A Singapore Government Agency Website How to identify

Official website links end with .gov.sg
Government agencies communicate via .gov.sg websites (e.g. go.gov.sg/open). Trusted websites
Secure websites use HTTPS
Look for a lock ( ) or https:// as an added precaution. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Our Energy Story
Consumer information, regulations & licences, news & events, partnerships.
Learn about EMA’s leadership, milestones and accomplishments.
- Board Members
- Corporate Structure
- Our Service Commitment
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Our Role as Power System Operator
Explore the career, scholarship and internship opportunities available in EMA.
- Scholarships
- Internships

VISION, MISSION AND VALUES
Forging Towards a Clean Energy Future for Singapore

Learn How You Can Be A Part of the Exciting Energy Sector
Discover how the Singapore Energy Story sets the vision towards a net-zero energy future.
Energy Supply
Gain insights into the four switches that power Singapore’s economy and our daily lives.
- Regional Power Grids
- Low-Carbon Alternatives
- Natural Gas
Energy Demand
Discover ways to enhance energy efficiency and lower your carbon footprint.
- Non-Residential Consumers
- Residential Consumers
Energy Grid
Explore how EMA ensures a reliable and secure energy supply for everyone.
- Energy Storage Systems
- Grid Digital Twin
- Micro-Grids
Energy Market Landscape
Learn about the intricacies of Singapore’s energy market structure and operations.
- Electricity Market

REGIONAL POWER GRIDS
Importing Low-Carbon Electricity
MEDIA RELEASES
Future-proofing Singapore's Energy Grid
Electricity
Get tips on buying electricity and protecting your family from electrical hazards.
- Buying Electricity
- Electrical Safety
- Electricity Conservation
- Engaging Licensed Workers
Learn about purchasing gas and safeguarding your family against gas hazards.
Access information on installing solar panels at your home and selling excess electricity to the national grid.
- Solar Installation Guide
- Solar Generation Profile
- Solar Irradiance Map

New Residential Demand Response Pilot Programme

BUYING ELECTRICITY
Learn About Your Options When Buying Electricity

ELECTRICAL SAFETY
All Homes Must Have A Residual Current Circuit Breaker
Regulations
Stay up-to-date with the latest regulations, policies and frameworks governing the energy sector.
- Acts & Regulations
- Policies & Frameworks
- Standards & Guidelines
- Enforcement Decisions
- Market Operations
Learn about the licences that EMA issues to different stakeholders in the energy sector.
- Worker Licences
- Installation Licences
- Industry Licences
Regulatory Publications
Read about the Codes of Practice and Circulars that EMA publishes to regulate the energy sector.

How Do Vesting Contracts Work?

WORKER LICENCES
Applying for an Electrical Worker Licence?
Get all the latest news and announcements by EMA.
- Feature Stories
- Media Releases
- Forum Replies
Stay informed about EMA’s flagship events.

FEATURE STORY
Celebrating EMA's 23rd Anniversary

Cooperation between EMA and JERA

5 Things You May Not Know About Solar Energy in Singapore
Calls for Proposal
Collaborate with EMA in co-creating innovative solutions for the energy sector.
Consultations
Give your comments and feedback on EMA’s policies and regulations.
R&D Partnerships
Discover how EMA works with stakeholders to catalyse new and innovative digital technologies.
Talent Development
Learn about EMA’s efforts in nurturing talent and cultivate interest in the energy sector.

CONSULTATIONS
Decision on Emission Standards Framework

Proposed Modifications to Gas Supply Code
Get quick access to EMA’s services for application of worker licences, scholarships and more.
Welcome to EMA's website. We would love to have your valuable feedback .
How do I test whether my Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) or Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) is working?
You can perform the following 3-step test to ensure your Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) or Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) is working and protects all electrical circuits in your home.
- Test the ELCB or RCCB by pressing the ‘Test’ button. The ELCB or RCCB switch will flip down and cut off all power supply in your home. If the ELCB or RCCB switch does not flip down, it is faulty. Homeowners should contact a Licensed Electrical Worker for assistance immediately.
- Test all light switches and power sockets in every room. The ELCB or RCCB is working if lights and power sockets do not turn on when the circuit breaker switch is flipped down. If any light or power socket continues to work when the circuit breaker switch is flipped down, the house is not fully protected by the circuit breaker. Homeowners should contact a Licensed Electrical Worker for assistance immediately.
- Flip up ELCB or RCCB switch to restore power supply. Switch on lights and appliances that you need.
For a detailed step-by-step guide, please visit our RCCB Safety . You are advised to test your ELCB or RCCB once a month to check that it is in good working condition.
All homeowners can engage a Licensed Electrical Worker to install an RCCB if necessary. It is recommended to contact a few LEWs to perform price comparisons before engaging one. HDB will be writing to the homeowners of 3-room and larger flat types, completed in and before 1985 without an RCCB, to share more information on the assistance programme for the installation of RCCB.
Related Questions

Expert Advice On Improving Your Home
We recommend the best products through an independent review process, and advertisers do not influence our picks. We may receive compensation if you visit partners we recommend. Read our advertiser disclosure for more info.
Troubleshooting a Tripped Circuit Breaker

Alora Bopray
Staff Writer
Alora Bopray is a digital content producer for the home warranty, HVAC, and plumbing categories at Today's Homeowner. She earned her bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of St. Scholastica and her master's degree from the University of Denver. Before becoming a writer for Today's Homeowner, Alora wrote as a freelance writer for dozens of home improvement clients and informed homeowners about the solar industry as a writer for EcoWatch. When she's not writing, Alora can be found planning her next DIY home improvement project or plotting her next novel.

Reviewed By
Roxanne Downer
Roxanne Downer is a commerce editor at Today’s Homeowner, where she tackles everything from foundation repair to solar panel installation. She brings more than 15 years of writing and editing experience to bear in her meticulous approach to ensuring accurate, up-to-date, and engaging content. She’s previously edited for outlets including MSN, Architectural Digest, and Better Homes & Gardens. An alumna of the University of Pennsylvania, Roxanne is now an Oklahoma homeowner, DIY enthusiast, and the proud parent of a playful pug.
April 22, 2024
If your air conditioner or heat pump unit is the culprit that caused a tripped circuit breaker in your house or office, there are a few possibilities why this happen.
The earth leakage circuit breaker(ELCB) that trips the entire power supply to the house when a lightning strike can easily be restored by switching the lever back to the ON position.
In the case of faulty air conditioner equipment, the ELCB may trip due to earth leakage. In this case, you will need to isolate the cause of the fault or repair the equipment before the power supply can be restored to the entire house.
If the miniature circuit breaker(MCB) trips, the fault could be due to an overcurrent or short circuit. Rectify the problem and power on the MCB.

These circuit breakers are protection devices that protect the electrical circuitry from further damage without which fire hazard and electrical shocks may occurred.
Tripped Circuit Breaker Due To Earth Leakage
Here are some of the possible causes of earth leakage that cause the earth leakage circuit breaker to trip.
The motor wires in the compressor touch the metal enclosure of the compressor. The wires of the motor may come off due to excessive vibration or fault in design.
Once these wires that are connected to the hot circuits touch the metal enclosure which is grounded, current will flow to the ground causing the ELCB to trip.
Disconnect the power and all the circuits to the terminal of the compressor. Use a multimeter and set the scale to measure resistance. Check the resistance between each of the terminals to the enclosure.
If the reading is close to zero, that means that the exposed wire closest to that terminal has touched the metal frame. Repair the fault or replace the compressor before the equipment can be operated again.
Similarly, if the fault is due to the compressor fan motor or indoor blower motor, disconnect the power and isolate the circuits to the motor. Check the resistance of each terminal to the casing(if metal). If it is close to zero, that means that the exposed wire is touching the casing causing it to trip. Remove the motor for repair or replace with a new motor before the equipment can be operational again.
In circuits that have live, neutral and earth wires bundled together, there is a possibility that the insulator of the wires breaks down (due to overheating, faults, under specs or inferior wires) causing the live or neutral conductor to touch the earth conductor. This will cause the circuit breaker to trip too. Troubleshooting this problem is more complicated as it involves not just a particular component but the electrical circuits.
Tripped Circuit Breaker Due To Overcurrent
Sometimes, the miniature circuit breaker tripped after operating the air conditioner for some time due to over-current. This problem will take more time to troubleshoot as the problem does not happen immediately. Here are the possible causes.
Disconnect the mains power before checking the connecting power from the mains to the equipment. For example, if there are 3 terminals that connect the power to the compressor, open up the housing and check the connection.
Look out for darkend or black spots on the terminal indicating that overcurrent had occurred. A loose connection will cause arching hence drawing excessive supply and damaging the wires and the parts that are connected to it.
Tightened the connection after removing and reconnecting the wire that has been damaged due to overheating.
A qualify technician will usually be able to troubleshoot this problem by using a tong clamp ammeter to measure the current of that particular conductor.
If the compressor has a mechanical part that malfunction causing it to lock, the current to operate it will be a few times more than the normal operation. When this happen continuously, the possibility of over-current to happen will occurred causing the circuit breaker to eventually tripped after a certain period of operation.
If the compressor or fan motor uses a 3-phase induction motor, a loss of one phase will cause overheating to occur when operating at full load. If the thermal overload protection does not trip, the circuit breaker will trip if the current exceeds its specification. A good design will usually has a phase loss protector built into the circuit to prevent the motor from running in the first place.

What Is a Fan Speed Controller?
April 25, 2024

What Are Roof Ventilators?
Do Vent Filters Work?
April 19, 2024
What Is an Air Curtain?
February 12, 2024

Innovative Pump Unclogs AC Condensation Drain Lines
February 9, 2024
What Is the Ideal Humidity Level for Your Home?
April 16, 2024

Air Duct Cleaning: Scam or Worth It?
What Is a Humidifier?
April 26, 2024
Dangers Of Radon Gas
February 5, 2024

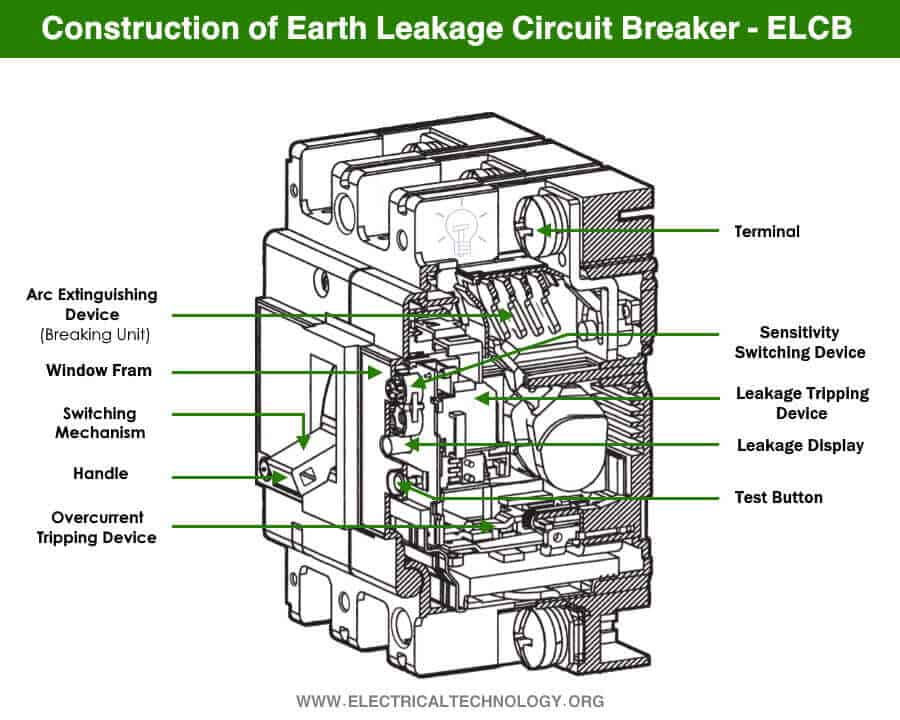
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
Earth leakage circuit breaker (elcb).
Full form of ELCB – Full form of ELCB is Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker.
What is ELCB – Definition of ELCB is given below –
Definition –
ELCB is a device that is used in electrical circuit to protect a person from an earth fault.
What is an earth fault –
An earth fault occurs when a live wire touches the body of the equipment (due to insulation failure etc) which causes metallic body of the equipment gets charged. When a person touches the charged body of equipment, he will get shock &person may die. Therefore, function of ELCB is to trip/interrupts the circuit when live wire touches the body of the equipment.
Types of ELCB –
There are two types of ELCB – A) Voltage operated ELCB & B) Current operated ELCB. The current operated ELCB is also called RCCB (or RCD)
Working Principle of ELCB –
It consists of a voltage operated coil (called search/sensing coil), fixed & moving contacts. This coil has two terminals, one terminal is connected with the metal body of the equipment while other terminal is connected with the earth.
Under normal condition, the voltage between metal body & earth is 0V, hence ELCB carries the normal current of the load. When earth fault occurs, it means phase wire touches the metal body of the equipment, the metal body gets charged & leakage current flows from body to earth. The search coil gets voltage difference across its terminals& actuates its tripping mechanism & trips the circuit. If fault is temporary, we may switch on ELCB again, but if fault persists, then ELCB will not be switched on again and we will have to rectify the fault first, then ELCB can be switched on.
(Note – For a human being 30mA current is a safe current & beyond this current is harmful so ELCB must trip on or less than 30mA current.)
Selection of ELCB –
- It should be capable to carry the rated current of load,
- Check ELCB is required for single phase or 3 phase load .
- Check number of poles – SP, SPN, DP,TP, TPN, 4P where SP = Single Pole which means only phase wire will be connected, DP = Double Pole which means phase & neutral wires will be connected, TP = Triple pole which means three phases will be connected, 4P = Fore pole which means 3 phases & a neutral will be connected.
- Fault current rating (in mA) on which relay should trip/interrupts the faulty circuit, for ex – 30mA, 100mA, 300mA etc
Ex – 40A DP ELCB with 30mA fault current.
LIMITATIONS OF VOLTAGE OPERATED ELCB –
- To operate ELCB, proper earthing is required. ELCB will not work If there is no body earthing of the equipment.
- ELCB works on metal body equipment,
(Note:- Due to above limitations ELCBs are not being used and should be replaced with RCCBs because earthing is not required for earth fault protection in RCCBs.)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on ELCB –
Q1) What is the difference between ELCB & RCCB?
Ans) The main difference between ELCB & RCCB is that ELCB is a voltage operated device & earth connection is required to operate it. On the other hand, RCCB is a current operated device & no need of earthing connection for the operation. ELCB works on metal body while RCCB works on leakage of current on metallic or non-metallic body.
Detail of ELCB is given in above sections of this page & details of RCCB is given in a separate chapter.
Q2) What is the difference between ELCB & MCB/MCCB?
Ans) The difference – ELCB is used for the protection from earth leakage in the system while MCB/MCCB is used for protection from overloading & short circuit in an equipment / electrical circuit.
Click on MCB & MCCB to get more details about these circuit breakers.
Q3) When does an ELCB trip?
Ans) ELCB tips when an earth fault occurs in an equipment or electrical circuit. Complete working principle of ELCB is given in above section of this page.
Q4) What type of current protection is not provided by ELCB?
Ans) ELCB provides protection against earth leakages only & it doesn’t provide protection against over-loading & short circuit.
Q5) Why 30mA ELCB used in electrical system?
Ans) 30mA ELCB is used in electrical system to protect user/operator/human being from earth fault. Beyond 30mA capacity ELCB is harmful for user, that is why we should ensure that ELCB of 30mA capacity must be used in lighting/power DBs for domestic purpose.
Q6) What is the purpose of ELCB?
Ans) The purpose of installation of ELCB in electrical system is to provide protection of user against earth fault which occur in an electrical equipment or electrical circuit. The leakage current is dangerous if it reaches on the metal enclosure of the equipment. The user will get shock if he touches metal body of the equipment. If earth leakage is there circuit then it will charge metallic part in which it is laid, if user will come in contact with than metallic part, he/she will get shock. In such situations / faults ELCB will trip & stop power supply to that equipment/circuit.
Q7) Why ELCB trips frequently?
Ans) ELCB trips only when earth leakage/ earth fault is there in either equipment/circuit. If ELCB is tripping again & again & not getting reset, it means fault persists in the system. Therefore, it is important to clear the fault from the system by identifying the problem. If it is not possible to clear the fault immediately, then identify the main circuit which has this fault & isolate it from the DB or turn off MCB which is connected with faulty circuit so that ELCB doesn’t trip & power could be available for healthy circuits. (Note- The faulty circuit should be properly taken care before putting it in use again).
Q8) How to check the working of ELCB?
Ans) there are two methods through which health of ELCB could be checked –
- a) ELCB comes with a test knob, ELCB will trip when knob is pressed manually. This process will work when power supply is connected to ELCB, without power this knob will not work.
- b) ELCB testing instruments (digital) are available in market. These instruments help to check whether ELCB is tripping on its rated fault current such as 30mA /100mA/300mA….etc. Process is very simple, instrument comes with a lead whose one end is connected with the instrument & other end has a plug which is to be connected with the socket/circuit whose ELCB is to be tested. Once both the ends are connected, then switch on digital device & set the fault setting which you want to test & press test button, ELCB will trip on its rated fault current if it is OK. If ELC is not tripping on rated fault current then check again, if again same status is their then replace ELCB with new one.

Q9) How sensitivity of ELCB is measured?
Ans) Sensitivity of ELCB can be checked with the help of hand-held/portable instrument which operates the ELCB on its rated fault capacity (in mA). Complete detail is given in above Q8.
Q10) What is ELCB Switch?
Ans) ELCB switch is nothing but ELCB itself which is called Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker. It is installed in electrical system to protect the user from earth fault which occurs in the equipment or electrical circuit. It trips automatically on earth fault, but can be operated manually.
Search Anything
Mail us at : [email protected]
Website : www.electricalwave.com
www.electricalwave.com
Study Material Web Portal
- Switch skin
Home > Protection > ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types & Working
What is an elcb types, working, and application of earth leakage circuit breaker.
ELCB or Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a protection device that protects against earth leakage. Initially, the earth leakage circuit breaker were voltage detection devices, now they are switched to current sensing devices. The current ELCB is renamed as RCCB or RCD while the voltage ELCBs are still known as ELCB but they are obsolete.
In this article, we are going to discuss ELCB in detail with both types.
Table of Contents
What is Earth Leakage?
The electrical current that flows from the live conductor to the earth through an unintended path is called earth leakage. It may flow between their poor insulation or through a person’s body and cause electrical shock. The consequence of electrical shock may prove fatal if the leakage current exceeds the only 30mA. Therefore, protection devices are used to disconnect the power source when such current leakage is detected
Causes of Earth Leakage?
Earth leakage can occur due to various reasons. It can occur due to damaged insulation of the live conductor or broken conductors. It can also occur when the live conductor comes in contact with the body of the equipment (if the equipment is not properly grounded). Upon touching the conductor or the equipment, the current can pass to the earth through the person’s body.
- Related Post: MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Working, Types and Applications
What is an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
ELCB or Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a type of circuit breaker that is used for protection against leakage current. it breaks the circuit and disconnects the power supply to the load when it senses the leakage current. The earth leakage can cause electrical shocks that can be fatal.
ELCB is mainly used for protection against electrical shock . They do not offer protection against overloading or short circuit. Therefore, they must be used in series with an MCB (miniature circuit breaker) .

Function of ELCB
ELCB is a safety device whose main function is to prevent electrical shock. It monitors the leakage current that flows out of the circuit through any unintended path. It cannot protect against overloading or short circuit current.
Operation of ELCB
Under normal conditions, the current from the source flows into the load through the live wire and flows out of the load through the neutral wire. In fact, both currents are equal in amount. If the current leaks through any unintended path, an imbalance between the live and neutral wire occurs. The ELCB can sense the imbalance using a current transformer and break the contacts using an electromagnetic relay.
- Related Post: What is an RCD (Residual Current Device)? – RCB and RCCB
Types of ELCBs
There are two types of ELCB classified based on its operation principle;
Voltage ELCB
- Current ELCB
Both types of ELCBs detect the leakage current but their sensitivity and the level of protection they offer are different. Voltage ELCB was invented before the current ELCB. voltage based ELCB is inferior to current ELCB. Therefore, to avoid confusion, the voltage ELCB is renamed ELCB while the current ELCB is renamed RCCB or RCD .
Voltage ELCB operates on the voltage level between the earth and the body of the equipment. The voltage difference is used to detect the leakage current and instantly break the circuit.
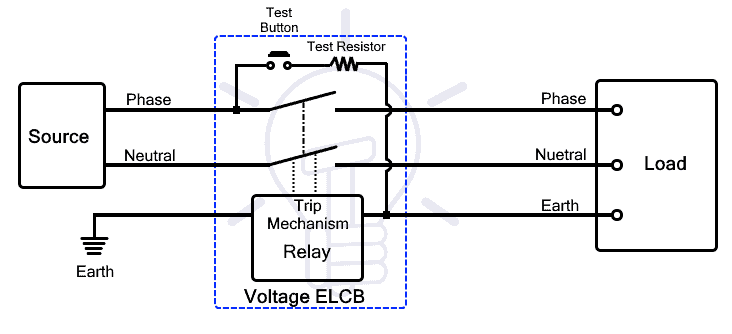
It has terminals for both phases and neutral on both supply and load sides. It has two extra terminals that connect with the equipment’s body and the earth. These terminals are actually connected with the electromagnetic relay and they play a vital role in breaking the circuit during current leakage.
- Related Posts: MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types and Working
Working Principle
One of the terminals of the relay coil is directly connected to the earth while the other terminal is connected to the body of the equipment. The coil can sense the voltage difference between the earth and the body of the equipment.
If the live wire breaks or its insulation fails and comes in contact with the body of the equipment, a voltage difference appears across the terminals of the coil. As a result, the current starts to flow through the coil and it is energized. The relay starts to generate electromagnetic force. When the current exceeds a certain limit, the relay produces sufficient force to pull the latch. By doing so, the latch break opens the contacts and disconnects the power supply to the equipment and prevents electrical shock.
Therefore, the earth connection is necessary as the relay only operates when the leakage current flows through it. if the current leaks through any other parts of the circuit and flows through any other unintended path, it will not break the circuit as the current must flow through the relay in order to break the circuit.
- Related Post: Types of Circuit Breakers – Working and Applications
Here are some of the advantages of voltage ELCB
- It helps in protection against electrical shocks.
- They are less sensitive and do not trip unnecessarily.
- They are less expensive.
Disadvantages
Here are some of the disadvantages of voltage ELCB
- It cannot sense the current leakage from phase to any other earthed body.
- It cannot prevent electrical shock in case of touching the phase conductor directly.
- It only trips when the leakage current flows through the earth conductor.
- It requires an extra connection with the body of the equipment and earth.
- It is less sensitive and cannot detect low leakage current.
- Electrical equipment that normally leaks voltage might trip ELCB unnecessarily.
It has far more disadvantages than advantages and they are obsolete. Therefore, if you have installed any old voltage ELCBs in your home, replace them with current ELCB or RCCB. They are more efficient, reliable and best at providing protection against any kind of leakage current.
- Related Post: Air Circuit Breaker (ACB): Construction, Operation, Types and Uses
Current ELCB (RCCB or RCD)
Current ELCB or commonly known as RCD (Residual Current Device) or RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is another type of ELCB that breaks the circuit upon sensing any leakage current. It operates on the current difference between the phase and neutral line. The difference appears when the current leaks from the phase line. Therefore, RCCB can provide protection against any kind of current leakage.
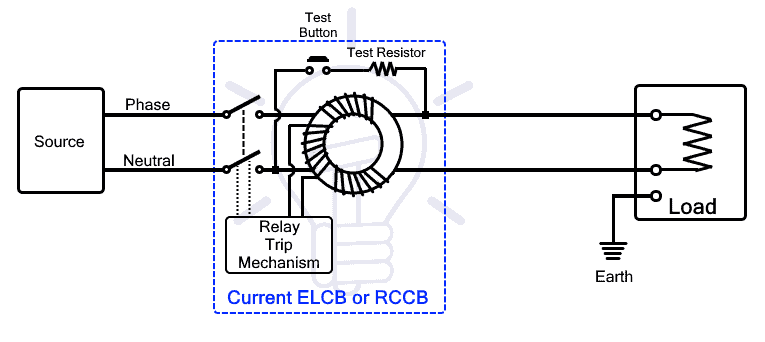
It has four terminals having two input and two output terminals for phase and neutral. The phase-in and neutral in are connected to the supply while phase-out and neutral out are connected to the load. It does not have that extra terminal for earth connection.
- Related Post: SF6 Circuit Breaker – Types, Construction, Working and Applications
The RCCB working is based on the current imbalance between the phase and neutral line. It continuously monitors the phase and neutral current. Under normal conditions, both phase and neutral current are equal because it is the same current flowing back from the load. If, the current leaks through any unintended path, the neutral current reduces and causes imbalance. When the imbalance exceeds a certain limit, the RCCB breaks the contacts and disconnects the power supply.
RCCB works on the principle of Kirchhoff’s current law, according to which the amount of current entering the load through the hot wire must be equal to the amount of current leaving the load through the neutral wire. The difference between the two currents known as residual current should be zero. If there is a difference then the current is leaking somewhere that causes the imbalance.
RCCB includes a zero-sequence current transformer that has three coils i.e. phase coil, neutral coil and search coil. It is used for detecting the imbalance or difference between two currents. The phase coil and neutral coil is wounded around the toroidal core in such a way to cancel out each other’s flux.
if the currents are equal as should be under normal conditions, the resultant flux will cancel out each other and there will be no induced current in the search coil. suppose, there is a leakage current, the current difference will produce flux that will induce a voltage in the search coil. as the search coil is connected to the relay trip mechanism, it will break the contacts and disconnect the power supply to the load.
- Related Post: Tripping Curves of Circuit Breakers – B, C, D, K and Z Trip Curve
Here are the advantages of the current ELCB or RCCB
- RCCB breaks the circuit when the current leaks from any part of the circuit.
- It is very reliable in providing protection against electrical shock.
- It is far more sensitive than voltage ELCB.
- It continuously monitors the residual current and instantaneously breaks when it exceeds its rated limit.
- It does not require an earth connection.
Here are the disadvantages of the current ELCB or RCCB
- It does not provide protection against short circuit current.
- It does not have overload protection .
- It is expensive than ELCB.
- It cannot provide protection against electrical shock due to touching both phases and neutral wire because the current still remains equal.
- Due to high sensitivity, it may trip unnecessarily when used with old appliances having small current leakage.
- It operates only on normal supply waveforms and cannot operate reliably on non-standard waveforms.
Related Post: Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCD
Types based on Poles
According to the poles of circuit breakers , the ELCB is classified into three types.
2-Pole ELCB: it is used for protection in a single-phase system. It has 2 ingoing and 2 outgoing terminals having phase and neutral connections.
3-Pole ELCB: It is used for protection in a three-wire three-phase system. It has three ingoing and three outgoing terminals.
4-Pole ELCB: It is used for protection in a four-wire three-phase system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ELCBs
- ELCB instantly breaks the circuit to avoid electrical shock.
- It prevents damage caused due to broken wires or damaged insulation.
- ELCB cannot protect against overloading and short circuit current.
- It cannot protect against live-neutral shock.
- It may trip unnecessarily due to small current leakages in old appliances.
Applications of ELCBs
ELCB is used for protection against current leakage. The current leakage causes electrical shock and faults in the system. It breaks the circuit instantly to prevents damage to the connected circuits. They are essential in wet locations having increased risks of electrical shocks.
Related Posts:
- HVDC Circuit Breaker – Types, Working and Applications
- Electronic Circuit Breaker – Schematic and Working
- Smart WiFi Circuit Breaker – Construction, Installation and Working
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Read MCB Nameplate Data printed on it?
- Why Circuit Breaker Capacity Was Rated in MVA and Now in kA and kV?
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
- Can We Use AC Circuit Breaker for DC Circuit and Vice Versa?
- AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
- GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
Electrical Technology
Related articles.

A Complete Guide About Solar Panel Installation. Step by Step Procedure with Calculation & Diagrams

How to Calculate the Battery Charging Time & Battery Charging Current – Example

Automatic UPS / Inverter Connection Diagram to the Home Panel Board

How to Find the Proper Size of Wire & Cable: Metric & Imperial Systems

Cable and Wire Size Calculator – Copper and Aluminum
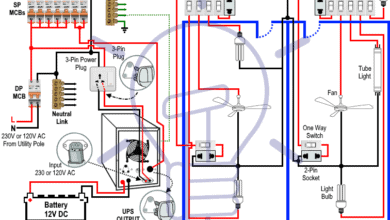
How to Connect Automatic UPS / Inverter to the Home Supply System?
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Email Verification
Please provide a valid Email ID to receive all updates from Schneider Electric.

- Compare Products
Please enter your pincode
Our Offerings May Vary Based On Your Location
Explore Better Deals By Providing Your Pincode!
I will do it later
- ELECTRICAL UPS & STABILIZERS
- Stabilizers
- Extended Warranty

- HOME UPS/ INVERTER

- UPS - LB Series

- WISER HOMES
- SWITCHES & SOCKETS

- Mobiya Solar Lamp

- ELECTRICAL PROTECTION & CONTROL

- Easypact TVS

- MPCB & THERMAL OVERLOAD RELAY

- CONTROL RELAY

- Easypact CVS
- Easypact EZC
- ComPact NSX

- DIGITAL METERS
- Basic Meter Range

- Easylogic PFC+ Capacitors

- Power Factor correction

- VARIABLE SPEED DRIVES & SOFT STARTERS
- POWER SUPPLY
- Phaseo Series
- Modicon Series
- ELECTROMECHANICAL RELAY
- PUSH BUTTON, SWITCHES, PILOT LIGHTS
- Harmony XA2E
- Harmony XB5
- Harmony XB4
- Harmony XB7
- Harmony XVB
- Harmony XAC
- Harmony XALD,XALK
- SIGNALING UNITS
- Harmony XVG
- LIMIT AND PRESSURE SWITCHES
- Automation Relay
- Servo Drives and Servo Motors
- PLC,PAC Controllers
- Control Station
- Switch Disconnector
- ComPact INS
- Tesys Vario
- Residual Current Relays
- PFC Controller
- Motor Starter
- Electronic Overcurrent Relay
- Motor Controller
- Foot Switches
- Biometric Switches
- HVAC Field Services
- Sensors- Living Spaces
- Sensors-Plant Room
- Valves and Actuators
- Design your space online
- Get your quotation online
- Experience Zone Video
- MERCHANDISE STORE
- Brand Connect

- Wiser - Smart Homes Package
- Fab Homes Bundle
- Book a free Consultation
- Educational Equipment Services
- SPECIAL DEALS
- TOP SELLERS
- DAZZLING DIWALI
- SAFETY FIRST
- Best Discount

- Customer Care Center 1800 103 0011 or 1800 419 4272
- [email protected]
- My Registration-ER
- My Registration-IR
- Support/Enquiry
- Registration Form

- Electrician Locator
- Retailer Locator
- Store / Shop Locator
- After Sales Services
- Installation support
- Easy Returns
- After Sales Service
- Customer Care Center 1800434231 [email protected] Please call back
- HELLO, SIGN IN
How Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker Work (ELCB) Explained
Become a Partner with Schneider Electric Architect, Contractor, Reseller SIGN UP

What is an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
An Earth Leakage Circuit (ELC), also known as an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) or Residual Current Device (RCD), is a crucial electrical safety device designed to protect people and property from electrical faults and the risk of electric shock. It operates by monitoring the electrical current flowing through a circuit and detecting any imbalance between the current entering and leaving the circuit.
ELCs are essential in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to protect against electrical faults. They are especially crucial in damp or wet environments, where the risk of electrical leakage is higher. By quickly disconnecting the power supply when a fault is detected, ELCs play a vital role in preventing accidents and ensuring electrical safety.
Types of ELCBs
- Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker - Voltage ELCBs are voltage operated. This ELCB works with the aid of a relay coil that is connected to a metal body. The other end of this coil is connected to the ground. To understand how voltage ELCBs work, let’s dig deeper into understanding voltage fluctuations.
If the voltage of equipment rises, maybe because of limited insulation, then this leads to a difference between the earth’s voltage and the voltage of the equipment. This discrepancy then causes an electric current to pass from the load metal framework to the earth. When a Voltage ELCB is installed, these current faults are detected in real-time. If a voltage ELCB detects a certain voltage across its coil, then it will automatically turn off. This will prevent any earth leakages and eliminate the chances of shock. You can always manually reset the voltage - ELCB to make it function again.
To summarise, Voltage-ELCBs monitor the voltage on the relay coil connected to the earth and immediately shut off the electrical supply if the voltage crossed 50 volts.
- - Advantages of Voltage ELCBs
- Aid in the prevention of electrical shocks
- These are less sensitive and hence do not trip unnecessarily.
- In comparison to current ELCBs, these are less expensive.
- - Disadvantages of Voltage ELCBs
- These do not prevent electrical shocks in instances where someone touches the phase conductor directly.
- This only trips when the leakage current flows through the conductor.
- Voltage ELCBs require an extra connection with the equipment body and earth.
- Due to its reduced sensitivity, there are instances where these cannot detect low levels of leakage current.
- Some equipment usually leaks voltages and such equipment can then trip the ELCBs, leading to false alarms.
- Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker - These are the more commonly used ELCBs and are also known as RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breakers). These ELCBs are built differently from voltage ELCBs. The core mechanism of a current ELCB consists of three winding transformers, with two primary windings and one secondary winding. These windings are made of phase, neutral, and wire-wound coils, respectively. These are collectively called the Core Balance Current Transformers (CBCT).
The current through the secondary winding, at its balanced state, is zero. This is known as the normal state and at this stage, the ELCB isn’t activated. When a electric fault does occur, it also flows to the ground. This creates an unbalanced magnetic field which is detected by the phase and neutral winding wires. This triggers a message to the secondary winding wire, which is connected to the sensing circuit. Hence, the fault is detected and a signal then trips the current.
- - Advantages of Current ELCBs
- The Current ELCB breaks supply to the complete circuit if power leaks from any part of the circuit.
- These are considered highly reliable when it comes to protection against electrical shocks.
- These have higher sensitivity and hence can detect minute anomalies and abnormalities.
- The current ELCBs have a consistent monitoring mechanism in place. This enables the device to break the electrical supply when the current threshold is exceeded.
- These do not require an earth connection.
Related Article: TYPES OF CIRCUIT BREAKERS AND THEIR IMPORTANCE
- - Disadvantages of Current ELCBs
- If ELCBs are used with older appliances with a small leakage, then these may trip unnecessarily owing to their sensitivity.
- These are more expensive than voltage-based ELCBs.
- These ELCBs do not offer overload protection.
- These offer no protection against short circuits.
Overall, though, you will benefit more by investing in a current ELCB or RCCB instead of a voltage ELCB. This is because voltage-based ELCBs function on redundant technology that offers very limited protection as compared to RCCBs. While current-based ELCBs may be more expensive, these are a more reliable option when it comes to protecting your space from earth leakages and short circuits.
Working Principle of Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker ELCB
The working principle of an ELCB is based on detecting ground faults or leakage currents and rapidly interrupting the circuit's power supply to prevent harm.
Here's how an ELC works
- Current Monitoring: The ELC continuously monitors the current in both the live (phase) and neutral wires of an electrical circuit. In a balanced circuit, where the current entering and leaving the circuit is equal, there is no leakage current.
- Detection of Leakage: If a ground fault or leakage current occurs, due to damaged insulation or contact with live conductors, an imbalance in the currents is detected. The ELCB has a built-in sensing coil or toroid that detects this imbalance.
- Differential Current Comparison: The ELCB compares the currents in the live and neutral conductors. If there is a difference exceeding a preset threshold (usually a very small value, often just a few milliamperes), it indicates a leakage current.
- Rapid Interruption: When an imbalance is detected, the ELC rapidly opens the circuit by tripping a switch or breaker. This action interrupts the flow of electricity and prevents potential electric shock or fire hazards.

ELCBs come in two main types
- voltage-operated ELCBs (VO-ELCBs)
- current-operated ELCBs (CO-ELCBs)
VO-ELCBs rely on voltage imbalances to detect ground faults, while CO-ELCBs use current imbalance detection, making them more sensitive and widely used today.
Difference Between ELCB And MCB
In summary, an ELCB is an essential safety device that constantly monitors electrical circuits, detecting any leakage currents or ground faults and swiftly disconnecting power to prevent electric shock and fire hazards.
Is it necessary to install earth leakage circuit Breakers (ELCB)?
Yes, it is strongly recommended to install Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCBs) or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in electrical circuits, especially in locations where electrical safety is paramount. These devices are crucial for protecting against electric shock and preventing electrical fires caused by ground faults or leakage currents. ELCBs provide an added layer of safety by rapidly disconnecting power when such faults occur, minimizing the risk of harm to individuals and property. Their installation is a fundamental safety measure and is often mandated by electrical codes and regulations in many regions.
What is medium-sensitivity Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
A medium-sensitivity Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is an electrical safety device designed to detect and respond to ground faults or leakage currents with a moderate sensitivity threshold. Unlike high-sensitivity ELCBs that can detect even small leakage currents (e.g., 10 milliamperes), medium-sensitivity ELCBs typically have a sensitivity threshold in the range of 30 to 300 milliamperes. These devices are commonly used in electrical installations where a slightly higher level of leakage current is acceptable, such as in industrial settings or for specific applications where a high-sensitivity ELCB might lead to false tripping. Medium-sensitivity ELCBs provide a balance between safety and practicality in various electrical systems.
No, an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) should never be connected in reverse. ELCBs are designed to be installed in a specific orientation to function properly and ensure electrical safety. The current sensing coil or toroid within the ELCB is configured to detect imbalances between the current in the live and neutral conductors. If it's installed in reverse, it won't operate as intended and may not detect ground faults or leakage currents accurately. Incorrect installation can lead to electrical hazards and a false sense of security.
- Covid 19 (ID: 3)
- Home Automation (ID: 4)
- Switches & Sockets (ID: 5)
- MCB (ID: 6)
- MCCB (ID: 7)
- Stabilizers (ID: 8)
- Home UPS/Inverter (ID: 9)
Monthly Archive
- March , 2024 (6)
- February , 2024 (6)
- January , 2024 (12)
- November , 2023 (6)
- October , 2023 (5)
Shipping all over India
Warranty & service, 100% secure payment.

- Knowledge Base
- Product Registration
What is an ELCB/RCD Tester? How is ELCB Testing done?
- Articles , Knowledge Base

What is ELCB / RCD Testing? How is an ELCB test done?
ELCB or RCD Testing refers to checking whether the Breaker is functional and working as it should be. ELCB Testing is done by using the Current Injection Method, wherein simulating an appropriate fault condition, a low magnitude fault current (30mA to 200mA) is injected to test whether the device trips or not. A functioning ELCB/RCD will trip the circuit during a Current Injection Test.
Why test ELCBs or RCDs?
Since the ELCBs and RCDs are important and critical protection devices, it is always in the interest of the end user to periodically check the health and functioning using this kind of test. Any test buttons built into the ELCB/RCD can only help test manual functioning of the breaker.
An ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) or RCD (Residual Current Device) detects and measures any fault currents from live wire to the ground wire, within the circuit installation that it is protecting. ELCB, RCD and RCCB are all Breakers and protect circuit installations.
What is an ELCB?
An ELCB is a device directly checks current leakage to earth. It protects by cutting off the power to the circuit. It switches off the power and remains off till it is manually reset.

What is an RCD?
An RCD protects a circuit by automatically disconnecting the electrical supply in a Three Phase Circuit when it detects an imbalance between live conductors. In case of Single Phase Circuits, an RCD monitors the difference in currents between the live and neutral conductors.
What is an RCCB?
An RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is a device which protects people from electrical fires, electrical shocks and/or electrocution, which might be caused because of earth faults or faulty wiring of circuits. When an RCCB is attached to a circuit and a person comes in contact accidentally with an open or live wire in the circuit, it helps avoid earth faults and any electrical shocks by tripping the circuit within a fraction of a second. Thus, RCCBs prevent accidents and it is a safe and good practice to always install RCCBs within circuits.
Metravi offers reliable and high-precision ELCB RCD Testers which have unique functionalities along with the basic trip testing feature.

The Metravi 1810D ELCB RCD Tester is the Basic test Equipment an Electrician cannot do without. It is a dual-function testing instrument which can verify electrical wiring connections and the functioning of ELCB / RCD devices by forcing them to trip. The protection device opens the mains power supply circuit when a current higher than a certain amplitude flows into the ground/earth wire, thus ensuring and verifying that the respective electrical installations meet safety and regulation requirements.

The Metravi 1811 ELCB/RCD Tester has an Intelligent microprocessor chip control, which ensures high accuracy, reliability and stability. It can perform RCD/ELCB Test wiring checks and phase angle selection. The RCD test can be selected to start from a positive (0°) or a negative (180°) half cycle. It features a contact voltage alarm – when the contact voltage is larger than the selected limit value during the RCD test, the RCD test is stopped. Auto-ramping during the test is available along with LINE-NEUTRAL voltage measurement, LINE-PHASE-EARTH voltage measurement, display L-PE input voltage and frequency measurement.

The Metravi 1813 is a ELCB/RCD Tester has the main function to test the ELCB/RCD and measure the trip values of ELCB/RCD in trip time (expressed in ms) or -in trip current value (expressed in mA). This enables 10mA / 30mA / 100mA / 300mA / 500mA and 1000mA differential circuit breakers to be tested irrespective of their type (normal or delayed). This comprehensive appliance is also used to test the conformity of the network and the connection of the earthing conductor.
Share this post

Metravi Instruments
Comments (1)
Mandatory provision for RCD in all service connections, Tamilnadu.
LINK: http://www.tnerc.gov.in/PressRelease/files/PR-050120230515Eng.pdf
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Related Posts

How To Choose Multimeter and Clamp Meter Test Leads?

Metravi: Spurring a Solution-based Approach to Electrical Instrumentation

What is a Gauss Meter?

A Case Study for Hot Axle detection – using the Metravi VIT-20 Video Infrared Thermometer

What is DC Regulated Power Supply?

How do Digital Non-contact Tachometers work?

Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
- June 30, 2023
- Post Views: 280
Table of Contents
What is an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker?
An earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB), also known as an earth leakage switch or earth leakage protector, is an electrical safety device. It is mainly used to automatically disconnect the power supply to protect the human body from electric shock when a leakage fault occurs in the equipment.
Some leakage circuit breakers on the market only have the function of leakage protection and power-off, and must cooperate with protective elements such as fuses, thermal relays, and over-current relays when used. Of course, some leakage circuit breakers also have protection functions such as leakage, electric shock, overload, and short circuit.
The Structure of ELCB
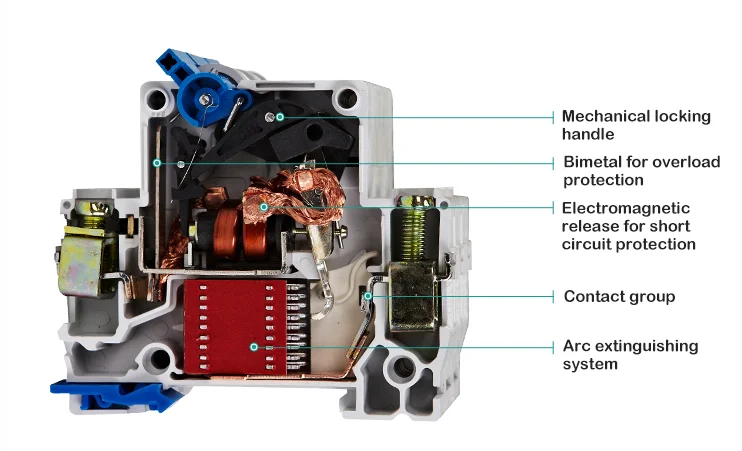
Leakage circuit breaker is actually a superposition of ordinary circuit breaker and leakage protection module, the details are as follows:
Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker is mainly composed of contacts, arc extinguishing system, electromagnetic release, transmission mechanism, and insulating shell, etc., and plays the functions of on-off, control, and protection in the circuit.
Leakage Protection Module
Leakage protection module is mainly composed of measurement components, calculation and amplification components, operation execution components, test components and so on.
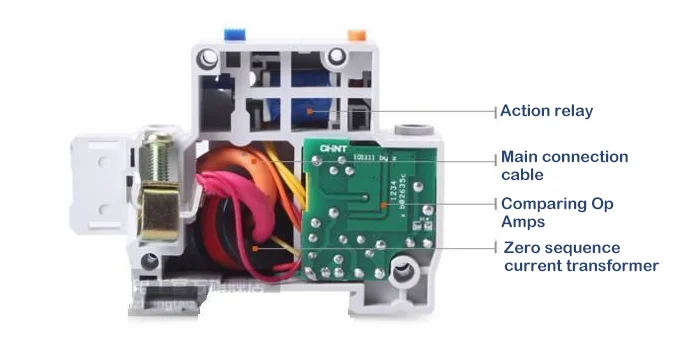
- The measuring element is mainly composed of zero-sequence transformers, which can detect leakage current and send out signals.
- The operational amplifier component is a complete set of circuit devices composed of rectifier bridge, thyristor, resistor and capacitor, etc., which can amplify the weak leakage current and conduct it to the actuator.
- The actuator is composed of relays and other parts, which can drive the main switch for protective tripping after receiving the signal.
- The test element is a set of independent circuits composed of test buttons and resistors, which can skillfully simulate the leakage state to test whether the function of the protector is normal.
How does ELCB Work?
As shown in the figure below, it is the working principle diagram of ELCB.
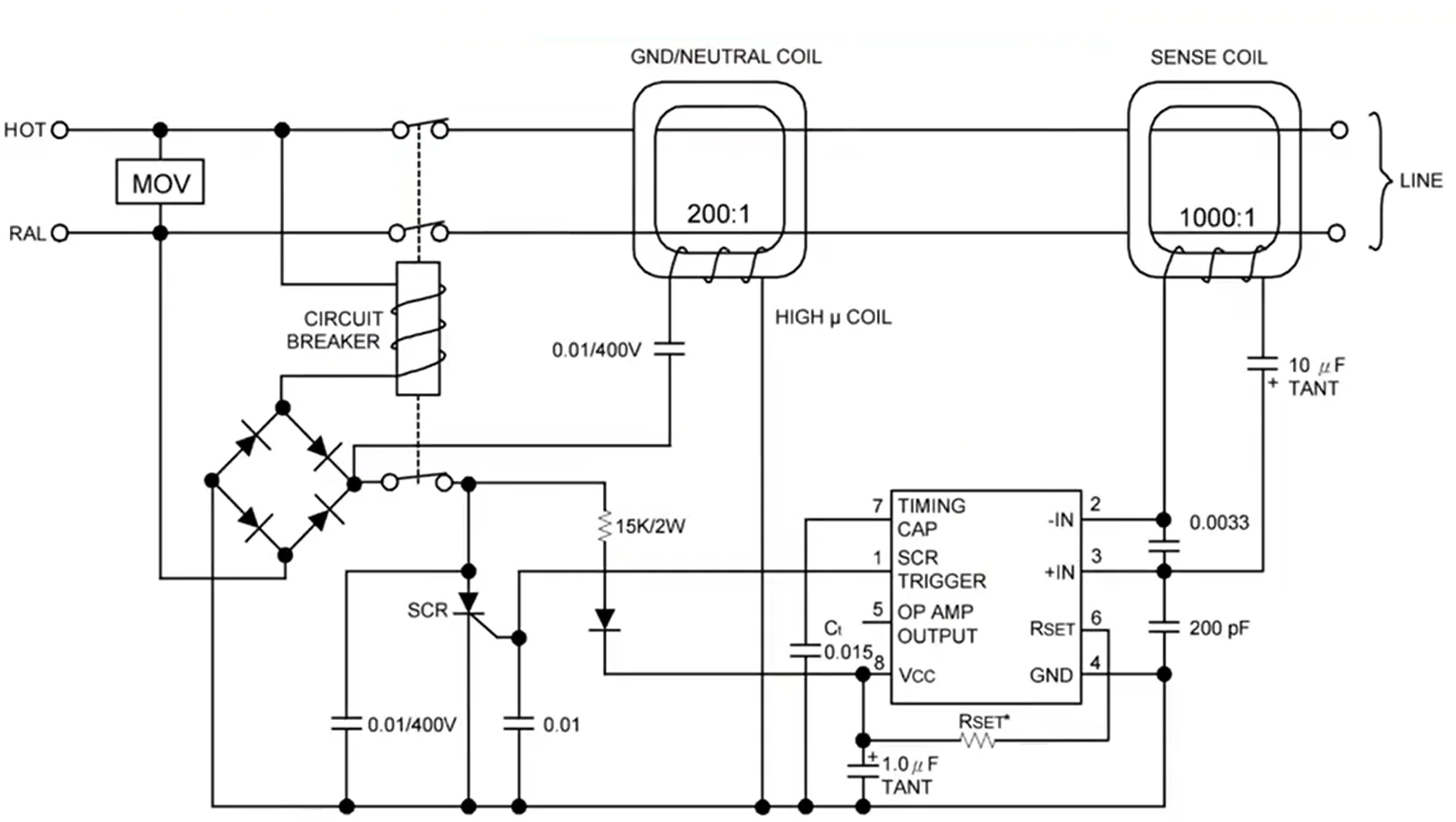
The pins of the circuit chip are described as follows:
- pin 1 is the SCR trigger pin
- pin 2 is the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier inside the chip
- pin 3 is the non-inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier inside the chip
- pin 4 is the ground pin
- pin 5 is the output terminal of the operational amplifier inside the chip
- pin 6 is the current sampling
- pin 7 is the delay capacitor
When the equipment is operating normally, the currents of the live wire and the neutral wire are equal, and the current transformer has no induction current at this time. The sum of the current vectors in the transformer is zero (the current is a directional vector, such as “+” in the direction of outflow, and “-” in the return direction. offset).
When a leakage occurs and the current is greater than 30mA, the current transformer generates an induced current, making the voltage at pin 2 of the chip greater than that at pin 3, and pin 1 of the chip outputs a high level. The thyristor is triggered and turned on after obtaining a high level, and the tripping coil is energized to trip. This is the working principle of earth leakage circuit breaker.
Types of ELCB
According to working principle, there are three main types of ELCBs:
Voltage-Operated ELCB (VO-ELCB)
This type of ELCB operates based on the voltage difference between the line and neutral conductors. When a fault occurs, causing a leakage current, the voltage difference triggers the ELCB to trip and disconnect the circuit. VO-ELCBs are commonly used in residential and small commercial applications.
Current-Operated ELCB (CO-ELCB)
CO-ELCBs work by monitoring the imbalance in current between the live and neutral conductors. When a fault occurs, causing a leakage current, the imbalance triggers the ELCB to trip and disconnect the circuit. CO-ELCBs are typically used in larger commercial and industrial applications.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
RCCBs are an advanced type of ELCB that can detect both AC and DC leakage currents. They use a sensitive current transformer to monitor the difference in current between the outgoing and returning conductors. If a leakage current is detected, the RCCB will trip and interrupt the circuit.
According to the number of circuit breakers, ELCB can also be divided into 1P+N, 2P, 3P, 3P+N, 4P types.
This type is composed of a single (1P) ordinary circuit breaker and a leakage protection module, and has two sets of terminals. The biggest feature of the device is that only one pole has thermal magnetic tripping breaking capacity, and the other pole does not have and is always in the conduction state. Therefore, when wiring the 1P+N type leakage circuit breaker, the live wire must be connected to the pole that can be broken, only in this way can safety be guaranteed.

In order to prevent wiring errors, the manufacturer specially marked the terminals. As shown in the figure, the terminal marked N must be connected to the neutral wire, and the unmarked terminal must be connected to the live wire.
This type of leakage circuit breaker is the most widely used. It is a combination of a double (2P) circuit breaker and a leakage protection module, and has two sets of terminals. Both poles of this device have thermal-magnetic tripping and breaking capabilities, so there is no strict distinction between the wiring positions of the live wire and the neutral wire. Generally, it can be installed according to the custom and the site environment.

This type of leakage circuit breaker is composed of a triple (3P) circuit breaker and a leakage protection module. It is used in a three-phase balanced circuit. It has 3 sets of terminals, and all three poles can be turned on and off and have thermal magnetic tripping capability. When wiring, follow the sequence of phase wires A, B, and C to connect in sequence.

This type of leakage circuit breaker is composed of a triple (3P) circuit breaker and a leakage protection module. It is used in a three-phase unbalanced circuit and has 4 sets of terminals. Similar to 1P+N, one of the poles is always on and has no thermal-magnetic tripping breaking capacity, and the manufacturer has marked N (neutral line). The other three poles are connected in sequence according to the phase line sequence A, B, and C.

This type of leakage circuit breaker is composed of a quadruple (4P) circuit breaker and a leakage protection module. It is applied in a three-phase unbalanced circuit. buckle ability. Due to the manufacturing process, the manufacturer has made fixed requirements on the access position of the neutral line N, as shown in the figure. For the phase lines A, B, and C, they are connected to the other three groups of terminals in sequence.

Common faults of ELCB
01: contacts can't be closed under manually operated.
Cause Analysis:
- The voltage-loss release has no voltage or the coil is burnt out;
- The energy storage spring is deformed, resulting in a decrease in the closing force;
- The reaction spring force is too large;
- The mechanism cannot reset and trip;
- The transmission mechanism is not flexible.
- Check the circuit, apply voltage or replace the coil;
- Replace the energy storage spring;
- Adjust the tripping contact surface to the specified value;
- Add a little engine oil to the transmission point.
02: Contacts Can't be Closed under Electrically Operated
- The operating power supply voltage does not match;
- The power capacity is not enough;
- The stroke of the electromagnet rod is not enough or the gap between the armature is too large;
- Motor operation positioning switch failure;
- The rectifier tube or capacitor in the controller is damaged.
- 1. Replace the power supply;
- Increase the operating power capacity;
- Readjust or replace the tie rod or raise the iron core;
- Readjust the operation positioning;
- Replace the rectifier tube or capacitor.
03: One Phase Contact Can't be Closed
- A connecting rod of the circuit breaker is broken;
- The angle of the transmission mechanism of the current limiting element is not suitable.
- Replace the connecting rod;
- Adjust to the requirements of the original technical conditions.
04: The Shunt Release Can't Disconnect the Circuit Breaker
- Coil short circuit;
- The power supply voltage is too low;
- The tripping contact surface is too large;
- The screws are loose.
- Replace the coil;
- Replace or increase the power supply voltage;
- Readjust the tripping contact surface;
- Tighten the screws.
05: Loss of Voltage Release Can't Break the Circuit Breaker
- The reaction force spring becomes smaller;
- The energy storage spring becomes smaller;
- The mechanism is stuck.
- Adjust the spring;
- Adjust the energy storage spring;
- Eliminate the cause of stuck.
06: The Circuit Breaker is Disconnected when Lauching the Motor
- The instantaneous setting current of the overcurrent release is too small;
- Phase failure protection or other protection actions.
- Adjust the instantaneous setting spring of the overcurrent release and other protections;
- If it is an air release, the valve may fail or the rubber membrane may be broken.
07: The Circuit Breaker Open Automatically after Closed
- The long delay setting value of the overcurrent release is wrong;
- Deterioration of heating element or semiconductor delay circuit element.
- Readjust the overcurrent release;
- Replace damaged components.
08: Loss of Voltage Release Produces Noise
- The reaction force spring is too strong;
- There is oil on the working surface of the iron core;
- The short circuit ring is broken.
- Readjust the reaction spring;
- Eliminate oil pollution;
- Replace the armature or core.
09: Circuit Breaker Overheating
- The contact pressure is too low;
- Excessive wear or poor contact on the contact surface;
- The connecting screws of the two conductive parts are loose.
- Adjust the contact pressure or replace the spring;
- Replace the contacts or clean the contact surface;
10: Auxiliary Switch Failure
- The movable contact bridge of the auxiliary switch is stuck or falls off;
- The drive rod of the auxiliary switch is broken or the roller falls off.
- Correct or reinstall the contact bridge;
- Replace the transmission rod and roller, or replace the entire auxiliary switch.
Pros and Cons of ELCB
- Enhanced safety
- Quick response time
- Easy installation
- Cost-effective
- Sensitivity limitations
- Potential nuisance tripping
- Limited protection range
- Maintenance requirements
Applications of ELCB
- Residential buildings, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and electric water heaters
- Entertainment place, such as swimming pools, spas, and outdoor recreational facilities
- Household appliances, such as air conditioning units, refrigerators, washing machines
- Industrial fields, such as manufacturing plants, workshops, and construction sites
Join our subscribers list to get monthly blog updates, technology news, case studies. We will never send spam, and you can unsubscribe at any time.
About Author

I am Aidan Taylor and I have over 10 years of experience in the field of PCB Reverse Engineering, PCB design and IC Unlock.
Recommended Post
Logic Gates: Tyles, Symbol, Truth Table
43 Popular PCB Design Software Tools

What is an embedded system?
SAMD21 Simulators Programming and Debugging
Don't hesitate - Get in touch today to find out how we can help take your project to the next level.
- +86 157-9847-6858

Well Done Technology was established in 2008, focus on reverse engineering, IC unlock, PCB Clone and design. Our technical team of more than 40 people includes senior engineers with rich experience.
- +86 157 9847 6858
- B205, Block 7, Phase 2, D & J Innovation Park, 73 Bulan Road, Longgang, Shenzhen, China

- Safe Privacy Guranteed
- Reply within 24 hours
- Honest and reasonable prices
- Accept small and large projects
- Talk directly to our experts
Start to Achieve Your PCB Project
404 Not found
ELCB TESTER
EARTH LEAKAGE CIRCUIT BREAKER
Elcb tester description, elcb specifications.
2000mS readout for testing latest delay action breakers
Fully programmed operation
Accurate digital read out of tripping time
Two LED lamps give quick check for correct wiring
Operates from mains supply. No need for batteries
Compact, lightweight and simple to operate
Zero cross circuitry permits testing at 0°and 180°portion of sine wave. At these two tests minimum (best) and maximum (worst) trip times will be displayed
Trip Current Setting : 5mA, 10mA, 30mA, 100mA, 300mA, 500mA
Operating Voltage: 220 / 230 / 240V AC, 50/60Hz
Data hold function to freeze the digital trip time display allows for easy readout and eliminates the possibility of reading error
View Catalog
FRANCHISEE REQUIRED PLACES
Instrumentation world, 2nd, 11-a, cross,, sundarar st, opp. to, lala mahall, nalvar layout, rathinapuri,, coimbatore,, tamil nadu 641027.
CUSTOMER CARE NO
- Español - Spanish (Castillian)
- 中文 - Chinese (Simplified)
- Français - French
- Safety Information
- Cybersecurity Safety Notice
- About the Book
- Introduction
- Hardware Description
- EcoStruxure Power Commission Software
- Technical Characteristics
- Firmware Update
- Schneider Electric Green Premium™ Ecolabel
- MicroLogic Trip Unit Compatibility
- Configuration Function
- Connection of the Service Interface to a MicroLogic Trip Unit
- Discovering Trip Units
- AMS/MMS Test
- Test Procedure
- Test Report
- Preconfigured Test Point
- Custom Test Point
- Troubleshooting of Automatic Trip Curve Test
- Troubleshooting of Zone-Selective Interlocking Test
- Troubleshooting of Primary Injection Test
- Alarm Simulation
- Automatic Trip Curve Tests with Preconfigured Test Points
- Automatic Trip Curve Tests with Custom Test Points
- Troubleshooting of Trip Unit Discovery
- Enerlin'X Device Compatibility
- Connection of the Service Interface to an Enerlin'X Device
For the best experience of this site, please enable Javascript for the www.productinfo.schneider-electric.com domain.
Preparation for Primary Injection Tests
Reset thermal memory : Thermal memory is a function that models temperature of the cables that are connected to the circuit breaker after a tripping event. This function causes the circuit breaker to trip faster than the published time-current curve, if the wiring had not cooled. Under normal conditions, 15 minutes delay is required following a device tripping to allow the system to cool before returning to normal functionality. The reset thermal memory function inhibits thermal memory, thus overriding the 15 minutes delay and allowing for multiple consecutive primary injection tests.
Inhibit ground fault protection : This function allows a single phase primary injected test current to be applied without causing the circuit breaker to trip on ground fault. It is used when testing the LSI protection functions of the circuit breaker.
After doing these actions, manually connect an external power source on the primary of the circuit breaker to do the test.
The secondary injection testing is the Schneider Electric preferred method for testing circuit breakers. Inappropriate primary injection testing can cause damage to the circuit breakers. Inability to conduct primary injection testing in the proper manner could result in inappropriate test results, while ultimately damaging the integrity of the circuit breaker long term.
For information on secondary injection testing, refer to Automatic Trip Curve Tests .
The circuit breaker is automatically restored to normal mode in 75 minutes, if the test functions are not manually stopped prior to that.
Show QR code for this page
Was this helpful?
Contact Information
Legal information.
The information provided in this document contains general descriptions, technical characteristics and/or recommendations related to products/solutions.
This document is not intended as a substitute for a detailed study or operational and site-specific development or schematic plan. It is not to be used for determining suitability or reliability of the products/solutions for specific user applications. It is the duty of any such user to perform or have any professional expert of its choice (integrator, specifier or the like) perform the appropriate and comprehensive risk analysis, evaluation and testing of the products/solutions with respect to the relevant specific application or use thereof.
The Schneider Electric brand and any trademarks of Schneider Electric SE and its subsidiaries referred to in this document are the property of Schneider Electric SE or its subsidiaries. All other brands may be trademarks of their respective owner.
This document and its content are protected under applicable copyright laws and provided for informative use only. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), for any purpose, without the prior written permission of Schneider Electric.
Schneider Electric does not grant any right or license for commercial use of the document or its content, except for a non-exclusive and personal license to consult it on an "as is" basis.
Schneider Electric reserves the right to make changes or updates with respect to or in the content of this document or the format thereof, at any time without notice.
To the extent permitted by applicable law, no responsibility or liability is assumed by Schneider Electric and its subsidiaries for any errors or omissions in the informational content of this document, as well as any non-intended use or misuse of the content thereof.
© 2023 Schneider Electric

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The test facility provided on the home ELCB will only confirm the health of the ELCB unit, but that test does not confirm that the ELCB will trip when an electric shock hazard does occur. It is a really sad fact that all the while this misunderstanding has left many homes totally unprotected from the risk of electric shocks.
The YouTube video "ELCB + MCB Tripping Testing by Electric Work Center shows how to test an ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) and an MCB (Miniature Circui...
An earth-leakage circuit breaker ( ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high Earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected. Once widely used, more recent installations instead use residual ...
The ELCB or RCCB switch will flip down and cut off all power supply in your home. If the ELCB or RCCB switch does not flip down, it is faulty. Homeowners should contact a Licensed Electrical Worker for assistance immediately. Test all light switches and power sockets in every room. The ELCB or RCCB is working if lights and power sockets do not ...
Learn, how the #Trip_Switch at home (#ELCB, #RCCB or #RCD) works.Also learn how to test it correctly, using an ELCB tester on Plug bases.If this video is use...
How to test Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker using external fault circuits.You can turn off annoying electronic devices.
In the case of faulty air conditioner equipment, the ELCB may trip due to earth leakage. In this case, you will need to isolate the cause of the fault or repair the equipment before the power supply can be restored to the entire house. If the miniature circuit breaker(MCB) trips, the fault could be due to an overcurrent or short circuit.
Once both the ends are connected, then switch on digital device & set the fault setting which you want to test & press test button, ELCB will trip on its rated fault current if it is OK. If ELC is not tripping on rated fault current then check again, if again same status is their then replace ELCB with new one.
An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations (both residential and commercial) with high Earth impedance to prevent electric shocks. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected.
ELCB or Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker is a type of circuit breaker that is used for protection against leakage current. it breaks the circuit and disconnects the power supply to the load when it senses the leakage current. The earth leakage can cause electrical shocks that can be fatal. ELCB is mainly used for protection against electrical shock.
Technical Test & Measurement Catalogue 1904. The TEL1 is the Basic Test Equipment an Electrician cannot do without. TEL1 is a Dual Function Test Instrument utilized to ... Current Detectors devices by forcing the ELCB/RCD to trip. TEL1 General ELCB Tester General ELCB Tester s Hoyt Electrical Instrument Works, Inc www.hoytmeter.com 1-800-258 ...
An Earth Leakage Circuit (ELC), also known as an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) or Residual Current Device (RCD), is a crucial electrical safety device designed to protect people and property from electrical faults and the risk of electric shock. It operates by monitoring the electrical current flowing through a circuit and detecting any ...
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
This device tests the integrity of the ELCB.An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high Earth imped...
RCD(ELCB) Tester. Measurement of RCD trip time. Conducting testing of rated residual non-operating currents at x 1/2 Range, measuring RCD trip time at x1 and x5 Ranges. Measurement of trip out current. Measuring trip out current by varying current automatically. Remote Test. Enabling a user to hold the Test Leads with his
The test element is a set of independent circuits composed of test buttons and resistors, which can skillfully simulate the leakage state to test whether the function of the protector is normal. ... When a fault occurs, causing a leakage current, the imbalance triggers the ELCB to trip and disconnect the circuit. CO-ELCBs are typically used in ...
The Metravi 1813 remains a ELCB/RCD Tester has the main function to test one ELCB/RCD and measure the tripping values of ELCB/RCD in trip time (expressed in ms) press -in trip actual value (expressed on mA). This enables 10mA / 30mA / 100mA / 300mA / 500mA press 1000mA differential switch breakers to breathe tested irrespective of own choose (normal or delayed).
Digital ELCB Tester with Current Rating up to 500mA, Trip Test, Fault Trip Time, Self Powered, verifies wiring connection, 2000mS readout for testing latest ELCB.Model 2820 Earth Leakage Tester, ELCB Tester is easy to use. It indicates tripping Phase Angle, operates in Voltages from 100V to 450V L-E, Checks ELCB Trip Time and Trip Point (Sensitivity).
The preparation for primary injection does not perform any test by itself. It only prepares the circuit breaker for doing the primary injection tests and fulfills some preconditions before the actual test is performed. Reset thermal memory: Thermal memory is a function that models temperature of the cables that are connected to the circuit ...
How to find out which of several circuit breakers supplies power to a specific load.I made a tester using a 6.8k ohm resistor and switch, a neon lamp for thi...
There are two types of trip mechanism for an ELCB. One is the electronic trip type (electronic type ELCB from now on) and the other is the ZCT trip type (ZCT type ELCB from now on). Electronic type ELCBs shown in Fig. 1 detect and amplify the leakage current of ZCT output by electronic circuit and transmit a trip signal to ELCB trip coil when the
Usually, RCCB testing with the Test Push button is also a safe way to check the RCCB. In this case, RCCB was tested through Tester, but didn't trip 2 times, so the 1st Precaution is if RCCB/ELCB ...
This video showing Earth leakage circuit breaker testing ( E L C B) With lamp.#hvacmalayalam #elcbtest#elcbtripping#electrical #elcb#elcbtripping#Rccb1) how ...