- Beaches and coves
- History of Tourism in Benidorm
- Benidorm Holy Week 2024
- Cultural and Urban Tourism
- Benidorm on your mobile
- Sustainability

- Active & Sports Tourism
- Benidorm Shopping
- Theme Parks in Benidorm
- Benidorm Music & Emotion
- Benidorm's Nightlife
- Health Tourism and Wellness
- Benidorm and it's surrounding areas

- How to Get to Benidorm
- Urban Transport of Benidorm
- Useful information
- Airport Transfers
- Where to sleep
- Where to eat
- Accesible Benidorm
- Digital Nomads
- Flight + Hotel

- Benidorm Always Summer
- Benidorm Senior
- Benidorm LGBT
- Benidorm Young people
- Benidorm Families
- Benidorm Petfriendly

- Restaurants
- Perfect Venues
- MICE Hotels
- Transport Companies
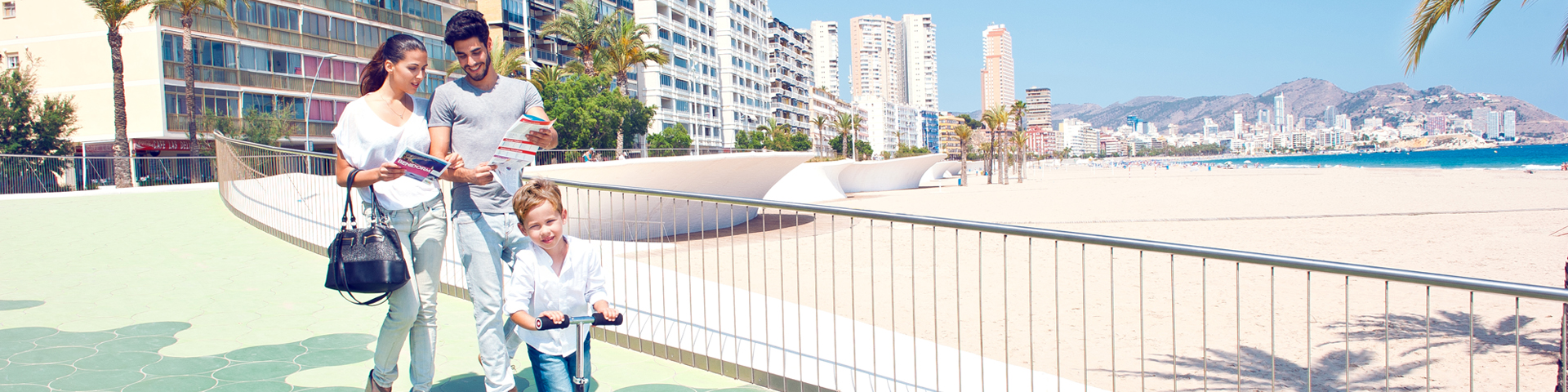

- Visit Benidorm ,
- Hablan de nosotros ,
- Benidorm first smart tourist...

Benidorm first smart tourist destination
"do smart tourist really work the case of benidorm".
Francisco Femenia Serra & Josep A. Ivars Baidal from the University Institute of Tourism Research, at the University of Alicante have published an article "Do smart tourist really work? The case of Benidorm" published in the Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, where they are echoed of the benefits of being a smart tourist destination, using the case of Benidorm .
In summary, the results of the research show that thanks to its DTI project and its smart solutions, Benidorm has managed to improve several aspects of its tourism management, including: 1) Greater knowledge of demand from big data; 2) More efficient marketing; 3) Better internal coordination; 4) Greater public-private collaboration for the promotion of innovation; 5) A repositioning of the image of the destination among professionals.
In addition, the results show that the DTI has p ositive effects on the experience of tourists who use technological solutions on issues such as: obtaining information, making decisions, navigation at destination, sharing experiences or saving time and effort, among others.
Do not miss the opportunity to read this article!

more Information
01/01/2019 al 31/12/2019
Unspecified
Related events

Do smart tourism destinations really work? The case of Benidorm
- Scinapse’s Top 10 Citation Journals & Affiliations graph reveals the quality and authenticity of citations received by a paper.
- Discover whether citations have been inflated due to self-citations, or if citations include institutional bias.
THE WEATHER IN BENIDORM NOW
TIME IN BENIDORM
TEMPERATURA
WIND DIRECTION AND SPEED
CHANCE OF SHOWERS
THE WEATHER IN BENIDORM NEXT 7 DAYS
Weather in benidorm the next 12 hours.
- NEXT 12 HOURS
- NEXT 7 DAYS
SELECT A PORTAL
Information to live in the city
COMMUNICATION
Press, Radio and TV
FILM OFFICE
Office of filming
Indicators of our destination
EUROPEAN FUNDS
Actions co-financed by the EU
CHOOSE YOUR PREFERENCES
Current size: 100%
Communicaction
News, Radio and TV
Film Office
European Funds
The manager of Visit Benidorm emphasizes that data analysis is vital in decision making
Benidorm, a model in the Smart Tourism and Data Forum
- tweet
- share

The UNWTO defends the opportunities that technology and data applied to tourism offer to increase social sustainability
Almost sixty years after Benidorm hosted the first edition of its European Week, its status as a tourism leader has led to the city hosting a new encounter with Europe as a backdrop. In this case, the Smart Tourism and Data Forum, organized within the framework of the Spanish Presidency of the Council of the European Union and in which the city, as a model for smart tourism and data, has starred in the first of the work tables of the day.
A table moderated by the president of Segittur, Enrique Martínez; in which the manager of Visit Benidorm, Leire Bilbao, and the director of Tourism and Hospitality of the Basque Government, Aroa Jilete, participated; and in which it has been addressed, from the experience of both, what types of data can be most useful to destinations to improve their management.
Bilbao has recalled that it was in 2015 when Benidorm opted for tourism intelligence, a path that led it to set itself the “challenge” of being “the first certified Intelligent Tourist Destination (DTI) in the world”, a goal that was achieved at the end of 2018 and that “it represented a paradigm shift.” Since then, the city, together with the private sector, has been implementing tools and sharing data.
The analysis of this data has made it possible to “detect needs and provide solutions”, as well as know “what is happening in the city”, “what tourists say” or “how many arrive from the airport”, guiding promotion, managing tourist flows and promoting events or actions at times when tourist activity is lower.
As an example of data monitoring, the Visit Benidorm manager has referred to the management of water, mobility, or the flows of people on the beaches, as well as the Biontrend tool of the Hosbec employers' association, which provides information on the type of client, accommodation regime or possible participation of a tour operator. All this data, Bilbao has transferred, “allows us to value what we are” and be in a process of “continuous improvement.”
Like her tablemate, Bilbao has advocated for “the standardization of data” and the use of common “nomenclatures” for all destinations. Before this table, the Forum featured a presentation by the executive director of the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) Natalia Bayona, entitled 'Education and tourism innovation: towards social sustainability by making decisions based on data'.
During his speech, Bayona outlined the growth that investment in tourism technology has experienced in the last five years, reaching 48 billion dollars, since the largest investors in technology are seeing tourism as an interesting opportunity and industry.
The UNWTO representative has delved into the need for Europe to increase its representation in this investment in line with its tourism weight. In this regard, she stated that the continent “has talent” and “hosts startups” that “will allow tourism to be more sustainable,” also on a “social” level.
Finally, she stated that “tourism is the most humane economic sector” and stated that “the investment framework must guarantee that people are at the center as the highest priority” and that sustainability – “our planet” – is the "main goal".

International Journal of Tourism Cities: Volume 9 Issue 1
Table of contents, the ghost city: chronicles of the apocalypse after covid-19.
The present conceptual paper evinces a new understanding of the present and future of the tourist city in a post-COVID-19 world. The pandemic has wreaked havoc in the tourism…
The role of culture as a determinant of tourism demand: evidence from European cities
The purpose of this paper is to examine the impact of various cultural amenities on tourism demand in 168 European cities.
Organizational flexibility and pioneering behavior: the indirect effect of market dynamism in tourism firms
The purpose of this study is to understand the moderating role of market dynamism in the relationship between organizational flexibility and pioneering behavior in tourism firms…
Smart tourism destinations really make sustainable cities: Benidorm as a case study
Tourism sustainability is a challenge for 21st-century destinations – this paper aims to analyse smart destinations' sustainability through a case study of Benidorm, the first…
Addressing dereliction and devaluation in urban tourism: the case of Cork, Ireland
This paper aims to focus on increasingly entrepreneurial approaches to urban governance in the country’s second city Cork, where neoliberal strategy has driven uneven spatial…
Hotel owners’ perception of tourism in India during the COVID-19 pandemic
The paper aims to study hotel owners’ perception of tourism in the five creative cities of India during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Sightseeing spot satisfaction of inbound tourists: comparative analysis of first-time visitors and repeat visitors in Japan
This study aims to enhance knowledge on marketing strategies to increase repeat visitors. Furthermore, the authors suggest using appropriate destination information tailored to…
Executing a destination branding strategy: Louisville Tourism’s Urban Bourbon Trail
The purpose of this study is to add new insights into the discussion of how a city’s destination marketing organization (DMO) can apply operant resources to act upon its operant…
Factors influencing green hotel revisit intentions after the COVID-19 in Bangladesh
The purpose of this study is to explore the factors influencing customers’ revisit intentions of green hotels after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Are consumers influenced by the use of green practices in five-star hotels: an assessment of guest's revisit intentions, inclusive ratings and hotel performance
This study aims to find out the influence of green practices used by the five-star hotels on the guest’s online hotel assessment and their revisit intentions. It also evaluated…

Afforestation intentions for mitigating carbon emissions in the post-COVID-19 perspective: the case of green hotel visitors in Bangladesh
This study aims to explore green hotel visitors’ afforestation intentions by extending the theory of planned behavior, including post-COVID-19 personal norms (PCPN) and…
The personas and motivation of religious tourists and their impact on intentions to visit religious sites in Saudi Arabia
The purpose of this paper is to provide comprehensive, theoretical and practical knowledge that will assist decision-makers in making informed decisions when promoting several…
Backpacker conceptualisation criteria: discussion, clarification and operationalisation proposal
Backpackers can be found all over the world, especially in urban areas where the main enclaves are established. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the operationalisation of…
Encouraging pro-conservation intentions in urban recreational spaces: a South African zoo perspective
Zoos are important urban tourism attractions. The challenge for zoos is finding a balance between attracting visitors and enhancing education and conservation management. This…
Investigating literary gaze through the orchestra model of the tourist experience
Considering the diversity of literary sites, various needs and motivations of literary visitors, and the limited research on literary tourists’ experiences, this study aims to…
Conflicting discursive representations of overtourism in Lisbon in the Portuguese digital press
This study aims to explore the ways in which Portuguese online news reports and opinion studies have framed the discussion about overtourism in Lisbon and its impacts on the city…
Destination social responsibility drives destination brand loyalty: a case study of domestic tourists in Danang city, Vietnam
This study aims to identify how perceived destination social responsibility (DSR) drives destination brand loyalty through a jointly and independently mediated mechanism of…

Online date, start – end:
Copyright holder:, open access:.
- Prof Andres Coca-Stefaniak
- Prof Alastair Morrison
Further Information
- About the journal (opens new window)
- Purchase information (opens new window)
- Editorial team (opens new window)
- Write for this journal (opens new window)
We’re listening — tell us what you think
Something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
- español
Universidad de Cádiz
- RODIN Home
- Producción Científica
- Artículos Científicos
Smart tourism destinations really make sustainable cities: Benidorm as a case study

Identificadores
URI: http://hdl.handle.net/10498/27669
DOI: 10.1108/IJTC-01-2022-0006
ISSN: 2056-5615
Metrics and citations

Collections
- Artículos Científicos [6907]
- Articulos Científicos Hist. Geog. Filos. [432]
- Artículos Científicos INDESS [571]
- Articulos Científicos Mark. Com. [238]
- Articulos Científicos Org. Emp. [144]
- Articulos Científicos Psicología [262]

Información adicional
Rodin is available through, related links.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Do smart tourism destinations really work? The case of Benidorm

2018, Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research
Related Papers
Congresos - Seminario Destinos Turisticos Inteligentes 2017 - Libro de Actas
Assumpció Huertas
"Management and sustainability: Creating shared value in the digital era". Proceedings of Sinergie - Sima Management Conference (Full Papers). Sapienza University of Rome
Alfonso Vargas-Sánchez , Mirko Perano
Objectives. In general, the smart approach allows strengthening the ability to solve problems (e.g. those related to sustainability) through an efficacious use of knowledge. Smart management of tourism rests on an information-driven logic, becoming critical the capacity of organizations to capturing data from diverse sources and makes them available to managers. It is recognized that smart tourism destinations are built around a number of areas, within which sustainability is one of them. The paper intends: to present how the literature has addressed the intersection between the smart and sustainability concepts and to display diverse cases in that intersection. Methodology. The study presents a review of the literature of smart tourism and sustainability, trying to unravel the link between both concepts. Then, it performs a collection of experiences on the components of smartness, implemented with satisfactory results and aligned to the management of sustainability issues. Findings. The analysis reveals several gaps that should be bridged for a full exploitation of the intersection between smartness and sustainability. Firstly, the need to move from a focus based on technology, to a more global and long-term perspective on how the data-driven logic of smartness can help to tackle sustainability issues in destinations. Secondly, the smart tourism approach has a potential for the preservation of local heritage, way of living and culture, connecting its capabilities with the social components of smart people, smart mobility and smart living. Finally, the insertion of tourism into the emergent paradigm of circular economy. Research limits. Although the completeness in the collection of experiences in a so vast and dynamic field is a utopia, it is honest to recognize that the speed of technological evolution prevents to present a set of initiatives fully updated, together with their outputs. Practical implications. The design of tourism destinations should not be based on harnessing the ICTs proliferation only, but, more importantly, on the need for balancing all the beneficiaries -from internal publics (residents, local people) and external ones (visitors in one single word, both excursionists and tourists)- through the paradigm of “smartness”, that, in the search for a more sustainable tourism industry, guides people’s living conditions. Originality of the study. The study promotes to moving forward in this area through a cross-fertilization between theory and practice, with the outline of a number of recommendations together with some suggestions for further research in a still under explored field of study.
Collaborative Networks of Cognitive Systems. IFIP AICT
Salvatore Ammirato
Recent developments of ICTs enable new ways to experience tourism and conducted to the concept of smart tourism. The adoption of cutting-edge technologies and its combination with innovative organizational models fosters cooperation, knowledge sharing, and open innovation among service providers in tourism destination. Moreover, it offers innovative services to visitors. In few words, they become smart tourism destinations. In this paper, we report first results of the SMARTCAL project aimed at conceiving a digital platform assisting Destination Management Organizations (DMOs) in providing smart tourism services. A DMO is the organization charged with managing the tourism offer of a collaborative network, made up of service providers acting in a destination. In this paper, we adopted a multiple case studies approach to analyze five Italian DMOs. Our aims were to investigate 1) if, and how, successful DMOs were able to offer smart tourism services to visitors; 2) if the ICTs adoption level was related to the collaboration level among DMO partners. First results highlighted that use of smart technologies was still in an embryonic stage of development, and it did not depend from collaboration levels.
Current Issues in Tourism
Josep A. Ivars Baidal
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology
roberto micera
PurposeThe aim of this paper is to provide a critical analysis of the main literature contributions that concern smart tourism development and management, highlighting gaps and logical inconsistencies. In addition, to further stress the importance of the issues at stake, a simulation is performed for showing how technology allows achieving better outcomes when a certain level of efficiency is obtained via re-engineering of main organizational and operational processes.Design/methodology/approachA content analysis of recent relevant literature is performed with the help of machine learning topic modelling algorithms. A network analytic approach to digital ecosystems, then, is used to study the relationship between technological tools and physical entities in a destination and how these and their combination affect the efficiency of the system at local and global levels.FindingsThe literature analyzed lacks a good discussion on the necessity to improve and rationalize the operational ...
Journal of Regional Research
Francisco Femenia-Serra , Barbara Neuhofer
«Smart tourism» has gained momentum in research fostered by the revolution of the latest generation of information and communication technologies and has rapidly become a leading stream of literature. The concept has permeated governments and the business sphere and has been accompanied by the quest for developing smart devices, services and tourist destinations. However, experiences as the main focus of smartness development in tourism and destinations have received comparably little attention in the smart discourse. Smart destinations, as new ecosystems backed by concrete geographical contexts, facilitate the co-creation of a rich, technology-based, smart tourism experience (STE). Yet, a clear definition and examination of the dimensions of what constitutes a smart tourism experience is still to be developed. This paper aims to discuss the main core precedent constructs of STEs, namely: a) technology enhanced experiences and b) smart destinations, to underpin a holistic definition of a smart tourism experience. Based on an in-depth literature review, a novel conceptual model for this concept is developed and an agenda for further research is proposed drawing on the identified key themes and dimensions of this construct. By mapping out smart tourism experiences and providing real examples, this research contributes to the theoretical foundations of smart tourism and tourist experiences.
Alessandro Inversini , Kim Boes , Professor Dimitrios Buhalis
The term ‘smart’ represents a marketing word for all things that are embedded or enhanced by technology. One smart concept, which has gained momentum in recent years, is Smart City. It mainly focuses on how to increase the quality of life of citizens by using Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). This paper aims to explore which dimensions except technology are critical for the development of a Smart City and a Smart Tourism Destination. Following a multiple case study approach, this paper develops a framework for smartness in cities and tourism destinations. This exploratory research argues that leadership, innovation, and social capital supported by human capital are the fundamental constructs of smartness. Technology applications and ICTs are enablers, which support the core constructs of smart destinations. Results open the ground for discussing how to transpose ‘smartness’ to tourism and destination levels.
Francisco Femenia-Serra , Barbara Neuhofer , Josep Ivars
‘Smart tourism’ and ‘smart destinations’ have been gaining attention as new frameworks within which to understand the impact the latest information and communication technologies (ICTs) have on the relationship between businesses, destinations and tourists. However, there is a crucial element of the smart tourism ecosystem that has been rather neglected in research hitherto: the tourists themselves. By acknowledging a shift in tourists’ behaviour due to the advent of disruptive factors, this paper conceptualises the recently emerged notion of ‘the smart tourist’. This new type of tourist is profiled through a description of their attitudes and behaviours, and their role within the smart destination scenario is depicted. By taking a consumer-centric perspective and framing the conceptualisation within the relevant theories, this paper contributes to the current body of knowledge on tourism in a highly technological context and facilitates bridging smart tourism theoretical foundations with empirical research. The observed transformation in tourists’ behaviour and its encapsulation in the smart tourist conceptualisation reveal critical managerial implications for both destination management organisations and businesses in the rapidly changing smart tourism ecosystem.
Maria Lexhagen
Professor Dimitrios Buhalis , Kim Boes
Boes, K., Buhalis, D., Inversini, A., 2016, Smart tourism destinations: ecosystems for tourism destination competitiveness", International Journal of Tourism Cities, Vol. 2(2), pp.108 – 124 Purpose – Grounded in service-dominant (S-D) logic, the purpose of this paper is to explore the core components of smartness to present a framework for the development of the smart tourism destination. Design/methodology/approach – The paper explores the core components of smartness through case study analysis of well-established smart cities. Findings – The paper conceptualises smartness and argues ICT, leadership, innovation and social capital supported by human capital are core components of smartness. Although ICT is a critical enabler for smart tourism destinations, it is insufficient on its own to introduce smartness. The combination of hard and soft smartness components within a S-D logic ecosystem structure holds the potential for sustained competitive advantage and enhancement of quality of life of both residents and tourists in smart tourism destinations. Originality/value – The paper extends the application of S-D logic to the context of smart tourism destinations, specifically to examine the smartness concept as a means for competitiveness in tourism destinations.
RELATED PAPERS
Annals of Clinical Biochemistry
Ramasamyiyer Swaminathan
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes
International Journal of Computer Applications
International Journal for Parasitology
Ernesto Monge
Margarita Núñez
Sisa Tempot
shabana banu
Prática e Pesquisa em Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos 2
joelaine santana
Engineering Proceedings
Ibrahim Sanusi
Obesity Surgery
Debora Kussunoki
International Journal of Family Business and Management
Shahzad Atta
JURNAL BIOLOGI PAPUA
kosasih kosasih
Clinical and molecular allergy : CMA
Ursula Ackermann-Liebrich
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Carolina Solomon , Ciprian Jurcut
Brazilian Journal of Development
Efraim Costa Pereira
ARTHUR CREMONEZI
Lotte Huniche
Kostas Boukouvalas
Arthroscopy techniques
Niek Van dijk
113th Annual GSA Cordilleran Section Meeting - 2017
Bill Bonnichsen
Current Opinion in Pharmacology
Mythili Dileepan
Revista Sociedade & Natureza
Dirce Suertegaray
Fulvio Cammarano
Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions
E. Schampaert
Jaydeep Sarma
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Smart Destinations (SDs) have gained momentum in tourism research, but despite the growing body of literature devoted to the topic, some critical dimensions continue to be under-researched. Real fulfilment of two of the main objectives of SDs, namely enhancing tourists' experiences and improving destinations management, remains largely unknown.
Case Study Background: Benidorm as a Smart Destination Benidorm (70.470 inhabitants) is a sun and sand mass destination located in the province of Alicante, south-eastern Mediterranean coast of Spain.
The case of Benidorm. Francisco Femenia-Serra, J. Ivars-Baidal. Published in Asia Pacific Journal of… 25 December 2018. Business. ABSTRACT Smart Destinations (SDs) have gained momentum in tourism research, but despite the growing body of literature devoted to the topic, some critical dimensions continue to be under-researched.
Tourism sustainability is a challenge for 21st-century destinations - this paper aims to analyse smart destinations' sustainability through a case study of Benidorm, the first world destination to be certified under the UNE 178501 standard as smart tourism destination (STD).,The methodological component has been divided into developing a ...
By taking as a relevant case the destination of Benidorm, its smart destination strategy and solutions, this paper investigates whether and how these smart destination efforts are actually transforming destination management, marketing processes and tourists' experiences. Through a sequence of qualitative methods including (i) documentary and ...
The second article, co-authored by Femenia-Serra and Ivars-Baidal, is "Do smart tourism destinations really work? The case of Benidorm," which investigated whether and how smart destination efforts are transforming destination management, marketing processes, and tourists' experiences.
Purpose -Tourism sustainability is a challenge for 21st-century destinations -this paper aims to analyse. smart destinations 'sustainability through a case study of Benidorm, the first world ...
The mayor stressed that Benidorm "has worked hard to be part of the smart tourism management model", which will mark "the repositioning of destinations"; and added that "in the very near future, tourism and the success of a destination will not be conceived without the application of tourism intelligence; an application in which Benidorm is ...
By taking as a relevant case the destination of Benidorm, its smart destination strategy and solutions, this paper investigates whether and how these smart destination efforts are actually transforming destination management, marketing processes and tourists' experiences. ... Do Smart Tourism Destinations Really Work? The Case of Benidorm ...
Benidorm has marked the road map with a Management Plan for the years 2015-2020, which aims to transform the city into a Smart Destination. At this time, and thanks to the efforts and actions already undertaken, Benidorm has reached the following milestones: Benidorm is one of the unique four cities where the the UNE 178501 of Intelligent ...
Francisco Femenia Serra & Josep A. Ivars Baidal from the University Institute of Tourism Research, at the University of Alicante have published an article "Do smart tourist really work? The case of Benidorm" published in the Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, where they are echoed of the benefits of being a smart tourist destination, using the case of Benidorm.
Do smart tourism destinations really work? The case of Benidorm. Francisco Femenia-Serra. 7, Josep Ivars-Baidal. 9. View details (2 authors) Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research. ... Do smart tourism destinations really work? The case of Benidorm. DOI. 10.1080/10941665.2018.1561478. Published Date. Apr 3, 2021. Journal. Asia Pacific Journal ...
Thus, many international tourist destinations have started to work towards this goal, including Benidorm, the subject of the case study. Benidorm is a Spanish municipality in the province of Alicante, in the Valencian Community. It is located on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea, in the Marina Baja region and is the most densely populated
In this case, the Smart Tourism and Data Forum, organized within the framework of the Spanish Presidency of the Council of the European Union and in which the city, as a model for smart tourism and data, has starred in the first of the work tables of the day.
Agarwal S., Managing coastal tourism resorts. A global perspective https://doi.org/10.21832/9781845410742 Benidorm City Council.
Purpose Tourism sustainability is a challenge for 21st-century destinations - this paper aims to analyse smart destinations' sustainability through a case study of Benidorm, the first world destination to be certified under the UNE 178501 standard as smart tourism destination (STD). Design/methodology/approach The methodological component has been divided into developing a framework for ...
Smart tourism destinations really make sustainable cities: Benidorm as a case study. Alexander Aguirre, Antonio Zayas, Diego Gómez-Carmona, José Antonio López Sánchez. Tourism sustainability is a challenge for 21st-century destinations - this paper aims to analyse smart destinations' sustainability through a case study of Benidorm, the ...
6 Figure 1. Smart tourism destination solutions. Own elaboration based on Ivars-Baidal et al. (2017) In their systemic understanding of smart destinations based on three interrelated levels (left
Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyse Benidorm, San Sebastián, Gijón, Málaga, Tenerife Island and Santander smart tourist destinations (STDs) as a touristic model and example to follow by other destinations in Spain and all over the world. Design/methodology/approach To fulfil the stated objective, this study follows several phases that introduce and classify a set of measures ...
Download scientific diagram | Benidorm smart solutions. Own elaboration from publication: Do smart tourism destinations really work? The case of Benidorm | Smart Destinations (SDs) have gained ...
Purpose Tourism sustainability is a challenge for 21st-century destinations - this paper aims to analyse smart destinations' sustainability through a case study of Benidorm, the first world destination to be certified under the UNE 178501 standard as smart tourism destination (STD). Design/methodology/approach The methodological component has ...
Moreover, Benidorm has enrolled the Spanish smart cities network (RECI) and is leading a regional project for developing smart destinations launched by the Valencian government together with the Valencian Tourism Technologies Institute (Invat.tur), which has just created in Benidorm the first technical office to assist destinations in their ...
This paper analyses the application of the cluster concept to tourist destinations using Benidorm as a case study. A questionnaire was administered to tourism firms based in Benidorm in order to determine whether this destination currently constitutes a tourism cluster or whether it possesses the ideal characteristics to become a cluster with the private agents' collaboration, that is, whether ...