North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) Russia Somalia South Sudan Sudan Syria Ukraine Venezuela Yemen
Afghanistan: The Central Asian country is wrestling with “terrorism, risk of wrongful detention, kidnapping and crime,” according to the State Department. U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for wrongful detention and kidnapping. In 2022, the government reinstituted public floggings and executions, and women’s rights are disappearing under Taliban control. The U.S. Embassy in Kabul halted operations in August 2021. Since the Taliban took control , many forms of international aid have been halted . Meanwhile, in 2023, some of the year’s deadliest earthquakes killed more than 2,400 in Afghanistan while the country continues to face a years-long extreme drought.
Belarus: Belarus, which shares a western border with Russia and a southern border with Ukraine, has been flagged for “Belarusian authorities’ continued facilitation of Russia’s war against Ukraine, the buildup of Russian military forces in Belarus, the arbitrary enforcement of local laws, the potential of civil unrest, the risk of detention, and the Embassy’s limited ability to assist U.S. citizens residing in or traveling to Belarus.” The U.S. Embassy in Minsk halted operations in February 2022.
Burkina Faso: Terrorism, crime and kidnapping are plaguing this West African nation. Terrorist attacks may target hotels, restaurants and schools with little to no warning, and the East and Sahel regions of the country are under a state of emergency. In late November 2023, hundreds died in clashes between state security forces and rebels near the country’s border with Mali. In June, more than 2 million people in Burkina Faso were displaced due to “violence linked to al-Qaida and the Islamic State group.”
Central African Republic: While there have not been specific incidents of U.S. citizens targeted with violence or crime, violent crime and sudden closure of roads and borders is common. The advisory states that “Embassy Bangui’s limited capacity to provide support to U.S. citizens, crime, civil unrest, and kidnapping” is a factor in its assessment. Recent data from UNICEF suggests the country has the worst drinking water accessibility of all countries in 2022.
Myanmar (Formerly Burma): Armed conflict and civil unrest are the primary reasons to not travel to this Southeast Asian country, which experienced a military coup in early 2021. Limited health care resources, wrongful detentions and “areas with land mines and unexploded ordnance” are also listed as risk factors. After Ukraine and Israel, Myanmar had the highest conflict-related death toll in 2023.
Gaza : Hamas, a foreign terrorist organization as designated by the State Department, controls much of the Gaza Strip, which shares borders with both Israel and Egypt. On Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas fighters broke across the border into Israel, killing hundreds of civilians and soldiers in a brazen attack that stunned Israelis. On Oct. 10, Israel hit the Gaza Strip with “the fiercest air strikes in its 75-year conflict” according to Reuters . The conflict has since escalated into war between Israel and Hamas, with regular Israeli airstrikes leading to extensive civilian casualties in Gaza. As of mid-December, nearly 85% of Gaza’s population were displaced from their homes, according to UN estimates . The region continues to face shortages of food , water, electricity and medical supplies , with conditions deemed “far beyond a humanitarian crisis.” The State Department warns of terrorism and armed conflict within Gaza’s borders.
Haiti: In July 2023, the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Port-au-Prince in response to the increased risk of kidnapping and violent crime in the country , as well as armed conflict between gangs and police. The travel advisory states that cases of kidnapping “often involve ransom negotiations and U.S. citizen victims have been physically harmed during kidnappings.” The travel advisory also states that “U.S. citizens in Haiti should depart Haiti as soon as possible” given “the current security situation and infrastructure challenges.” A series of gang attacks in late September 2023 caused thousands to flee their homes, and many aid groups have been forced to cut or suspend operations amid escalating violence in recent months.
Iran: Terrorism, kidnapping and civil unrest are risk factors for all travelers to Iran, while U.S. citizens are specifically at risk for “arbitrary arrest.” U.S.-Iranian nationals such as students, journalists and business travelers have been arrested on charges of espionage and threatening national security. Executions in Iran rose sharply between 2021 and 2022, bringing the country’s total to nearly 580 people over the year, according to a report by Amnesty International released in May 2023.
Iraq: The State Department cites “terrorism, kidnapping, armed conflict [and] civil unrest” as cause for the country’s Level 4 distinction. Iraq’s northern borders, and its border with Syria, are especially dangerous. Since the escalation of conflict in neighboring Israel in October, there has been an increase in attacks against Iraqi military bases, which host U.S. troops and other international forces. In October 2023, non-emergency U.S. government personnel and eligible family members were ordered to leave the U.S. embassy in Baghdad.
Libya: Following the end of its dictatorship over a decade ago, Libya has been wrought with internal conflict between armed groups in the East and West. Armed conflict, civil unrest, crime, kidnapping and terrorism are all risk factors. U.S. citizens have been targets of kidnapping for ransom, with terrorists targeting hotels and airports frequented by Westerners. The U.S. Embassy in Tripoli halted operations in 2014. In mid-September 2023, floods, which some say were intensified by climate change , killed thousands in eastern Libya. Clashes between armed factions escalated across the country in the latter half of 2023, including in the capital city of Tripoli and in Benghazi.
Mali: After experiencing military coups in 2020 and 2021, crime, terrorism and kidnapping are all prevalent threats in this West African landlocked nation. In July 2022, non-emergency U.S. government employees and their families were ordered to leave the country due to higher risk of terrorist activity. A U.N. report in August 2023 said that military groups in the country, including both Mali security forces and possibly Russian Wagner mercenaries, were spreading terror through the use of violence against women and human rights abuses. Democratic elections were supposed to occur in February 2024, but Mali’s military junta postponed the plans indefinitely. In December, the U.N. officially ended a decade-long peacekeeping presence in the country, which had been among the agency’s deadliest missions, with hundreds of the mission personnel killed since 2013.
Mexico: Each state in Mexico is assessed separately for travel advisory levels. Six of the 32 states in Mexico are designated as Level 4: Colima, Guerrero, Michoacan, Sinaloa, Tamaulipas and Zacatecas. Crime and kidnapping are listed as the primary risk factors throughout the country. Nearly 112,000 people were missing across the country as of October, a number the U.N. has called “alarming.”
North Korea (Democratic People’s Republic of Korea): U.S. passports are not valid for travel “to, in, or through” this country, home to one of the world's longest-running dynastic dictatorships. The travel advisory states that the Level 4 distinction is due to “the continuing serious risk of arrest and long-term detention of U.S. nationals.” In July 2023, a U.S. soldier fled across the border into North Korea, where he is believed to be in North Korean custody, the first American detained in the North in nearly five years. He was returned to U.S. custody in September 2023.
Russia: The travel advisory for Russia cites its invasion of Ukraine , harassment of U.S. citizens by Russian government officials and arbitrary law enforcement as a few of the reasons for the Level 4 designation. Chechnya and Mount Elbrus are specifically listed as Level 4 regions. Terrorism, civil unrest, health, kidnapping and wrongful detention are all noted as risks.
Russia Invades Ukraine: A Timeline

Somalia: A severe drought resulting from five failed rainy seasons in a row killed 43,000 people in 2022, and caused a famine amid conflict with Islamist insurgents . Violent crime is common throughout Somalia , pirates frequent its coast off the Horn of Africa, and medical facilities, where they exist, have limited capacity. Crime, terrorism, civil unrest, health and kidnapping are all risk factors. In January 2024, some passengers aboard a U.N.-contracted helicopter were taken hostage by al-Shabaab militants after the vehicle crashed in central Somalia.
South Sudan: Crime, kidnapping and armed conflict are the primary risk factors for South Sudan, which separated from Sudan in 2011, making it the world’s newest country . Weapons are readily available, and travelers have been victims of sexual assault and armed robbery.
Sudan: The U.S. evacuated its embassy in Khartoum in April 2023, and the country closed its airspace due to the ongoing conflict in the country, only permitting humanitarian aid and evacuation efforts. Fighting has escalated in the region between two warring generals seeking to gain control after a military coup in 2021 ousted the country’s prime minister. Civil unrest is the primary risk factor for Africa’s third largest country by area. Crime, terrorism, kidnapping and armed conflict are also noted. The International Criminal Court began investigating alleged war crimes and violence against African ethnic groups in the country in 2023. Millions have fled their homes due to conflict, and the U.N. has said its efforts to provide aid have been hindered by a lack of support, safety and resources. As recently as December 2023, the United Nations warned of catastrophic famine , with millions of children at-risk for malnutrition .
Syria: The advisory states that “No part of Syria is safe from violence,” with terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, armed conflict and risk of unjust detention all potential risk factors. U.S. citizens are often a target for kidnappings and detention. The U.S. Embassy in Damascus halted operations in 2012. Fighting in neighboring Israel has escalated since October, and the conflict has spilled over into Syria, where the U.S. has carried out air strikes following drone and rocket attacks against American troops in Syria and Iraq, triggered by the Israel-Hamas war.
Ukraine: Russian setbacks in their invasion of Ukraine buoyed hopes in Ukraine in 2023. However, Ukraine is a Level 4 country due to Russia’s invasion, with crime and civil unrest also noted as risk factors. The country’s forces shot down two Russian fighter jets on Christmas Eve 2023, in a move Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said “sets the right mood for the entire year ahead.”
Venezuela: Human rights abuses and lack of health care plague this South American nation, which has been in a political crisis since 2014. In 2019, diplomatic personnel were withdrawn from the U.S. Embassy in Caracas. Threats in the country include crime, civil unrest, kidnapping, wrongful detention and poor health infrastructure.
Yemen: Six of the nine risk factors defined by the State Department – terrorism, civil unrest, health risks, kidnapping, armed conflict and landmines – are all present in Yemen. Despite private companies offering tourist visits to the Yemeni island of Socotra, the U.S. government argues those arranging such visits “are putting tourists in danger.” Civil war and cholera are also both present throughout the country. The U.S. Embassy in Sanaa halted operations in 2015. The country has experienced a relative lull in the civil war fighting, but as peace negotiations have gotten traction, flare ups in the fighting have jeopardized progress. Most recently, the U.S. and U.K. have carried out a series of airstrikes in the country, targeting Iran-backed Houthi sites.
Other Countries to Watch
Since Jan. 1, the State Department has updated travel advisories for 17 different countries as well as for the West Bank and Gaza, adding information about specific regions or risk factors, or simply renewing an existing advisory. Travel advisory levels can change based on several factors in a nation, such as increased civil unrest, policies that affect human rights or higher risks of unlawful detention.
The State Department has given about 25 countries an assessment of Level 3, meaning it recommends people “reconsider travel” to those destinations.
On Oct. 14, one week after the deadly Hamas attack on Israel, Israel and the West Bank were both moved from Level 2 to Level 3, while Gaza remains at Level 4. The region’s travel advisory was updated in November to reflect travel restrictions for certain government employees who have not already left the area, and it was updated again on Jan. 3.
Following the outbreak of the Israel-Hamas war in early October, the U.S. State Department raised Lebanon ’s travel advisory level from a Level 3 to a Level 4 level due to “the unpredictable security situation related to rocket, missile, and artillery exchanges” between Israel and Hezbollah or other militant groups. In December, the U.S. Embassy in Beirut returned to normal staffing and presence, and on Jan. 29, the country was moved back to Level 3. Crime, terrorism, armed conflict, civil unrest, kidnapping and unexploded landmines are listed as the country’s primary risk factors. However, the country’s borders with Syria and with Israel, as well as refugee settlements within Lebanon, are specifically noted as Level 4 regions.
China became a Level 3 country in late 2020, with an update in December 2022 citing “the surge in COVID-19 cases, arbitrary enforcement of local laws, and COVID-19-related restrictions” as the reason for the advisory. In June 2023, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR) was moved from the Level 3 to the Level 2 list, but travelers are still advised to be cautious in the area due to “arbitrary enforcement of local laws.” Meanwhile, Macau remains at Level 3.
Following an attempted coup in August 2023, Niger was elevated to Level 4 in August and the Department of State ordered all non-emergency U.S. government personnel and family members to leave the U.S. Embassy in Niamey. In early January 2024, the overall risk level for the country was lowered back to Level 3. Despite the new classification, the State Department still asks non-emergency government personnel and eligible family members to depart the country.
In mid-December 2023 there was an explosion at Guinea’s main fuel depot which has since affected access to health care and basic goods and services. The country was subsequently designated a Level 3 nation after having previously been Level 2. Concerns about civil unrest, health, crime and fuel shortages impacting local infrastructure were listed as the primary risk factors contributing to the change.
Several Level 3 countries are among the worst countries for human trafficking, as designated by the State Department’s annual Trafficking in Persons Report . Level 3 countries on this list include Papua New Guinea, Guinea Bissau, China and Chad. There are also nine Level 4 countries designated as among the worst for human trafficking: Afghanistan, Belarus, Iran, Myanmar, North Korea, Russia, Syria, South Sudan and Venezuela.
Over 70 countries are currently at Level 2, meaning the State Department recommends travelers “exercise increased caution” when traveling to those destinations.
Botswana became the newest Level 2 country on Feb. 26 after having previously been Level 1, with crime noted as the primary risk factor.
France, which saw nationwide protests throughout 2023, has civil unrest and terrorism noted as risk factors for its Level 2 status, and Sweden’s Level 2 status is associated with risks of terrorism.
The Level 2 travel advisory for the Bahamas was updated in January to reflect water safety concerns. The advisory warns that “activities involving commercial recreational watercraft, including water tours, are not consistently regulated” and notes that government personnel are “not permitted to use independently operated jet-ski rentals on New Providence and Paradise Islands.” It also warns visitors to be mindful of sharks, weather and water conditions. The advisory also says that crime is a primary risk factor with gang-on-gang violence contributing to high homicide rates in some areas. Visitors are asked to “be vigilant” and to not physically resist robbery attempts.
Bangladesh 's Level 2 travel advisory was updated in October 2023 to add a note about the country’s general election , which took place Jan. 7, 2024. The advisory states “demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence.” The U.S. has since claimed the country’s election was not free nor fair.
In November 2023, several Level 2 travel advisories were updated with new cautionary information. The advisory for Ghana was updated to reflect threats against LGBTQI+ travelers specifically, noting “anti-LGBTQI+ rhetoric and violence have increased in recent years.” Meanwhile, the advisory for South Africa was updated in February to note that routes recommended by GPS may be unsafe with higher risk for crime.
Turkmenistan was moved off of the Level 2 list to become the newest addition to the Level 1 list on Jan. 22, meaning normal precautions are recommended but there are no risk factors causing travelers to practice increased caution.
The State Department asks travelers to pay attention to travel advisory levels and alerts , review country information pages for their destinations and read related country security reports before going abroad.
Join the Conversation
Tags: Russia , Ukraine , Travel , Coronavirus , Travel Tips , Israel , Gaza , violence , Civil War , crime , kidnapping
Recent Articles
Best countries.

Education News

Best Countries Rankings
- # 1 Switzerland
- # 5 Australia
- # 5 United States
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
Switzerland is world's best country.
Julia Haines Sept. 6, 2023

Photos: Best Countries Around the World
Sept. 6, 2023

The 25 Best Countries in the World
Elliott Davis Jr. Sept. 6, 2023

Supporters of Spain's Prime Minister Rally in Madrid to Urge Him Not to Quit
Reuters April 28, 2024

US Secretary of State to Travel to Jordan and Israel — State Dept

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Explore sell to government
- Ways you can sell to government
- How to access contract opportunities
- Conduct market research
- Register your business
- Certify as a small business
- Become a schedule holder
- Market your business
- Research active solicitations
- Respond to a solicitation
- What to expect during the award process
- Comply with contractual requirements
- Handle contract modifications
- Monitor past performance evaluations
- Explore real estate
- 3D-4D building information modeling
- Art in architecture | Fine arts
- Computer-aided design standards
- Commissioning
- Design excellence
- Engineering
- Project management information system
- Spatial data management
- Facilities operations
- Smart buildings
- Tenant services
- Utility services
- Water quality management
- Explore historic buildings
- Heritage tourism
- Historic preservation policy, tools and resources
- Historic building stewardship
- Videos, pictures, posters and more
- NEPA implementation
- Courthouse program
- Land ports of entry
- Prospectus library
- Regional buildings
- Renting property
- Visiting public buildings
- Real property disposal
- Reimbursable services (RWA)
- Rental policy and procedures
- Site selection and relocation
- For businesses seeking opportunities
- For federal customers
- For workers in federal buildings
- Explore policy and regulations
- Acquisition management policy
- Aviation management policy
- Information technology policy
- Real property management policy
- Relocation management policy
- Travel management policy
- Vehicle management policy
- Federal acquisition regulations
- Federal management regulations
- Federal travel regulations
- GSA acquisition manual
- Managing the federal rulemaking process
- Explore small business
- Explore business models
- Research the federal market
- Forecast of contracting opportunities
- Events and contacts
- Explore travel
- Per diem rates
- Transportation (airfare rates, POV rates, etc.)
- State tax exemption
- Travel charge card
- Conferences and meetings
- E-gov travel service (ETS)
- Travel category schedule
Federal travel regulation
- Travel policy
- Explore technology
- Cloud computing services
- Cybersecurity products and services
- Data center services
- Hardware products and services
- Professional IT services
- Software products and services
- Telecommunications and network services
- Work with small businesses
- Governmentwide acquisition contracts
- MAS information technology
- Software purchase agreements
- Cybersecurity
- Digital strategy
- Emerging citizen technology
- Federal identity, credentials, and access management
- Mobile government
- Technology modernization fund
- Explore about us
- Annual reports
- Mission and strategic goals
- Role in presidential transitions
- Get an internship
- Launch your career
- Elevate your professional career
- Discover special hiring paths
- Events and training
- Agency blog
- Congressional testimony
- GSA does that podcast
- News releases
- Leadership directory
- Staff directory
- Office of the administrator
- Federal Acquisition Service
- Public Buildings Service
- Staff offices
- Board of Contract Appeals
- Office of Inspector General
- Region 1 | New England
- Region 2 | Northeast and Caribbean
- Region 3 | Mid-Atlantic
- Region 4 | Southeast Sunbelt
- Region 5 | Great Lakes
- Region 6 | Heartland
- Region 7 | Greater Southwest
- Region 8 | Rocky Mountain
- Region 9 | Pacific Rim
- Region 10 | Northwest/Arctic
- Region 11 | National Capital Region
- Per Diem Lookup
To eliminate the confusion caused by a duplicate regulation, we discontinued hosting the FTR. Follow the link below to view the official copy.
Access the federal travel regulation on eCFR.gov
Explore the official regulation publications on the Electronic Code of Federal Regulations.
Explore eCFR
The eCFR allows you to:
- Browse the Code of Federal Regulations as it existed at any point in time.
- Compare the regulations as they existed on any two dates.
- View a timeline of how the eCFR content has changed.
- Search for specific terms.
- Subscribe to changes in the regulations.
The Federal Travel Regulation summarizes the travel and relocation policy for all federal civilian employees and others authorized to travel at the government’s expense. Federal employees and agencies may use the FTR as a reference to ensure official travel and relocation is conducted in a responsible and cost effective manner.
Download the FTR (41 CFR) [PDF]
Last annual edition updated July 1, 2021. Prior years may be found at Code of Federal Regulations (Annual Edition) . Contents may be out of date. Refer to eCFR.gov for the most up-to-date regulation information.
Explore bulletins and other documents .
PER DIEM LOOK-UP
1 choose a location.
Error, The Per Diem API is not responding. Please try again later.
No results could be found for the location you've entered.
Rates for Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. Territories and Possessions are set by the Department of Defense .
Rates for foreign countries are set by the State Department .
2 Choose a date
Rates are available between 10/1/2021 and 09/30/2024.
The End Date of your trip can not occur before the Start Date.
Traveler reimbursement is based on the location of the work activities and not the accommodations, unless lodging is not available at the work activity, then the agency may authorize the rate where lodging is obtained.
Unless otherwise specified, the per diem locality is defined as "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city, including independent entities located within those boundaries."
Per diem localities with county definitions shall include "all locations within, or entirely surrounded by, the corporate limits of the key city as well as the boundaries of the listed counties, including independent entities located within the boundaries of the key city and the listed counties (unless otherwise listed separately)."
When a military installation or Government - related facility(whether or not specifically named) is located partially within more than one city or county boundary, the applicable per diem rate for the entire installation or facility is the higher of the rates which apply to the cities and / or counties, even though part(s) of such activities may be located outside the defined per diem locality.
An official website of the United States government Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
FACT SHEET: Biden-Harris Administration Announces Rules to Deliver Automatic Refunds and Protect Consumers from Surprise Junk Fees in Air Travel
Newly finalized rules will mandate automatic, cash refunds for cancelled or significantly delayed flights and save consumers over half a billion dollars every year in airline fees
WASHINGTON – Building on a historic record of expanding consumer protections and standing up for airline passengers, the Biden-Harris Administration announced final rules that require airlines to provide automatic cash refunds to passengers when owed and protect consumers from costly surprise airline fees. These rules will significantly expand consumer protections in air travel, provide passengers an easier pathway to refunds when owed, and save consumers over half a billion dollars every year in hidden and surprise junk fees.
“Passengers deserve to know upfront what costs they are facing and should get their money back when an airline owes them - without having to ask,” said U.S. Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg . “Today’s announcements will require airlines to both provide passengers better information about costs before ticket purchase, and promptly provide cash refunds to passengers when they are owed — not only saving passengers time and money, but also preventing headaches.”
The rules are part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s work to lower costs for consumers and take on corporate rip-offs. President Biden signed an Executive Order on Promoting Competition in 2021 that encouraged DOT to take steps to promote fairer, more transparent, and competitive markets.
Requiring Automatic Cash Airline Refunds The first rule requires airlines to promptly provide passengers with automatic cash refunds when owed because their flights are cancelled or significantly changed, their checked bags are significantly delayed, or the ancillary services, like Wi-Fi, they purchased are not provided.
Without this rule, consumers have to navigate a patchwork of cumbersome processes to request and receive a refund — searching through airline websites to figure out how to make the request, filling out extra “digital paperwork,” or at times waiting for hours on the phone. Passengers would also receive a travel credit or voucher by default from many airlines instead of getting their money back, so they could not use their refund to rebook on another airline when their flight was changed or cancelled without navigating a cumbersome request process.
DOT’s rule makes it simple and straightforward for passengers to receive the money they are owed. The final rule requires refunds to be:
- Automatic: Airlines must automatically issue refunds without passengers having to explicitly request them or jump through hoops.
- Prompt: Airlines and ticket agents must promptly issue refunds within seven business days of refunds becoming due for credit card purchases and 20 calendar days for other payment methods.
- Cash or original form of payment: Airlines and ticket agents must provide refunds in cash or whatever original payment method the individual used to make the purchase, such as credit card or airline miles. Airlines may not substitute vouchers, travel credits, or other forms of compensation unless the passenger affirmatively chooses to accept alternative compensation.
- Full amount: Airlines and ticket agents must provide full refunds of the ticket purchase price, minus the value of any portion of transportation already used. The refunds must include all government-imposed taxes and fees and airline-imposed fees.
Protecting Against Surprise Airline Junk Fees Secondly, DOT is requiring airlines and ticket agents to tell consumers upfront what fees they charge for checked bags, a carry-on bag, for changing a reservation, or cancelling a reservation. This ensures that consumers can avoid surprise fees when they purchase tickets from airlines or ticket agents, including both brick-and-mortar travel agencies or online travel agencies.
The rule will help consumers avoid unneeded or unexpected charges that can increase quickly and add significant cost to what may, at first, look like a cheap ticket. Extra fees, like checked baggage and change fees, have been a growing source of revenue for airlines, while also becoming more complex and confusing for passengers over time. In total, thanks to the final rule, consumers are expected to save over half a billion dollars every year that they are currently overpaying in airline fees.
DOT’s rule ensures that consumers have the information they need to better understand the true costs of air travel. Under the final rule, airlines are required to:
- Disclose baggage, change, and cancellation fees upfront: Each fee must be disclosed the first time that fare and schedule information is provided on the airline’s online platform -- and cannot be displayed through a hyperlink.
- Explain fee policies before ticket purchase: For each type of baggage, airlines and ticket agents must spell out the weight and dimension limitations that they impose. They must also describe any prohibitions or restrictions on changing or cancelling a flight, along with policies related to differences in fare when switching to a more or less expensive flight.
- Share fee information with third parties: An airline must provide useable, current, and accurate information regarding its baggage, change, and cancellation fees and policies to any company that is required to disclose them to consumers and receives fare, schedule, and availability information from that airline.
- Inform consumers that seats are guaranteed: When offering an advance seat assignment for a fee, airlines and ticket agents must let consumers know that purchasing a seat is not necessary to travel, so consumers can avoid paying unwanted seat selection fees.
- P rovide both standard and passenger-specific fee information: Consumers can choose to view passenger-specific fee information based on their participation in the airline’s rewards program, their military status, or the credit card that they use — or they can decide to stay anonymous and get the standard fee information.
- End discount bait-and-switch tactics: The final rule puts an end to the bait-and-switch tactics some airlines use to disguise the true cost of discounted flights. It prohibits airlines from advertising a promotional discount off a low base fare that does not include all mandatory carrier-imposed fees.
DOT’s Historic Record of Consumer Protection Under the Biden-Harris Administration Both of these actions were suggested for consideration by the DOT in the Executive Order on Promoting Competition and build on historic steps the Biden-Harris Administration has already taken to expand consumer protections, promote competition, and protect air travelers. Under the Biden-Harris Administration, DOT has advanced the largest expansion of airline passenger rights, issued the biggest fines against airlines for failing consumers, and returned more money to passengers in refunds and reimbursements than ever before in the Department’s history.
- DOT launched the flightrights.gov dashboard, and now all 10 major U.S. airlines guarantee free rebooking and meals, and nine guarantee hotel accommodations when an airline issue causes a significant delay or cancellation. These are new commitments the airlines added to their customer service plans that DOT can legally ensure they adhere to and are displayed on flightrights.gov .
- Since President Biden took office, DOT has helped return more than $3 billion in refunds and reimbursements owed to airline passengers – including over $600 million to passengers affected by the Southwest Airlines holiday meltdown in 2022.
- DOT has issued over $164 million in penalties against airlines for consumer protection violations. Between 1996 and 2020, DOT collectively issued less than $71 million in penalties against airlines for consumer protection violations.
- DOT recently launched a new partnership with a bipartisan group of state attorneys general to fast-track the review of consumer complaints, hold airlines accountable, and protect the rights of the traveling public.
- In 2023, the flight cancellation rate in the U.S. was a record low at under 1.2% — the lowest rate of flight cancellations in over 10 years despite a record amount of air travel.
- DOT is undertaking its first ever industry-wide review of airline privacy practices and its first review of airline loyalty programs
In addition to finalizing the rules to require automatic refunds and protect consumers from surprise fees, DOT is also pursuing rulemakings that would:
- Propose to ban family seating junk fees and guarantee that parents can sit with their children for no extra charge when they fly. Before President Biden and Secretary Buttigieg pressed airlines last year, no airline committed to guaranteeing fee-free family seating. Now, four airlines guarantee fee-free family seating, as the Department is working on its family seating junk fee ban proposal.
- Propose to make passenger compensation and amenities mandatory so that travelers are taken care of when airlines cause flight delays or cancellations.
- Expand the rights for passengers who use wheelchairs and ensure that they can travel safely and with dignity . The comment period on this proposed rule closes on May 13, 2024.
Travelers can learn more about their protections when they fly at FlightRights.gov . Consumers may file an airline complaint with the Department here .
- ABC7 Bay Area 24/7 live stream Watch Now
- Watch ABC7 newscasts on demand Full Story
New federal rules on airline refunds require cash instead of vouchers
Airline canceled your flight? The plane arrived hours late after a maintenance issue? The inflight Wi-Fi didn't work?
New federal rules say travelers deserve cash refunds when inconvenienced by their airline - not vouchers or travel credits.
The rules, announced by the Transportation Department on Wednesday, also require airlines to provide upfront information about fees for baggage and changing flights.
Although many airlines have done away with change fees and disclose fees on their websites, Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg estimated more transparency with some airlines and websites would make it easier for travelers to shop around - ultimately saving consumers millions every year.
The rule would formalize a requirement that passengers receive refunds if a domestic flight is delayed by more than three hours or if an international flight is delayed by more than six hours.
It would also require a refund of any baggage fees for bags that arrive more than 12 hours late, and a refund of the fee for a purchased service like Wi-Fi or upgraded seating if the airline doesn't deliver.
'Without headaches or haggling'
"Our new rule sets a new standard to require airlines to promptly provide cash refunds to their passengers," Buttigieg said in a statement, saying the refunds were due "without headaches or haggling."
There's also a provision for travelers frustrated with call center hold times or filling out online claim forms. The rules require the fees to be automatic and prompt: Within seven days for a credit card refund and 20 days for other forms of payment.
Airlines for America, which represents the country's largest passenger carriers, said its airline members "offer transparency and vast choice to consumers from first search to touchdown."
"U.S. airlines are committed to providing the highest quality of service, which includes clarity regarding prices, fees and ticket terms," the group said in a statement.
Surge in complaints in 2022
The Biden Administration proposed its change to the refund rules in 2022 after a surge in complaints about refunds when the coronavirus brought air travel to a standstill.
That year, DOT received nearly 47,600 complaints, more than double the number of complaints received in 2021. More than half of the complaints involved flight disruptions or refunds.
Many travelers complained at that time that airlines pushed noncash flight credit or required extended time on customer service phone lines to request a refund. Some of those credits expired long before the effects of the virus receded and travel returned to more normal levels.
This spring, DOT and other executive branch agencies are finalizing key rule changes from Biden's term in office in case Republicans take control of Washington in November's election. A federal law allows Congress to unravel recently implemented executive branch rules.
The cutoff date depends on the House and Senate legislative calendar but is likely to fall in May, meaning rules finalized before that date are not eligible for review under the Congressional Review Act.
Related Topics
- U.S. & WORLD

Best carry-on luggage 2024

Douglas DC-4 plane crashes near river in Fairbanks, Alaska

Proposed bill could ban airport security line skipping services in CA

Close call at JFK airport after 4 planes cleared to cross runway
Top stories.

Bay Area doctor heads to Gaza border despite possible Israeli invasion

1 year ago Banko Brown was fatally shot by a SF security guard

1 killed in crash on southbound Hwy 101 in San Jose, CHP says

SUV flips over in violent California freeway crash caught on camera

4-month-old baby among 4 killed in OK tornadoes, officials say | VIDEO
- 2 hours ago
Man arrested in Piedmont after trying to flee with police chief's car
Which companies do protesting Stanford students want divestment from?
$150K settlement approved for witness to George Floyd's murder
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !

Travel advice and advisories by destination
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
The Government of Canada’s official source of travel information and advice, the Travel Advice and Advisories help you to make informed decisions and travel safely while you are outside Canada. Check the page for your destination often, because safety and security conditions may change. See Travel Advice and Advisories – FAQ for more information.
Where are you going?
Take normal security precautions
Exercise a high degree of caution
Avoid non-essential travel
Avoid all travel
Travel advice from other countries
Travel advice is also provided by the governments of Australia , New Zealand , the United Kingdom and the United States .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
What fliers need to know about new refund rules for airlines
Starting in about six months, u.s. airlines will have to offer customers cash refunds before vouchers.

New federal rules for airlines will go into effect later this year, giving travelers a better picture of the full cost of flights before they book — and getting them an easier refund if things go awry.
After a process that lasted more than a year, the Biden administration announced the rules on passenger protections Wednesday.
“This is a big day for America’s flying public,” Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg said in a news conference at Reagan National Airport.
While the trade group Airlines for America said its members “abide by — and frequently exceed — DOT regulations regarding consumer protections,” consumer advocates praised the administration’s move.
“These rules are not only critical but also common sense,” said William McGee, senior fellow for aviation and travel at the American Economic Liberties Project, who spoke at Wednesday’s event.
Most new rules go into effect in the fall
At the event Wednesday, Buttigieg said that “the bulk of these protections” will go into effect in about six months. Others will start in a year.
That means refund rules that get customers automatic cash refunds when airlines cancel or significantly change flights won’t be in place during the busy summer travel season. But they should be set in time for the Thanksgiving and winter holiday season rush.
Buttigieg said that the department expects airlines to take some time to develop the processes to return cash to travelers, but added that he doesn’t want them to drag their feet.
“They don’t have to wait the number of months that it’ll technically take for this to go into effect,” Buttigieg said Wednesday. “They could and should be doing this right now.”
You should get refunds without having to ask
Instead of first offering a voucher or credit, airlines “must automatically issue refunds without passengers having to explicitly request them or jump through hoops,” the Transportation Department says. The refunds need to be issued within seven business days for credit card purchases and 20 calendar days when bought through other methods.
However a traveler originally paid is the way the refund needs to be issued, the rule says, whether that’s by credit card or airline miles . Other types of compensation are allowed only if a passenger chooses one of those alternatives.
“No more defaulting to vouchers or credits when consumers may not even realize that they were entitled to cash,” Buttigieg said.
You can still choose to be rebooked
If travelers’ flights have been canceled or significantly changed, they can still continue with their trip. Passengers are only eligible for a refund if they have declined to accept alternative transportation.
Airlines will have to pay for delayed bags and broken WiFi
There are many ways for a trip to go awry, and the new rules cover more than just a late or canceled flight.
If a checked bag isn’t delivered within 12 hours of a domestic flight arriving at the gate, or within 15 to 30 hours of an international flight arriving, depending on how long that flight is, passengers will be entitled to a refund of their checked-bag fee. They will need to file a mishandled baggage report.
Refunds will also be given if passengers pay for a service such as WiFi, seat selection or in-flight entertainment and the airline fails to provide.
‘Significant’ changes will be the same for all airlines
Automatic cash refunds are due to passengers if their flight experiences a “significant change.” But what does that mean? Previously, the definition could vary from airline to airline.
The new rules provide some consistency. A change is considered significant if a departure or arrival is different by more than three hours for domestic flights or six hours for international trips.
Other changes considered significant: the departure or arrival is from a different airport; there are more connections; passengers are downgraded to a lower class; or service or flights are on planes that are less accessible for a person with a disability.
No more hidden fees for bags and seat selection
The rule on extra fees — what the Biden administration refers to as “surprise junk fees in air travel” — will require airlines and online travel booking sites to disclose up front the fees for a checked bag, carry-on bag, reservation change and reservation cancellation. Those fees must be clearly noted and not shown through a hyperlink, the rule says.
Consumers must also be informed that they don’t have to pay for a seat assignment to travel and that a seat will be provided without an additional price.
“Healthy competition requires that, as a consumer, you comparison shop, which means knowing the real price of a trip before and not after you buy,” Buttigieg said. “Airlines will now be required to show you these costs up front, so you have all the information you need to decide what travel option is best for you.”
Travelers can either search without providing their personal information to see standard fees or, after entering their information, see more tailored fees that might apply given their military status, frequent-flier membership or credit card use.
“The final rule puts an end to the bait-and-switch tactics some airlines use to disguise the true cost of discounted flights,” the Transportation Department said in a news release. “Prior to the rule, some airlines were offering deceptive discounts that consumers may have believed applied to the full fare that was being advertised but only applied to a small portion of the ticket price.”
You will still have to report complaints
Buttigieg said the main way for the department to find out about a violation of the rules is when people submit complaints through the site flightrights.gov . But he said he hopes that by making refunds automatic, there will be less need for complaints — and more flexibility for employees to perform audits or spot-checks of airline compliance.
Europe-style compensation is still not in the rules
Some travelers heading to or from Europe who experience delays under certain circumstances are entitled to compensation worth more than $600. That kind of system does not exist for domestic flights in the United States, but Buttigieg said it is on the agenda.
“On compensation, we continue to develop that — and to be clear, with this rule on the books, that does not stop or slow the progress that we’re driving in terms of a compensation rule,” he said.
More on air travel
Leave flying to the pros: Think you could land a plane in an emergency? Experts say you’re wrong . Here’s what you should actually do if something goes awry during a flight .
Pet peeves: Why do “gate lice” line up early for a flight ? Psychologists explained for us. Another move that annoys airline workers: abusing the flight attendant call button . For more on how to behave on a flight, check out our 52 definitive rules of flying .
Plane mess: Stories about extremely disgusting airplanes have been grossing out travelers. The question of plane cleanups became the subject of a recent debate after a flight attendant allegedly told a pregnant passenger to pick up the popcorn spilled by her toddler.
Frequent flying: Airline status isn’t what it used to be, but at least there are some good movies and TV shows to watch in the air. And somewhere out there, experts are trying to make airline food taste good.

New Biden administration rules require airlines to refund changed flights and abolish surprise fees

Airlines will now have to provide automatic refunds to travelers if flights are canceled or significantly altered under new US Department of Transportation rules, a significant change for consumers that could drive up costs across the industry.
The final regulations released Wednesday outline the circumstances where passengers are entitled to refunds for all travel to, from and within the US. The goal is to make it easier for people to get money back and to make refund policies more consistent from one airline to the next.
According to the department, complaints related to airlines and ticket agents rejecting or delaying refunds made up 87% of all air-travel service complaints at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020.
“Passengers deserve to get their money back when an airline owes them — without headaches or haggling,” Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg said in a statement.
Under the new rule, passengers will be entitled to refunds if there is a “significant change” to their flights. These include:
- Departure or arrival time that moves by more than three hours domestically or six hours for international flights
- Being downgraded to a lower class than originally purchased, as from first class to economy
- Change of departure or arrival airport
- Increase in number of connections
- Changes to connecting airports or planes flown if they are less accommodating for people with disabilities
Travelers will also get refunds for checked bag fees if the bag is lost and not delivered within 12 hours of a domestic flight’s gate arrival. International flights will have from 15 to 30 hours to return a lost bag, depending on their length.
Anyone who pays for a service, such as in-flight Wi-Fi or entertainment, and doesn’t receive it will also get their money back.
In addition, DOT made changes to make it easier for the passengers to receive the money they’re owed by requiring prompt automatic refunds in cash or through the original form of payment. Buttigieg said during a news conference at Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport Wednesday that the bulk of the new requirements will go into effect in about six months.
The refund changes are poised to add significant costs across the airline industry, which could have a disproportionate impact on low-cost carriers, according to Seaport Research analyst Daniel McKenzie. “To the extent low cost carriers have to add costs to comply, reduce growth and/or downsize, they become less competitive,” McKenzie said in a note.
The Airlines for America trade group said in a statement that its member carriers already abide by and often exceed regulation on consumer protection.
“US airlines are providing more options and better services while ticket prices, including ancillary revenues, are at historic lows,” the group said in a release.
Also on Wednesday, the department released a final rule requiring airlines to clearly communicate their extra fees upfront for checked luggage, carry-on bags or for canceling or changing reservations. According to DOT, airlines saw a 30% increase in revenue from baggage fees between 2018 and 2022.
“Airlines should compete with one another to secure passengers’ business — not to see who can charge the most in surprise fees,” Buttigieg said in a separate statement, adding that the rule will save travelers more than half a billion dollars a year.
Buttigieg told reporters at the news conference that more rules are on the way, including to expand rights for passengers who use wheelchairs and to allow parents to sit with their children on flights without being charged a fee.
DOT will also continue to pursue more aggressive enforcement when airlines violate rules, he said, pointing to the department’s $140 million record fine against Southwest Airlines Co. for a meltdown in its operations that left more than 2 million passengers stranded in December 2022.
“The level of toughness reflected in the Southwest enforcement is not an exception, but the new standard,” Buttigieg said.
Latest in Politics
- 0 minutes ago

A new law will ban TikTok unless China sells most of it. An expert says it’s ‘unconstitutional’ and backed by no evidence

U.S. Secretary of State buys Taylor Swift album in China to wrap up key visit after warning on EV overproduction, Russia

Commercial tax-prep companies lost out on $5 billion in fees thanks to IRS’ direct file, government says

Fed’s favorite inflation gauge accelerated in March, spelling trouble for rate cuts—and Biden’s re-election bid

Scientists inspired the right guardrails for nuclear energy, the internet, and DNA research. Let them do the same for AI

China signals TikTok should fight ‘robbers’ sell-or-ban U.S. law meant ‘to snatch from others all the good things that they have’. Here’s what’s next
Most popular.

The meteoric rise and stunning fall of Prime, Logan Paul’s energy drink that was once resold for almost $1,500 a can: ‘A brand cannot live on hype alone’

‘Americans just work harder’ than Europeans, says CEO of Norway’s $1.6 trillion oil fund, because they have a higher ‘general level of ambition’

Pottery Barn parent Williams-Sonoma fined for marketing furniture as ‘crafted’ in the U.S. when it was made in China

Amazon should be forced to disclose how Jeff Bezos and others were instructed to use the Signal disappearing-message app, FTC says

Jamie Dimon says America needs to ‘take a deep breath’ before facing off with China, because the U.S. is actually in a ‘very good position’ to negotiate

Tesla’s Elon Musk speeds past Mark Zuckerberg on the billionaires list after Meta stock plummets on its cash-sucking AI plans
Promises Donald Trump has made so far in his campaign for a second term
Former President Donald Trump, now the presumptive Republican nominee, has made a number of promises on the campaign trail, including rolling back car pollution rules, building 10 new cities and appointing a special prosecutor to investigate President Joe Biden and his family.
While some of Trump’s plans are lacking in detail, here are some of the policies he says he would enact if elected for a second term.
Immigration
Trump has made immigration and the border a central campaign issue, successfully pressuring Republicans to reject a major bipartisan border deal last month and making a trip to the southern border on February 29, where he touted his previous hard-line immigration policies.
In a Des Moines Register op-ed published roughly a week before winning the Iowa caucuses in January, Trump vowed to use the “Alien Enemies Act to remove known or suspected gang members, drug dealers, or cartel members from the United States.”
“We will shift massive portions of federal law enforcement to immigration enforcement — including parts of the DEA, ATF, FBI, and DHS,” he wrote.
In a video posted on Truth Social in late February before his border visit, Trump also promised to “carry out the largest domestic deportation operation in American history.”
We will shift massive portions of federal law enforcement to immigration enforcement — including parts of the DEA, ATF, FBI, and DHS.”
After the Israel-Hamas war began last October, Trump also promised to terminate the visas of “Hamas’ sympathizers.”
“We’ll get them off our college campuses, out of our cities and get them the hell out of our country, if that’s OK with you,” he added.
Drug cartels
The former president has also made waging “war” on drug cartels a priority for his second term. If elected, Trump said in his November 2022 campaign announcement that he would ask Congress to ensure that drug smugglers and human traffickers can receive the death penalty for their “heinous acts.”
Trump also vowed to “take down” drug cartels by imposing naval embargos on cartels, cutting off cartels’ access to global financial systems and using special forces within the Department of Defense to damage the cartels’ leadership.
Trump announced plans in a September 2023 campaign video to close the Department of Education and send “all education and education work and needs back to the states.”
“We want them to run the education of our children, because they’ll do a much better job of it,” he added.
The former president has also promised to “put parents back in charge and give them the final say” in education. In a January 2023 campaign video , the former president said he would give funding preferences and “favorable treatment” to schools that allow parents to elect principals, abolish teacher tenure for K-12 teachers, use merit pay to incentivize quality teaching and cut the number of school administrators, such as those overseeing diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives.
We want them to run the education of our children, because they’ll do a much better job of it.”
Trump also said in that campaign video that he would cut funding for schools that teach critical race theory and gender ideology. In a later speech , Trump said he would bring back the 1776 Commission , which was launched in his previous administration to “teach our values and promote our history and our traditions to our children.”
The former president said he would charge the Department of Justice and the Department of Education with investigating civil rights violations of race-based discrimination in schools while also removing “Marxists” from the Department of Education. A second Trump administration would pursue violations in schools of both the Constitution’s Establishment and Free Exercise clauses, which prohibit the government establishment of religion and protect a citizen’s right to practice their own religion, he said.
Health care
Last November, Trump promised to replace the Affordable Care Act , known colloquially as Obamacare, in a series of posts on Truth Social. A Trump-backed effort to repeal and replace Obamacare failed in 2017 after three Republicans senators joined with Democrats to vote against the bill.
“Getting much better Healthcare than Obamacare for the American people will be a priority of the Trump Administration,” he said .
“It is not a matter of cost, it is a matter of HEALTH. America will have one of the best Healthcare Plans anywhere in the world. Right now it has one of the WORST!,” he continued. He also doubled down on his vow during a speech in early January.
Getting much better Healthcare than Obamacare for the American people will be a priority of the Trump Administration.”
Trump also vowed in a June 2023 campaign video to reinstate his previous executive order so that the US government would pay the same price for pharmaceuticals as other developed countries. Some of the former president’s pharmaceutical policies were overturned by Biden.
Gender care
“I will revoke every Biden policy promoting the chemical castration and sexual mutilation of our youth and ask Congress to send me a bill prohibiting child sexual mutilation in all 50 states,” Trump said at the 2023 Conservative Political Action Conference last March.
Trump added in a campaign video that he would issue an executive order instructing federal agencies to cut programs that promote gender transitions, as well as asking Congress to stop the use of federal dollars to promote and pay for gender-affirming procedures. The former president added that his administration would not allow hospitals and health care providers to meet the federal health and safety standards for Medicaid and Medicare if they provide chemical or physical gender-affirming care to youth.
Justice system
Trump has promised to use the Department of Justice to attack critics and former allies. In several videos and speeches, the former president also laid out plans to gut the current justice system by firing “radical Marxist prosecutors that are destroying America.”
“I will appoint a real special prosecutor to go after the most corrupt president in the history of the United States of America, Joe Biden, and the entire Biden crime family,” Trump said in June 2023 remarks . “I will totally obliterate the Deep State.”
Trump said in a campaign video last year that he would reinstate a 2020 executive order to remove “rogue” bureaucrats and propose a constitutional amendment for term limits on members of Congress.
I will appoint a real special prosecutor to go after the most corrupt president in the history of the United States of America, Joe Biden, and the entire Biden crime family.”
To address what he labeled the “disturbing” relationship between technology platforms and the government, the former president said in a January 2023 video that he would enact a seven-year cooling off period before employees at agencies such as the FBI or CIA can work for platforms that oversee mass user data.
Trump added in multiple campaign releases that he would task the Justice Department with investigating online censorship, ban federal agencies from “colluding” to censor citizens and suspend federal money to universities participating in “censorship-supporting activities.”
In a September 2023 speech at the Family Research Council’s Pray Vote Stand Summit in Washington, DC, Trump also touted plans to continue appointing conservative judges.
“I will once again appoint rock-solid conservative judges to do what they have to do in the mold of Justices Antonin Scalia; Samuel Alito, a great gentleman; and another great gentleman, Clarence Thomas,” he said.
Trump has also pledged to “appoint U.S. Attorneys who will be the polar opposite of the Soros District Attorneys and others that are being appointed throughout the United States.”
In a September 2023 speech in Washington, DC, Trump also announced that he would appoint a task force to review the cases of people he claimed had been “unjustly persecuted by the Biden administration.” Trump noted that he wanted to “study the situation very quickly, and sign their pardons or commutations on day one.”
It’s a move that could lead to potential pardons of many rioters from the January 6, 2021, insurrection – which he suggested he would do at a CNN town hall in May 2023.
* Only promises on judge appointments and congressional term limits are similar to prior campaigns
Trump said in two February 2023 campaign videos that if “Marxist” prosecutors refuse to charge crimes and surrender “our cities to violent criminals,” he “will not hesitate to send in federal law enforcement to restore peace and public safety.”
Trump added that he would instruct the Department of Justice to open civil rights investigations into “radical left” prosecutors’ offices that engaged in racial enforcement of the law, encourage Congress to use their legal authority over Washington, DC, to restore “law and order” and overhaul federal standards of disciplining minors to address rising crimes like carjackings.
Addressing policies made in what Trump calls the “Democrats’ war on police,” the former president vowed in a campaign video that he would pass a “record investment” to hire and retrain police, strengthen protections like qualified immunity, increase penalties for assaulting law enforcement officers and deploy the National Guard when local law enforcement “refuses to act.”
The former president added that he would require law enforcement agencies that receive money from his funding investment or the Department of Justice to use “proven common sense” measures such as stop-and-frisk.
Foreign policy
Trump has continued his attacks against member countries of NATO, a European and North American defense alliance. At a South Carolina rally last month, Trump said he would not abide by the alliance’s collective-defense clause and would encourage Russia to do “whatever the hell they want” if a member country didn’t meet spending guidelines.
“NATO was busted until I came along,” Trump said. “I said, ‘Everybody’s gonna pay.’ They said, ‘Well, if we don’t pay, are you still going to protect us?’ I said, ‘Absolutely not.’ They couldn’t believe the answer.”
The former president has also previously pledged to end the war in Ukraine, though he’s offered no details on how he would do so. “Shortly after I win the presidency, I will have the horrible war between Russia and Ukraine settled,” Trump said at a New Hampshire campaign event last year, adding in another speech that it would take him “no longer than one day” to settle the war if elected.
NATO was busted until I came along. I said, ‘Everybody’s gonna pay.’ They said, ‘Well, if we don’t pay, are you still going to protect us?’ I said, ‘Absolutely not.’”
Trump further addressed his strategy of stopping the “never-ending wars” by vowing to remove “warmongers,” “frauds” and “failures in the senior ranks of our government,” and replace them with national security officials who would defend America’s interests. The former president added in a campaign video that he would stop lobbyists and government contractors from pushing senior military officials toward war.
In addition, Trump has said he would restore his “wonderful” travel ban on individuals from several majority-Muslim countries to “keep radical Islamic terrorists out of our country” after Biden overturned the ban in 2021.
New cities and flying cars
Trump said in multiple campaign videos that he would spearhead an effort to build so-called “Freedom Cities” to “reopen the frontier, reignite American imagination, and give hundreds of thousands of young people and other people, all hardworking families, a new shot at home ownership and in fact, the American Dream.”
In his plan, the federal government would charter 10 new cities on federal land, awarding them to areas with the best development proposals. The former president said in a campaign video that the Freedom Cities would bring the return of US manufacturing, economic opportunity, new industries and affordable living.
In the March 2023 video, Trump added that the US under a second Trump administration would lead in efforts to “develop vertical-takeoff-and-landing vehicles for families and individuals,” not letting China lead “this revolution in air mobility.” The former president said these airborne vehicles would change commerce and bring wealth into rural communities.
Electric vehicles
Trump has promised to roll back new car pollution rules at the Environmental Protection Agency that could require electric vehicles to account for up to two-thirds of new cars sold in the US by 2032. Biden’s electrical vehicle-related policies, Trump claimed at a Michigan rally last September , “spell the death of the US auto industry.”
“On day one, I will terminate Joe Biden’s electrical vehicle mandate, and I will cancel every job-killing regulation that is crushing American autoworkers,” Trump added.
Trump has promised to reduce energy prices by increasing domestic production. In several campaign appearances, he has laid out plans to end delays in federal drilling permits and leases.
“We’re going to ‘drill, baby, drill’ right away,” Trump told a crowd of supporters in Des Moines, Iowa, during a victory speech after winning the state’s Republican caucuses in January.
At a South Carolina rally in February, he pledged to remove limits on American natural gas exports.
At the same rally in South Carolina, Trump pledged to impose “stiff penalties on China and other trade abusers.”
“It’s called you screw us, and we screw you,” Trump said.
Under his proposed “Trump Reciprocal Trade Act,” the former president said if other countries impose tariffs on the US, the country would impose “a reciprocal, identical” tariff right back .
It was the same pledge Trump made in a campaign video in 2023: to impose the same tariffs that other countries may impose on the US on those countries. The goal, the former president said then, is to get other countries to drop their tariffs.
It’s called you screw us, and we screw you.”
As part of a larger strategy to bring jobs back into the US, Trump also said he would implement his so-called “ America First ” trade agenda if elected. By setting universal baseline tariffs on a majority of foreign goods, the former president said Americans would see taxes decrease as tariffs increase. His proposal also includes a four-year plan to phase out all Chinese imports of essential goods , as well as stopping China from buying up America and stopping the investment of US companies in China.
Trump also said in February that he would consider imposing a tariff upward of 60% on all Chinese imports if he’s reelected.
The former president has particularly focused on China, vowing in a January 2023 campaign video to restrict Chinese ownership of US infrastructure such as energy, technology, telecommunications and natural resources. Trump also said he would force the Chinese to sell current holdings that may put national security at risk. “Economic security is national security,” he said.
Trump has promised to extend the cuts from his 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, notably the TCJA’s individual income tax breaks. The former president has also talked about reducing the corporate tax rate from the current 21% to 15%.
“I will make the Trump tax cuts the largest tax cut in history,” the former president said last month at the Black Conservative Federation’s Honors Gala in South Carolina. “We’ll make it permanent and give you a new economic boom.”
I will make the Trump tax cuts the largest tax cut in history.”
Trump has also pledged to repeal Biden’s tax hikes , “immediately tackle” inflation and end what he called Biden’s “war” on American energy production.
Second Amendment
“I will take Biden’s executive order directing the federal government to target the firearms industry, and I will rip it up and throw it out on day one,” Trump said at the 2023 National Rifle Association Institute for Legislative Action leadership forum last April.
The former president also promised in the speech that the government would not infringe on citizens’ Second Amendment rights and that he would push Congress to pass a concealed carry reciprocity.
“I will create a special team to rapidly review every action taken by federal agencies under Biden’s ‘equity’ agenda that will need to be reversed. We will reverse almost all of them,” Trump said in a campaign video .
Trump added in multiple campaign videos that he would revoke Biden’s equity executive order that required federal agencies to deliver equitable outcomes in policy and conduct equity training. If elected, Trump said he would also fire staffers hired to implement Biden’s policy, and then reinstate his 2020 executive order banning racial and sexual stereotyping in the federal government.
Related links

A flurry of new rules from the Biden administration attempt to ban noncompetes, boost overtime pay, and increase refunds for delayed flights
- The Biden administration issued new rules designed to boost workers' wages and business competition.
- They aim to raise an overtime threshold, ban noncompetes, and offer refunds for flight delays.
- The rules, already facing legal challenges, could reshape labor-market dynamics and consumer rights.

The Biden administration this week pushed out a slate of rules it says are meant to boost competitiveness and put more money into workers' pockets.
There are already challenges to at least one of the rules — but together they could land overtime pay for millions more workers, ban noncompetes that prevent workers from moving into jobs in similar industries, and help people get automatic refunds for delayed or canceled flights.
"By increasing competition, these rules give workers their fairly earned wages and gives consumers more power to purchase the best option," Lael Brainard, the director of the National Economic Council, told Business Insider.
More workers eligible for overtime pay
Under the Department of Labor's new rule , many workers who make under $43,888 will be eligible for overtime pay effective July 1. That's nearly $10,000 higher than the existing threshold of $35,568; next January it's set to rise to $58,656.
The department estimates the change will affect 4 million workers.
Judy Conti, the government affairs director at the National Employment Law Project, previously told BI that "the current salary threshold beneath which all workers are entitled to overtime is pitifully low."
In 2016, a federal judge blocked a similar attempt to raise the cutoff.
Automatic refunds for canceled or delayed flights
The Department of Transportation announced a new rule that would mean travelers get refunds automatically when their flights are canceled or delayed for over three hours domestically and six hours internationally.
The department also said it was looking to ensure that parents are able to sit with their children without having to pay extra.
Related stories
"Passengers deserve to get their money back when an airline owes them — without headaches or haggling," Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg said in a statement .
A ban on noncompetes that keep workers from taking new jobs
Perhaps the most sweeping action for workers came from the Federal Trade Commission, which finalized a rule to ban noncompetes in most cases. That means workers would no longer be restricted from taking roles in similar industries or starting up new businesses in the same field.
"For workers and employers, it tilts that playing field back more in favor of workers," Brainard said.
The agency estimates the new rule will lead to 8,500 more new businesses every year — a 2.7% increase in business formation — and an average of $524 extra annually for workers. That's not chump change for many Americans, especially those with lower wages who have ended up stifled in finding new work .
"These new regulations will promote healthier labor-market competition," Aaron Sojourner, a senior researcher at the W.E. Upjohn Institute for Employment Research, told BI. "One in five American employees will benefit from the new freedom to accept job offers from any competing employer rather than live bound to their current employer, unable to work for many employers who value their skills and time more."
That rule is already getting pushback from businesses and business interests. Ryan, a company that provides tax services and software, said it filed a lawsuit against the FTC, accusing it of taking "lawless action."
"With history, logic, law, and the Constitution on our side, we look forward to righting this wrong by the FTC against employees and employers alike," John Smith, Ryan's chief legal officer and general counsel, said in a press release.
The US Chamber of Commerce, the Business Roundtable, and the Texas Association of Business have also sued to block the rule .
"The Federal Trade Commission's decision to ban employer noncompete agreements across the economy is not only unlawful but also a blatant power grab that will undermine American businesses' ability to remain competitive," Suzanne Clark, the president and CEO of the Chamber of Commerce, said in a statement.
Jeremy Merkelson, a partner at the law firm Davis Wright Tremaine, speculated that the groups challenging the rule were likely to succeed. Merkelson said that while a Supreme Court majority would "likely reject that such a broad concept gives the FTC specific authority to upend millions of worker contracts," a court might let the ban on noncompetes survive for lower-level workers while invalidating the rule for senior executives.
Brainard argued that "a lot of Republicans and some of the businesses and special interests that they're supporting will try to challenge these actions because it means that they have to pass on savings to consumers," adding, "They have to lower prices; they have to give working families a break."
Elizabeth Wilkins, the former chief of staff to the chair and director of the Office of Policy and Planning at the FTC, described noncompetes as "fundamentally at odds" with the American promise of being able to find opportunities that fit workers' skills and talents. Zooming out, she said, the ban might make a labor market with less friction, where workers can match with employers that make sense for them, boosting productivity.
"To me," Wilkins said, "this rule represents the absolute best of government working for people."
Will a ban on noncompetes, new overtime thresholds, or airline refunds affect your life? Contact this reporter at [email protected] .
Watch: Why flying is so terrible even though airlines spend billions
- Main content

IMAGES
COMMENTS
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State. Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov ...
Office of the Spokesperson. April 19, 2021. State Department Travel Advisory Updates. In order to provide U.S. travelers detailed and actionable information to make informed travel decisions, the Department of State regularly assesses and updates our Travel Advisories, based primarily on the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC ...
What to Know: U.S. Travel Restrictions. Lauren Hard 📍 Reporting from New Jersey. Reuters. The new policy ends an 18-month ban on nonessential travel from 33 countries, including China, Brazil ...
Section 1. Policy. Science-based public health measures are critical to preventing the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by travelers within the United States and those who enter the ...
The U.S. lifted restrictions Monday on travel from a long list of countries including Mexico, Canada and most of Europe, allowing tourists to make long-delayed trips and family members to ...
Travel restrictions can also be used for other suspected or confirmed communicable diseases that could pose a public health threat during travel, including viral hemorrhagic fevers such as Ebola. For specific details about these criteria, please visit the Notice in the Federal Register external icon on FederalRegister.gov, for more information ...
This updated policy puts in place an international travel system that is stringent, consistent across the globe, and guided by public health. Starting on November 8, non-citizen, non-immigrant air ...
The U.S. restricts travel from 8 countries as omicron variant spreads. Travelers exit the International Arrivals area at Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, on Monday. The Biden ...
The continued spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global threat to our health and safety. COVID-19 has resulted in more than 733,000 deaths in the ...
The development follows a September announcement in which the White House said that, come November, it will lift the 18-month ban on visitors from the European Union, China, Iran, South Africa ...
During 2020-2022, CDC used these authorities to restrict travel of people with COVID-19 and close contacts who were recommended to quarantine. These authorities were also used for mpox during 2022. Travel restrictions can also be used for other suspected or confirmed contagious diseases that could pose a public health threat during travel ...
Leslie Josephs @lesliejosephs. Key Points. The U.S. on Monday will lift a pandemic travel ban on international visitors from more than 30 countries after 19 months. New rules will replace the ban ...
Yes, as of 12:01 a.m. ET on December 31, the travel bans are lifted. The bans announced on November 26 barred entry into the US of noncitizens coming from eight countries in southern Africa.
Jerome H. Powell, the Federal Reserve chair, ... After Mr. Biden made the decision to impose the travel ban, State Department officials told diplomats in the affected countries, and administration ...
A: No. There are no Government-wide limits on official travel (i.e., travel conducted under an official travel authorization) for Federal employees, regardless of their vaccination status. Individuals should follow their agency's travel policy. In approving official travel for an individual, agencies should: Inform the traveling individual ...
So far in 2024, the State Department made changes to the existing Level 4 advisories for Myanmar, Iran and Gaza, and moved Niger and Lebanon off of the Level 4 list. Places With a Level 4 Travel ...
The Federal Travel Regulation summarizes the travel and relocation policy for all federal civilian employees and others authorized to travel at the government's expense. Federal employees and agencies may use the FTR as a reference to ensure official travel and relocation is conducted in a responsible and cost effective manner.
the federal government has taken to restrict the movement of foreign nationals through ports of entry on the land borders with Canada and Mexico. ... Administration's imposition of the so-called "travel ban" on certain foreign nationals from designated countries. In the context of a challenge to that invocation of Section 212(f), the ...
Media Contact. Press Office. US Department of Transportation 1200 New Jersey Ave, SE Washington, DC 20590 United States. Email: [email protected] Phone: 1 (202) 366-4570 If you are deaf, hard of hearing, or have a speech disability, please dial 7-1-1 to access telecommunications relay services.
With about two weeks to go before the United States lifts a travel ban on visitors from 33 countries, federal health officials offered more specifics for travelers and airlines before restrictions ...
Federal buildings have cut emissions by 7% since 2020 and as of 2022 have seen a 39% overall reduction from 2008 levels. The administration is investing $1 billion from the Inflation Reduction Act ...
Federal judges in Maryland and Hawaii blocked the order, but ultimately in December 2017, the Supreme Court ruled the ban could be fully enforced despite pending lawsuits and challenges in lower courts. Chad was later removed from the list in April 2018. The Supreme Court's decision now upholds the travel ban for the remaining seven countries.
Surge in complaints in 2022. The Biden Administration proposed its change to the refund rules in 2022 after a surge in complaints about refunds when the coronavirus brought air travel to a standstill.
The Government of Canada's official source of travel information and advice, the Travel Advice and Advisories help you to make informed decisions and travel safely while you are outside Canada. Check the page for your destination often, because safety and security conditions may change. See Travel Advice and Advisories - FAQ for more ...
April 24, 2024 at 7:26 p.m. EDT. (Washington Post illustration; iStock) Most new rules go into effect in the fall. You should get refunds without having to ask. You can still choose to be rebooked ...
Several senators are looking to ban most facial recognition technology at airports, a move that the U.S. Travel Association says would "undermine aviation security, delay millions of flyers [and ...
According to the department, complaints related to airlines and ticket agents rejecting or delaying refunds made up 87% of all air-travel service complaints at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic ...
In addition, Trump has said he would restore his "wonderful" travel ban on individuals from several majority-Muslim countries to "keep radical Islamic terrorists out of our country" after ...
Under the Department of Labor's new rule, many workers who make under $43,888 will be eligible for overtime pay effective July 1. That's nearly $10,000 higher than the existing threshold of ...